From Uremic Toxins to Hemodialysis Access Failure: IL-8 and MCP-1 Chemokines as a Link Between Endothelial Activation and AV Access Complications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. IL-8 and MCP-1 Are Upregulated by Indolic Toxins in Cultured Endothelial Cells
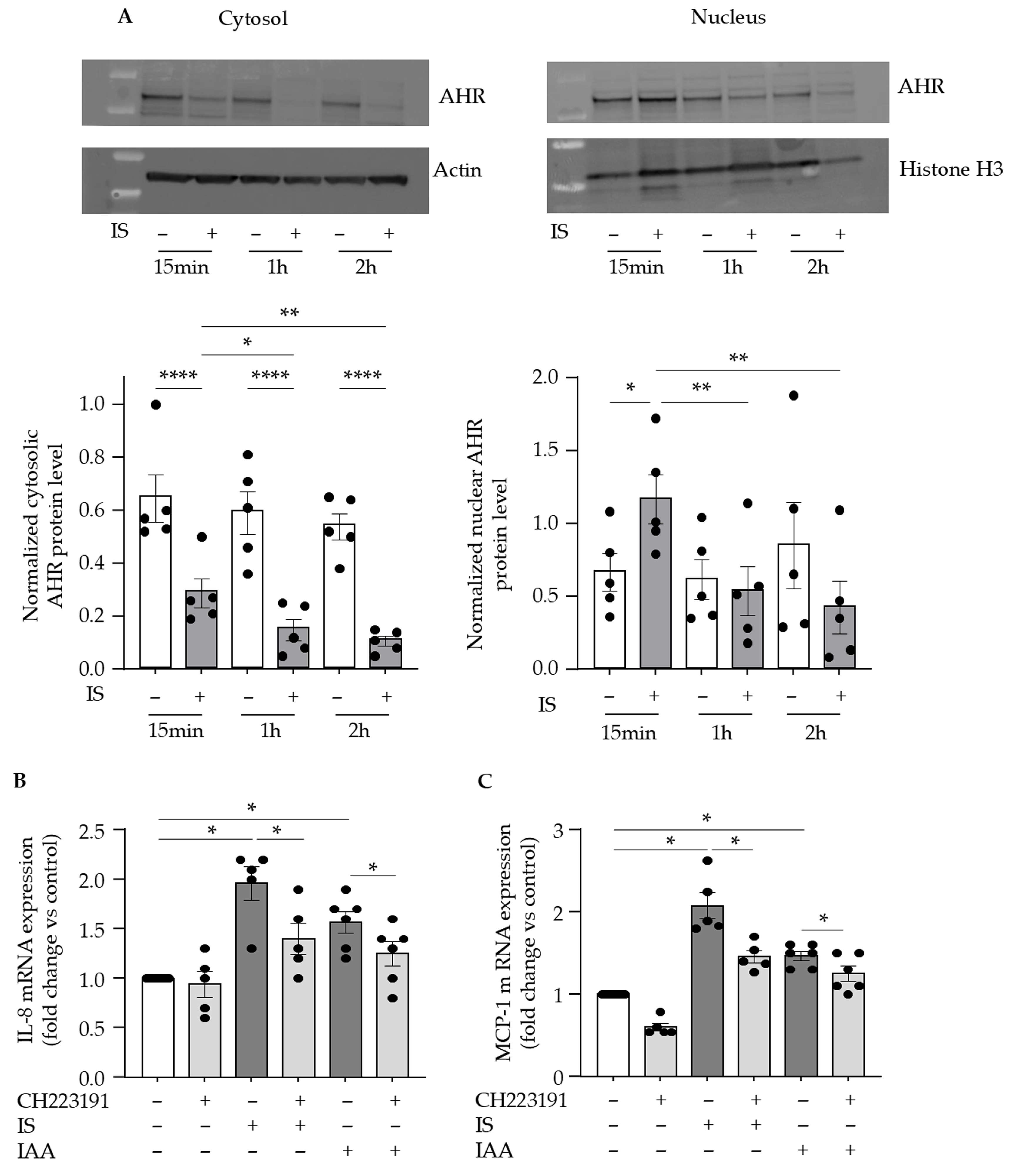
2.2. AHR Activation Is Involved in Indolic Toxin-Induced Upregulation of IL-8 and MCP-1 in Endothelial Cells
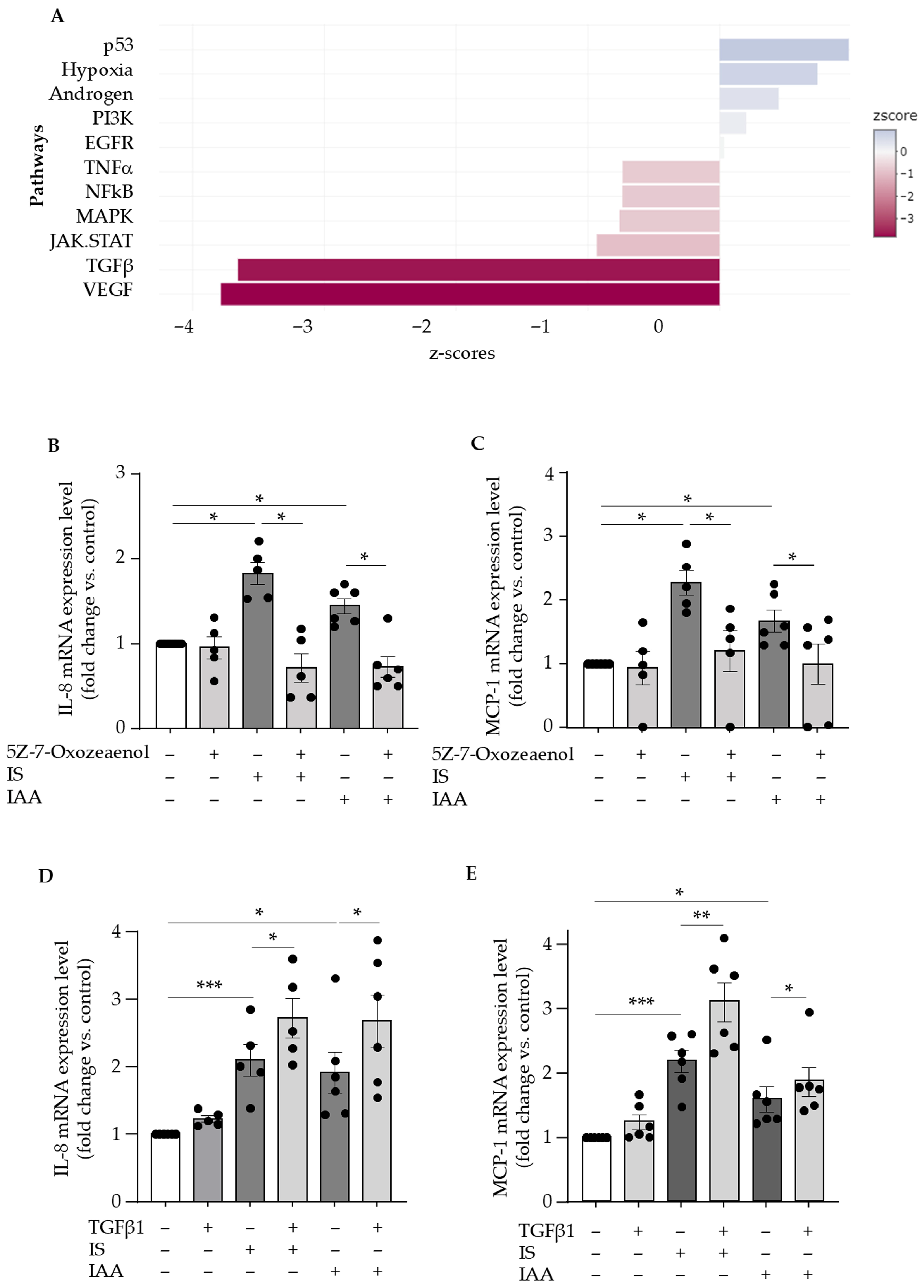
2.3. Indolic Toxins Upregulate Endothelial IL-8 and MCP-1 Through Activation of the TAK1 Non-Canonical TGFβ Signaling Pathway
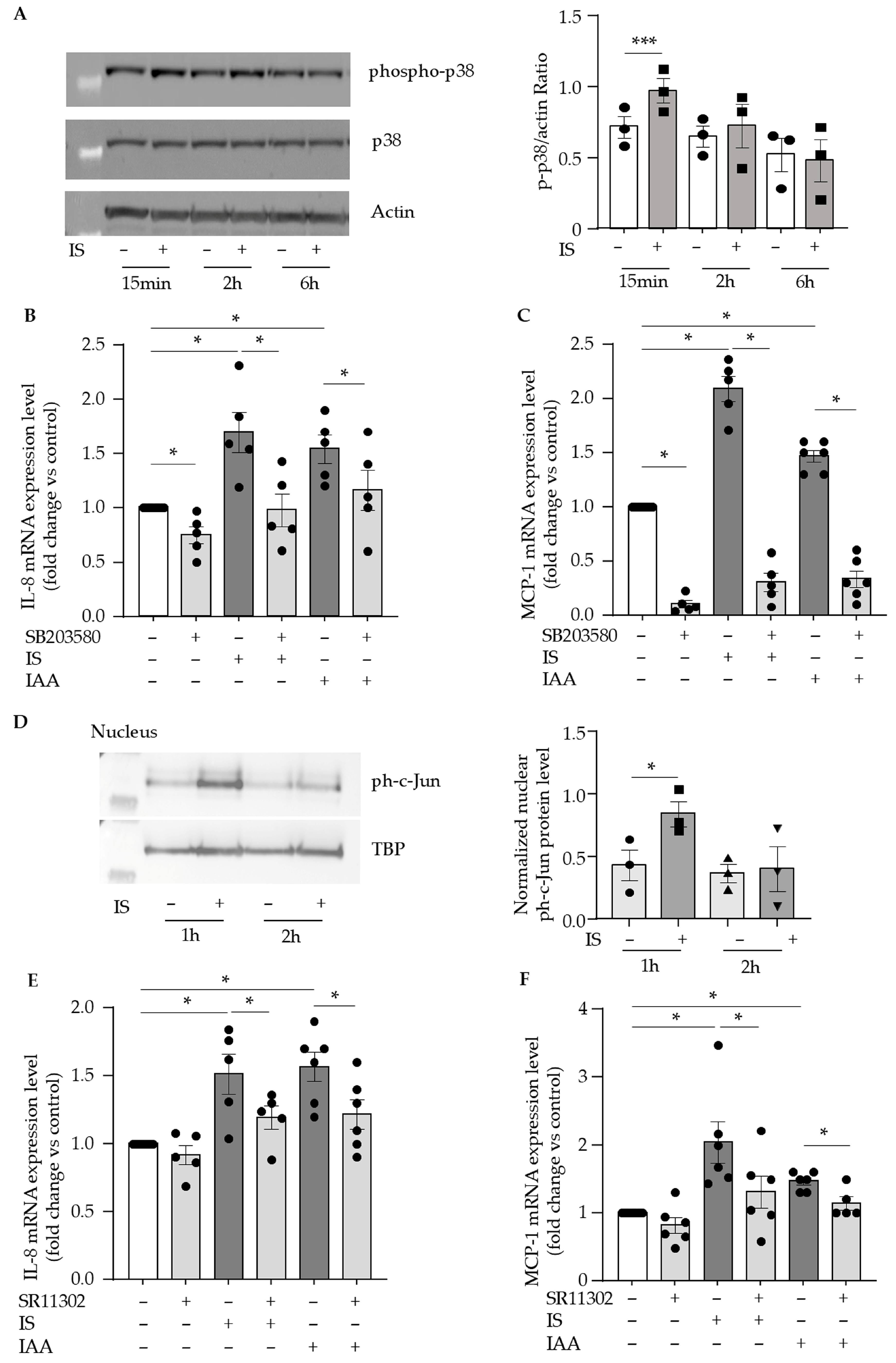
2.4. Indolic Toxins Upregulate Endothelial IL-8 and MCP-1 via the Activation of p38 MAPK/AP-1 Signaling Pathway
2.5. IL-8 and MCP-1 Serum Concentrations Correlate with Indolic Toxins and TGFβ1 in Hemodialysis Patients
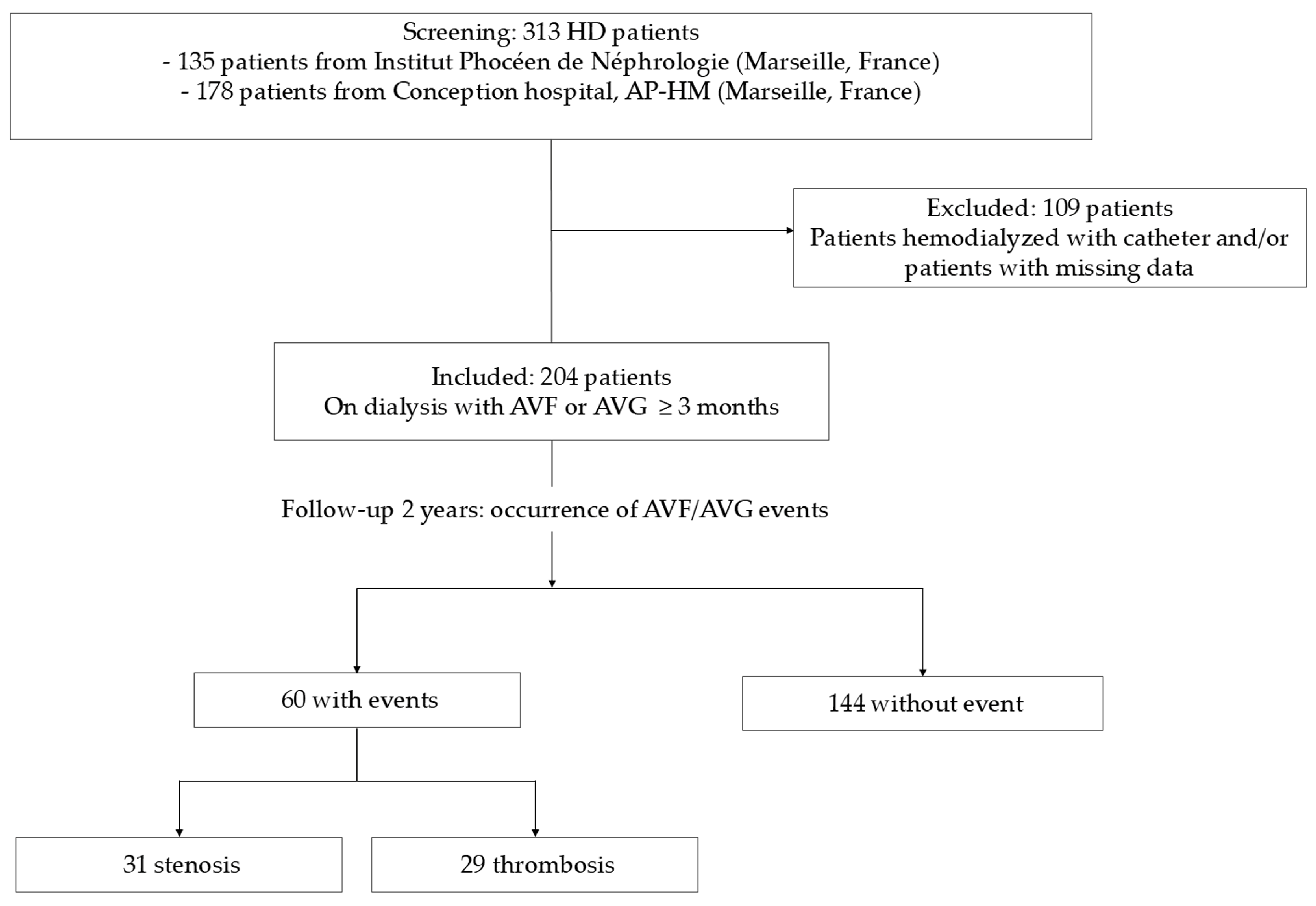
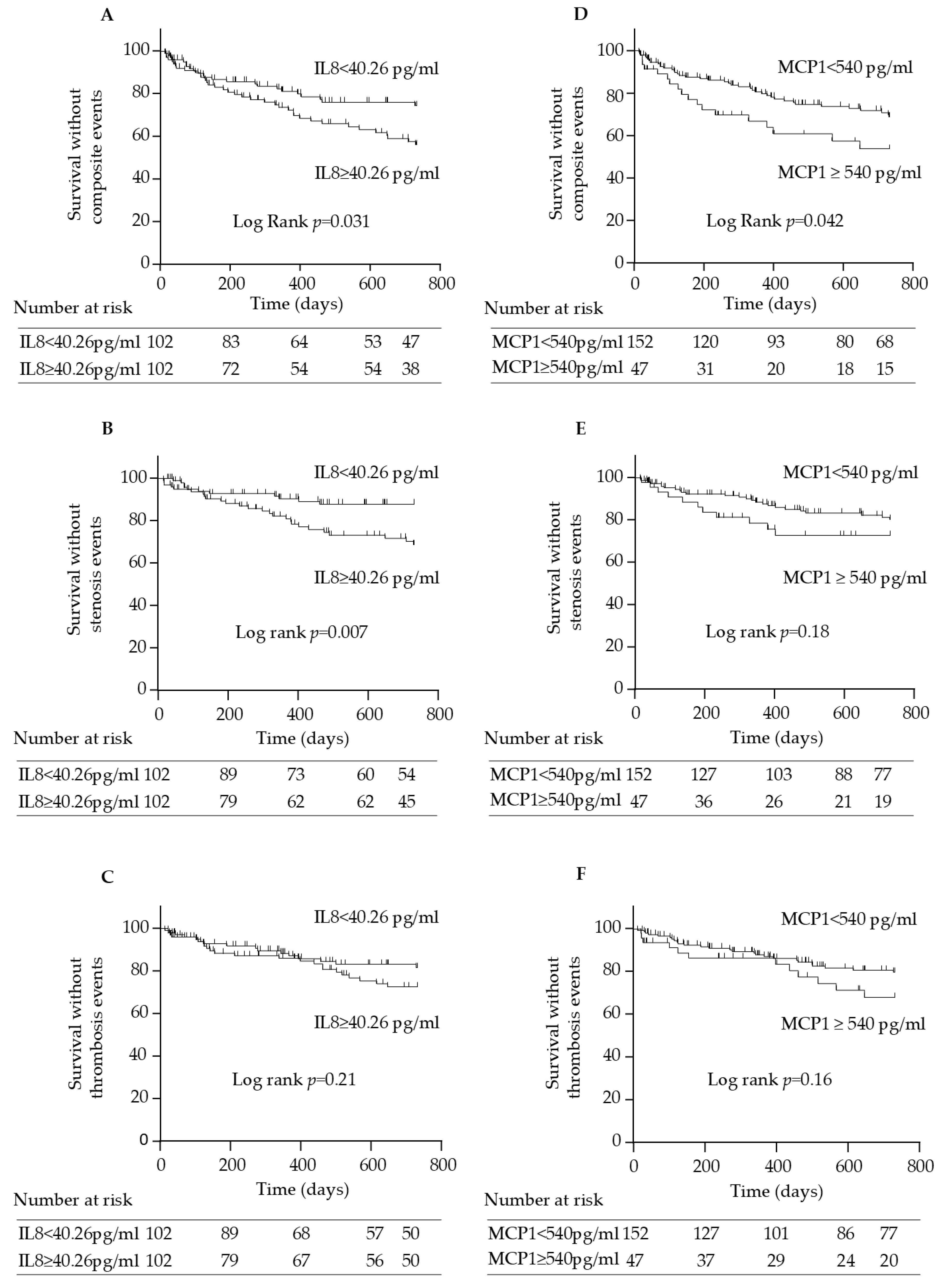
2.6. IL-8 and MCP-1 Serum Concentrations Are Associated with Arteriovenous Access Events in Hemodialysis Patients
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Patients
5.2. Laboratory Tests in Patients
5.3. Endothelial Cell Culture and Treatment
5.4. mRNA Extraction and Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
5.5. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
5.6. Study of IL-8 and MCP-1 Release in Supernatants
5.7. Study of Signaling Pathways from Transcriptomic Analyses
5.8. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lok, C.E.; Huber, T.S.; Orchanian-Cheff, A.; Rajan, D.K. Arteriovenous Access for Hemodialysis: A Review. JAMA 2024, 331, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Duan, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Intimal Hyperplasia of Arteriovenous Fistula. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2022, 85, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothuizen, T.C.; Wong, C.; Quax, P.H.A.; van Zonneveld, A.J.; Rabelink, T.J.; Rotmans, J.I. Arteriovenous Access Failure: More than Just Intimal Hyperplasia? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy-Chaudhury, P.; Sukhatme, V.P.; Cheung, A.K. Hemodialysis Vascular Access Dysfunction: A Cellular and Molecular Viewpoint. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1112–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yi, J.; Zhang, R.; Peng, Y.; Dong, J.; Sha, L. Risk Factors for Arteriovenous Fistula Thrombus Development: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2022, 47, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Yu, J.; Li, G.; Fu, S.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Luo, X. The Risk Factors for Arteriovenous Fistula Dysfunction in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Hemodial. Int. 2024, 28, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciucanu, C.C.; Mureșan, A.; Florea, E.; Réka, B.; Mureșan, A.V.; Szanto, L.-A.; Arbănași, E.-M.; Hosu, I.; Russu, E.; Arbănași, E.