Non-Invasive Quantification of the Growth of Cancer Cell Colonies by a Portable Optical Coherence Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Formation of Cell Colonies Based on Liquid Overlay Technique
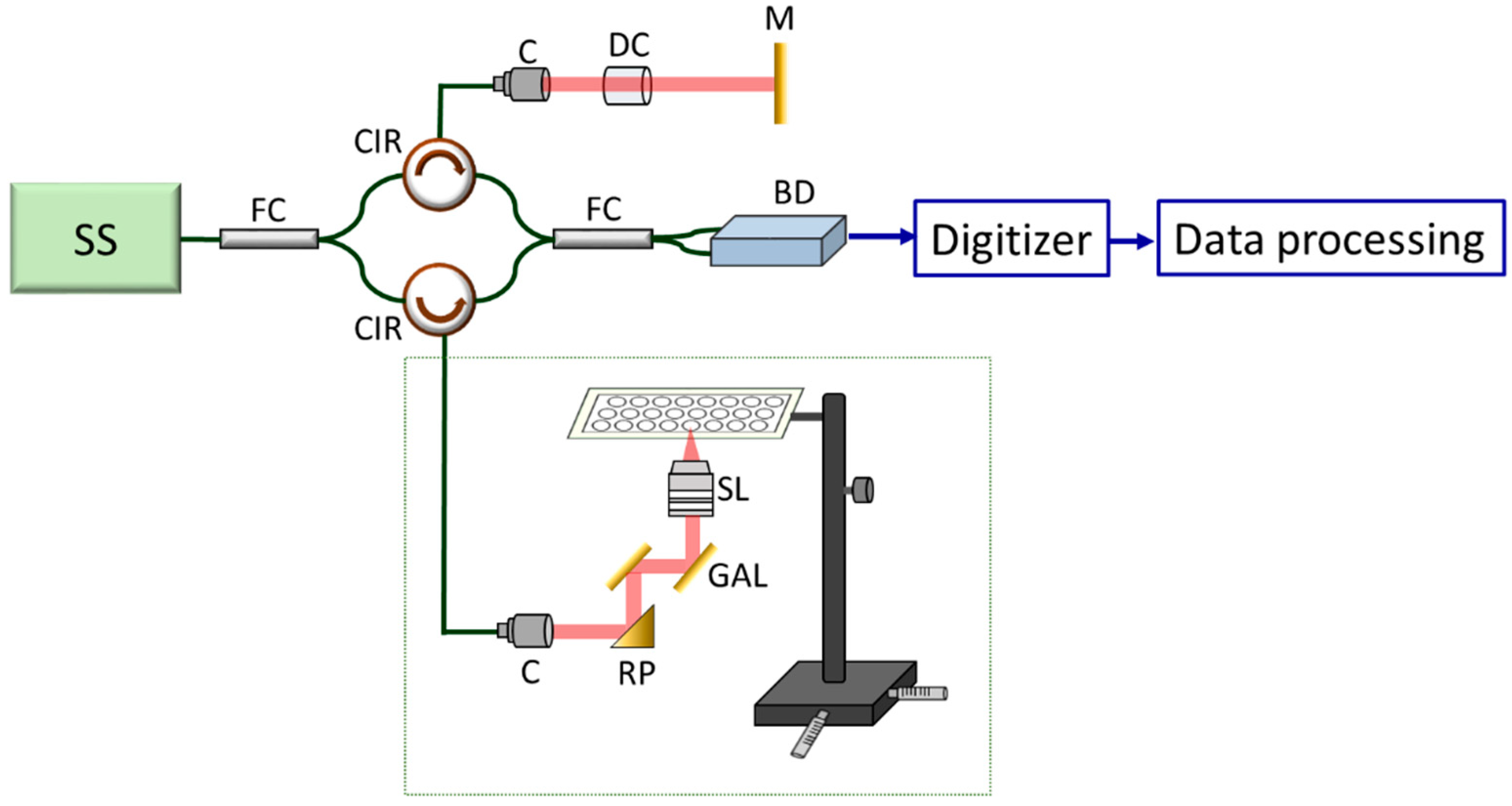
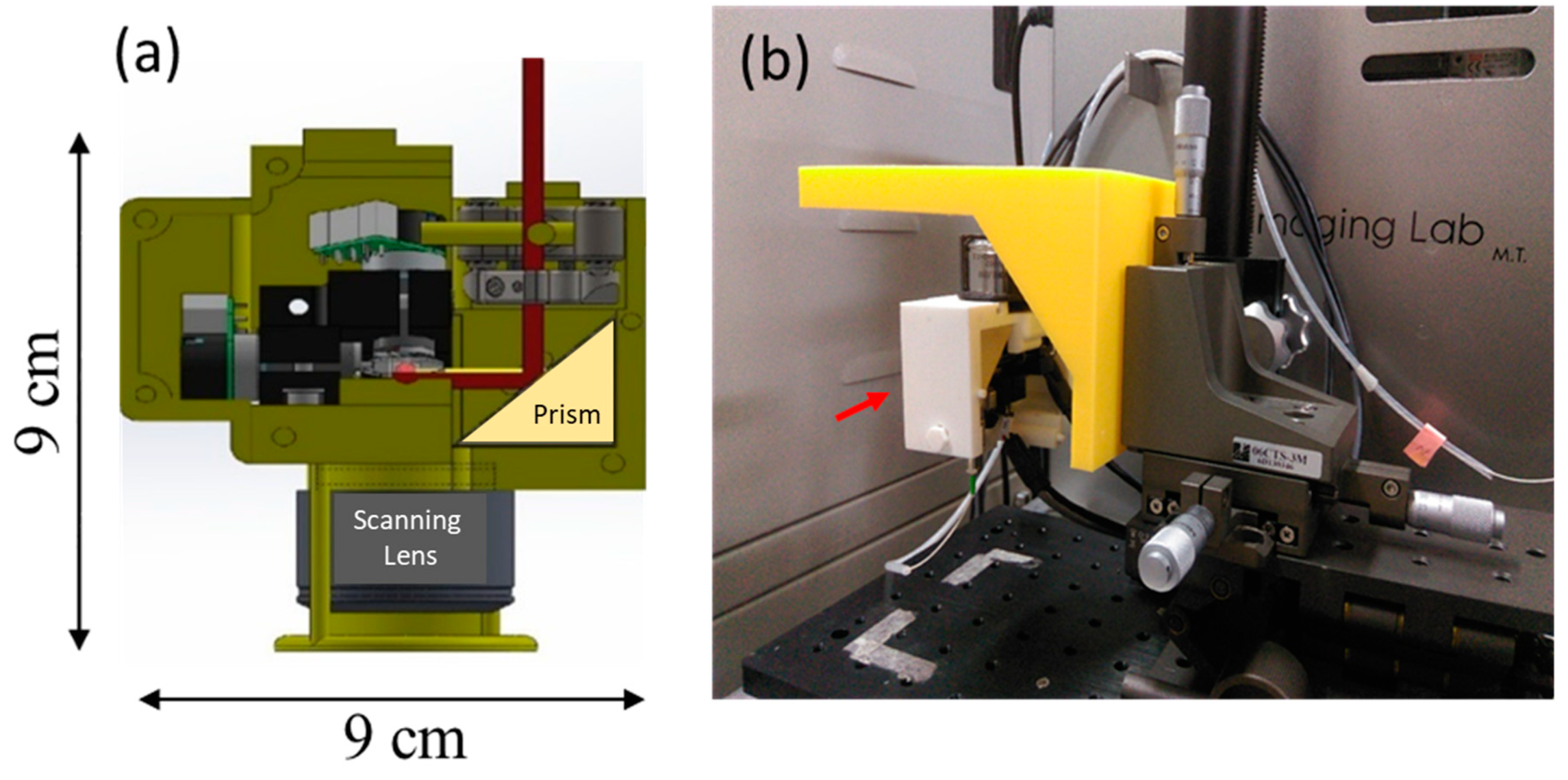
2.3. Description of the Portable Optical Coherence Tomography
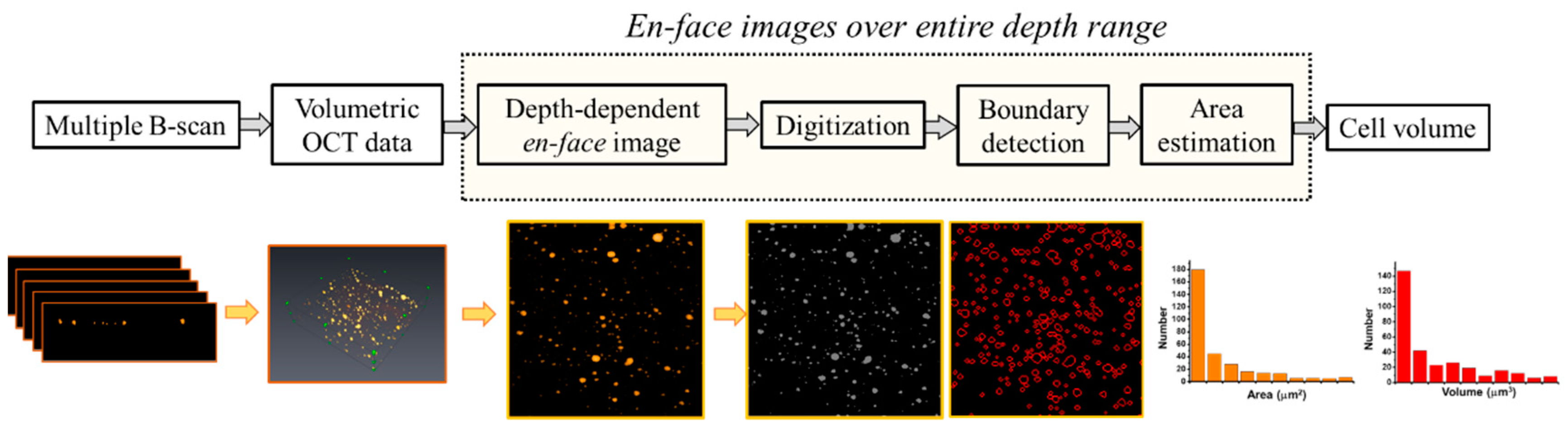
2.4. Quantification of the Cell colonies Based on OCT Imaging
3. Results and Discussion
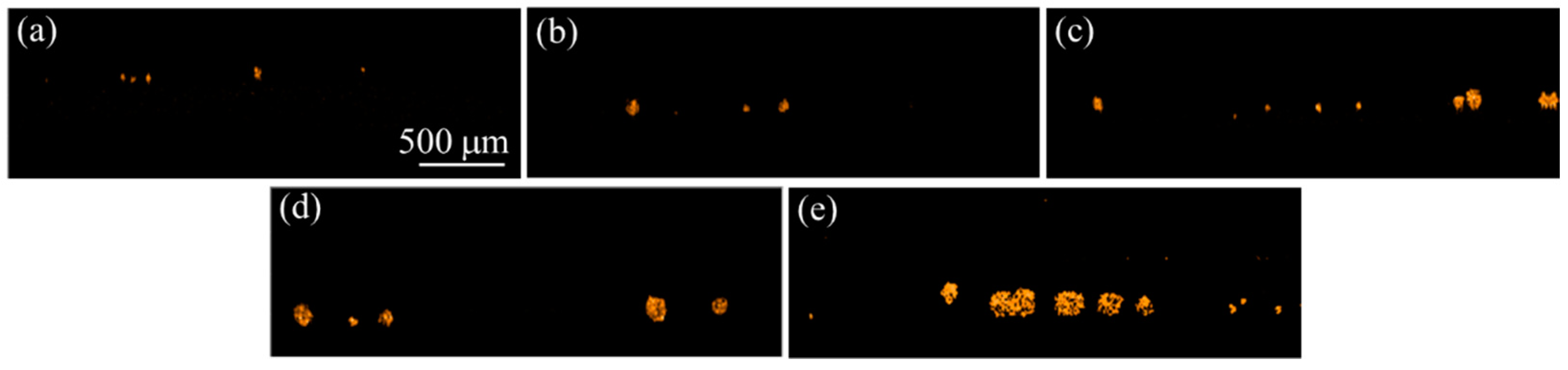
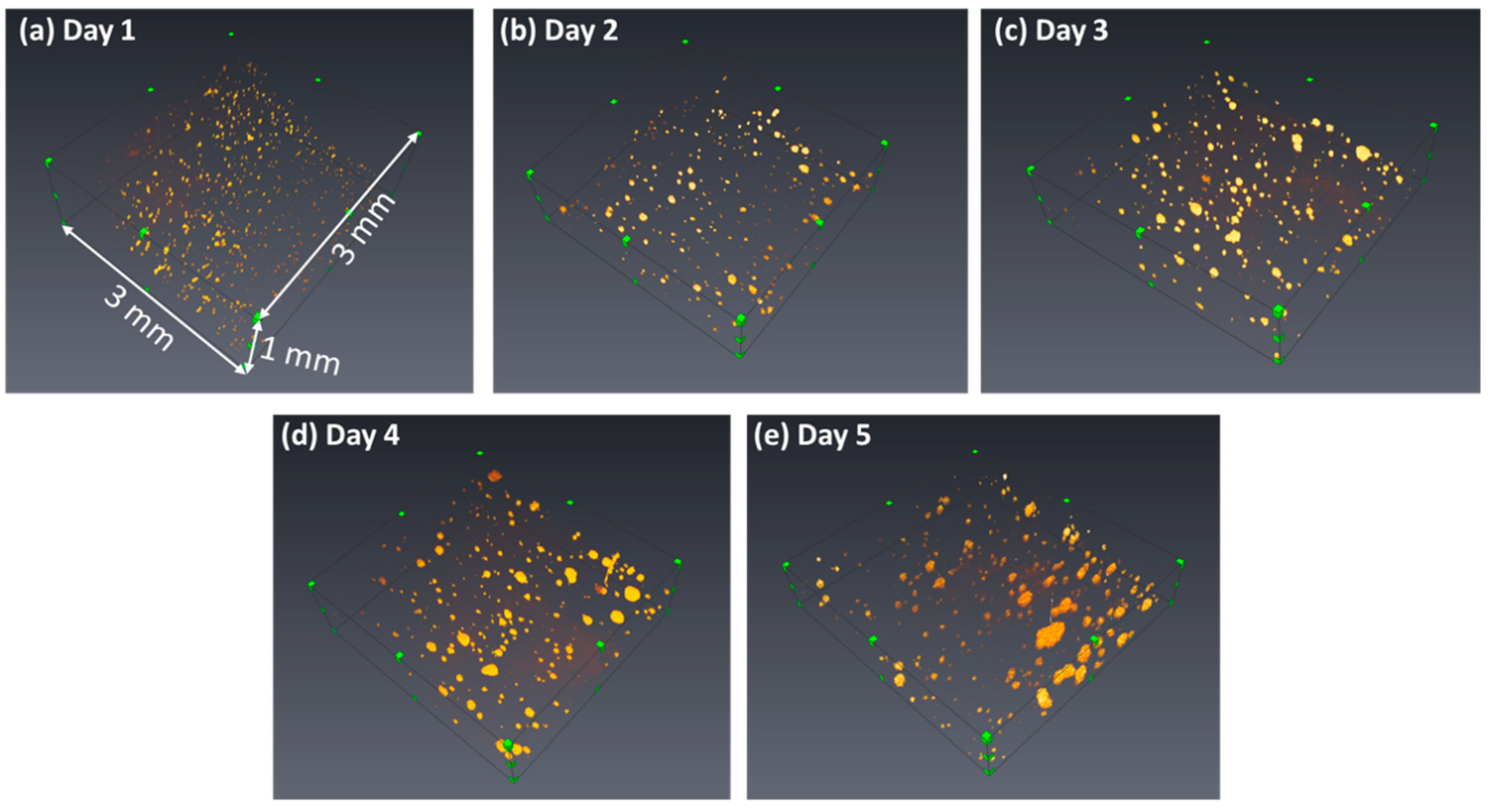
3.1. Construction of the OCT Images
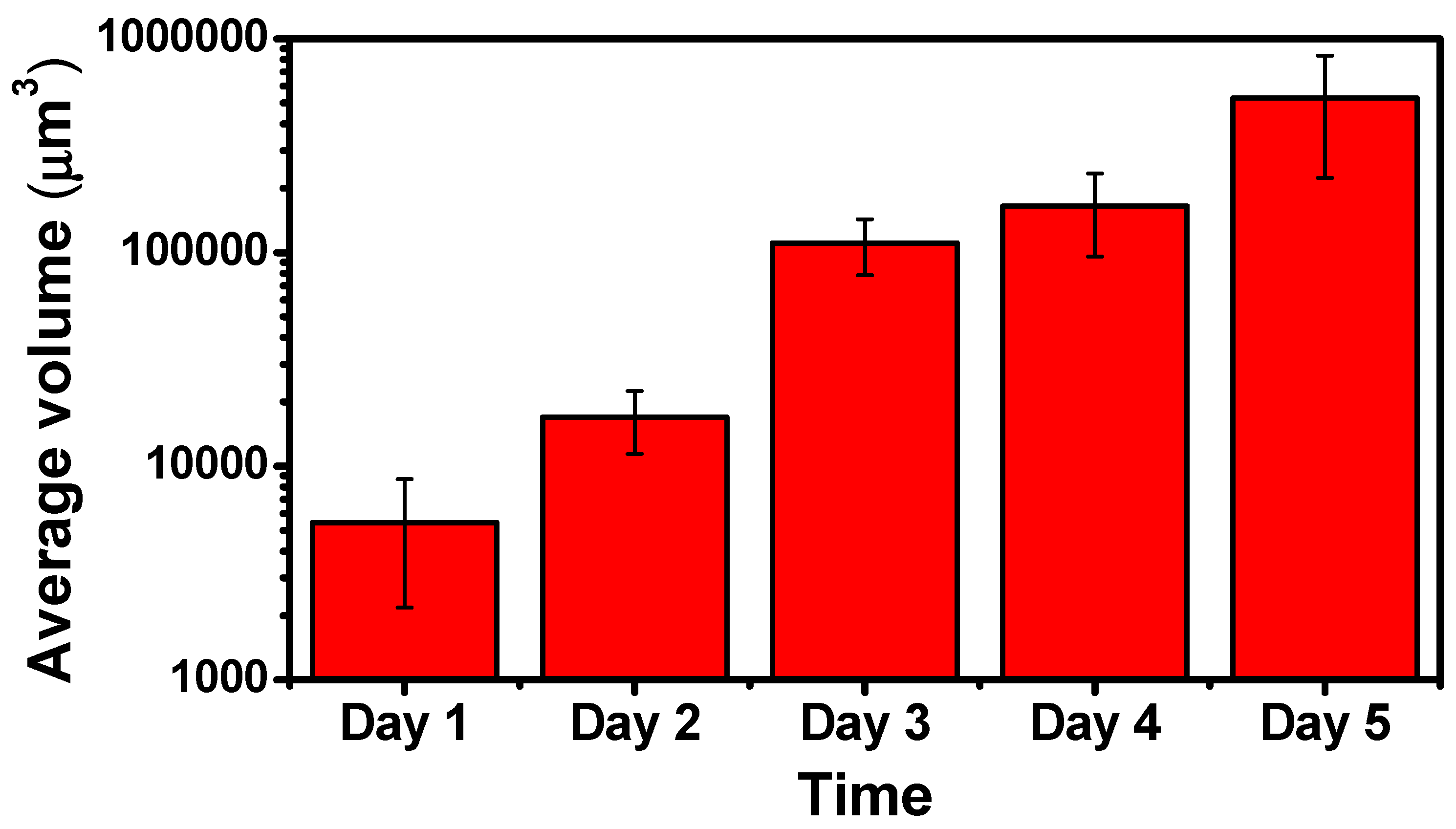
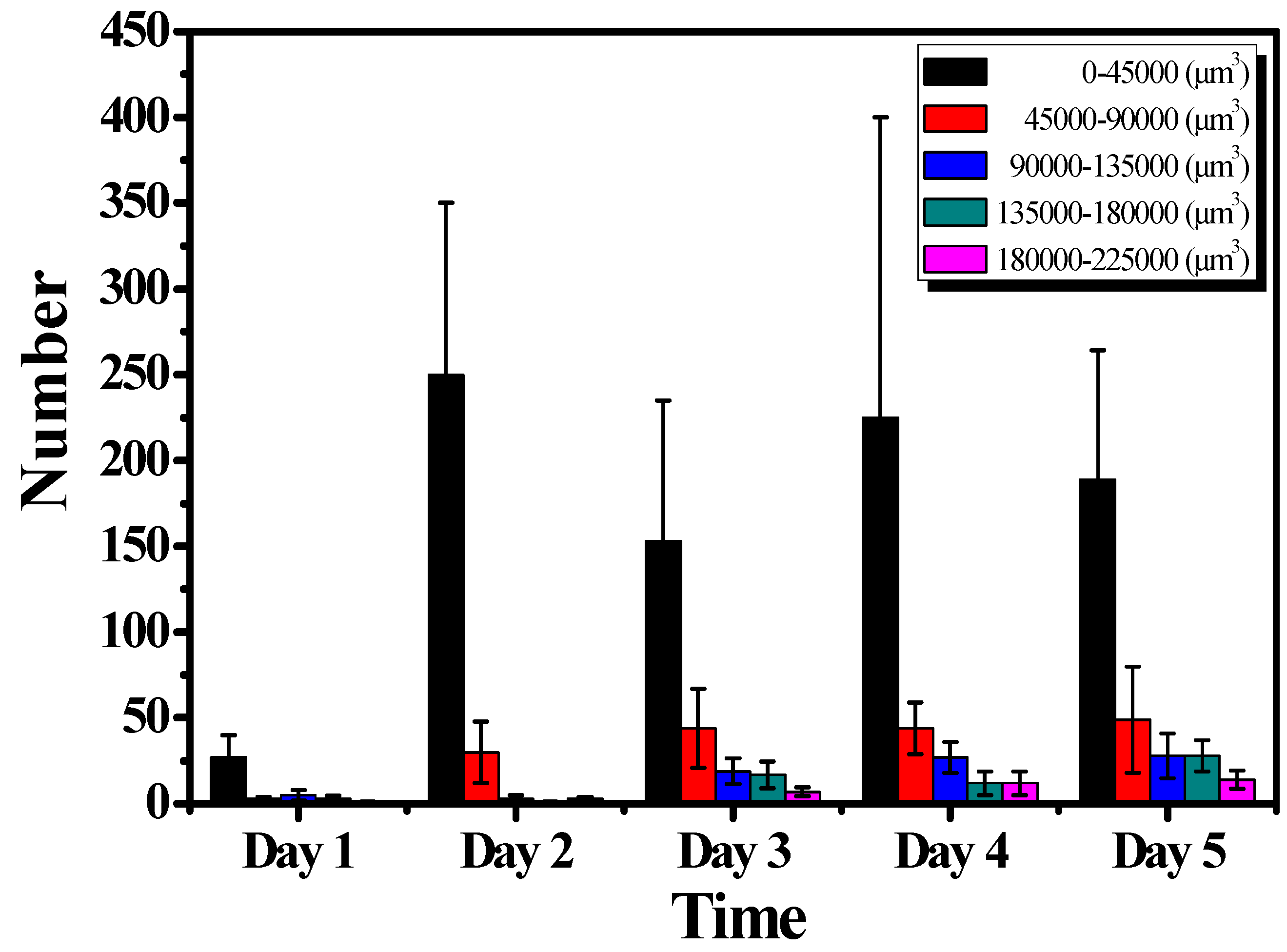
3.2. Quantification of the Growth of the Cell Colonies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Piao, L.; Yuan, F. Radiotherapy combined with an engineered Salmonella typhimurium inhibits tumor growth in a mouse model of colon cancer. Exp. Anim. 2016, 65, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Weng, W.; Peng, J.; Hong, L.; Yang, L.; Toiyama, Y.; Gao, R.; Liu, M.; Yin, M.; Pan, C.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum increases proliferation of colorectal cancer cells and tumor development in mice by activating toll-like receptor 4 signaling to nuclear factor-κB, and up-regulating expression of microRNA-21. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.M.; Summers, B.C.; Wang, Y.; Melikian, A.; Berahovich, R.; Miao, Z.; Penfold, M.E.; Sunshine, M.J.; Littman, D.R.; Kuo, C.J.; et al. A novel chemokine receptor for SDF-1 and I-TAC involved in cell survival, cell adhesion, and tumor development. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A. Cell culture: Biology’s new dimension. Nature 2003, 424, 870–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pampaloni, F.; Reynaud, E.G.; Stelzer, E.H.K. The third dimension bridges the gap between cell culture and live tissue. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, V.M.; Peterson, O.W.; Wang, F.; Larabell, C.A.; Briand, P.; Damsky, C.; Bissell, M.J. Reversion of the malignant phenotype of human breast cells in three-dimensional culture and in vivo by integrin blocking antibodies. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 137, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowicz, S.; Van Scoyk, M.; Avasarala, S.; Rathinam, M.K.K.; Tauler, J.; Bikkavilli, R.K.; Winn, R.A. The soft agar colony formation assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 92, 51998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Scoville, D.; He, X.C.; Mahe, M.M.; Box, A.; Perry, J.M.; Smith, N.R.; Lei, N.Y.; Davies, P.S.; Fuller, M.K.; et al. Isolation and characterization of intestinal stem cells based on surface marker combinations and colony-formation assay. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.Z.; Chang, H.Y. Recent advances in three-dimensional multicellular spheroid culture for biomedical research. Biotechnol. J. 2008, 3, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, P.; Chen, J.; Poh, Y.C.; Tang, K.; Wang, N.; Huang, B. Soft fibrin gels promote selection and growth of tumorigenic cells. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastrana, E.; Silva-Vargas, V.; Doetsch, F. Eyes wide open: A critical review of sphere-formation as an assay for stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, P.C.; Lee, R.M.; Vitolo, M.I.; Pratt, S.J.P.; Ory, E.; Chakrabarti, K.; Lee, C.J.; Thompson, K.N.; Martin, S.S. Single-cell tracking of breast cancer cells enables prediction of sphere formation from early cell divisions. iScience 2018, 8, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Brien, R.; Yoon, E. Scaling and automation of a high-throughput single-cell-derived tumor sphere assay chip. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3708–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, M.; Piccinini, F.; Arienti, C.; Zamagni, A.; Santi, S.; Polico, R.; Bevilacqua, A.; Tesei, A. 3D tumor spheroid models for in vitro therapeutic screening: A systematic approach to enhance the biological relevance of data obtained. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Ingram, P.N.; Fouladdel, S.; McDermott, S.P.; Azizi, E.; Wicha, M.S.; Yoon, E. High-throughput single-cell derived sphere formation for cancer stem-like cell identification and analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.C.; Chang, J.F. Label-free selection and enrichment of liver cancer stem cells by surface niches build up with polyelectrolyte multilayer films. Colloid Surf. B 2015, 125, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Zhu, L.F.; Xu, X.H.; Ning, T.Y.; Ye, J.H.; Liu, L.K. Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase induces and epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like properties in SCC9 cells. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, B.; Peng, C.C.; Liao, W.H.; Lee, C.H.; Tung, Y.C. Drug testing and flow cytometry analysis on a large number of uniform sized tumor spheroids using a microfluidic device. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.F.; Wu, Z.M.; Huang, C.H. Impedimetric quantification of the formation process and the chemosensitivity of cancer cell colonies suspended in 3D environment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.F.; Kao, C.H.; Tsang, N.M. High throughput and automatic colony formation assay based on impedance measurement technique. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 3271–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.F.; Lin, B.Y.; Tsang, N.M. Real-time and label-free impedimetric analysis of the formation and drug testing of tumor spheroids formed via the liquid overlay technique. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 13939–13946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, L.M.; Deleon-Ortega, J.; Sakata, V.; Girkin, C.A. Optical coherence tomography of the retina and optic nerve—A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 37, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffel, O.C.; Akasaka, T.; Jang, I.-K. Cardiac optical coherence tomography. Heart 2008, 94, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Baran, U.; Wang, R.K. In vivo blood flow imaging of inflammatory human skin induced by tape stripping using optical microangiography. J. Biophotonics 2015, 8, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.C.; Gaspar, V.M.; Coutinho, P.; Correia, I.J. Optimization of liquid overlay technique to formulate heterogenic 3D co-culture models. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 1672–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennema, E.; Rivron, N.; Rouwkema, J.; Van Blitterswijk, C.; De Boer, J. Spheroid culture as a tool for creating 3D complex tissues. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.F.; Peng, C.; Escher, B.I.; Fantino, E.; Giles, C.; Were, S.; Duffy, L.; Ng, J.C. Hanging drop: An in vitro air toxic exposure model using human lung cells in 2D and 3D structures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziółkowska, K.; Stelmachowska, A.; Kwapiszewski, R.; Chudy, M.; Dybko, A.; Brzózka, Z. Long-term three-dimensional cell culture and anticancer drug activity evaluation in a microfluidic chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, S.R. Grayscale morphology. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1986, 35, 333–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Guo, Q.; Kessel, S.; Rubinoff, I.; Chan, L.L.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, C. Optical coherence tomography detects necrotic regions and volumetrically quantifies multicellular tumor spheroids. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6011–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.T.; Yang, C.H.; Shen, S.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Chang, F.Y.; Feng, C.S. Monitoring of wound healing process of human skin after fractional laser treatments with optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 2362–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.T.; Chen, Y.; Lee, C.Y.; Huang, B.H.; Trung, N.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Wang, Y.L. Noninvasive structural and microvascular anatomy of oral mucosae using handheld optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 5001–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Ahsen, O.O.; Liang, K.; Wang, Z.; Figueiredo, M.; Giacomelli, M.G.; Potsaid, B.; Huang, Q.; Mashimo, H.; Fujimoto, J.G. Endoscopic optical coherence tomography angiography microvascular features associated with dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 86, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Ahsen, O.O.; Liu, J.J.; Tsai, T.H.; Huang, Q.; Mashimo, H.; Fujimoto, J.G. Assessment of the radiofrequency ablation dynamics of esophageal tissue with optical coherence tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 76001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai-Qazwini, Z.; Ko, Z.Y.G.; Mehta, K.; Chen, N. Ultrahigh-speed line-scan SD-OCT for fourdimensional in vivo imaging of small animal models. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, M.-T.; Huang, B.-H.; Yeh, C.-C.; Lei, K.F.; Tsang, N.-M. Non-Invasive Quantification of the Growth of Cancer Cell Colonies by a Portable Optical Coherence Tomography. Micromachines 2019, 10, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10010035
Tsai M-T, Huang B-H, Yeh C-C, Lei KF, Tsang N-M. Non-Invasive Quantification of the Growth of Cancer Cell Colonies by a Portable Optical Coherence Tomography. Micromachines. 2019; 10(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Meng-Tsan, Bo-Huei Huang, Chun-Chih Yeh, Kin Fong Lei, and Ngan-Ming Tsang. 2019. "Non-Invasive Quantification of the Growth of Cancer Cell Colonies by a Portable Optical Coherence Tomography" Micromachines 10, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10010035
APA StyleTsai, M.-T., Huang, B.-H., Yeh, C.-C., Lei, K. F., & Tsang, N.-M. (2019). Non-Invasive Quantification of the Growth of Cancer Cell Colonies by a Portable Optical Coherence Tomography. Micromachines, 10(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10010035





