Dehydropyrrolizidine Alkaloid Toxicity, Cytotoxicity, and Carcinogenicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Toxicity, Cytotoxicity, and Carcinogenicity
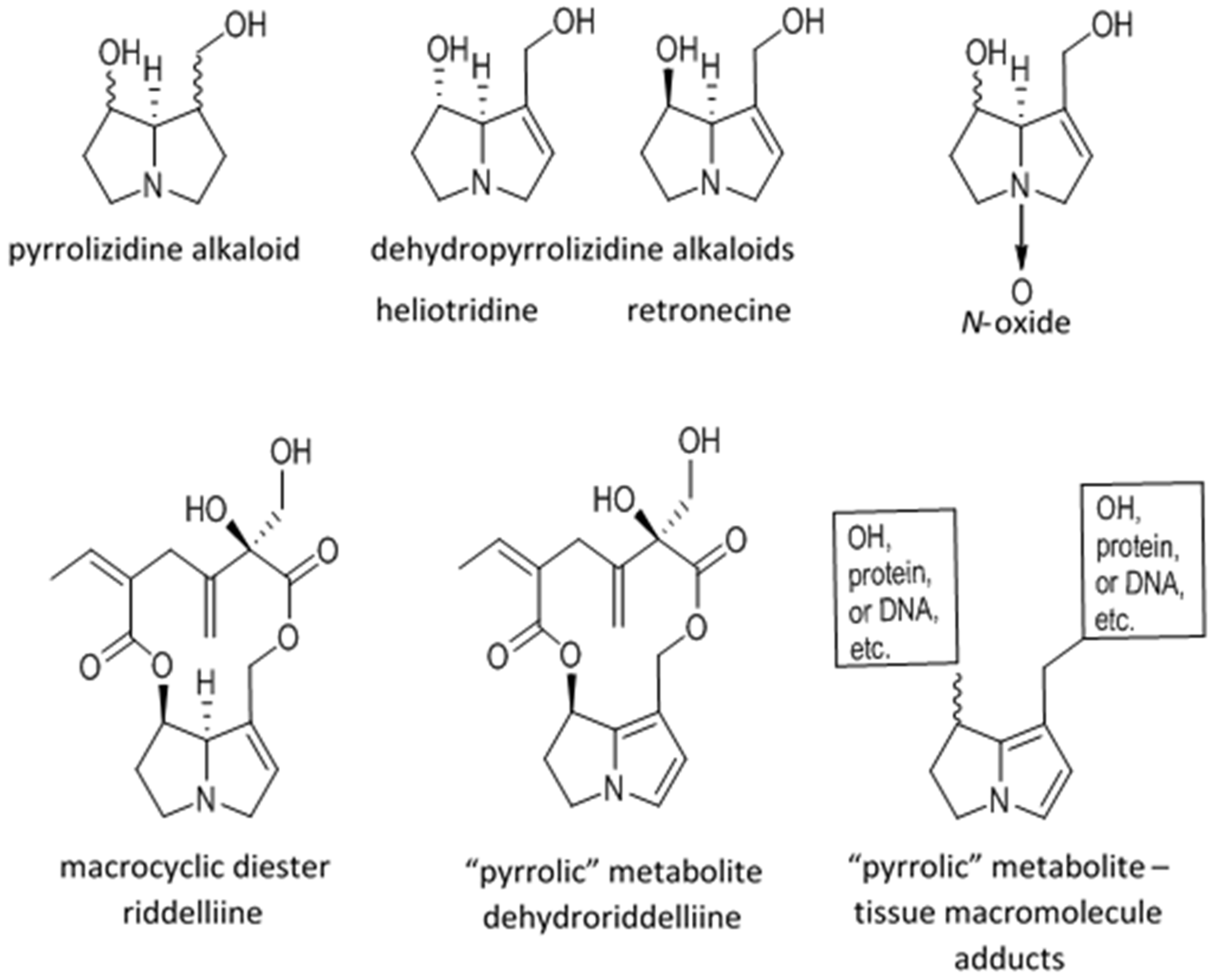
2.1. Metabolic Activation and Sequelae
2.2. Conditions of Poisonings
2.3. Toxicokinetics
2.4. Clinical, Pathological, and Histological Signs of Poisoning
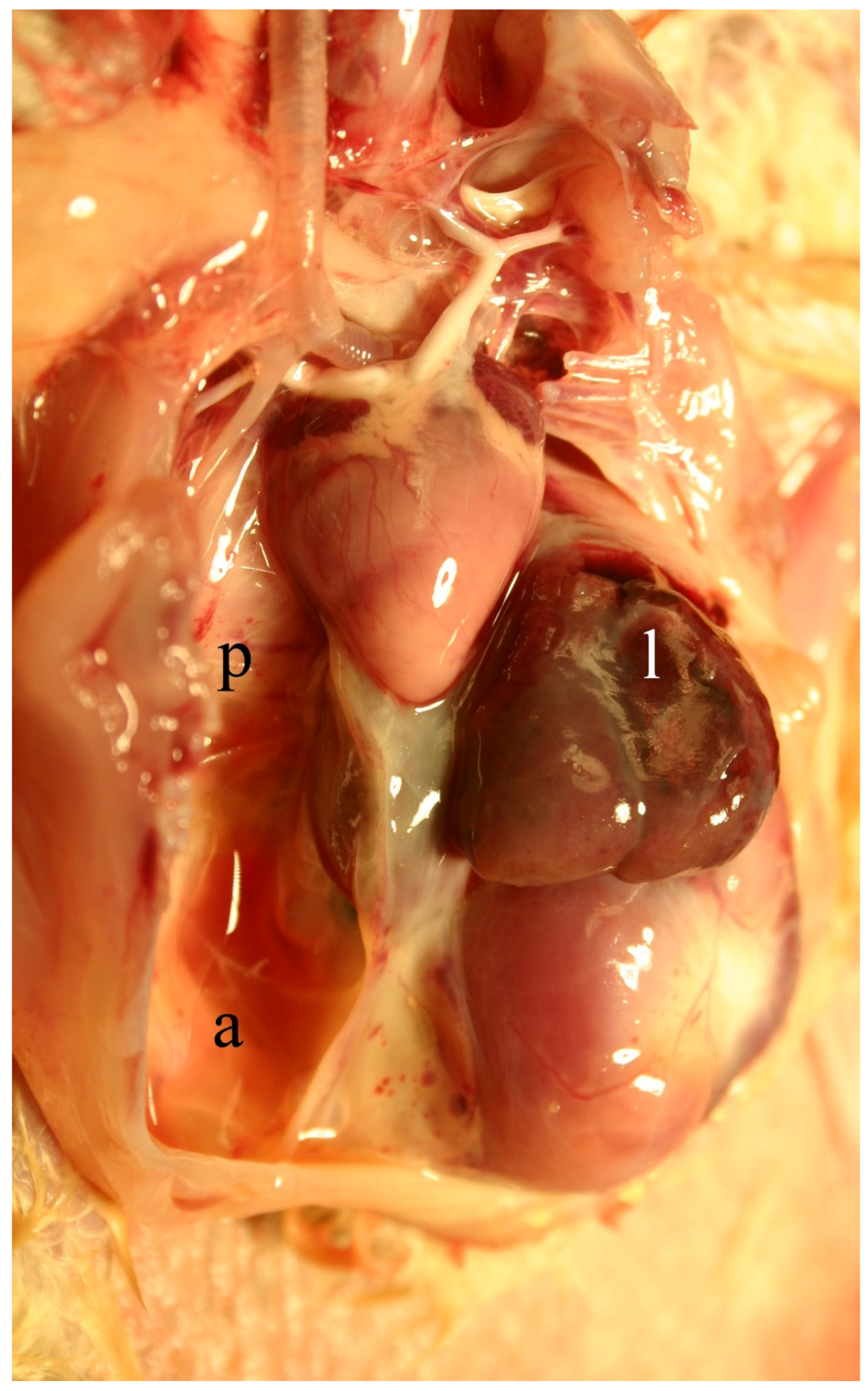
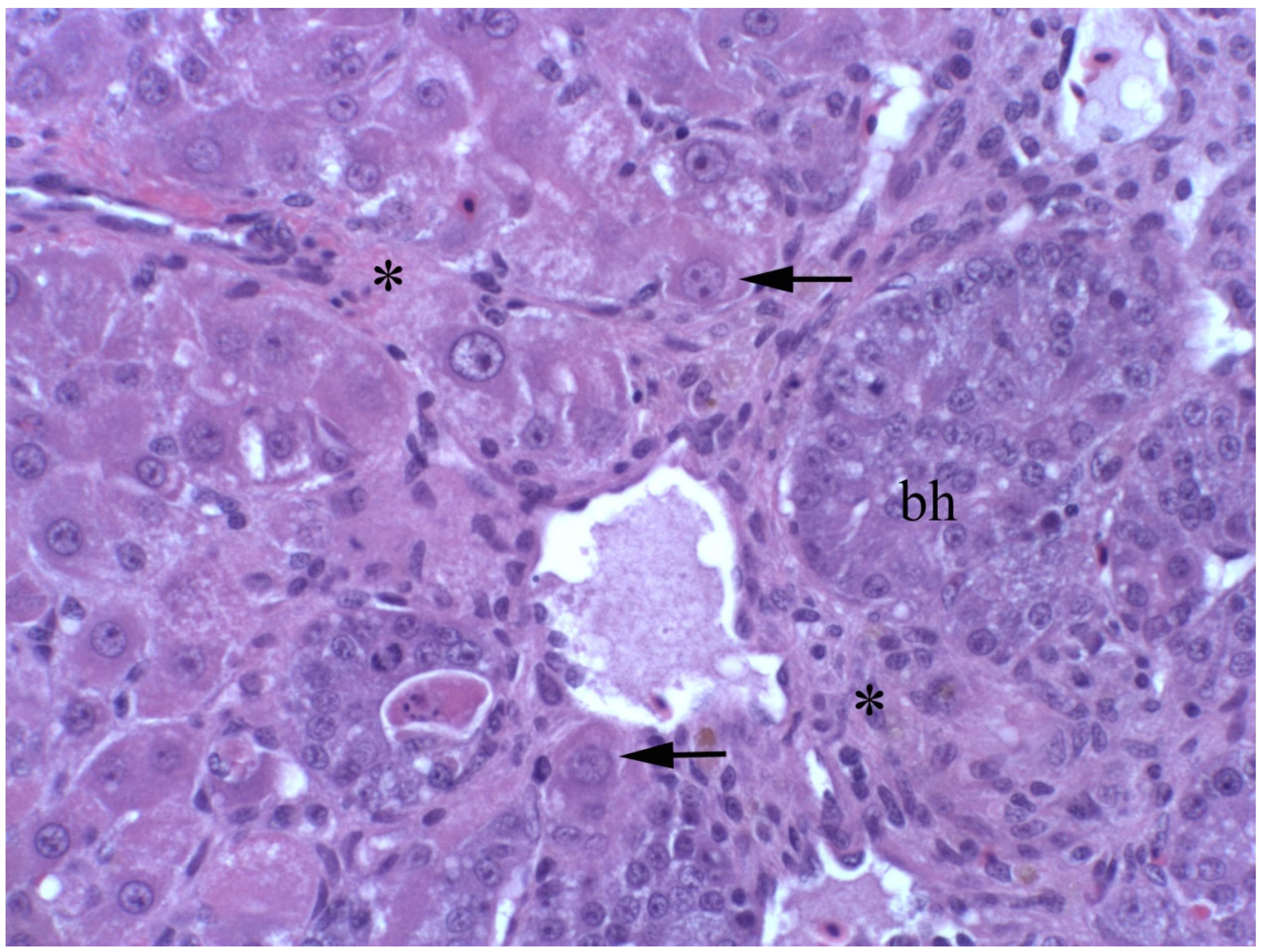
2.4.1. Livestock
2.4.2. Humans
2.5. Diagnosis
2.6. Assessment of Safe Levels
2.6.1. Chicken Hepatocarcinoma Cytotoxicity
2.6.2. Primary Hepatocyte Cultures
2.6.3. In Vivo Chick Bioassay
2.6.4. Heterozygous p53 Knockout Mouse
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattocks, A.R. Chemistry and Toxicology of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1986; pp. 1–390. [Google Scholar]
- Stegelmeier, B.L.; Edgar, J.A.; Colegate, S.M.; Gardner, D.R.; Schoch, T.K.; Coulombe, R.A.; Molyneux, R.J. Pyrrolizidine alkaloid plants, metabolism and toxicity. J. Nat. Toxins 1999, 8, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mattocks, A. Hepatotoxic effects due to pyrrolizidine alkaloid N-oxides. Xenobiotica 1971, 1, 583–585. [Google Scholar]
- Stegelmeier, B.L.; Field, R.A.; Panter, K.E.; Hall, J.O.; Welch, K.D.; Pfister, J.A.; Gardner, D.R.; Lee, S.T.; Colegate, S.M.; Davis, T.Z.; et al. Selected poisonous plants affecting animal and human health. In Haschek and Rousseaux’s Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology, 3rd ed.; Haschek, W.M., Rousseaux, C.G., Willig, M.A., Bolon, B., Ochoa, R., Mahler, B.W., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 1259–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, J.A. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids and food safety. Chem. Aust. 2003, 70, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bodi, D.; Ronczka, S.; Gottschalk, C.; Behr, N.; Skibba, A.; Wagner, M.; Lahrssen-Wiederholt, M.; Preiss-Weigert, A.; These, A. Determination of pyrrolizidine alkaloids in tea, herbal drugs and honey. Food Addit. Contam. 