Proteolysis in Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric Cancer
Abstract
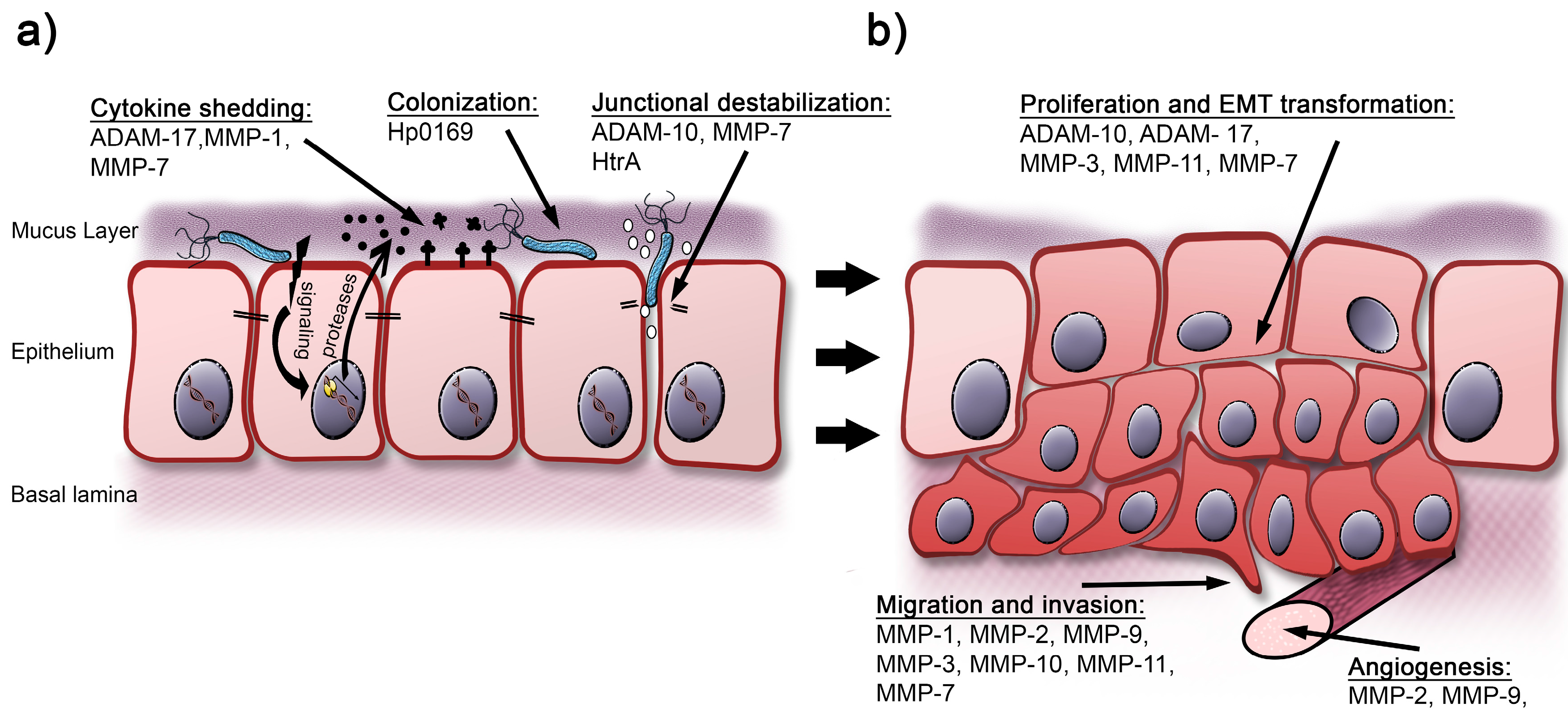
:1. Introduction: The Gastric Epithelium in Health and Disease
Helicobacter Pylori-Dependent Gastric Pathologies
2. Deregulation of Extracellular Host Proteases by H. pylori
2.1. A disintegrin and Metallopeptidase ADAM
2.2. Matrix Metalloproteinases MMP
2.2.1. H. pylori-Induced MMPs: The Collagenases MMP-1, MMP-8, and MMP-13
2.2.2. H. pylori-Induced MMPs: The Gelatinases MMP-2, and MMP-9
2.2.3. H. pylori-Induced MMPs: The Stromelysins MMP-3, MMP-10, and MMP-11
2.2.4. Matrilysin, Macrophage Metallo-Elastase, and Membrane-Type MMPs
2.3. Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases TIMPs
3. H. pylori Expresses Proteases Exhibiting a Direct Influence on the Integrity of the Epithelial Barrier Function
H. pylori HtrA Induced E-Cadherin Ectodomain Shedding
4. Concluding Remarks
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. Current Status on Stem Cells and Cancers of the Gastric Epithelium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19153–19169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moens, E.; Veldhoen, M. Epithelial barrier biology: Good fences make good neighbours. Immunology 2012, 135, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fihn, B.M.; Sjöqvist, A.; Jodal, M. Permeability of the rat small intestinal epithelium along the villus-crypt axis: Effects of glucose transport. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Anderson, J.M. Architecture of tight junctions and principles of molecular composition. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 36, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, A.; Niazi, A.K.; Ahmed, M.Z.; Iqbal, B.; Anwer, S.M.; Khan, H.H. The role of Wnt signaling pathway in carcinogenesis and implications for anticancer therapeutics. Hered. Cancer Clin. Pract. 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhash, V.V.; Ho, B. Inflammation and proliferation—A causal event of host response to Helicobacter pylori infection. Microbiology 2015, 161, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.Y.; Liu, X.Z.; Liang, C.M. Inflammatory microenvironment contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6619–6628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagy, T.A.; Wroblewski, L.E.; Wang, D.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Delgado, A.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Noto, J.; Israel, D.A.; Ogden, S.R.; Correa, P.; et al. Beta-Catenin and p120 mediate PPARdelta-dependent proliferation induced by Helicobacter pylori in human and rodent epithelia. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schistosomes, liver flukes and Helicobacter pylori. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Lyon, France, 7–14 June 1994. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 1994, 61, 1–241.
