Cardiac Implantable Electronic Miniaturized and Micro Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
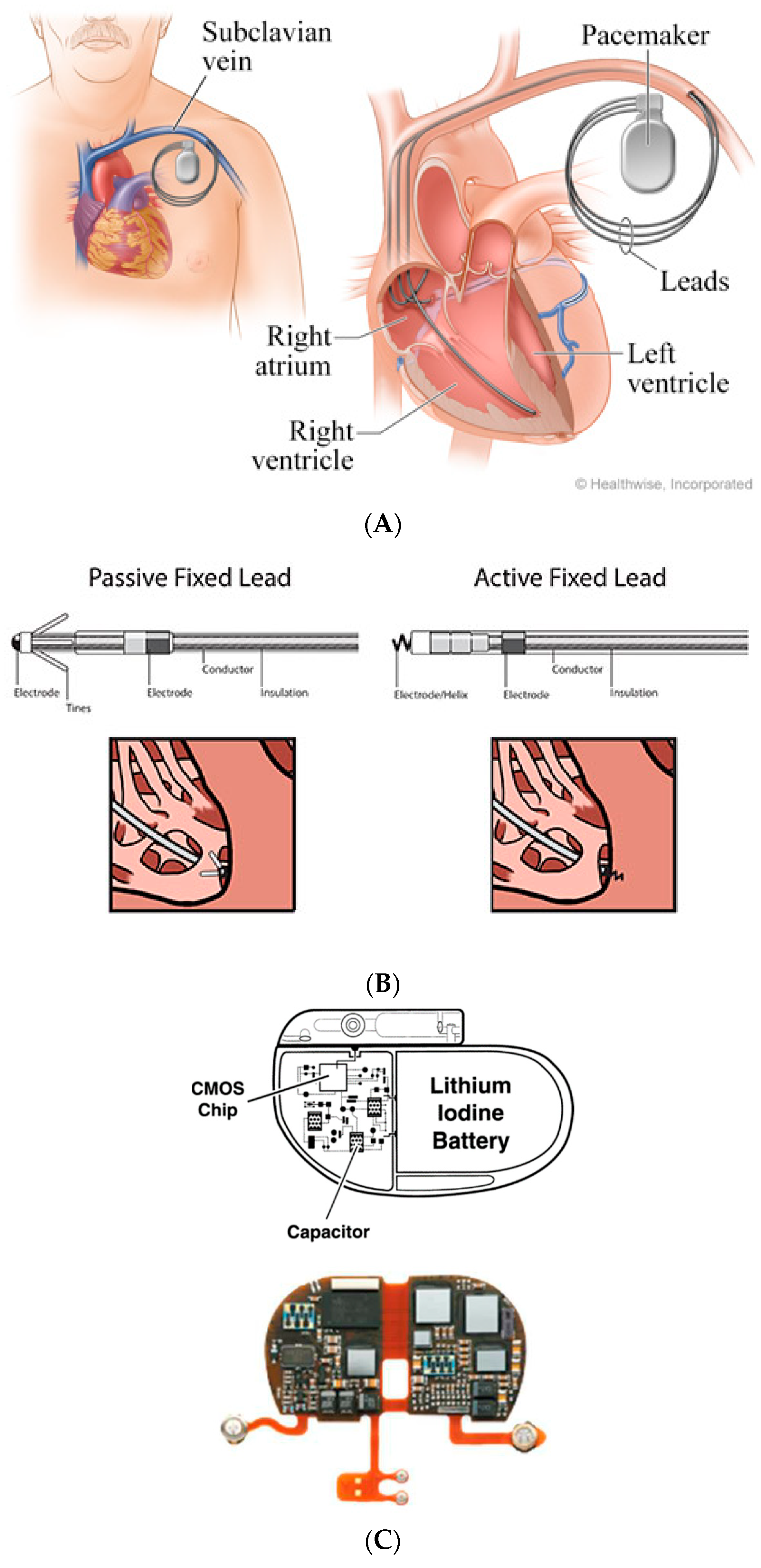
2. Conventional Pacing Devices
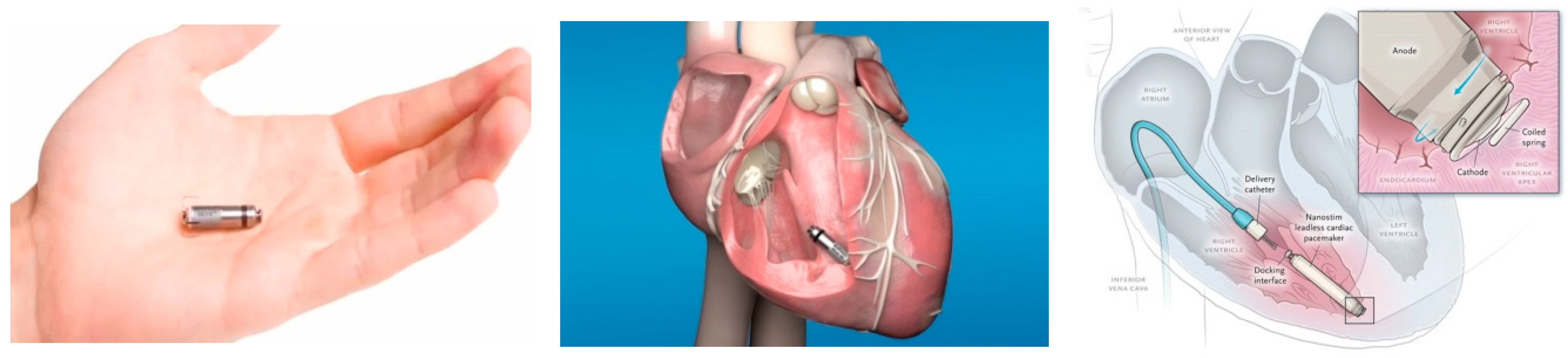
3. Leadless PPM
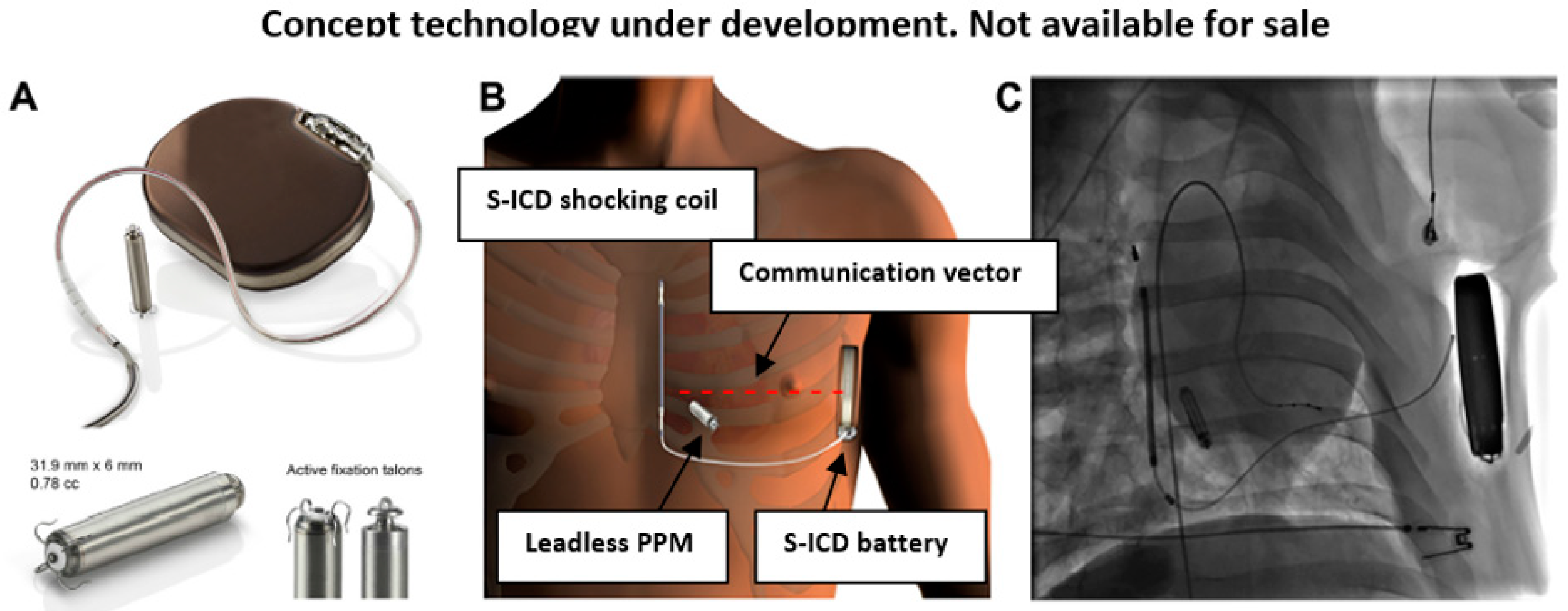
4. Modular Subcutaneous ICD and Leadless PPM
5. Multi-Component Leadless Cardiac Resynchronization Pacing System
6. Implantable Long-Term Electrocardiographic Monitoring Device
7. Implantable Devices to Monitor Heart Failure (HF) Hemodynamics
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moss, A.J.; Hall, W.J.; Cannom, D.S.; Daubert, J.P.; Higgins, S.L.; Klein, H.; Levine, J.H.; Saksena, S.; Waldo, A.L.; Wilber, D.; et al. Improved survival with an implantable defibrillator in patients with coronary artery disease at high risk for ventricular arrhythmia (MADIT-I). N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, A.E.; Lee, K.L.; Fisher, J.D.; Josephson, M.E.; Prystowsky, E.N.; Hafley, G.M.S. A randomized study of the prevention of sudden death in patients with coronary artery disease (MUSTT trial). N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1882–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, A.J.; Zareba, W.; Hall, W.J.; Klein, H.; Wilber, D.J.; Cannom, D.S.; Daubert, J.P.; Higgins, S.L.; Brown, M.W.; Andrews, M.L. Prophylactic implantation of a defibrillator in patients with myocardial infarction and reduced ejection fraction (MADIT-II). N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bardy, G.H.; Lee, K.L.; Mark, D.B.; Poole, J.E.; Packer, D.L.; Boineau, R.; Domanski, M.; Troutman, C.; Anderson, J.; Johnson, G. Amiodarone or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for congestive heart failure (SCD-HefT). N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadish, A.; Dyer, A.; Daubert, J.P.; Quigg, R.; Estes, N.M.; Anderson, K.P.; Calkins, H.; Hoch, D.; Goldberger, J.; Shalaby, A.; et al. Prophylactic defibrillator implantation in patients with nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy (DEFINITE). N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2151–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cleland, J.G.; Daubert, J.C.; Erdmann, E.; Freemantle, N.; Gras, D.; Kappenberger, L.; Tavazzi, L. The effect of cardiac resynchronization on morbidity and mortality in heart failure (CARE-HF). N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moss, A.J.; Hall, W.J.; Cannom, D.S.; Klein, H.; Brown, M.W.; Daubert, J.P.; Estes, M.N.A.; Foster, E.; Greenberg, H.; Higgins, S.L.; et al. Cardiac resynchronization therapy for the prevention of heart failure events (MADIT-CRT). N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haqqani, H.M.; Epstein, L.M.; Coope, J.M. Engineering and Construction of Pacemaker and ICD Leads. In Clinical Cardiac Pacing, Defibrillation and Resynchronization Therapy; Elsevier: Amstredam, The Netherlands, 2011; Available online: https://clinicalgate.com/engineering-and-construction-of-pacemaker-and-icd-leads (accessed on 25 September 2020).
