Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions in T-2 Toxin Studied Using Solution and Solid-State NMR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
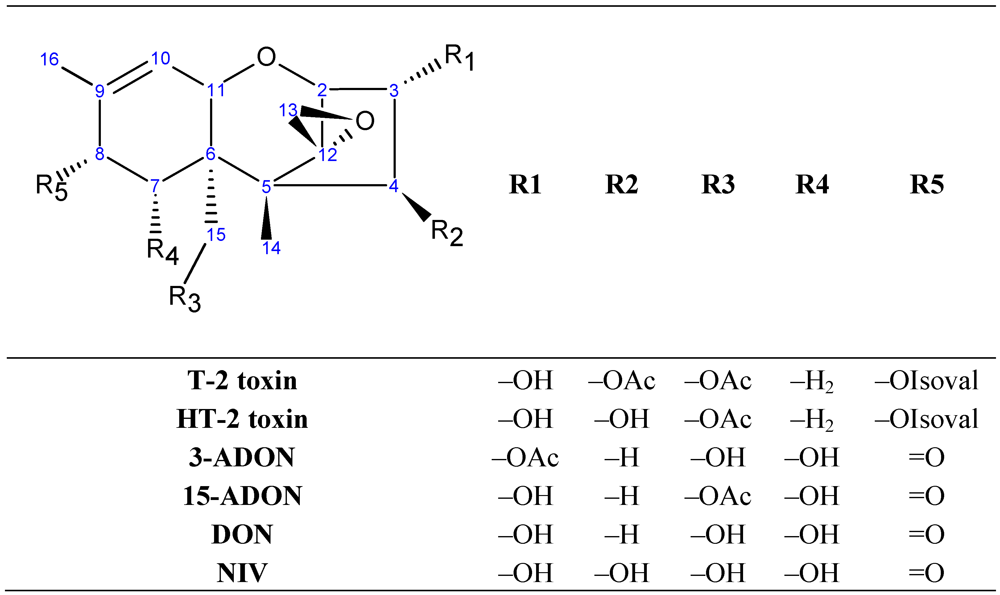
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Solution-State NMR Measurements
2.2. Solid-State NMR Measurements
2.3. Spectral Simulations and X-ray Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Structural Rigidity and Water Bridging
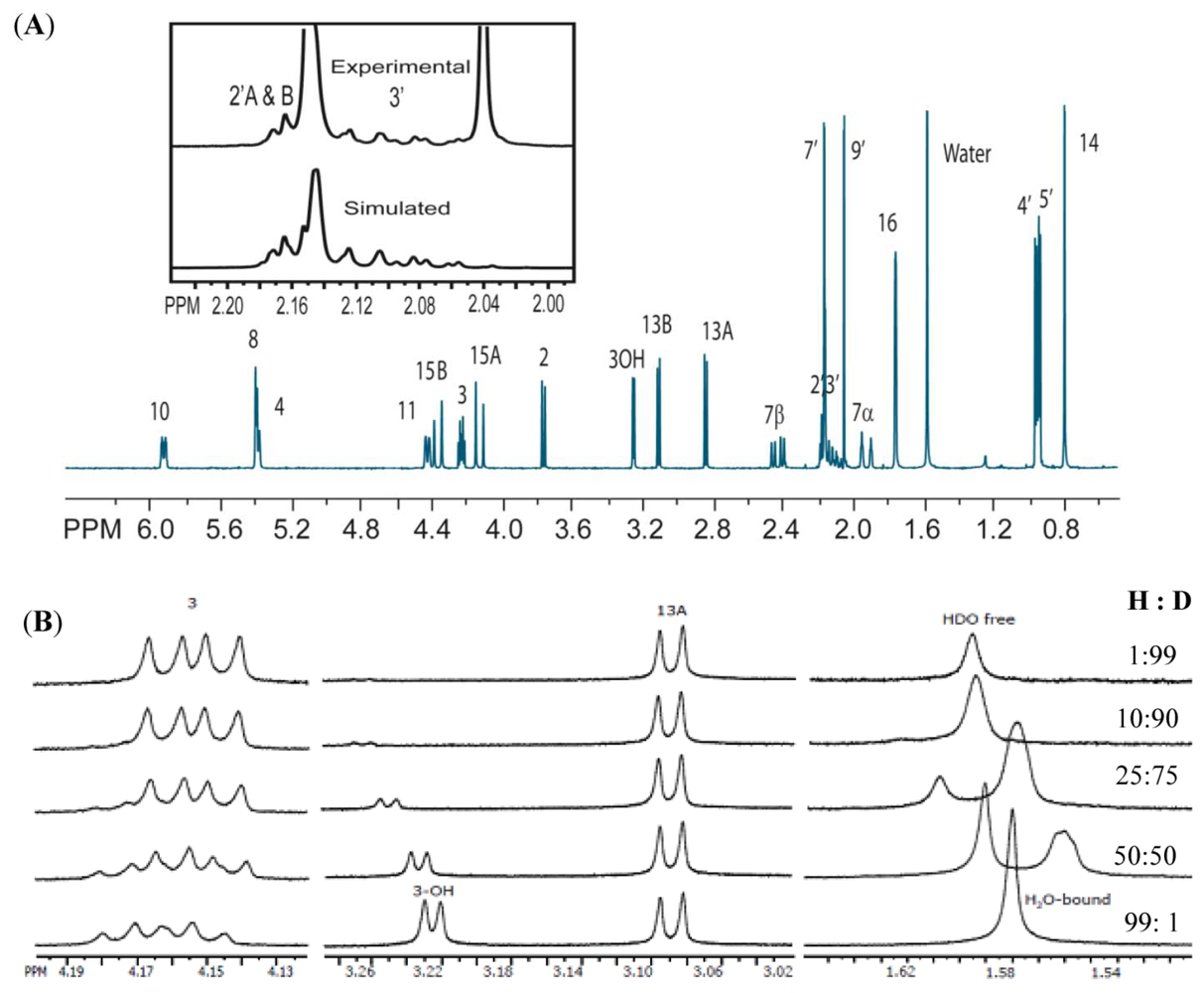
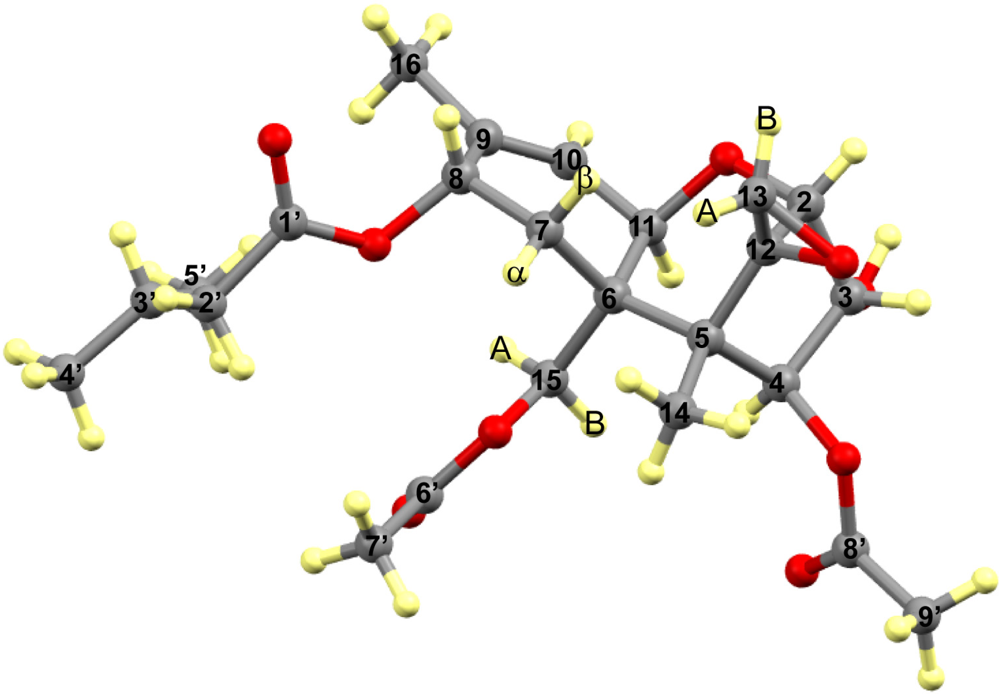
3.2. Carbon Spectral Analysis
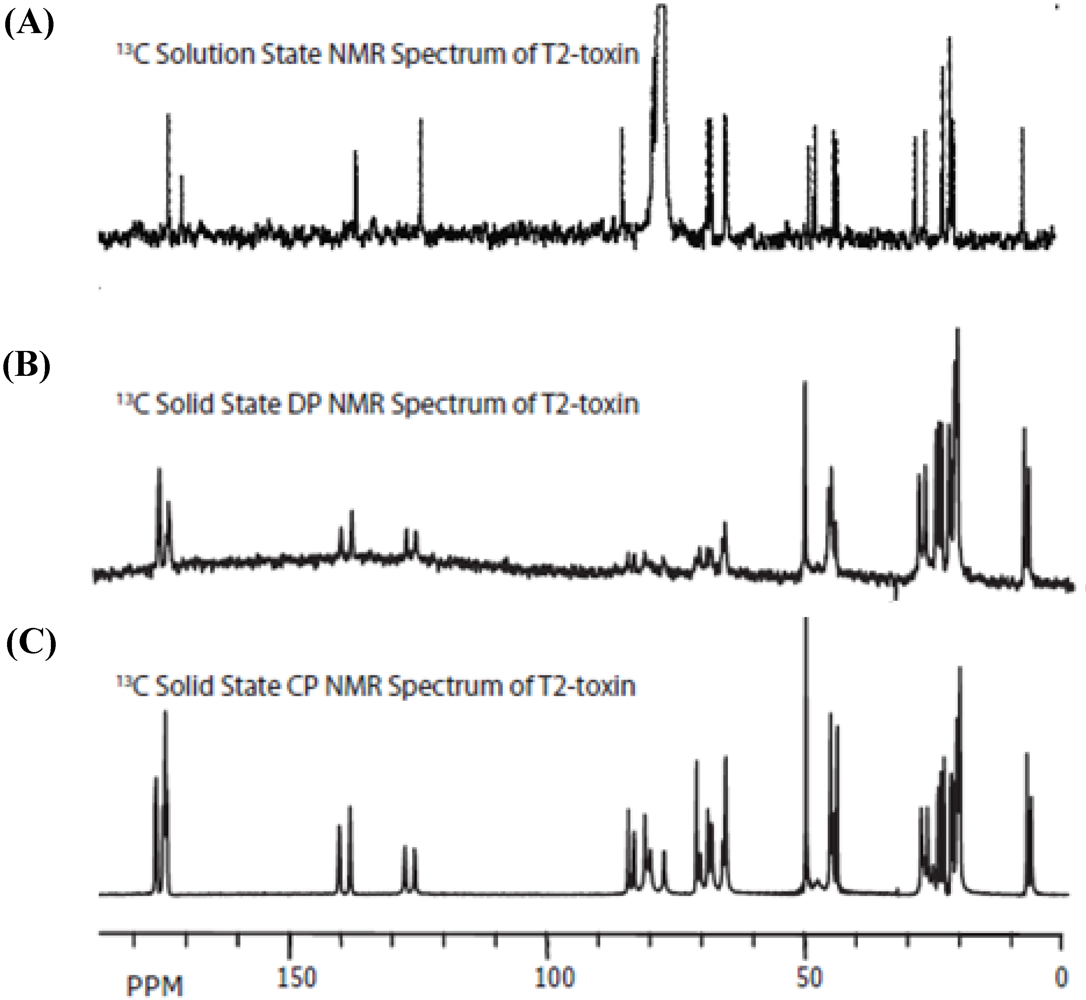
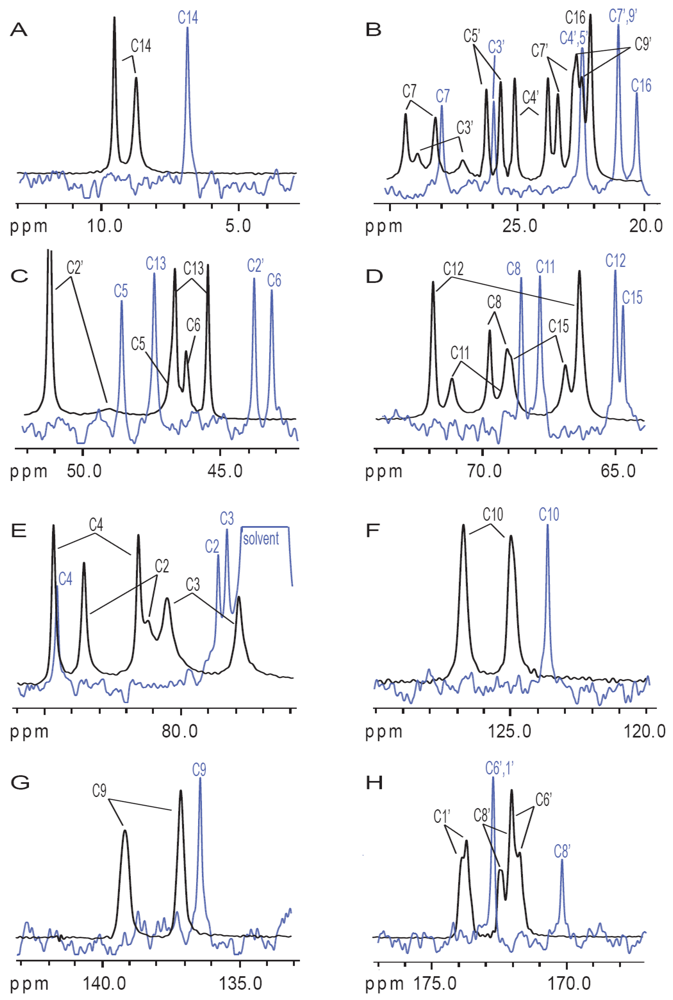
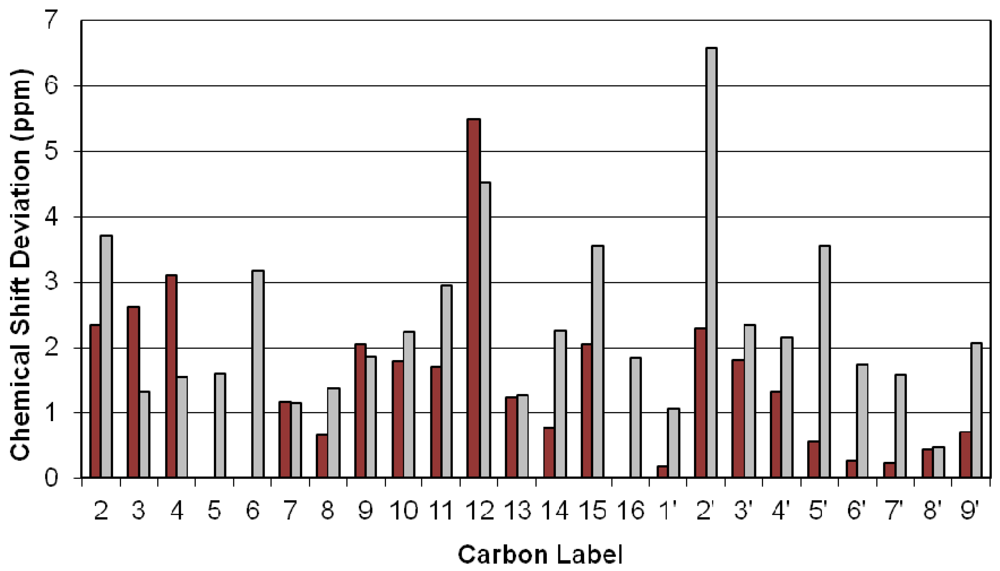
4. Discussion
4.1. Hydrogen-Bonding in Solution
4.2. Solid-State Configurations
4.3. Ribosomal Interaction

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Supporting Information Available
Supplementary Files
References
- Foroud, N.A.; Eudes, F. Trichothecenes in cereal grains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 147–173. [Google Scholar]
- Grove, J.F. The trichothecenes and their biosynthesis. Fort. Chem. Org. Nat. 2007, 88, 63–130. [Google Scholar]
- Parry, D.W.; Jenkinson, P.; McLeod, L. Fusarium ear blight (scab) in small grain cereals-A review. Plant Pathol. 1995, 44, 207–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, Y. The toxicology of mycotoxins. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1985, 14, 99–133. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, C.; Casteel, M.; Didier, A.; Dietrich, R.; Märtlbauer, E. Trichothecene-induced cytotoxicity on human cell lines. Mycotoxin Res. 2009, 25, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Schollenberger, M.; Suchy, S.; Jara, H.T.; Drochner, W.; Müller, H.