-M. Elevated Interleukin-6 Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Long-Term Arteriovenous Fistula Failure for Dialysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Xv, C.; Wang, D.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, P.; Tang, D.; Yang, J.; Meng, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The Predictive Value of Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index for Vascular Access Survival in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1382970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, I.; Knoflach, M.; Seubert, A.; Kreutmayer, S.B.; Stelzmüller, M.E.; Wallnoefer, E.; Blunder, S.; Frotschnig, S.; Messner, B.; Willeit, J.; et al. Lead Contributes to Arterial Intimal Hyperplasia through Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor-Mediated Endothelial Interleukin 8 Synthesis and Subsequent Invasion of Smooth Muscle Cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Q.; Fei, T.; Han, J.-D.J.; Chen, Y.-G. MCP-1 Mediates TGF-Beta-Induced Angiogenesis by Stimulating Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Migration. Blood 2007, 109, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juncos, J.P.; Grande, J.P.; Kang, L.; Ackerman, A.W.; Croatt, A.J.; Katusic, Z.S.; Nath, K.A. MCP-1 Contributes to Arteriovenous Fistula Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Fan, F.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wei, X.; Kohama, K.; Gordon, J.R.; Li, F.; Gao, Y. Recombinant Human CXCL8(3-72)K11R/G31P Regulates Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Migration through Blockage of Interleukin-8 Receptor. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinetti, G.; Wang, M.; Monticone, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, D.; Lakatta, E.G. Rat Aortic MCP-1 and Its Receptor CCR2 Increase with Age and Alter Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Function. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, T.L.; Wang, X.; Sung, C.P.; Olson, B.; McKenna, P.J.; Gu, J.L.; Feuerstein, G.Z. Interleukin-8. A Mitogen and Chemoattractant for Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Circ. Res. 1994, 75, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papayianni, A.; Alexopoulos, E.; Giamalis, P.; Gionanlis, L.; Belechri, A.-M.; Koukoudis, P.; Memmos, D. Circulating Levels of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and MCP-1 Are Increased in Haemodialysis Patients: Association with Inflammation, Dyslipidaemia, and Vascular Events. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisowska, K.A.; Storoniak, H.; Soroczyńska-Cybula, M.; Maziewski, M.; Dębska-Ślizień, A. Serum Levels of α-Klotho, Inflammation-Related Cytokines, and Mortality in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, I.; Moutabarrik, A.; Okada, N.; Kitamura, E.; Hayashi, A.; Syouji, T.; Namiki, M.; Ishibashi, M.; Zaid, D.; Tsubakihara, Y. Interleukin-8 in Chronic Renal Failure and Dialysis Patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1994, 9, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, M.; Cattaneo, I.; Longaretti, L.; Figliuzzi, M.; Ene-Iordache, B.; Remuzzi, A. Endothelial Cell Activation by Hemodynamic Shear Stress Derived from Arteriovenous Fistula for Hemodialysis Access. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 310, H49–H59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi, S.; Falleti, E.; Giacomello, R.; Stel, G.; Cecchin, E.; Sepiacci, G.; Bortolotti, N.; Zanello, F.; Gonano, F.; Bartoli, E. Risk Factors for Vascular Disease and Arteriovenous Fistula Dysfunction in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1996, 7, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-C.; Chen, T.-Y.; Hsieh, M.-Y.; Lin, L.; Yang, C.-W.; Chuang, S.-Y.; Tarng, D.-C. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Levels and Postangioplasty Restenosis of Arteriovenous Fistulas. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, C.R.; Ding, K.; Xue, H.; Tao, M.; Longchamp, A.; Belkin, M.; Kristal, B.S.; Ozaki, C.K. Adipose Phenotype Predicts Early Human Autogenous Arteriovenous Hemodialysis Remodeling. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 63, 171–176.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chermiti, R.; Burtey, S.; Dou, L. Role of Uremic Toxins in Vascular Inflammation Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, I.; Tatebe, J.; Namba, S.; Koizumi, M.; Yamazaki, J.; Morita, T. Activation of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Mediates Indoxyl Sulfate-Induced Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Expression in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Circ. J. 2012, 77, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondouin, B.; Cerini, C.; Dou, L.; Sallée, M.; Duval-Sabatier, A.; Pletinck, A.; Calaf, R.; Lacroix, R.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Poitevin, S.; et al. Indolic Uremic Solutes Increase Tissue Factor Production in Endothelial Cells by the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Pathway. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lano, G.; Laforêt, M.; Von Kotze, C.; Perrin, J.; Addi, T.; Brunet, P.; Poitevin, S.; Burtey, S.; Dou, L. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation and Tissue Factor Induction by Fluid Shear Stress and Indoxyl Sulfate in Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, L.; Sallee, M.; Cerini, C.; Poitevin, S.; Gondouin, B.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Fallague, K.; Brunet, P.; Calaf, R.; Dussol, B.; et al. The Cardiovascular Effect of the Uremic Solute Indole-3 Acetic Acid. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addi, T.; Poitevin, S.; McKay, N.; El Mecherfi, K.E.; Kheroua, O.