The Composition-Dependent Photoluminescence Properties of Non-Stoichiometric ZnxAgyInS1.5+x+0.5y Nanocrystals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, W.S.; Chen, N.; Dong, C.H.; Tu, Y.; Chang, J.; Zhang, B.B. One-pot synthesis of hydrophilic ZnCuInS/ZnS quantum dots for in vivo imaging. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 9470–9475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.T.; Wang, Y.C.; Yang, C.B.; Hu, S.Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.P.; Wang, Y.; Demir, H.V.; Liu, L.W.; Yong, K.T. The composition effect on the optical properties of aqueous synthesized Cu-In-S and Zn-Cu-In-S quantum dot nanocrystals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 25133–25141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.S.; Chen, N.; Tu, Y.; Dong, C.H.; Zhang, B.B.; Hu, C.H.; Chang, J. Synthesis of Zn-Cu-In-S/ZnS core/shell quantum dots with inhibited blue-shift photoluminescence and applications for tumor targeted bioimaging. Theranostics 2013, 3, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Kato, W.; Uehara, M.; Nose, K.; Omata, T.; Otsuka-Yao-Matsuo, S.; Miyazaki, M.; Maeda, H. Tunable photoluminescence wavelength of chalcopyrite CuInS2-based semiconductor nanocrystals synthesized in a colloidal system. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 3330–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewerenz, H.J. Development of copperindiumdlsulfide into a solar material. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2004, 83, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.C.; Oh, J.H.; Ko, M.; Yoo, H.; Do, Y.R. Synthesis and characterization of green Zn-Ag-In-S and red Zn-Cu-In-S quantum dots for ultrahigh color quality of down-converted white LEDs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 7342–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.X.; Mora-Sero, I.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wang, J.; Zhong, X.H.; Bisquert, J. High-efficiency “green” quantum dot solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 9203–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, P.M.; Bawendi, M.G. Ternary I-III-VI quantum dots luminescent in the red to near infrared. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9240–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Hinds, S.; Kelley, S.O.; Sargent, E.H. Synthesis of colloidal CuGaSe2, CuInSe2, and Cu(InGa)Se2 nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 6906–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.C.; Wang, X.L.; Zhou, Z.H.; Chen, W.; Xu, C.L.; Lu, Y.F. Synthesis of quaternary semiconductor nanocrystals with tunable band gaps. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 2489–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Gardner, J.S.; Long, G.; Bajracharya, C.; Thurber, A.; Punnoose, A.; Rodriguez, R.G.; Pak, J.J. Controlled stoichiometry for quaternary CuInxGa1−xS2 chalcopyrite nanoparticles from single-source precursors via microwave irradiation. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 2699–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobosko, S.M.; Jara, D.H.; Kamat, P.V. AgInS2-ZnS quantum dots: Excited state interactions with TiO2 and photovoltaic performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 33379–33388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinchi, H.; Wakao, M.; Nagata, N.; Sakamoto, M.; Mochizuki, E.; Uematsu, T.; Kuwabata, S.; Suda, Y. Cadmium-free sugar-chain-immobilized fluorescent nanoparticles containing low-toxicity ZnS-AgInS2 cores for probing lectin and cells. Bioconjugate Chem. 2014, 25, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.W.; Cao, J.; Qu, L.Z.; Achilefu, S.; Gu, Y.Q. Highly luminescent water-soluble quaternary Zn-Ag-In-S quantum dots for tumor cell-targeted imaging. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 5078–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Vittal, J.J. Synthesis and characterization of ternary AgInS2 nanocrystals by dual and multiple-source methods. New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 2083–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Kinoshita, K. Electrical and optical-properties of AgInS2. Solid-State Electron. 1976, 19, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redjai, E.; Masse, G. Donor-Acceptor Pair Transitions in AgInS2. Phys. Status Solidi B 1985, 131, K157–K159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, T.; Doko, A.; Torimoto, T.; Oohora, K.; Hayashi, T.; Kuwabata, S. Photoinduced electron transfer of ZnS-AgInS2 solid-solution semiconductor nanoparticles: emission quenching and photocatalytic reactions controlled by electrostatic forces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 15667–15676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, G.; Redjai, E. S-Vacancy energy-levels in AgInS2. J. Appl. Phys. 1986, 59, 1544–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krustok, J.; Raudoja, J.; Krunks, M.; Mändar, H.; Collan, H. Nature of the native deep localized defect recombination centers in the chalcopyrite and orthorhombic AgInS2. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamanaka, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Tsuzuki, M.; Kuzuya, T. Photoluminescence properties and its origin of AgInS2 quantum dots with chalcopyrite structure. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 1786–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Rutherford, M.; Peng, X. Formation of high-quality I-III-VI semiconductor nanocrystals by tuning relative reactivity of cationic precursors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5691–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, W.; Xie, C.; Wang, J.; Zhong, J.; Liang, X.; Yang, H.; Luo, L.; Chen, Z. Studies on highly luminescent AgInS2 and Ag-Zn-In-S quantum dots. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 588, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.P.; Park, H.K.; Oh, J.H.; Yang, H.; Do, Y.R. Comparisons of the structural and optical properties of o-AgInS2, t-AgInS2, and c-AgIn5S8 nanocrystals and their solid-solution nanocrystals with ZnS. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 18939–18949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Jiang, T.; Guo, T.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Xia, T.; Zhang, W.; Ye, X.; Yang, M.; Zhu, L. Facile synthesis of water-soluble Zn-Doped AgIn5S8/ZnS core/shell fluorescent nanocrystals and their biological application. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, M.; Yoon, H.C.; Yoo, H.; Oh, J.H.; Yang, H.; Do, Y.R. Highly efficient green Zn-Ag-In-S/Zn-In-S/ZnS QDs by a strong exothermic reaction for down-converted green and tripackage white LEDs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1602638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, R.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, G.; Su, J.; Dinh, C.T.; Li, J. 0D-2D quantum dot: Metal dichalcogenide nanocomposite photocatalyst achieves efficient hydrogen generation. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, T.; Takahashi, T.; Machida, T.; Kamiya, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Kuwabata, S.; Torimoto, T. Controlling the electronic energy structure of ZnS-AgInS2 solid solution nanocrystals for photoluminescence and photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 24740–24749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, I.; Kato, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Kudo, A. photocatalytic H2 evolution under visible-light irradiation over band-structure-controlled (CuIn)xZn2(1-x)S2 solid solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 7323–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.W. CuInS2/ZnS core/shell quantum dots by cation exchange and their blue shifted photoluminescence. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3745–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torimoto, T.; Adachi, T.; Okazaki, K.; Sakuraoka, M.; Shibayama, T.; Ohtani, B.; Kudo, A.; Kuwabata, S. Facile Synthesis of ZnS-AgInS2 Solid solution nanoparticles for a color adjustable luminophore. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12388–12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogihara, Y.; Yukawa, H.; Kameyama, T.; Nishi, H.; Onoshima, D.; Ishikawa, T.; Torimoto, T.; Baba, Y. Labeling and in vivo visualization of transplanted adipose tissue-derived stem cells with safe cadmium-free aqueous ZnS coating of ZnS-AgInS2 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevallier, T.; Blevennec, G.L.; Chandezon, F. Photoluminescence properties of AgInS2-ZnS nanocrystals: The critical role of the surface. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7612–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.K.; Hirata, S.; Bujak, L.; Biju, V.; Kameyama, T.; Kishi, M.; Torimotoc, T.; Vacha, M. Influence of Zn on the photoluminescence of colloidal (AgIn)xZn2(1−x)S2 nanocrystals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 3963–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Sun, M.; Yang, F.; Yang, X.R. A facile approach to synthesize high-quality ZnxCuyInS1.5+x+0.5y nanocrystal emitters. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6422–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, C.; Qin, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, P.; Peng, X. Syntheticcontrolofexcitonbehaviorincolloidalquantumdots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3302–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torimoto, T.; Kamiya, Y.; Kameyama, T.; Nishi, H.; Uematsu, T.; Kuwabata, S.; Shibayama, T. controlling shape anisotropy of ZnS-AgInS2 solid solution nanoparticles for improving photocatalytic activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27151–27161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.H.; Hong, K.J.; Youn, C.J.; Jeong, T.S.; Moon, J.D.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.S. Origin of point defects in AgInS2/GaAs epilayer obtained from photoluminescence measurement. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 3894–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
