Structural and Functional Elucidation of Peptide Ts11 Shows Evidence of a Novel Subfamily of Scorpion Venom Toxins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
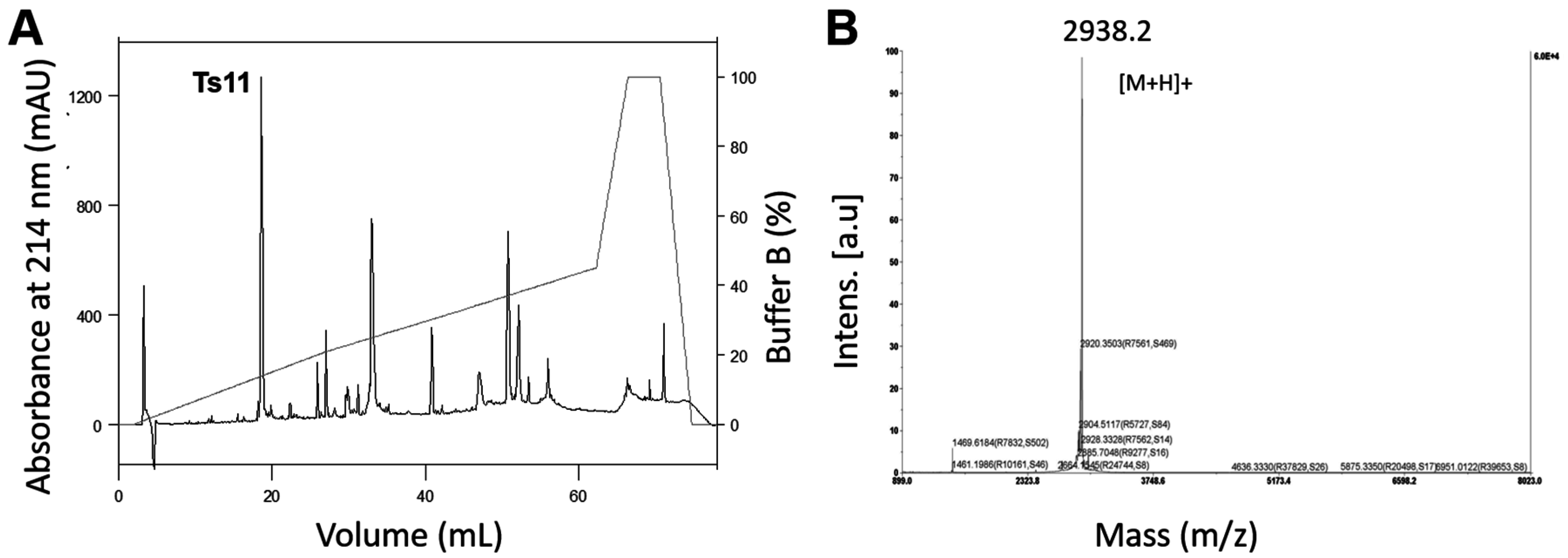
2.1. Isolation of Native Ts11 and Biochemical Characterization
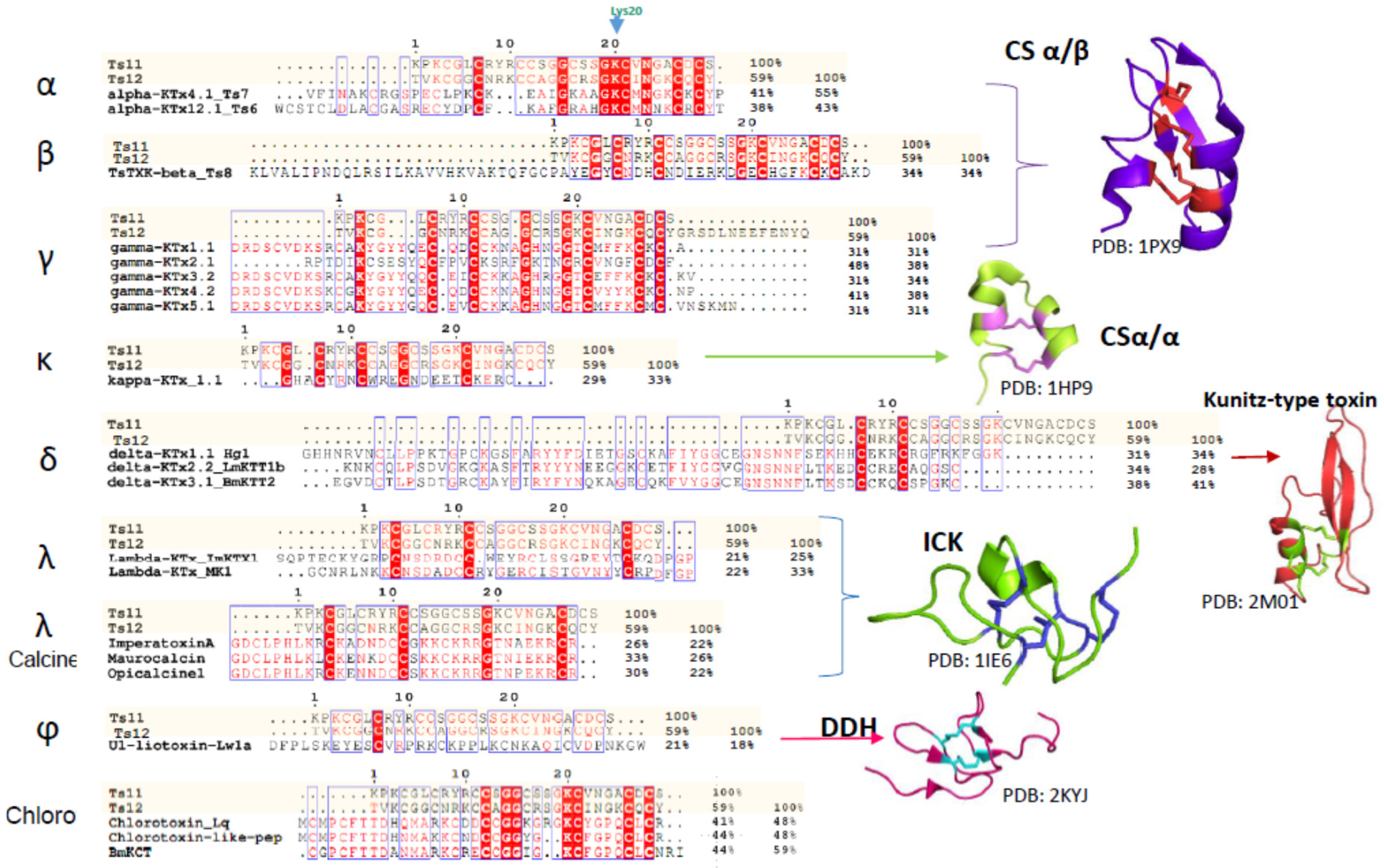
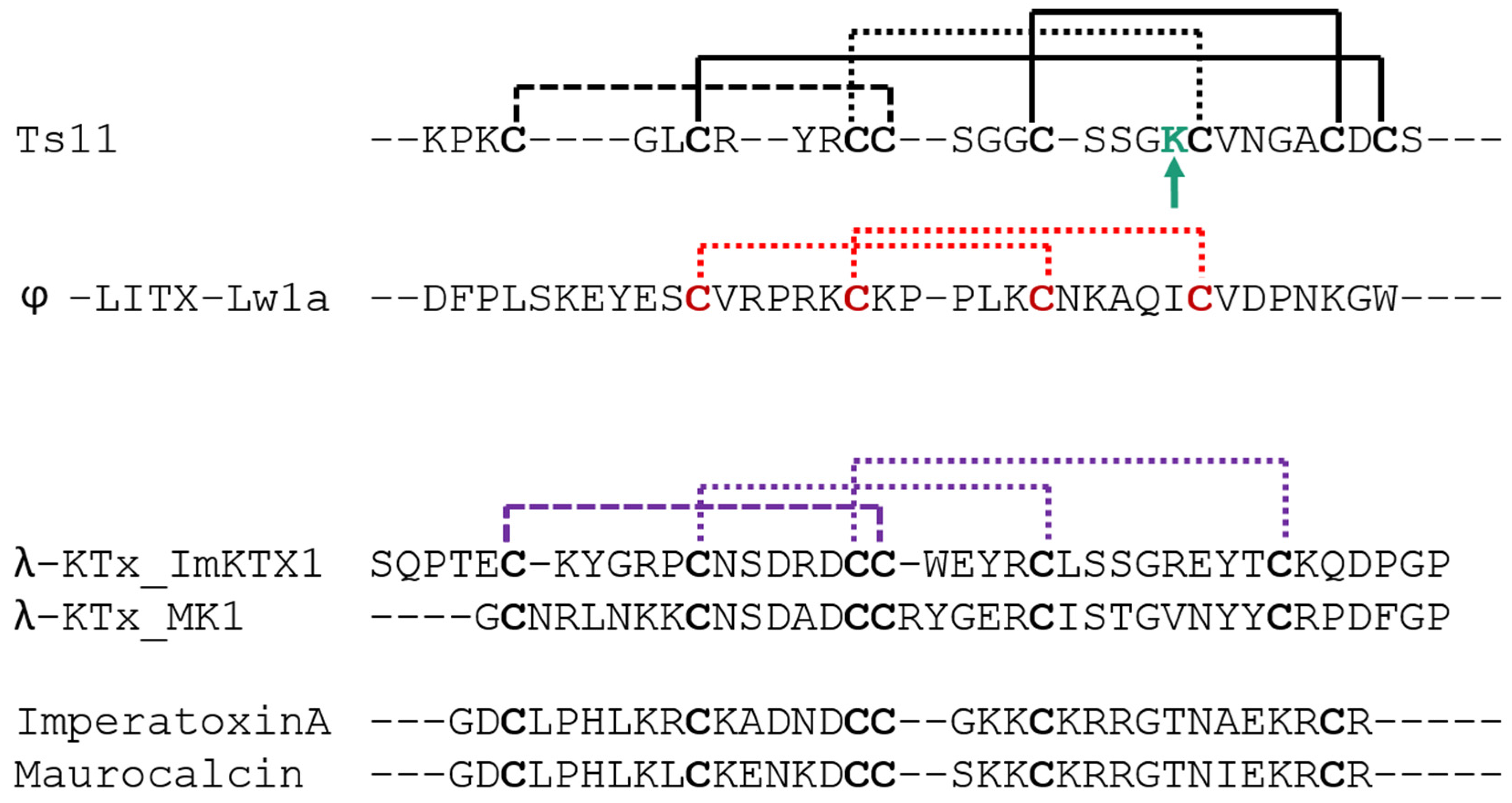
2.2. Structural Elucidation of Ts11
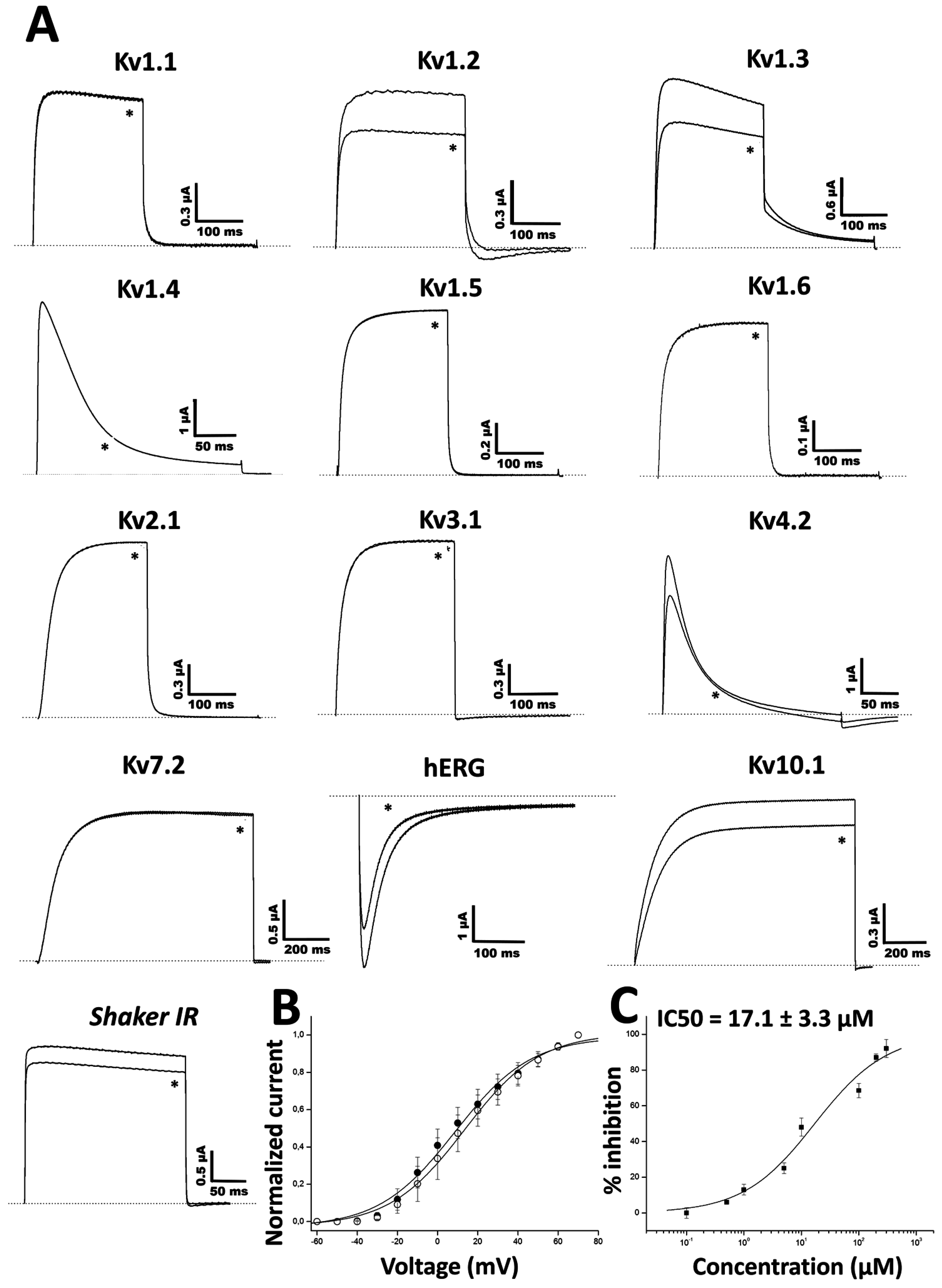
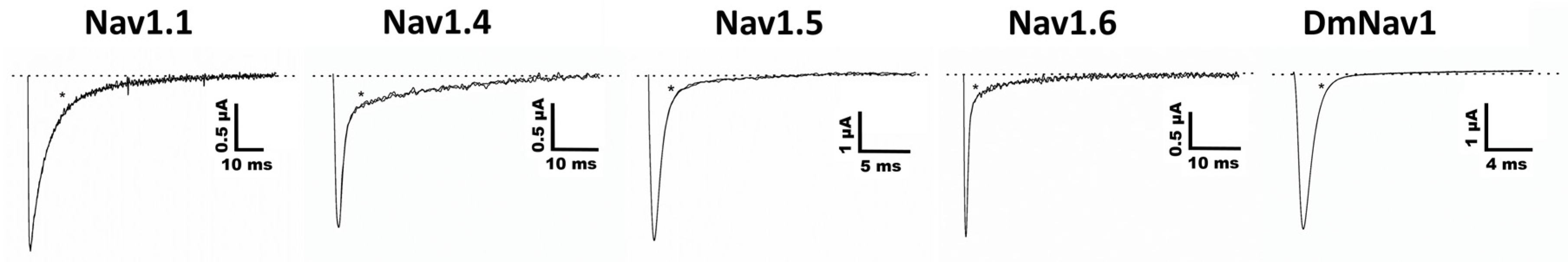
2.3. Functional Characterization of Ts11
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Experimental Section
5.1. Ts11 and Ts12 Isolation Procedures
