Characterization and Recombinant Expression of Terebrid Venom Peptide from Terebra guttata
Abstract
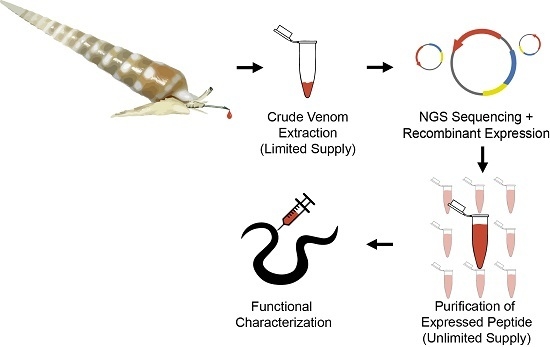
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
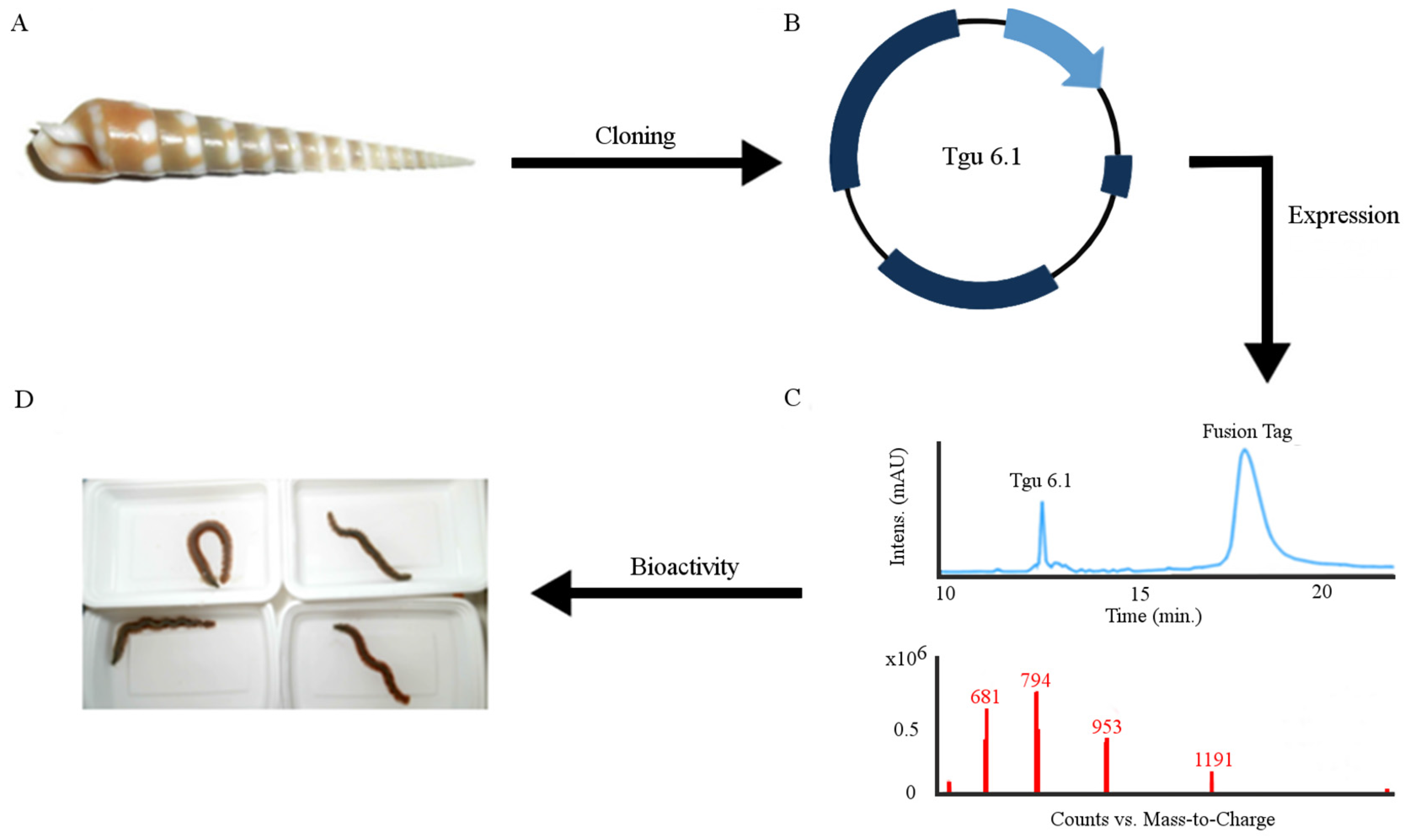
2.1. Design and Construction of Teretoxin Tgu6.1 Expression System
2.2. Expression and Purification of Tgu6.1
2.3. Polychaete Functional Assay
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Construction of Recombinant Plasmid
3.2. Induction and Expression
3.3. Protein Extraction and His-Tag Affinity Purification
3.4. Enterokinase Cleavage
3.5. RP-HPLC Purification and Mass Spectrometry
3.6. Polychaete Worm Assay
randomFrame ≤ videoStream
FUNCTION LearnPalette(randomFrame, [binSize1, binSize2, ..., binSizeN])
RETURN optimalNumberOfImageSegments, learnedPalette
ENDFUNCTION
FOR frame ≤ videoStreamStart TO videoStreamEnd
FUNCTION FindCountoursWithPalette(frame, learnedPalette)
IF foundCountours > optimalNumberOfImageSegments THEN
newOptimalNumberOfImageSegments, newPalette = LearnPalette(frame, [binSize1, binSize2, ..., binSizeN])
newContours = FindContoursWithPalette(frame, newPalette)
RETURN newContours
ELSE
RETURN foundContours
ENDIF
ENDFUNCTION
FUNCTION GetWormCountours(foundCountours)
wormContours = SizeAndBoundingBoxFilter(foundContours)
RETURN wormContours
ENDFUNCTION
FUNCTION GetMassWeightedCentroids(wormContours)
RETURN wormCentroids
ENDFUNCTION
ENDFOR
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, G.F. Venoms as a platform for human drugs: Translating toxins into therapeutics. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wüster, W.; Vonk, F.J.; Harrison, R.A.; Fry, B.G. Complex cocktails: The evolutionary novelty of venoms. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modica, M.; Holford, M. The Neogastropoda: Evolutionary Innovations of Predatory Marine Snails with Remarkable Pharmacological Potential. In Evolutionary Biology–Concepts, Molecular and Morphological Evolution; Pontarotti, P., Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 249–270. [Google Scholar]
- Terryn, Y.; Holford, M. The Terebridae of the Vanuatu Archipelago with a Revision of the Genus Granuliterebra Oyama 1961, 3rd ed.; ConchBook: Hackenheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Terryn, Y. A Collectors Guide to Recent Terebridae (Mollusca: Neogastropoda); ConchBooks & NaturalArt: Hackenheim, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Puillandre, N.; Kantor, Y.I.; Sysoev, A.; Couloux, C.; Meyer, C.; Rawlings, T.; Todd, J.A.; Bouchet, P. The dragon tamed? A molecular phylogeny of the Conoidea (Gastropoda). J. Mollus. Stud. 2011, 77, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperial, J.S.; Kantor, Y.; Watkins, M.; Heralde, F.M., III; Stevenson, B.; Chen, P.; Hansson, K.; Stenflo, J.; Ownby, J.; Bouchet, P.; et al. Venomous auger snail Hastula (Impages) hectica (Linnaeus, 1758): Molecular phylogeny, foregut anatomy and comparative toxinology. J. Exp. Zool. 2007, 756, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puillandre, N.; Holford, M. The Terebridae and teretoxins: Combining phylogeny and anatomy for concerted discovery of bioactive compounds. BMC Chem. Biol. 2010, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, P.; Grigoryan, A.; Bhuiyan, M.H.; Ueberheide, B.; Russell, V.; Quinoñez, J.; Moy, P.; Chait, B.T.; Poget, S.F.; Holford, M. Sample limited characterization of a novel disulfide-rich venom peptide toxin from terebrid marine snail Terebra variegata. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terlau, H.; Olivera, B.M. Conus venoms: A rich source of novel ion channel-targeted peptides. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, R.S.; Olivera, B.M. Conotoxins down under. Toxicon 2006, 48, 780–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, R.A.; Cruz, L.J.; Rivier, J.; Olivera, B.M. Conus peptides as chemical probes for receptors and ion channels. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1923–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holford, M.; Zhang, M.M.; Gowd, K.H.; Azam, L.; Green, B.R.; Watkins, M.; Ownby, J.P.; Bulaj, G.; Olivera, B.M. Pruning nature: Biodiversity-derived discovery of novel sodium channel blocking conotoxins from Conus bullatus. Toxicon 2009, 53, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.; Terlau, H. Toxins from cone snails: Properties, applications and biotechnological production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essack, M.; Bajic, V.B.; Archer, J.A.C. Conotoxins that confer therapeutic possibilities. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1244–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.J.; Jensen, J.; Nevin, S.T.; Callaghan, B.P.; Adams, D.J.; Craik, D.J. The engineering of an orally active conotoxin for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6545–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelin, M.; Puillandre, N.; Kantor, Y.I.; Modica, M.V.; Terryn, Y.; Cruaud, C.; Bouchet, P.; Holford, M. Macroevolution of venom apparatus innovations in auger snails (Gastropoda; Conoidea; Terebridae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 64, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendel, Y.; Melaun, C.; Kurz, A.; Nicke, A.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J.; Wunder, C.; Mebs, D.; Kauferstein, S. Venomous secretions from marine snails of the Terebridae family target acetylcholine receptors. Toxins 2013, 5, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperial, J.S.; Watkins, M.; Chen, P.; Hillyard, D.R.; Cruz, L.J.; Olivera, B.M. The augertoxins: Biochemical characterization of venom components from the toxoglossate gastropod Terebra subulata. Toxicon 2003, 42, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorson, J.; Ramrattan, G.; Verdes, A.; Wright, M.; Kantor, Y.I.; Srinivasan, R.; Musunuri, R.; Packer, D.; Albano, G.; Qiu, W.; et al. Molecular diversity and gene evolution of the venom arsenal of terebridae predatory marine snails. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 1761–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheneval, O.; Schroeder, C.I.; Durek, T.; Walsh, P.; Huang, Y.H.; Liras, S.; Price, D.A.; Craik, D.J. Fmoc-based synthesis of disulfide-rich cyclic peptides. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 5538–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, A.M.; Bulaj, G. Optimization of oxidative folding methods for cysteine-rich peptides: A study of conotoxins containing three disulfide bridges. J. Pept. Sci. 2011, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klint, J.K.; Senff, S.; Saez, N.J.; Seshadri, R.; Lau, H.Y.; Bende, N.S.