-M. A survey of Fusarium toxins in cereal-based foods marketed in an area of southwest Germany. Mycopathologia 1999, 147, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scudamore, K.A.; Patel, S.; Edwards, S.G. HT-2 toxin and T-2 toxin in commercial cereal processing in the United Kingdom, 2004-2007. World Mycotoxin J. 2009, 2, 357–365. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, C.F. Endemic panmyelotoxicosis in the Russian grain belt. I. The clinical aspects of alimentary toxic aleukia (ATA); a comprehensive review. Mil. Surg. 1953, 113, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yagen, B.; Joffe, A.Z. Screening of toxic isolates of fusarium-poae and fusarium-sporotrichioides involved in causing alimentary toxic aleukia. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1976, 32, 423–427. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin, C.S.; Vaughn, M.H.; Campbell, J.M.; Wei, C.M.; Stafford, M.E. Inhibition of Protein Synthesis by Trichothecenes. In Mycotoxins in Human and Health; Rodricks, J.V., Hesseltine, C.W., Mehlman, M.A., Eds.; Pathotox Publishers: Park Forest South, IL, USA, 1977; pp. 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, Y.; Hosoya, M.; Morita, Y.; Ueno, I.; Tatsuno, T. Inhibition of the protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte by nivalenol, a toxic principle isolated from Fusarium nivale-growing rice. J. Biochem. 