The Effect of Displacement Constraints on the Failure of MEMS Tuning Fork Gyroscopes under Shock Impact
Abstract
1. Introduction
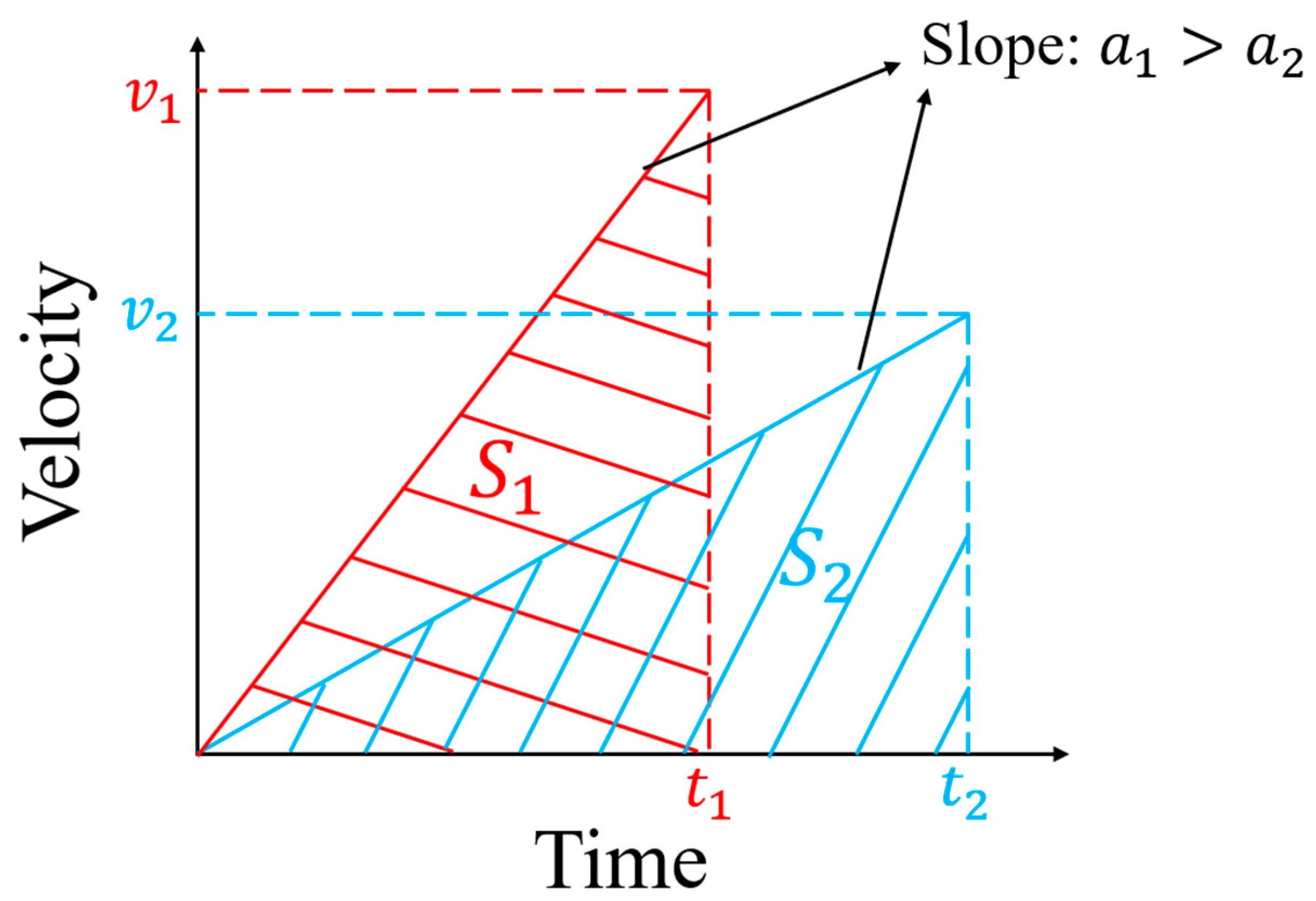
2. Theory and Equations
3. Simulation and Analysis
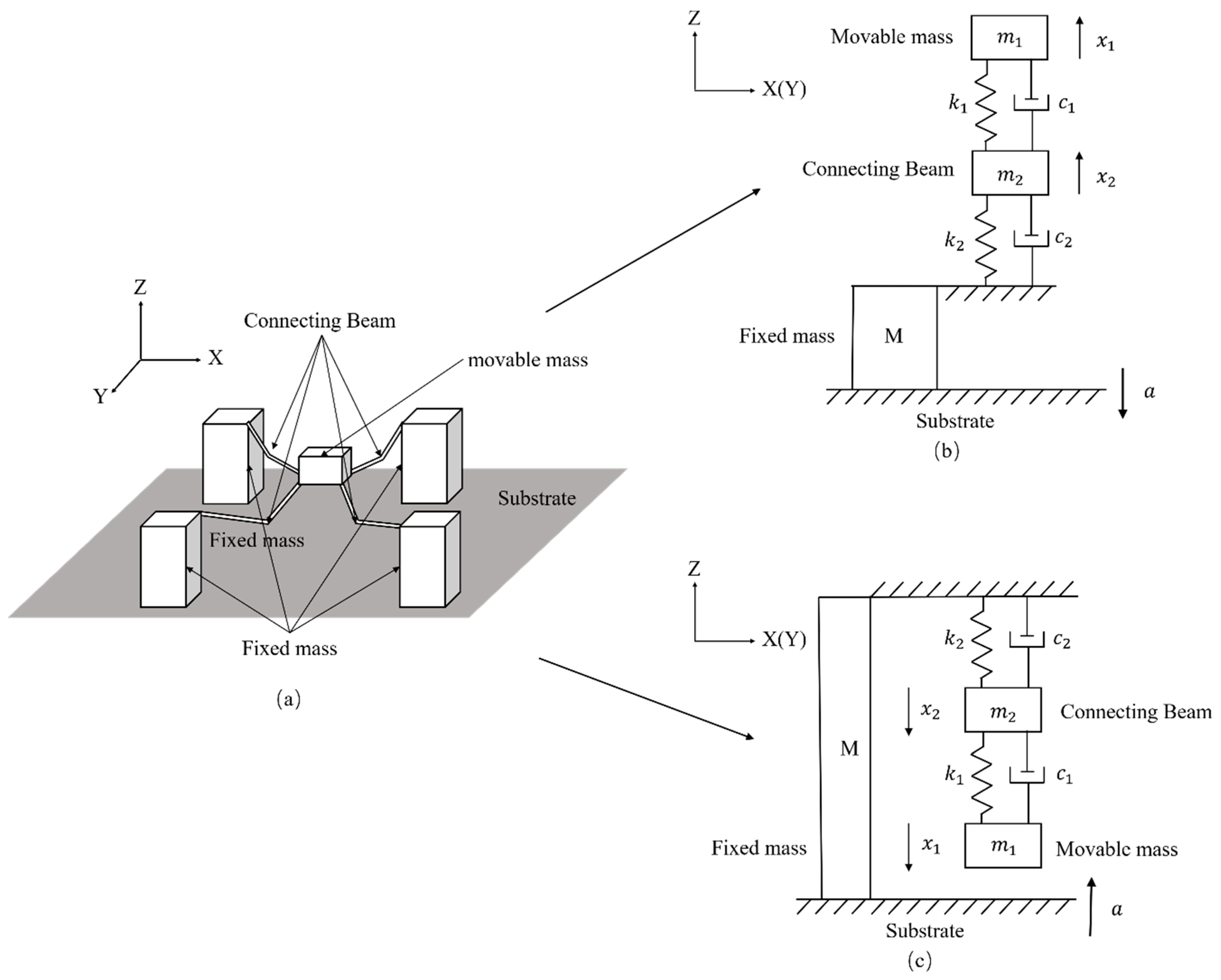
3.1. FEA Model and Setting
3.2. FEA Results and Discussion
3.2.1. Failure Analysis of MEMS Tuning Fork Gyroscope under Z-Axis Shock Impact
3.2.2. Failure Analysis of MEMS Tuning Fork Gyroscope under X-Axis/Y-Axis Shock Impact
4. Shock Test
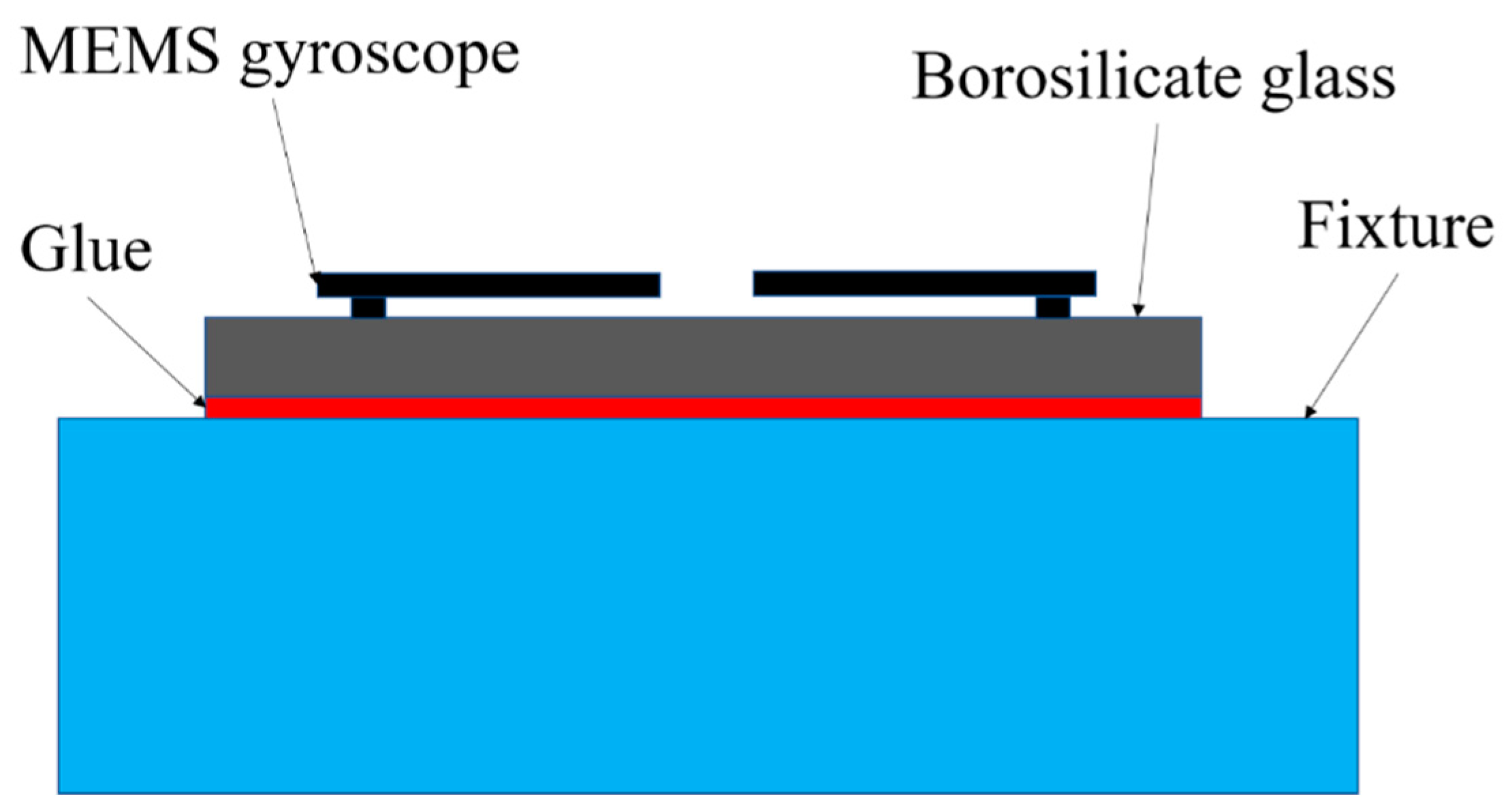
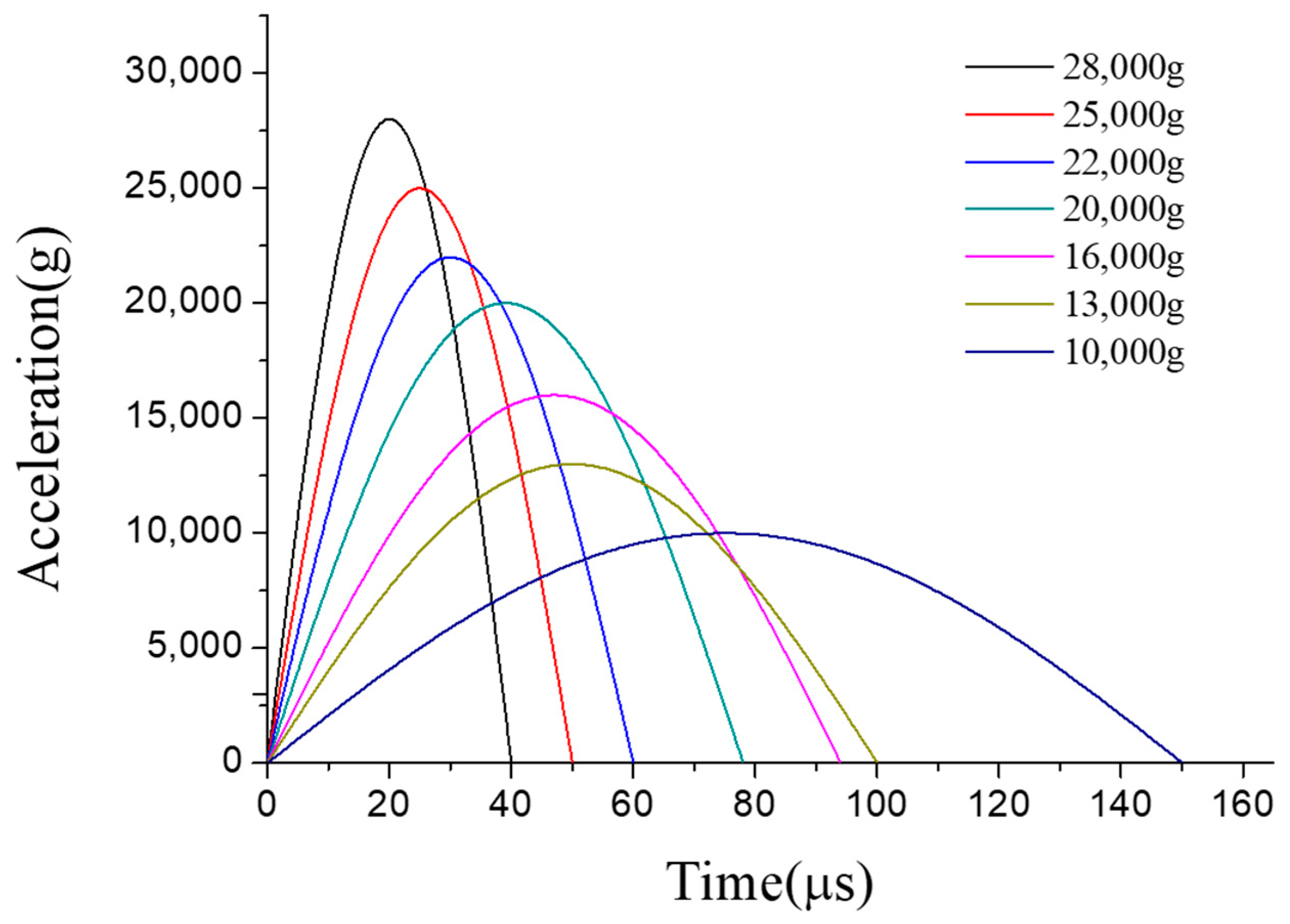
4.1. Experimental Method
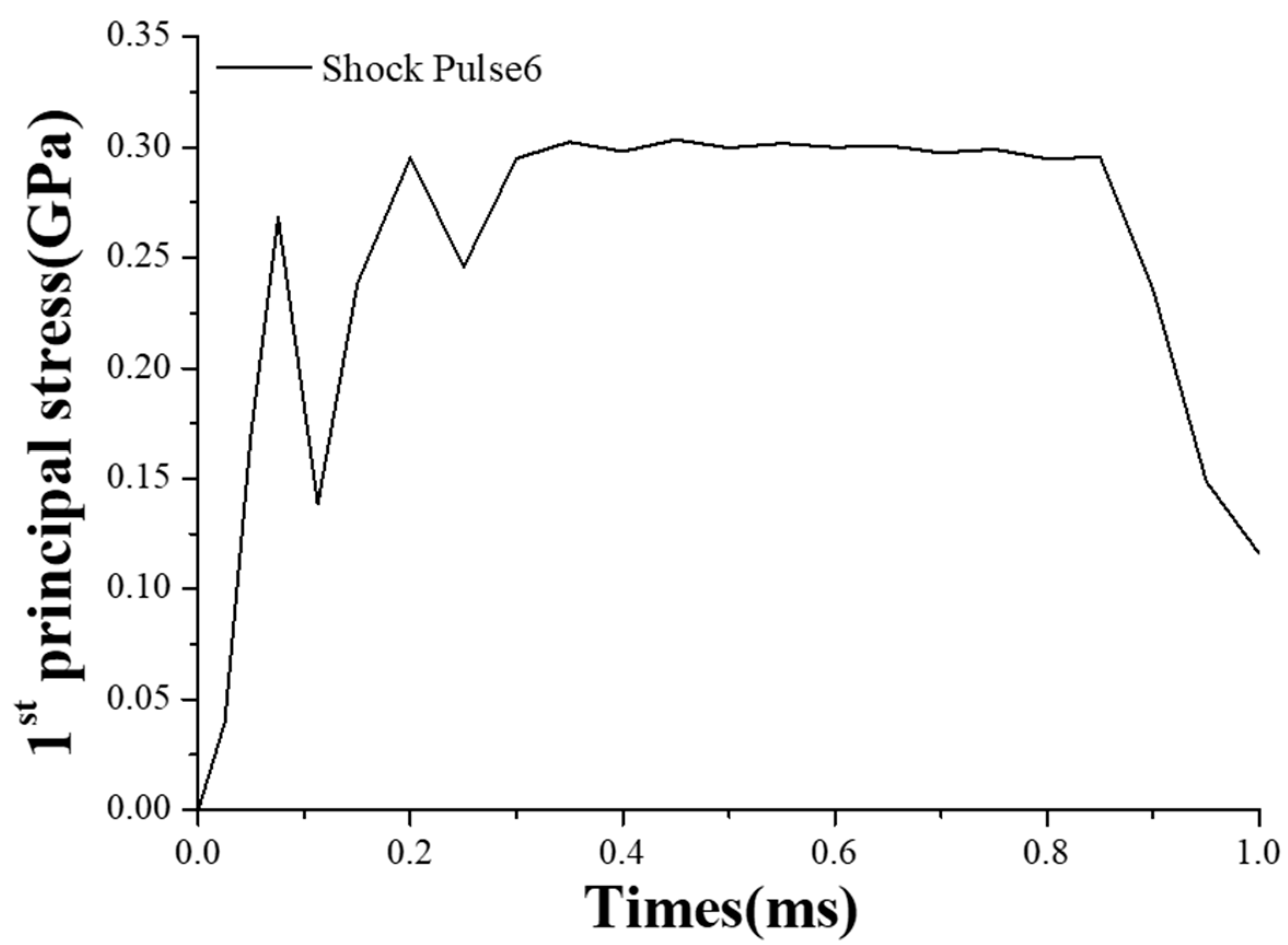
4.2. Experimental Results
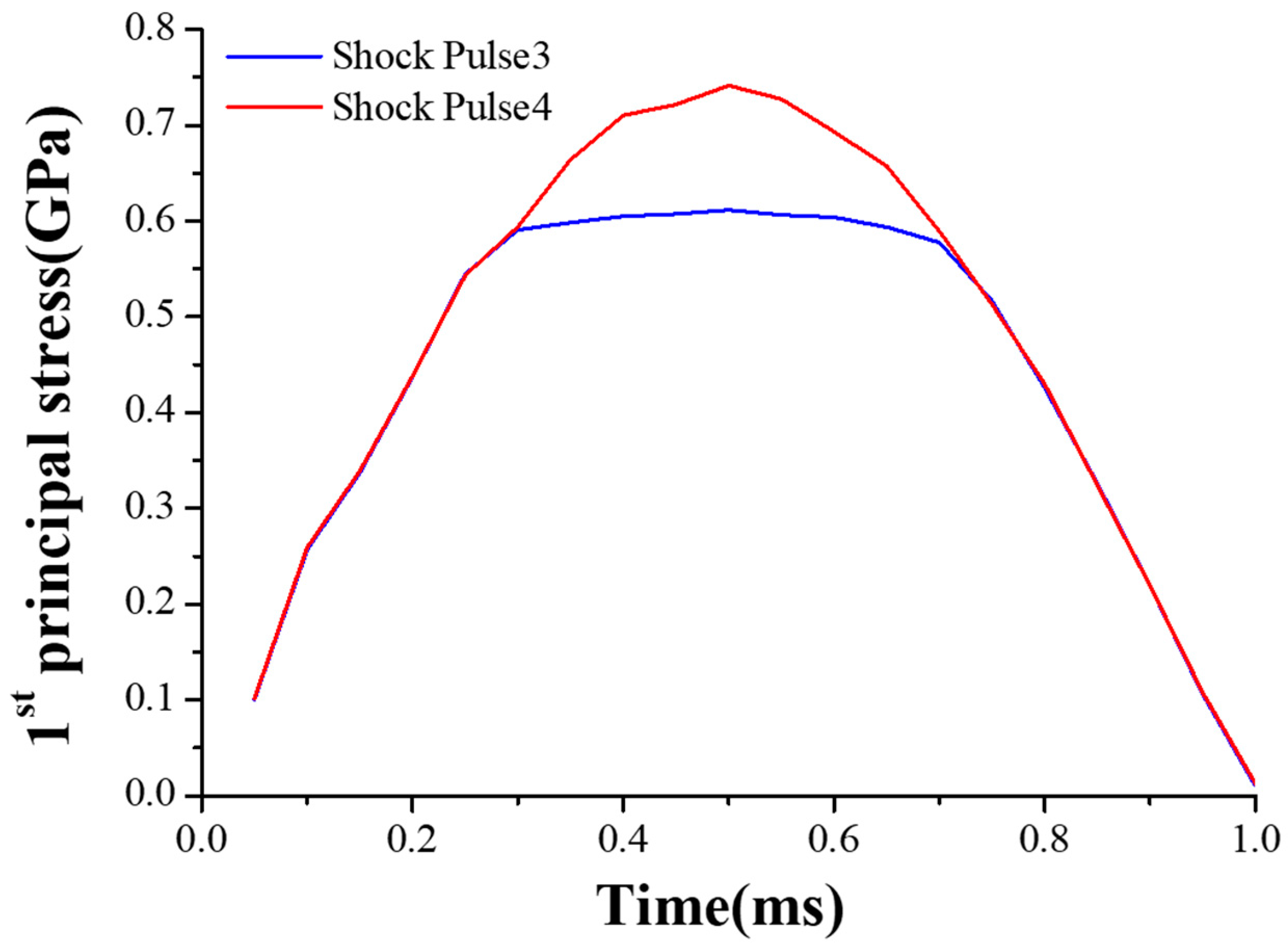
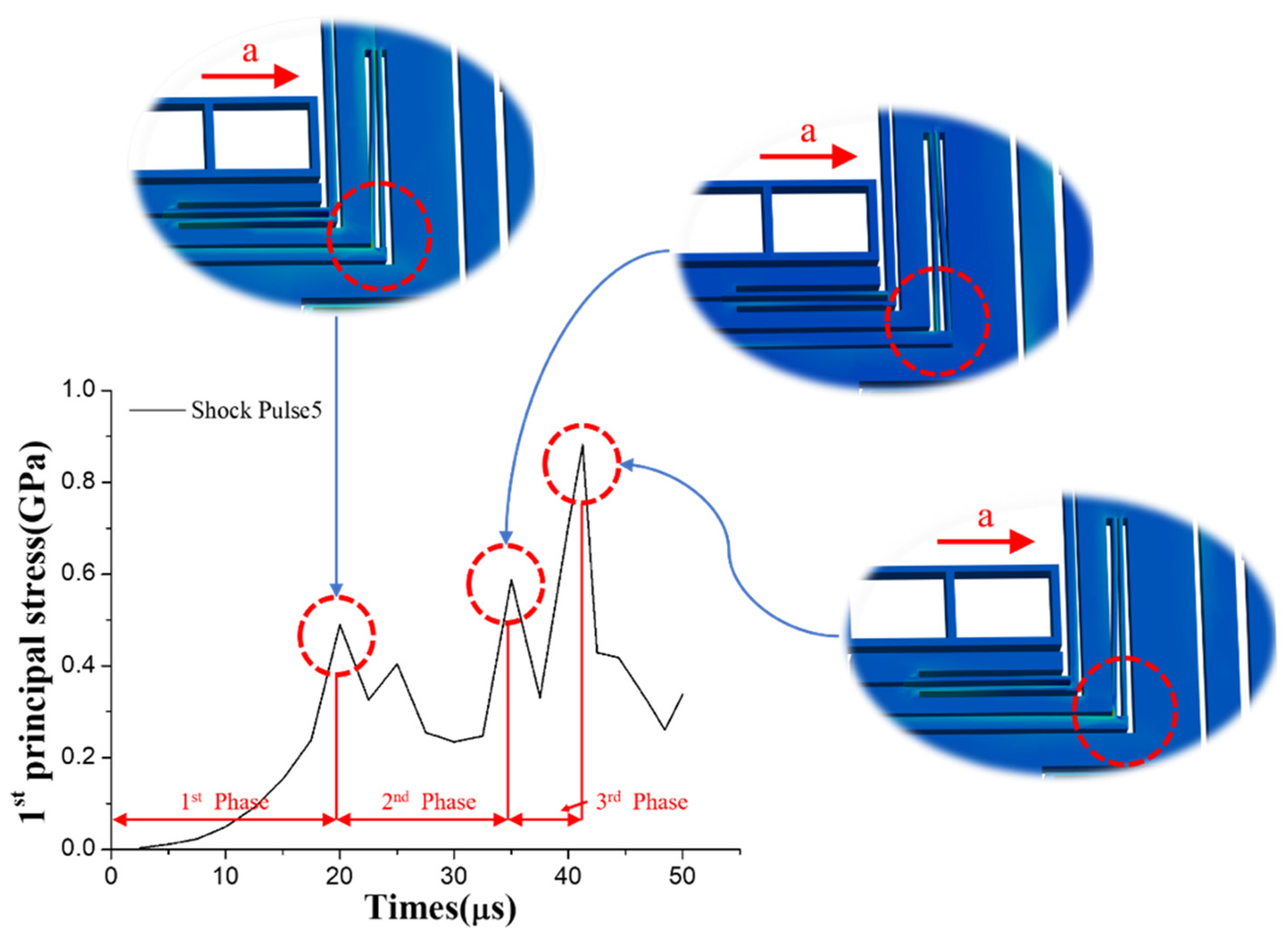
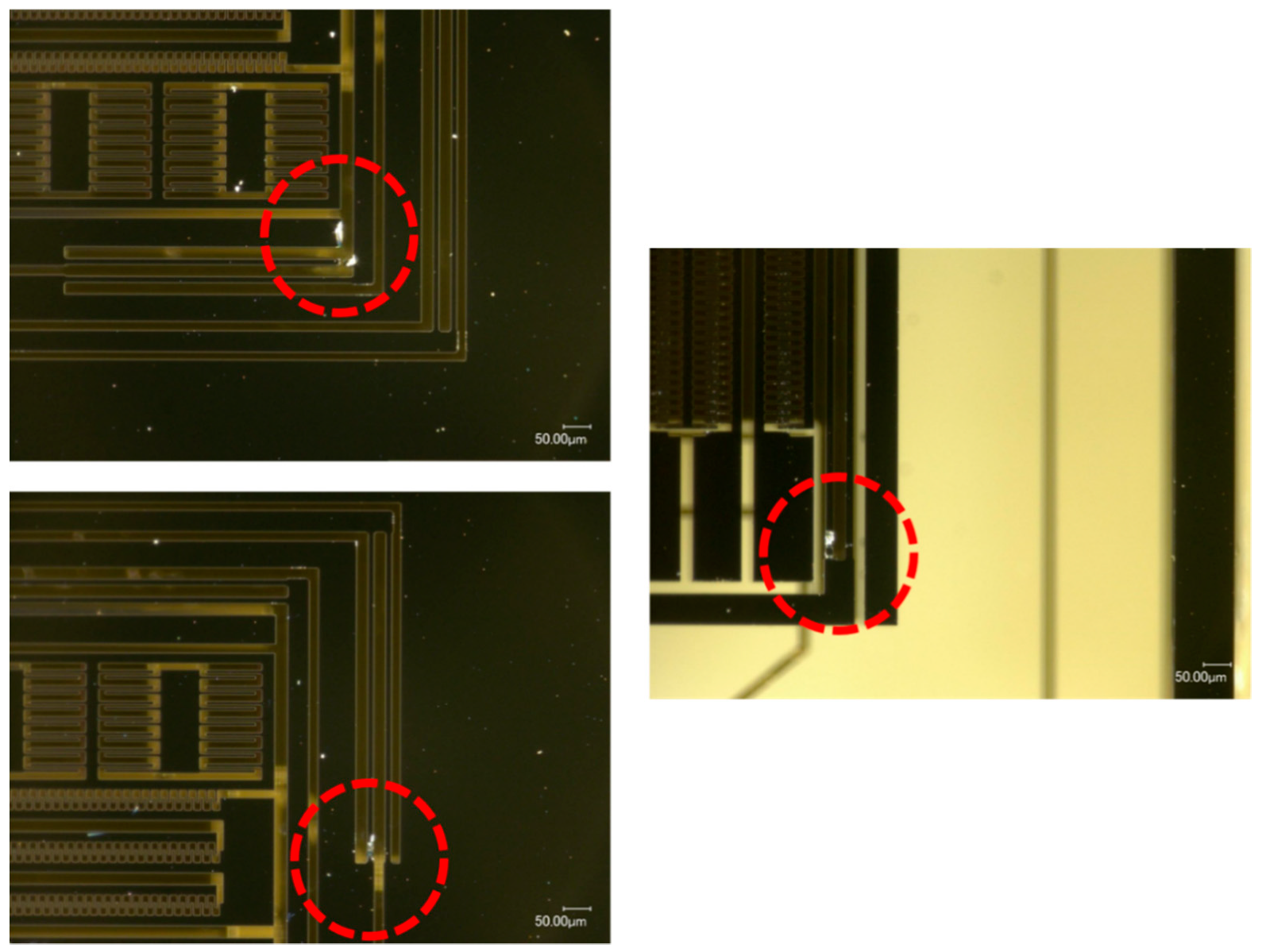
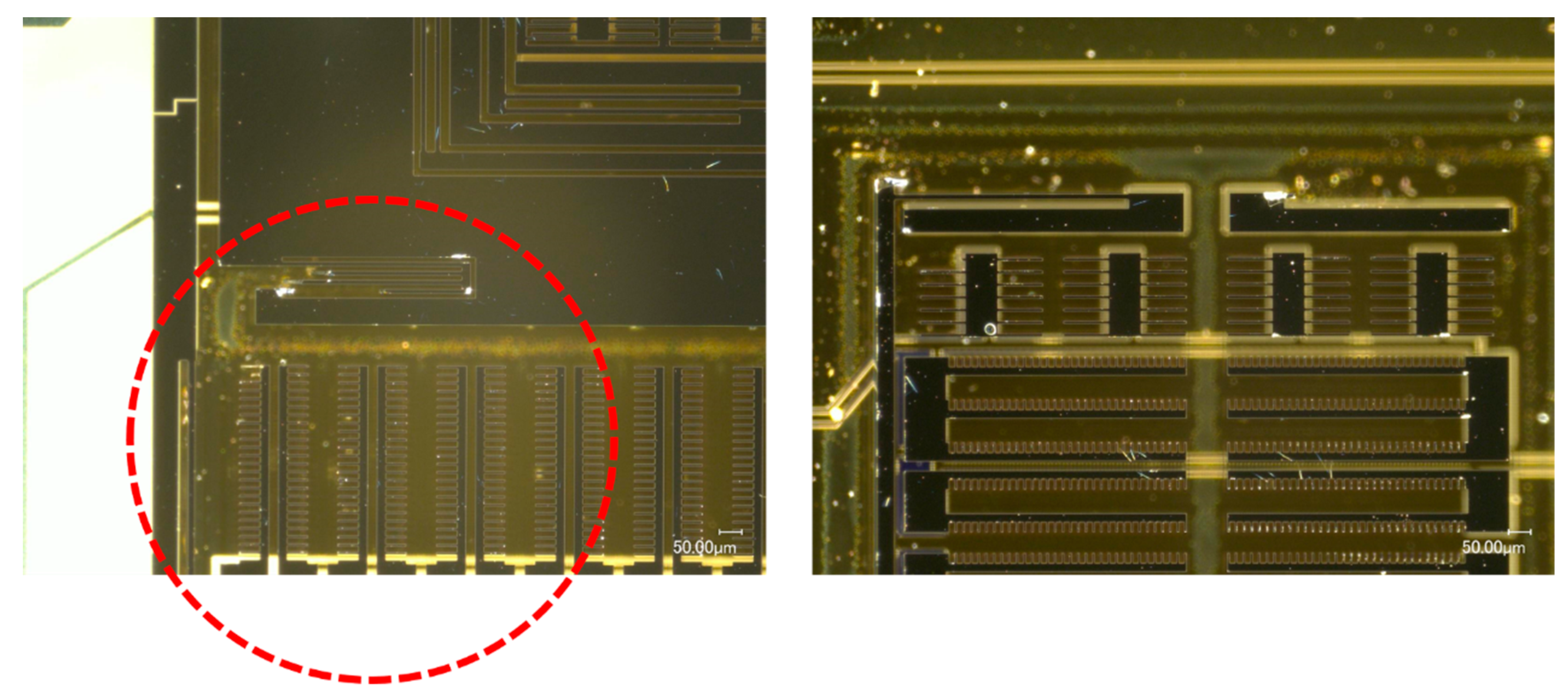
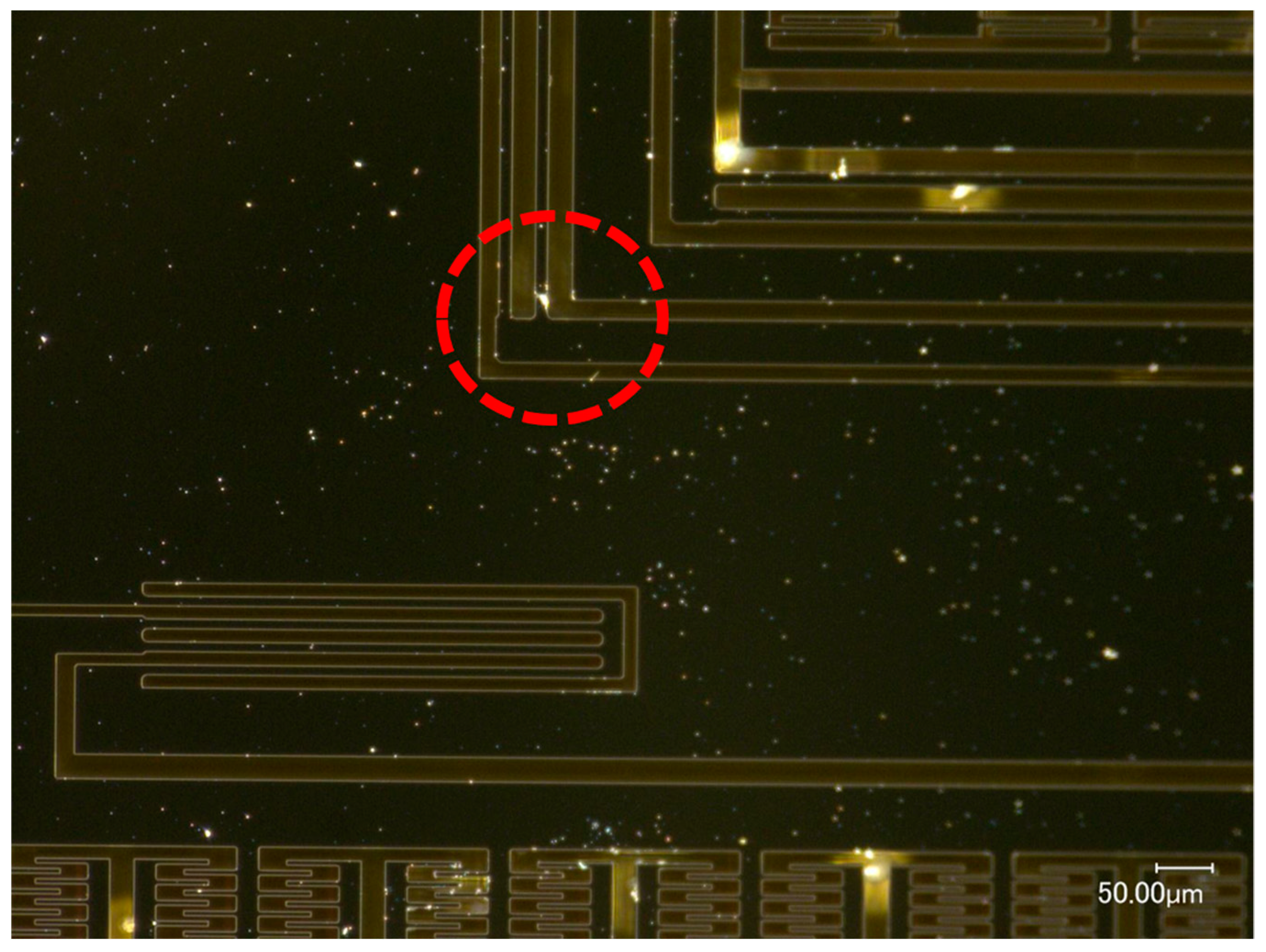
4.2.1. MEMS Tuning Fork Gyroscope Failure under Z-Axis Shock Impact
4.2.2. MEMS Tuning Fork Gyroscope Failure under X-Axis/Y-Axis Shock Impact
