Preparative Separation of Main Ustilaginoidins from Rice False Smut Balls by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction

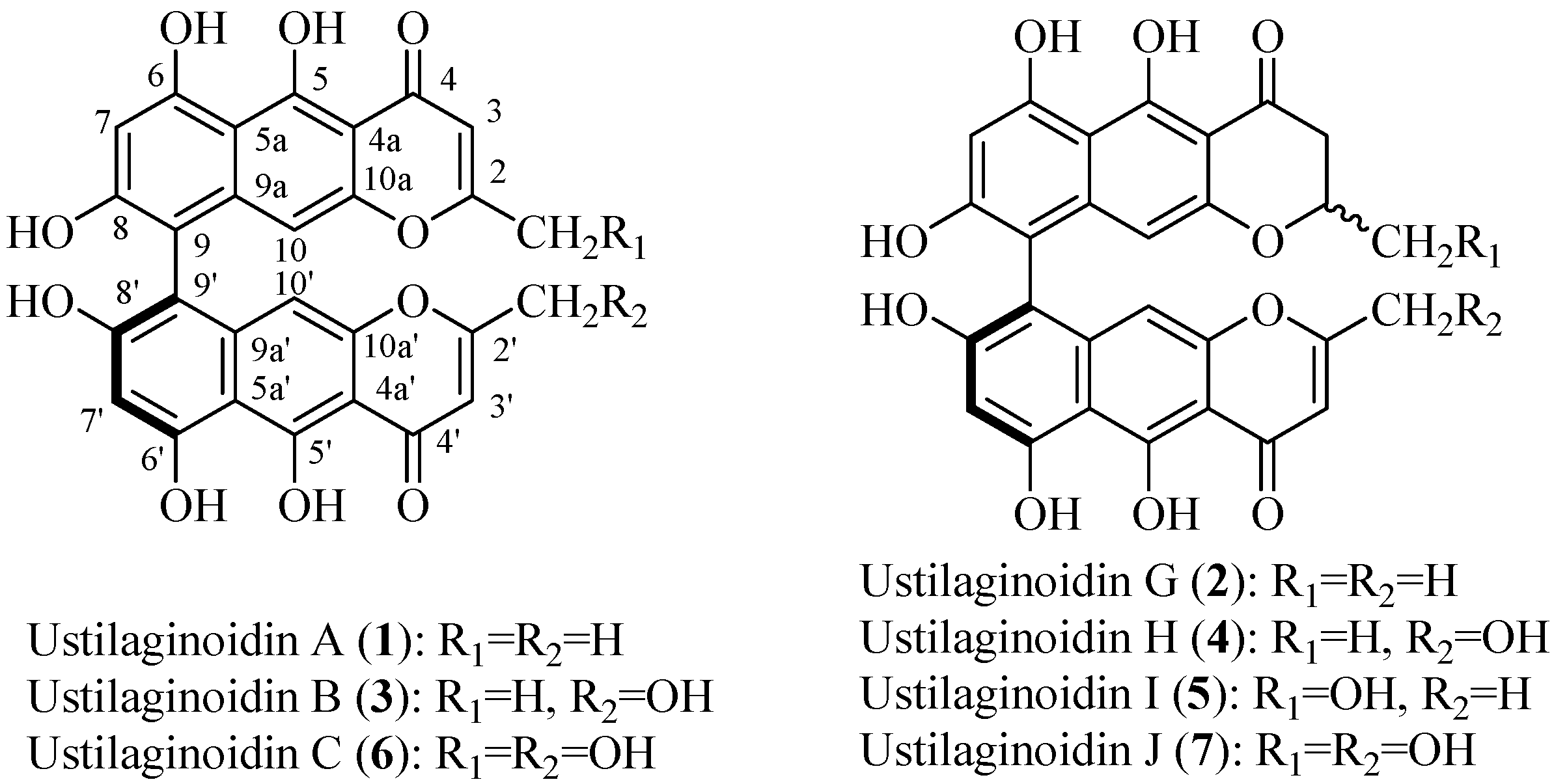
2. Results and Discussion
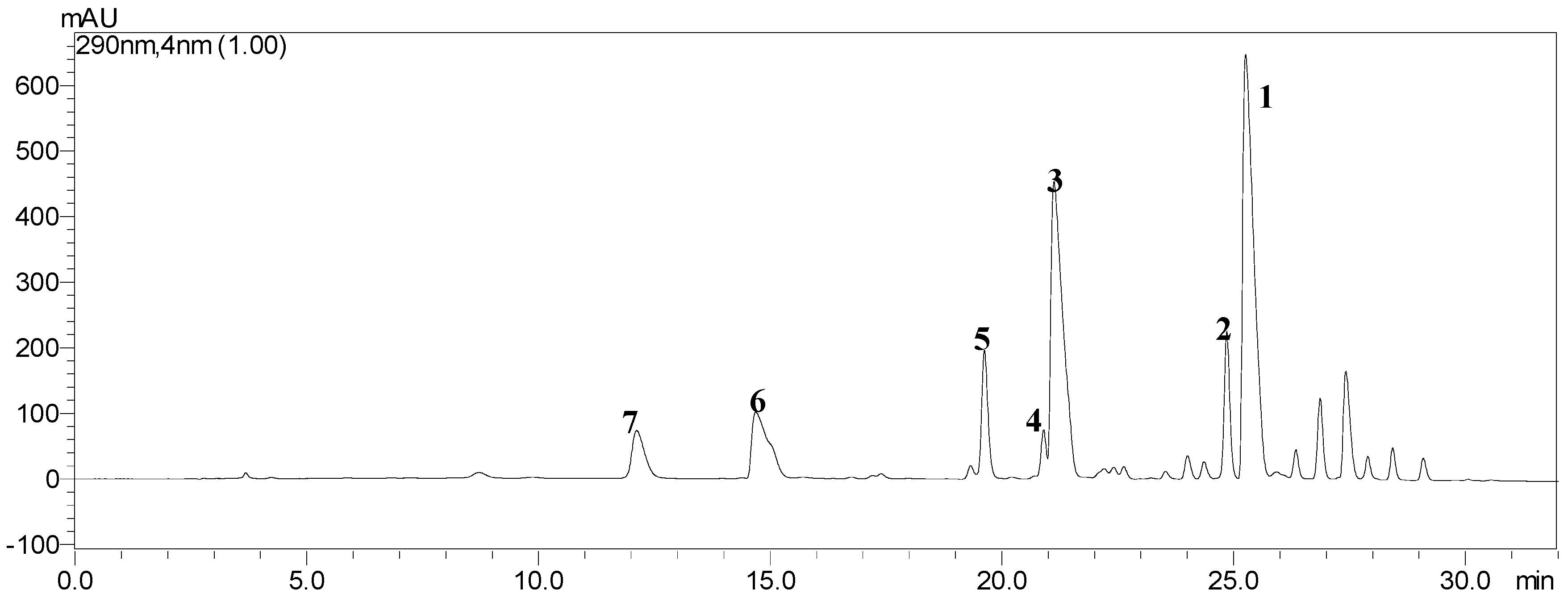
2.1. HPLC Analysis of the Crude Extract
2.2. Selection of the Suitable Two-Phase Solvent System
| System No. | Ratio (v/v) | K Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||
| S1 | 3.0:5.0:3.0:5.0 | + | + | 2.77 | 2.81 | 2.25 | 1.33 | 1.13 |
| S2 | 3.0:5.0:4.0:6.7 | + | + | 2.72 | 2.90 | 2.46 | 1.25 | 0.92 |
| S3 | 4.0:5.0:4.0:5.0 | 5.17 | 5.49 | 2.35 | 2.65 | 2.31 | 1.29 | 1.16 |
| S4 | 4.0:5.0:5.0:6.0 | 2.23 | 2.45 | 1.07 | 1.28 | 0.72 | 0.39 | 0.34 |
| S5 | 6.5:3.5:5.0:5.0 | 0.89 | 1.26 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.08 | – | – |
| S6 | 7.0:3.0:5.0:5.0 | 0.58 | 0.61 | – | – | – | – | – |
2.3. HSCCC Separation of the Samples
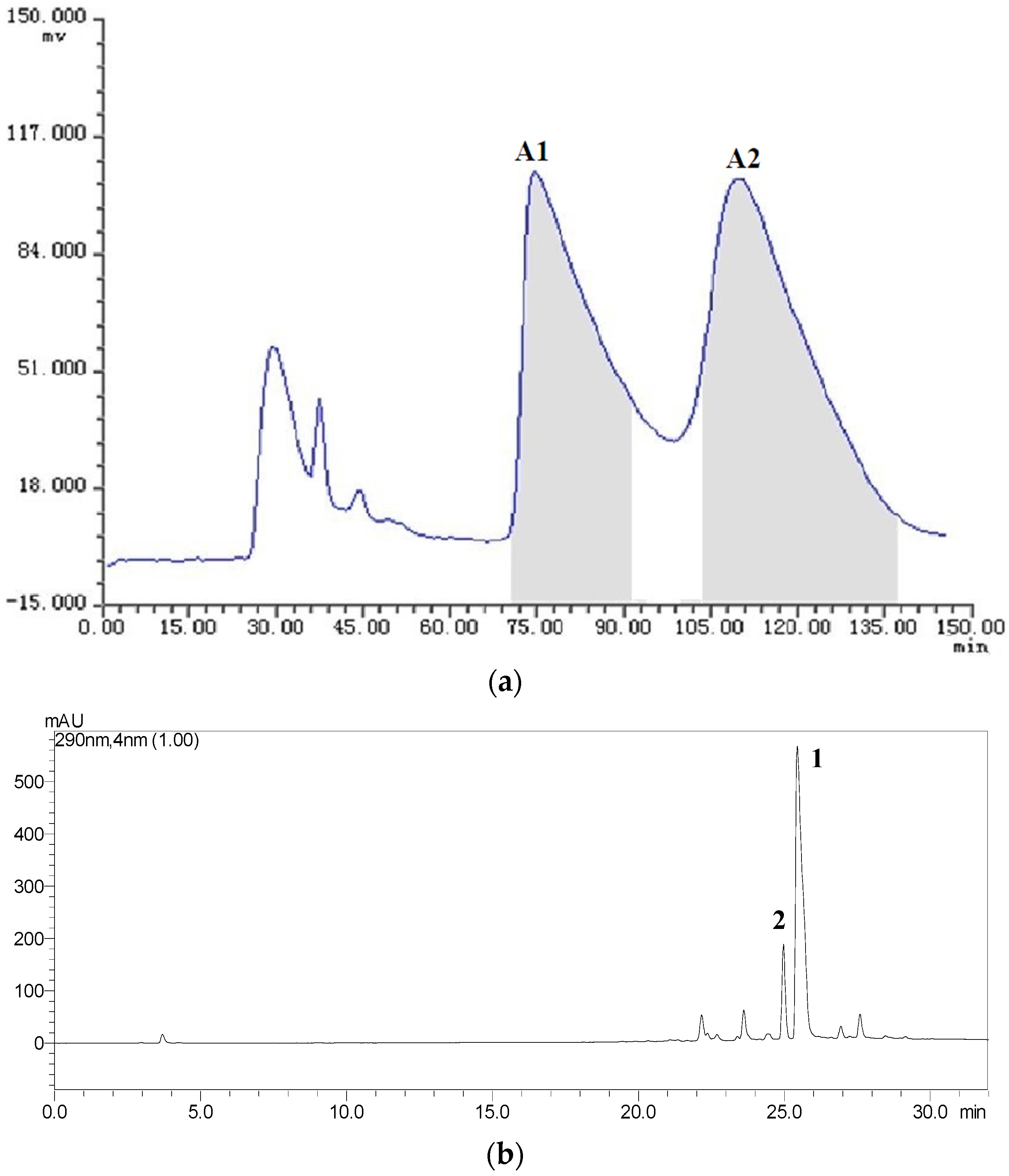
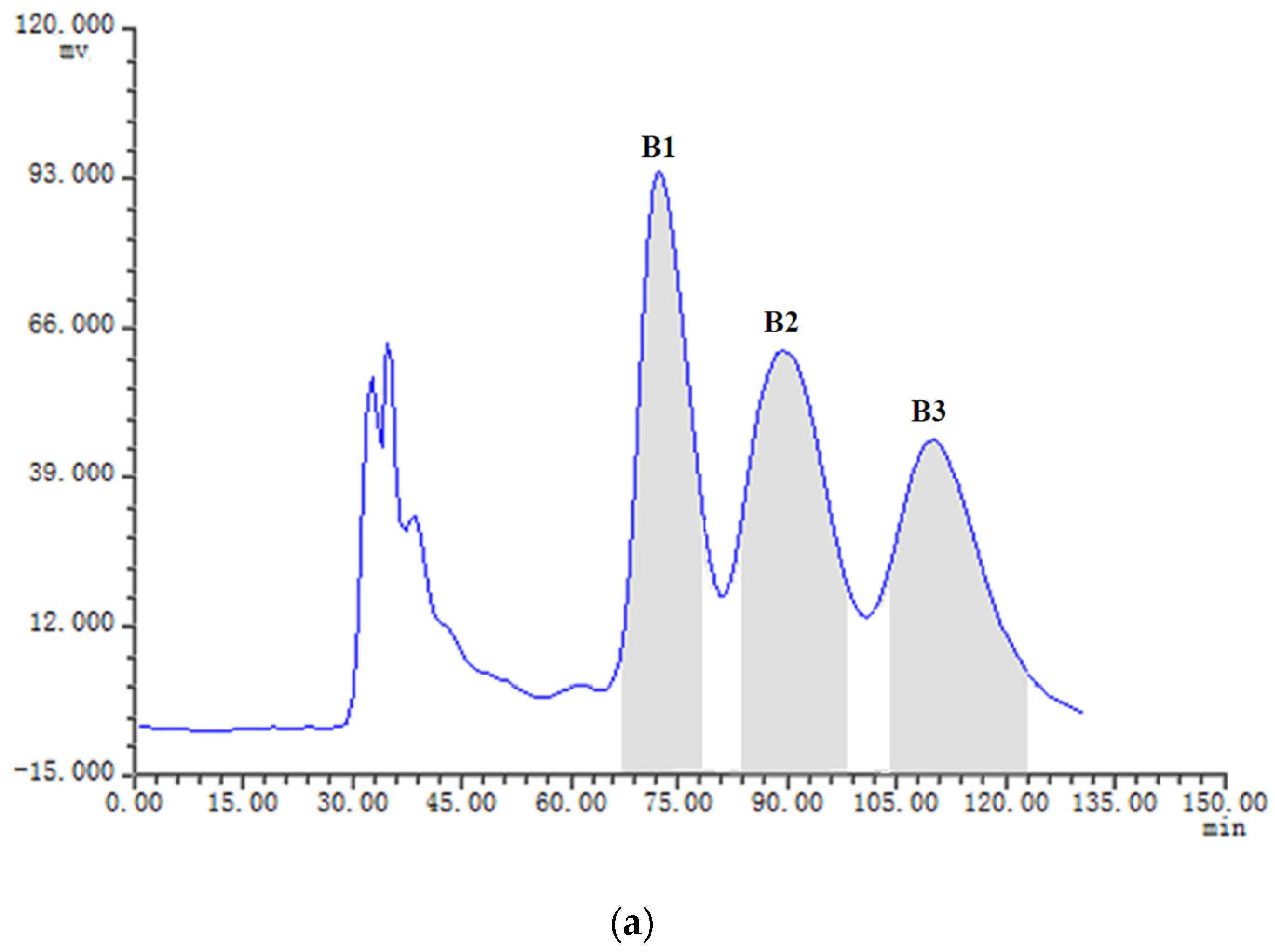
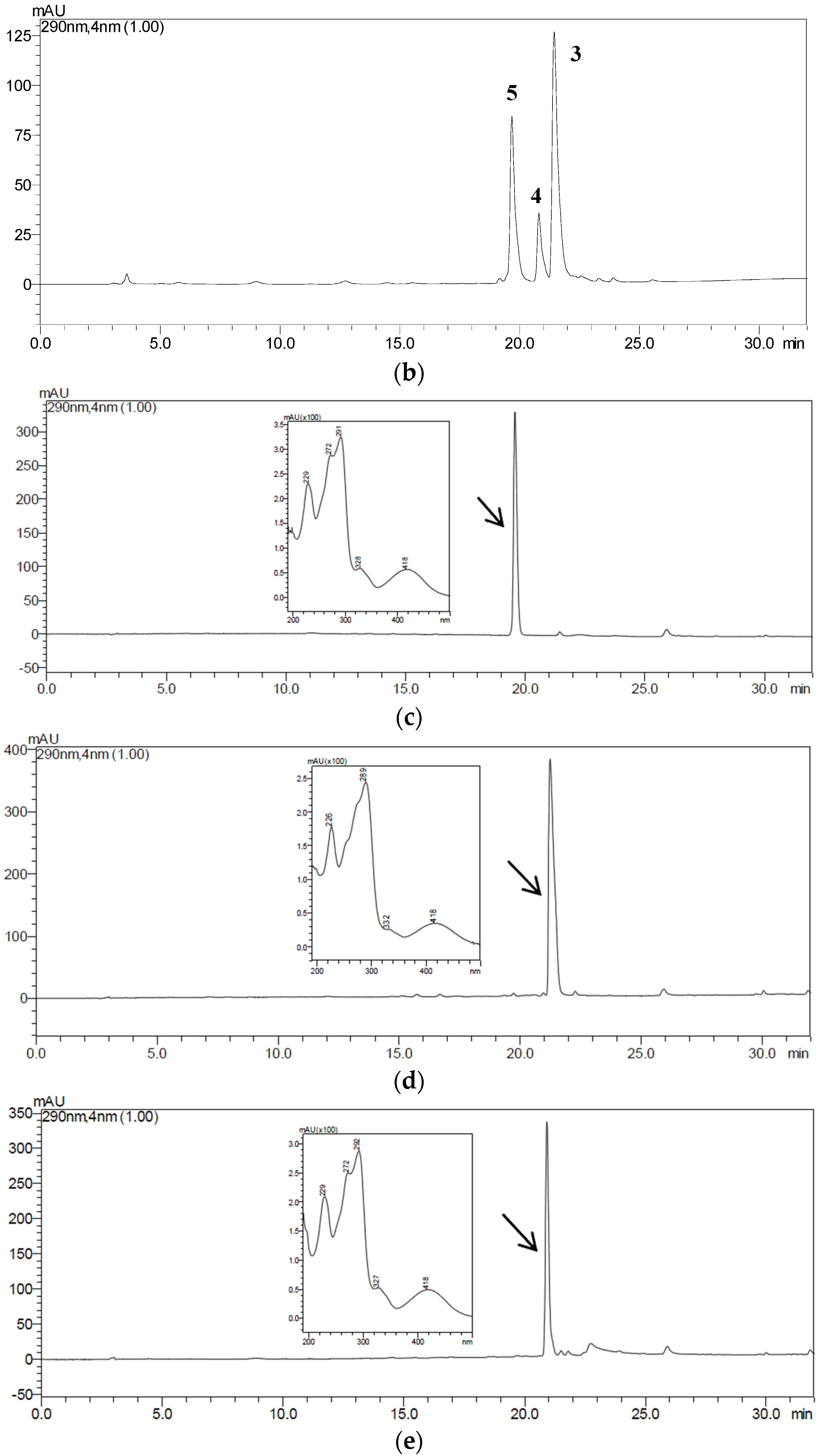
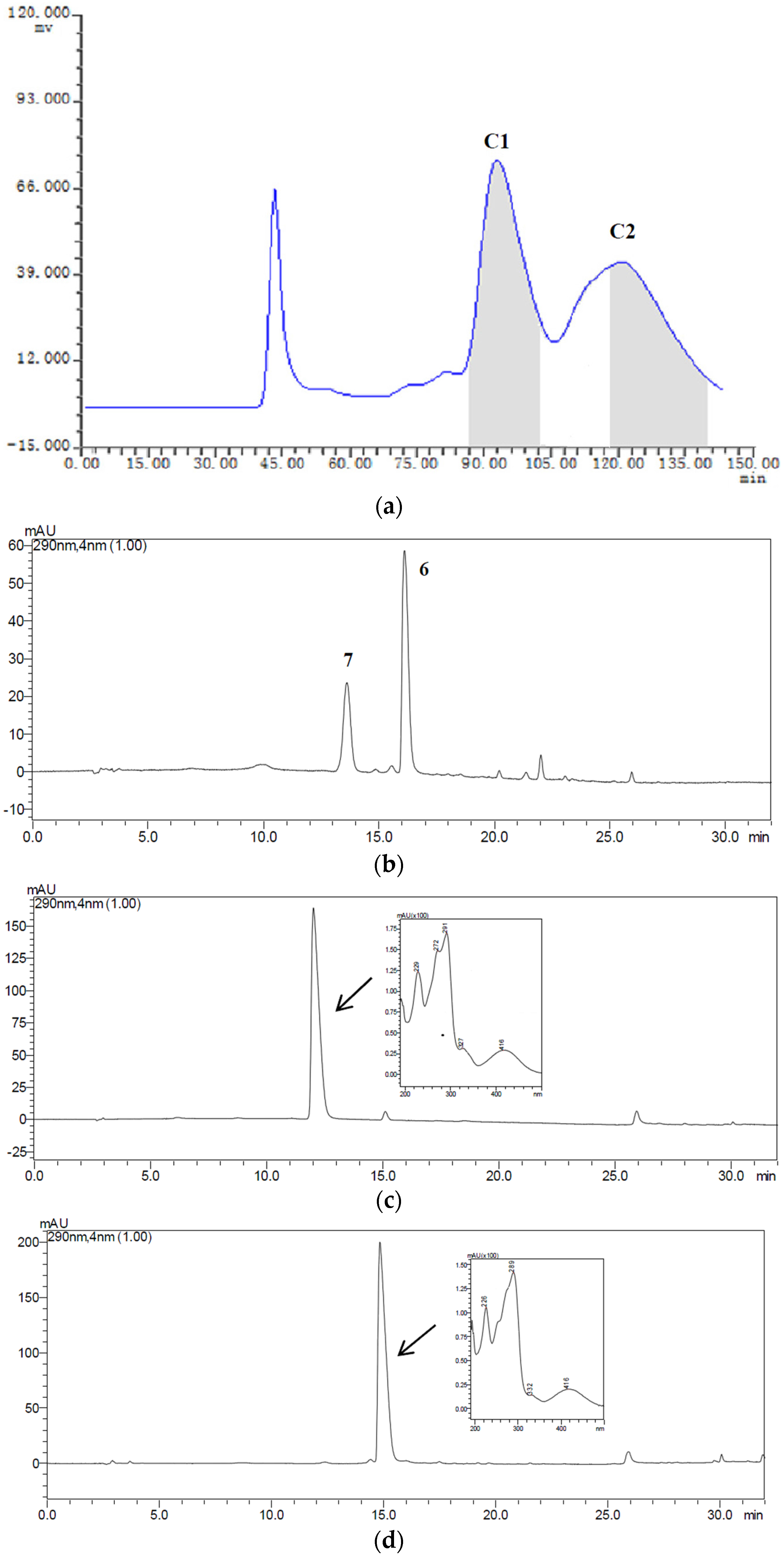
| Fraction Sample and Quantity | HSCCC Peak Fraction and Corresponding Compound | Purity before HSCCC (%) | Purity after HSCCC (%) | Quantity of HSCCC Peak Fraction (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fr.A, 19 mg | A1 (1) | 35 | 88 | 6.2 |