5.2. Biochemical Characterization of Toxins
5.3. Expression of Voltage-Gated Ion Channels in Xenopus Laevis Oocytes
5.4. Electrophysiological Recordings
5.5. NMR Spectroscopy
5.6. Structural Constraints
5.7. Structure Calculations
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Authors Contribution
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mouhat, S.; Jouirou, B.; Mosbah, A.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.M. Diversity of folds in animal toxins acting on ion channels. Biochem. J. 2004, 378, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Harvey, P.J.; Craik, D.J.; Ronjat, M.; De Waard, M.; Zhu, S. Functional evolution of scorpion venom peptides with an inhibitor cystine knot fold. Biosci. Rep. 2013, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez de la Vega, R.C.; Possani, L.D. Current views on scorpion toxins specific for k+-channels. Toxicon 2004, 43, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimenta, A.M.; Legros, C.; Almeida Fde, M.; Mansuelle, P.; De Lima, M.E.; Bougis, P.E.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F. Novel structural class of four disulfide-bridged peptides from tityus serrulatus venom. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 301, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cologna, C.T.; Marcussi, S.; Giglio, J.R.; Soares, A.M.; Arantes, E.C. Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom and toxins: An overview. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordon, K.C.F.; Cologna, C.T.; Arantes, E.C. Scorpion venom research around the world: Tityus serrulatus. In Scorpion Venoms; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Possani, L.D., Schwartz, E.F., Rodríguez de la Vega, R.C., Eds.; Springer: Houten, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 411–438. [Google Scholar]
- Cerni, F.A.; Pucca, M.B.; Peigneur, S.; Cremonez, C.M.; Bordon, K.C.; Tytgat, J.; Arantes, E.C. Electrophysiological characterization of Ts6 and Ts7, k+ channel toxins isolated through an improved tityus serrulatus venom purification procedure. Toxins 2014, 6, 892–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuthrich, K. NMR of Porteins and Nucleic Acids; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- UniProt (Universal Protein Resource). Scorpktx: Scorpion Potassium Channel Toxins: Nomenclature and List of Entries. Available online: http://www.uniprot.org/docs/scorpktx (accessed on 30 September 2016).