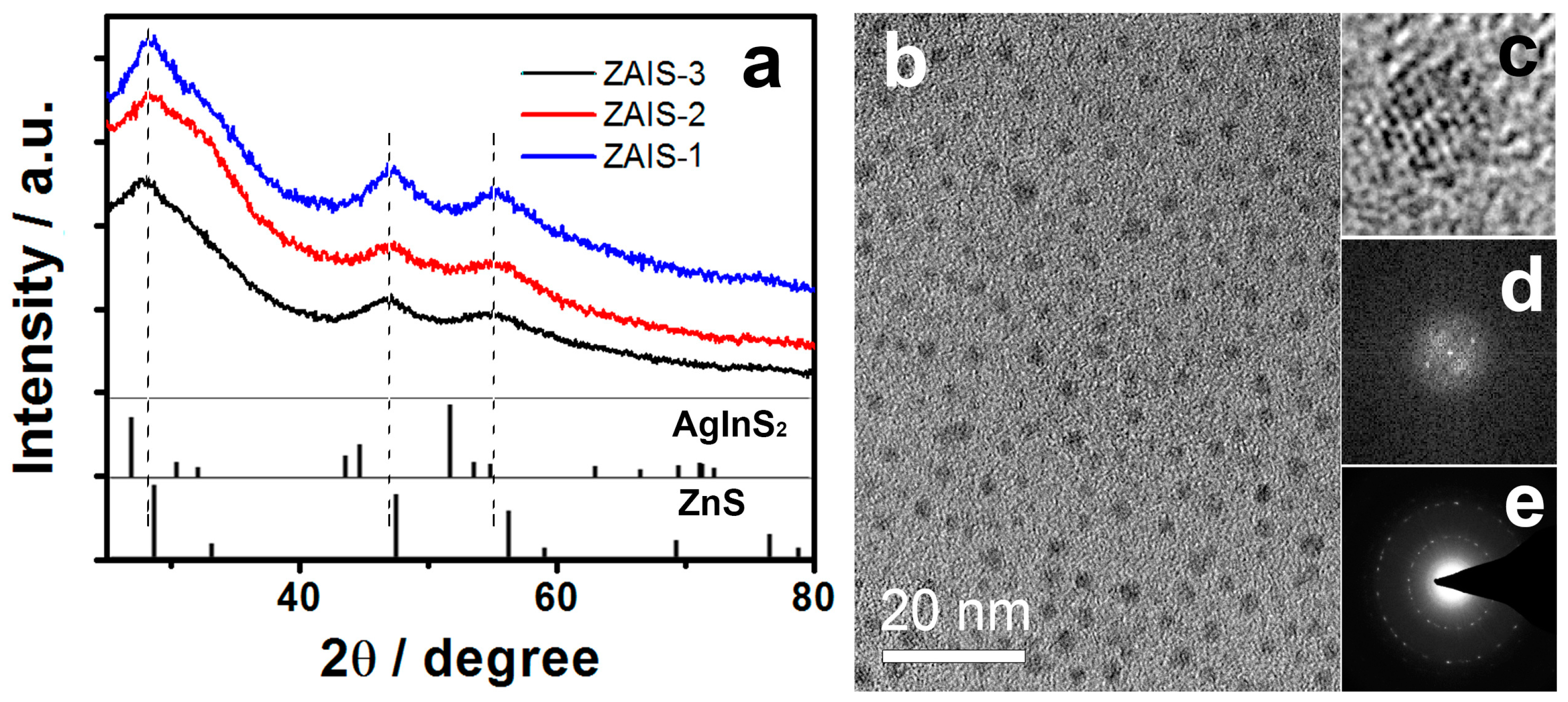
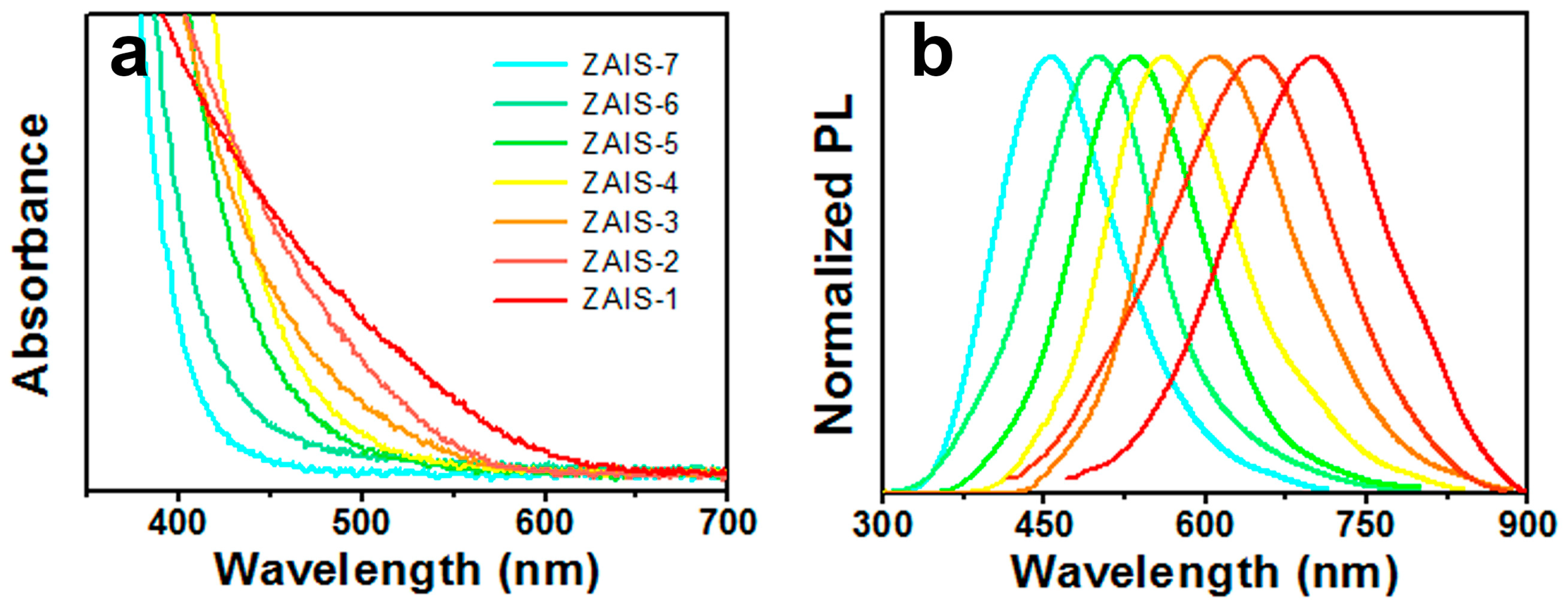
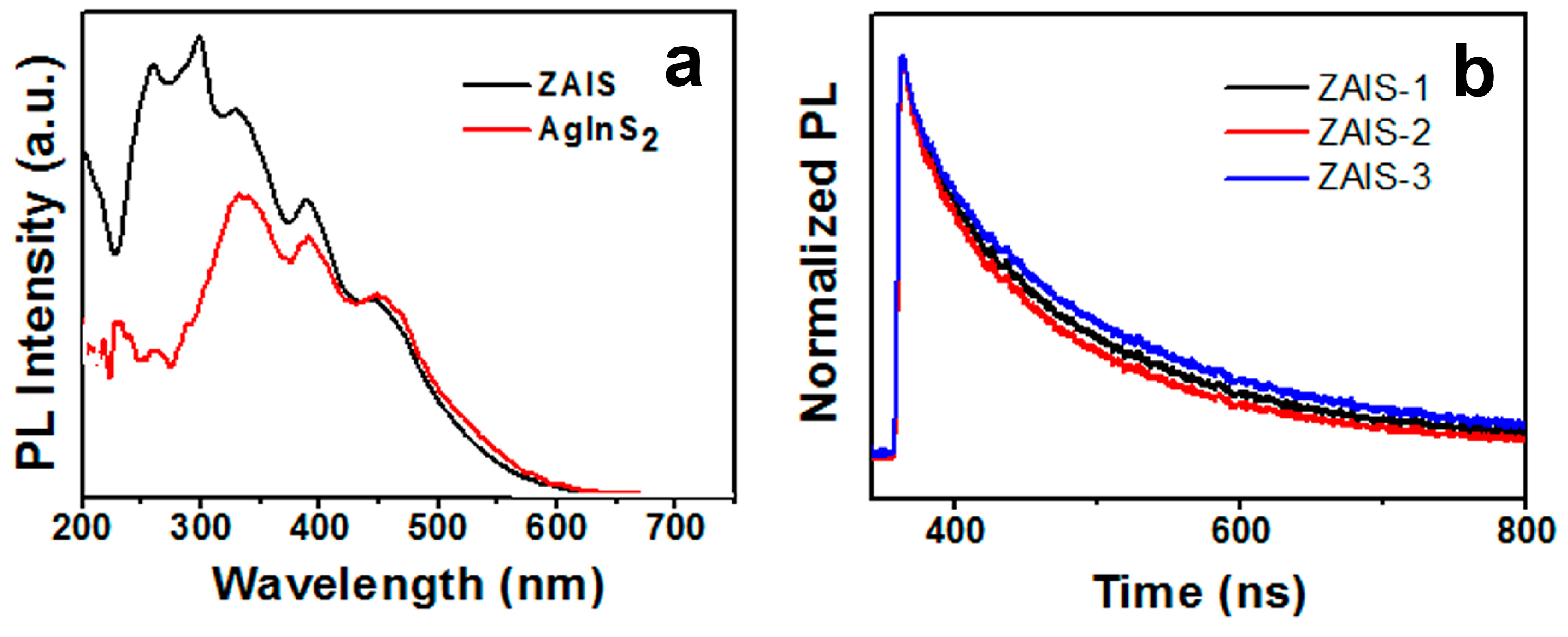
| Sample | PL Emission Wavelength (nm) | Relative Quantum Yield | Silver Dosage in the Precursor y (%) | Composition of the Nanoparticle | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | Ag (%) | Zn (%) | |||
| ZAIS-1 | 700.5 | 8 | 15.0 | 14.1 | 22.9 |
| ZAIS-2 | 647.5 | 15 | 10.0 | 9.12 | 23.1 |
| ZAIS-3 | 607.0 | 30 | 5.00 | 4.47 | 24.9 |
| ZAIS-4 | 561.0 | 35 | 2.50 | 2.33 | 24.1 |
| ZAIS-5 | 533.5 | 23 | 1.25 | 1.15 | 23.5 |
| ZAIS-6 | 500.5 | 11 | 0.625 | 0.564 | 24.1 |
| ZAIS-7 | 456.0 | 5 | - | - | 24.4 |
| Sample | PL Emission Wavelength (nm) | Relative Quantum Yield | DDT Dosage in the Precursor (mmol) | Composition of the Nanoparticle | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | Ag (%) | Zn (%) | |||
| Sample1 | 542.5 | 4 | 0.25 | 1.57 | 21.5 |
| Sample2 | 550.0 | 12 | 0.5 | 2.04 | 23.7 |
| Sample3 | 561.0 | 35 | 1.0 | 2.33 | 24.1 |
| Sample4 | 572.0 | 18 | 1.5 | 2.55 | 26.2 |
| Sample5 | 573.5 | 7 | 2.0 | 2.47 | 25.6 |
| Sample | ZAIS-1 | ZAIS-2 | ZAIS-3 | (AgIn)xZn2(1−x)S2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| τ1/ns | 115 | 146 | 148 | 127–131 |
| a | 0.423 | 0.562 | 0.577 | - |
| τ2/ns | 455 | 481 | 483 | 538–655 |
| b | 0.0324 | 0.0615 | 0.0641 | - |
| average | 194 | 234 | 237 | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, J.; Yang, X.; Li, R.; Yang, X.; Feng, G. The Composition-Dependent Photoluminescence Properties of Non-Stoichiometric ZnxAgyInS1.5+x+0.5y Nanocrystals. Micromachines 2019, 10, 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10070439
Feng J, Yang X, Li R, Yang X, Feng G. The Composition-Dependent Photoluminescence Properties of Non-Stoichiometric ZnxAgyInS1.5+x+0.5y Nanocrystals. Micromachines. 2019; 10(7):439. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10070439
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Jian, Xiaosheng Yang, Rong Li, Xianjiong Yang, and Guangwei Feng. 2019. "The Composition-Dependent Photoluminescence Properties of Non-Stoichiometric ZnxAgyInS1.5+x+0.5y Nanocrystals" Micromachines 10, no. 7: 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10070439
APA StyleFeng, J., Yang, X., Li, R., Yang, X., & Feng, G. (2019). The Composition-Dependent Photoluminescence Properties of Non-Stoichiometric ZnxAgyInS1.5+x+0.5y Nanocrystals. Micromachines, 10(7), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10070439






