Ultrasound-Guided Multi-Branch Rectus Femoris Nerve Block for Spasticity Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods, Procedure and Results
2.1. Patient Positioning and Equipment
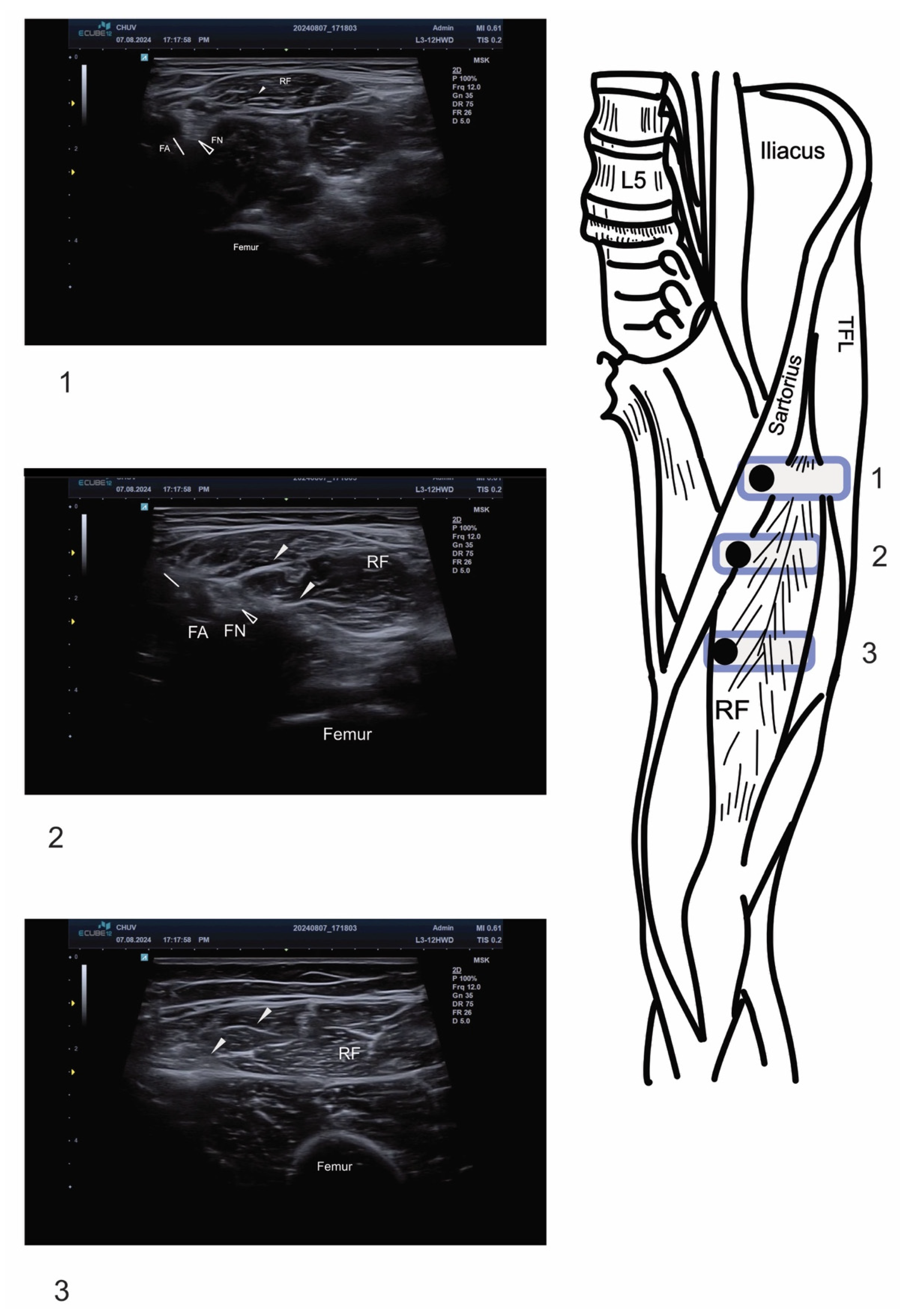
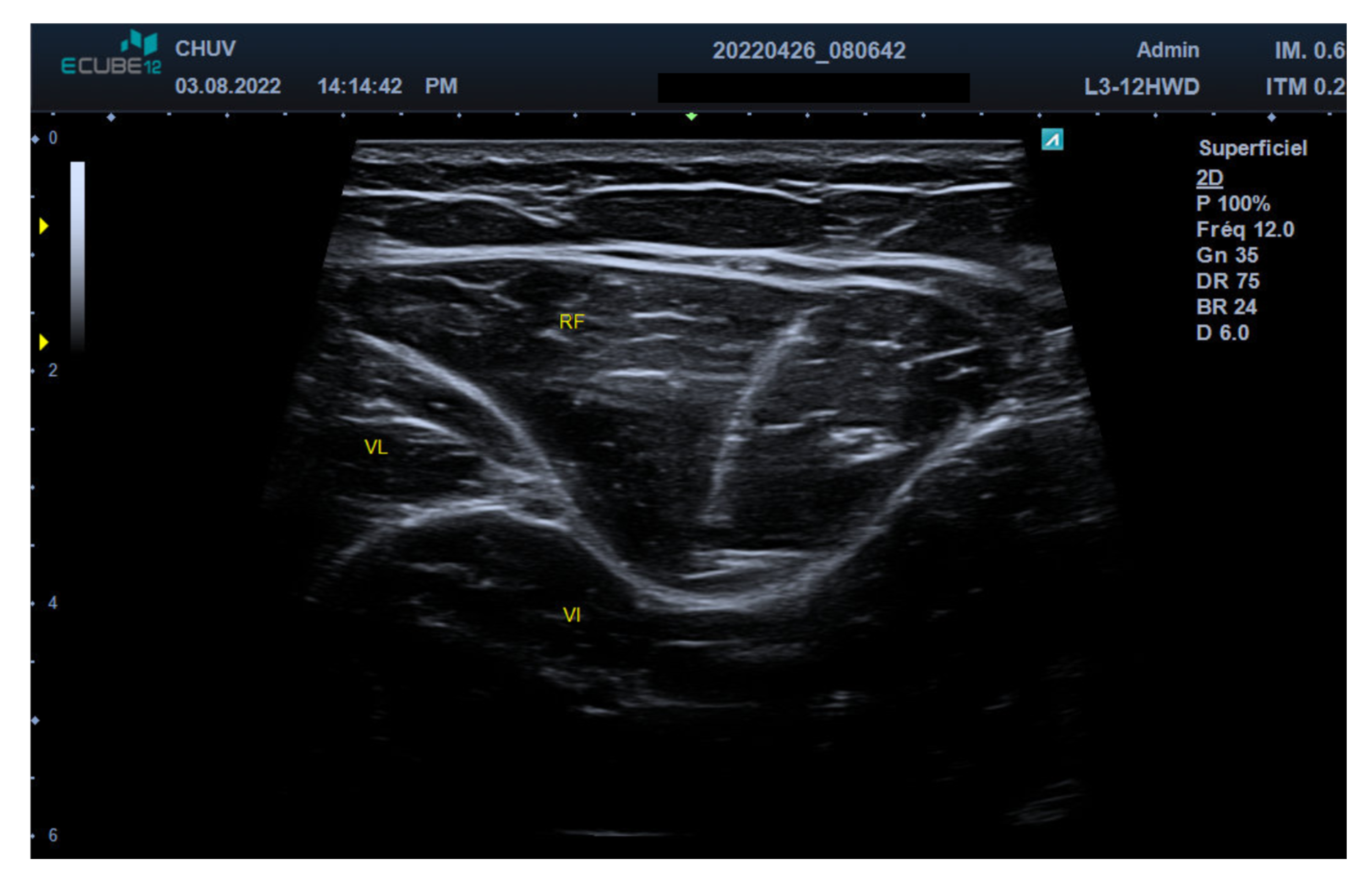
2.2. Ultrasound Technique and Anatomical Identification
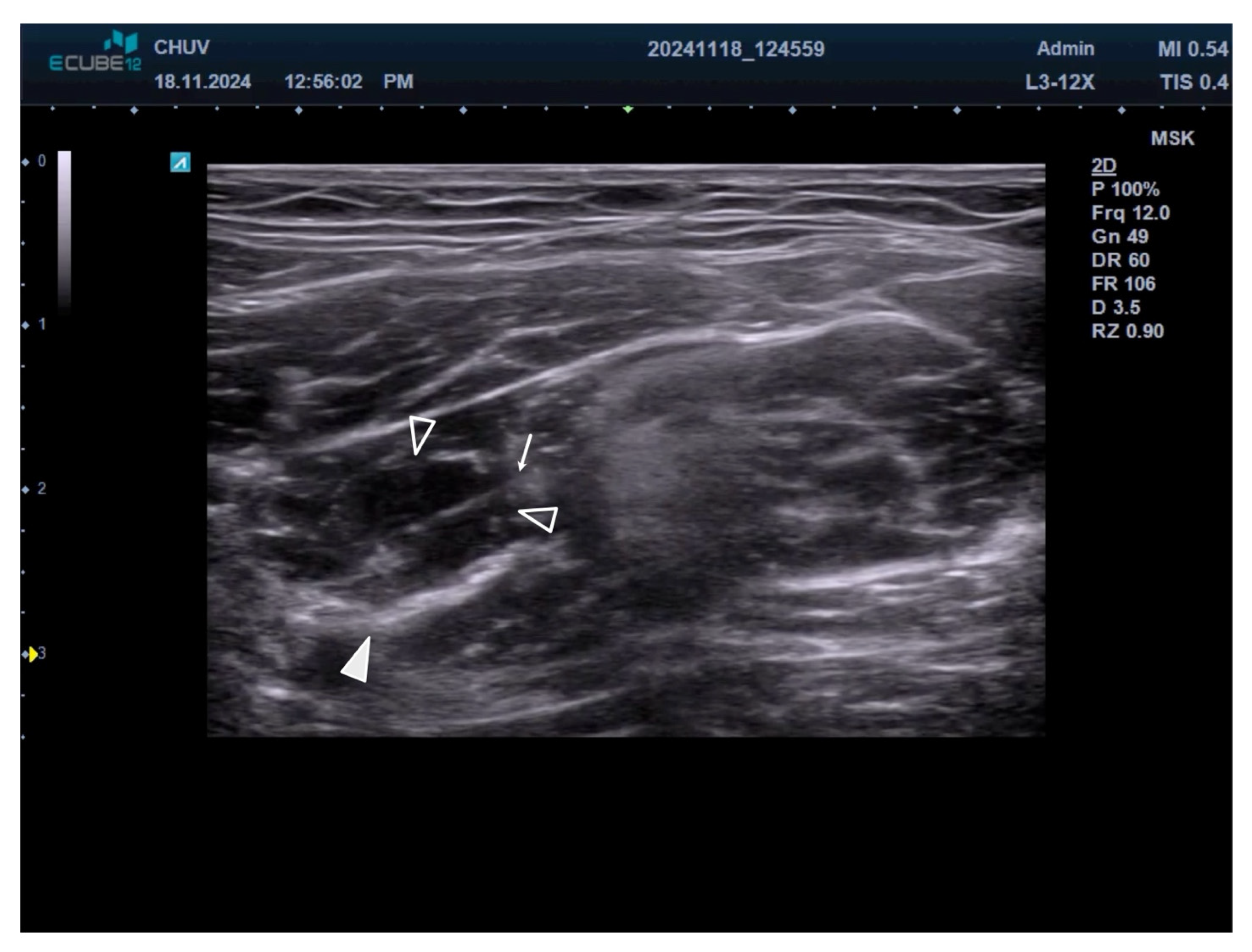
2.3. Motor Nerve Branch Identification
2.4. Injection Technique
2.5. Procedure Documentation and Assessment
3. Discussion
Addressing Fundamental Limitations of Existing Techniques
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Quervain, I.A.; Simon, S.R.; Leurgans, S.; Pease, W.S.; McAllister, D. Gait pattern in the early recovery period after stroke. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1996, 78, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olney, S.J.; Richards, C. Hemiparetic gait following stroke. Part I: Charateristics. Gait Posture 1996, 4, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nene, A.; Byrne, C.; Hermens, H. Is rectus femoris really a part of quadriceps? Assessment of rectus femoris function during gait in able-bodied adults. Gait Posture 2004, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerrigan, D.C.; Roth, R.S.; Riley, P.O. The modelling of adult spastic paretic stiff-legged gait swing period based on actual kinematic data. Gait Posture 1998, 7, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoli, D.; Giannotti, E.; Manca, M.; Longhi, M.; Prati, P.; Cosma, M.; Ferraresi, G.; Morelli, M.; Zerbinati, P.; Masiero, S.; et al. Electromyographic activity