- Tytgat, J.; Chandy, K.G.; Garcia, M.L.; Gutman, G.A.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; van der Walt, J.J.; Possani, L.D. A unified nomenclature for short-chain peptides isolated from scorpion venoms: Alpha-ktx molecular subfamilies. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999, 20, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Hernandez, V.; Jimenez-Vargas, J.M.; Gurrola, G.B.; Valdivia, H.H.; Possani, L.D. Scorpion venom components that affect ion-channels function. Toxicon 2013, 76, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saucedo, A.L.; Flores-Solis, D.; Rodriguez de la Vega, R.C.; Ramirez-Cordero, B.; Hernandez-Lopez, R.; Cano-Sanchez, P.; Noriega Navarro, R.; Garcia-Valdes, J.; Coronas-Valderrama, F.; de Roodt, A.; et al. New tricks of an old pattern: Structural versatility of scorpion toxins with common cysteine spacing. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 12321–12330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajloun, Z.; Mosbah, A.; Carlier, E.; Mansuelle, P.; Sandoz, G.; Fathallah, M.; di Luccio, E.; Devaux, C.; Rochat, H.; Darbon, H.; et al. Maurotoxin versus Pi1/HsTx1 scorpion toxins. Toward new insights in the understanding of their distinct disulfide bridge patterns. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39394–39402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, K.N.; Sivaraja, V.; Huys, I.; Sasaki, T.; Cheng, B.; Kumar, T.K.; Sato, K.; Tytgat, J.; Yu, C.; San, B.C.; et al. Kappa-hefutoxin1, a novel toxin from the scorpion Heterometrus fulvipes with unique structure and function. Importance of the functional diad in potassium channel selectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30040–30047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargos, T.S.; Restano-Cassulini, R.; Possani, L.D.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J.; Schwartz, C.A.; Alves, E.M.; de Freitas, S.M.; Schwartz, E.F. The new kappa-KTx 2.5 from the scorpion opisthacanthus cayaporum. Peptides 2011, 32, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peigneur, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Goto, H.; Srinivasan, K.N.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Tytgat, J.; Sato, K. Synthesis and characterization of amino acid deletion analogs of kappa-hefutoxin 1, a scorpion toxin on potassium channels. Toxicon 2013, 71, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Wu, Y. Cloning and characterization of a novel kunitz-type inhibitor from scorpion with unique cysteine framework. Toxicon 2013, 72, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Luo, F.; Feng, J.; Yang, W.; Zeng, D.; Zhao, R.; Cao, Z.; Liu, M.; Li, W.; Jiang, L.; et al. Genomic and structural characterization of kunitz-type peptide lmktt-1a highlights diversity and evolution of scorpion potassium channel toxins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.Y.; Darbon, H.; Dyason, K.; Verdonck, F.; Tytgat, J. Evolutionary origin of inhibitor cystine knot peptides. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1765–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.J.; Hill, J.M.; Little, M.J.; Nicholson, G.M.; King, G.F.; Alewood, P.F. Unique scorpion toxin with a putative ancestral fold provides insight into evolution of the inhibitor cystine knot motif. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10478–10483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.J.; Vetter, I.; Lewis, R.J.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J.; Lam, A.; Gallant, E.M.; Beard, N.A.; Alewood, P.F.; Dulhunty, A.F. Multiple actions of phi-litx-lw1a on ryanodine receptors reveal a functional link between scorpion ddh and ICK toxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8906–8911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Undheim, E.A.; Mobli, M.; King, G.F. Toxin structures as evolutionary tools: Using conserved 3D folds to study the evolution of rapidly evolving peptides. BioEssays 2016, 38, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edman, P.; Begg, G. A protein sequenator. Eur. J. Biochem. 1967, 1, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corpet, F. Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 10881–10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClustalW. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2 (accessed on 27 April 2016).
- Expasy Software. Available online: http://www.expasy.org/ (accessed on 28 May 2016).
- Liman, E.R.; Tytgat, J.; Hess, P. Subunit stoichiometry of a mammalian k+ channel determined by construction of multimeric cdnas. Neuron 1992, 9, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, R. The Computer Aided Resonance Assignment Tutorial, 1st ed.; Cantina: Goldau, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, T.L.; Shaka, A.J. Water suppression that works—Excitation sculpting using arbitrary wave-forms and pulsed-field gradients. J. Magn. Reson. Ser. A 1995, 112, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaka, A.J.; Lee, C.J.; Pines, A. Iterative schemes for bilinear operators—Application to spin decoupling. J. Magn. Reson. 1988, 77, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derome, A.E.; Williamson, M.P. Rapid-pulsing artifacts in double-quantum-filtered cosy. J. Magn. Reson. 1990, 88, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwieters, C.D.; Kuszewski, J.J.; Tjandra, N.; Clore, G.M. The Xplor-NIH NMR molecular structure determination package. J. Magn. Reson. 2003, 160, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.G.; Rice, L.M.; Brunger, A.T. Torsion-angle molecular dynamics as a new efficient tool for NMR structure calculation. J. Magn. Reson. 1997, 124, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spronk, C.A.; Linge, J.P.; Hilbers, C.W.; Vuister, G.W. Improving the quality of protein structures derived by nmr spectroscopy. J. Biomol. NMR 2002, 22, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Macarthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. Procheck—A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 3JHNHα < 6 Hz,
3JHNHα < 6 Hz,  3JHNHα = 6–8 Hz,
3JHNHα = 6–8 Hz,  3JHNHα > 8 Hz. The filled squares above and below the horizontal line represent CSI values of +1 and −1 respectively.
