Charge-Based Separation of Micro- and Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Devices and Experimental Setup
2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Sample Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
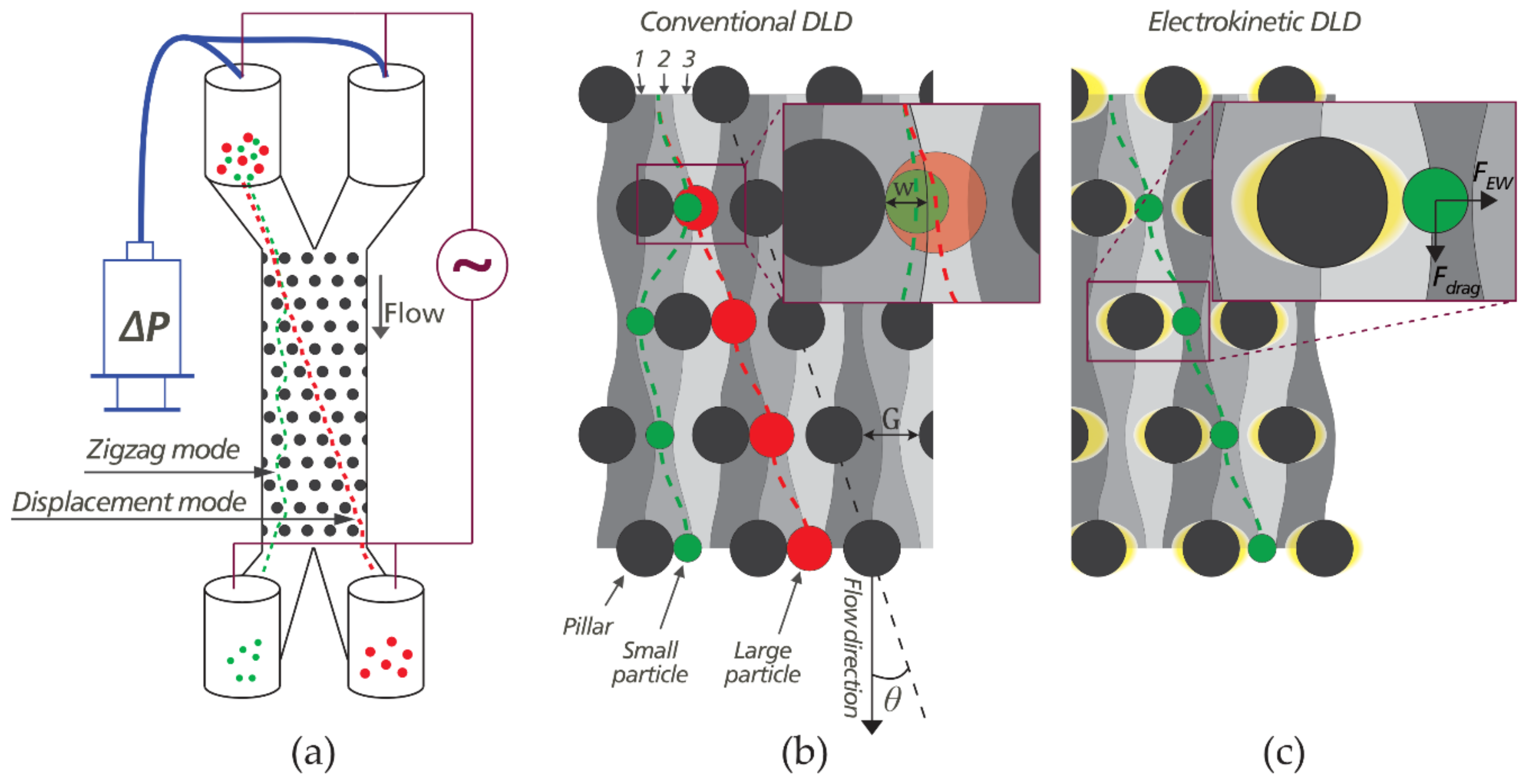
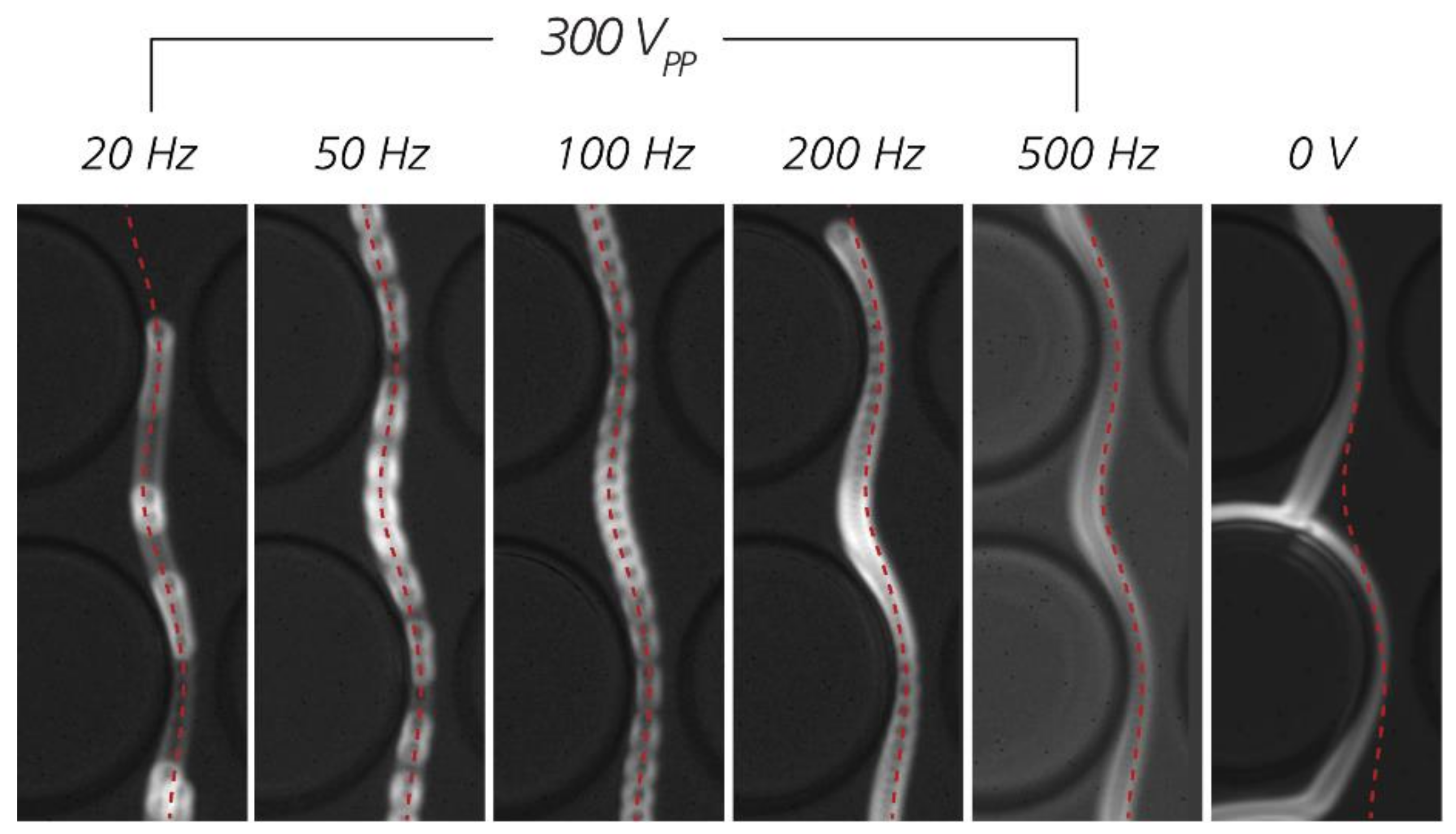
3.1. Important Sorting Parameters
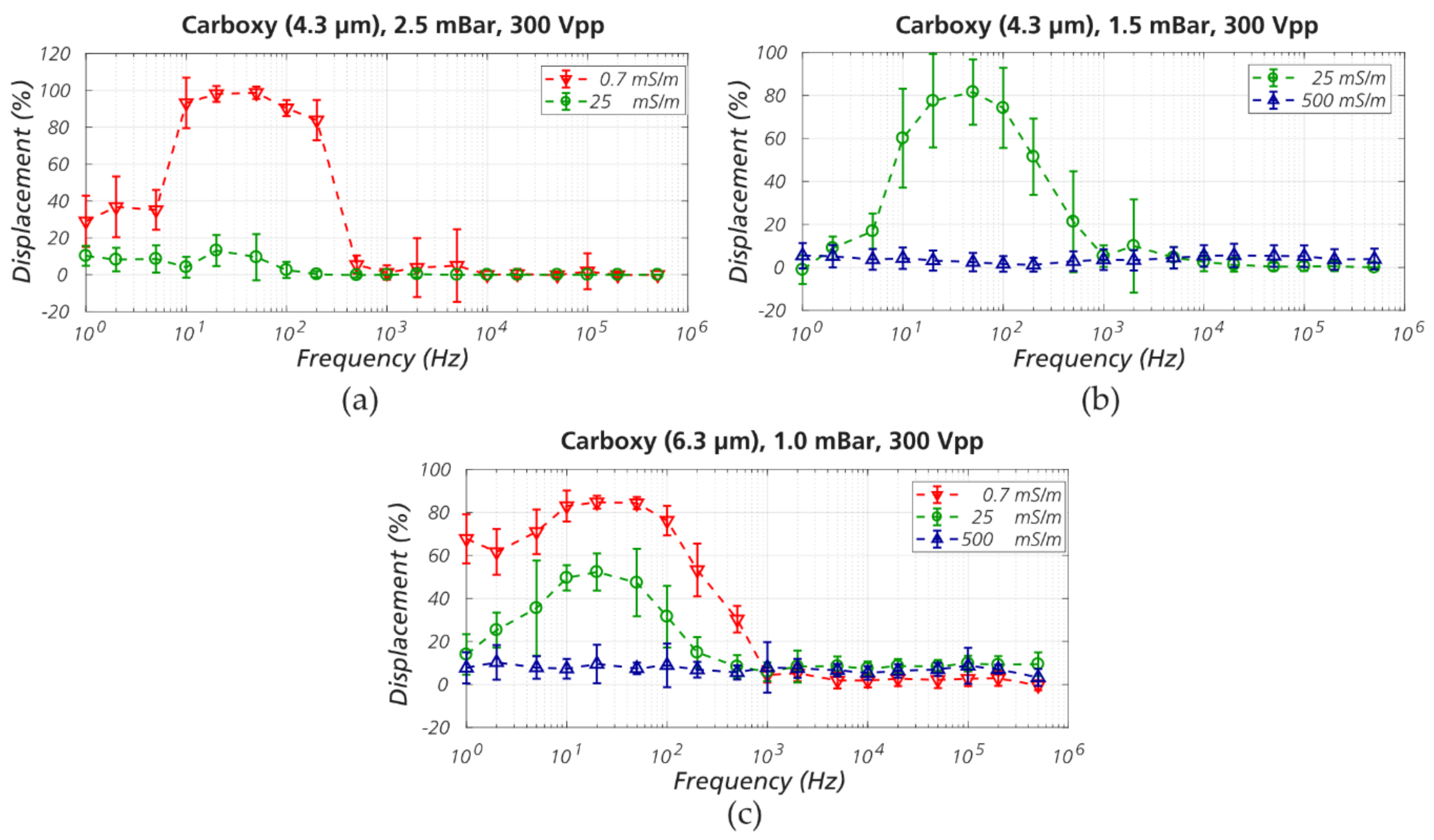
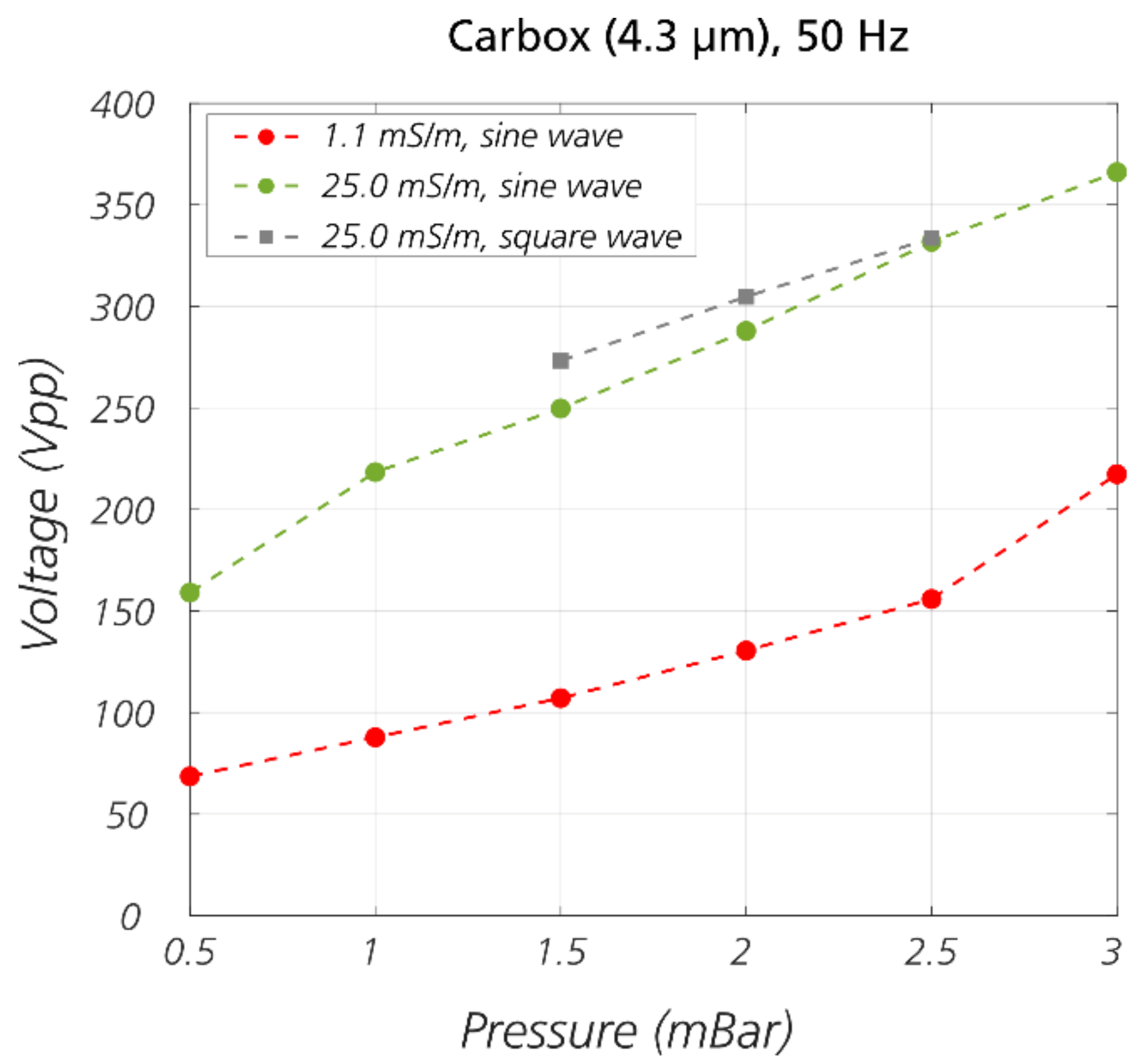
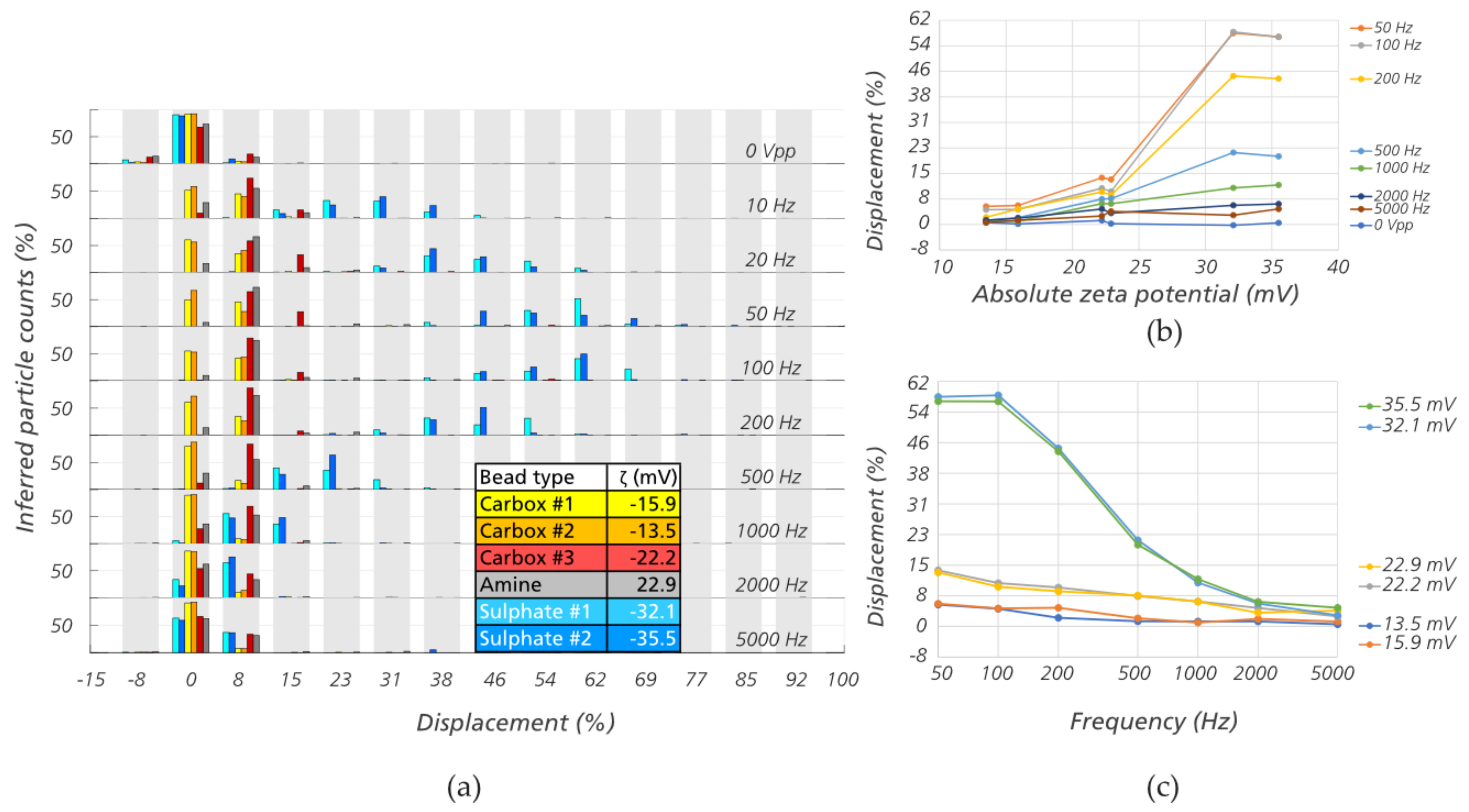
3.2. Sorting Polystyrene Microspheres by Zeta Potential
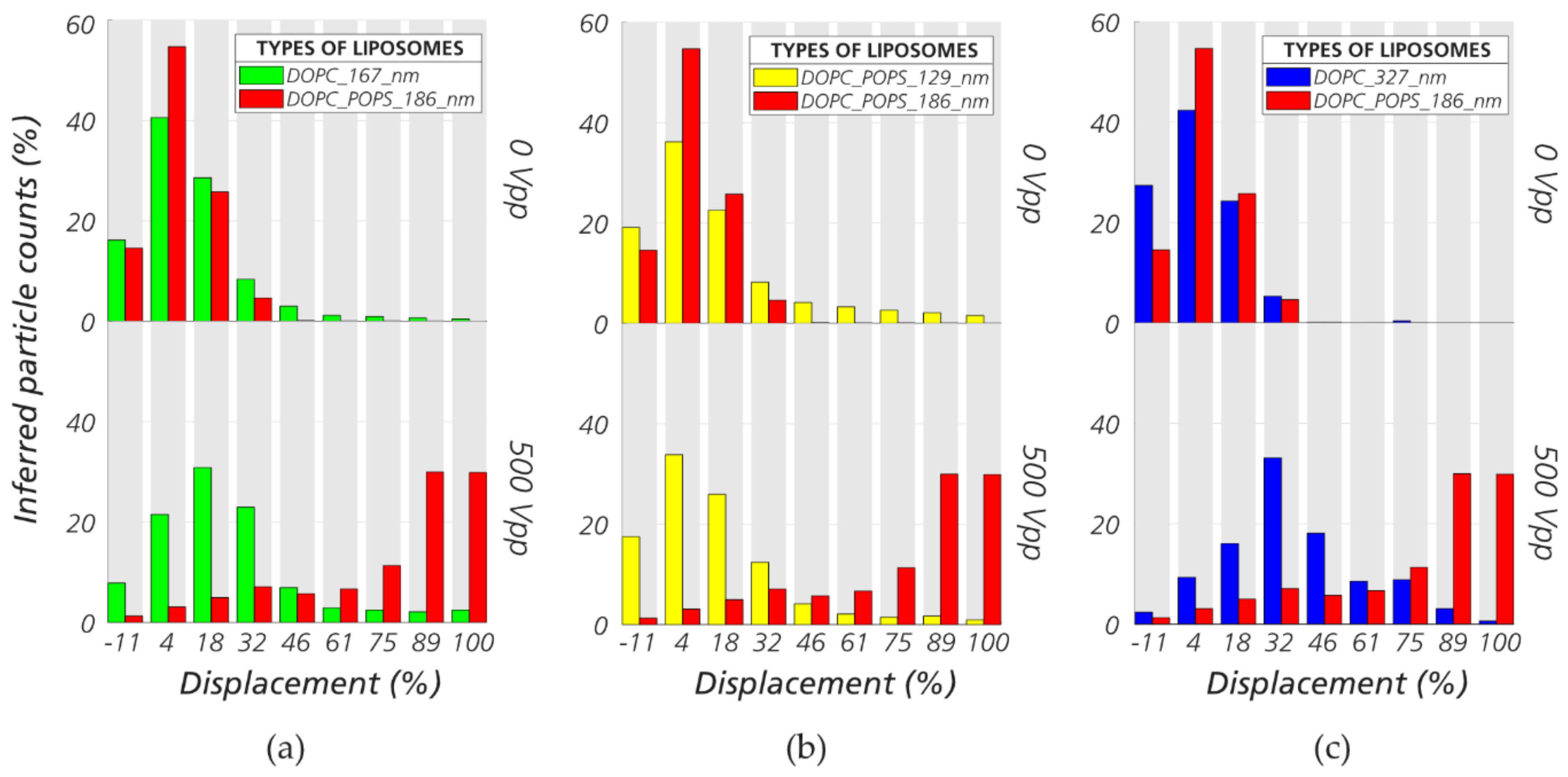
3.3. Sorting Polystyrene Nanospheres and Nano Liposomes
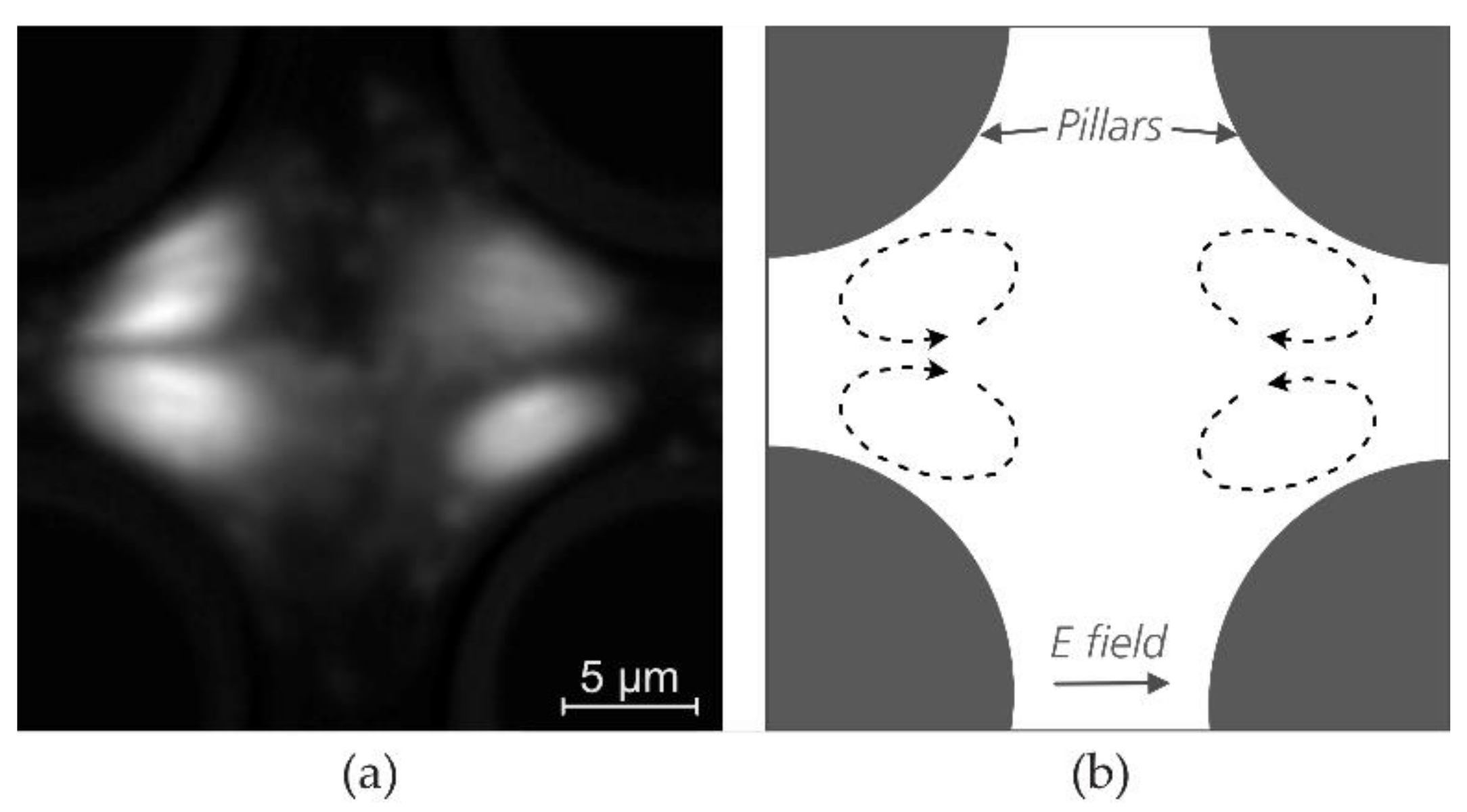
3.4. The Role of Electrokinetic Driving Forces
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, L.R.; Cox, E.C.; Austin, R.H.; Sturm, J.C. Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science 2004, 304, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyang, Z.; Yung, R.; Yu-Chong, T.; Kasdan, H. Deterministic lateral displacement MEMS device for continuous blood cell separation. In Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 30 January–3 February 2005; pp. 851–854. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.A.; Inglis, D.W.; Morton, K.J.; Lawrence, D.A.; Huang, L.R.; Chou, S.Y.; Sturm, J.C.; Austin, R.H. Deterministic hydrodynamics: Taking blood apart. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14779–14784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Kamei, D.T.; Ho, C.M. On-chip continuous blood cell subtype separation by deterministic lateral displacement. In Proceedings of the 2007 2nd IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, Bangkok, Thailand, 16–19 January 2007; pp. 932–936. [Google Scholar]
- Inglis, D.W.; Lord, M.; Nordon, R.E. Scaling deterministic lateral displacement arrays for high throughput and dilution-free enrichment of leukocytes. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 2011, 21, 054024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.; Whyte, G.; Bailey, J.; Vergara-Irigaray, N.; Ekpenyong, A.; Guck, J.; Duke, T. Separation of blood cells with differing deformability using deterministic lateral displacement. Interface Focus 2014, 4, 20140011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loutherback, K.; D’Silva, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, A.; Austin, R.H.; Sturm, J.C. Deterministic separation of cancer cells from blood at 10 mL/min. AIP Adv. 2012, 2, 42107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, F.; Du, J.; Shu, W.; Feng, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y. Rapid isolation of cancer cells using microfluidic deterministic lateral displacement structure. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 11801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabacak, N.M.; Spuhler, P.S.; Fachin, F.; Lim, E.J.; Pai, V.; Ozkumur, E.; Martel, J.M.; Kojic, N.; Smith, K.; Chen, P.I.; et al. Microfluidic, marker-free isolation of circulating tumor cells from blood samples. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 694–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okano, H.; Konishi, T.; Suzuki, T.; Suzuki, T.; Ariyasu, S.; Aoki, S.; Abe, R.; Hayase, M. Enrichment of circulating tumor cells in tumor-bearing mouse blood by a deterministic lateral displacement microfluidic device. Biomed. Microdevices 2015, 17, 9964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, S.H.; Edd, J.; Stoddard, A.E.; Wong, K.H.K.; Fachin, F.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A.; Stott, S.L.; Kapur, R.; Toner, M. Microfluidic isolation of circulating tumor cell clusters by size and asymmetry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Xia, X.; Qin, L. Integrated microfluidic chip for efficient isolation and deformability analysis of circulating tumor cells. Adv. Biosyst. 2018, 2, 1800200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, S.H.; Beech, J.P.; Barrett, M.P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Separation of parasites from human blood using deterministic lateral displacement. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, S.H.; Beech, J.P.; Barrett, M.P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Simplifying microfluidic separation devices towards field-detection of blood parasites. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 3291–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, R.; Barber, T.A.; Schmidt, M.A.; Tompkins, R.G.; Toner, M.; Bianchi, D.W.; Kapur, R.; Flejter, W.L. A microfluidics approach for the isolation of nucleated red blood cells (NRBCs) from the peripheral blood of pregnant women. Prenat. Diagn. 2008, 28, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laki, A.J.; Botzheim, L.; Ivan, K.; Szabo, T.; Tamasi, V.; Buzas, E.; Civera, P. Microvesicle fractionation using deterministic lateral displacement effect. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems (NEMS), Waikiki Beach, HI, USA, 13–16 April 2014; pp. 490–493. [Google Scholar]
- Laki, A.J.; Botzheim, L.; Ivan, K.; Tamasi, V.; Civera, P. Separation of microvesicles from serological samples using deterministic lateral displacement effect. Bionanoscience 2015, 5, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Silva, J.; Austin, R.H.; Sturm, J.C. Inhibition of clot formation in deterministic lateral displacement arrays for processing large volumes of blood for rare cell capture. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, J.V.; Radisic, M.; Murthy, S.K. Deterministic lateral displacement as a means to enrich large cells for tissue engineering. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9178–9182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Green, J.V.; Murthy, S.K.; Radisic, M. Label-free enrichment of functional cardiomyocytes using microfluidic deterministic lateral flow displacement. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lee, Y.; Jang, J.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Yokoi, K.; Ferrari, M.; Zhou, L.; Qin, L. Microfluidic cytometric analysis of cancer cell transportability and invasiveness. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tottori, N.; Nisisako, T.; Park, J.; Yanagida, Y.; Hatsuzawa, T. Separation of viable and nonviable mammalian cells using a deterministic lateral displacement microfluidic device. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, M.; Holm, S.H.; Beech, J.P.; Spencer, D.; Tegenfeldt, J.O.; Oreffo, R.O.C.; Morgan, H. Label-free enrichment of primary human skeletal progenitor cells using deterministic lateral displacement. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inglis, D.W.; Herman, N.; Vesey, G. Highly accurate deterministic lateral displacement device and its application to purification of fungal spores. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joensson, H.N.; Uhlen, M.; Svahn, H.A. Droplet size based separation by deterministic lateral displacement-separating droplets by cell—Induced shrinking. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tottori, N.; Hatsuzawa, T.; Nisisako, T. Separation of main and satellite droplets in a deterministic lateral displacement microfluidic device. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35516–35524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beech, J.P.; Ho, B.D.; Garriss, G.; Oliveira, V.; Henriques-Normark, B.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Separation of pathogenic bacteria by chain length. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1000, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, B.H.; Kim, S.C.; Gifford, S.M.; Astier, Y.; Wang, C.; Bruce, R.L.; Patel, J.V.; Duch, E.A.; Dawes, S.; Stolovitzky, G.; et al. Gel-on-a-chip: Continuous, velocity-dependent DNA separation using nanoscale lateral displacement. Lab A Chip 2019, 19, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, B.H.; Smith, J.T.; Gifford, S.M.; Wang, C.; Brink, M.; Bruce, R.L.; Austin, R.H.; Stolovitzky, G.; Astier, Y. Nanoscale lateral displacement arrays for the separation of exosomes and colloids down to 20 nm. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, J.; Jimenez, M.; Bridle, H. Deterministic lateral displacement for particle separation: A review. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 4139–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salafi, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. A review on deterministic lateral displacement for particle separation and detection. Nano Micro Lett. 2019; 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeming, K.K.; Thakor, N.V.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.H. Real-time modulated nanoparticle separation with an ultra-large dynamic range. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, B.R.; Smith, K.C.; Edd, J.F.; Nadar, P.; Dlamini, M.; Kapur, R.; Toner, M. Non-equilibrium inertial separation array for high-throughput, large-volume blood fractionation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frechette, J.; Drazer, G. Directional locking and deterministic separation in periodic arrays. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 627, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, J.A. Microfluidic Separation of Blood Components through Deterministic Lateral Displacement. Ph.D. Thesis, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Beech, J.P.; Holm, S.H.; Adolfsson, K.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Sorting cells by size, shape and deformability. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1048–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.L.; Budzan, K.; Drazer, G. Fractionation by shape in deterministic lateral displacement microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2015, 19, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, E.; Holm, S.H.; Zhang, Z.; Beech, J.P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O.; Fedosov, D.A.; Gompper, G. Sorting cells by their dynamical properties. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calero, V.; Garcia-Sanchez, P.; Ramos, A.; Morgan, H. Combining DC and AC electric fields with deterministic lateral displacement for micro- and nano-particle separation. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 054110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, D. The cataphoresis of suspended particles. Part I.—The equation of cataphoresis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Contain. Pap. A Math. Phys. Character 1931, 133, 106–129. [Google Scholar]
- Wiersema, P.H.; Loeb, A.L.; Overbeek, J.T.G. Calculation of the electrophoretic mobility of a spherical colloid particle. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1966, 22, 78–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrison Jr, F.A. Electrophoresis of a particle of arbitrary shape. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1970, 34, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viovy, J.L. Electrophoresis of DNA and other polyelectrolytes: Physical mechanisms. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2000, 72, 813–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, H.A. Dielectrophoresis: The Behavior of Neutral Matter in Nonuniform Electric Fields (Cambridge Monographs on Physics); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Pethig, R. Review article-dielectrophoresis: Status of the theory, technology, and applications. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pethig, R.R. Dielectrophoresis: Theory, Methodology and Biological Applications; Wiley: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, H.A.; Hawk, I. Separation of living and dead cells by dielectrophoresis. Science 1966, 152, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markx, G.H.; Talary, M.S.; Pethig, R. Separation of viable and non-viable yeast using dielectrophoresis. J. Biotechnol. 1994, 32, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markx, G.H.; Pethig, R. Dielectrophoretic separation of cells: Continuous separation. Biotechnol. Bioeng 1995, 45, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Tzeng, T.R.; Xuan, X. Electrokinetic focusing and filtration of cells in a serpentine microchannel. Biomicrofluidics 2009, 3, 44109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, Y.; Li, D.; Kalams, S.A.; Eid, J.E. DC-Dielectrophoretic separation of biological cells by size. Biomed. Microdevices 2008, 10, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo-Villanueva, R.C.; Jesus-Perez, N.M.; Martinez-Lopez, J.I.; Pacheco, A.; Lapizco-Encinas, B.H. Assessment of microalgae viability employing insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2011, 10, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapizco-Encinas, B.H.; Simmons, B.A.; Cummings, E.B.; Fintschenko, Y. Dielectrophoretic concentration and separation of live and dead bacteria in an array of insulators. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapizco-Encinas, B.H.; Simmons, B.A.; Cummings, E.B.; Fintschenko, Y. Insulator-based dielectrophoresis for the selective concentration and separation of live bacteria in water. Electrophoresis 2004, 25, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braff, W.A.; Willner, D.; Hugenholtz, P.; Rabaey, K.; Buie, C.R. Dielectrophoresis-based discrimination of bacteria at the strain level based on their surface properties. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, H.; Hughes, M.P.; Green, N.G. Separation of submicron bioparticles by dielectrophoresis. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, C.F.; Tegenfeldt, J.O.; Bakajin, O.; Chan, S.S.; Cox, E.C.; Darnton, N.; Duke, T.; Austin, R.H. Electrodeless dielectrophoresis of single- and double-stranded DNA. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, P.V.; Salmon, G.L.; Ros, A. Continuous separation of dna molecules by size using insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.T.; Tsegaye, M.; Chaurey, V.; Chou, C.F.; Swami, N.S. Nano-constriction device for rapid protein preconcentration in physiological media through a balance of electrokinetic forces. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, B.G.; Chao, T.C.; Kupitz, C.; Fromme, P.; Ros, A. Dielectrophoretic sorting of membrane protein nanocrystals. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9129–9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lapizco-Encinas, B.H. On the recent developments of insulator-based dielectrophoresis: A review. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, J.A.; Burt, J.P.; Pethig, R. Applications of a new optical technique for measuring the dielectrophoretic behaviour of micro-organisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 964, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethig, R.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.B.; Burt, J.P.H. Positive and negative dielectrophoretic collection of colloidal particles using interdigitated castellated microelectrodes. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1992, 25, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pethig, R. Electrode design for negative dielectrophoresis. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1991, 2, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoettges, K.F.; Hughes, M.P.; Cotton, A.; Hopkins, N.A.; McDonnell, M.B. Optimizing particle collection for enhanced surface-based biosensors. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2003, 22, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoettges, K.F.; Hubner, Y.; Broche, L.M.; Ogin, S.L.; Kass, G.E.; Hughes, M.P. Dielectrophoresis-activated multiwell plate for label-free high-throughput drug assessment. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2063–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuda, S.; Washizu, M.; Nanba, T. Novel method of cell fusion in field constriction area in fluid integration circuit. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1989, 25, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pysher, M.D.; Hayes, M.A. Electrophoretic and dielectrophoretic field gradient technique for separating bioparticles. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4552–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braff, W.A.; Pignier, A.; Buie, C.R. High sensitivity three-dimensional insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, L.M.; Skulan, A.J.; Singh, A.K.; Cummings, E.B.; Fiechtner, G.J. Dielectrophoretic manipulation of particles and cells using insulating ridges in faceted prism microchannels. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6798–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, B.G.; Smith, A.E.; Syed, Y.A.; Kirby, B.J. Continuous-flow particle separation by 3D insulative dielectrophoresis using coherently shaped, dc-biased, ac electric fields. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 7291–7300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Xuan, X. Particle electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis in curved microchannels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 340, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, E.B.; Singh, A.K. Dielectrophoretic trapping without embedded electrodes. In Proceedings of the SPIE: Conference on Microfluidic Devices and Systems III, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 18–19 September 2000; Volume 4177, pp. 164–173. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, E.B.; Singh, A.K. Dielectrophoresis in microchips containing arrays of insulating posts: Theoretical and experimental results. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4724–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Alanis, F.; Gan, L.; Ros, A. Transitioning streaming to trapping in DC insulator-based dielectrophoresis for biomolecules. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 173, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanasoge, S.; Devendra, R.; Diez, F.J.; Drazer, G. Electrokinetically driven deterministic lateral displacement for particle separation in microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2015, 18, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beech, J.P.; Jonsson, P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Tipping the balance of deterministic lateral displacement devices using dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2698–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.S.H.; Ho, B.D.; Beech, J.P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Open channel deterministic lateral displacement for particle and cell sorting. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3592–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beech, J.P.; Keim, K.; Ho, B.D.; Guiducci, C.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Active posts in deterministic lateral displacement devices. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calero, V.; Garcia-Sanchez, P.; Honrado, C.; Ramos, A.; Morgan, H. AC electrokinetic biased deterministic lateral displacement for tunable particle separation. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero, V.; Garcia-Sanchez, P.; Ramos, A.; Morgan, H. Electrokinetic biased deterministic lateral displacement: Scaling analysis and simulations. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1623, 461151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Joo, S.W.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stremersch, S.; De Smedt, S.C.; Raemdonck, K. Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of extracellular vesicles. J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiklander, O.P.B.; Brennan, M.A.; Lotvall, J.; Breakefield, X.O.; El Andaloussi, S. Advances in therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busatto, S.; Zendrini, A.; Radeghieri, A.; Paolini, L.; Romano, M.; Presta, M.; Bergese, P. The nanostructured secretome. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 8, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochstetter, A.; Vernekar, R.; Austin, R.H.; Becker, H.; Beech, J.P.; Fedosov, D.A.; Gompper, G.; Kim, S.-C.; Smith, J.T.; Stolovitzky, G.; et al. Deterministic lateral displacement: Challenges and perspectives. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 10784–10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft lithography. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1998, 37, 550–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbalzarini, I.F.; Koumoutsakos, P. Feature point tracking and trajectory analysis for video imaging in cell biology. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 151, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, R.J.; Ottewill, R.H.; Rowell, R.L. Zeta Potential in Colloid Science: Principles and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Russel, W.B.; Russel, W.B.; Saville, D.A.; Schowalter, W.R. Colloidal Dispersions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bazant, M.Z. Nonlinear Electrokinetic Phenomena. In Encyclopedia of Microfluidics and Nanofluidics; Li, D., Ed.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.G.; Ramos, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Morgan, H.; Castellanos, A. Fluid flow induced by nonuniform ac electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes. I. Experimental measurements. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Phys. Plasmas Fluids Relat. Interdiscip. Top. 2000, 61, 4011–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Ramos, A.; Green, N.G.; Castellanos, A.; Morgan, H. Fluid flow induced by nonuniform ac electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes. II. A linear double-layer analysis. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Phys. Plasmas Fluids Relat. Interdiscip. Top. 2000, 61, 4019–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, N.G.; Ramos, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Morgan, H.; Castellanos, A. Fluid flow induced by nonuniform ac electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes. III. Observation of streamlines and numerical simulation. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter. Phys. 2002, 66, 026305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramos, A.; Morgan, H.; Green, N.G.; Castellanos, A. AC electric-field-induced fluid flow in microelectrodes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 217, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazant, M.Z.; Squires, T.M. Induced-charge electrokinetic phenomena: Theory and microfluidic applications. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 066101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levitan, J.A.; Devasenathipathy, S.; Studer, V.; Ben, Y.X.; Thorsen, T.; Squires, T.M.; Bazant, M.Z. Experimental observation of induced-charge electro-osmosis around a metal wire in a microchannel. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 267, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thamida, S.K.; Chang, H.C. Nonlinear electrokinetic ejection and entrainment due to polarization at nearly insulated wedges. Phys. Fluids 2002, 14, 4315–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Dingari, N.N.; Buie, C.R. Nonlinear electrokinetic effects in insulator-based dielectrophoretic systems. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 2576–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, H.; Green, N.G. AC Electrokinetics: Colloids and Nanoparticles; Research Studies Press: Hertfordshire, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, W.M.; Schwan, H.P.; Zimmermann, U. Surface conductance and other properties of latex-particles measured by electrorotation. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 5093–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolina, I.; Morgan, H. The electrokinetic properties of latex particles: Comparison of electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 285, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
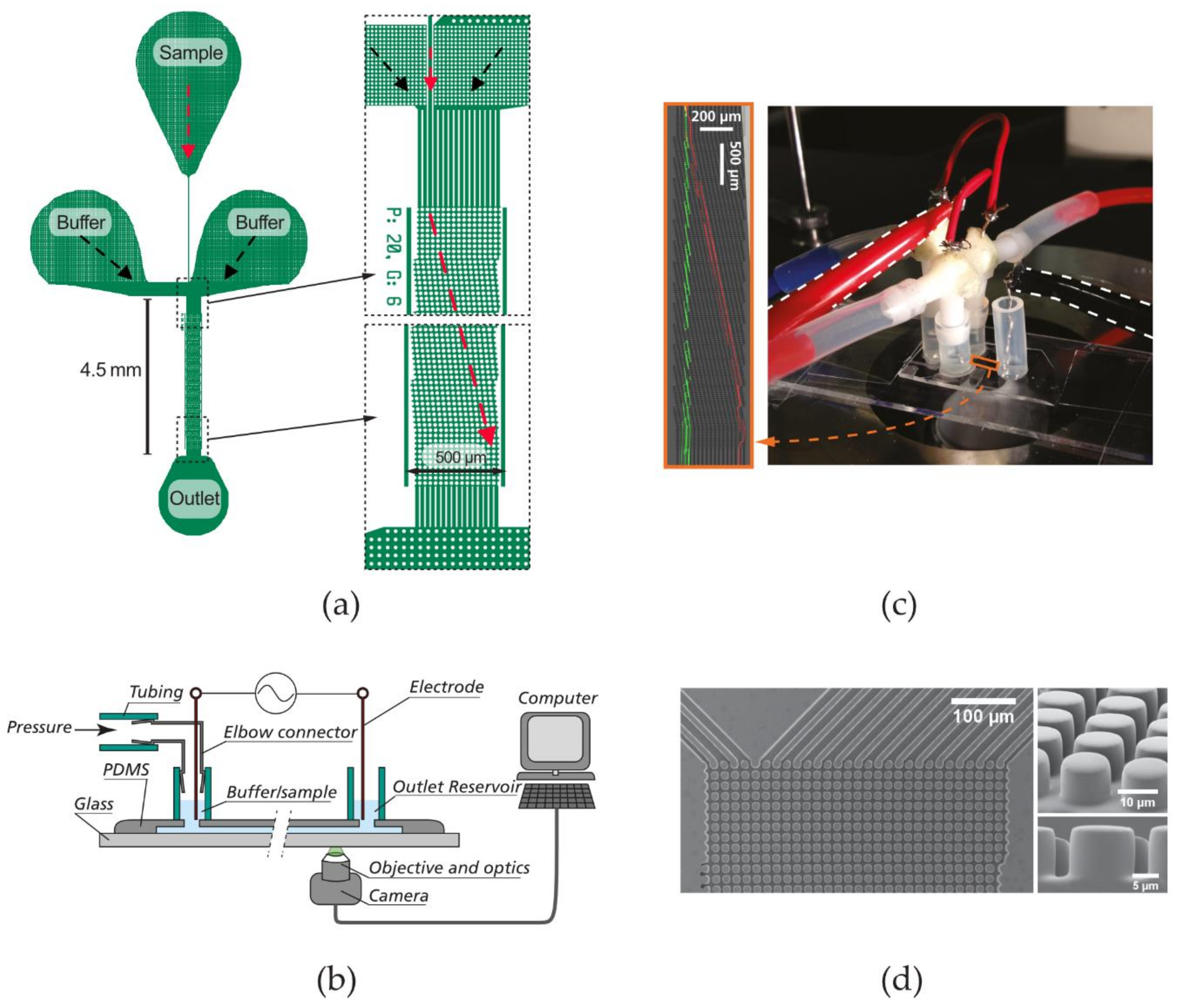

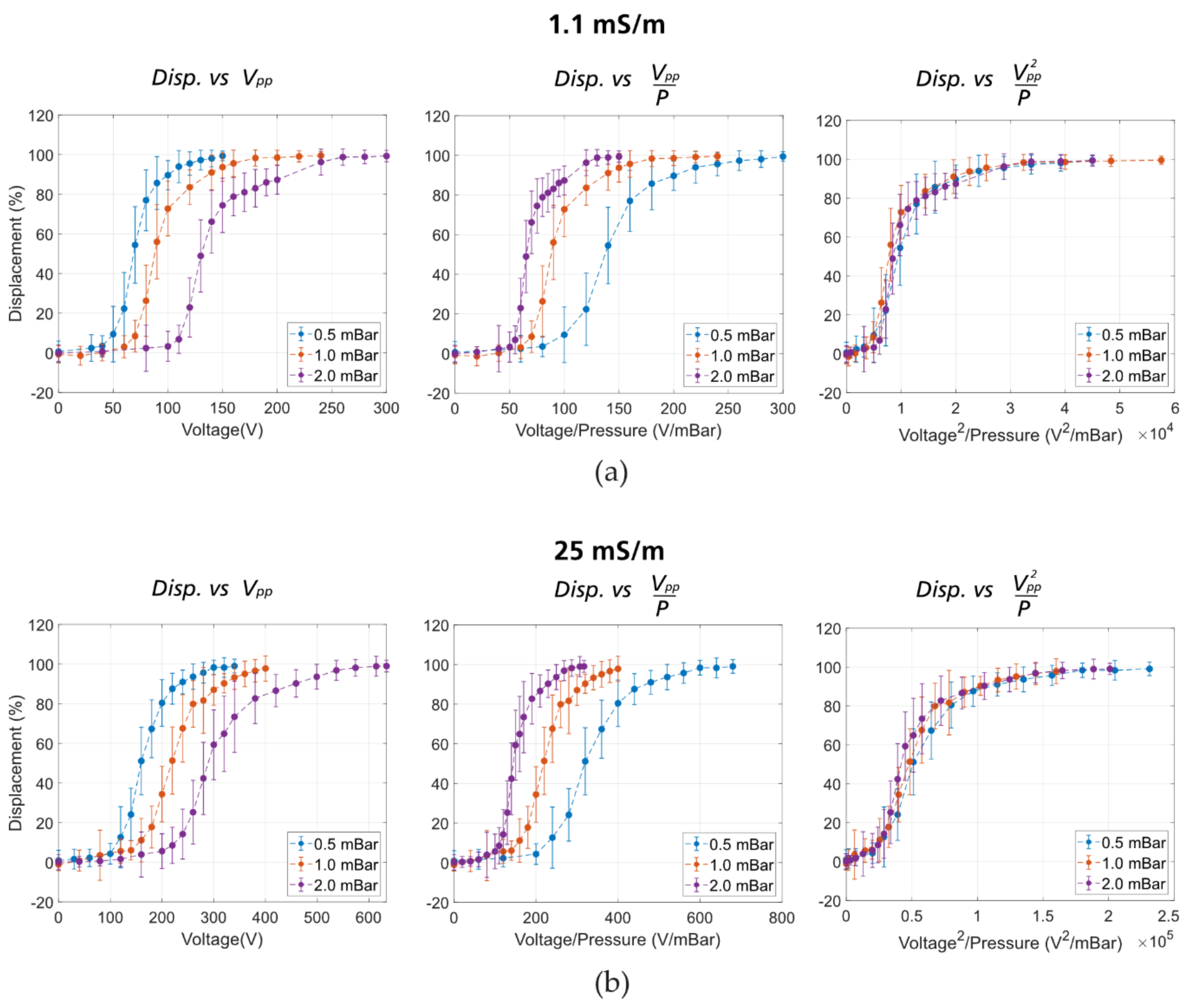
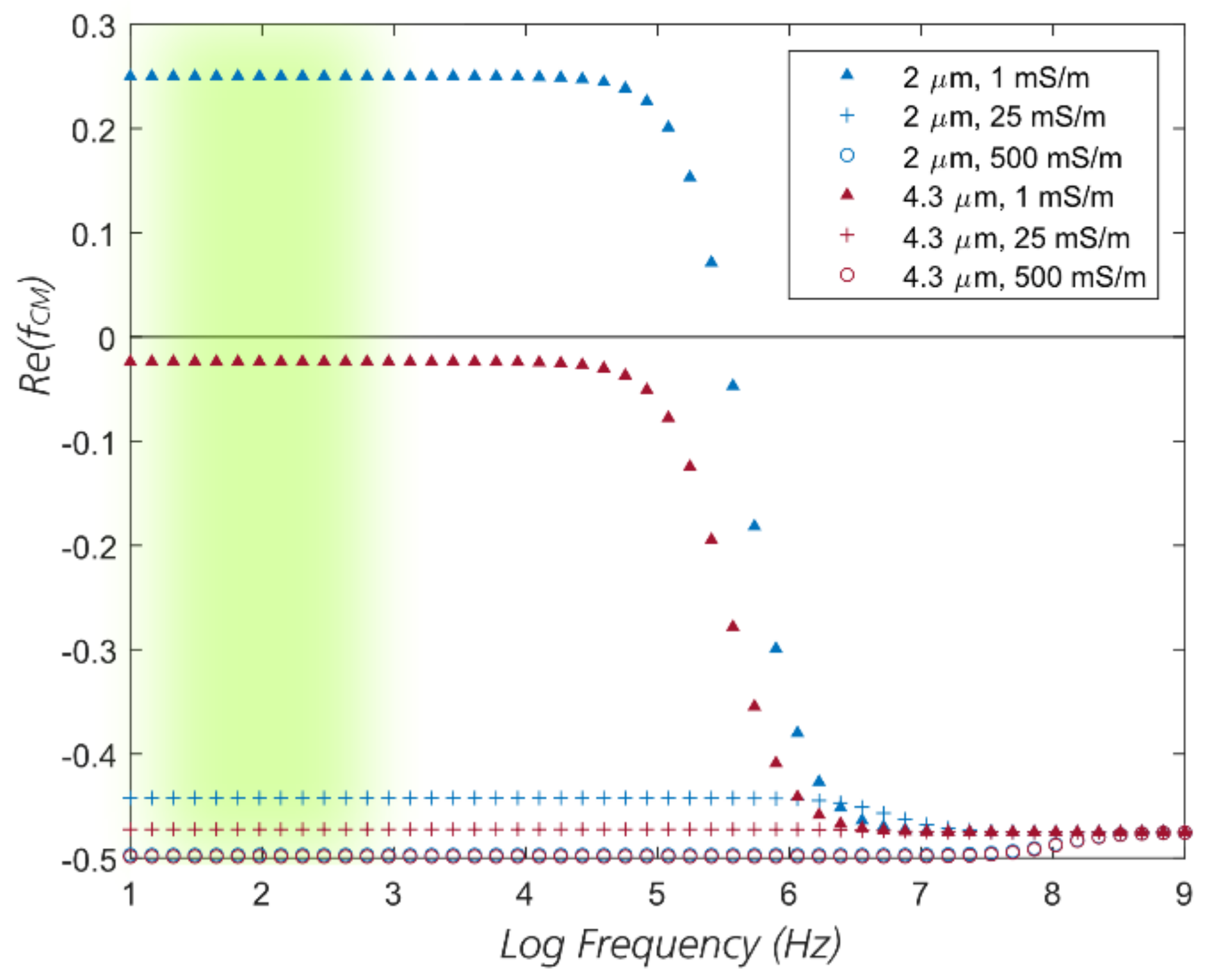
| Device Name | Gap (µm) | N | DC (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Device #1 | 2 | 20 | 0.66 |
| Device #2 | 5 | 10 | 2.32 |
| Device #3 | 6 | 10 | 2.78 |
| Device #4 | 8 | 10 | 3.71 |
| Device #5 | 13 | 10 | 6.03 |
| Device #6 | 13 | 5 | 8.41 |
| Device #7 | 4 | 23 | 1.24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, B.D.; Beech, J.P.; Tegenfeldt, J.O. Charge-Based Separation of Micro- and Nanoparticles. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11111014
Ho BD, Beech JP, Tegenfeldt JO. Charge-Based Separation of Micro- and Nanoparticles. Micromachines. 2020; 11(11):1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11111014
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Bao D., Jason P. Beech, and Jonas O. Tegenfeldt. 2020. "Charge-Based Separation of Micro- and Nanoparticles" Micromachines 11, no. 11: 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11111014
APA StyleHo, B. D., Beech, J. P., & Tegenfeldt, J. O. (2020). Charge-Based Separation of Micro- and Nanoparticles. Micromachines, 11(11), 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11111014