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maluf, N. An introduction to microelectromechanical systems engineering. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokka, J.; Raami, J.; Hyvonen, H. Methods for reliability assessment of MEMS devices—Case studies of a MEMS microphone and a 3-axis MEMS gyroscope. In Proceedings of the 62nd IEEE Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), San Diego, CA, USA, 29 May–01 June 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, R.; Tang, H.; Chen, W. High-g testing of MEMS devices, and why. In SENSORS, 2008 IEEE; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Scaysbrook, I.W.; Cooper, S.J.; Whitley, E.T. A miniature, gun-hard MEMS IMU for guided projectiles, rockets and missiles. In Proceedings of the IEEE Position Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Monterey, CA, USA, 26–29 April 2004; pp. 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Habibi, S.; Cooper, S.J.; Stauffer, J.M.; Dutoit, B. Gun hard inertial measurement unit based on MEMS capacitive accelerometer and rate sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Position Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Monterey, CA, USA, 5–8 May 2008; pp. 232–237. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Broas, M.; Makkonen, J.; Mattila, T.T.; Hokka, J.; Paulasto-Kröckel, M. Shock impact reliability and failure analysis of a three-axis MEMS tuning fork gyroscope. J. Microelectromechan. Syst. 2014, 23, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.B.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Liu, X.P.; Liu, J.; Tan, Q.L. Dynamic property test of a novel high-g micro-accelerometer. In Proceedings of the IEEE 8th international conference on ASIC, Changsha, China, 20–23 October 2009; pp. 633–635. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, U.; Muller-Fiedler, R.; Bagdahn, J.; Michel, B.; Paul, O. Mechanical reliability of epipoly MEMS structures under shock load. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, Boston, MA, USA, 8–12 June 2003; pp. 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, K.R.; Wang, X.F.; Yi, F.; Yin, Y.J.; Jiang, C.; Niu, S.M.; Li, Q.Y.; You, Z. Discharge voltage behavior of electric double-layer capacitors during high-g impact and their application to autonomously sensing high-g accelerometers. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, B.; Chen, D.J.; Lin, L.W. Drop-shock dynamic analysis of MEMS/package system. In Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Hong Kong, China, 24–28 January 2010; pp. 520–523. [Google Scholar]
- Srikar, V.T.; Senturia, S.D. The reliability of microelectromechanical systems in shock environments. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2002, 11, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.I.; Miles, R. Response of MEMS devices under shock loads. In ASME 2005 international mechanical engineering congress and exposition; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York City, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 499–506. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram, S.; Torment, M.; Timotijevic, B.; Lockhart, R.; Overstolz, T.; Stanley, R.P.; Shea, H.R. Vibration and shock reliability of MEMS: Modelling and experimental validation. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; He, C.H.; Zhang, J.M.; Zhao, Q.C.; Yang, Z.C.; Zhang, D.C.; Yan, G.Z. Investigation of reliability of MEMS gyroscopes under different shock conditions. In Proceedings of the IEEE 10th International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems (NEMS), Xian, China, 7–11 April 2015; pp. 441–444. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, T.; Jiao, J.W.; Wu, M. Design and fabrication of a micromachined gyroscope with high shock resistance. Microsyst. Technol. 2014, 20, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhou, J.; Feng, F. Study on designs of stops for MEMS devices in shock environment. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 184, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.X.; Shemansky, F.A. Drop test and analysis on micromachined structures. Sens. Actuators. 2000, 85, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisi, A.; Fachin, F.; Mariani, S.; Zerbini, S. Multi-scale analysis of polysilicon MEMS sensors subject to accidental drops: Effect of packaging. Microelectron. Reliab. 