- Machado, J.C.; Figueiredo, C.; Canedo, P.; Pharoah, P.; Carvalho, R.; Nabais, S.; Castro Alves, C.; Campos, M.L.; Van Doorn, L.J.; Caldas, C.; et al. A proinflammatory genetic profile increases the risk for chronic atrophic gastritis and gastric carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Omar, E.M.; Rabkin, C.S.; Gammon, M.D.; Vaughan, T.L.; Risch, H.A.; Schoenberg, J.B.; Stanford, J.L.; Mayne, S.T.; Goedert, J.; Blot, W.J.; et al. Increased risk of noncardia gastric cancer associated with proinflammatory cytokine gene polymorphisms. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, M. Helicobacter pylori CagA and gastric cancer: A paradigm for hit-and-run carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backert, S.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Fischer, W. Composition, structure and function of the Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity island encoded type IV secretion system. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posselt, G.; Backert, S.; Wessler, S. The functional interplay of Helicobacter pylori factors with gastric epithelial cells induces a multi-step process in pathogenesis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachathundikandi, S.K.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Backert, S. Signal transduction of Helicobacter pylori during interaction with host cell protein receptors of epithelial and immune cells. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 454–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backert, S.; Schmidt, T.P.; Harrer, A.; Wessler, S. Exploiting the Gastric Epithelial Barrier: Helicobacter pylori’s Attack on Tight and Adherens Junctions. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 400, 195–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herszenyi, L.; Plebani, M.; Carraro, P.; De Paoli, M.; Roveroni, G.; Cardin, R.; Foschia, F.; Tulassay, Z.; Naccarato, R.; Farinati, F. Proteases in gastrointestinal neoplastic diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2000, 291, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frejlich, E.; Rudno-Rudzinska, J.; Janiszewski, K.; Salomon, L.; Kotulski, K.; Pelzer, O.; Grzebieniak, Z.; Tarnawa, R.; Kielan, W. Caspases and their role in gastric cancer. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 22, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.L.; Huang, C.Z. Ubiquitin proteasome system research in gastrointestinal cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 8, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, K.N.; Muller, A. Helicobacter pylori activates the TLR2/NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-18 axis to induce regulatory T-cells, establish persistent infection and promote tolerance to allergens. Gut Microbes 2015, 6, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitzler, I.; Sayi, A.; Kohler, E.; Engler, D.B.; Koch, K.N.; Hardt, W.D.; Muller, A. Caspase-1 has both proinflammatory and regulatory properties in Helicobacter infections, which are differentially mediated by its substrates IL-1beta and IL-18. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3594–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potthoff, A.; Ledig, S.; Martin, J.; Jandl, O.; Cornberg, M.; Obst, B.; Beil, W.; Manns, M.P.; Wagner, S. Significance of the caspase family in Helicobacter pylori induced gastric epithelial apoptosis. Helicobacter 2002, 7, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashktorab, H.; Neapolitano, M.; Bomma, C.; Allen, C.; Ahmed, A.; Dubois, A.; Naab, T.; Smoot, D.T. In vivo and in vitro activation of caspase-8 and -3 associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Nagy, T.A.; Vilgelm, A.; Zaika, E.; Ogden, S.R.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Correa, P.; Washington, M.K.; El-Rifai, W.; et al. Regulation of p53 tumor suppressor by Helicobacter pylori in gastric epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, Y.H.; Lamb, A.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Huang, B.; Ito, K.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Ito, Y.; Chen, L.F. Helicobacter pylori CagA targets gastric tumor suppressor RUNX3 for proteasome-mediated degradation. Oncogene 2010, 29, 5643–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, M.; Bravo, D.; Canales, J.; Sanhueza, C.; Diaz, N.; Almarza, O.; Toledo, H.; Quest, A.F. Helicobacter pylori-induced loss of survivin and gastric cell viability is attributable to secreted bacterial gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, P.M.; Lapointe, T.K.; Jackson, S.; Beck, P.L.; Jones, N.L.; Buret, A.G. Helicobacter pylori activates calpain via toll-like receptor 2 to disrupt adherens junctions in human gastric epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3887–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teller, A.; Jechorek, D.; Hartig, R.; Adolf, D.; Reissig, K.; Roessner, A.; Franke, S. Dysregulation of apoptotic signaling pathways by interaction of RPLP0 and cathepsin X/Z in gastric cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2015, 211, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.H.; Edwards, D.R.; Murphy, G. Metalloproteinase inhibitors: Biological actions and therapeutic opportunities. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 3719–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khokha, R.; Murthy, A.; Weiss, A. Metalloproteinases and their natural inhibitors in inflammation and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.; Bischoff, R. Physiology and pathophysiology of matrix metalloproteases. Amino Acids 2011, 41, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.; Bischoff, R. Active metalloproteases of the A Disintegrin and Metalloprotease (ADAM) family: Biological function and structure. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, G. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Genome Biol. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.C.; Rustagi, S.; Dempsey, P.J. ADAM Proteases and Gastrointestinal Function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 243–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, T.; Tomita, T.; Dixon, M.F.; Axon, A.T.; Robinson, P.A.; Crabtree, J.E. ADAMs (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase) messenger RNA expression in Helicobacter pylori-infected, normal, and neoplastic gastric mucosa. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carl-McGrath, S.; Lendeckel, U.; Ebert, M.; Roessner, A.; Rocken, C. The disintegrin-metalloproteinases ADAM9, ADAM12, and ADAM15 are upregulated in gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 26, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, W.; Aleksandra, S.-M.; Kalinski, T.; Roessner, A.; Malfertheiner, P.; Naumann, M.; Lendecket, U. Expression of adam 19 in helicobacter pylori-mediated diseases and gastric cancer. In Gastric Cancer Research Trends; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 171. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, J.M.; Clayton, C.L.; Tomita, T.; Wallace, D.M.; Robinson, P.A.; Crabtree, J.E. cDNA array analysis of cag pathogenicity island-associated Helicobacter pylori epithelial cell response genes. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 6970–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, A.; Backert, S.; Hammond, C.E.; Gooz, M.; Smolka, A.J. Helicobacter pylori CagL activates ADAM17 to induce repression of the gastric H, K-ATPase alpha subunit. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClurg, U.L.; Danjo, K.; King, H.O.; Scott, G.B.; Robinson, P.A.; Crabtree, J.E. Epithelial cell ADAM17 activation by Helicobacter pylori: Role of ADAM17 C-terminus and Threonine-735 phosphorylation. Microbes Infect. 2015, 17, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slomiany, B.L.; Slomiany, A. Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric mucosal TGF-alpha ectodomain shedding and EGFR transactivation involves Rac1/p38 MAPK-dependent TACE activation. Inflammopharmacology 2016, 24, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joh, T.; Kataoka, H.; Tanida, S.; Watanabe, K.; Ohshima, T.; Sasaki, M.; Nakao, H.; Ohhara, H.; Higashiyama, S.; Itoh, M. Helicobacter pylori-stimulated interleukin-8 (IL-8) promotes cell proliferation through transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) by disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) activation. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2005, 50, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Cao, H.; Chaturvedi, R.; Krishna, U.; Hobbs, S.S.; Dempsey, P.J.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Cover, T.L.; Washington, M.K.; Wilson, K.T.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor activation protects gastric epithelial cells from Helicobacter pylori-induced apoptosis. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabtree, J.E.; Jeremy, A.H.; Duval, C.; Dixon, M.F.; Danjo, K.; Carr, I.M.; Pritchard, D.M.; Robinson, P.A. Effects of EGFR Inhibitor on Helicobacter pylori Induced Gastric Epithelial Pathology In Vivo. Pathogens 2013, 2, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, B.; Lower, M.; Weydig, C.; Carra, G.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Geppert, T.; Schroder, P.; Sewald, N.; Backert, S.; Schneider, G.; et al. Helicobacter pylori HtrA is a new secreted virulence factor that cleaves E-cadherin to disrupt intercellular adhesion. EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirrmeister, W.; Gnad, T.; Wex, T.; Higashiyama, S.; Wolke, C.; Naumann, M.; Lendeckel, U. Ectodomain shedding of E-cadherin and c-Met is induced by Helicobacter pylori infection. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 3500–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.J.; Wu, D.C.; Cheng, K.H.; Chen, L.T.; Hung, W.C. RECK inhibits stemness gene expression and tumorigenicity of gastric cancer cells by suppressing ADAM-mediated Notch1 activation. J. Cell Physiol. 2014, 229, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, N.; MacDonald, T.T. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Stromal/Epithelial Interactions in the Gut. Physiology 2007, 22, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, S.; Hundertmark, T.; Kalinski, T.; Peitz, U.; Wex, T.; Malfertheiner, P.; Naumann, M.; Roessner, A. Helicobacter pylori encoding the pathogenicity island activates matrix metalloproteinase 1 in gastric epithelial cells via JNK and ERK. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 2868–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.M.; Ferreira, R.M.; Pinto-Ribeiro, I.; Sougleri, I.S.; Oliveira, M.J.; Carreto, L.; Santos, M.A.; Sgouras, D.N.; Carneiro, F.; Leite, M.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Activates Matrix Metalloproteinase 10 in Gastric Epithelial Cells via EGFR and ERK-mediated Pathways. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, N.; Sato, H.; Hayashibara, T.; Senba, M.; Geleziunas, R.; Wada, A.; Hirayama, T.; Yamamoto, N. Helicobacter pylori induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 through activation of nuclear factor kappaB. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, S. Significance of cell-surface expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors on gastric epithelium and infiltrating mucosal lymphocytes in progression of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 39, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, S. Enhanced Cell Surface Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors, and Tumor-Induced Host Response in Progression of Human Gastric Carcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautelin, H.I.; Oksanen, A.M.; Veijola, L.I.; Sipponen, P.I.; Tervahartiala, T.I.; Sorsa, T.A.; Lauhio, A. Enhanced systemic matrix metalloproteinase response in Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Ann. Med. 2009, 41, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.A.O.