2014, 31, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, B.D.; Gaul, K.L.; Noble, J.W. Poisoning of feedlot cattle by seeds of Heliotropium europaeum. Aust. Vet. J. 1997, 75, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeder, E.; Wiedenfeld, H. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids in plants used in the traditional medicine of Madagascar and the Mascarene Islands. Pharmazie 2011, 66, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zurer, P.; Hanson, D. Chemistry put herbal supplements to the test. Chem. Eng. News 2004, 82, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, E.; Wiedenfeld, H.; Edgar, J.A. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids in medicinal plants from North America. Pharmazie 2015, 70, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Griffin, C.T.; Gosetto, F.; Danaher, M.; Sabatini, S.; Furey, A. Investigation of targeted pyrrolizidine alkaloids in traditional Chinese medicines and selected herbal teas sourced in Ireland using LC-ESI-MS/MS. Food Addit. Contam. 2014, 31, 940–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colegate, S.M.; Boppre, M.; Monzon, J.; Betz, J.M. Protoxic dehydropyrrolizidine alkaloids in the traditional Andean herbal medicine “asmachilca”. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 172, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakar, F.; Akbarian, Z.; Leslie, T.; Mustafa, M.L.; Watson, J.; van Egmond, H.P.; Omar, M.F.; Mofleh, J. An outbreak of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in western Afghanistan associated with exposure to wheat flour contaminated with pyrrolizidine alkaloids. J. Toxicol. 2010, 2010, 313280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauvin, P.; Dillon, J.C.; Moren, A. An outbreak of heliotrope food poisoning, Tajikistan, November 1992-March 1993. Sante 1994, 4, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schoch, T.K.; Gardner, D.R.; Stegelmeier, B.L. GC/MS/MS detection of pyrrolic metabolites in animals poisoned with the pyrrolizidine alkaloid