- Mulpuru, S.K.; Madhavan, M.; McLeod, C.J.; Cha, Y.M.; Friedman, P.A. Cardiac Pacemakers: Function, Troubleshooting, and Management. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 6, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.B.; Braly, A.; Cobian, K.; Craig, M.B.; Voegtlin, L.; Haddad, T.; McVenes, R. Effect of insulation material in aging pacing leads: Comparison of impedance and other electricals: Time-dependent pacemaker insulation changes. Pacing Clin. Electroiphysiol. 2012, 35, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggins, M.J.; Wilkoff, B.; Anderson, J.M.; Hiltner, A. Biodegradation of polyether polyurethane inner insulation in bipolar pacemaker leads. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 58, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Hung, S.P.; Chen, P.R.; Yang, C.H.; Wo, H.T.; Chang, P.C.; Wang, C.C.; Chou, C.C.; Wen, M.S.; Chung, C.M.; et al. Risk factors influencing complications of cardiac implantable electronic device implantation: Infection, pneumothorax and heart perforation: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Medicine 2014, 93, e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rav Acha, M.; Rafael, A.; Keaney, J.J.; Elitzur, Y.; Danon, A.; Shauer, A.; Taha, L.; Shechter, Y.; Bogot, N.R.; Luria, D.; et al. The management of cardiac implantable electronic device lead perforations: A multicentre study. Europace 2019, 21, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbag, A.; Deshmukh, A.J. Lead perforation extending beyond the pericardium: Can we treat it percutaneously? Poke, pause, pray, and perform. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2019, 30, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.M.; Fu, H.X.; Zhong, L.; Osborn, M.J.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Sinak, L.J.; Cao, J.; Friedman, P.A.; Cha, Y.M. Outcomes of lead revision for myocardial perforation after cardiac implantable electronic device placement. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2014, 25, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döring, M.; Müssigbrodt, A.; Ebert, M.; Bode, K.; Lucas, J.; Dagres, N.; Hindricks, G.; Richter, S. Transvenous revision of leads with cardiac perforation following device implantation-Safety, outcome, and complications. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ze, F.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Li, X. Outcomes of transvenous lead extraction in patients with lead perforation: A single-center experience. Clin. Cardiol. 2020, 43, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Res, J.C.; de Priester, J.A.; van Lier, A.A.; van Engelen, C.L.; Bronzwaer, P.N.; Tan, P.H.; Visser, M. Pneumothorax resulting from subclavian puncture: A complication of permanent pacemaker lead implantation. Neth Heart J. 2004, 12, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, A.; Gandhi, M. Pneumopericardium and pneumothorax due to right atrial permanent pacemaker lead perforation. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 59, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehaman, A.; Ramesh, A.; Prajapati, S.; Basavappa, R. Lead displacement due to tension pneumothorax following permanent pacemaker implantation. J. Cardiol. Cases 2016, 15, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, F., Jr. Reducing CIED lead dislodgements: Faithful alignment to small things. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 42, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afzal, M.R.; Horner, S.; Matre, N.B.; Blake, P.; Dunham, K.; Pinkhas, D.; Okabe, T.; Tyler, J.; Houmsse, M.; Kalbfleisch, S.J.; et al. Comprehensive strategy to reduce the incidence of lead dislodgement for cardiac implantable electronic devices. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 42, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eulert-Grehn, J.J.; Schmidt, G.; Kempfert, J.; Starck, C. Inadvertent pacemaker lead dislodgement. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 41, 1266–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, W.; Zhou, C.; Yin, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, G.; Duan, C.; Cao, M.; Li, M.; Toft, E.S.; et al. Meta-analysis of the incidence of lead dislodgement with conventional and leadless pacemaker systems. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 41, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharawat, R.; Saadat, M. Twiddler’s syndrome. Acta Med. Acad. 2016, 45, 169–170. [Google Scholar]