3JHNHα > 8 Hz. The filled squares above and below the horizontal line represent CSI values of +1 and −1 respectively.
 3JHNHα < 6 Hz,
3JHNHα < 6 Hz,  3JHNHα = 6–8 Hz,
3JHNHα = 6–8 Hz,  3JHNHα > 8 Hz. The filled squares above and below the horizontal line represent CSI values of +1 and −1 respectively.
3JHNHα > 8 Hz. The filled squares above and below the horizontal line represent CSI values of +1 and −1 respectively.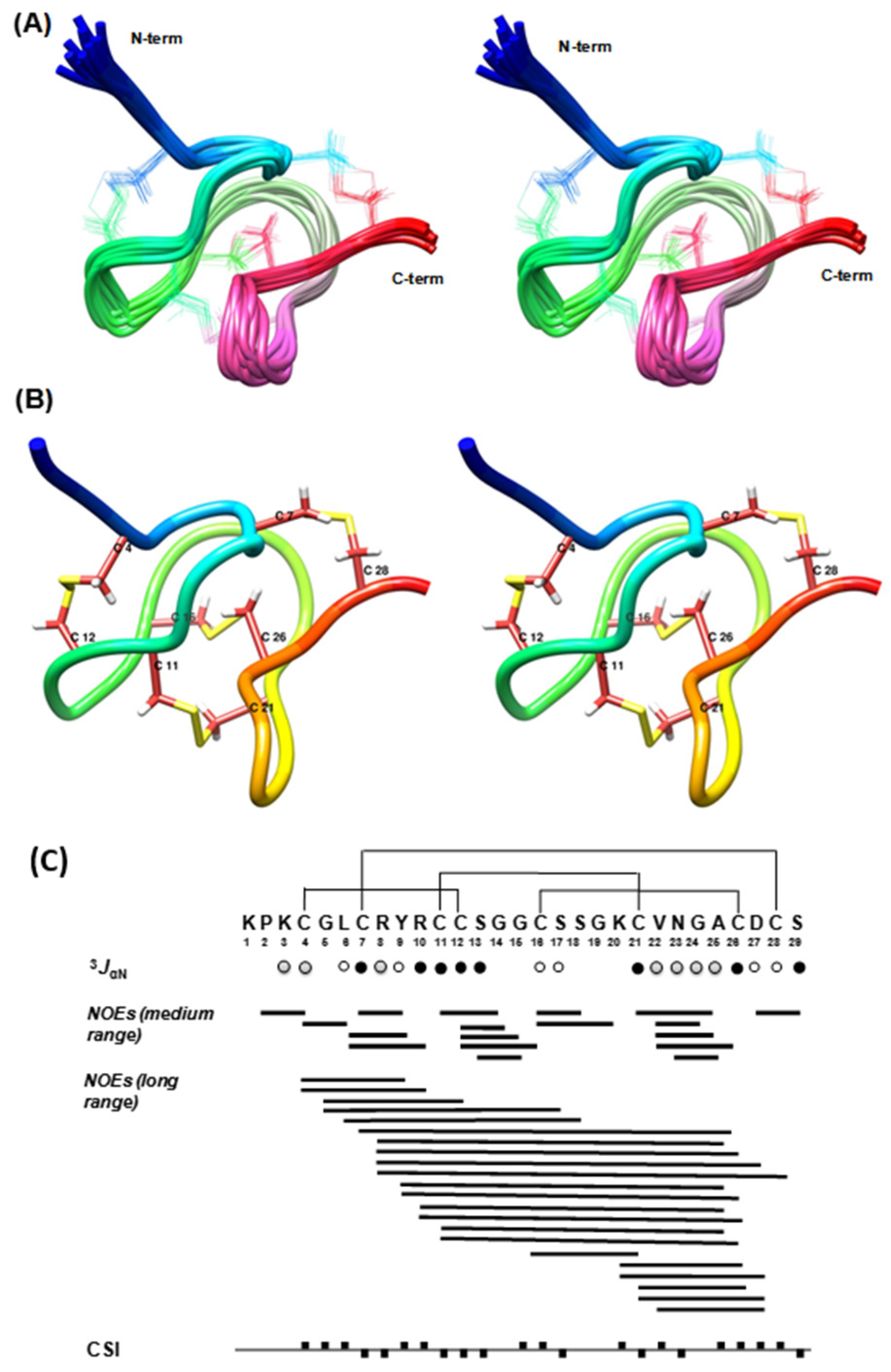
| PROPERTIES | VALUES |
|---|---|
| Total NOE Distance Restraints | 224 |
| Intra residue | 69 |
| Sequential (׀i − j׀ = 1) | 84 |
| Medium range (2 ≤ ׀i − j׀ ≤ 4) | 29 |
| Long range (׀i − j׀ ≥ 5) | 42 |
| Dihedral angle restraints | 13 (ϕ = 12, ωX-Pro = 1) |
| RMSD from the average structure (Ǻ) | |
| Backbone atoms (N, Cα, C’) | 0.44 ± 0.08 |
| All heavy atoms | 1.03 ± 0.08 |
| RMS deviation from the idealized covalent geometry | |
| Bond (Ǻ) | 0.000007 ± 0.000000 |
| Angle (°) | 2.918 ± 0.110 |
| Improper (°) | 2.907 ± 0.311 |
| Ramachandran analysis (%) | |
| Residues in favored regions | 43.8 |
| Residues in additional allowed regions | 42.5 |
| Residues in generously allowed regions | 8.3 |
| Residues in disallowed regions | 5.4 (C4 & N23) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cremonez, C.M.; Maiti, M.; Peigneur, S.; Cassoli, J.S.; Dutra, A.A.A.; Waelkens, E.; Lescrinier, E.; Herdewijn, P.; De