Further Insights into Brevetoxin Metabolism by de Novo Radiolabeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
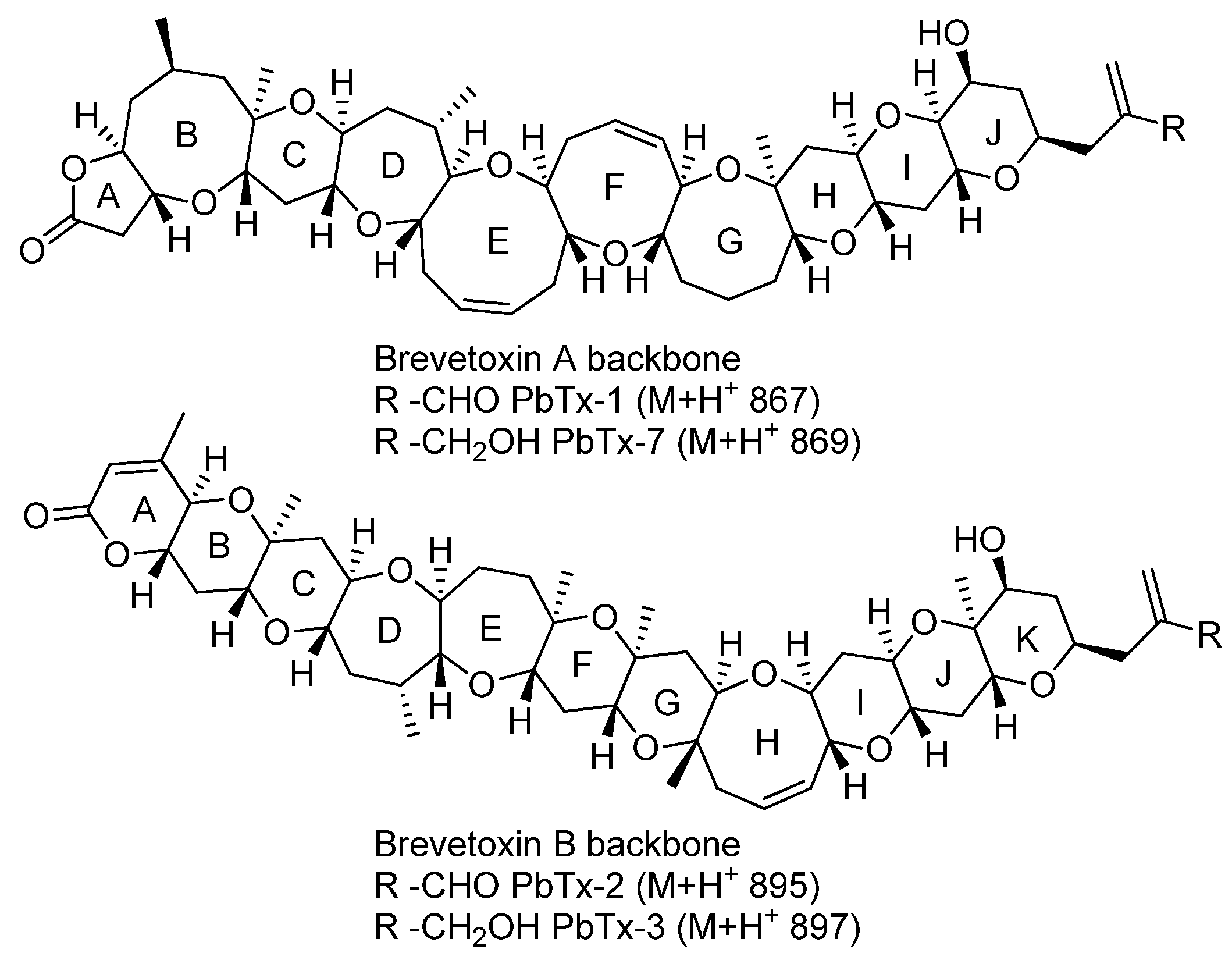
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Culture Growth Rates
2.2. Metabolomic Profiling
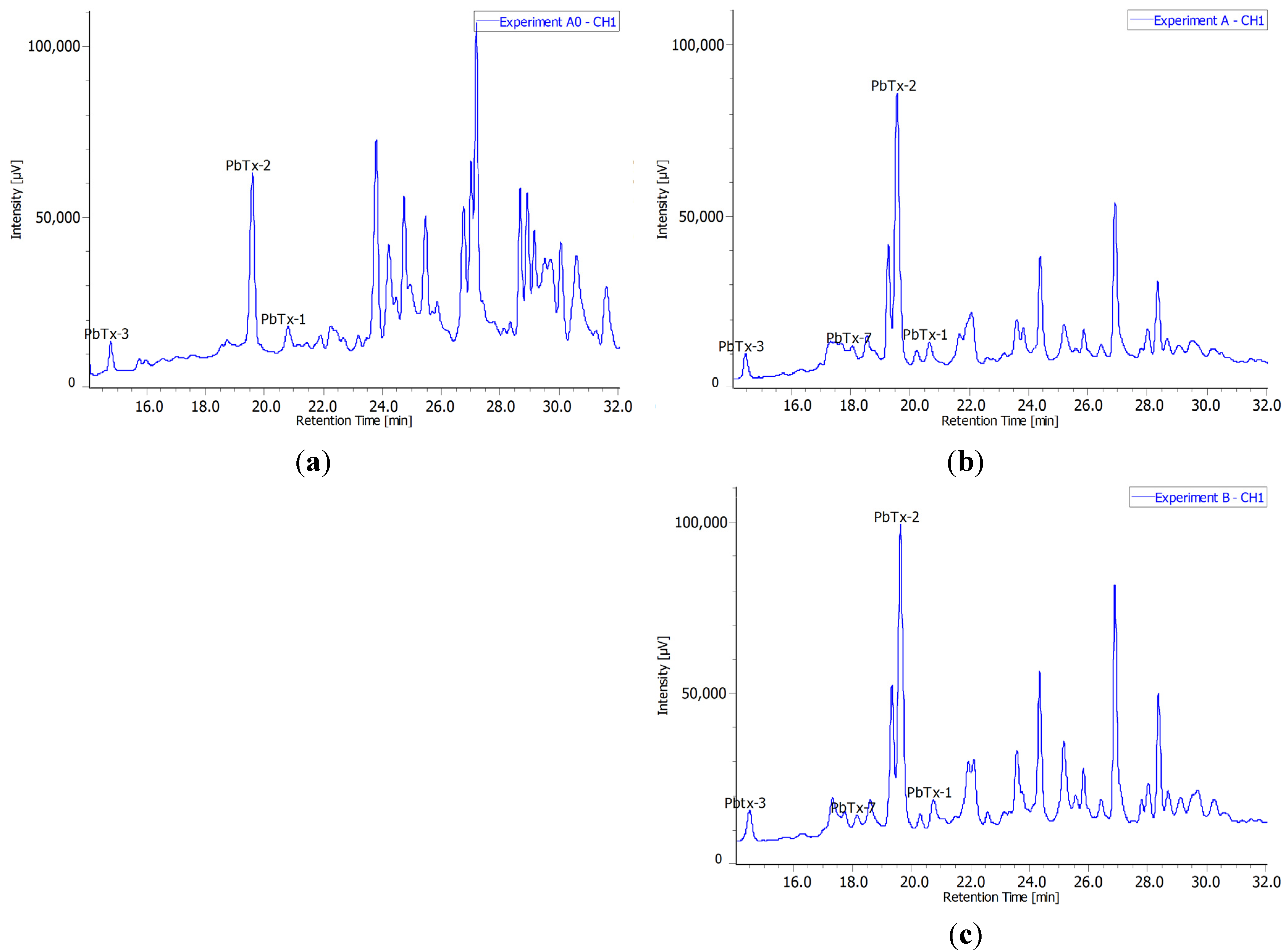
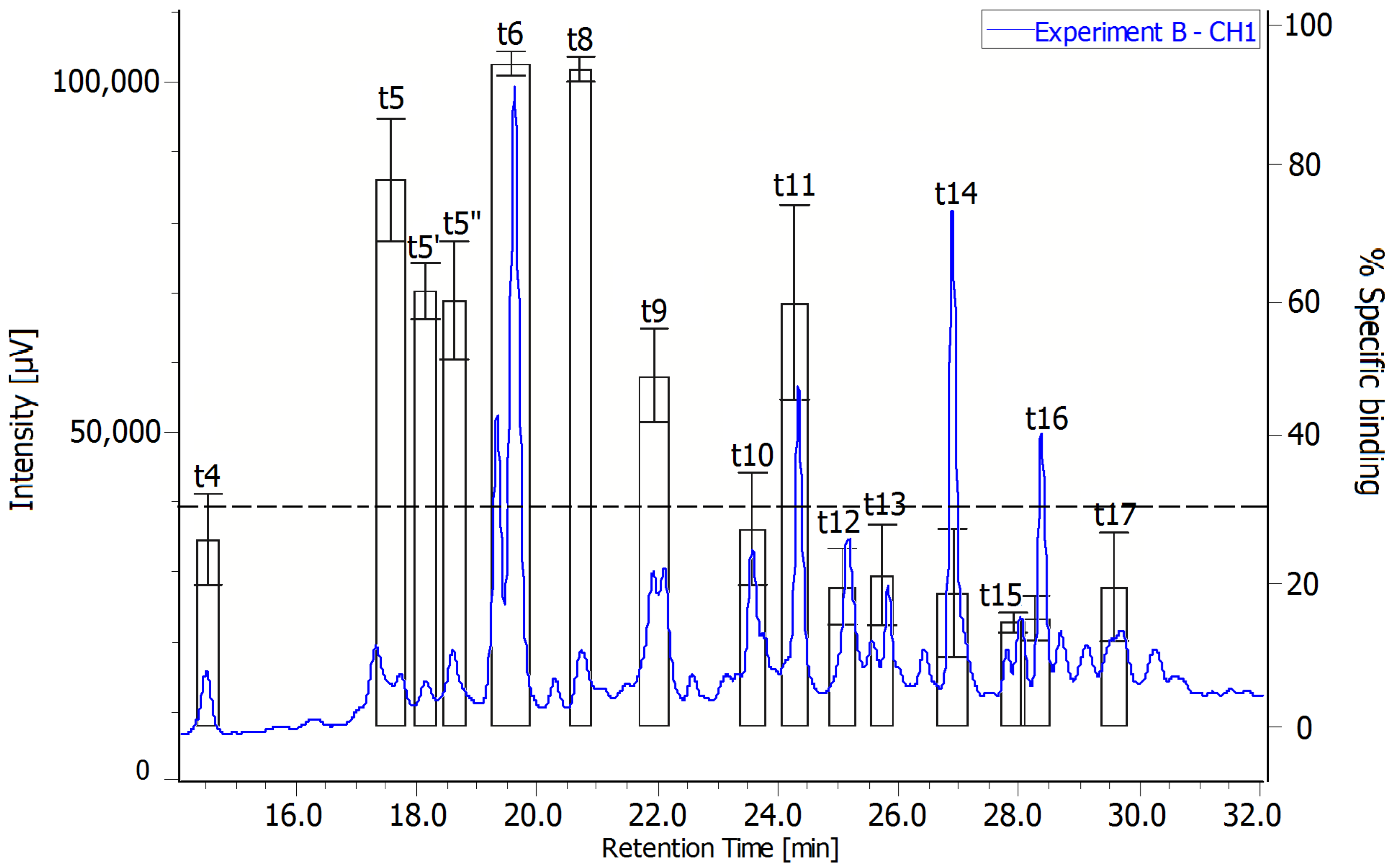
2.3. Radiochromatograms and Specific Activity
| Experiment | Toxin | Quantity (nmol) | Radioactivity (Bq) | Specific Activty (Bq·nmol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | PbTx-2 | 18 | 55 | 3.1 |
| B | PbTx-2 | 13 | 8.9 | 0.67 |
| PbTx-3 | 9.7 | 15 | 1.5 | |
| PbTx-1 | 1.9 | 15 | 7.9 | |
| PbTx-7 | 2.5 | 27 | 11 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture Maintenance and Counting
3.2. Feeding with of Labeled Sodium Acetate
3.2.1. First Set of Experiments

3.2.2. Second Set of Experiments
3.3. Extraction of Metabolites
3.4. Receptor Binding Assay
3.5. Analytical Methods
3.5.1. Liquid Chromatography
3.5.2. Identification of the Metabolite by HRESIMS
3.5.3. Quantification of PbTxs by UHPLC-UV
3.5.4. Quantification of the Radioactivity by Radio-Thin Layer Chromatography and Specific Activity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Landsberg, J.H.; Flewelling, L.J.; Naar, J. Karenia brevis red tides, brevetoxins in the food web, and impacts on natural resources: Decadal advancements. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flewelling, L.J.; Naar, J.P.; Abbott, J.P.; Baden, D.G.; Barros, N.B.; Bossart, G.D.; Bottein, M.-Y.D.; Hammond, D.G.; Haubold, E.M.; Heil, C.A.; et al. Brevetoxicosis: Red tides and marine mammal mortalities. Nature 2005, 435, 755–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagoner, R.M.; Satake, M.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Baden, D.G.; Wright, J.L.C. Absolute configuration of brevisamide and brevisin: Confirmation of a universal biosynthetic process for karenia brevis polyethers. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truxal, L.T.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Jacocks, H.; Abraham, W.M.; Baden, D.G. Characterization of tamulamides a and b, polyethers isolated from the marine dinoflagellate karenia brevis. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, P.B.; Twiner, M.J.; Wang, Z.; Bottein Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Doucette, G.J. Fate and distribution of brevetoxin (PbTx) following lysis of karenia brevis by algicidal bacteria, including analysis of open a-ring derivatives. Toxicon 2007, 50, 1175–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdelais, A.J.; Jacocks, H.M.; Wright, J.L.C.; Bigwarfe, P.M., Jr.; Baden, D.G. A new polyether ladder compound produced by the dinoflagellate karenia brevis. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, D.G.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Jacocks, H.; Michelliza, S.; Naar, J. Natural and derivative brevetoxins: Historical background, multiplicity, and effects. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.V.K.; Shimizu, Y. The structure of hemibrevetoxin-b: A new type of toxin in the gulf of mexico red tide organism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 6476–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, J.; Tempesta, M.S.; Golik, J.; Zagorski, M.G.; Lee, M.S.; Nakanishi, K.; Iwashita, T.; Gross, M.L.; Tomer, K.B. Structure of brevetoxin a as constructed from nmr and mass spectral data. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Chou, H.N.; Bando, H.; Van Duyne, G.; Clardy, J. Structure of brevetoxin a (GB-1 toxin), the most potent toxin in the florida red tide organism Gymnodinium breve (Ptychodiscus brevis). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 514–515. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.S.; Repeta, D.J.; Nakanishi, K.; Zagorski, M.G. Biosynthetic origins and assignments of carbon 13 NMR peaks of brevetoxin b. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 7855–7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.N.; Shimizu, Y.; Van Duyne, G.; Clardy, J. Isolation and structures of two new polycyclic ethers from gymnodinium breve davis (=Ptychodiscus brevis). Tetrahedron Lett. 1985, 26, 2865–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golik, J.; James, J.C.; Nakanishi, K.; Lin, Y.Y. The structure of brevetoxin C. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 2535–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-Y.; Risk, M.; Ray, S.M.; van Engen, D.; Clardy, J.; Golik, J.; James, J.C.; Nakanishi, K. Isolation and structure of brevetoxin b from the “red tide” dinoflagellate Ptychodiscus brevis (Gymnodinium breve). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 6773–6775. [Google Scholar]
- Morey, J.; Monroe, E.; Kinney, A.; Beal, M.; Johnson, J.; Hitchcock, G.; van Dolah, F. Transcriptomic response of the red tide dinoflagellate, karenia brevis, to nitrogen and phosphorus depletion and addition. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dolah, F.M.; Lidie, K.B.; Monroe, E.A.; Bhattacharya, D.; Campbell, L.; Doucette, G.J.; Kamykowski, D. The florida red tide dinoflagellate karenia brevis: New insights into cellular and molecular processes underlying bloom dynamics. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, E.P.; Jacocks, H.M.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Baden, D.G. Brevenal, a brevetoxin antagonist from karenia brevis, binds to a previously unreported site on mammalian sodium channels. Harmful Algae 2013, 26, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekan, D.K.; Tomas, C.R. The brevetoxin and brevenal composition of three karenia brevis clones at different salinities and nutrient conditions. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errera, R.M.; Bourdelais, A.; Drennan, M.A.; Dodd, E.B.; Henrichs, D.W.; Campbell, L. Variation in brevetoxin and brevenal content among clonal cultures of karenia brevis may influence bloom toxicity. Toxicon 2010, 55, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellmann, R.; Stüken, A.; Orr, R.J.S.; Svendsen, H.M.; Jakobsen, K.S. Biosynthesis and molecular genetics of polyketides in marine dinoflagellates. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1011–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y. Microalgal metabolites. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dolah, F.M.; Zippay, M.L.; Pezzolesi, L.; Rein, K.S.; Johnson, J.G.; Morey, J.S.; Wang, Z.; Pistocchi, R. Subcellular localization of dinoflagellate polyketide synthases and fatty acid synthase activity. J. Phycol. 2013, 49, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, E.A.; Johnson, J.G.; Wang, Z.; Pierce, R.K.; van Dolah, F.M. Characterization and expression of nuclear-encoded polyketide synthases in the brevetoxin-producing dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, E.A.; van Dolah, F.M. The toxic dinoflagellate Karenia brevis encodes novel type I-like polyketide synthases containing discrete catalytic domains. Protist 2008, 159, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Qin, G.; Nakanishi, K.; Zagorski, M.G. Biosynthetic studies of brevetoxins, potent neurotoxins produced by the dinoflagellate gymnodinium breve. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 6234–6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.N.; Shimizu, Y. Biosynthesis of brevetoxins. Evidence for the mixed origin of the backbone carbon chain and possible involvement of dicarboxylic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 2184–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K. The chemistry of brevetoxins: A review. Toxicon 1985, 23, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genta-Jouve, G.; Thomas, O.P. Biosynthesis in marine sponges: The radiolabelling strikes back. Phytochem. Rev. 2013, 12, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genta-Jouve, G.; Cachet, N.; Holderith, S.; Oberhänsli, F.; Teyssié, J.