Coagulating Colubrids: Evolutionary, Pathophysiological and Biodiscovery Implications of Venom Variations between Boomslang (Dispholidus typus) and Twig Snake (Thelotornis mossambicanus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
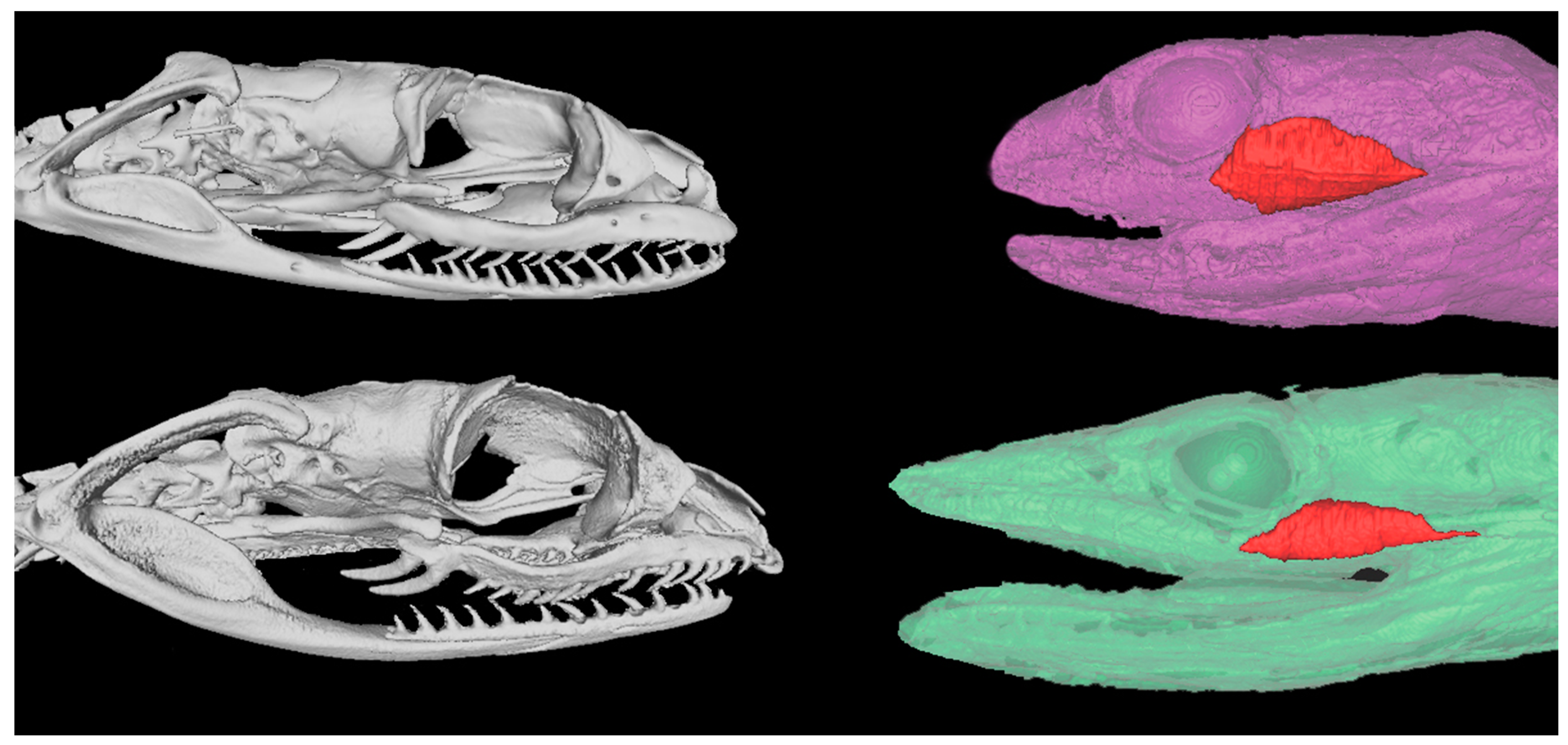
2.1. Skull and Venom Gland Anatomical Comparisons
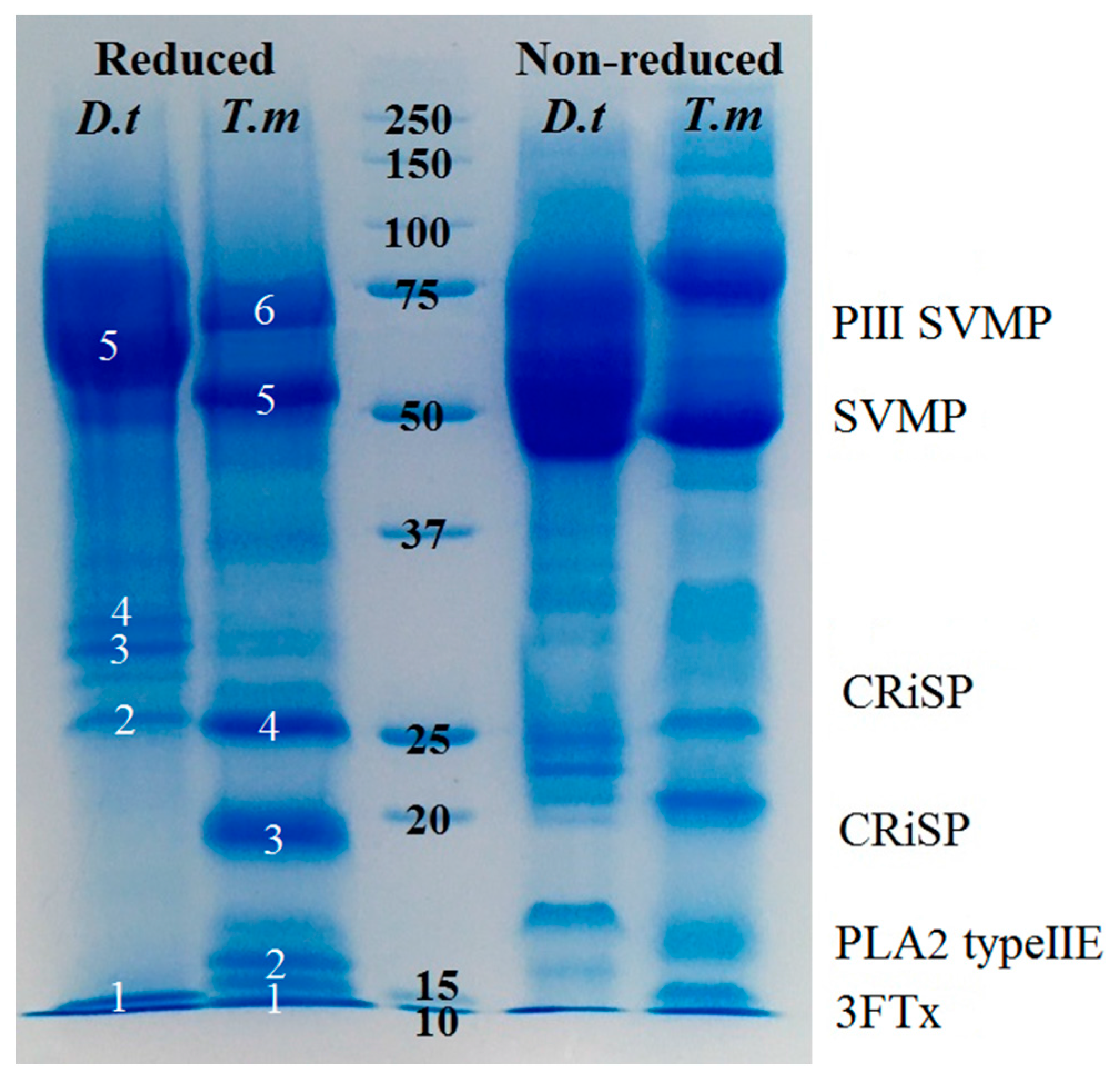
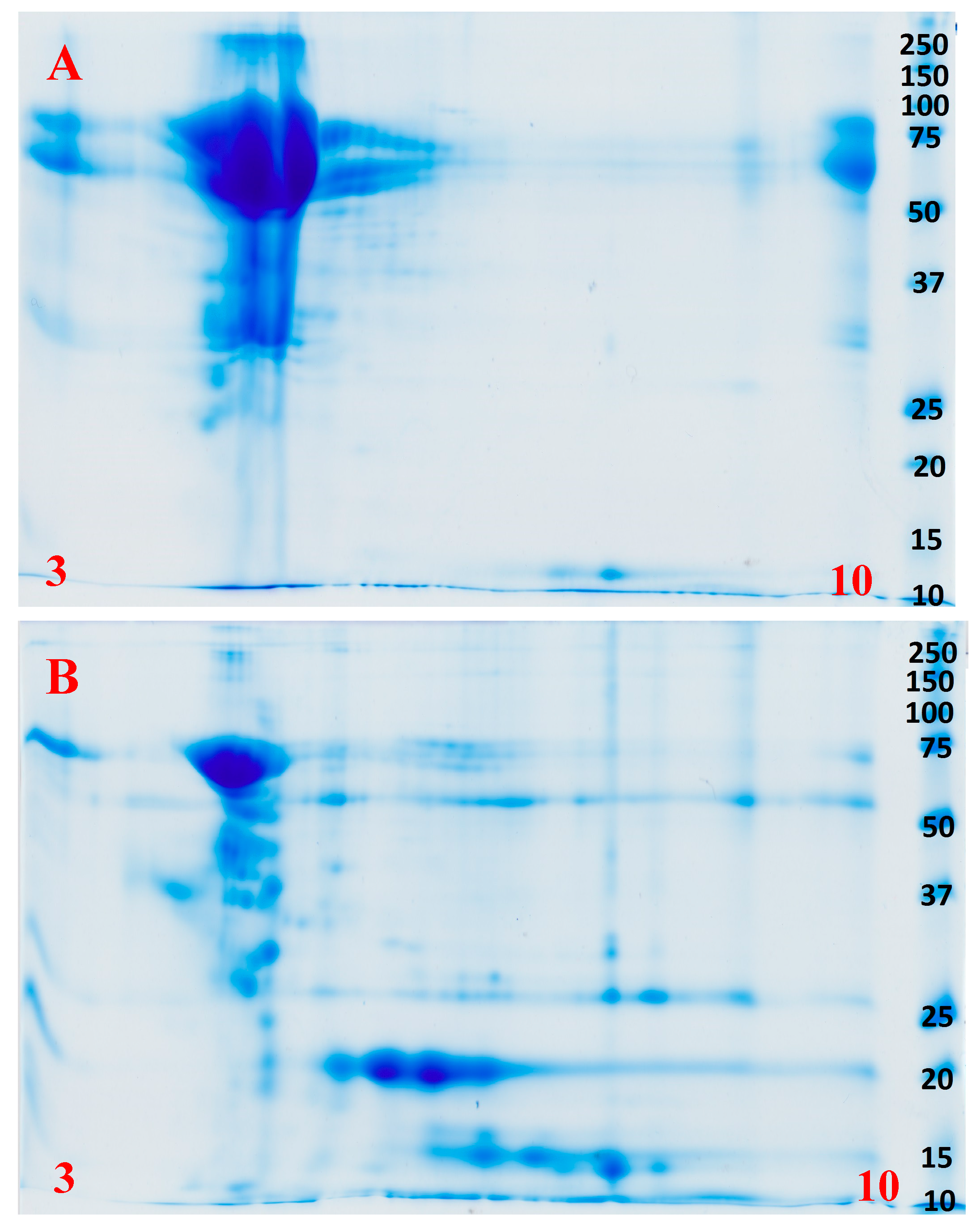
2.2. Proteomics
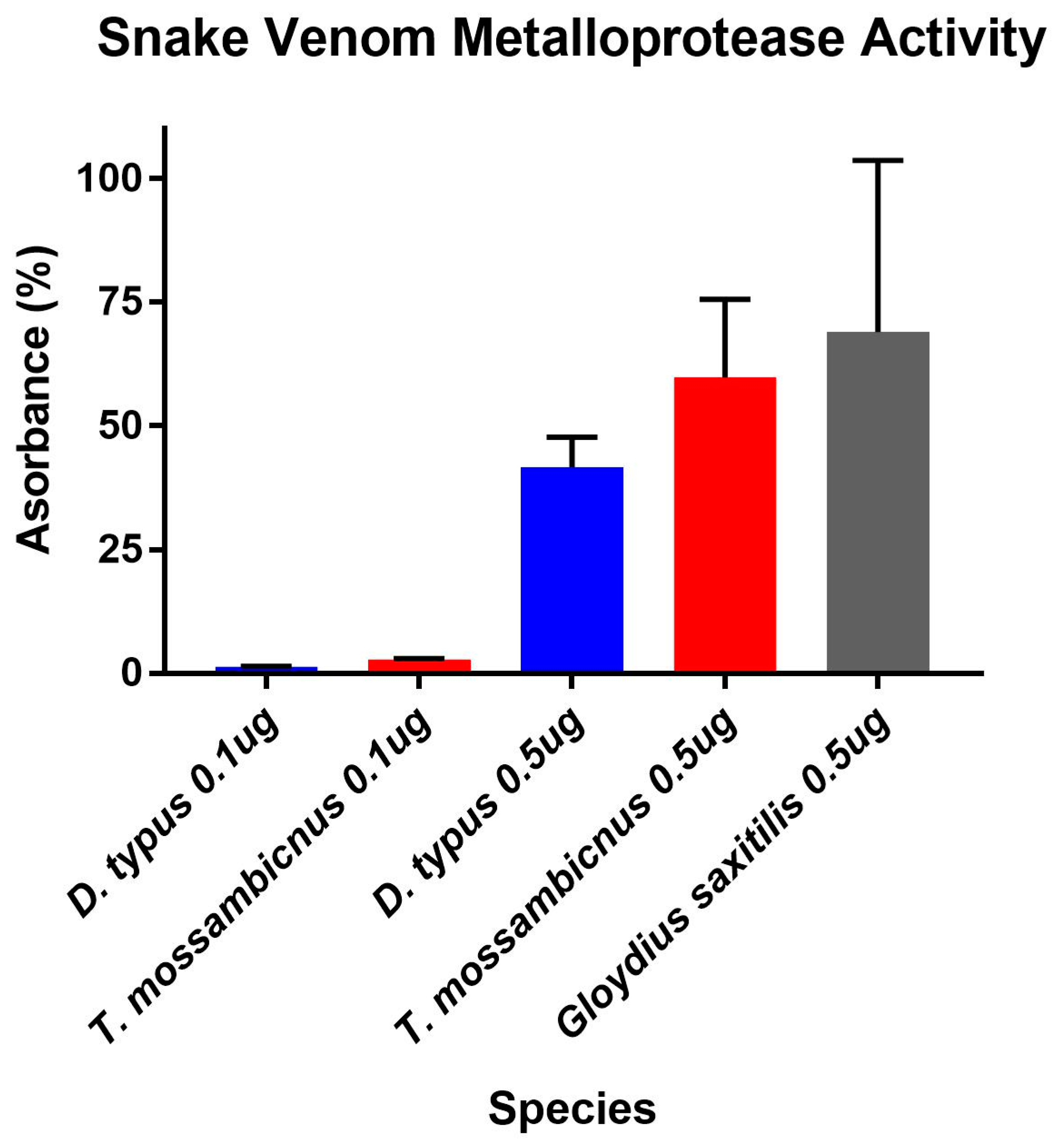
2.3. Enzymatic Assays
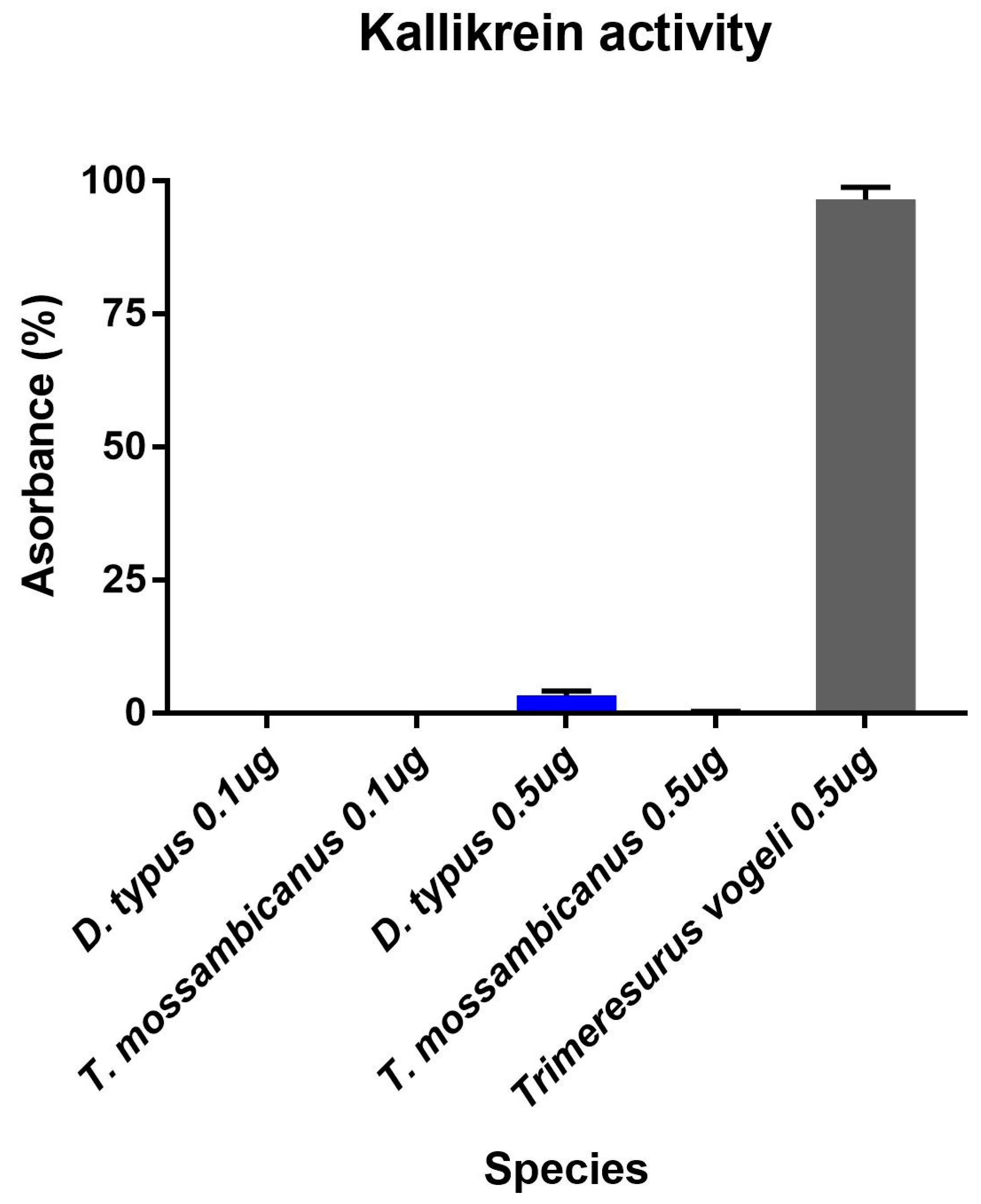
Fluorescent Determination of Matrix Metalloprotease and Kallikrein Activity
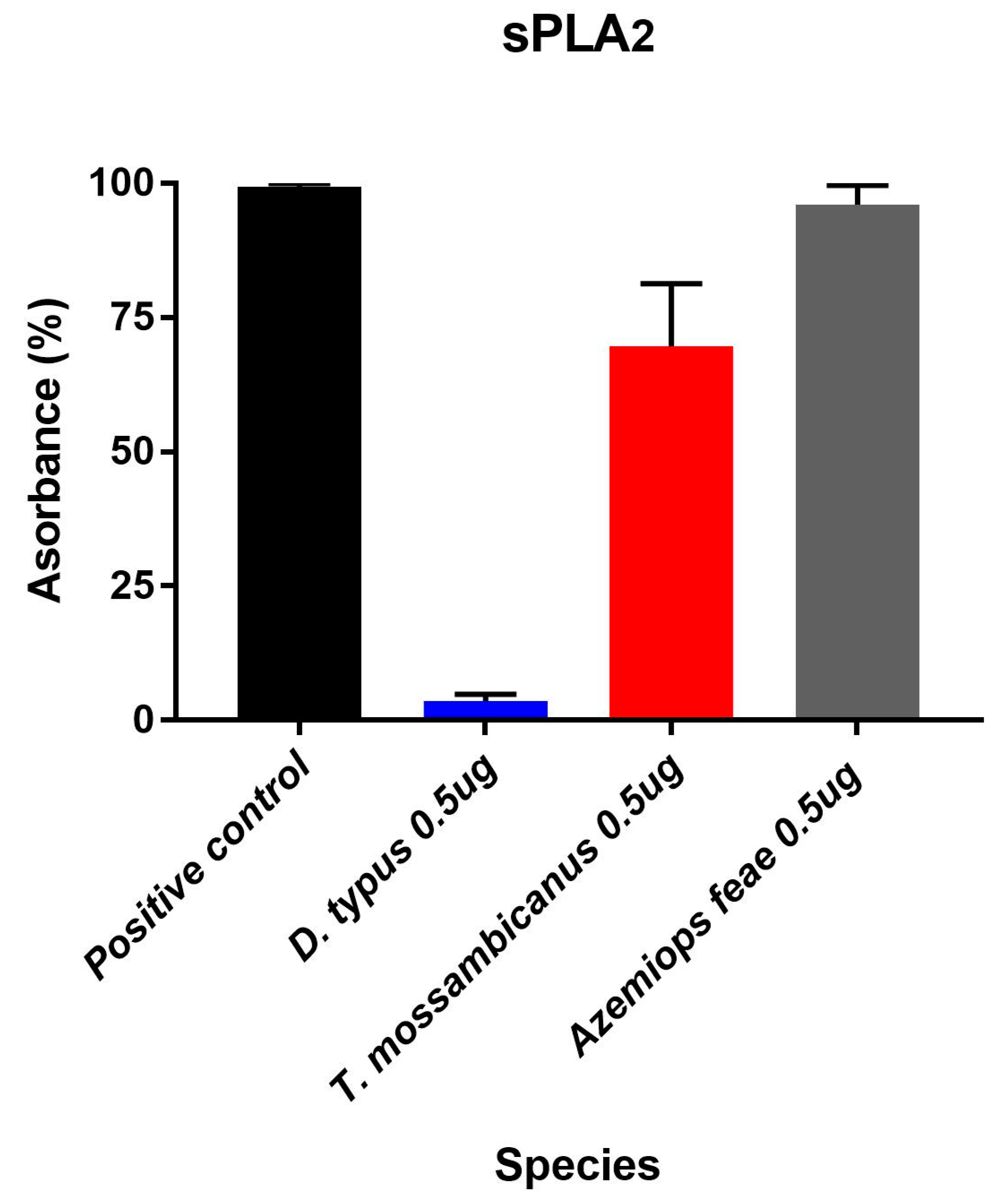
2.4. Fluorescent Determination of sPLA2 Activity
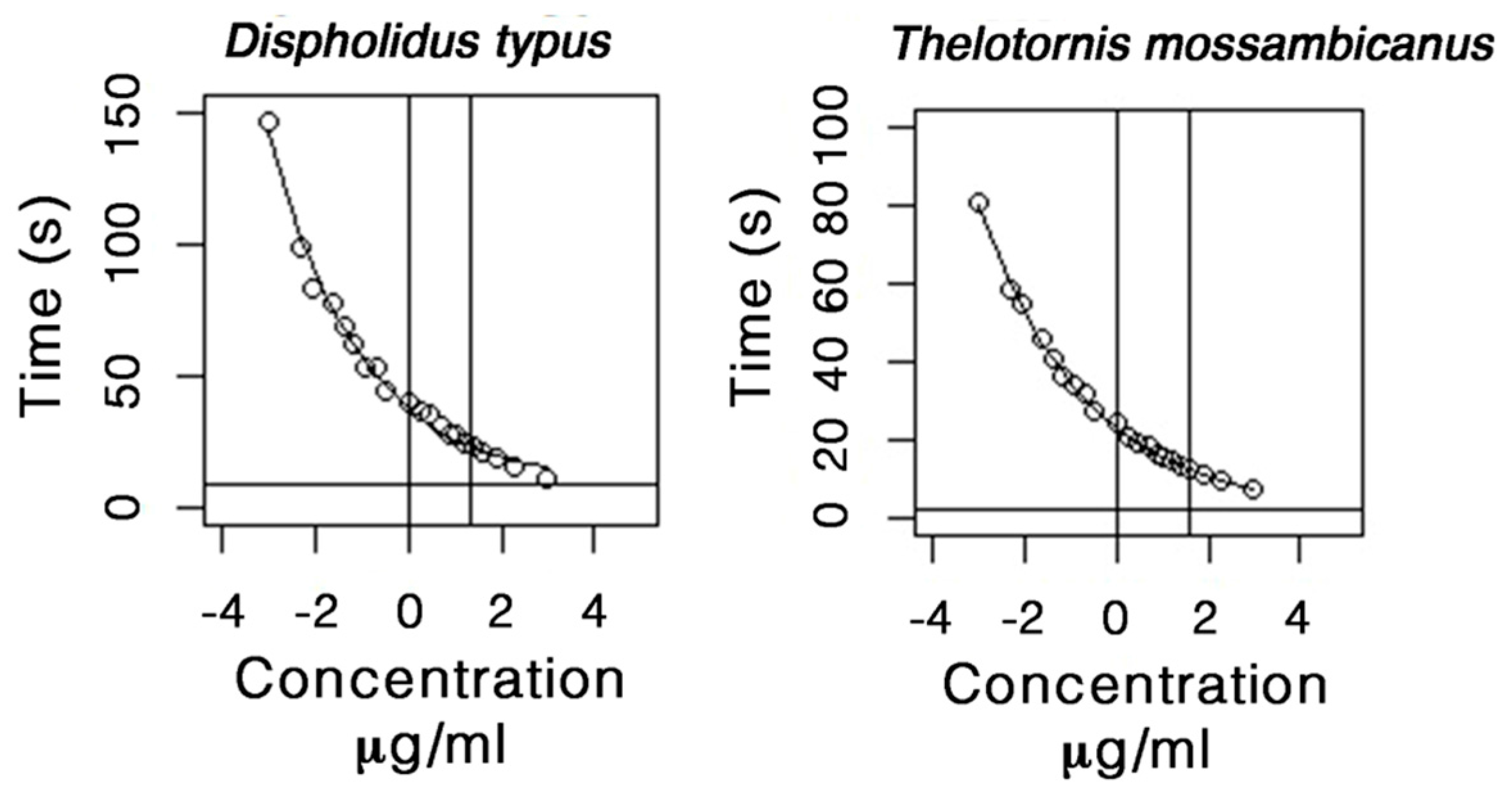
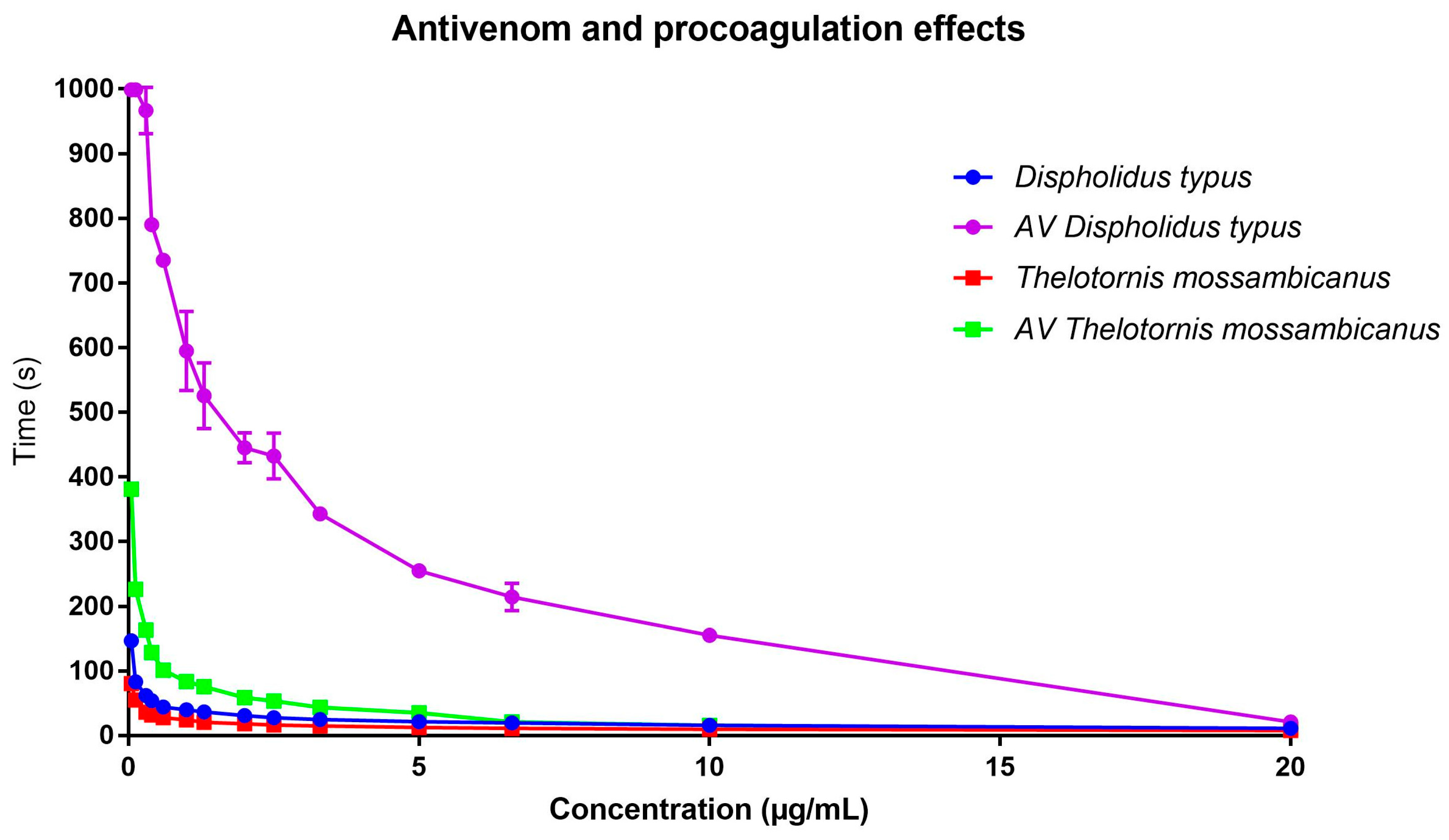
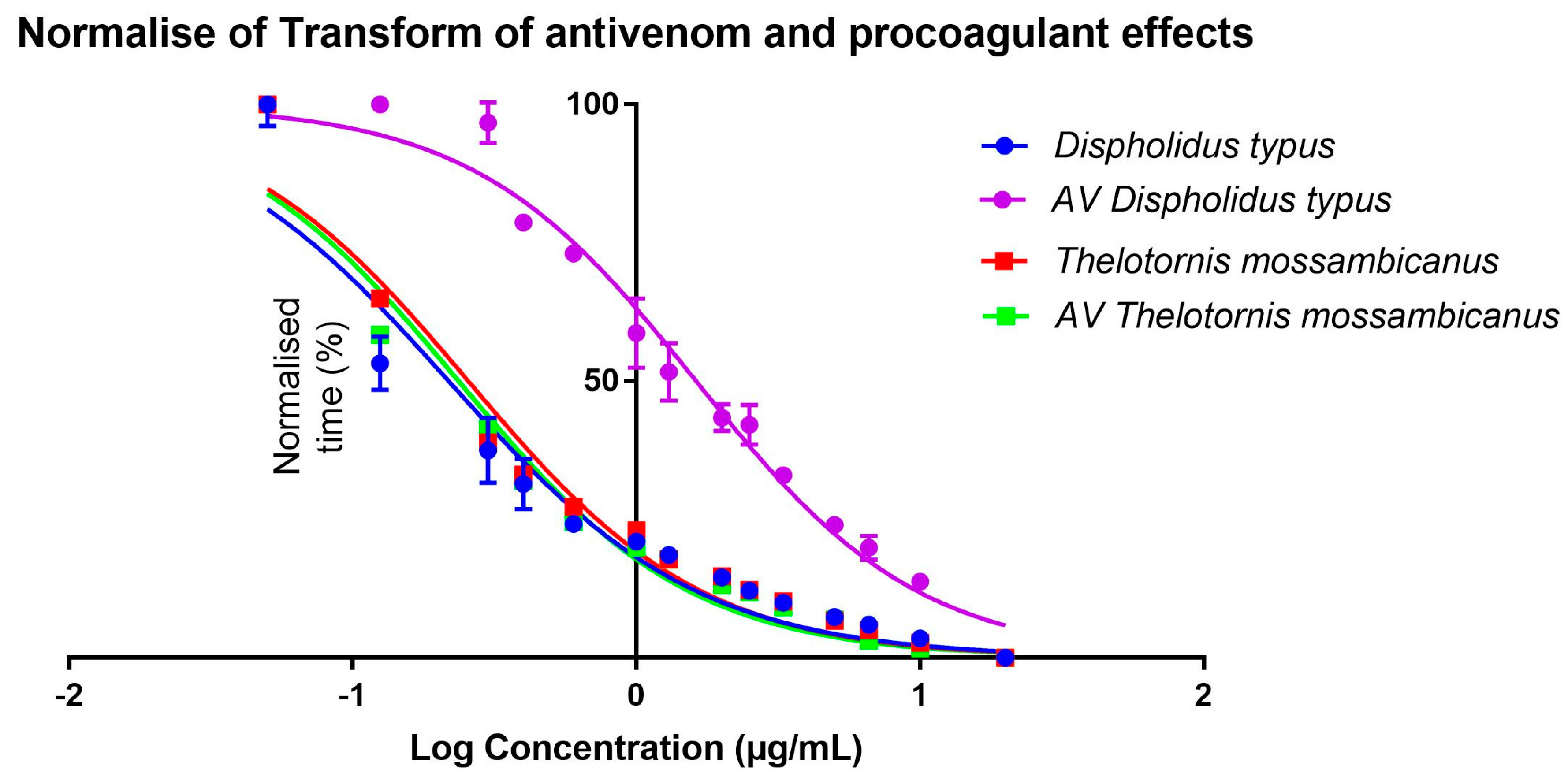
2.5. Procoagulation Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Venom Supplies
4.2. Micro-Computed Tomography (CT)
4.3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
4.4. Proteomics
4.4.1. Nano HPLC-ESI-Triple Time of Flight (TOF) Mass Spectral Analysis
4.4.2. Protein Identification
4.4.3. Orbitap Elite Mass Spectrometer for SHOTGUNS
4.5. Enzymatic Activity Assays
4.5.1. Fluorescent Determination of Matrix Metalloprotease and Kallikrein Activity
4.5.2. Fluorescent Determination of PLA2 Activity
4.5.3. Enzymatic Statistical Analysis
4.6. Procoagulation Analysis
4.6.1. Whole Plasma Clotting
4.6.2. Antivenom Studies
4.6.3. Statistical Analysis
Whole Plasma Clotting EC50 Concentration and Asymptotic Time
Antivenom EC50 Concentration
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | confidence interval |
| aPTT | activated partial thromboplastin time |
| SVMP | snake venom metalloprotease |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| CRiSP | cysteine rich secretory protein |
| HPLC | high pressure liquid chromatography |
| SD | standard deviations |
| ACN | acetonitrile |
| 1D | one dimensional |
| 2D | two dimensional |
| 3FTx | three finger toxin |
| PLA2 | phospholipase A2 |
References
- Fry, B.G.; Roelants, K.; Champagne, D.E.; Scheib, H.; Tyndall, J.D.; King, G.F.; Nevalainen, T.J.; Norman, J.A.; Lewis, R.J.; Norton, R.S.; et al. The toxicogenomic multiverse: Convergent recruitment of proteins into animal venoms. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 483–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B. Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, B.G.; Wüster, W.; Ramjan, R.; Fadil, S.; Jackson, T.; Martelli, P.; Kini, R.M. Analysis of Colubroidea snake venoms by liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry: Evolutionary and toxinological implications. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 2047–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowell, N.L.; Giorgianni, M.W.; Kassner, V.A.; Selegue, J.E.; Sanchez, E.E.; Carroll, S.B. The deep origin and recent loss of venom toxin genes in rattlesnakes. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2434–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, T.N.W.; Sunagar, K.; Undheim, E.A.; Koludarov, I.; Chan, A.H.; Sanders, K.; Ali, S.A.; Hendrikx, I.; Dunstan, N.; Fry, B.G. Venom down under: Dynamic evolution of Australian elapid snake toxins. Toxins 2013, 5, 2621–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.C.; Deuis, J.R.; Dashevsky, D.; Dobson, J.; Jackson, T.N.; Brust, A.; Xie, B.; Koludarov, I.; Debono, J.; Hendrikx, I.; et al. The snake with the scorpion’s sting: Novel three-finger toxin sodium channel activators from the venom of the long-glanded blue coral snake (Calliophis bivirgatus). Toxins 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, T.N.; Koludarov, I.; Ali, S.A.; Dobson, J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Dashevsky, D.; Masci, P.P.; Nouwens, A.; Josh, P.; Goldenberg, J. Rapid radiations and the race to redundancy: An investigation of the evolution of Australian elapid snake venoms. Toxins 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Z.; Gould, R.; Jacobs, J.; Friedman, P.; Polokoff, M. Echistatin. A potent platelet aggregation inhibitor from the venom of the viper, Echis carinatus. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 19827–19832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gould, R.J.; Polokoff, M.A.; Friedman, P.A.; Huang, T.F.; Holt, J.C.; Cook, J.J.; Niewiarowski, S. Disintegrins: A family of integrin inhibitory proteins from viper venoms. Exp. Biol. Med. 1990, 195, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Schaefer, W.; Soszka, T.; Lu, W.; Cook, J.; Jameson, B.A.; Niewiarowski, S. Identification of the disulfide bond pattern in albolabrin, an RGD-containing peptide from the venom of Trimeresurus albolabris: Significance for the express of platelet aggregation inhibitory activity. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 5225–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assafim, M.; Frattani, F.S.; Ferreira, M.S.; Silva, D.M.; Monteiro, R.Q.; Zingali, R.B. Exploiting the antithrombotic effect of the (pro) thrombin inhibitor bothrojaracin. Toxicon 2016, 119, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samel, M.; Vija, H.; Rönnholm, G.; Siigur, J.; Kalkkinen, N.; Siigur, E. Isolation and characterization of an apoptotic and platelet aggregation inhibiting l-amino acid oxidase from Vipera berus berus (common viper) venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1764, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracheva, E.O.; Ingolia, N.T.; Kelly, Y.M.; Cordero-Morales, J.F.; Hollopeter, G.; Chesler, A.T.; Sánchez, E.E.; Perez, J.C.; Weissman, J.S.; Julius, D. Molecular basis of infrared detection by snakes. Nature 2010, 464, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panzano, V.C.; Kang, K.; Garrity, P.A. Infrared snake eyes: Trpa1 and the thermal sensitivity of the snake pit organ. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, M.; Fernández, J.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; Segura, Á.; León, G.; Angulo, Y.; Paiva, O.; Matainaho, T.; Jensen, S.D. Comparative proteomic analysis of the venom of the taipan snake, Oxyuranus scutellatus, from Papua New Guinea and Australia: Role of neurotoxic and procoagulant effects in venom toxicity. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2128–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, J.; Chapman, D. Snakes and Snakebite: Venomous Snakes and Management of Snakebite in Southern Africa; Purnell and Sons: Cape Town, South Africa, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein, S.A.; Warrell, D.A.; White, J.; Keyler, D.E. Medically significant bites by ‘colubrid’ snakes. In ‘Venomous’ Bites from Non-Venomous Snakes: A Critical Analysis of Risk and Management of Colubrid Snake Bites; Elsevier: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Grasset, E.; Schaafsma, A. Studies on the venom of the “boom-slang” (Dispholidus typus). S. Afr. Med. J. 1940, 14, 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, H.M.; FitzSimons, D.C. Another rear-fanged South African snake lethal to humans. Herpetologica 1958, 14, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, D.S. Treatment of bites of snakes of africa. In Venomous Animals and Their Venoms: Venomous Vertebrates; Bucherl, W., Buckley, E.E., Deulofeu, V., Eds.; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1968; Volume 1, pp. 463–527. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein, S.A.; White, J.; Keyler, D.E.; Warrell, D.A. Non-front-fanged colubroid snakes: A current evidence-based analysis of medical significance. Toxicon 2013, 69, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiguti, A.S.