of the vastus intermedius muscle in patients with stiff-knee gait after stroke. A retrospective observational study. Gait Posture 2018, 60, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenniglo, M.J.B.; Nederhand, M.J.; Fleuren, J.F.; Rietman, J.S.; Buurke, J.H.; Prinsen, E.C. Does the Duncan-Ely test predict abnormal activity of the rectus femoris in stroke survivors with a stiff knee gait? J. Rehabil. Med. 2022, 54, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, D.H.; Bang, H.J. Motor branch block of the rectus femoris: Its effectiveness in stiff-legged gait in spastic paresis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2000, 81, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elovic, E.P.; Esquenazi, A.; Alter, K.E.; Lin, J.L.; Alfaro, A.; Kaelin, D.L. Chemodenervation and Nerve Blocks in the Diagnosis and Management of Spasticity and Muscle Overactivity. PMR 2009, 1, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, D.H.; Jung, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-D.; Ha, B.J.; Ko, Y.J. Motor branch of the rectus femoris: Anatomic location for selective motor branch block in stiff-legged gait 11No commercial party having a direct financial interest in the results of the research supporting this article has or will confer a benefit upon the author(s) or upon any organization with which the author(s) is/are associated. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, T.; Yelnik, A.; Colle, F.; Bonan, I.; Lassau, J.P. Anatomic motor point localization for partial quadriceps block in spasticity. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2000, 81, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, S.; Spina, S.; Gasperini, G.; Picelli, A.; Filippetti, M.; Molteni, F.; Santamato, A. Anatomical landmarks for ultrasound-guided rectus femoris diagnostic nerve block in post-stroke spasticity. Australas. J. Ultrason. Med. 2023, 26, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winston, P.; Reebye, R.; Picelli, A.; David, R.; Boissonnault, E. Recommendations for Ultrasound Guidance for Diagnostic Nerve Blocks for Spasticity. What Are Benefits? Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 104, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plante, D.; Janelle, N.; Angers-Goulet, M.; Corbeil, P.; Takech, M.A.; Belzile, E.L. Anatomical variants of the rectus femoris motor innervation. J. Hip Preserv. Surg. 2019, 6, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelnik, A.P.; Hentzen, C.; Cuvillon, P.; Allart, E.; Bonan, I.V.; Boyer, F.C.; Coroian, F.; Genet, F.; Honore, T.; Jousse, M.; et al. French clinical guidelines for peripheral motor nerve blocks in a PRM setting. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 62, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzic, A. How to Improve US Image in 15 Seconds: Crash Course with Dr. Hadzic [Internet]. NYSORA. 2025. Available online: https://www.nysora.com/topics/equipment/crash-course-with-dr-hadzic-improve-us-image/ (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Kowalska, B.; Sudoł-Szopińska, I. Normal and sonographic anatomy of selected peripheral nerves. Part I: Sonohistology and general principles of examination, following the example of the median nerve. J. Ultrason. 