1968, 64, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tatsuno, T. Toxicologie research on substances from Fusarium nivale. Cancer Res. 1968, 28, 2393–2396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, Z.; Buchenauer, H. Immunocytochemical localization of fusarium toxins in infected wheat spikes by Fusarium culmorum. Physiol. Mol. Plant P. 1999, 55, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunner, D.L.; Morris, E.R. Alteration of multiple cell membrane functions in L-6 myoblasts by T-2 toxin an important mechanism of action. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 1988, 92, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Johannisson, A.; Björkhag, B.; Hansson, W.; Gadhasson, I.-L.; Thuvander, A. Effects of four trichothecene mycotoxins on activation marker expression and cell proliferation of human lymphocytes in culture. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 1999, 15, 203–215. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin, J.E.; Bin-Umer, M.A.; Tortora, A.; Mendez, N.; McCormick, S.; Tumer, N.E. A genome-wide screen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals a critical role for the mitochondria in the toxicity of a trichothecene mycotoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21883–21888. [Google Scholar]
- Bouaziz, C.; Martel, C.; Sharaf el dein, O.; Abid-Essefi, S.; Brenner, C.; Lemaire, C.; Bacha, H. Fusarial toxin-induced toxicity in cultured cells and in isolated mitochondria involves PTPC-dependent activation of the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 110, 363–375. [Google Scholar]