2009, 49, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleem, F.; Younis, M.I.; Miles, R. An investigation into the effect of the PCB motion on the dynamic response of MEMS devices under mechanical shock loads. J. Electron. Packag. 2008, 130, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maboudian, R.; Howe, R.T. Critical review: Adhesion in surface micromechanical structures. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 1997, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.P.; Wang, L.S.; Yu, T.X. Mechanics of adhesion in MEMS—a review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2003, 17, 519–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.W.; Parameswaran, M. Theoretical limits on the freestanding length of cantilevers produced by surface micromachining technology. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2002, 12, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.S.; Song, J.T. An effective method to prevent stiction problems using a photoresist sacrificial layer. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 17, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafri, I.H.; Busta, H.; Walsh, S.T. Critical point drying and cleaning for MEMS technology. In MEMS Reliability for Critical and Space Applications; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 1999; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Suwito, W.; Dunn, M.L.; Cunningham, S.J.; Read, D.T. Elastic moduli, strength, and fracture initiation at sharp notches in etched single crystal silicon microstructures. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 3519–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, S.; Schweitz, J.A.; Tenerz, L.; Tiren, J. Fracture testing of silicon microelements in situ in a scanning electron microscope. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 63, 4799–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, C.; Dux, F. Chattering and related behaviour in impact oscillators. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A. 1994, 347, 365–389. [Google Scholar]








| Material | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Crystal Silicon | 130 | 0.28 |
| Borosilicate Glass | 64 | 0.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lian, J.; Li, J.; Xu, L. The Effect of Displacement Constraints on the Failure of MEMS Tuning Fork Gyroscopes under Shock Impact. Micromachines 2019, 10, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10050343
Lian J, Li J, Xu L. The Effect of Displacement Constraints on the Failure of MEMS Tuning Fork Gyroscopes under Shock Impact. Micromachines. 2019; 10(5):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10050343
Chicago/Turabian StyleLian, Jiangkai, Jianhua Li, and Lixin Xu. 2019. "The Effect of Displacement Constraints on the Failure of MEMS Tuning Fork Gyroscopes under Shock Impact" Micromachines 10, no. 5: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10050343
APA StyleLian, J., Li, J., & Xu, L. (2019). The Effect of Displacement Constraints on the Failure of MEMS Tuning Fork Gyroscopes under Shock Impact. Micromachines, 10(5), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10050343