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, Q.; Ouyang, H. Helicobacter pylori infection promotes the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer through increasing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and matrix metalloproteinase-10. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.S.; Chu, Y.Q.; Ye, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tao, H.Q. Overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase 11 in human gastric carcinoma and its clinicopathologic significance. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clendeninn, N.J.; Appelt, K. Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, G.I.; Duncan, M.E.; O’Neil, P.; Melvin, W.T.; Fothergill, J.E. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gooz, M.; Gooz, P.; Smolka, A.J. Epithelial and bacterial metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in H. pylori infection of human gastric cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 281, G823–G832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Lu, H.; Sun, Y.; Graham, D.Y.; Cheung, H.S.; Yamaoka, Y. Balance between polyoma enhancing activator 3 and activator protein 1 regulates Helicobacter pylori-stimulated matrix metalloproteinase 1 expression. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, O.; Vieth, M.; Naumann, M. Protein kinase C isozymes regulate matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression and cell invasion in Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut 2013, 62, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillinger, M.H.; Marjanovic, N.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Scher, J.U.; Roper, J.; Abeles, A.M.; Izmirly, P.I.; Axelrod, M.; Pillinger, M.Y.; et al. Helicobacter pylori stimulates gastric epithelial cell MMP-1 secretion via CagA-dependent and -independent ERK activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 18722–18731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, J.D.; Steele, I.; Moore, A.R.; Murugesan, S.V.; Rakonczay, Z.; Venglovecz, V.; Pritchard, D.M.; Dimaline, R.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Varro, A.; et al. Gastrin stimulates MMP-1 expression in gastric epithelial cells: Putative role in gastric epithelial cell migration. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G78–G86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaishi, S.; Wang, T.C. Gene expression profiling in a mouse model of Helicobacter-induced gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitadai, Y.; Sasaki, A.; Ito, M.; Tanaka, S.; Oue, N.; Yasui, W.; Aihara, M.; Imagawa, K.; Haruma, K.; Chayama, K. Helicobacter pylori infection influences expression of genes related to angiogenesis and invasion in human gastric carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 311, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Sorokin, L.M. In Vivo processing of CXCL5 (LIX) by matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 promotes early neutrophil recruitment in IL-1beta-induced peritonitis. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Xi, H.; Wei, B.; Chen, L. The prognostic role of matrix metalloproteinase 2 in gastric cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torii, A.; Kodera, Y.; Uesaka, K.; Hirai, T.; Yasui, K.; Morimoto, T.; Yamamura, Y.; Kato, T.; Hayakawa, T.; Fujimoto, N.; et al. Plasma concentration of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in gastric cancer. Br. J. Surg. 1997, 84, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Y.; Wu, M.S.; Chiang, E.P.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, C.J.; Chi, N.H.; Shih, Y.T.; Chen, G.H.; Lin, J.T. Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 level is better than serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 level to predict gastric cancer evolution. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubben, F.J.; Sier, C.F.; van Duijn, W.; Griffioen, G.; Hanemaaijer, R.; van de Velde, C.J.; van Krieken, J.H.; Lamers, C.B.; Verspaget, H.W. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 is a consistent prognostic factor in gastric cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergin, P.J.; Anders, E.; Sicheng, W.; Erik, J.; Jennie, A.; Hans, L.; Pierre, M.; Qiang, P.H.; Marianne, Q.J. Increased production of matrix metalloproteinases in Helicobacter pylori-associated human gastritis. Helicobacter 2004, 9, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubben, F.J.; Sier, C.F.; Schram, M.T.; Witte, A.M.; Veenendaal, R.A.; van Duijn, W.; Verheijen, J.H.; Hanemaaijer, R.; Lamers, C.B.; Verspaget, H.W. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection favourably affects altered gastric mucosal MMP-9 levels. Helicobacter 2007, 12, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergin, P.J.; Raghavan, S.; Svensson, H.; Starckx, S.; Van Aelst, I.; Gjertsson, I.; Opdenakker, G.; Quiding-Jarbrink, M. Gastric gelatinase B/matrix metalloproteinase-9 is rapidly increased in Helicobacter felis-induced gastritis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 52, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, P.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Patra, R.; Banerjee, A.; Berg, D.E.; Swarnakar, S. Cag pathogenicity island-independent up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases-9 and -2 secretion and expression in mice by Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 34651–34662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, Y.H.; Ryu, E.; Lee, D.; Shim, H.