- Shifrin, V.I.; Anderson, P. Trichothecene mycotoxins trigger a ribotoxic stress response that activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and induces apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13985–13992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilly, M.; Benson, N.R.; Pellegrini, M. Affinity labeling the ribosome with eukaryotic-specific antibiotics: (bromoacetyl)trichodermin. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 5787–5792. [Google Scholar]
- Meskauskas, A.; Dinman, J.D. Ribosomal protein L3 functions as a “rocker switch” to aid in coordinating of large subunit-associated functions in eukaryotes and Archaea. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 6175–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitterbauer, R.; Poppeberger, B.; Raditschnig, A.; Lucyshyn, D.; Lemmens, M.; Glössl, J.; Adam, G. Toxin-dependent utilization of engineered ribosomal protein L3 limits trichothecene resistance in transgenic plants. Plant Biotechnol. 2004, 2, 329–340. [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe, E.; Cannon, M.; Davies, J. Mechanism of inhibition of eukaryotic protein synthesis by trichothecene fungal toxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, D. Two classes of inhibitors of peptidyl transferase activity in eukaryotes. Nature 1974, 249, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe, E.; Davies, J.E. Inhibition of initiation, elongation, and termination of eukaryotic protein synthesis by trichothecene fungal toxin. Antimicrob. AgentsChemother. 1977, 11, 491–499. [Google Scholar]