riddelliine. J. Nat. Toxins 2000, 9, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mattocks, A.R.; Jukes, R. Detection of sulphur-conjugated pyrrolic metabolites in blood and fresh or fixed liver tissue from rats given a variety of toxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Toxicol. Lett. 1992, 63, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.W.; Stegelmeier, B.L.; Colegate, S.M.; Panter, K.E.; Knoppel, E.L.; Hall, J.O. Heterozygous p53 knockout mouse model for dehydropyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced carcinogenesis. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneux, R.J.; Gardner, D.L.; Colegate, S.M.; Edgar, J.A. Pyrrolizidine alkaloid toxicity in livestock: A paradigm for human poisoning? Food Addit. Contam. 2011, 28, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeong, M.L.; Wakefield, S.J.; Ford, H.C. Hepatocyte membrane injury and bleb formation following low dose comfrey toxicity in rats. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 1993, 74, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.; Chou, M.W.; Yan, J.; Young, J.F.; Chan, P.C.; Doerge, D.R. Toxicokinetics of riddelliine, a carcinogenic pyrrolizidine alkaloid, and metabolites in rats and mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2002, 182, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estep, J.E.; Lame, M.W.; Morin, D.; Jones, A.D.; Wilson, D.W.; Segall, H.J. [14C]monocrotaline kinetics and metabolism in the rat. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1991, 19, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; He, Y.; Xiong, A.; Yang, L.; Cheng, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Z. The comparative pharmacokinetics of two pyrrolizidine alkaloids, senecionine and adonifoline, and their main metabolites in rats after intravenous and oral administration by HPLC/ESIMS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, M.M.; Miser, J.S.; Smithson, W.A.; Coccia, P.F.; Hughes, C.S.; Davis, D.M. Pharmacokinetic study of indicine N-oxide in pediatric cancer patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1982, 10, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, M.W.; Jian, Y.; Williams, L.D.; Xia, Q.; Churchwell, M.; Doerge, D.R.; Fu, P.P. Identification of DNA adducts derived from riddelliine, a carcinogenic pyrrolizidine alkaloid. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2003, 16, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, P.P.; Chou, M.W.; Churchwell, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, Q.; Gamboa da Costa, G.; Marques, M.M.; Beland, F.A.; Doerge, D.R. High-performance liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry for the detection and quantitation of pyrrolizidine alkaloid-derived DNA adducts in vitro and in vivo. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, P.T. Pyrrolizidine alkaloid poisoning-pathology with particular reference to differences in animal and plant species. In Effects of Poisonous Plants on Livestock; Keeler, R.F., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Small, A.C.; Kelly, W.R.; Seawright, A.A.; Mattocks, A.R.; Jukes, R. Pyrrolizidine alkaloidosis in a two month old foal. Zentralblatt für Veterinärmedizin Reihe A 1993, 40, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasenack, R.; Muller, C.; Kleinschmidt, M.; Rasenack, J.; Wiedenfeld, H. Veno-occlusive disease in a fetus caused by pyrrolizidine alkaloids of food origin. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2003, 18, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roulet, M.; Laurini, R.; Rivier, L.; Calame, A. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease in newborn infant of a woman drinking herbal tea. J. Pediatr. 1988, 112, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattocks, A.R.; Jukes, R. Recovery of the pyrrolic nucleus of pyrrolizidine alkaloid metabolites from sulphur conjugates in tissues and body fluids. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1990, 75, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.W.; Stegelmeier, B.L.; Colegate, S.M.; Gardner, D.R.; Panter, K.E.; Knoppel, E.L.; Hall, J.O. The comparative toxicity of a reduced, crude comfrey (Symphytum officinale) alkaloid extract and the pure, comfrey-derived pyrrolizidine alkaloids, lycopsamine and intermedine in chicks (Gallus gallus domesticus). J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.W. Relative Toxicity of Select Dehydropyrrolizidine Alkaloids and Evaluation of a Heterozygous P53 Knockout Mouse Model for Dehydropyrrolizidine Alkaloid Induced Carcinogenesis. Ph.D. Theise, Utah State University, Logan, UT, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, J.A.; Molyneux, R.J.; Colegate, S.M. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids: Potential role in the etiology of cancers, pulmonary hypertension, congenital anomalies, and liver disease. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.C.; Haseman, J.K.; Prejean, J.D.; Nyska, A. Toxicity and carcinogenicity of riddelliine in rats and mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 144, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.E.; Molyneux, R.J.; Ralphs, M.H. Senecio: A dangerous plant for man and beast. Rangelands 1989, 11, 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Field, R.A.; Stegelmeier, B.L.; Colegate, S.M.; Brown, A.W.; Green, B.T. An in vitro comparison of the cytotoxic potential of selected dehydropyrrolizidine alkaloids and some N-oxides. Toxicon 2015, 97, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z. Pyrrolizidine alkaloid clivorine induced oxidative injury on primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edgar, J.A.; Colegate, S.M.; Boppre, M.; Molyneux, R.J. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids in food: A spectrum of potential health consequences. Food Addit. Contam. 2011, 28, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P. NTP Technical Report on the Toxicity Studies of Riddelliine (Case No. 23246-96-0) Administered by Gavage to f344 Rats and b6c3f1 Mice; Toxicity Report Series National Toxicology Program; United States Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 27, pp. 1–D9.