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, S.T. CagA phosphorylation-dependent MMP-9 expression in gastric epithelial cells. Helicobacter 2011, 16, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, R.; Fina, D.; Peluso, I.; Fantini, M.C.; Tosti, C.; Del Vecchio Blanco, G.; Paoluzi, O.A.; Caprioli, F.; Andrei, F.; Stolfi, C.; et al. IL-21 is highly produced in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa and promotes gelatinases synthesis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5957–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deryugina, E.I.; Quigley, J.P. Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gooz, M.; Shaker, M.; Gooz, P.; Smolka, A.J. Interleukin 1beta induces gastric epithelial cell matrix metalloproteinase secretion and activation during Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut 2003, 52, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przybylo, J.A.; Radisky, D.C. Matrix metalloproteinase-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Tumor progression at Snail’s pace. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternlicht, M.D.; Bissell, M.J.; Werb, Z. The matrix metalloproteinase stromelysin-1 acts as a natural mammary tumor promoter. Oncogene 2000, 19, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sougleri, I.S.; Papadakos, K.S.; Zadik, M.P.; Mavri-Vavagianni, M.; Mentis, A.F.; Sgouras, D.N. Helicobacter pylori CagA protein induces factors involved in the epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in infected gastric epithelial cells in an EPIYA-phosphorylation-dependent manner. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Q.; Song, S.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, S.L. Expression of MMP-3 and TIMP-3 in gastric cancer tissue and its clinical significance. Oncol. Lett. 2011, 2, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.C.; Sheu, B.S.; Cheng, H.C.; Wang, Y.L.; Yang, H.B.; Wu, J.J. Elevated serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 and -7 in H. pylori-related gastric cancer can be biomarkers correlating with a poor survival. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gencer, S.; Cebeci, A.; Irmak-Yazicioglu, M.B. Silencing of the MMP-3 gene by siRNA transfection in gastric cancer AGS cells. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2011, 20, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg, C.; Ghesquière, B.; Impens, F.; Gevaert, K.; Kumar, J.D.; Cash, N.; Kandola, S.; Hegyi, P.; Wang, T.C.; Dockray, G.J.; et al. Mapping Proteolytic Processing in the Secretome of Gastric Cancer-Associated Myofibroblasts Reveals Activation of MMP-1, MMP-2, and MMP-3. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 3413–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.-H.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Hua, K.-T.; Chang, K.-C.; Kuo, M.-L.; Lin, M.-T. Eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid inhibit macrophage-induced gastric cancer cell migration by attenuating the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 10. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, Y.B.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zhao, B.L.; Ding, R.; Liu, H.; Li, S. Knockdown of MMP11 inhibits proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2013, 26, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wroblewski, L.E.; Noble, P.J.; Pagliocca, A.; Pritchard, D.M.; Hart, C.A.; Campbell, F.; Dodson, A.R.; Dockray, G.J.; Varro, A. Stimulation of MMP-7 (matrilysin) by Helicobacter pylori in human gastric epithelial cells: Role in epithelial cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3017–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, H.C.; Krishna, U.S.; Israel, D.A.; Matrisian, L.M.; Washington, M.K.; Peek, R.M., Jr. Helicobacter pylori strain-selective induction of matrix metalloproteinase-7 in vitro and within gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebb, J.R.; Letley, D.P.; Thomas, R.J.; Aviles, F.; Collins, H.M.; Watson, S.A.; Hand, N.M.; Zaitoun, A.; Atherton, J.C. Helicobacter pylori upregulates matrilysin (MMP-7) in epithelial cells in vivo and in vitro in a Cag dependent manner. Gut 2003, 52, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, W.C.; Jung, S.H.; Lee, K.M.; Paik, C.N.; Kawk, J.W.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, Y.K. The detection of Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity islands (PAIs) and expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) in gastric epithelial dysplasia and intramucosal cancer. Gastric Cancer 2010, 13, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Grabowska, A.M.; Clarke, P.A.; Whelband, E.; Robinson, K.; Argent, R.H.; Tobias, A.; Kumari, R.; Atherton, J.C.; Watson, S.A. Helicobacter pylori potentiates epithelial:mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer: Links to soluble HB-EGF, gastrin and matrix metalloproteinase-7. Gut 2010, 59, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, S.R.; Wroblewski, L.E.; Weydig, C.; Romero-Gallo, J.; O’Brien, D.P.; Israel, D.A.; Krishna, U.S.; Fingleton, B.; Reynolds, A.B.; Wessler, S.; et al. p120 and Kaiso regulate Helicobacter pylori-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 4110–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varro, A.; Kenny, S.; Hemers, E.; McCaig, C.; Przemeck, S.; Wang, T.C.; Bodger, K.; Pritchard, D.M. Increased gastric expression of MMP-7 in hypergastrinemia and significance for epithelial-mesenchymal signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G1133–G1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T.; Choi, E.; Petersen, C.P.; Noto, J M.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Washington, M.K.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Goldenring, J.R. Characterization of progressive metaplasia in the gastric corpus mucosa of Mongolian gerbils infected with Helicobacter pylori. J. Pathol. 2016, 239, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCaig, C.; Duval, C.; Hemers, E.; Steele, I.; Pritchard, D.M.; Przemeck, S.; Dimaline, R.; Ahmed, S.; Bodger, K.; Kerrigan, D.D.; et al. The role of matrix metalloproteinase-7 in redefining the gastric microenvironment in response to Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, S.R.; Noto, J.M.; Allen, S.S.; Patel, D.A.