Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus on Farms with Small Scale Production of Raw Milk Cheeses in Poland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
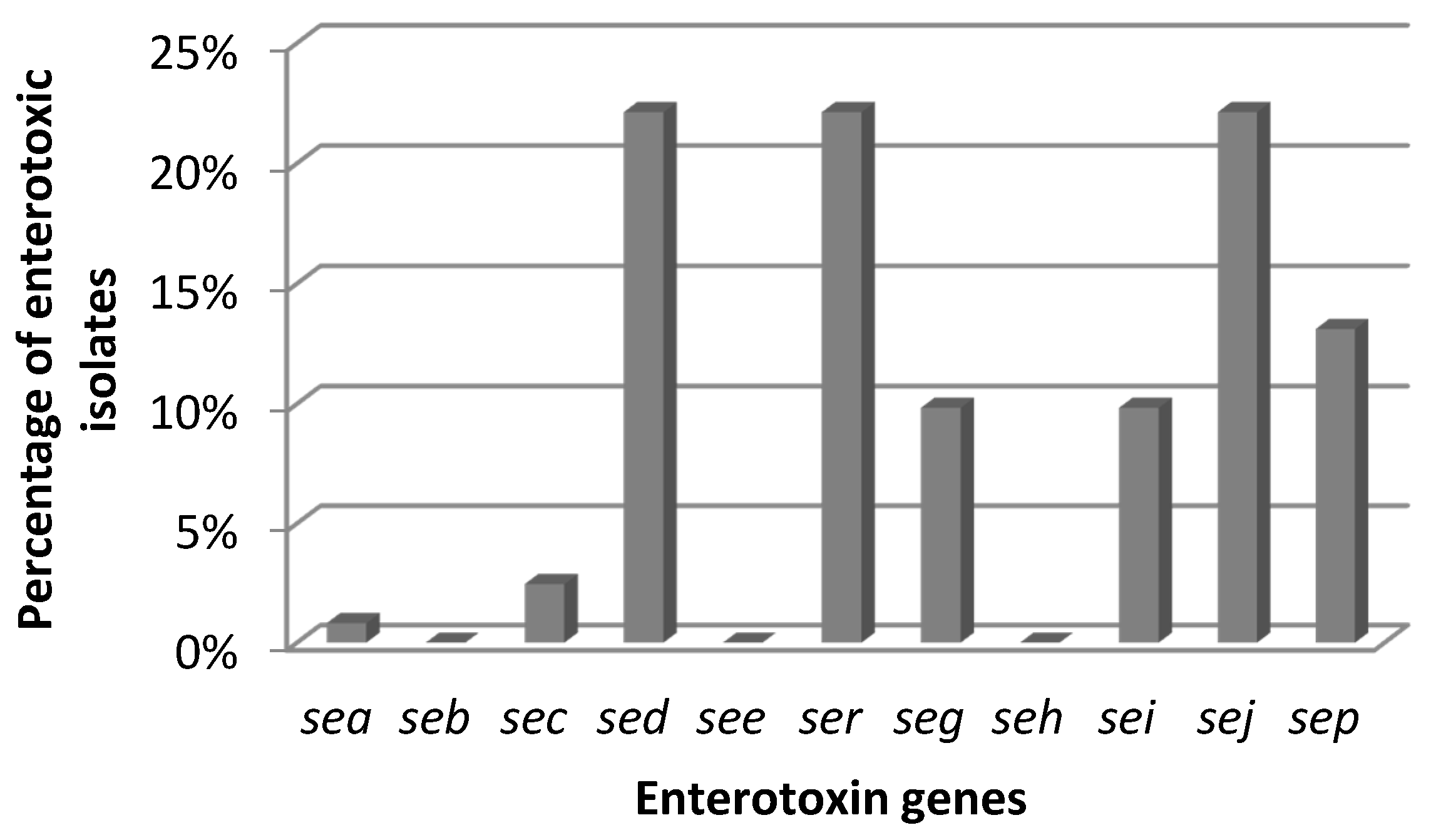
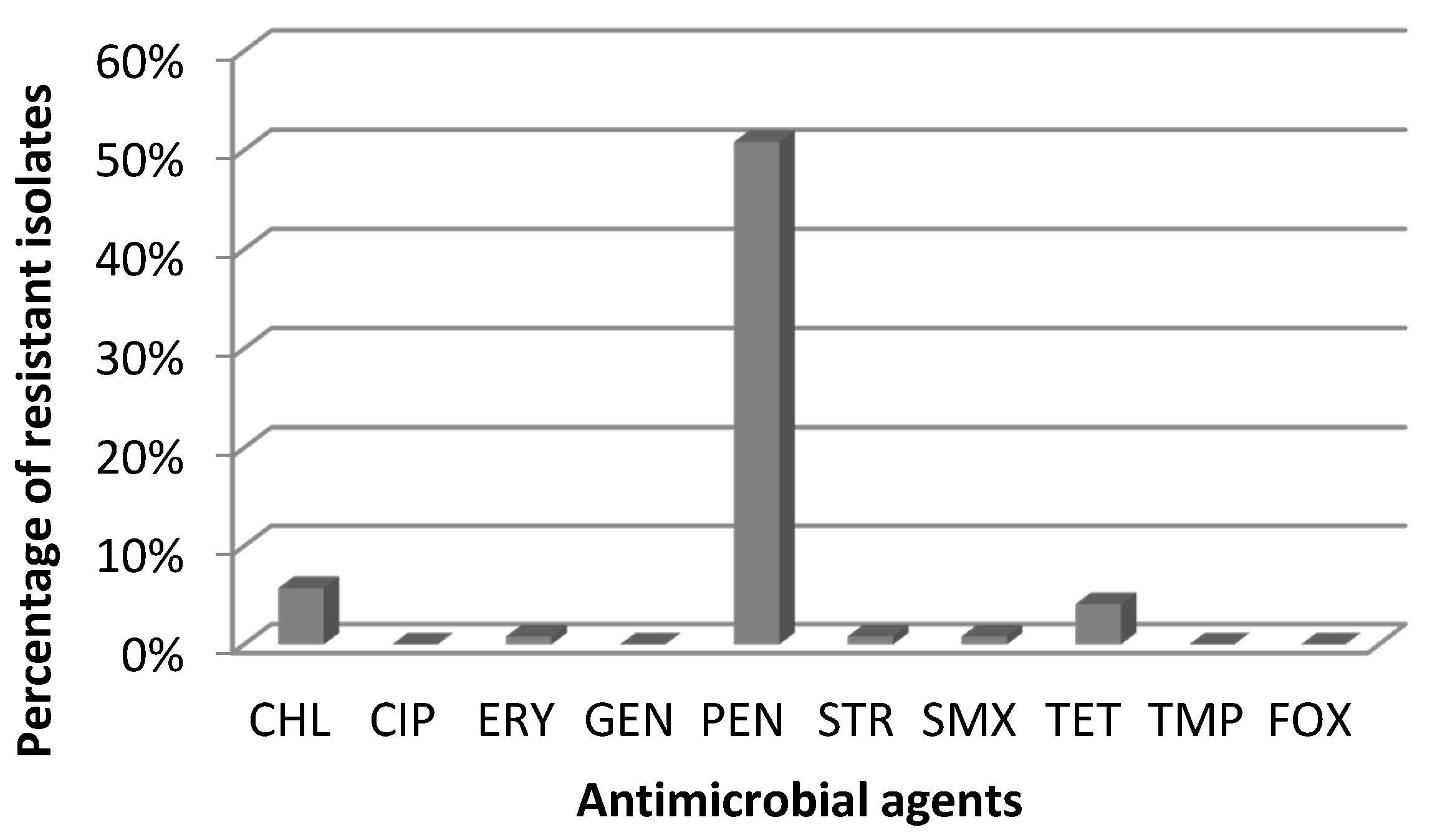
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Enumeration of CPS
4.3. Identification of S. aureus
4.4. Detection of Staphylococcal Enterotoxins Genes
4.5. Detection of Staphylococcal Enterotoxins A-E
4.6. Antimicrobial Resistance
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Argudin, M.A.; Mendoza, M.C.; Rodicio, M.R. Food poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 1751–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennekinne, J.A.; de Buyser, M.L.; Dragacci, S. Staphylococcus aureus and its food poisoning toxins: Characterization and outbreak investigation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Loir, Y.; Baron, F.; Gautier, M. Staphylococcus aureus and food poisoning. Genet. Mol. Res. 2003, 2, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Waage, S.; Mørk, T.; Røros, A.; Aasland, D.; Hunshamar, A.; Odegaard, S.A. Bacteria associated with clinical mastitis in dairy heifers. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuvier, E.; Buchin, S. Raw milk cheeses. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology; Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Cogan, T.M., Guinee, T.P., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 319–345. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.G.; Withers, S.E. Microbiological characterisation of artisanal farm house cheeses manufactured in Scotland. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2010, 63, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Buyser, M.L.; Dufour, B.; Maire, M.; Lafarge, V. Implication of milk and milk products in food-borne diseases in France and in different industrialised countries. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, M.C.D.P.B.; Campos, M.R.H.; Borges, L.J.; Kipnis, A.; Pimenta, F.C.; Serafini, A.B. Comparison of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from food handlers, raw bovine milk and Minas Frescal cheese by antibiogram and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis following Smal digestion. Food Control. 2008, 19, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normanno, G.; Corrente, M.; La Salandra, G.; Dambrosio, A.; Quaglia, N.C.; Parisi, A.; Greco, G.; Ballacicco, A.L.; Virgilio, S.; Celano, G.V. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in foods of animal origin product in Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loncarevic, S.; Jørgensen, H.J.; Løvseth, A.; Mathisen, T.; Rørvik, L.M. Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin types within single samples of raw milk and raw milk products. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinchuk, I.V.; Beswick, E.J.; Reyes, V.E. Staphylococcal enterotoxins . Toxins 2010, 2, 2177–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EC—European Commission. Opinion on Staphylococcal Enterotoxins in milk products, particularly cheeses (adopted on 26–27 March 2003). 2003. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/food/fs/sc/scv/out61_en.pdf (accessed on 26–27 March 2003).
- EFSA and ECDC (European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2013. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3991. [Google Scholar]
- Rola, J.G.; Korpysa-Dzirba, W.; Osek, J. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcal enterotoxins at different stages of production of raw milk cheeses—Preliminary results. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy. 2013, 57, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, D.M.; Gallina, S.; Bellio, A.; Chiesa, F.; Civera, T.; Decastelli, L. Enterotoxin gene profiles of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from milk and dairy products in Italy. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 58, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, B.; Smythe, B.; Lindsay, D.; Shepherd, J. Microbiology of raw milk in New Zealand. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, K.; Schelin, J.; Radström, P.; Butler, F.; Jordan, K. Classical enterotoxins of coagulase-positive Staphylococcus aureus isolates from raw milk and products for raw milk cheese production in Ireland. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2012, 92, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, R.A.; Heggebo, R.; Sunde, E.B.; Skjervheim, M. Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes in Norwegian raw milk cheese production. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, H.J.; Mork, T.; Hogasen, H.R.; Rorvik, L.M. Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in bulk milk in Norway. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peles, F.; Wagner, M.; Varga, L.; Hein, I.; Rieck, P.; Gutser, K.; Kereszturi, P.; Kardos, G.; Turcsanyi, I.; Beri, B.; et al. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from bovine milk in Hungary. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 118, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tondo, E.C.; Guimaraes, M.C.; Henriques, J.A.; Ayub, M.A. Assessing and analysing contamination of a dairy products processing plant by Staphylococcus aureus using antibiotic resistance and PFGE. Can. J. Microbiol. 2000, 46, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callon, C.; Gilbert, F.B.; Cremoux, R.D.; Montel, M.C. Application of variable number of tandem repeat analysis to determine the origin of S. aureus contamination from milk to cheese in goat cheese farms. Food Control. 2008, 19, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asperger, H.; Zangerl, P. Staphylococcus aureus . In Encyclopaedia of Dairy Sciences; Roginski, H., Fuquay, J.W., Fox, P.F., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 2563–2569. [Google Scholar]
- Tatini, S.R.; Jezeski, J.J.; Morris, H.A.; Olson, J.C., Jr.; Casman, E.P. Production of staphylococcal enterotoxin A in cheddar and Colby cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 1971, 54, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Marc, Y.; Valík, L.; Medveďová, A. Modelling the effect of the starter culture on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus in milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 129, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrynowicz-Paciorek, M.; Kochman, M.; Piekarska, K.; Grochowska, A.; Windyga, B. The distribution of enterotoxin and enterotoxin-like genes in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from nasal carriers and food samples. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Iandolo, J.J.; Stewart, G.C. The enterotoxin D plasmid of Staphylococcus aureus encodes a second enterotoxin determinant (sej). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 168, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummerjohann, J.; Naskova, J.; Baumgartner, A.; Graber, H.U. Enterotoxin-producing Staphylococcus aureus genotype B as a major contaminant in Swiss raw milk cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremonesi, P.; Perez, G.; Pisoni, G.; Moroni, P.; Morandi, S.; Luzzana, M.; Brasca, M.; Castiglioni, B. Detection of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus isolates in raw milk cheese. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandi, S.; Brasca, M.; Lodi, R.; Cremonesi, P.; Castiglioni, B. Detection of classical enterotoxins and identification of enterotoxin genes in Staphylococcus aureus from milk and dairy products. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 124, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuda, K.; Hata, E.; Kobayashi, H.; Kohmoto, M.; Kawashima, K.; Tsunemitsu, H.; Eguchi, M. Molecular typing of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitic milk on the basis of toxin genes and coagulase gene polymorphisms. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 105, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villard, L.; Lamprell, H.; Borges, E.; Maurin, F.; Noel, Y.; Beuvier, E.; Chamba, J.F.; Kodjo, A. Enterotoxin D producing strains of Staphylococcus aureus are typeable by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Food Microbiol. 2005, 22, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kav, K.; Col, R.; Ardic, M. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from white-brined Urfa cheese. J. Food Prot. 2011, 74, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werckenthin, C.; Cardoso, M.; Martel, J.L.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial resistance in staphylococci from animals with particular reference to bovine Staphylococcus aureus and porcine Staphylococcus hyicus and canine Staphylococcus intermedius. Vet. Res. 2001, 32, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasucka, D.; Cybulski, W.; Klimowicz, A.; Dzierżawski, A. Evaluation of antimicrobial agents consumption in swine and cattle in Poland based on a questionnaire in 2010. Medycyna. Wet. 2012, 68, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency, European Surveillance of Veterinary Antimicrobial Consumption. Sales of veterinary antimicrobial agents in 26 EU/EEA countries in 2012. (EMA/333921/2014). Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Report/2014/10/WC500175671.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2014).
- Berendsen, B.; Stolker, L.; de Jong, J.; Nielsen, M.; Ttserendorj, E.; Sodnomdarjaa, R.; Cannavan, A.; Elliott, C. Evidence of natural occurrence of the banned antibiotic chloramfenicol in herbs and grass. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 6888–2, 1999. In Microbiology of Food Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci (Staphylococcus Aureus and Other Species). Part 2: Technique Using Rabbit Plasma Fibrynogen Agar Medium; International Standard Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999; pp. 1–7.
- Anonymous. Multiplex PCR for the detection of mecA gene and identification of Staphylococcus aureus. Available online: http//www.crl-ar.eu/data/images/tc_april-2009/6-detailed%20meca-pcr_protocol.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2009).