- Polyzos, K.A.; Konstantelias, A.A.; Falagas, M.E. Risk factors for cardiac implantable electronic device infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Europace 2015, 17, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoe, J.A.; Barlow, G.; Chambers, J.B.; Gammage, M.; Guleri, A.; Howard, P.; Olson, E.; Perry, J.D.; Prendergast, B.D.; Spry, M.J.; et al. British Heart Rhythm Society; British Cardiovascular Society; British Heart Valve Society; British Society for Echocardiography. Guidelines for the diagnosis, prevention and management of implantable cardiac electronic device infection. Report of a joint Working Party project on behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (BSAC, host organization), British Heart Rhythm Society (BHRS), British Cardiovascular Society (BCS), British Heart Valve Society (BHVS) and British Society for Echocardiography (BSE). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 325–359. [Google Scholar]
- Erba, P.A.; Pizzi, M.N.; Roque, A.; Salaun, E.; Lancellotti, P.; Tornos, P.; Habib, G. Multimodality Imaging in Infective Endocarditis: An Imaging Team Within the Endocarditis Team. Circulation 2019, 140, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddour, L.M.; Wilson, W.R.; Bayer, A.S.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Tleyjeh, I.M.; Rybak, M.J.; Barsic, B.; Lockhart, P.B.; Gewitz, M.H.; Levison, M.E.; et al. American Heart Association Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, Council on Clinical Cardiology, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, and Stroke Council. Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications: A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 132, 1435–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Özcan, C.; Raunsø, J.; Lamberts, M.; Køber, L.; Lindhardt, T.B.; Bruun, N.E.; Laursen, M.L.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Gislason, G.H.; Hansen, M.L. Infective endocarditis and risk of death after cardiac implantable electronic device implantation: A nationwide cohort study. Europace 2017, 19, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulpuru, S.K.; Friedman, P.A. Infective endocarditis after cardiac implantable electronic device implantation: Incidence and associated mortality: ‘The real path to enlightenment starts with recognition’. Buddha. Europace 2017, 19, 885–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Knops, R.E.; Sperzel, J.; Miller, M.A.; Petru, J.; Simon, J.; Sediva, L.; De Groot, J.R.; Tjong, F.V.; Jacobson, P.; et al. Permanent leadless cardiac pacing: Results of the LEADLESS trial. Circulation 2014, 129, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Exner, D.V.; Cantillon, D.J.; Doshi, R.; Bunch, T.J.; Tomassoni, G.F.; Friedman, P.A.; Estes, N.A.; Niazi, I.; Plunkitt, K.; et al. Percutaneous implantation of an entirely intra cardiac leadless pacemaker. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ritter, P.; Duray, G.Z.; Zhang, S.; Narasimhan, C.; Soejima, K.; Omar, R.; Laager, V.; Stromberg, K.; Williams, E.; Reynolds, D. The rationale and design of the Micra trans-catheter pacing study: Safety and efficacy of a novel miniaturized pacemaker. Europace 2015, 17, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D.; Duray, G.Z.; Omar, R.; Oejima, K.; Neuzil, P.; Zhang, S.; Narasimhan, C.; Steinwender, C.; Brugada, J.; Lloyd, M.; et al. A leadless intracardiac trans-catheter pacing system. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 374, 534–541. [Google Scholar]
- Greatbach, W.; Holmes, C.F.; Takeuchi, E.S.; Ebel, S.J. Lithium/carbon monofluordie: A new pacemaker battery. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1996, 19, 1836–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, S.; Thwaites, B. The strength–duration curve and its importance in pacing efficiency: A study of 325 pacing leads in 229 patients. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2000, 23, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knops, R.E.; Tjong, F.V.; Neuzil, P.; Perzel, J.; Miller, M.A.; Petru, J.; Simon, J.; Sediva, L.; de Groot, J.R.; Dukkipati, S.R.; et al. Chronic performance of a leadless cardiac pacemaker: 1 year follow-up of the LEADLESS trial. JACC 2015, 65, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duray, G.Z.; Ritter, P.; El-Chami, M.; Arasimhan, C.; Omar, R.; Tolosana, J.M.; Zhang, S.; Soejima, K.; Steinwender, C.; Rapallini, L.; et al. Long-term performance of a transcatheter pacing system: 12-month results from the Micra transcatheter Pacing study. Heart Rhythm 2017, 14, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richter, S.; Doring, M.; Ebert, M.; Bode, K.; Müssigbrodt, A.; Sommer, P.; Husser, D.; Hindricks, G. Battery malfunction of a leadless cardiac pacemaker. Worrisome single center experience. Circulation 2018, 137, 2408–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docking Button Detachment in Nanostim Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker. 2018. Available online: https://www.cardiovascular.abbott/content/dam/bss/divisionalsites/cv/pdf/reports/Nanostim_Field_Safety_Notice_Update_05April2018_GL.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2020).