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Washington, M.K.; Fingleton, B.; Israel, D.A.; Lewis, N.D.; Wilson, K.T.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 and premalignant host responses in Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.J.; Du, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ma, L.Y.; Cao, G.W. Inflammation-related factors predicting prognosis of gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 4586–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Chu, D.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ji, G.; Zhao, H.; Wu, G.; Du, J.; Zhao, Q. Matrix metalloproteinase-12 is associated with overall survival in Chinese patients with gastric cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 107, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ries, C. Cytokine functions of TIMP-1. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Seo, D.-W. TIMP-2: An endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis. Trends Mol. Med. 2005, 11, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, J.G.; Ko, J.H. Expression level and glycan dynamics determine the net effects of TIMP-1 on cancer progression. BMB Rep. 2012, 45, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodger, K.; Ahmed, S.; Pazmany, L.; Pritchard, D.M.; Micheal, A.; Khan, A.L.; Dimaline, R.; Dockray, G.J.; Varro, A. Altered gastric corpus expression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in human and murine Helicobacter infection. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 61, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.L.; Zhao, J.R.; Ren, X.Y.; Xie, J.P.; Ma, Q.Z.; Rong, Q.H. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 associated with gastric ulcer recurrence. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 4590–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.C.; Yang, H.B.; Chang, W.L.; Chen, W.Y.; Yeh, Y.C.; Sheu, B.S. Expressions of MMPs and TIMP-1 in gastric ulcers may differentiate H. pylori-infected from NSAID-related ulcers. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 539316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, K.H.; Hung, H.W.; Yang, H.B.; Lu, C.C.; Wu, J.J.; Sheu, B.S. Host single nucleotide polymorphisms of MMP-9-1562/TIMP-1 372 have gender differences in the risk of gastric intestinal metaplasia after Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2009, 14, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubben, F.J.; Sier, C.F.; Meijer, M.J.; van den Berg, M.; van der Reijden, J.J.; Griffioen, G.; van de Velde, C.J.; Lamers, C.B.; Verspaget, H.W. Clinical impact of MMP and TIMP gene polymorphisms in gastric cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slomiany, B.L.; Bilski, J.; Sarosiek, J.; Murty, V.L.; Dworkin, B.; VanHorn, K.; Zielenski, J.; Slomiany, A. Campylobacter pyloridis degrades mucin and undermines gastric mucosal integrity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1987, 144, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, J.; Slomiany, A.; Slomiany, B.L. Suppression of Helicobacter pylori protease activity towards growth factors by sulglycotide. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1997, 48, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slomiany, B.L.; Piotrowski, J.; Slomiany, A. Susceptibility of growth factors to degradation by Helicobacter pylori protease: Effect of ebrotidine and sucralfate. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1996, 40, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.W.; Chahal, B.; French, G.L. The human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori has a gene encoding an enzyme first classified as a mucinase In Vibrio cholerae. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 13, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windle, H.J.; Kelleher, D. Identification and characterization of a metalloprotease activity from Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3132–3137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kavermann, H.; Burns, B.P.; Angermuller, K.; Odenbreit, S.; Fischer, W.; Melchers, K.; Haas, R. Identification and characterization of Helicobacter pylori genes essential for gastric colonization. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lower, M.; Weydig, C.; Metzler, D.; Reuter, A.; Starzinski-Powitz, A.; Wessler, S.; Schneider, G. Prediction of extracellular proteases of the human pathogen Helicobacter pylori reveals proteolytic activity of the Hp1018/19 protein HtrA. PLoS ONE 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegtmeyer, N.; Moodley, Y.; Yamaoka, Y.; Pernitzsch, S.R.; Schmidt, V.; Traverso, F.R.; Schmidt, T.P.; Rad, R.; Yeoh, K.G.; Bow, H.; et al. Characterisation of worldwide Helicobacter pylori strains reveals genetic conservation and essentiality of serine protease HtrA. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 925–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegtmeyer, N.; Rivas Traverso, F.; Rohde, M.; Oyarzabal, O.A.; Lehn, N.; Schneider-Brachert, W.; Ferrero, R.L.; Fox, J.G.; Berg, D.E.; Backert, S. Electron microscopic, genetic and protein expression analyses of Helicobacter acinonychis strains from a Bengal tiger. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumann, D.; Aksu, S.; Wendland, M.; Janek, K.; Zimny-Arndt, U.; Sabarth, N.; Meyer, T.F.; Jungblut, P.R. Proteome analysis of secreted proteins of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3396–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.G.; Lim, J.M.; Weinberg, M.V.; Wells, L.; Hoover, T.R. Direct analysis of the extracellular proteome from two strains of Helicobacter pylori. Proteomics 2007, 7, 2240–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frees, D.; Brondsted, L.; Ingmer, H. Bacterial proteases and virulence. Subcell. Biochem. 