Revealing the Function and the Structural Model of Ts4: Insights into the “Non-Toxic” Toxin from Tityus serrulatus Venom
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
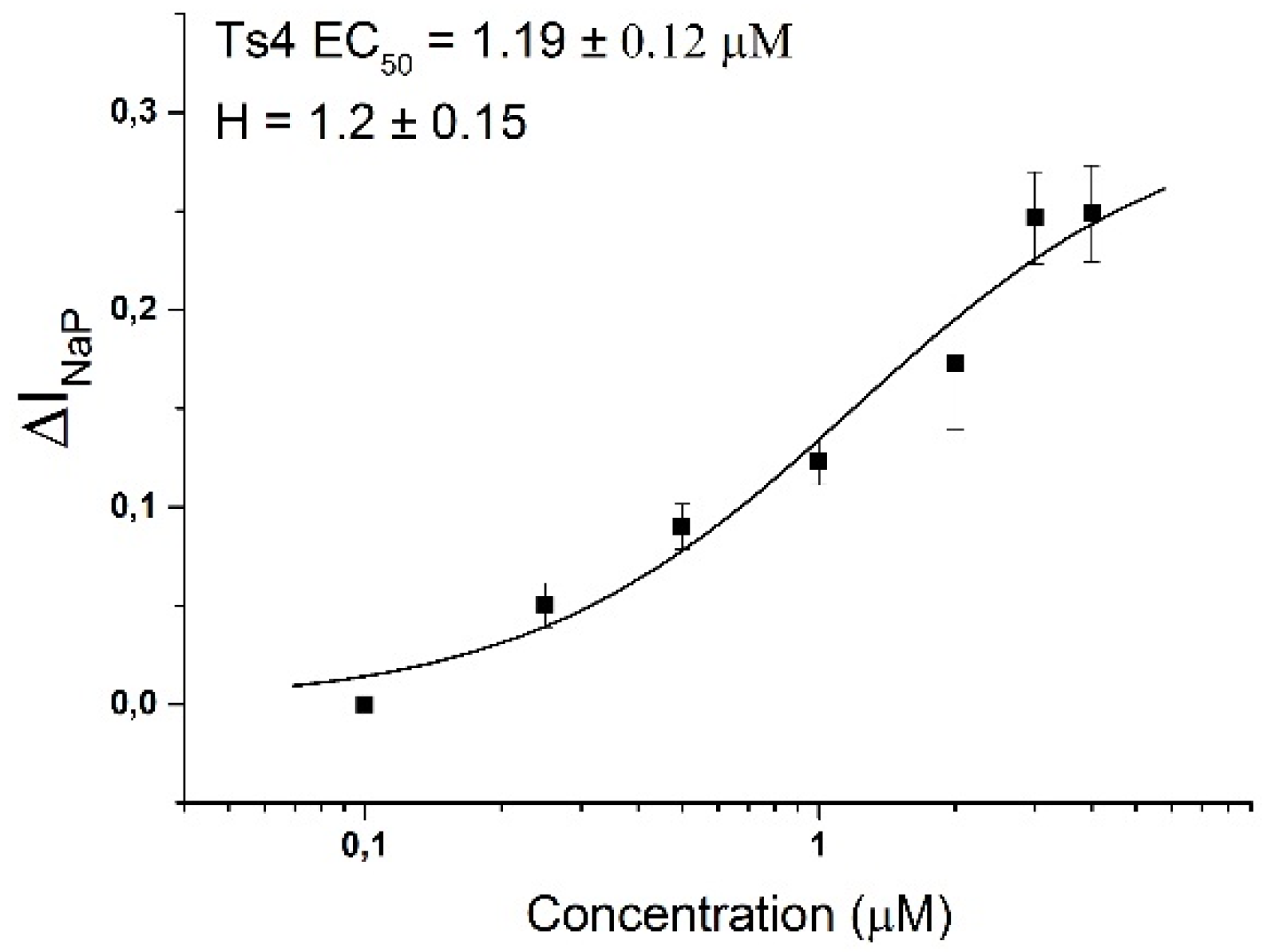
2.1. Ts4 Was Successfully Purified

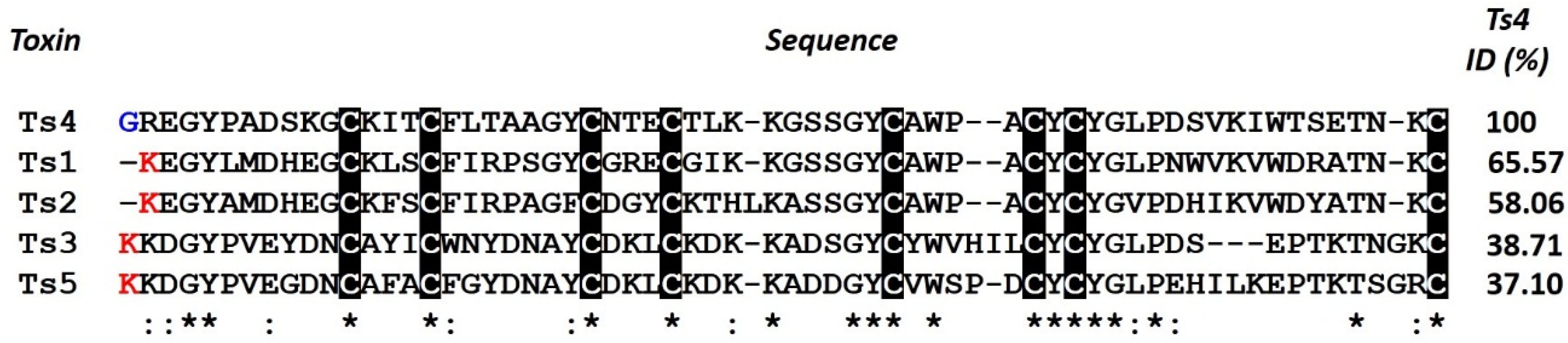
2.3. Ts4 3D-Structural Model and Amino Acids Implicated in Activity
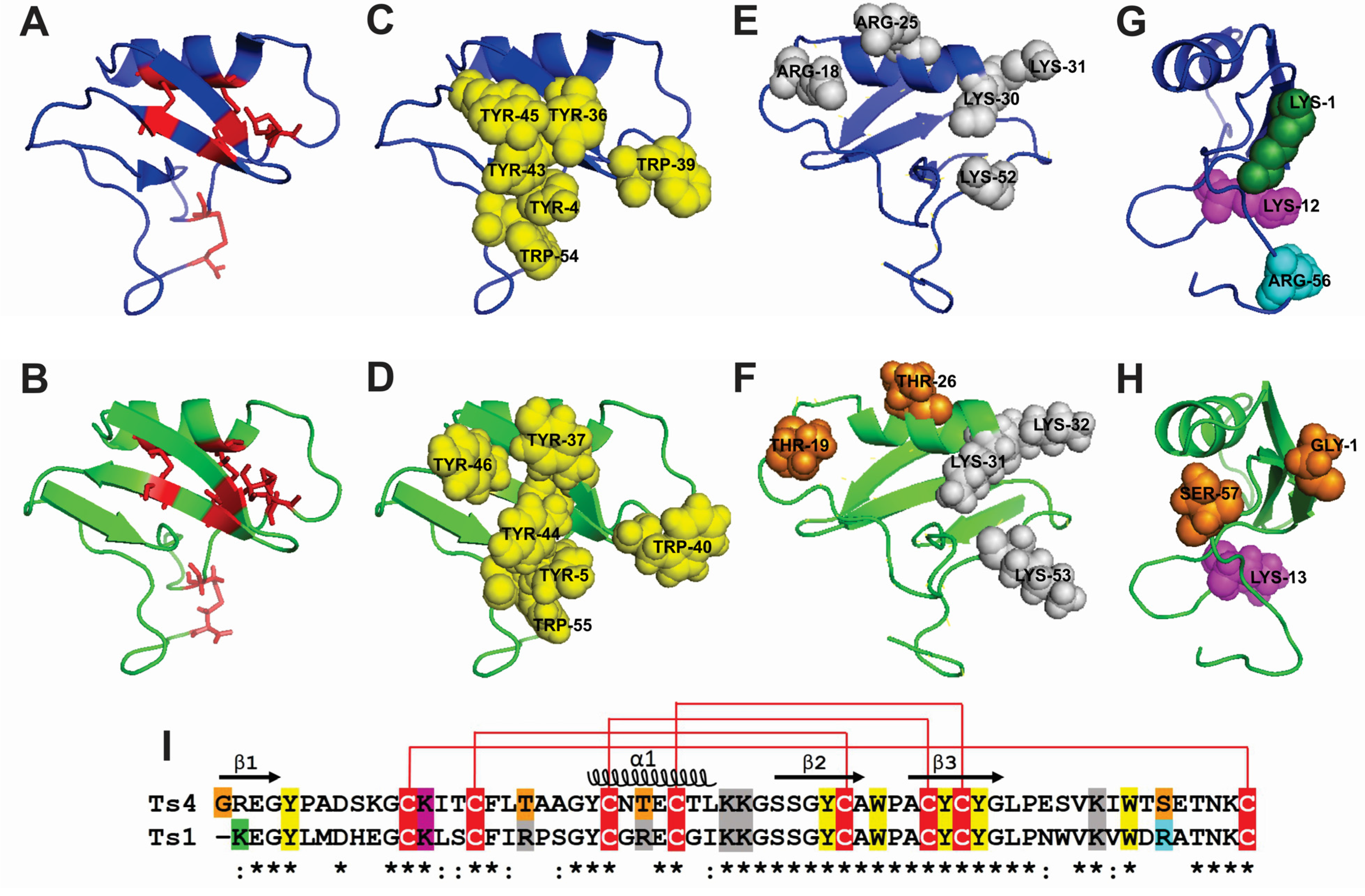
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Ts4 Isolation
4.2. Electrophysiological Experiments
4.2.1. Sodium Channel Expression
4.2.2. Electrophysiological Measurements
4.3. Amino Acid Sequence Alignment and Structural Modeling
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chippaux, J.P.; Goyffon, M. Epidemiology of scorpionism: A global appraisal. Acta Trop. 2008, 107, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucca, M.B.; Oliveira, F.N.; Schwartz, E.F.; Arantes, E.C.; Lira-da-Silva, R.M. Scorpionism and dangerous species of Brazil. In Scorpion Venoms; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 4, pp. 299–324. [Google Scholar]
- Verano-Braga, T.; Rocha-Resende, C.; Silva, D.M.; Ianzer, D.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Bougis, P.E.; de Lima, M.E.; Santos, R.A.; Pimenta, A.M. Tityus serrulatus hypotensins: A new family of peptides from scorpion venom. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 371, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessini, A.C.; Takao, T.T.; Cavalheiro, E.C.; Vichnewski, W.; Sampaio, S.V.; Giglio, J.R.; Arantes, E.C. A hyaluronidase from Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom: isolation, characterization and inhibition by flavonoids. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.A.; Alves, E.W.; Henriques, O.B. Peptide T, a novel bradykinin potentiator isolated from Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom. Toxicon 1993, 31, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cologna, C.T.; Marcussi, S.; Giglio, J.R.; Soares, A.M.; Arantes, E.C. Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom and toxins: An overview. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmo, A.O.; Oliveira-Mendes, B.B.; Horta, C.C.; Magalhaes, B.F.; Dantas, A.E.; Chaves, L.M.; Chavez-Olortegui, C.; Kalapothakis, E. Molecular and functional characterization of metalloserrulases, new metalloproteases from the Tityus serrulatus venom gland. Toxicon 2014, 90, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarenga, E.R.; Mendes, T.M.; Magalhaes, B.F.; Siqueira, F.F.; Dantas, A.E.; Barroca, T.M.; Horta, C.C.; Kalapothakis, E. Transcriptome analysis of the Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom gland. Open J. Genet. 2012, 2, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril, B.; Marangoni, S.; Possani, L.D. Toxins and genes isolated from scorpions of the genus Tityus. Toxicon 1997, 35, 821–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, E.; Gurrola, G.B.; Schwartz, E.F.; Possani, L.D. Scorpion venom components as potential candidates for drug development. Toxicon 2015, 93, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possani, L.D.; Becerril, B.; Delepierre, M.; Tytgat, J. Scorpion toxins specific for Na+-channels. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosmans, F.; Tytgat, J. Voltage-gated sodium channel modulation by scorpion alpha-toxins. Toxicon 2007, 49, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, H.; Moran, Y.; Gordon, D.; Turkov, M.; Kahn, R.; Gurevitz, M. Positions under positive selection—Key for selectivity and potency of scorpion alpha-toxins. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Ayeb, M.; Darbon, H.; Bahraoui, E.M.; Vargas, O.; Rochat, H. Differential effects of defined chemical modifications on antigenic and pharmacological activities of scorpion alpha and beta toxins. Eur. J. Biochem. 1986, 155, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordon, K.C.F.; Cologna, C.T.; Arantes, E.C. Scorpion venom research around the world: Tityus serrulatus. In Scorpion Venoms; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Possani, L.D., Schwartz, E.F., de la Vega, R.C.R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 4, pp. 411–437. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, Y.; Leppla, S.H.; Bhatnagar, R.; Friedlander, A.M. Internalization and processing of Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin by toxin-sensitive and -resistant cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 11099–11102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bosmans, F.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Swartz, K.J. Deconstructing voltage sensor function and pharmacology in sodium channels. Nature 2008, 456, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tytgat, J.; Chandy, K.G.; Garcia, M.L.; Gutman, G.A.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; van der Walt, J.J.; Possani, L.D. A unified nomenclature for short-chain peptides isolated from scorpion venoms: alpha-KTx molecular subfamilies. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999, 20, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez de la Vega, R.C.; Possani, L.D. Current views on scorpion toxins specific for K+-channels. Toxicon 2004, 43, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peigneur, S.; Cologna, C.T.; Cremonez, C.M.; Mille, B.G.; Pucca, M.B.; Cuypers, E.; Arantes, E.C.; Tytgat, J. A gamut of undiscovered electrophysiological effects produced by Tityus serrulatus toxin 1 on Na-type isoforms. Neuropharmacology 2015, 95, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, V.A.; Cremonez, C.M.; Anjolette, F.A.; Aguiar, J.F.; Varanda, W.A.; Arantes, E.C. Functional and structural study comparing the C-terminal amidated beta-neurotoxin Ts1 with its isoform Ts1-G isolated from Tityus serrulatus venom. Toxicon 2014, 83, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cologna, C.T.; Peigneur, S.; Rustiguel, J.K.; Nonato, M.C.; Tytgat, J.; Arantes, E.C. Investigation of the relationship between the structure and function of Ts2, a neurotoxin from Tityus serrulatus venom. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucca, M.B.; Peigneur, S.; Cologna, C.T.; Cerni, F.A.; Zoccal, K.F.