2012, 12, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltombe, T.; De Wispelaere, J.-F.; Gustin, T.; Jamart, J.; Hanson, P. Selective blocks of the motor nerve branches to the soleus and tibialis posterior muscles in the management of the spastic equinovarus foot. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moresco, G.; Carda, S.; Grana, E.; Deltombe, T.; Reebye, R. Rectus Femoris Selective Nerve Block. Description of a New Ultrasound-Guided Technique. In Proceedings of the Spasticity X, Houston, TX, USA, 24–26 October 2025. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carda, S.; Grana, E.; Deltombe, T.; Reebye, R. Ultrasound-Guided Multi-Branch Rectus Femoris Nerve Block for Spasticity Assessment. Toxins 2025, 17, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090437
Carda S, Grana E, Deltombe T, Reebye R. Ultrasound-Guided Multi-Branch Rectus Femoris Nerve Block for Spasticity Assessment. Toxins. 2025; 17(9):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090437
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarda, Stefano, Elisa Grana, Thierry Deltombe, and Rajiv Reebye. 2025. "Ultrasound-Guided Multi-Branch Rectus Femoris Nerve Block for Spasticity Assessment" Toxins 17, no. 9: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090437
APA StyleCarda, S., Grana, E., Deltombe, T., & Reebye, R. (2025). Ultrasound-Guided Multi-Branch Rectus Femoris Nerve Block for Spasticity Assessment. Toxins, 17(9), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090437