Lima, M.E.; Pimenta, A.M.C.; et al. Structural and Functional Elucidation of Peptide Ts11 Shows Evidence of a Novel Subfamily of Scorpion Venom Toxins. Toxins 2016, 8, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100288
Cremonez CM, Maiti M, Peigneur S, Cassoli JS, Dutra AAA, Waelkens E, Lescrinier E, Herdewijn P, De Lima ME, Pimenta AMC, et al. Structural and Functional Elucidation of Peptide Ts11 Shows Evidence of a Novel Subfamily of Scorpion Venom Toxins. Toxins. 2016; 8(10):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100288
Chicago/Turabian StyleCremonez, Caroline M., Mohitosh Maiti, Steve Peigneur, Juliana Silva Cassoli, Alexandre A. A. Dutra, Etienne Waelkens, Eveline Lescrinier, Piet Herdewijn, Maria Elena De Lima, Adriano M. C. Pimenta, and et al. 2016. "Structural and Functional Elucidation of Peptide Ts11 Shows Evidence of a Novel Subfamily of Scorpion Venom Toxins" Toxins 8, no. 10: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100288
APA StyleCremonez, C. M., Maiti, M., Peigneur, S., Cassoli, J. S., Dutra, A. A. A., Waelkens, E., Lescrinier, E., Herdewijn, P., De Lima, M. E., Pimenta, A. M. C., Arantes, E. C., & Tytgat, J. (2016). Structural and Functional Elucidation of Peptide Ts11 Shows Evidence of a Novel Subfamily of Scorpion Venom Toxins. Toxins, 8(10), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100288