- Chou, M.W.; Yan, J.; Nichols, J.; Xia, Q.; Beland, F.A.; Chan, P.C.; Fu, P.P. Correlation of DNA adduct formation and riddelliine-induced liver tumorigenesis in F344 rats and B6C3F1 mice. Cancer Lett. 2003, 207, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsalis, J.C.; Steinmetz, K.L.; Blazak, W.F.; Spalding, J.W. Evaluation of the potential of riddelliine to induce unscheduled DNA synthesis, S-phase synthesis, or micronuclei following in vivo treatment with multiple doses. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1993, 21, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyska, A.; Moomaw, C.R.; Foley, J.F.; Maronpot, R.R.; Malarkey, D.E.; Cummings, C.A.; Peddada, S.; Moyer, C.F.; Allen, D.G.; Travlos, G.; et al. The hepatic endothelial carcinogen riddelliine induces endothelial apoptosis, mitosis, S phase, and p53 and hepatocytic vascular endothelial growth factor expression after short-term exposure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2002, 184, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department of Health and Human Services. Riddelliine. In National Toxicology Program Reports; Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, Q.; da Costa, G.G.; Yu, H.; Cai, L.; Fu, P.P. Full structure assignments of pyrrolizidine alkaloid DNA adducts and mechanism of tumor initiation. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1985–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQueen, C.A.; Williams, G.M. The hepatocyte primary culture: DNA repair test using hepatocytes from several species. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 1987, 3, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, A.S.; Pereira, T.N.; Reilly, P.E.; Seawright, A.A. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids in human diet. Mutat. Res. 1999, 443, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, L.F.; Culvenor, C.C.J.; Dick, A.T. The Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids: Their Chemistry, Pathogenicity and Other Biological Properties; North Holland Publications: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1968; pp. 1–397. [Google Scholar]
- Mattocks, A.R. Acute hepatotoxicity and pyrrolic metabolites in rats dosed with pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1972, 5, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids, Health and Safety Guide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerlands, 1988; Volume 26, p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Cheeke, P.R. Natural Toxicants in Feeds, Forages, and Poisonous Plants; Interstate Publishers Inc.: Danville, IL, USA, 1998; pp. 3–463. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, C.L.; Harris, P.N.; Chen, K.K. Some pharmacological actions of supine and lasiocarpine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1959, 126, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids; Environmental Health Criteria; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerlands, 1988; Volume 88, pp. 1–345. [Google Scholar]
- Mattocks, A.R.; White, I.N.H. Toxicity of pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Nat. Lond. 1968, 217, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, D.T.; Peterson, J.E. Quantitative assessment of the persistent antimitotic effect of certain hepatotoic pyrrolizidine alkaloid on rat liver. Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 1968, 46, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Reserach on Cancer. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids. In Some Naturally Occurring Substances; International Agency for Reserach on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1976; Volume 10, pp. 265–342. [Google Scholar]
- Dalefield, R.R.; Gosse, M.A.; Barholomaeus, A.; Schyvens, C.G.; Hutchinson, K.J.; Mueller, U. Determination of the single-dose 72-hour oral gavage LD50 values of monocrotaline and riddelliine in male Han Wistar rats using the up-and-down procedure. J. Herbal Med. Toxicol. 2012, 6, 153–165. [Google Scholar]
- Newberne, P.M.; Wilson, R.; Rogers, A.E. Effects of a low-lipotrope diet on the response of young male rats to the pyrrolizidine alkaloid, monocrotaline. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1971, 18, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Toxicity of Chemicals in Food, and the Environment. Statement on Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Food; Food Standards Agency: London, UK, 2008.