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Rash, L.D.; Mobli, M.; King, G.F. Production of recombinant disulfide-rich venom peptides for structural and functional analysis via expression in the periplasm of E. coli. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, P.; Zhang, R.Y.; Menon, V.; Bingham, J.-P. Native chemical ligation: A boon to peptide chemistry. Molecules 2014, 19, 14461–14483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holford, M.; Muir, T.W. Adding “splice” to protein engineering. Structure 1998, 6, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, P.E.; Muir, T.W.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Kent, S.B. Synthesis of proteins by native chemical ligation. Science 1994, 266, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craik, D.J. Microwave-assisted Boc-solid phase peptide synthesis of cyclic cysteine-rich peptides. J. Pept. Sci. 2008, 14, 683–689. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, S.B.H. The critical role of peptide chemistry in the life sciences. J. Pept. Sci. 2015, 21, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Qiu, J.; Ma, F.; Wang, K.; Zheng, S. A fusion protein of conotoxin MVIIA and thioredoxin expressed in Escherichia coli has significant analgesic activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 311, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braud, S.; Belin, P.; Dassa, J.; Pardo, L.; Mourier, G.; Caruana, A.; Priest, B.T.; Dulski, P.; Garcia, M.L.; Ménez, A.; et al. BgK, a disulfide-containing sea anemone toxin blocking K+ channels, can be produced in Escherichia coli cytoplasm as a functional tagged protein. Protein Expr. Purif. 2004, 38, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.S.; Ramasamy, P.; Sikdar, S.K.; Sarma, S.P. Overexpression, purification, and pharmacological activity of a biosynthetically derived conopeptide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 335, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayrhuber, M.; Graf, R.; Ferber, M.; Zweckstetter, M.; Imperial, J.; Garrett, J.E.; Olivera, B.M.; Terlau, H.; Becker, S. Production of recombinant Conkunitzin-S1 in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 47, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Tang, S.; Pi, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Zhou, W.; Xu, A. Discovery of a novel class of conotoxin from Conus litteratus, lt14a, with a unique cysteine pattern. Peptides 2006, 27, 2174–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, C.A.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; Cao, X.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Han, B.; Jing, X.; Sam, L.; Barrette, T.; Palanisamy, N.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Transcriptome sequencing to detect gene fusions in cancer. Nature 2009, 458, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiezia, M.C.; Chiarabelli, C.; Polticelli, F. Recombinant expression and insecticidal properties of a Conus ventricosus conotoxin-GST fusion protein. Toxicon 2012, 60, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Cuebas, L.M.; White, M.M. Expression of a biologically-active conotoxin PrIIIE in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2012, 82, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Zhangsun, D.