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Faccioli, L.H.; Tytgat, J.; Arantes, E.C. Electrophysiological characterization of the first Tityus serrulatus alpha-like toxin, Ts5: Evidence of a pro-inflammatory toxin on macrophages. Biochimie 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerni, F.A.; Pucca, M.B.; Peigneur, S.; Cremonez, C.M.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Tytgat, J.; Arantes, E.C. Electrophysiological characterization of Ts6 and Ts7, K+ channel toxins isolated through an improved Tityus serrulatus venom purification procedure. Toxins 2014, 6, 892–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cologna, C.T.; Peigneur, S.; Rosa, J.C.; Selistre-de-Araujo, H.S.; Varanda, W.A.; Tytgat, J.; Arantes, E.C. Purification and characterization of Ts15, the first member of a new alpha-KTX subfamily from the venom of the Brazilian scorpion Tityus serrulatus. Toxicon 2011, 58, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saucedo, A.L.; Flores-Solis, D.; de la Vega, R.C.R.; Ramirez-Cordero, B.; Hernandez-Lopez, R.; Cano-Sanchez, P.; Navarro, R.N.; Garcia-Valdes, J.; Coronas-Valderrama, F.; de Roodt, A.; et al. New tricks of an old pattern structural versatility of scorpion toxins with common cysteine spacing. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 12321–12330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangoni, S.; Ghiso, J.; Sampaio, S.V.; Arantes, E.C.; Giglio, J.R.; Oliveira, B.; Frangione, B. The complete amino acid sequence of toxin TsTX-VI isolated from the venom of the scorpion Tityus serrulatus. J. Protein Chem. 1990, 9, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M. The scorpion envenoming syndrome. Toxicon 1995, 33, 825–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, S.V.; Coutinho-Netto, J.; Arantes, E.C.; Marangoni, S.; Oliveira, B.; Giglio, J.R. Isolation of toxin TsTX-VI from Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom. Effects on the release of neurotransmitters from synaptosomes. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1996, 39, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, P.E.; Wheeler, M.B. Voltage-dependent K+ channels in pancreatic beta cells: Role, regulation and potential as therapeutic targets. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1046–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashimoto, T.; Ueno, S.; Koga, T.; Fukudome, S.; Ehara, H.; Komai, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Susa, N. The Aromatic Ring of Phenylalanine 334 Is Essential for Oligomerization of Vibrio vulnificus Hemolysin. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbalat, R.; Ewald, S.E.; Mouchess, M.L.; Barton, G.M. Nucleic acid recognition by the innate immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indarte, M.; Madura, J.D.; Surratt, C.K. Dopamine transporter comparative molecular modeling and binding site prediction using the LeuT(Aa) leucine transporter as a template. Proteins-Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2008, 70, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, B.J.; Ehrlich, E.S.; Short, L.; Yu, Y.K.; Xiao, Z.X.; Yu, X.F.; Xiong, Y. Structural insight into the human immunodeficiency virus Vif SOCS box and its role in human E3 ubiquitin ligase assembly. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8656–8663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Levine, S.J. Toll-like receptor, RIG-I-like receptors and the NLRP3 inflammasome: Key modulators of innate immune responses to double-stranded RNA viruses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011, 22, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, S.; Gerzanich, V.; Chen, M.; Dong, Y.; Shuba, Y.; Simard, J.M. Chlorotoxin-sensitive Ca2+-activated Cl-channel in type R2 reactive astrocytes from adult rat brain. Glia 2003, 42, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBin, J.A.; Maggio, J.E.; Strichartz, G.R. Purification and characterization of chlorotoxin, a chloride channel ligand from the venom of the scorpion. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 264, C361–C369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fischer, F.G.; Bohn, H. Venoms of the Brazilian scorpions Tityus serrulatus and Tityus bahiensis. Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 1957, 306, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, C.R.; Valeri, V. Effects of a toxin present in a purified extract of telsons from the scorpion Tityus serrulatus on smooth muscle preparations and in mice. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1959, 121, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gomez, M.V.; Diniz, C.R. Separation of toxic components from the brazillian scorpion Tityus serrulatus venom. Mem. Inst. Butantan. 1966, 33, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arantes, E.C.; Prado, W.A.; Sampaio, S.V.; Giglio, J.R. A simplified procedure for the fractionation of Tityus serrulatus venom: Isolation and partial characterization of TsTX-IV, a new neurotoxin. Toxicon 1989, 27, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guatimosim, S.C.; Prado, V.F.; Diniz, C.R.; Chavez-Olortegui, C.; Kalapothakis, E. Molecular cloning and genomic analysis of TsNTxp: an immunogenic protein from Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom. Toxicon 1999, 37, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, L.M.; Diniz, C.R.; Granier, C.; Chavez-Olortegui, C. Induction of neutralizing antibodies against Tityus serrulatus scorpion toxins by immunization with a mixture of defined synthetic epitopes. Toxicon 2002, 40, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Ferreira, A.M.B.; Kalapothakis, E.; Diniz, C.R.; Chavez-Olortegui, C. In vivo protection against Tityus serrulatus scorpion toxins by immunization of mice with a non-toxic protein. Toxicon 1998, 36, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Olortegui, C.; Molina, F.; Granier, C. Molecular basis for the cross-reactivity of antibodies elicited by a natural anatoxin with alpha- and beta-toxins from the venom of Tityus serrulatus scorpion. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 38, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Olortegui, C.; Kalapothakis, E.; Ferreira, A.M.; Ferreira, A.P.; Diniz, C.R. Neutralizing capacity of antibodies elicited by a non-toxic protein purified from the venom of the scorpion Tityus serrulatus. Toxicon 1997, 35, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroui, S.; Ram, N.; Appaix, F.; Ronjat, M.; Kenani, A.; Pirollet, F.; de Waard, M. Maurocalcine as a non toxic drug carrier overcomes doxorubicin resistance in the cancer cell line MDA-MB 231. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, S.; Castro, M.S.; Barbosa, J.A.; Fontes, W.; Schwartz, E.N.; Sebben, A.; Pires, O.R., Jr.; Sousa, M.V.; Schwartz, C.A. Purification and primary structure determination of Tf4, the first bioactive peptide isolated from the venom of the Brazilian scorpion Tityus fasciolatus. Toxicon 2003, 41, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldin, A.L. Resurgence of sodium channel research. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2001, 63, 871–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargus, N.J.; Nigam, A.; Bertram, E.H., 3rd; Patel, M.K. Evidence for a role of Nav1.6 in facilitating increases in neuronal hyperexcitability during epileptogenesis. J. Neurophysiol. 2013, 110, 1144–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogawski, M.A.; Loscher, W. The neurobiology of antiepileptic drugs. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilha, L.; Cendes, F.; Ghizoni, E.; Vieira, R.J.; Li, L.M. Epilepsy due to a destructive brain lesion caused by a scorpion sting. Arch. Neurol. 2004, 61, 1294–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, C.; Camfield, C. Modes of onset of epilepsy and differential diagnosis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 111, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levin, V.A. Relationship of octanol/water partition coefficient and molecular weight to rat brain capillary permeability. J. Med. Chem. 1980, 23, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajouhesh, H.; Lenz, G.R. Medicinal chemical properties of successful central nervous system drugs. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omidi, Y.; Barar, J. Impacts of blood-brain barrier in drug delivery and targeting of brain tumors. Bioimpacts 2012, 2, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oller-Salvia, B.; Teixido, M.; Giralt, E. From venoms to BBB shuttles: Synthesis and blood-brain barrier transport assessment of apamin and a nontoxic analog. Biopolymers 2013, 100, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kievit, F.M.; Veiseh, O.; Fang, C.; Bhattarai, N.; Lee, D.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Zhang, M. Chlorotoxin labeled magnetic nanovectors for targeted gene delivery to glioma. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4587–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccal, K.F.; Bitencourt, C.S.; Paula-Silva, F.W.; Sorgi, C.A.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Arantes, E.C.; Faccioli, L.H. TLR2, TLR4 and CD14 recognize venom-associated molecular patterns from Tityus serrulatus to induce macrophage-derived inflammatory mediators. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccal, K.F.; Bitencourt, C.S.; Secatto, A.; Sorgi, C.A.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Sampaio, S.V.; Arantes, E.C.; Faccioli, L.H. Tityus serrulatus venom and toxins Ts1, Ts2 and Ts6 induce macrophage activation and production of immune mediators. Toxicon 2011, 57, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccal, K.F.; Bitencourt, C.S.; Sorgi, C.A.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Sampaio, S.V.; Arantes, E.C.; Faccioli, L.H. Ts6 and Ts2 from Tityus serrulatus venom induce inflammation by mechanisms dependent on lipid mediators and cytokine production. Toxicon 2013, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petricevich, V.L. Scorpion venom and the inflammatory response. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petricevich, V.L. Effect of Tityus serrulatus venom on cytokine production and the activity of murine macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2002, 11, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petricevich, V.L.; Reynaud, E.; Cruz, A.H.; Possani, L.D. Macrophage activation, phagocytosis and intracellular calcium oscillations induced by scorpion toxins from Tityus serrulatus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 154, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrithers, M.D.; Dib-Hajj, S.; Carrithers, L.M.; Tokmoulina, G.; Pypaert, M.; Jonas, E.A.; Waxman, S.G. Expression of the voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1.5 in the macrophage late endosome regulates endosomal acidification. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 7822–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaïr-Yousfi, I.; Laraba-Djebari, F.; Hammoudi-Triki, D. Androctonus australis hector venom contributes to the interaction between 2 neuropeptides and mast cells in pulmonary hyperresponsiveness. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landon, C.; Sodano, P.; Cornet, B.; Bonmatin, J.M.; Kopeyan, C.; Rochat, H.; Vovelle, F.; Ptak, M. Refined solution structure of the anti-mammal and anti-insect LqqIII scorpion toxin: comparison with other scorpion toxins. Proteins 1997, 28, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Wang, D.C.; Zeng, Z.H.; Jin, L.; Hu, R.Q. Crystal structure of an acidic neurotoxin from scorpion Buthus martensii Karsch at 1.85 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 261, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontecillacamps, J.C.; Almassy, R.J.; Ealick, S.E.; Suddath, F.L.; Watt, D.D.; Feldmann, R.J.; Bugg, C.E. Architecture of Scorpion Neurotoxins—A class of membrane-binding proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1981, 6, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possani, L.D.; Martin, B.M.; Svendsen, I.; Rode, G.S.; Erickson, B.W. Scorpion toxins from Centruroides noxius and Tityus serrulatus. Primary structures and sequence comparison by metric analysis. Biochem. J. 1985, 229, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kharrat, R.; Darbon, H.; Granier, C.; Rochat, H. Structure-activity relationships of scorpion alpha-neurotoxins: contribution of arginine residues. Toxicon 1990, 28, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbon, H.; Jover, E.; Couraud, F.; Rochat, H. Alpha-scorpion neurotoxin derivatives suitable as potential markers of sodium channels. Preparation and characterization. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1983, 22, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, C.B.; Marangoni, S.; Toyama, M.H.; Polikarpov, I. Structural analysis of Tityus serrulatus Ts1 neurotoxin at atomic resolution: Insights into interactions with Na+ channels. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2003, 59, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarchum, I.; Pamer, E.G. Regulation of innate and adaptive immunity by the commensal microbiota. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, R.M.; Farrell, P.M. A portable device for the electrical extraction of scorpion venom. Toxicon 2011, 57, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edman, P.; Begg, G. A protein sequenator. Eur. J. Biochem. 1967, 1, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liman, E.R.; Tytgat, J.; Hess, P. Subunit stoichiometry of a mammalian K+ channel determined by construction of multimeric cDNAs. Neuron 1992, 9, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, G.; Liman, E.R.; Logothetis, D.E.; Nadal-Ginard, B.; Hess, P. Gating mechanism of a cloned potassium channel expressed in frog oocytes and mammalian cells. Neuron 1990, 4, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikarpov, I.; Junior, M.S.; Marangoni, S.; Toyama, M.H.; Teplyakov, A. Crystal structure of neurotoxin Ts1 from Tityus serrulatus provides insights into the specificity and toxicity of scorpion toxins. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 290, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Peigneur, S.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Tytgat, J.; Arantes, E.C. Revealing the Function and the Structural Model of Ts4: Insights into the “Non-Toxic” Toxin from Tityus serrulatus Venom. Toxins 2015, 7, 2534-2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072534
Pucca MB, Cerni FA, Peigneur S, Bordon KCF, Tytgat J, Arantes EC. Revealing the Function and the Structural Model of Ts4: Insights into the “Non-Toxic” Toxin from Tityus serrulatus Venom. Toxins. 2015; 7(7):2534-2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072534
Chicago/Turabian StylePucca, Manuela B., Felipe A. Cerni, Steve Peigneur, Karla C. F. Bordon, Jan Tytgat, and Eliane C. Arantes. 2015. "Revealing the Function and the Structural Model of Ts4: Insights into the “Non-Toxic” Toxin from Tityus serrulatus Venom" Toxins 7, no. 7: 2534-2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072534
APA StylePucca, M. B., Cerni, F. A., Peigneur, S., Bordon, K. C. F., Tytgat, J., & Arantes, E. C. (2015). Revealing the Function and the Structural Model of Ts4: Insights into the “Non-Toxic” Toxin from Tityus serrulatus Venom. Toxins, 7(7), 2534-2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7072534