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Sherman, N.; Fox, J.W. Mass spectrophotometric evidence for P-III/P-IV metalloproteinases in the venom of the boomslang (Dispholidus typus). Toxicon 2000, 38, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Scheib, H.; van der Weerd, L.; Young, B.; McNaughtan, J.; Ramjan, S.R.; Vidal, N.; Poelmann, R.E.; Norman, J.A. Evolution of an arsenal structural and functional diversification of the venom system in the advanced snakes (caenophidia). Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 215–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Whiteley, G.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Harrison, R.A.; Casewell, N.R.; Calvete, J.J. What killed Karl Patterson Schmidt? Combined venom gland transcriptomic, venomic and antivenomic analysis of the South African green tree snake (the boomslang), Dispholidus typus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1861, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosing, J.; Tans, G. Structural and functional properties of snake venom prothrombin activators. Toxicon 1992, 30, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.S.; Kini, R.M. Snake venom prothrombin activators homologous to blood coagulation factor Xa. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2002, 31, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardoni, J.L.; Sousa, L.F.; Wermelinger, L.S.; Lopes, A.S.; Prezoto, B.C.; Serrano, S.M.; Zingali, R.B.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Functional variability of snake venom metalloproteinases: Adaptive advantages in targeting different prey and implications for human envenomation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbister, G.K. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis. In Procoagulant Snake Toxins: Laboratory Studies, Diagnosis, and Understanding Snakebite Coagulopathy; Thieme Medical Publishers: Stuttgart, Germany, 2009; pp. 093–103. [Google Scholar]
- Tans, G.; Rosing, J. Snake venom activators of factor X: An overview. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2002, 31, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, P.; Bradlow, B.; White, J.; Greig, H.; Gaillard, M. Clinical features of twig snake (Thelotornis capensis) envenomation. S. Afr. Med. J. 1980, 58, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.K. Characterization of a novel pro-coagulant metalloprotease (RVBCMP) possessing α-fibrinogenase and tissue haemorrhagic activity from venom of Daboia russelli russelli (Russell’s viper): Evidence of distinct coagulant and haemorrhagic sites in RVBCMP. Toxicon 2008, 51, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.K. The pro-coagulant fibrinogenolytic serine protease isoenzymes purified from Daboia russelii russelii venom coagulate the blood through factor V activation: Role of glycosylation on enzymatic activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, L.; Herrmann, R. Coagulant and anticoagulant actions of Australian snake venoms. Thromb. Aemost. 1983, 50, 707–711. [Google Scholar]
- Isbister, G.K.; Scorgie, F.; O’Leary, M.; Seldon, M.; Brown, S.G.; Lincz, L. Factor deficiencies in venom-induced consumption coagulopathy resulting from Australian elapid envenomation: Australian snakebite project (asp-10). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 2504–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, M.H.; Camire, R.M. Procoagulant adaptation of a blood coagulation prothrombinase-like enzyme complex in Australian elapid venom. Toxins 2010, 2, 1554–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shine, R.; Harlow, P.S.; Branch, W.R.; Webb, J.K. Life on the lowest branch: Sexual dimorphism, diet, and reproductive biology of an African twig snake, Thelotornis capensis (serpentes, Colubridae). Copeia 1996, 1996, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzSimons, V.F.M. Snakes of Southern Africa; Purnell: Cape Town, South Africa, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, C.H. Fatal bite of captive African rear-fanged snake (Dispholidus). Copeia 1958, 1958, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzSimons, F.W. XXXIV.—On the toxic action of the bite of the boomslang or South-African tree-snake (Dispholidus typus). J. Nat. Hist. 1909, 3, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzSimons, F.W. The Snakes of South Africa: Their Venom and the Treatment of Snake Bite; TM Miller: Cape Town, South Africa, 1919. [Google Scholar]
- White, J. Snake venoms and coagulopathy. Toxicon 2005, 45, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C. On some effects upon the blood produced by the injection of the venom of the Australian black snake (Pseudechis porphyriacus). J. Physiol. 