Triggering of Programmed Erythrocyte Death by Alantolactone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion

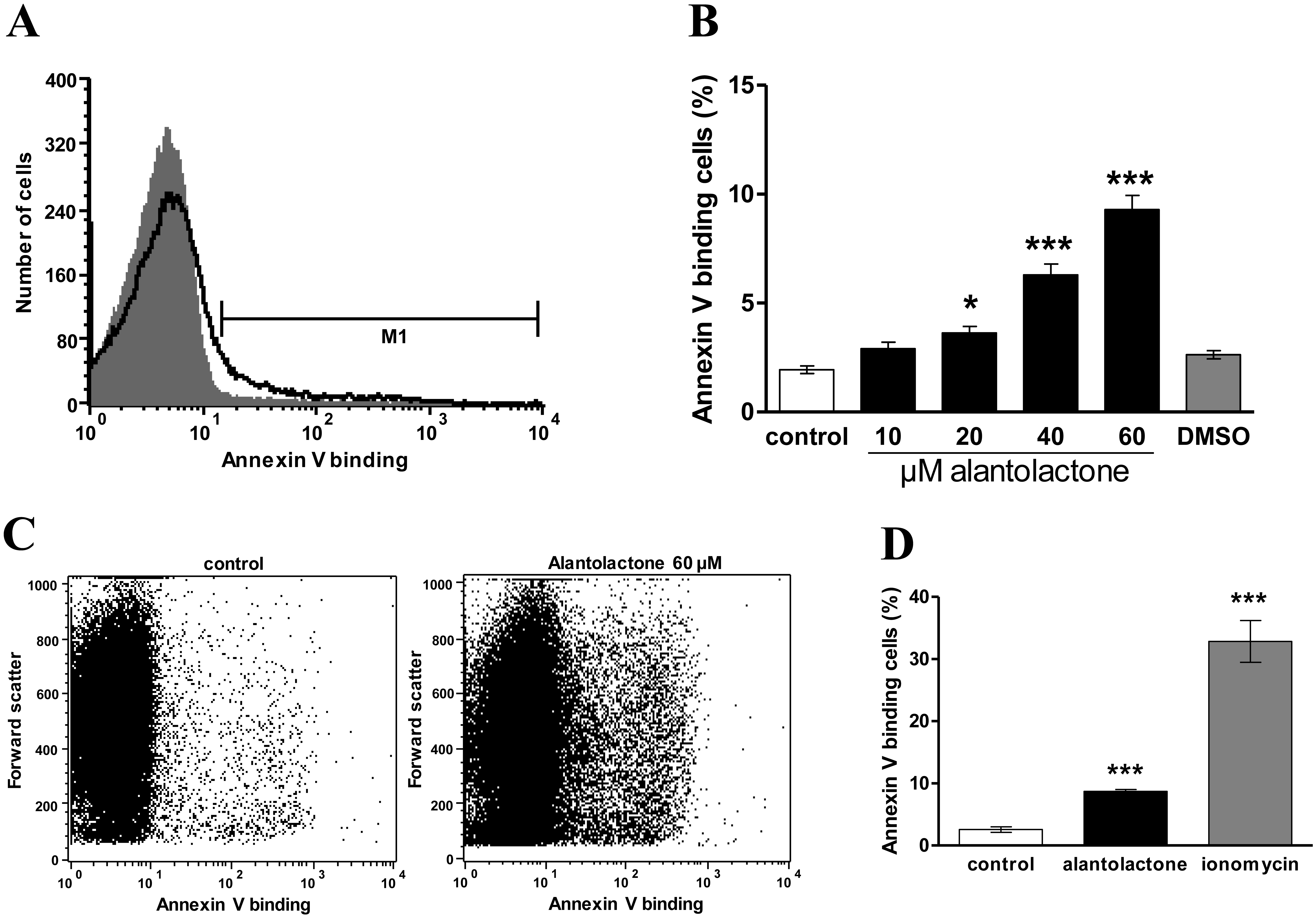

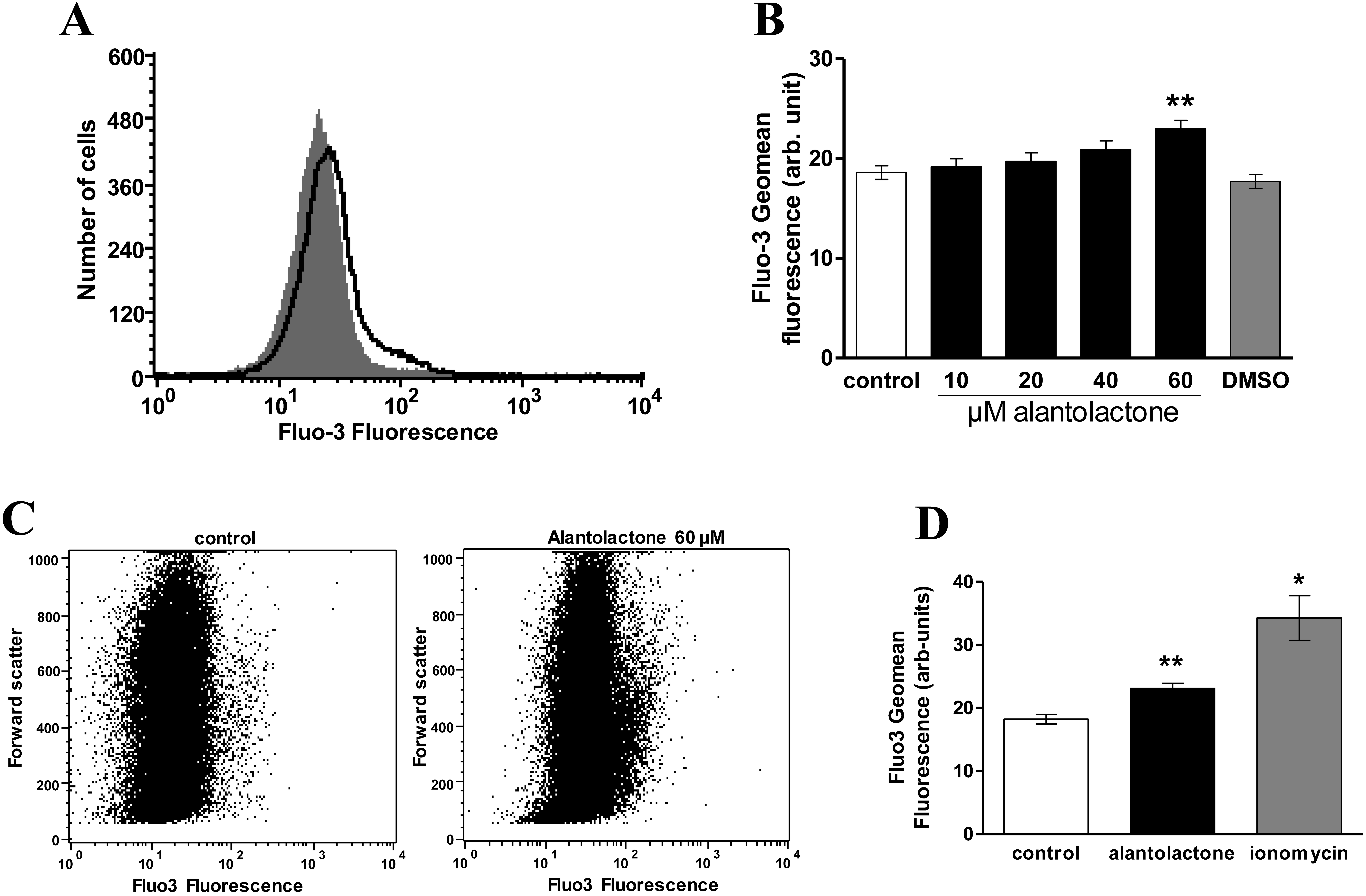
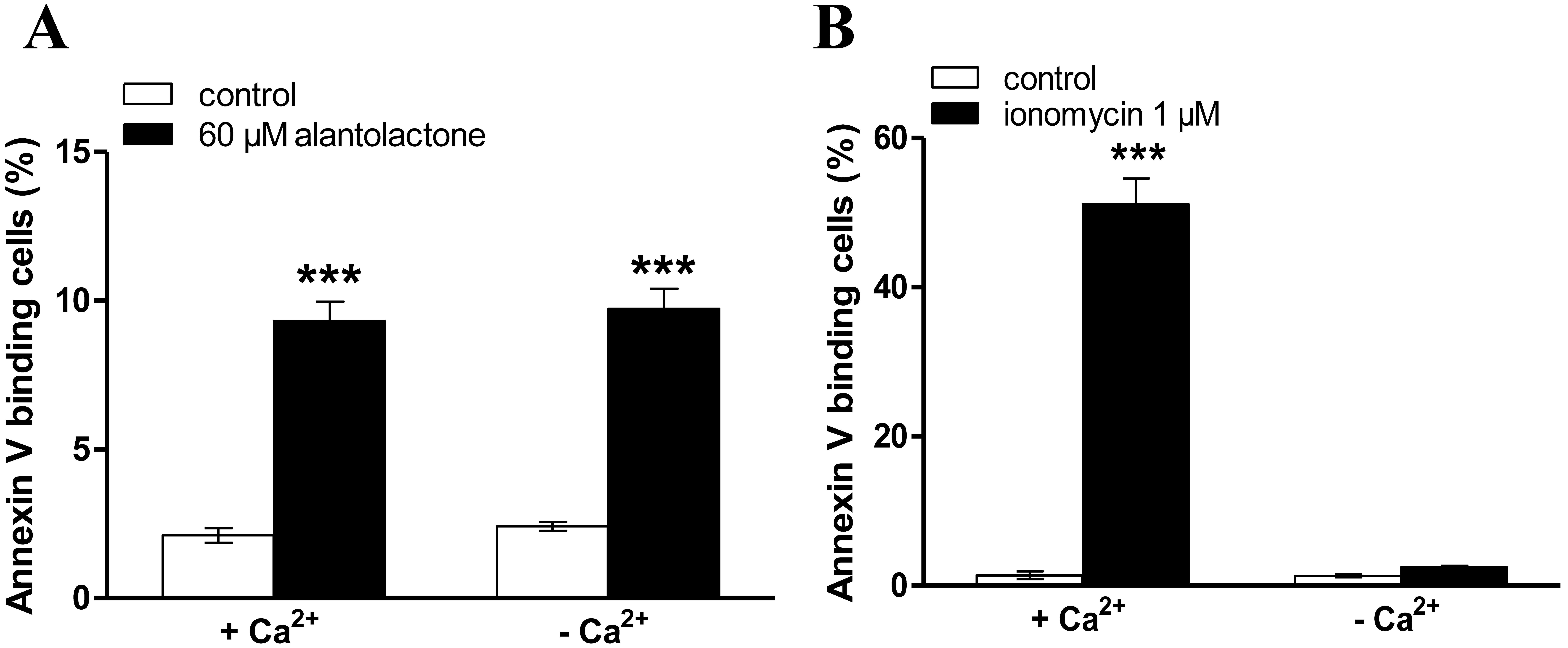
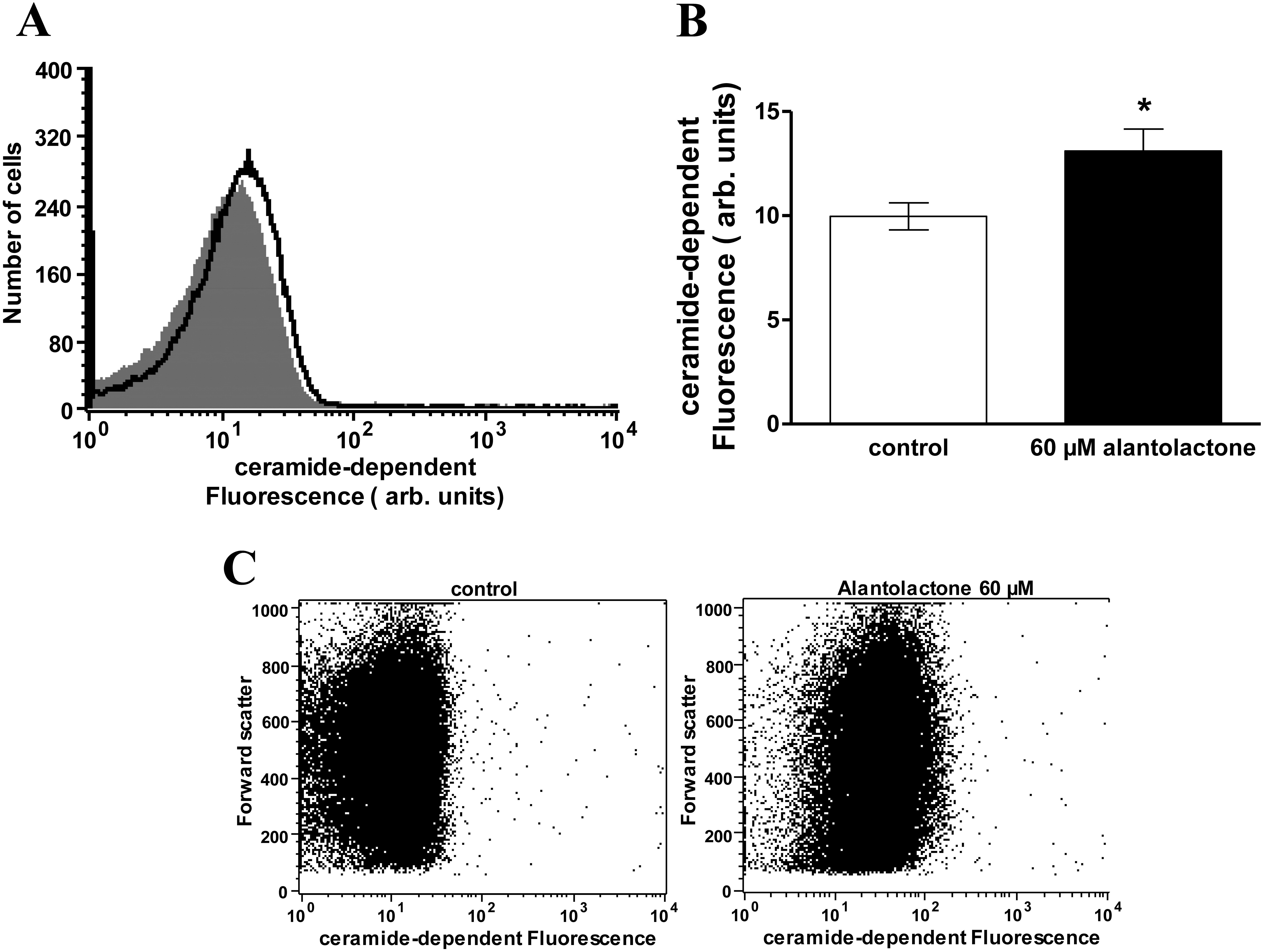
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Erythrocytes, Solutions and Chemicals
3.2. Analysis of Annexin-V-Binding and Forward Scatter
3.3. Measurement of Intracellular Ca2+
3.4. Determination of Ceramide Formation
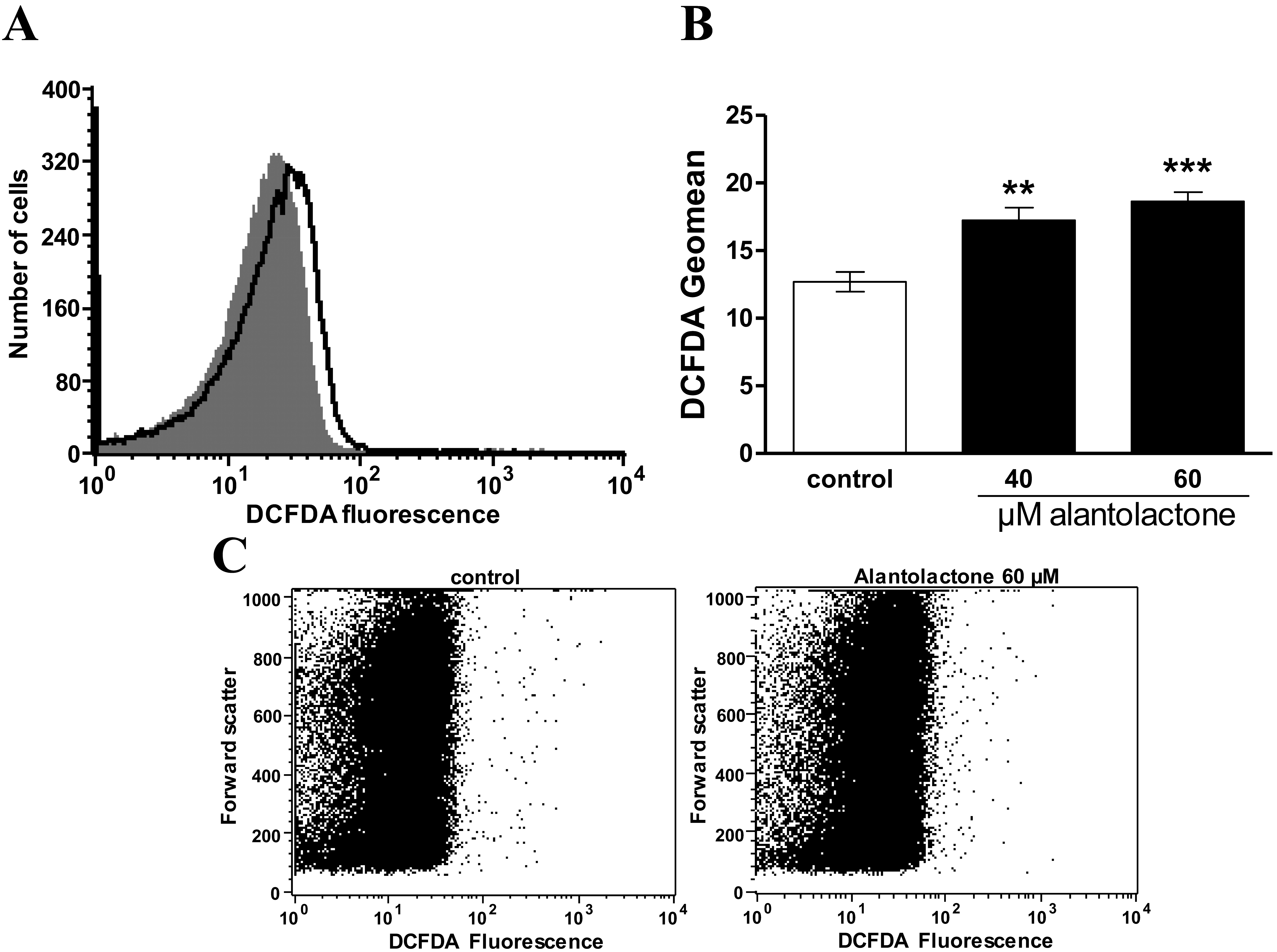
3.5. Determination of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
3.6. Measurement of Phospholipid Translocation
3.7. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasul, A.; Khan, M.; Ali, M.; Li, J.; Li, X. Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer with alantolactone and isoalantolactone. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 248532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirsch, V.M.; Stuppner, H.; Vollmar, A.M. Cytotoxic sesquiterpene lactones mediate their death-inducing effect in leukemia T cells by triggering apoptosis. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Li, T.; Ahmad Khan, M.K.; Rasul, A.; Nawaz, F.; Sun, M.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, T. Alantolactone induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells through GSH depletion, inhibition of STAT3 activation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 719858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Yi, F.; Rasul, A.; Li, T.; Wang, N.; Gao, H.; Gao, R.; Ma, T. Alantolactone induces apoptosis in glioblastoma cells via GSH depletion, ROS generation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. IUBMB Life 2012, 64, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, N.J.; McGown, A.T.; Nduka, J.; Hadfield, J.A.; Pritchard, R.G. Cytotoxic Michael-type amine adducts of alpha-methylene lactones alantolactone and isoalantolactone. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.C.; Yu, J.Q.; Yin, Y.; Liu, Y.W.; Zou, G.L. Alantolactone induces activation of apoptosis in human hepatoma cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3313–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, X.G.; Song, Z.B.; Wu, P.; Zhang, Y.W.; Sun, L.G.; Bao, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.H.; Sun, Y.; Yu, C.L.; et al. Alantolactone induces cell apoptosis partially through down-regulation of testes-specific protease 50 expression. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 224, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, H.C.; Sehar, I.; Bhushan, S.; Gupta, B.D.; Saxena, A.K. Activation of caspases and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage to induce apoptosis in leukemia HL-60 cells by Inula racemosa. Toxicol. Vitr. 2010, 24, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Huang, H.