- Langseth, W.; Rundberget, T. The occurrence of HT-2 toxin and other trichothecenes in Norwegian cereals. Mycopathologia 1999, 147, 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, S.G.; Barrier-Guillot, B.; Clasen, P.-E.; Hietaniemi, V.; Pettersson, H. Emerging issues of HT-2 and T-2 toxins in European cereal production. World Mycotoxin J. 2009, 2, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Biselli, S.; Hummert, C. Development of a multicomponent method for Fusarium toxins using LC-MS/MS and its application during a survey for the content of T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol in various feed and food samples. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imathiu, S.M.; Ray, R.V.; Back, M.; Hare, M.C.; Edwards, S.G. Fusarium langsethiae pathogenicity and aggressiveness towards oats and wheat in wounded and unwounded in vitro detached leaf assays. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2009, 124, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, Y. Toxicological features of T-2 toxin and related trichothecenes. Toxicol. Sci. 1984, 4, 124–132. [Google Scholar]
- Mesilaakso, M.; Rahkamaa, E. H-1 and C-13 study of the trichothecenes T-2 toxin and T-2 triol. Journal für Praktische Chemie/Chemiker-Zeitung 1992, 334, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, B.B.; Mazzocchi, D.B.; Ammon, H.L.; Mazzola, E.P.; Flippen-Anderson, J.L.; Gilardi, R.D.; George, C.F. Conformational effects in trichothecenes: structures of 15-hydroxy C4 and C8 ketones. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 3660–3662. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, J.; Bergdahl, B.M.; Separovic, F.; Brownlee, R.T.C.; Metzger, R.P. Difference in conformation of virginiamycin M1 in chloroform and bound form in the 50S ribosome or streptogramin acetyltransferase. Aust. J. Chem. 2004, 57, 415–418. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, J.; Separovic, F.; Bergdahl, M.; Brownlee, R.T.C.; Metzger, R.P. Solvent affects the conformation of virginiamycin M1 (pristinamycin IIA, streptogramin A). Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 2919–2924. [Google Scholar]
- Rovnyak, D. Tutorial on analytic theory for cross-polarization in solid state NMR. Concepts Magn. Reso. A 2008, 32A, 254–276. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, R.E. Setting up C-13 CP/MAS experiments. Concepts Magn. Reso. A 2004, 22A, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, I.J. Free induction decays of rotating solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1959, 2, 285–287. [Google Scholar]
- Andrew, E.R.; Bradbury, A.; Eades, R.G. Removal of dipolar broadening of nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of solids by specimen rotation. Nature 1959, 183, 1802–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, A.E.; Rienstra, A.E.; Auger, M.I.; Lakshmi, K.V.; Griffin, R.G. Heteronuclear decoupling in rotating solids. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 6951–6958. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, M. Heteronuclear spin decoupling in solid-state NMR under magic-angle sample spinning. J. Magn. Res. 2003, 162, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kupce, E.; Freeman, R. Stretched adiabatic pulses for broadband spin inversion. J. Mag. Res. Ser. A 1995, 115, 273–276. [Google Scholar]
- Marat, K. SpinWorks 3.1.6, 2009. Available online: ftp://davinci.chem.umanitoba.ca/pub/marat/SpinWorks/ (accessed on 1 May 2009).