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; de Macedo, A.; Gondouin, B.; Cerini, C.; Brunet, P.; et al. Mechanisms of Tissue Factor Induction by the Uremic Toxin Indole-3 Acetic Acid through Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor/Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Signaling Pathway in Human Endothelial Cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval-Sabatier, A.; Burtey, S.; Pelletier, M.; Laforet, M.; Dou, L.; Sallee, M.; Lorec, A.-M.; Knidiri, H.; Darbon, F.; Berland, Y.; et al. Systematic Comparison of Uremic Toxin Removal Using Different Hemodialysis Modes: A Single-Center Crossover Prospective Observational Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltombe, O.; Van Biesen, W.; Glorieux, G.; Massy, Z.; Dhondt, A.; Eloot, S. Exploring Protein Binding of Uremic Toxins in Patients with Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease and during Hemodialysis. Toxins 2015, 7, 3933–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REDERT Study group; Panichi, V.; Rocchetti, M.T.; Scatena, A.; Rosati, A.; Migliori, M.; Pizzarelli, F.; Gesualdo, L. Long Term Variation of Serum Levels of Uremic Toxins in Patients Treated by Post-Dilution High Volume on-Line Hemodiafiltration in Comparison to Standard Low-Flux Bicarbonate Dialysis: Results from the REDERT Study. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, F.C.; Barreto, D.V.; Liabeuf, S.; Meert, N.; Glorieux, G.; Temmar, M.; Choukroun, G.; Vanholder, R.; Massy, Z.A. Serum Indoxyl Sulfate Is Associated with Vascular Disease and Mortality in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouabdallah, J.; Zibara, K.; Issa, H.; Lenglet, G.; Kchour, G.; Caus, T.; Six, I.; Choukroun, G.; Kamel, S.; Bennis, Y. Endothelial Cells Exposed to Phosphate and Indoxyl Sulphate Promote Vascular Calcification through Interleukin-8 Secretion. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savira, F.; Kompa, A.R.; Magaye, R.; Xiong, X.; Huang, L.; Jucker, B.M.; Willette, R.N.; Kelly, D.J.; Wang, B.H. Apoptosis Signal-Regulating Kinase 1 Inhibition Reverses Deleterious Indoxyl Sulfate-Mediated Endothelial Effects. Life Sci. 2021, 272, 119267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, N.A.; Barros, A.F.; Nakao, L.S.; Dolenga, C.J.; Fouque, D.; Mafra, D. Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins from Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Markers in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2016, 26, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hong, W.; Jin, X.; Li, G.; Zhou, G.; Fan, L. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Is a Novel Negative Regulator of Interleukin-17-Mediated Signaling and Inflammation in Vitro. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzavlaki, K.; Moustakas, A. TGF-β Signaling. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Yisireyili, M.; Nishijima, F.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl Sulfate Enhances P53-TGF-Β1-Smad3 Pathway in Proximal Tubular Cells. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 37, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekawanvijit, S.; Kompa, A.R.; Manabe, M.; Wang, B.H.; Langham, R.G.; Nishijima, F.; Kelly, D.J.; Krum, H. Chronic Kidney Disease-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis Is Ameliorated by Reducing Circulating Levels of a Non-Dialysable Uremic Toxin, Indoxyl Sulfate. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, R.; Ohashi, Y.; Lee, J.S.; Hu, H.; Gonzalez, L.; Zhang, W.; Langford, J.; Matsubara, Y.; Yatsula, B.; Tellides, G.; et al. Endothelial Cell TGF-β (Transforming Growth Factor-Beta) Signaling Regulates Venous Adaptive Remodeling to Improve Arteriovenous Fistula Patency. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2022, 42, 868–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Lee, S.-R.; Bai, H.; Guo, J.; Hashimoto, T.; Isaji, T.; Guo, X.; Wang, T.; Wolf, K.; Liu, S.; et al. TGFβ (Transforming Growth Factor-Beta)-Activated Kinase 1 Regulates Arteriovenous Fistula Maturation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, e203–e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stracke, S.; Konner, K.; Köstlin, I.; Friedl, R.; Jehle, P.M.; Hombach, V.; Keller, F.; Waltenberger, J. Increased Expression of TGF-Beta1 and IGF-I in Inflammatory Stenotic Lesions of Hemodialysis Fistulas. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, A.; Salway, F.; Dressman, H.K.; Kröner-Lux, G.; Hafner, M.; Day, P.J.R.; Marchuk, D.A.; Garland, J. ALK1 Signalling Analysis Identifies Angiogenesis Related Genes and Reveals Disparity between TGF-Beta and Constitutively Active Receptor Induced Gene Expression. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2006, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Han, J.-D.; Wang, N.; Chen, Y.-G. Distinct Regulation of Gene Expression in Human Endothelial Cells by TGF-Beta and Its Receptors. Microvasc. Res. 2006, 71, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solignac, J.; Dou, L.; Chermiti, R.; McKay, N.; Giaime, P.; Pedinielli, N.; Benjelloun, H.; Lano, G.; Mancini, J.; Burtey, S.; et al. Myostatin Exacerbates Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulfate and Is Associated with Hemodialysis Arteriovenous Access Complications. Toxins 2025, 17, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Juni, R.; Harakalova, M.; Duncker, D.J.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Koolwijk, P.; van Hinsbergh, V.; Verhaar, M.C.; Mokry, M.; Cheng, C. Indoxyl Sulfate Stimulates Angiogenesis by Regulating Reactive Oxygen Species Production via CYP1B1. Toxins 2019, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Deng, L.; Hong, M.; Akkaraju, G.R.; Inoue, J.; Chen, Z.J. TAK1 Is a Ubiquitin-Dependent Kinase of MKK and IKK. Nature 2001, 412, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Bolick, D.T.; Hatley, M.E.; Natarajan, R.; Reilly, K.B.; Yeh, M.; Chrestensen, C.; Sturgill, T.W.; Hedrick, C.C. Glucose Regulates Interleukin-8 Production in Aortic Endothelial Cells through Activation of the P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway in Diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31930–31936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Osaka, M.; Edamatsu, T.; Itoh, Y.; Yoshida, M. Crucial Role of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) in Indoxyl Sulfate-Induced Vascular Inflammation. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2016, 23, 960–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.H.; Park, H.; Kim, S.J. The Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate-Induced Endothelial Microparticles on Neointimal Hyperplasia Formation in an Ex Vivo Model. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2017, 93, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Yu, P.; Tao, M.; Gupta, T.; Moldawer, L.L.; Berceli, S.A.; Jiang, Z. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1/CCR2 Axis Promotes Vein Graft Neointimal Hyperplasia through Its Signaling in Graft-Extrinsic Cell Populations. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2418–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Poitevin, S.; Sallée, M.; Addi, T.; Gondouin, B.; McKay, N.; Denison, M.S.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Duval-Sabatier, A.; Cerini, C.; et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Is Activated in Patients and Mice with Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 986–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gonzalez, L.; Li, X.; Bai, H.; Li, Z.; Taniguchi, R.; Langford, J.; Ohashi, Y.; Thaxton, C.; Aoyagi, Y.; et al. Endothelial TGF-β Signaling Regulates Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition During Arteriovenous Fistula Remodeling in Mice with Chronic Kidney Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2024, 44, 2509–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallée, M.; Dou, L.; Cerini, C.; Poitevin, S.; Brunet, P.; Burtey, S. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Activating Effect of Uremic Toxins from Tryptophan Metabolism: A New Concept to Understand Cardiovascular Complications of Chronic Kidney Disease. Toxins 2014, 6, 934–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolachalama, V.B.; Shashar, M.; Alousi, F.; Shivanna, S.; Rijal, K.; Belghasem, M.E.; Walker, J.; Matsuura, S.; Chang, G.H.; Gibson, C.M.; et al. Uremic Solute-Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Tissue Factor Axis Associates with Thrombosis after Vascular Injury in Humans. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitalia, V.C.; Shivanna, S.; Martorell, J.; Balcells, M.; Bosch, I.; Kolandaivelu, K.; Edelman, E.R. Uremic Serum and Solutes Increase Post-Vascular Interventional Thrombotic Risk through Altered Stability of Smooth Muscle Cell Tissue Factor. Circulation 2013, 127, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addi, T.; Dou, L.; Burtey, S. Tryptophan-Derived Uremic Toxins and Thrombosis in Chronic Kidney Disease. Toxins 2018, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Aken, B.E.; den Heijer, M.; Bos, G.M.; van Deventer, S.J.; Reitsma, P.H. Recurrent Venous Thrombosis and Markers of Inflammation. Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 83, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Hsieh, M.Y.; Hung, S.C.; Kuo, K.L.; Tsai, T.H.; Lai, C.L.; Chen, J.W.; Lin, S.J.; Huang, P.H.; Tarng, D.C. Serum Indoxyl Sulfate Associates with Postangioplasty Thrombosis of Dialysis Grafts. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munjal, A.; Khandia, R. Atherosclerosis: Orchestrating Cells and Biomolecules Involved in Its Activation and Inhibition. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2020, 120, 85–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataille, S.; Landrier, J.-F.; Astier, J.; Giaime, P.; Sampol, J.; Sichez, H.; Ollier, J.; Gugliotta, J.; Serveaux, M.; Cohen, J.; et al. The “Dose-Effect” Relationship Between 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Muscle Strength in Hemodialysis Patients Favors a Normal Threshold of 30 Ng/mL for Plasma 25-Hydroxyvitamin D. J. Ren. Nutr. 2016, 26, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lano, G.; Sallée, M.; Pelletier, M.; Bataille, S.; Fraisse, M.; Berda-Haddad, Y.; Brunet, P.; Burtey, S. Mean Platelet Volume Predicts Vascular Access Events in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calaf, R.; Cerini, C.; Genovesio, C.; Verhaeghe, P.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Berge-Lefranc, D.; Gondouin, B.; Dou, L.; Morange, S.; Argiles, A.; et al. Determination of Uremic Solutes in Biological Fluids of Chronic Kidney Disease Patients by HPLC Assay. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 2281–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, R.; De Smet, R.; Glorieux, G.; Argiles, A.; Baurmeister, U.; Brunet, P.; Clark, W.; Cohen, G.; De Deyn, P.P.; Deppisch, R.; et al. Review on Uremic Toxins: Classification, Concentration, and Interindividual Variability. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| All Patients (n = 204) | IL8< 40.26 pg/mL (n = 102) | IL8≥ 40.26 pg/mL (n = 102) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 71.2 [18; 94] | 71.1 [20; 94] | 71.5 [18; 94] | 0.391 |
| Gender ratio (F/M) | 75/129 | 37/65 | 38/64 | >0.999 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.7 [12.9; 41.5] | 24.5[12.9; 35.5] | 24.8[16.4; 41.5] | 0.211 |
| Arteriovenous graft | 33 (16%) | 19 (19%) | 14 (14%) | 0.447 |
| SBP before dialysis (mmHg) | 140 [83; 210] | 135 [84; 208] | 144 [83; 210] | 0.005 |
| DBP before dialysis (mmHg) | 70 [40; 119] | 69 [40; 115] | 71 [42; 119] | 0.060 |
| Dialysis vintage (months) | 43 [3; 432] | 37 [3; 421] | 48 [3; 432] | 0.657 |
| History of hypertension | 172 (84%) | 80 (78%) | 92 (90%) | 0.033 |
| History of diabetes | 80 (39%) | 30 (29%) | 50 (49%) | 0.006 |
| History of CAD | 68 (33%) | 26 (25%) | 42 (41%) | 0.025 |
| History of heart failure | 45 (22%) | 16 (16%) | 29 (28%) | 0.042 |
| History of atrial fibrillation | 60 (29%) | 29 (28%) | 31 (30%) | 0.878 |