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.X.; Chen, L.; Li, J.M.; Wu, Y.L.; Yan, H. Alantolactone induces apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia sensitive or resistant to imatinib through NF-kappaB inhibition and Bcr/Abl protein deletion. Apoptosis 2013, 18, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Yang, J.; Sun, M.; Yan, J.; Meng, X.; Ma, T. Alantolactone inhibits growth of K562/adriamycin cells by downregulating Bcr/Abl and P-glycoprotein expression. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bao, Y.L.; Wu, Y.; Yu, C.L.; Huang, Y.X.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.H.; Li, Y.X. Alantolactone induces apoptosis in RKO cells through the generation of reactive oxygen species and the mitochondrial pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lang, E.; Qadri, S.M.; Lang, F. Killing me softly—Suicidal erythrocyte death. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, P.A.; Kaiser, S.; Myssina, S.; Wieder, T.; Lang, F.; Huber, S.M. Role of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in human erythrocyte apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2003, 285, C1553–C1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, M.; Towhid, S.T.; Mia, S.; Pakladok, T.; Alesutan, I.; Borst, O.; Gawaz, M.; Gulbins, E.; Lang, F. Sphingomyelinase-induced adhesion of eryptotic erythrocytes to endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012, 303, C991–C999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, F.; Abed, M.; Lang, E.; Foller, M. Oxidative stress and suicidal erythrocyte death. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, S.K.; Bobbala, D.; Xuan, N.T.; Foller, M.; Lang, F. Stimulation of suicidal erythrocyte death by alpha-lipoic acid. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 26, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foller, M.; Feil, S.; Ghoreschi, K.; Koka, S.; Gerling, A.; Thunemann, M.; Hofmann, F.; Schuler, B.; Vogel, J.; Pichler, B.; et al. Anemia and splenomegaly in cGKI-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6771–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foller, M.; Mahmud, H.; Gu, S.; Wang, K.; Floride, E.; Kucherenko, Y.; Luik, S.; Laufer, S.; Lang, F. Participation of leukotriene C(4) in the regulation of suicidal erythrocyte death. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 60, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lau, I.P.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Ong, H.C.; Leung, K.C.; Ho, H.P.; Kong, S.K. In vitro effect of CTAB- and PEG-coated gold nanorods on the induction of eryptosis/erythroptosis in human erythrocytes. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maellaro, E.; Leoncini, S.; Moretti, D.; Del Bello, B.; Tanganelli, I.; de Felice, C.; Ciccoli, L. Erythrocyte caspase-3 activation and oxidative imbalance in erythrocytes and in plasma of type 2 diabetic patients. Acta Diabetol. 