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sheng, L.; Fang, L.; Wu, X.; Yu, J.; Luo, S. Expression and secretion of functional recombinant μO-conotoxin MrVIB-His-tag in Escherichia coli. Toxicon 2013, 72, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sermadiras, I.; Revell, J.; Linley, J.E.; Sandercock, A.; Ravn, P. Recombinant expression and in vitro characterisation of active Huwentoxin-IV. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, S.; You, Y.; Ren, Z.; Xu, A. Soluble expression, purification and functional identification of the framework XV conotoxins derived from different Conus species. Peptides 2014, 56, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaas, Q.; Westermann, J.C.; Halai, R.; Wang, C.K.; Craik, D.J. Conoserver, a database for conopeptide sequences and structures. Bioinformatics 2008, 3, 445–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaas, Q.; Yu, R.; Jin, A.H.; Dutertre, S.; Craik, D.J. Conoserver: updated content, knowledge, and discovery tools in the conopeptide database. Nucleic Acids Research 2012, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, R.B.; McDougal, O.M. The M-superfamily of conotoxins: A review. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.D.; Norton, R.S. Conotoxin gene superfamilies. Marine Drugs 2014, 12, 6058–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, R.A. The Genomic Structure of Delta Conotoxins and Other O-Superfamily Conotoxins. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, B.; Ferrari, D.M.; Klappa, P.; Pohlmann, N.; Soling, H.D. Functional roles and efficiencies of the thioredoxin boxes of calcium-binding proteins 1 and 2 in protein folding. Biochem. J. 2001, 357, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bals, C.; Schambach, A.; Meyer, J.; Scheper, T.; Rinas, U. Expression and purification of bioactive soluble murine stem cell factor from recombinant Escherichia coli using thioredoxin as fusion partner. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 152, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Su, Y.; Wang, S.; Shen, M.; Chen, F.; Chen, M.; Ran, X.; Cheng, T.; Wang, J. High efficiency preparation of bioactive human alpha-defensin 6 in Escherichia coli Origami(DE3)pLysS by soluble fusion expression. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, E.J.; Aslund, F.; Beckwith, J. Disulfide bond formation in the Escherichia coli cytoplasm: An in vivo role reversal for the thioredoxins. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5543–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, A. Strategies for successful recombinant expression of disulfide bond-dependent proteins in Escherichia coli. Microb. Cell Fact. 2009, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahravan, S.H.; Qu, X.; Chan, I.-S.; Shin, J.A. Enhancing the specificity of the enterokinase cleavage reaction to promote efficient cleavage of a fusion tag. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 59, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, N.C.; Wong, M.H.; Shiu, K.K.; Qiu, J.W. Dependency of copper toxicity to polychaete larvae on algal concentration. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 77, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MS-Product tool. Available online: http://prospector.ucsf.edu/prospector/mshome.htm (accessed on 6 November 2013).