1893, 15, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbister, G.K.; Woods, D.; Alley, S.; O’Leary, M.A.; Seldon, M.; Lincz, L.F. Endogenous thrombin potential as a novel method for the characterization of procoagulant snake venoms and the efficacy of antivenom. Toxicon 2010, 56, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Scheib, H.; de Azevedo, I.D.L.J.; Silva, D.A.; Casewell, N.R. Novel transcripts in the maxillary venom glands of advanced snakes. Toxicon 2012, 59, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornalik, F.; Blombäck, B. Prothrombin activation induced by Ecarin-a prothrombin converting enzyme from Echis carinatus venom. Thromb. Res. 1975, 6, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.C.; Tsai, I.H. Functional characterization of a slow and tight-binding inhibitor of plasmin isolated from Russell’s viper venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masci, P.; Whitaker, A.; Sparrow, L.; De Jersey, J.; Winzor, D.; Watters, D.; Lavin, M.; Gaffney, P. Textilinins from Pseudonaja textilis textilis. Characterization of two plasmin inhibitors that reduce bleeding in an animal model. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2000, 11, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debono, J.; Cochran, C.; Kuruppu, S.; Nouwens, A.; Rajapakse, N.W.; Kawasaki, M.; Wood, K.; Dobson, J.; Baumann, K.; Jouiaei, M.; et al. Canopy venom: Proteomic comparison among new world arboreal pit-viper venoms. Toxins 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aman, J.W.; Imperial, J.S.; Ueberheide, B.; Zhang, M.M.; Aguilar, M.; Taylor, D.; Watkins, M.; Yoshikami, D.; Showers-Corneli, P.; Safavi-Hemami, H. Insights into the origins of fish hunting in venomous cone snails from studies of Conus tessulatus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5087–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.H.; Vetter, I.; Hamilton, B.; Sunagar, K.; Lavergne, V.; Dutertre, V.; Fry, B.G.; Antunes, A.; Venter, D.J. Evolution of separate predation-and defence-evoked venoms in carnivorous cone snails. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, A.H.; Israel, M.R.; Inserra, M.C.; Smith, J.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Vetter, I.; Dutertre, S. α-conotoxin suvia suggests an evolutionary link between ancestral predator defence and the origin of fish-hunting behaviour in carnivorous cone snails. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20150817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.; Sunagar, K.; Casewell, N.; Kochva, E.; Roelants, K.; Scheib, H.; Wüster, W.; Vidal, N.; Young, B.; Burbrink, F. The origin and evolution of the toxicofera reptile venom system. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, A.; Anderson, A. Dendrotoxins: Snake toxins that block potassium channels and facilitate neurotransmitter release. Pharmacol. Ther. 1985, 31, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.; Karlsson, E. Dendrotoxin from the venom of the green mamba, Dendroaspis angusticeps. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1980, 312, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, E.; Mbugua, P.; Rodriguez-Ithurralde, D. Fasciculins, anticholinesterase toxins from the venom of the green mamba Dendroaspis angusticeps. J. Physiol. 1983, 79, 232–240. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, O.; Ismail, M.; El-Asmar, M. Pharmacological studies of snake (Dendroaspis angusticeps) venom. Toxicon 1973, 11, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, Y.; Sunagar, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Reeks, T.; Fry, B.G. Three-finger toxins (3FTXs). In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 215–227. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, B.G.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Takacs, Z.; Reeks, T.; Sunagar, K. C-type natriuretic peptides. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 318–326. [Google Scholar]
- Eng, W.S.; Fry, B.G.; Sunagar, K.; Takacs, Z.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Guddat, L.W. Kunitz peptides. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, 3.3.1; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D.; R Core Team. Nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models, 3.1-128; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D. Mixed-Effects Models in S and S-Plus; Springer Science & Business Media Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
| Concentration | Without Antivenom | With Antivenom | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D. typus | T. mossambicanus | D. typus | T. mossambicanus | |||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| 20 µg/mL | 11.27 | 0.06 | 7.57 | 0.15 | 20.73 | 1.07 | 9.6 | 0.17 |
| 10 µg/mL | 15.95 | 1.88 | 9.55 | 0.17 | 155 | 5.2 | 16 | 0.17 |
| 6.66 µg/mL | 19.34 | 0.21 | 11.20 | 0.34 | 214.56 | 21.28 | 21.16 | 0.23 |
| 5 µg/mL | 21.22 | 0.22 | 12.43 | 0.08 | 255 | 10.56 | 35.13 | 1.32 |
| 3.33 µg/mL | 24.72 | 0.22 | 14.95 | 0.65 | 343.2 | 8.97 | 43.33 | 1.86 |
| 2.5 µg/mL | 27.63 | 0.14 | 16.45 | 0.18 | 432.3 | 35.32 | 53.43 | 0.11 |
| 2 µg/mL | 30.91 | 0.47 | 18.27 | 0.13 | 444.93 | 23.43 | 58.46 | 1.29 |