2013, 50, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foller, M.; Sopjani, M.; Koka, S.; Gu, S.; Mahmud, H.; Wang, K.; Floride, E.; Schleicher, E.; Schulz, E.; Munzel, T.; et al. Regulation of erythrocyte survival by AMP-activated protein kinase. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelenak, C.; Foller, M.; Velic, A.; Krug, K.; Qadri, S.M.; Viollet, B.; Lang, F.; Macek, B. Proteome analysis of erythrocytes lacking AMP-activated protein kinase reveals a role of PAK2 kinase in eryptosis. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupescu, A.; Jilani, K.; Zelenak, C.; Zbidah, M.; Qadri, S.M.; Lang, F. Hexavalent chromium-induced erythrocyte membrane phospholipid asymmetry. Biometals 2012, 25, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik, N.; Lupescu, A.; Lang, F. Sunitinib-sensitive suicidal erythrocyte death. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucherenko, Y.; Zelenak, C.; Eberhard, M.; Qadri, S.M.; Lang, F. Effect of casein kinase 1alpha activator pyrvinium pamoate on erythrocyte ion channels. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelenak, C.; Eberhard, M.; Jilani, K.; Qadri, S.M.; Macek, B.; Lang, F. Protein kinase CK1alpha regulates erythrocyte survival. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 29, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, S.K.; Gu, S.; Bobbala, D.; Lang, F. Janus kinase 3 is expressed in erythrocytes, phosphorylated upon energy depletion and involved in the regulation of suicidal erythrocyte death. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 27, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klarl, B.A.; Lang, P.A.; Kempe, D.S.; Niemoeller, O.M.; Akel, A.; Sobiesiak, M.; Eisele, K.; Podolski, M.; Huber, S.M.; Wieder, T.; et al. Protein kinase C mediates erythrocyte “programmed cell death” following glucose depletion. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 290, C244–C253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gatidis, S.; Zelenak, C.; Fajol, A.; Lang, E.; Jilani, K.; Michael, D.; Qadri, S.M.; Lang, F. p38 MAPK activation and function following osmotic shock of erythrocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 28, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, M.; Feger, M.; Alzoubi, K.; Pakladok, T.; Frauenfeld, L.; Geiger, C.; Towhid, S.T.; Lang, F. Sensitization of erythrocytes to suicidal erythrocyte death following water deprivation. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2013, 37, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abed, M.; Herrmann, T.; Alzoubi, K.; Pakladok, T.; Lang, F. Tannic Acid induced suicidal erythrocyte death. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Langer, H.; Abed, M.; Voelkl, J.; Lang, F. The uremic toxin acrolein promotes suicidal erythrocyte death. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2013, 37, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aithal, K.B.; Kumar, S.; Rao, B.N.; Udupa, N.; Rao, S.B. Tumor growth inhibitory effect of juglone and its radiation sensitizing potential: In vivo and in vitro studies. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzoubi, K.; Honisch, S.; Abed, M.; Lang, F. Triggering of suicidal erythrocyte death by penta-O-galloyl-β-d-glucose. Toxins (Basel) 2014, 6, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Bissinger, R.; Lang, F. Mitoxantrone-Induced suicidal erythrocyte death. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 1756–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissinger, R.; Lupescu, A.; Zelenak, C.; Jilani, K.; Lang, F. Stimulation of eryptosis by cryptotanshinone. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottger, E.; Multhoff, G.; Kun, J.F.; Esen, M. Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes induce granzyme B by NK cells through expression of host-Hsp70. PLoS One 2012, 7, e33774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, J.I.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, K.A.; Cho, M.K.; Nam, H.S.; Woo, K.M.; Lee, S.H.; Shim, J.H. Phosphoinositol 3-kinase, a novel target molecule for the inhibitory effects of juglone on TPA-induced cell transformation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Firat, U.; Kaya, S.; Cim, A.; Buyukbayram, H.; Gokalp, O.; Dal, M.S.; Tamer, M.N. Increased caspase-3 immunoreactivity of erythrocytes in STZ diabetic rats. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 316384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Cheung, K.L.; Lau, I.P.; Yu, W.S.; Fung, K.P.; Yu, B.; Loo, J.F.; Kong, S.K. Polyphyllin D induces apoptosis in human erythrocytes through Ca2+ rise and membrane permeabilization. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghashghaeinia, M.; Cluitmans, J.C.; Akel, A.; Dreischer, P.; Toulany, M.; Koberle, M.; Skabytska, Y.; Saki, M.; Biedermann, T.; Duszenko, M.; et al. The impact of erythrocyte age on eryptosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 157, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghashghaeinia, M.; Cluitmans, J.C.; Toulany, M.; Saki, M.; Koberle, M.; Lang, E.; Dreischer, P.; Biedermann, T.; Duszenko, M.; Lang, F.; et al. Age sensitivity of NFkappaB abundance and programmed cell death in erythrocytes induced by NFkappaB inhibitors. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobi, J.; Lang, E.; Bissinger, R.; Frauenfeld, L.; Modicano, P.; Faggio, C.; Abed, M.; Lang, F. Stimulation of erythrocyte cell membrane scrambling by mitotane. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jilani, K.; Enkel, S.; Bissinger, R.; Almilaji, A.; Abed, M.; Lang, F. Fluoxetine induced suicidal erythrocyte death. Toxins (Basel) 2013, 5, 1230–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilani, K.; Lang, F. Carmustine-induced phosphatidylserine translocation in the erythrocyte membrane. Toxins (Basel) 2013, 5, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilani, K.; Lupescu, A.; Zbidah, M.; Abed, M.; Shaik, N.; Lang, F. Enhanced apoptotic death of erythrocytes induced by the mycotoxin ochratoxin A. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2012, 36, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jilani, K.; Qadri, S.M.; Lang, F. Geldanamycin-induced phosphatidylserine translocation in the erythrocyte membrane. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kucherenko, Y.V.; Lang, F. Inhibitory effect of furosemide on non-selective voltage-independent cation channels in human erythrocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, E.; Qadri, S.M.; Jilani, K.; Zelenak, C.; Lupescu, A.; Schleicher, E.; Lang, F. Carbon monoxide-sensitive apoptotic death of erythrocytes. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 111, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.J.; Bao, J.L.; Wu, G.S.; Xu, W.S.; Huang, M.Q.; Chen, X.P.; Wang, Y.T. Quinones derived from plant secondary metabolites as anti-cancer agents. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lupescu, A.; Bissinger, R.; Herrmann, T.; Oswald, G.; Jilani, K.; Lang, F. Induction of suicidal erythrocyte death by novobiocin. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupescu, A.; Bissinger, R.; Jilani, K.; Lang, F. Triggering of suicidal erythrocyte death by celecoxib. Toxins (Basel) 2013, 5, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupescu, A.; Bissinger, R.; Warsi, J.; Jilani, K.; Lang, F. Stimulation of erythrocyte cell membrane scrambling by gedunin. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 1838–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupescu, A.; Jilani, K.; Zbidah, M.; Lang, F. Patulin-induced suicidal erythrocyte death. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, M.T.; Ljungman, M. The natural toxin juglone causes degradation of p53 and induces rapid H2AX phosphorylation and cell death in human fibroblasts. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 209, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polak-Jonkisz, D.; Purzyc, L. Ca influx versus efflux during eryptosis in uremic erythrocytes. Blood Purif. 2012, 34, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, E.W.; Ge, D.T.; Kong, S.K. Salidroside protects human erythrocytes against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik, N.; Zbidah, M.; Lang, F. Inhibition of Ca2+ entry and suicidal erythrocyte death by naringin. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesoriere, L.; Attanzio, A.; Allegra, M.; Cilla, A.; Gentile, C.; Livrea, M.A. Oxysterol mixture in hypercholesterolemia-relevant proportion causes oxidative stress-dependent eryptosis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 1075–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vota, D.M.; Maltaneri, R.E.; Wenker, S.D.; Nesse, A.B.; Vittori, D.C. Differential erythropoietin action upon cells induced to eryptosis by different agents. Cell. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 65, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, E.; Cytlak, U.M.; Rees, D.C.; Osei, A.; Gibson, J.S. Deoxygenation-induced and Ca2+ dependent phosphatidylserine externalisation in red blood cells from normal individuals and sickle cell patients. Cell Calcium 2012, 51, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yu, X.; Qu, S.; Sui, D. Juglone, isolated from Juglans mandshurica Maxim, induces apoptosis via down-regulation of AR expression in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3631–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbidah, M.; Lupescu, A.; Jilani, K.; Lang, F. Stimulation of suicidal erythrocyte death by fumagillin. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 112, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelenak, C.; Pasham, V.; Jilani, K.; Tripodi, P.M.; Rosaclerio, L.; Pathare, G.; Lupescu, A.; Faggio, C.; Qadri, S.M.; Lang, F. Tanshinone IIA stimulates erythrocyte phosphatidylserine exposure. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Xiang, Y.; Ran, Q.; Deng, X.; Xiao, Y.; Xiang, L.; Li, Z. Involvement of calcium, reactive oxygen species, and ATP in hexavalent chromium-induced damage in red blood cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 1780–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voelkl, J.; Alzoubi, K.; Mamar, A.K.; Ahmed, M.S.; Abed, M.; Lang, F. Stimulation of suicidal erythrocyte death by increased extracellular phosphate concentrations. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2013, 38, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, E.; Gatidis, S.; Freise, N.F.; Bock, H.; Kubitz, R.; Lauermann, C.; Orth, H.M.; Klindt, C.; Schuier, M.; Keitel, V.; et al. Conjugated bilirubin triggers anemia by inducing erythrocyte death. Hepatology 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, H.E.; Bunting, H.; Ordway, N.K.; Albrink, W.S. The pathogenesis of the renal injury produced in the dog by hemoglobin or methemoglobin. J. Exp. Med. 1947, 86, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foller, M.; Bobbala, D.; Koka, S.; Huber, S.M.; Gulbins, E.; Lang, F. Suicide for survival—Death of infected erythrocytes as a host mechanism to survive malaria. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 24, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranton, C.; Huber, S.; Tanneur, V.; Lang, K.; Brand, V.; Sandu, C.; Lang, F. Electrophysiological properties of the Plasmodium Falciparum-induced cation conductance of human erythrocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 13, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, K. Membrane transport in the malaria-infected erythrocyte. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 495–537. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koka, S.; Foller, M.; Lamprecht, G.; Boini, K.M.; Lang, C.; Huber, S.M.; Lang, F. Iron deficiency influences the course of malaria in Plasmodium berghei infected mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayi, K.; Giribaldi, G.; Skorokhod, A.; Schwarzer, E.; Prendergast, P.T.; Arese, P. 16alpha-bromoepiandrosterone, an antimalarial analogue of the hormone dehydroepiandrosterone, enhances phagocytosis of ring stage parasitized erythrocytes: A novel mechanism for antimalarial activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 3180–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayi, K.; Turrini, F.; Piga, A.; Arese, P. Enhanced phagocytosis of ring-parasitized mutant erythrocytes: A common mechanism that may explain protection against falciparum malaria in sickle trait and beta-thalassemia trait. Blood 2004, 104, 3364–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappadoro, M.; Giribaldi, G.; O’Brien, E.; Turrini, F.; Mannu, F.; Ulliers, D.; Simula, G.; Luzzatto, L.; Arese, P. Early phagocytosis of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)-deficient erythrocytes parasitized by Plasmodium falciparum may explain malaria protection in G6PD deficiency. Blood 1998, 92, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koka, S.; Huber, S.M.; Boini, K.M.; Lang, C.; Foller, M.; Lang, F. Lead decreases parasitemia and enhances survival of Plasmodium berghei-infected mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 363, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koka, S.; Lang, C.; Boini, K.M.; Bobbala, D.; Huber, S.M.; Lang, F. Influence of chlorpromazine on eryptosis, parasitemia and survival of Plasmodium berghe infected mice. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 22, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koka, S.; Lang, C.; Niemoeller, O.M.; Boini, K.M.; Nicolay, J.P.; Huber, S.M.; Lang, F. Influence of NO synthase inhibitor L-NAME on parasitemia and survival of Plasmodium berghei infected mice. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 21, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, S.K.; Abdel-Monem, H.; Guchhait, P.; Nagata, S.; Thiagarajan, P. Role of lactadherin in the clearance of phosphatidylserine-expressing red blood cells. Transfusion 2008, 48, 2370–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foller, M.; Biswas, R.; Mahmud, H.; Akel, A.; Shumilina, E.; Wieder, T.; Goetz, F.; Lang, F. Effect of peptidoglycans on erythrocyte survival. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 299, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandelwal, S.; Saxena, R.K. A role of phosphatidylserine externalization in clearance of erythrocytes exposed to stress but not in eliminating aging populations of erythrocyte in mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2008, 43, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadri, S.M.; Mahmud, H.; Lang, E.; Gu, S.; Bobbala, D.; Zelenak, C.; Jilani, K.; Siegfried, A.; Foller, M.; Lang, F. Enhanced suicidal erythrocyte death in mice carrying a loss-of-function mutation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borst, O.; Abed, M.; Alesutan, I.; Towhid, S.T.; Qadri, S.M.; Foller, M.; Gawaz, M.; Lang, F. Dynamic adhesion of eryptotic erythrocytes to endothelial cells via CXCL16/SR-PSOX. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012, 302, C644–C651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, D.A.; Low, P.S. Role of red blood cells in thrombosis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 1999, 6, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.M.; Bae, O.N.; Lim, K.M.; Noh, J.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Jung, Y.S.; Chung, J.H. Lysophosphatidic acid induces thrombogenic activity through phosphatidylserine exposure and procoagulant microvesicle generation in human erythrocytes. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwaal, R.F.; Comfurius, P.; Bevers, E.M. Surface exposure of phosphatidylserine in pathological cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 971–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Closse, C.; Dachary-Prigent, J.; Boisseau, M.R. Phosphatidylserine-related adhesion of human erythrocytes to vascular endothelium. Br. J. Haematol. 1999, 107, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, P.G.; Chang, S.H.; Rettig, M.P.; Neely, J.E.; Hillery, C.A.; Smith, B.D.; Low, P.S. Altered erythrocyte endothelial adherence and membrane phospholipid asymmetry in hereditary hydrocytosis. Blood 2003, 101, 4625–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandolfi, A.; Di Pietro, N.; Sirolli, V.; Giardinelli, A.; Di Silvestre, S.; Amoroso, L.; Di Tomo, P.; Capani, F.; Consoli, A.; Bonomini, M. Mechanisms of uremic erythrocyte-induced adhesion of human monocytes to cultured endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 213, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, B.L.; Gibson, D.F.; Tait, J.F. Increased erythrocyte phosphatidylserine exposure in sickle cell disease: Flow-cytometric measurement and clinical associations. Blood 1996, 88, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hilarius, P.M.; Ebbing, I.G.; Dekkers, D.W.; Lagerberg, J.W.; de Korte, D.; Verhoeven, A.J. Generation of singlet oxygen induces phospholipid scrambling in human erythrocytes. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 4012–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzoubi, K.; Calabrò, S.; Egler, J.; Faggio, C.; Lang, F. Triggering of Programmed Erythrocyte Death by Alantolactone. Toxins 2014, 6, 3596-3612. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6123596
Alzoubi K, Calabrò S, Egler J, Faggio C, Lang F. Triggering of Programmed Erythrocyte Death by Alantolactone. Toxins. 2014; 6(12):3596-3612. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6123596
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzoubi, Kousi, Salvatrice Calabrò, Jasmin Egler, Caterina Faggio, and Florian Lang. 2014. "Triggering of Programmed Erythrocyte Death by Alantolactone" Toxins 6, no. 12: 3596-3612. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6123596
APA StyleAlzoubi, K., Calabrò, S., Egler, J., Faggio, C., & Lang, F. (2014). Triggering of Programmed Erythrocyte Death by Alantolactone. Toxins, 6(12), 3596-3612. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6123596