| Organism | Peptide Features | N-terminal Fusion Tag | Purification Method | Soluble/Insoluble | E. coli Host | Fusion Tag Cleavage | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVIIA (Conus magus) | 25 aa and 3 disulfide | Thioredoxin | His tag | Soluble | BL21 (DE3) | No cleavage | Zhan et al., 2003 [29] |
| BgK (Bunodosoma granulifera) | 37 aa and 3 disulfide | S-tag (C-terminal) | S-protein | Soluble | OrigamiB (DE3) Tuner (DE3) | No cleavage | Braud et al., 2004 [30] |
| Mo1659 (Conus monile) | 13 aa and no cysteine | Cytochrome-b5 | His tag | Soluble | Bl21 (DE3) | CnBr | Kumar et al., 2005 [31] |
| Conkunitzin-S1 (Conus striatus) | 60 aa and 2 disulfide | Chitin binding domain | His tag | Insoluble | BL21 (DE3) | Intein | Bayrhuber et al., 2006 [32] |
| Lt7a (Conus litteratus) | 27 aa and 3 disulfide | Thioredoxin | His tag | Soluble | BL21 (DE3) | Factor Xa | Pi et al., 2006 [33] |
| BTK-2 (Mesobuthus tamulus) | 32 aa and 3 disulfide | Cytochrome-b5 | His tag | Soluble | BL21 (DE3) | Tev protease | Kumar et al., 2009 [34] |
| Vn2 (Conus ventricosus) | 33 aa and 3 disulfide | Glutathione-S-transferase | His tag | Soluble | BL21 (DE3) | No cleavage | Spiezia et al., 2012 [35] |
| PrIIIE (Conus parius) | 22 aa and 3 disulfide | Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) | His tag | Soluble | Rosetta-gami B (DE3) | SUMO protease | Hernandez et al., 2012 [36] |
| MrVIB (Conus marmoreus) | 31 aa and 3 disulfide | Pe1B leader signal peptide | His tag | Soluble | BL21 (DE3) | No His tag cleavage | Gao et al., 2013 [37] |
| Huwenotoxin-IV (Ornithoctunus huwena) | 35 aa and 3 disulfide | SUMO | His tag | Soluble | Shuffle T7 Express | SUMO protease | Sermadiras et al., 2013 [38] |
| spider, sea anemone, scorpion, cone snail, centipede | Varied length disulfide-rich peptides | Various | various | Soluble | BL21 (DE3) | various | Klint et al., 2013 [23] |
| Framework XV conotoxins (various species) | Varied length and 4 disulfide | Thioredoxin | His tag | Soluble | BL21 (DE3) | Enterokinase | Wu et al., 2014 [39] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, J.; Gorson, J.; Wright, M.E.; Yee, L.; Khawaja, S.; Shin, H.Y.; Karma, Y.; Musunri, R.L.; Yun, M.; Holford, M. Characterization and Recombinant Expression of Terebrid Venom Peptide from Terebra guttata. Toxins 2016, 8, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030063
Moon J, Gorson J, Wright ME, Yee L, Khawaja S, Shin HY, Karma Y, Musunri RL, Yun M, Holford M. Characterization and Recombinant Expression of Terebrid Venom Peptide from Terebra guttata. Toxins. 2016; 8(3):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030063
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, John, Juliette Gorson, Mary Elizabeth Wright, Laurel Yee, Samer Khawaja, Hye Young Shin, Yasmine Karma, Rajeeva Lochan Musunri, Michelle Yun, and Mande Holford. 2016. "Characterization and Recombinant Expression of Terebrid Venom Peptide from Terebra guttata" Toxins 8, no. 3: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030063
APA StyleMoon, J., Gorson, J., Wright, M. E., Yee, L., Khawaja, S., Shin, H. Y., Karma, Y., Musunri, R. L., Yun, M., & Holford, M. (2016). Characterization and Recombinant Expression of Terebrid Venom Peptide from Terebra guttata. Toxins, 8(3), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030063