2013, 66, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skorko-Glonek, J.; Zurawa-Janicka, D.; Koper, T.; Jarzab, M.; Figaj, D.; Glaza, P.; Lipinska, B. HtrA protease family as therapeutic targets. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 977–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, G.; Hilgenfeld, R. Architecture and regulation of HtrA-family proteins involved in protein quality control and stress response. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, B.; Brandstetter, H.; Wessler, S. The stability and activity of recombinant Helicobacter pylori HtrA under stress conditions. J. Basic Microbiol. 2013, 53, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, N.R.; Shepherd, B.; Falkow, S. Global transposon mutagenesis and essential gene analysis of Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 7926–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, B.; Geppert, T.; Boehm, M.; Reisen, F.; Plattner, P.; Gadermaier, G.; Sewald, N.; Ferreira, F.; Briza, P.; Schneider, G.; et al. Distinct roles of secreted HtrA proteases from gram-negative pathogens in cleaving the junctional protein and tumor suppressor E-cadherin. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 10115–10120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, T.; Zabler, D.; Urman, S.; Rohde, M.; Hartig, R.; Wessler, S.; Misselwitz, R.; Berger, J.; Sewald, N.; Konig, W.; et al. Helicobacter exploits integrin for type IV secretion and kinase activation. Nature 2007, 449, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Soto, L.F.; Kutter, S.; Sewald, X.; Ertl, C.; Weiss, E.; Kapp, U.; Rohde, M.; Pirch, T.; Jung, K.; Retta, S.F.; et al. Helicobacter pylori type IV secretion apparatus exploits beta1 integrin in a novel RGD-independent manner. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Necchi, V.; Candusso, M.E.; Tava, F.; Luinetti, O.; Ventura, U.; Fiocca, R.; Ricci, V.; Solcia, E. Intracellular, intercellular, and stromal invasion of gastric mucosa, preneoplastic lesions, and cancer by Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damsky, C.H.; Richa, J.; Solter, D.; Knudsen, K.; Buck, C.A. Identification and purification of a cell surface glycoprotein mediating intercellular adhesion in embryonic and adult tissue. Cell 1983, 34, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.M.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Dishonorable discharge: The oncogenic roles of cleaved E-cadherin fragments. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2917–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouxhon, S.M.; Kyrkanides, S.; Teng, X.; Athar, M.; Ghazizadeh, S.; Simon, M.; O’Banion, M.K.; Ma, L. Soluble E-cadherin: A critical oncogene modulating receptor tyrosine kinases, MAPK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Oncogene 2014, 33, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.O.; Chu, K.M.; Lam, S.K.; Wong, B.C.; Kwok, K.F.; Law, S.; Ko, S.; Hui, W.M.; Yueng, Y.H.; Wong, J. Soluble E-cadherin is an independent pretherapeutic factor for long-term survival in gastric cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2288–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, M.; Hirai, S.; Kamihagi, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Yasumoto, M.; Kato, I. Soluble E-cadherin fragments increased in circulation of cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 1994, 69, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuefer, R.; Hofer, M.D.; Gschwend, J.E.; Pienta, K.J.; Sanda, M.G.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Rubin, M.A.; Day, M.L. The role of an 80 kDa fragment of E-cadherin in the metastatic progression of prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 6447–6452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.P.; Goetz, C.; Huemer, M.; Schneider, G.; Wessler, S. Calcium binding protects E-cadherin from cleavage by Helicobacter pylori HtrA. Gut Pathog. 2016, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.P.; Perna, A.M.; Fugmann, T.; Bohm, M.; Jan, H.; Haller, S.; Gotz, C.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Hoy, B.; Rau, T.T.; et al. Identification of E-cadherin signature motifs functioning as cleavage sites for Helicobacter pylori HtrA. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klenner, A.; Hahnke, V.; Geppert, T.; Schneider, P.; Zettl, H.; Haller, S.; Rodrigues, T.; Reisen, F.; Hoy, B.; Schaible, A.M.; et al. From Virtual Screening to Bioactive Compounds by Visualizing and Clustering of Chemical Space. Mol. Inform. 2012, 31, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lower, M.; Geppert, T.; Schneider, P.; Hoy, B.; Wessler, S.; Schneider, G. Inhibitors of Helicobacter pylori protease HtrA found by ‘virtual ligand’ screening combat bacterial invasion of epithelia. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, A.M.; Reisen, F.; Schmidt, T.P.; Geppert, T.; Pillong, M.; Weisel, M.; Hoy, B.; Simister, P.C.; Feller, S.M.; Wessler, S.; et al. Inhibiting Helicobacter pylori HtrA protease by addressing a computationally predicted allosteric ligand binding site. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 3583–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, A.M.; Rodrigues, T.; Schmidt, T.P.; Bohm, M.; Stutz, K.; Reker, D.; Pfeiffer, B.; Altmann, K.H.; Backert, S.; Wessler, S.; et al. Fragment-Based De Novo Design Reveals a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Helicobacter Pylori HtrA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 10244–10248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maretzky, T.; Reiss, K.; Ludwig, A.; Buchholz, J.; Scholz, F.; Proksch, E.; de Strooper, B.; Hartmann, D.; Saftig, P. ADAM10 mediates E-cadherin shedding and regulates epithelial cell-cell adhesion, migration, and beta-catenin translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9182–9187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noe, V.; Fingleton, B.; Jacobs, K.; Crawford, H.C.; Vermeulen, S.; Steelant, W.; Bruyneel, E.; Matrisian, L.M.; Mareel, M. Release of an invasion promoter E-cadherin fragment by matrilysin and stromelysin-1. J. Cell. Sci. 2001, 114, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.M.; Borchert, G.L.; Donald, S.P.; Phang, J.M. Matrix metalloproteinase(s) mediate(s) NO-induced dissociation of beta-catenin from membrane bound E-cadherin and formation of nuclear beta-catenin/LEF-1 complex. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 2119–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marambaud, P.; Shioi, J.; Serban, G.; Georgakopoulos, A.; Sarner, S.; Nagy, V.; Baki, L.; Wen, P.; Efthimiopoulos, S.; Shao, Z.; et al. A presenilin-1/gamma-secretase cleavage releases the E-cadherin intracellular domain and regulates disassembly of adherens junctions. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weydig, C.; Starzinski-Powitz, A.; Carra, G.; Lower, J.; Wessler, S. CagA-independent disruption of adherence junction complexes involves E-cadherin shedding and implies multiple steps in Helicobacter pylori pathogenicity. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 3459–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, O.; Bozko, P.M.; Naumann, M. Helicobacter pylori suppresses glycogen synthase kinase 3beta to promote beta-catenin activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 29367–29374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, A.T.; Israel, D.A.; Washington, M.K.; Krishna, U.; Fox, J.G.; Rogers, A.B.; Neish, A.S.; Collier-Hyams, L.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; Hatakeyama, M.; et al. Activation of beta-catenin by carcinogenic Helicobacter pylori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10646–10651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, S.; Hundertmark, T.; Kuester, D.; Kalinski, T.; Peitz, U.; Roessner, A. Helicobacter pylori alters the distribution of ZO-1 and p120ctn in primary human gastric epithelial cells. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2007, 203, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurashima, Y.; Murata-Kamiya, N.; Kikuchi, K.; Higashi, H.; Azuma, T.; Kondo, S.; Hatakeyama, M. Deregulation of beta-catenin signal by Helicobacter pylori CagA requires the CagA-multimerization sequence. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata-Kamiya, N.; Kurashima, Y.; Teishikata, Y.; Yamahashi, Y.; Saito, Y.; Higashi, H.; Aburatani, H.; Akiyama, T.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Azuma, T.; et al. Helicobacter pylori CagA interacts with E-cadherin and deregulates the beta-catenin signal that promotes intestinal transdifferentiation in gastric epithelial cells. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4617–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Mimuro, H.; Suzuki, T.; Park, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Sasakawa, C. Interaction of CagA with Crk plays an important role in Helicobacter pylori-induced loss of gastric epithelial cell adhesion. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1235–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| MMP Type | Subgroup | Members |
|---|---|---|
| Soluble MMPs | Collagenases | MMP-1, -8, -13 |
| Gelatinases | MMP-2, -9 | |
| Stromelysins | MMP-3, -10, -11 | |
| Heterogeneous Group | MMP-7, -12, -26, -28 | |
| Membrane anchored MMPs | MT-MMPs | MMP-14, -15, -16, -17, -24, -25, |
| Protease | Putative Target | Inducing Factors | Involved Signalling Pathways | Cellular Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADAM-10 | E-cadherin, c-Met, Notch1 | H. pylori [39] | unknown | loss of AJ [ 47], stem-like phenotype in cancer stem cells [48] |
| ADAM-17 | proTNF-α, TGF-α, HB-EGF | CagL, IL-8, LPS H. pylori cagPAI+/− [41] | Rac1, p38, EGFR transactivation via HB-EGF | pro-inflammtory response [ 41,42], reduces apoptosis [44] |
| MMP-1 | vitronectin, fibronectin, collagen, proTNF-α, proIL-1β, proMMP-2, proMMP-9 | cagPAI, OipA, gastrin | PKC, JNK, Erk, p38 | migration through collagen matrices [ 62], activation of gelatinase-type MMPs [58] |
| MMP-8, -13 | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown |
| MMP-2, -9 | ECM, type IV collagen | MMP-9: CagA * MMP-2: unknown | MMP-9: NF-κB, Erk MMP-2: unknown | neutrophil recruitment [ 67], invasive growth, angiogenesis [32,78] |
| MMP-3 | unknown | pCagA *, IL-1 β | unknown | EMT [ 80], migration and invasion [85] |
| MMP-10 | unknown | CagA * | EGFR, Src, Erk | Invasion [ 51] |
| MMP-11 | unknown | unknown | unknown | IGF-1 production, proliferation, invasion [ 88] |
| MMP-7 | proTNF-α, HB-EGF, E-cadherin, IGFBP5 | cagPAI, gastrin | NF-κB, MEK, p120 | EMT [ 93], migration, invasion [89], IGFII release [97] |
| MMP-12 | unknown | unknown | unknown | macrophage transmigration, reduced angiogenesis [ 32] |
| Hp0169 | Type I collagen | na | unknown | Colonization of Mongolian gerbils [ 114] |
| HtrA | E-cadherin, fibronectin | na | unknown | Disruption of AJs, access to intercellular space [ 46,125] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Posselt, G.; Crabtree, J.E.; Wessler, S. Proteolysis in Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric Cancer. Toxins 2017, 9, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9040134
Posselt G, Crabtree JE, Wessler S. Proteolysis in Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric Cancer. Toxins. 2017; 9(4):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9040134
Chicago/Turabian StylePosselt, Gernot, Jean E. Crabtree, and Silja Wessler. 2017. "Proteolysis in Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric Cancer" Toxins 9, no. 4: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9040134
APA StylePosselt, G., Crabtree, J. E., & Wessler, S. (2017). Proteolysis in Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric Cancer. Toxins, 9(4), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9040134