- De Buyser, M.L.; Grout, J.; Brisabois, A.; Assere, A.; Lombard, B. Detection of Genes Encoding Staphylococcal Enterotoxins. Multiplex PCR for Sea to See and Ser. Method of the CRL for Coagulase Positive Staphylococci Including Staphylococcus aureus, 1st ed.; CRL CPS; AFSSA: Maisons-Alfort, France, 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- De Buyser, M.L.; Grout, J.; Brisabois, A.; Assere, A.; Lombard, B. Detection of Genes Encoding Staphylococcal Enterotoxins. Multiplex PCR for Seg to Sej and Sep. Method of the CRL for Coagulase Positive Staphylococci Including Staphylococcus aureus, 1st ed.; CRL CPS; AFSSA: Maisons-Alfort, France, 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ostyn, A.; Prufer, A.L.; Papinaud, J.; Hennekinne, J.-A.; Assere, A.; Lombard, B. Detection of Staphylococcal Enteritoxins Types SEA to SEE in All Types of Food Matrices. European Screening Method of the EU-RL for “Coagulase Positive Staphylococci Including Staphylococcus aureus”, 5th ed.; EU-RL CPS; ANSES: Maisons-Alfort, France, 2010; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
| Collected Material | Source | No. of Samples | No. (%) of CPS Positive Samples | Ranges of CPS at Different Production Stages | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farm No. | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||||
| Swab | Log10 CFU/swab or CFU/cm2 | |||||||||||
| Hands of cheese maker | 26 | 11 (42.3) | 0 | 0 | 0–4.34 | 0 | 0–3.23 | 0–2.72 | 0–2.70 | 0–3.81 | 0–3.12 | |
| Milk tank | 26 | 7 (26.9) | 0 | 0 | 0.24–1.70 | 0 | 0–0.18 | 0 | 0–0.30 | 0–0.81 | 0–0.30 | |
| Strainer/sacks | 26 | 3 (11.5) | 0 | 0 | 0–2.83 | 0 | 0 | 0–2.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Cheese mould | 24 | 4 (16.7) | 0–1.40 | 0 | 0–2.54 | 0 | 0–2.10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0–2.00 | |
| Sample | Log10 CFU mL−1 or CFU g−1 | |||||||||||
| Raw milk | 26 | 12 (46.2) | 0 | 0 | 0–3.63 | 0–1.18 | 0–4.74 | 0–2.63 | 0 | 0–5.00 | 1.08–3.04 | |
| Milk after heat treatment | 12 | 8 (66.7) | 0–1.70 | 0–0.18 | 0.70–1.48 | 1.18 | 2.36 | 1.73 | 0 | 0 | 3.90 | |
| Curd | 27 | 19 (70.4) | <1–2.64 | 2.18–2.53 | <1–4.77 | <1–1.60 | <1–4.65 | 2.89–4.89 | <1–3.83 | <1–5.83 | 1–4.26 | |
| Grains after rinsing | 25 | 19 (76.0) | <1–3.36 | <1–2.57 | 2.61–5.92 | 1.30–2.04 | 1.74–5.15 | 4.08–5.32 | <1–4.74 | <1 | 3.28–5.00 | |
| Formed cheese | 26 | 21 (80.8) | <1–3.95 | <1–2.40 | 3.23–5.08 | 1–2.46 | 1.30–6.04 | 4.53–5.63 | <1–4.74 | <1–5.60 | 3.62–5.59 | |
| Mature cheese | 26 | 18 (69.2) | 2.60–3.82 | <1–5.53 | 1–3.08 | <1 | <1–4.91 | <1–5.74 | 2.83–6.58 | <1–7.41 | 4.81–7.11 | |
| Total | 244 | 122 (50.0) | ||||||||||
| Antimicrobial Class | Antimicrobials | Dilution Range (mg/L) | Cut off Values (mg/L) Resistant > |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amphenicols | Chloramphenicol (CHL) | 2–64 | 16 |
| Fluoroqinolones | Ciprofloxacin (CIP) | 0.12–8 | 1 |
| Macrolides | Erythromycin (ERY) | 0.25–16 | 1 |
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin (GEN) | 0.25–16 | 2 |
| Streptomycin (STR) | 4–64 | 16 | |
| β-Lactames | Penicillin (PEN) | 0.06–16 | 0.125 |
| Cephalosporins | Cefoxitin (FOX) | 0.5–32 | 4 |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline (TET) | 0.5–32 | 1 |
| Sulfonamides | Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) | 32–512 | 128 |
| Other | Trimethoprim (TMP) | 0.5–32 | 4 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rola, J.G.; Czubkowska, A.; Korpysa-Dzirba, W.; Osek, J. Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus on Farms with Small Scale Production of Raw Milk Cheeses in Poland. Toxins 2016, 8, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030062
Rola JG, Czubkowska A, Korpysa-Dzirba W, Osek J. Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus on Farms with Small Scale Production of Raw Milk Cheeses in Poland. Toxins. 2016; 8(3):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030062
Chicago/Turabian StyleRola, Jolanta G., Anna Czubkowska, Weronika Korpysa-Dzirba, and Jacek Osek. 2016. "Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus on Farms with Small Scale Production of Raw Milk Cheeses in Poland" Toxins 8, no. 3: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030062
APA StyleRola, J. G., Czubkowska, A., Korpysa-Dzirba, W., & Osek, J. (2016). Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus on Farms with Small Scale Production of Raw Milk Cheeses in Poland. Toxins, 8(3), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030062