| A2 (2) | 29 | 82 | 5.1 | |
| Fr.B, 21 mg | B1 (5) | 28 | 92 | 5.7 |
| B2 (3) | 31 | 91 | 3.9 | |
| B3 (4) | 12 | 80 | 1.2 | |
| Fr.C, 22 mg | C1 (7) | 31 | 83 | 6.1 |
| C2 (6) | 26 | 81 | 3.5 |
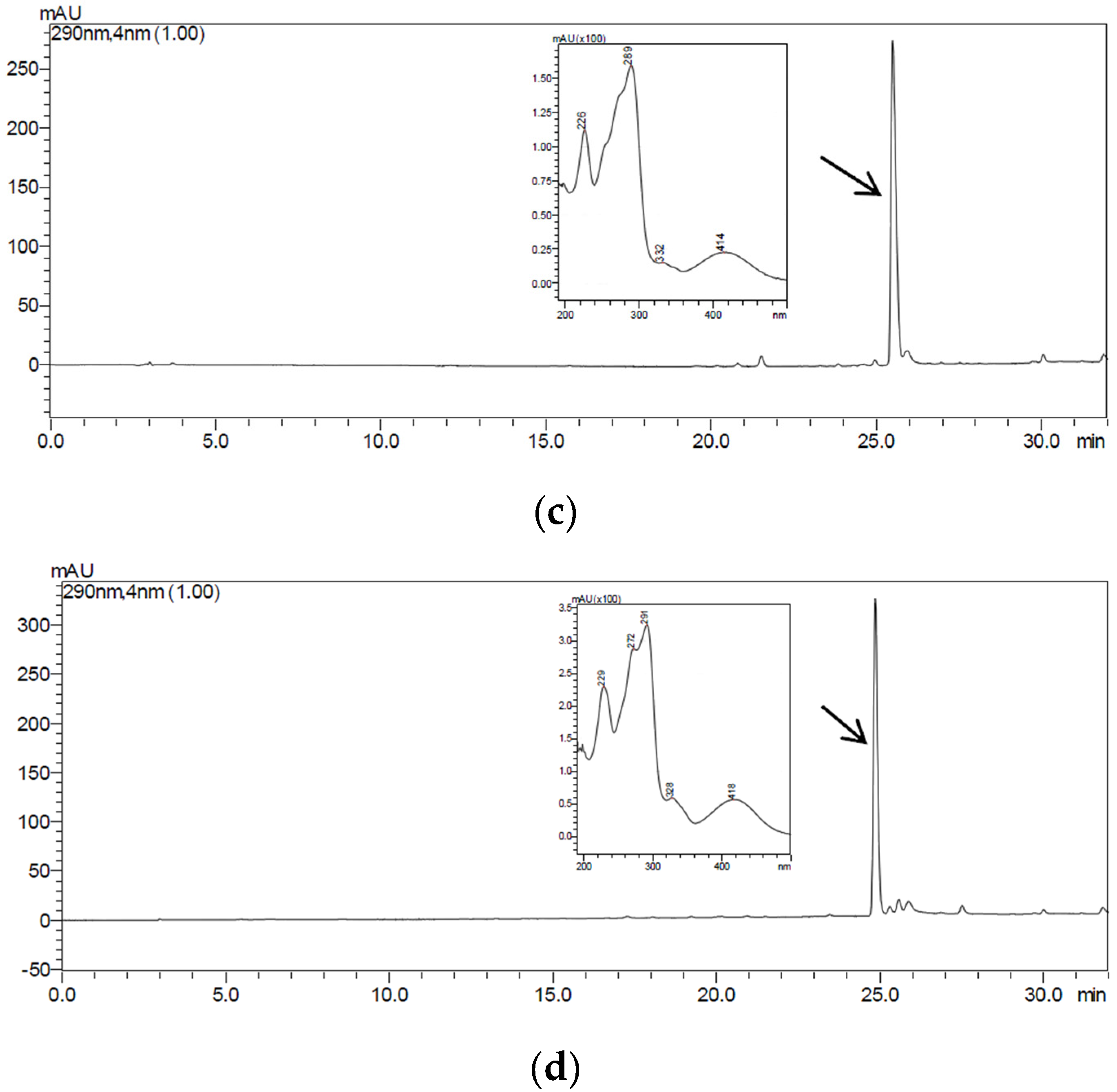
2.4. Purification and Structural Identification of the Compounds
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Rice False Smut Balls
3.3. Preparation of the Crude Extract
3.4. Measurement of Partition Coefficient
3.5. Preparation of the Solvent Systems and Sample Solutions
3.6. HSCCC Separation Procedure
3.7. HPLC Analysis and Identification of Ustilaginoidins
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanaka, E.; Ashizawa, T.; Sonoda, R.; Tanaka, C. Villosiclava virens gen. nov., comb. nov., teleomorph of Ustilaginoidea virens, the causal agent of rice false smut. Mycotaxon 2008, 106, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, L.; Huang, F.; Wang, W. Progress in the study of false smut disease in rice. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, S.A.; Anders, M.M.; Yeater, K.M. Effect of cultural management practices on the severity of false smut and kernel smut of rice. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladhalakshmi, D.; Laha, G.S.; Singh, R.; Karthikeyan, A.; Mangrauthia, S.K.; Sundaram, R.M.; Thukkaiyannan, P.; Viraktamath, B.C. Isolation and characterization of Ustilaginoidea virens and survey of false smut disease of rice in India. Phytoparasitica 2012, 40, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Guo, X.-Y.; Huang, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.-F.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.-J.; Zhao, J.-Q.; Xiong, H.; Yu, J.-J.; et al. Epiphytic colonization of Ustilaginoidea virens on biotic and abiotic surfaces implies the widespread presence of primary inoculum for rice false smut disease. Plant Pathol. 2014, 63, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashizawa, T.; Takahashi, M.; Arai, M.; Arie, T. Rice false smut pathogen, Ustilaginoidea virens, invades through small gap at the apex of a rice spikelet before heading. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2012, 78, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Jin, J.; Hu, D.; Yong, M.; Xu, Y.; He, L. Elucidation of the infection process of Ustilaginoidea virens (teleomorph: Villosiclava virens) in rice spikelets. Plant Pathol. 2013, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lu, S.; Shan, T.; Wang, P.; Sun, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S. Chemistry and biology of mycotoxins from rice false smut pathogen. In Mycotoxins: Properties, Applications and Hazards; Melborn, B.J., Greene, J.C., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Koiso, Y.; Morisaki, N.; Yamashita, Y.; Mitsui, Y.; Shirai, R.; Hashimoto, Y.; Iwasaki, S. Isolation and structure of an antimitotic cyclic peptide, ustiloxin F: Chemical interelation with a homologous peptide, ustiloxin B. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, T.; Sun, W.; Liu, H.; Gao, S.; Lu, S.; Wang, M.; Sun, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L. Determination and analysis of ustiloxins A and B by LC-ESI-MS and HPLC in false smut balls of rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11275–11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, K.; Natori, S. Further characterization of seven bis (naphtho-γ-pyrone) congeners of ustilaginoidins, coloring matters of Claviceps virens (Ustilaginoidea virens). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Tian, J.; Sun, W.; Meng, J.; Wang, X.; Fu, X.; Wang, A.; Lai, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L. Bis-naphtho-γ-pyrones from fungi and their bioactivities. Molecules 2014, 19, 7169–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, K.; Natori, S.; Iitaka, Y. Absolute configurations of chaetochromin A and related bis(naphtho-γ-pyrone) mold metabolites. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 4049–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, T.; Sekita, S.; Koyama, K.; Natori, S.; Takahashi, A. Effect of chaetochromin A, chaetochromin D and ustilaginoidin A, bis (naphtho-γ-pyrone) derivatives, on the mouse embryo limb bud and midbrain cells in culture. Congenit. Anom. 1987, 27, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, K.; Hisada, K.; Mori, S.; Nozawa, Y.; Koyama, K.; Natori, S. The impairing effect of chaetochromin A and related mycotoxins on mitochondrial respiration. Proc. Jpn. Assoc. Mycotoxicol. 1991, 33, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, K.; Ominato, K.; Natori, S.; Tashiro, T.; Tsuruo, T. Cytotoxicity and antitumor activities of fungal bis (naphtho-γ-pyrone) derivatives. J. Pharmacobiodyn. 1988, 11, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Sun, W.; Meng, J.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Tian, J.; Fu, X.; Dai, J.; Liu, Y.; Lai, D.; et al. Bioactive bis-naphtho-γ-pyrones from rice false smut pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3501–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y. Golden rules and pitfalls in selecting optimum conditions for high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1065, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, G.F.; Pro, S.M.; Friesen, J.B. Countercurrent separation of natural products. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1489–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gao, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Han, J.; Yu, Z.; Yang, F. Preparative separation of phenolic compounds from Halimodendron halodendron by high-speed counter-current chromatography. Molecules 2010, 15, 5998–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Mou, Y.; Shan, T.; Li, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhou, L. Preparative separation of helvolic acid from the endophytic fungus Pichia guilliermondii Ppf9 by high-speed counter-current chromatography. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Luo, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, B.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, L. Preparative separation of 3-O-methylkaempferol from Caragana leucophloea by high-speed counter-current chromatography and its antimicrobial activity. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, T.; Lu, S.; Luo, C.; Luo, R.; Mou, Y.; Wang, M.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, L. Preparative separation of spirobisnaphthalenes from endophytic fungus Berkleasmium sp. Dzf12 by high-speed counter-current chromatography. Molecules 2013, 18, 12896–12908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Countercurrent separation of natural products: An update. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1765–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Fu, J.; Di, D. Preparative isolation and purification of steviol glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni using high-speed counter-current chromatography. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, W.; Dong, X.; Xu, D.; Meng, J.; Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Lai, D.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Y. Preparative Separation of Main Ustilaginoidins from Rice False Smut Balls by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography. Toxins 2016, 8, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010020
Sun W, Dong X, Xu D, Meng J, Fu X, Wang X, Lai D, Zhou L, Liu Y. Preparative Separation of Main Ustilaginoidins from Rice False Smut Balls by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography. Toxins. 2016; 8(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Weibo, Xuejiao Dong, Dan Xu, Jiajia Meng, Xiaoxiang Fu, Xiaohan Wang, Daowan Lai, Ligang Zhou, and Yang Liu. 2016. "Preparative Separation of Main Ustilaginoidins from Rice False Smut Balls by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography" Toxins 8, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010020
APA StyleSun, W., Dong, X., Xu, D., Meng, J., Fu, X., Wang, X., Lai, D., Zhou, L., & Liu, Y. (2016). Preparative Separation of Main Ustilaginoidins from Rice False Smut Balls by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography. Toxins, 8(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8010020