| 1.33 µg/mL | 36.32 | 1.61 | 20.50 | 0.58 | 525.86 | 51.19 | 75.43 | 2.15 |
| 1 µg/mL | 39.60 | 0.54 | 24.30 | 0.74 | 594.86 | 61.15 | 83.33 | 3.86 |
| 0.66 µg/mL | 43.91 | 0.56 | 27.44 | 1.03 | 735.3 | 6.94 | 100.8 | 1.97 |
| 0.4 µg/mL | 53.77 | 6.21 | 31.67 | 0.19 | 790.36 | 9.41 | 128.4 | 0.52 |
| 0.25 µg/mL | 61.95 | 7.95 | 35.91 | 0.64 | 966.76 | 35.88 | 163.23 | 2.6 |
| 0.125 µg/mL | 83.31 | 6.51 | 54.89 | 0.14 | 999 | 0 | 226.33 | 2.6 |
| 0.05 µg/mL | 146.65 | 5.23 | 80.44 | 0.52 | 999 | 0 | 381.23 | 4.71 |
| Species | Coefficient Estimates | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Aym ϕ1 | R0 ϕ2 | lrc ϕ3 | |
| D. typus | 9.095161 (s) | 37.83835 (s) | −0.6711807 |
| T. mossambicanus | 2.068652 (s) | 23.17609 (s) | −0.8289048 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Debono, J.; Dobson, J.; Casewell, N.R.; Romilio, A.; Li, B.; Kurniawan, N.; Mardon, K.; Weisbecker, V.; Nouwens, A.; Kwok, H.F.; et al. Coagulating Colubrids: Evolutionary, Pathophysiological and Biodiscovery Implications of Venom Variations between Boomslang (Dispholidus typus) and Twig Snake (Thelotornis mossambicanus). Toxins 2017, 9, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9050171
Debono J, Dobson J, Casewell NR, Romilio A, Li B, Kurniawan N, Mardon K, Weisbecker V, Nouwens A, Kwok HF, et al. Coagulating Colubrids: Evolutionary, Pathophysiological and Biodiscovery Implications of Venom Variations between Boomslang (Dispholidus typus) and Twig Snake (Thelotornis mossambicanus). Toxins. 2017; 9(5):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9050171
Chicago/Turabian StyleDebono, Jordan, James Dobson, Nicholas R. Casewell, Anthony Romilio, Bin Li, Nyoman Kurniawan, Karine Mardon, Vera Weisbecker, Amanda Nouwens, Hang Fai Kwok, and et al. 2017. "Coagulating Colubrids: Evolutionary, Pathophysiological and Biodiscovery Implications of Venom Variations between Boomslang (Dispholidus typus) and Twig Snake (Thelotornis mossambicanus)" Toxins 9, no. 5: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9050171
APA StyleDebono, J., Dobson, J., Casewell, N. R., Romilio, A., Li, B., Kurniawan, N., Mardon, K., Weisbecker, V., Nouwens, A., Kwok, H. F., & Fry, B. G. (2017). Coagulating Colubrids: Evolutionary, Pathophysiological and Biodiscovery Implications of Venom Variations between Boomslang (Dispholidus typus) and Twig Snake (Thelotornis mossambicanus). Toxins, 9(5), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9050171





_Kwok.png)