- Tjong, F.V.Y.; Stam, O.C.G.; Van Fer Wal, A.C.; Beenen, L.F.; Bouma, B.J.; de Groot, J.R.; Wilde, A.A.; Knops, R.E. Postmortem histo-pathological examination of a leadless pacemaker shows partial encapsulation after 19 months. Circ. Arrhyth. Elecrrophysiol. 2015, 8, 1293–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kypta, A.; Blessberger, H.; Kammler, J.; Lichtenauer, M.; Lambert, T.; Silye, R.; Steinwender, C. First Autopsy Description of Changes 1 Year After Implantation of a Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker: Unexpected Ingrowth and Severe Chronic Inflammation. Can. J. Cardiol. 2016, 32, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiani, S.; Merchant, F.M.; El-Chami, M.F. Extraction of a 4-year-old leadless pacemaker with a tine-based fixation. Heart Rhythm 2019, 5, 424–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kroman, A.; Saour, B.; Prutkin, J.M. Leadless pacemakers: Recent and future developments. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 21, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, M.R.; Shah, N.; Daoud, G.; Houmsse, M. Current state of leadless pacemakers: State of the art review. Expert Review cardiovascular Therapy. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2019, 17, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubman, E.; Ritter, P.; Ellis, C.R.; Giocondo, M.; Augostini, R.; Neuzil, P.; Ravindran, B.; Patel, A.M.; Omdahl, P.; Pieper, K.; et al. To retrieve or not to retrieve: System revisions with the Micra transcatheter pacemaker. Heart Rhythm 2017, 14, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chinitz, L.; Ritter, P.; Khelae, S.K.; Iacopino, S.; Garweg, C.; Grazia-Bongiorni, M.; Neuzil, P.; Johansen, J.B.; Mont, L.; Gonzalez, E.; et al. Accelerometer-based atrioventricular synchronous pacing with a ventricular leadless pacemaker: Results from the Micra atrioventricular feasibility studies. Heart Rhythm 2018, 15, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.; Rassaf, T.; Wakili, R. Subcutaneous ICD: Current standards and future perspective. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2019, 24, 100409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, F.V.Y.; Koop, B.E. Modular cardiac rhythm management system: The EMPOWER leadless pacemaker and the EMBLEM subcutaneous ICD. Herzshcrittmacherther Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quast, A.B.E.; Tjong, F.V.Y.; Koop, B.E.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Knops, R.E.; Burke, M.C. Device orientation of a leadless pacemaker and subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator in canine and human subjects and the effect on intra-body communication. Ep Eur. 2018, 20, 1866–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, F.V.Y.; Brouwer, T.F.; Koop, B.; Soltis, B.; Shuros, A.; Schmidt, B.; Swackhamer, B.; Quast, A.E.B.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Burke, M.C.; et al. Acute and 3-month performance of a communicating leadless anti tachycardia pacemaker and subcutaneous implantable defibrillator. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knops, R.E.; Olde Nordkamp, L.R.A.; Delnoy, P.H.M.; Boersma, L.V.A.; Kuschyk, J.; El-Chami, M.F.; Bonnemeier, H.; Behr, E.R.; Brouwer, T.F.; Kääb, S.; et al. PRAETORIAN Investigators. Subcutaneous or Transvenous Defibrillator Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullens, W.; Nijst, P. Leadless Left Ventricular Pacing: Another Step Toward Improved CRT Response. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 2130–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auricchio, A.; Delnoy, P.P.; Butter, C.; Brachmann, J.; Van Erven, L.; Spitzer, S.; Moccetti, T.; Seifert, M.; Markou, T.; Laszo, K.; et al. Feasability, safety and short-term outcome of the leadless ultrasound-based endocardial left ventricular resynchronization in hear failure patients: Results of the Wireless Stimulation Endocardially for CRT (Wise-CRT) study. Europace 2014, 16, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.; Sedivy, P.; Mraz, T. Wireless LV endocardial stimulation for cardiac resynchronization: Initial experience from the SELECT-LV study. Heart Rhythm 2014, 11, S41. [Google Scholar]
- Sieniewicz, B.J.; Betts, T.R.; James, S.; Turley, A.; Butter, C.; Seifert, M.; Boersma, L.V.A.; Riahi, S.; Neuzil, P.; Biffi, M.; et al. Real-world experience of leadless left ventricular endocardial resynchronization therapy: A multicenter international registry of the WISE-CRT pacing system. Heart Rhythm 2020, 17, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereuter, L.; Niederhauser, T.; Kucera, M.; Loosli, D.; Steib, I.; Schildknecht, M.; Zurbuchen, A.; Noti, F.; Tanner, H.; Reichlin, T.; et al. Leadless cardiac resynchronization therapy: An in-vivo proof-of–concept study of wireless pacemaker synchronization. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemerlo, E.; Pozzi, M.; De Ceglia, S.; Santini, F.; Piazzi, E.; Rovaris, G. First-in-man fully leadless transvenous CRT-P with a transseptal implant of WISE-CRT® system and Micra® PM. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 42, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maria, E.; Ziacchi, M.; Diemberger, I.; Biffi, M. Leadless left ventricular endocardial pacing: A real alternative or a luxury for a few? Cardiovas. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 8, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, B.S.; Gould, J.; Porter, B.; Elliott, M.; Mehta, V.; Niederer, S.; Rinaldi, C.A. Completely Leadless Cardiac Resynchronization Defibrillator System. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galand, V.; Polin, B.; Martins, R.P.; Leclercq, C. Entirely leadless cardiac resynchronization therapy. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 858–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawhney, V.; Domenichini, G.; Gamble, J.; Furniss, G.; Panagopoulos, D.; Lambiase, P.; Rajappan, K.; Chow, A.; Lowe, M.; Sporton, S.; et al. Thrombo-embolic events in left ventricular endocardial pacing: Long-term outcomes from a multicentre UK registry. Europace 2018, 20, 1997–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
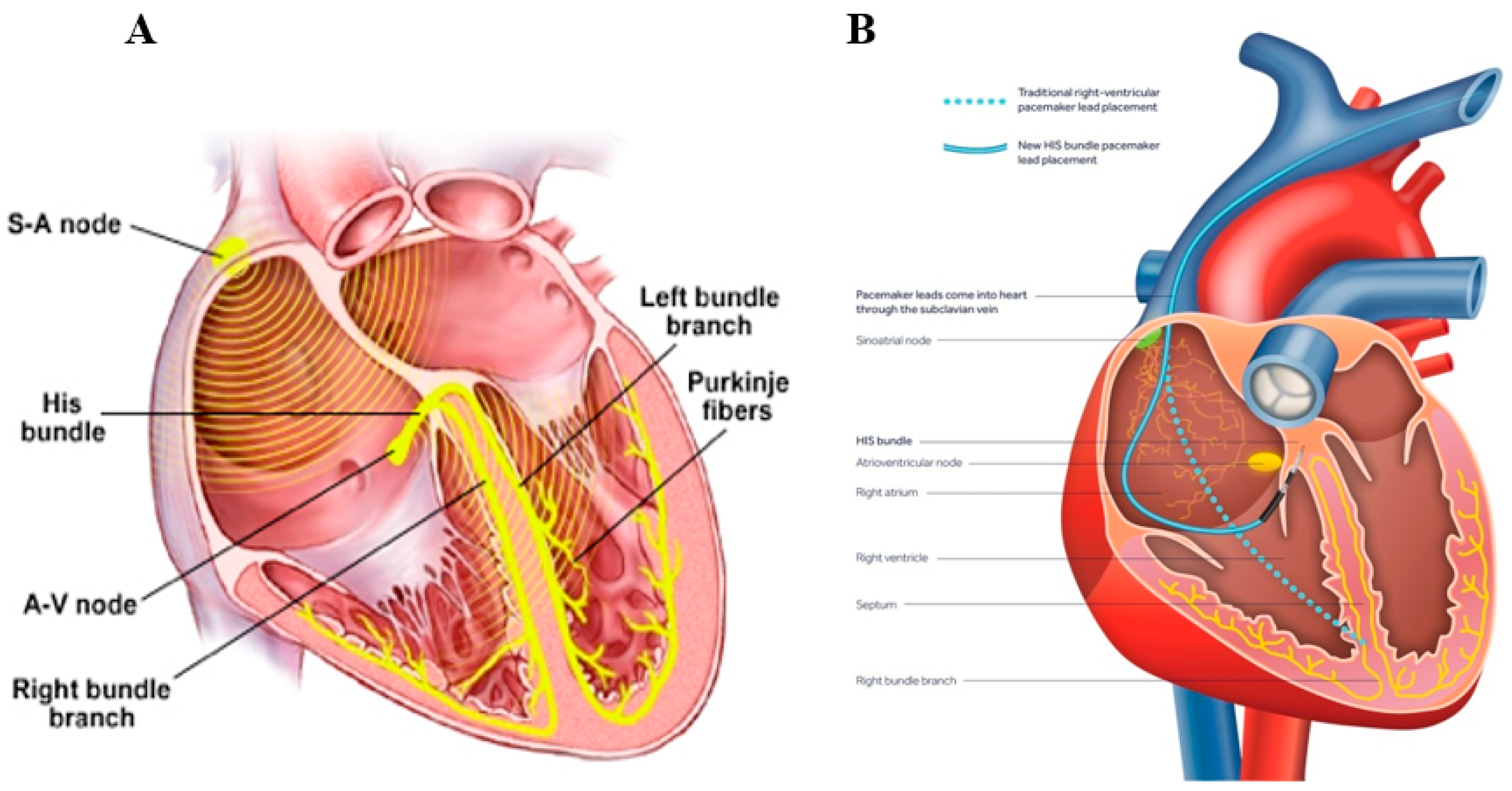
- Lewis, A.J.M.; Foley, P.; Whinnett, Z.; Keene, D.; Chandrasekaran, B. His bundle pacing: A new strategy for physiological ventricular activation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vijayaraman, P. His-bundle Pacing to Left Bundle Branch Pacing: Evolution of His-Purkinje Conduction System Pacing. J. Innov. Card. Rhythm Manag. 2019, 10, 3668–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraman, P.; Chung, M.K.; Dandamudi, G.; Upadhyay, G.A.; Krishnan, K.; Crossley, G.; Bova Campbell, K.; Lee, B.K.; Refaat, M.M.; Saksena, S.; et al. ACC’s Electrophysiology Council. His Bundle Pacing. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 927–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Trohman, R.G. Permanent His Bundle Pacing: The Past, Present, and Future. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2017, 28, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraman, P.; Dandamudi, G.; Zanon, F.; Sharma, P.S.; Tung, R.; Huang, W.; Koneru, J.; Tada, H.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Lustgarten, D.L. Permanent His bundle pacing: Recommendations from a Multicenter His Bundle Pacing Collaborative Working Group for standardization of definitions, implant measurements, and follow-up. Heart Rhythm 2018, 15, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Upadhyay, G.A.; Tung, R. His Bundle Pacing for Cardiac Resynchronization. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2018, 10, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Su, L.; Wu, S.; Xu, L.; Xiao, F.; Zhou, X.; Ellenbogen, K.A. A Novel Pacing Strategy With Low and Stable Output: Pacing the Left Bundle Branch Immediately Beyond the Conduction Block. Can. J. Cardiol. 2017, 33, 1736.e1–1736.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraman, P.; Subzposh, F.A.; Naperkowski, A.; Panikkath, R.; John, K.; Mascarenhas, V.; Bauch, T.D.; Huang, W. Prospective evaluation of feasibility and electrophysiologic and echocardiographic characteristics of left bundle branch area pacing. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundaram, S.; Vijayaraman, P. Left bundle branch pacing. Herzschrittmacherther. Elektrophysiol. 2020, 31, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvardsson, N.; Frykman, V.; van Mechelen, R.; Mitro, P.; Mohii-Oskarsson, A.; Pasquié, J.L.; Ramanna, H.; Schwertfeger, F.; Ventura, R.; Voulgaraki, D.; et al. Use of an implantable loop recorder to increase the diagnostic yield in unexplained syncope: Results from the PICTURE registry. Europace 2011, 13, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solbiati, M.; Costantino, G.; Casazza, G.; Dipaola, F.; Galli, A.; Furlan, R.; Montano, N.; Sheldon, R. Implantable loop recorder versus conventional diagnostic workup for unexplained recurrent syncope. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 4, CD011637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, J.; Borobio, M.C. Atrial fibrillation diagnosed by a loop recorder in a patient with cryptogenic stroke. JACC 2014, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.; Mittal, S. Utility and limitations of long-term monitoring of atrial fibrillation using an implantable loop recorder. Heart Rhythm 2018, 15, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidemann, F.; Maier, S.K.; Störk, S.; Brunner, T.; Liu, D.; Hu, K.; Seydelmann, N.; Schneider, A.; Becher, J.; Canan-Kühl, S.; et al. Usefulness of an Implantable Loop Recorder to Detect Clinically Relevant Arrhythmias in Patients With Advanced Fabry Cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 118, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milstein, N.S.; Musat, D.L.; Allred, J.; Seiler, A.; Pimienta, J.; Oliveros, S.; Bhatt, A.G.; Preminger, M.; Sichrovsky, T.; Shaw, R.E.; et al. Detection of atrial fibrillation using an implantable loop recorder following cryptogenic stroke: Implications for post-stroke electrocardiographic monitoring. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2020, 57, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Víctor, C.U.; Carolina, P.E.; Jorge, T.R.; Joaquín, C.R.; Manuel, S.G.; Marta, C.M.; José María, F.V.; Chinh, P.T.; Javier, O.M.; Susana, M.S.; et al. Incidence and Predictive Factors of Hidden Atrial Fibrillation Detected by Implantable Loop Recorder After an Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2018, 11, 2078. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, A.; Joza, J.; Malkani, K.; Mendelson, T.B.; Priori, S.G.; Chinitz, L.A.; Fowler, S.J.; Cerrone, M. Implantable Loop Recorder in Inherited Arrhythmia Diseases: A Critical Tool for Symptom Diagnosis and Advanced Risk Stratification. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 4, 1372–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avari Silva, J.N.; Bromberg, B.I.; Emge, F.K.; Bowman, T.M.; Van Hare, G.F. Implantable Loop Recorder Monitoring for Refining Management of Children With Inherited Arrhythmia Syndromes. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e003632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakhi, R.; Theuns, D.A.; Bhagwandien, R.E.; Michels, M.; Schinkel, A.F.; Szili-Torok, T.; Zijlstra, F.; Roos-Hesselink, J.W.; Yap, S.C. Value of implantable loop recorders in patients with structural or electrical heart disease. J. Interv. Cardiac. Electrophysiol. 2018, 52, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisignani, A.; De Bonis, S.; Mancuso, L.; Ceravolo, G.; Bisignani, G. Implantable loop recorder in clinical practice. J. Arrhythm. 2018, 35, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, G.J.; Krahn, A.; Yee, R.; Skanes, A. The implantable loop recorder: The herald of a new age of implantable monitors. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2000, 23, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, D.; Kancharla, K.; El-Harasis, M.A.; Isath, A.; Makkar, N.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Friedman, P.A.; Cha, Y.M.; Kapa, S. Diagnostic and therapeutic value of implantable loop recorder: A tertiary care center experience. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 42, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abraham, W.T.; Perl, L. Implantable Hemodynamic Monitoring for Heart Failure Patients. JACC 2017, 70, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emani, S. Remote Monitoring to Reduce Heart Failure Readmissions. Curr. Heart Fail Rep. 2017, 14, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, A.M.; Fong, M.; Grazette, L.; Rahman, J.E.; Shavelle, D.M. Chronic heart failure management and remote haemodynamic monitoring. Heart 2018, 104, 1910–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourge, R.C.; Abraham, W.T.; Adamson, P.B.; Aaron, M.F.; Aranda, J.M.; Magalski, A.; Zile, M.R.; Smith, A.; Smart, F.W.; O’Shaughnessy, M.A.; et al. Randomized Controlled Trial of an Implantable Continuous Hemodynamic Monitor in Patients With Advanced Heart Failure: The COMPASS-HF Study. JACC 2008, 18, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Givertz, M.M.; Stevenson, L.W.; Costanzo, M.R.; Bourge, R.C.; Bauman, J.G.; Ginn, G.; Abraham, W.T.; CHAMPION Trial Investigators. Pulmonary Artery Pressure-Guided Management of Patients With Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1875–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, W.T.; Stevenson, L.W.; Bourge, R.C.; Lindenfeld, J.A.; Bauman, J.G.; Adamson, P.B.; CHAMPION Trial Study Group. Sustained efficacy of pulmonary artery pressure to guide adjustment of chronic heart failure therapy: Complete follow-up results from the CHAMPION randomised trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, W.T.; Adamson, P.B.; Bourge, R.C.; Aaron, M.F.; Costanzo, M.R.; Stevenson, L.W.; Strickland, W.; Neelagaru, S.; Raval, N.; Krueger, S.; et al. Wireless Pulmonary Artery Haemodynamic Monitoring in Chronic Heart Failure: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.S.; Adamson, P.B.; Costanzo, M.R.; Eigler, N.; Gilbert, J.; Gold, M.R.; Klapholz, M.; Saxon, L.A.; Singh, J.P.; Troughton, R.; et al. Rationale and Design of the Left Atrial Pressure Monitoring to Optimize Heart Failure Therapy Study (LAPTOP-HF). J. Card. Fail. 2015, 21, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perl, L.; Soifer, E.; Bartunek, J.; Erdheim, D.; Köhler, F.; Abraham, W.T.; Meerkin, D. A Novel Wireless Left Atrial Pressure Monitoring System for Patients With Heart Failure, First Ex-Vivo and Animal Experience. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2019, 12, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gierula, J.; Kearney, M.T.; Witte, K.K. Devices in heart failure; diagnosis, detection and disease modification. Br. Med. Bull. 2018, 125, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindricks, G.; Taborsky, M.; Glikson, M.; Heinrich, U.; Schumacher, B.; Katz, A.; Brachmann, J.; Lewalter, T.; Goette, A.; Block, M.; et al. Implant-based multiparameter telemonitoring of patients with heart failure (IN-TIME): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padeletti, L.; Botto, G.L.; Curnis, A.; De Ruvo, E.; D’Onofrio, A.; Gronda, E.; Ricci, R.P.; Vado, A.; Zanotto, G.; Zecchin, M.; et al. Selection of potential predictors of worsening heart failure: Rational and design of the SELENE HF study. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 16, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, A.; Tajstra, M.; Gadula-Gacek, E.; Buchta, P.; Skrzypek, M.; Pyka, L.; Wasiak, M.; Swietlinska, M.; Hawranek, M.; Polonski, L.; et al. Impact of Remote Monitoring on Long-Term Prognosis in Heart Failure Patients in a Real-World Cohort: Results From All-Comers COMMIT-HF Trial. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2017, 28, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolina, M.; Gasparini, M.; Lunati, M.; Santini, M.; Rordorf, R.; Vincenti, A.; Diotallevi, P.; Montenero, A.S.; Bonanno, C.; De Santo, T.; et al. Heart rate variability monitored by the implanted device predicts response to CRT and long-term clinical outcome in patients with advanced heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2008, 10, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, A.C.; Leather, R.A.; Novak, P.G.; Sterns, L.D.; Tang, A.S. The role of device diagnostic algorithms in the assessment and management of patients with systolic heart failure: A review. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2011, 2011, 908921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conraads, V.M.; Tavazzi, L.; Santini, M.; Oliva, F.; Gerritse, B.; Yu, C.M.; Cowie, M.R. Sensitivity and positive predictive value of implantable intrathoracic impedance monitoring as a predictor of heart failure hospitalizations: The SENSE-HF trial. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 2266–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vamos, M.; Nyolczas, N.; Bari, Z.; Bogyi, P.; Muk, B.; Szabo, B.; Ancsin, B.; Kiss, R.G.; Duray, G.Z. Refined heart failure detection algorithm for improved clinical reliability of OptiVol alerts in CRT-D recipients. Cardiol. J. 2018, 25, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cowie, M.R.; Sarkar, S.; Koehler, J.; Whellan, D.J.; Crossley, G.H.; Tang, W.H.; Abraham, W.T.; Sharma, V.; Santini, M. Development and validation of an integrated diagnostic algorithm derived from parameters monitored in implantable devices for identifying patients at risk for heart failure hospitalization in an ambulatory setting. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2472–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | Micra (Medtronic, Inc., USA) | Nanostim (Saint Jude Medical, USA) |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | 0.8 cm3 | 1 cm3 |
| Size | 25.9 mm × 6.7 mm | 42 mm × 5.99 mm |
| Weight | 1.75 g | 2 g |
| Fixation | Passive nitinol tines | Active helix screw |
| Battery | lithium silver oxide/carbon monofluoride | lithium carbon monofluoride |
| Estimated battery longevity | 10 years | 14.7 years |
| Rate response mechanism | 3-D accelerometer | Blood temperature sensing |
| Communication with remote programmer-‘telemetry’ | Radio-frequency signals | Conductive communication through skin electrodes |
| Parameter | Chronicle | CardioMEMS | HeartPOD | V-LAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site of pressure readout | Right ventricle | Pulmonary artery | Left atrium | Left atrium |
| Structure | Subcutaneous device with intravenous lead in right ventricle | Implant and external antenna | subcutaneous antenna coil with intravenous trans-septal lead | Implanted within interatrial septum |
| Energy source | Subcutaneous battery | External | External | External |
| Clinical study | COMPASS-HF [33] | CHAMPION [34] | LAPTOP-HF [35] | Ongoing |
| Key findings | Failed in primary outcome | Reduced HF hospitalizations | Stopped early for implant-related complications | Pending |
| Current status | Not available for clinical use | FDA approved | Not available for clinical use | On trial |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rav Acha, M.; Soifer, E.; Hasin, T. Cardiac Implantable Electronic Miniaturized and Micro Devices. Micromachines 2020, 11, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100902
Rav Acha M, Soifer E, Hasin T. Cardiac Implantable Electronic Miniaturized and Micro Devices. Micromachines. 2020; 11(10):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100902
Chicago/Turabian StyleRav Acha, Moshe, Elina Soifer, and Tal Hasin. 2020. "Cardiac Implantable Electronic Miniaturized and Micro Devices" Micromachines 11, no. 10: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100902
APA StyleRav Acha, M., Soifer, E., & Hasin, T. (2020). Cardiac Implantable Electronic Miniaturized and Micro Devices. Micromachines, 11(10), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100902