- Chou, M.W.; Wang, Y.P.; Yan, J.; Yang, Y.C.; Beger, R.D.; Williams, L.D.; Doerge, D.R.; Fu, P.P. Riddelliine N-oxide is a phytochemical and mammalian metabolite with genotoxic activity that is comparable to the parent pyrrolizidine alkaloid riddelliine. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 145, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, L.B.; Dick, A.T.; McKenzie, J.S. The acute toxic effects of heliotrine and lasiocarpine and their N-oxides on the rat. J. Pathol. Bacteriol. 1958, 75, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culvenor, C.C.; Edgar, J.A.; Jago, M.V.; Qutteridge, A.; Peterson, J.E.; Smith, L.W. Hepato- and pneumotoxicity of pyrrolizidine alkaloids and derivatives in relation to molecular structure. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1976, 12, 299–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dehydro Pyrrolizidine Alkaloid | CRL-2118 Cytology Mean CT50 ± SD MTTuM | Chick Survival Log Rank | Chick Hepatocyte Necrosis (Ranking) | Chick Pyrrole nmol/g/Day | LD50 mg/kg Male Rat IP (Unless Otherwise Indicated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lasiocarpine Diester heliotridine | 1 (31 ± 15 A) | 4 (4.8 A–C) | 7 | 2 (3.7 A) | 77 [47,48] 72 [49,50] 88 IV Rat [51] |
| Seneciphylline Macrocyclic retronecine | 2 (76 ± 35 A) | 2 (5.4 A–C) | 5 | 4 (1.6 B) | 77 [47,48] |
| Senecionine Macrocyclic retronecine | 3 (96 ± 35 A,B) | 5 (3.6 A–C) | 2 | 5 (1.0 B,C) | 50 [47,48] 77 mg/kg [52] 85 [50] 57.3 (171 umol/kg) PO mice [22] |
| Heliotrine Mono ester heliotridine | 4 (73 ± 9 A) | 1 (8.7 A) | 1 | 3 (3.4 A) | 296 [47,48] 300 [53,54] 5000 heliotine-N-oxide IP male rat [54] |
| Riddelliine Macrocyclic retronecine | 5 (162 ± 43 B) | 3 (5.1 A–D) | 3 | 1 (11.1 D) | 105 IV mouse [50,55] 80 PO male rat [56] |
| Monocrotaline Macrocyclic retronecine | 6 (256 ± 65 C) | NA * | NA * | NA * | 71 [57] 109 [47,48] 175 [50,58] 510 PO male rat [56] |
| Riddelliine N-oxide | 7 (267 ± 280 C) | 7 (−1.3 B–D) | 6 | 8 (0.7 E) | ~250 PO male rat estimated from adduct production [59] |
| Intermedine Mono ester retronecine | 8 (>300 C) | NA * | NA * | NA * | 1500 [50] |
| Lycopsamine Mono ester retronecine | 9 (>300 C) | 9 (−13.6 E) | 9 | 9 (0.004 F) | 1500 [50] |
| Lasiocarpine N-oxide | 10 (>300 C) | 8 (−4.9 C,D) | 8 | 7 (0.8 C,E) | 547 [60] ~1100 [61] |
| Senecionine N-oxide | 11 (>300 C) | 6 (−0.6 C,D) | 4 | 6 (1.2 C) | ~2000 [61] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stegelmeier, B.L.; Colegate, S.M.; Brown, A.W. Dehydropyrrolizidine Alkaloid Toxicity, Cytotoxicity, and Carcinogenicity. Toxins 2016, 8, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8120356
Stegelmeier BL, Colegate SM, Brown AW. Dehydropyrrolizidine Alkaloid Toxicity, Cytotoxicity, and Carcinogenicity. Toxins. 2016; 8(12):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8120356
Chicago/Turabian StyleStegelmeier, Bryan L., Steven M. Colegate, and Ammon W. Brown. 2016. "Dehydropyrrolizidine Alkaloid Toxicity, Cytotoxicity, and Carcinogenicity" Toxins 8, no. 12: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8120356
APA StyleStegelmeier, B. L., Colegate, S. M., & Brown, A. W. (2016). Dehydropyrrolizidine Alkaloid Toxicity, Cytotoxicity, and Carcinogenicity. Toxins, 8(12), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8120356