- Savard, M.E.; Blackwell, B.A.; Greenhalgh, R. An H-1 Nuclear-magnetic-resonance study of derivatives of 3-hydroxy-12,13-epoxytrichothec-9-enes. Can. J. Chem. 1987, 65, 2254–2262. [Google Scholar]
- Savard, M.E.; Blackwell, B.A. Spectral characteristics of secondary metabolites from fusarium fungi. In Mycotoxins in Grain; Miller, J.D., Trenholm, H.L., Eds.; Eagen Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2004; pp. 59–258. [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell, B.A.; Greenhalgh, R.; Bain, A.D. Carbon-13 and proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectral assignments of deoxynivalenol and other mycotoxins from Fusarium graminearum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1984, 32, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, R.; Blackwell, B.A.; Savard, M.; Miller, J.D.; Taylor, A. Secondary metabolites produced by Fusarium sporotrichioides DAOM 165006 in liquid culture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988, 36, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doddrell, D.M.; Pegg, D.T.; Bendall, M.R. Distortionless enhancement of NMR signals by polarization transfer. J. Mag. Res. 1982, 49, 323–327. [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi, R.; George, C.; Flippen-Anderson, J.L. The structure of T-2 toxin. Acta Cryst. 1990, C46, 645–648. [Google Scholar]
- Pickard, C.J.; Payne, M.C. Second-order k center dot p perturbation theory with Vanderbilt pseudopotentials and plane waves. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 4383–4388. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzea, X.; Amadond, B.; Angladee, P.-M.; Beukena, J.-M.; Bottind, F.; Boulangera, P.; Brunevalq, F.; Calistej, D.; Caracasl, R.; Côté, M.; et al. ABINIT: First-principles approach to material and nanosystem properties. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2009, 180, 2582–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, A.; Auger, C.; Caldarelli, S.; Emsley, L. Determination of through-bond carbon-carbon connectivities in solid-state NMR using the INADEQUATE experiment. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 7867–7868. [Google Scholar]
- Lesage, A.; Bardet, M.; Emsley, L. Through-bond carbon-carbon connectivities in disordered solids by NMR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 10997–10993. [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus, D. Nuclear Overhauser Effec. In Encyclopedia of Magnetic Resonance; Grant, D.M., Harris, R.K., Eds.; John Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh, J.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Palmer, A.G.; Skelton, N.J. Relaxation and dynamic processes. In Protein NMR Spectroscopy: Principles and Practice; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 243–300. [Google Scholar]
- Krska, R.; Baumgartner, S.; Josephs, R. The state-of-the-art in the analysis of type-A and -B trichothecene mycotoxins in cereals. Fresen. J. Anal. Chem. 2001, 371, 288–295. [Google Scholar]
- Bamburg, J.R. Chemical and biochemical studies of trichothecene mycotoxins. Mycotoxins and other fungal related food problems. Adv. Chem. 1976, 149, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, E.P.; Szafraniec, L.L. Hypochlorite-promoted transformations of trichothecenes. Verrucarol. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 1494–1497. [Google Scholar]
- Rodnina, M.V.; Beringer, M.; Wintermeyer, W. How ribosomes make peptide bonds. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Meskauskas, A.; Petrov, A.N.; Dinman, J.D. Identification of functionally important amino acids of ribosomal protein L3 by saturation mutagenesis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 10863–10874. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, D.J.; Moore, P.B.; Steitz, T.A. The roles of ribosomal proteins in structure assembly, and evolution of the large ribosomal subunit. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 340, 141–177. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.W.; Black, R.M.; Lee, C.G.; Pottage, C.; Rickard, R.L.; Sandford, M.S.; Webber, T.D.; William, N.E. Structure-activity studies of trichothecenes: cytotoxicity of analogues and reaction products derived from T-2 toxin and neosalaniol. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 555–562. [Google Scholar]
- Lucyshyn, D.; Busch, B.L.; Abolmaali, S.; Steiner, B.; Chandler, E.; Sanjarian, F.; Mousavi, A.; Nicholson, P.; Buertsmayr, H.; Adam, G. Cloning and characterization of the ribosomal protein L3 (RPL3) gene family from Triticum aestivum. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2007, 277, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaudhary, P.; Shank, R.A.; Montina, T.; Goettel, J.T.; Foroud, N.A.; Hazendonk, P.; Eudes, F. Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions in T-2 Toxin Studied Using Solution and Solid-State NMR. Toxins 2011, 3, 1310-1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins3101310
Chaudhary P, Shank RA, Montina T, Goettel JT, Foroud NA, Hazendonk P, Eudes F. Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions in T-2 Toxin Studied Using Solution and Solid-State NMR. Toxins. 2011; 3(10):1310-1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins3101310
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaudhary, Praveen, Roxanne A. Shank, Tony Montina, James T. Goettel, Nora A. Foroud, Paul Hazendonk, and François Eudes. 2011. "Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions in T-2 Toxin Studied Using Solution and Solid-State NMR" Toxins 3, no. 10: 1310-1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins3101310
APA StyleChaudhary, P., Shank, R. A., Montina, T., Goettel, J. T., Foroud, N. A., Hazendonk, P., & Eudes, F. (2011). Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions in T-2 Toxin Studied Using Solution and Solid-State NMR. Toxins, 3(10), 1310-1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins3101310