-L.; Jeffree, R.; Al Mourabit, A.; Thomas, O.P. New insight into marine alkaloid metabolic pathways: Revisiting oroidin biosynthesis. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 2298–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Naar, J.; Pauillac, S.; Legrand, A.-M. Ciguatoxins and brevetoxins, neurotoxic polyether compounds active on sodium channels. Toxicon 1999, 37, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Calabro, K.; Guigonis, J.-M.; Teyssié, J.-L.; Oberhänsli, F.; Goudour, J.-P.; Warnau, M.; Bottein, M.-Y.D.; Thomas, O.P. Further Insights into Brevetoxin Metabolism by de Novo Radiolabeling. Toxins 2014, 6, 1785-1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061785
Calabro K, Guigonis J-M, Teyssié J-L, Oberhänsli F, Goudour J-P, Warnau M, Bottein M-YD, Thomas OP. Further Insights into Brevetoxin Metabolism by de Novo Radiolabeling. Toxins. 2014; 6(6):1785-1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061785
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalabro, Kevin, Jean-Marie Guigonis, Jean-Louis Teyssié, François Oberhänsli, Jean-Pierre Goudour, Michel Warnau, Marie-Yasmine Dechraoui Bottein, and Olivier P. Thomas. 2014. "Further Insights into Brevetoxin Metabolism by de Novo Radiolabeling" Toxins 6, no. 6: 1785-1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061785
APA StyleCalabro, K., Guigonis, J.-M., Teyssié, J.-L., Oberhänsli, F., Goudour, J.-P., Warnau, M., Bottein, M.-Y. D., & Thomas, O. P. (2014). Further Insights into Brevetoxin Metabolism by de Novo Radiolabeling. Toxins, 6(6), 1785-1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6061785