| History of PAD | 50 (24%) | 20 (20%) | 30 (29%) | 0.145 |
| History of stroke/TIA | 28 (14%) | 14 (14%) | 14 (14%) | >0.999 |
| History of DVT/PE | 25 (12%) | 14 (14%) | 11 (11%) | 0.670 |
| History of renal transplantation | 19 (9%) | 8 (8%) | 11 (11%) | 0.630 |
| History of dyslipidemia | 60 (29%) | 25 (25%) | 35 (34%) | 0.166 |
| Antihypertensive drugs | 137 (67%) | 68 (67%) | 69 (68%) | >0.999 |
| Antidiabetic treatments | 76 (37%) | 29 (28%) | 47 (46%) | 0.013 |
| Antiplatelet drugs | 103 (50%) | 48 (47%) | 55 (54%) | 0.409 |
| Anticoagulant drugs | 38 (18%) | 17 (17%) | 21 (21%) | 0.590 |
| Hypolipidemic drugs | 60 (29%) | 26 (25%) | 34 (33%) | 0.282 |
| Erythropoiesis stimulating agents | 154 (75%) | 83 (81%) | 71 (70%) | 0.072 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.8 [6.1; 13.7] | 10.6 [6.1; 13.3] | 10.9 [8.0; 13.7] | 0.327 |
| Serum albumin (g/L) | 38.8 [21.6; 52.1] | 38.0 [23.3; 47.2] | 39.0 [21.6; 52.1] | 0.265 |
| Parathyroid hormone (ng/L) | 27 [1; 2217] | 37 [1; 2217] | 19 [2; 656] | 0.045 |
| Serum ferritin (ng/mL) | 385 [26; 5000] | 395 [26; 5000] | 347 [26; 1625] | 0.486 |
| Serum calcium (mmol/L) | 2.34 [1.84; 3.09] | 2.33 [1.84; 3.09] | 2.34 [1.84; 2.85] | 0.360 |
| Serum phosphate (mmol/L) | 1.50 [0.38; 4.03] | 1.45 [0.65; 4.03] | 1.59 [0.38; 3.73] | 0.310 |
| Serum potassium (mmol/L) | 5.01 [2.91; 7.20] | 5.05 [2.91; 6.82] | 5.00 [3.39; 7.2] | 0.644 |
| Serum indoxyl sulfate (µM) | 87.8 [0; 301] | 88.6 [0; 276] | 86.3 [0; 301] | 0.698 |
| Serum indole-3 acetic acid (µM) | 3.1 [0.2; 33.5] | 2.7 [0.2; 22.2] | 3.8 [1.3; 33.5] | 0.002 |
| Serum p-cresyl sulfate (µM) | 148 [0; 1227] | 144 [0; 1227] | 153 [8; 438] | 0.394 |
| Serum CRP (mg/L) | 6.3 [0.2; 418.9] | 7.5 [0.2; 107.3] | 5.4 [0.6; 418.9] | 0.461 |
| Serum IL-6 (pg/mL) | 4 [0; 232] | 2.75 [0; 92.1] | 5.3 [0; 232.2] | 0.014 |
| Serum MCP-1 (pg/mL) | 432 [112; 1333] | 425 [153; 1333] | 444 [115; 930] | 0.069 |
| Serum TGFβ1 (ng/mL) | 22.5 [6.9; 51.8] | 20.1 [8.0; 51.8] | 24.7 [6.9; 39.8] | 0.004 |
| Serum IL-8 (pg/mL) | 40.26 [0; 1299] | 26.3 [0; 40.25] | 73.8 [40.26; 1299] | <0.0001 |
| Variable | Rho | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Serum TGFβ1 | 0.26 | 0.0004 |
| Serum IL-6 | 0.22 | 0.006 |
| Serum MCP-1 | 0.18 | 0.01 |
| Serum IAA | 0.14 | 0.05 |
| Systolic blood pressure before dialysis | 0.17 | 0.02 |
| Diastolic blood pressure before dialysis | 0.15 | 0.03 |
| Variable | Rho | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Serum indoxyl sulfate | 0.22 | 0.002 |
| Serum TGFβ1 | 0.22 | 0.003 |
| Serum parathyroid hormone | 0.21 | 0.003 |
| Body mass index | 0.18 | 0.02 |
| Serum ferritin | −0.21 | 0.002 |
| Hazard Ratio | HR 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate analysis | |||
| IL-8 ≥ 40.26 pg/mL | 1.76 | [1.05–2.96] | 0.033 |
| MCP-1 ≥ 540 pg/mL | 1.77 | [1.01–3.09] | 0.043 |
| MCP-1 (per 100 pg/mL increase) | 1.23 | [1.06–1.43] | 0.006 |
| Body mass index (BMI) | 1.11 | [1.06–1.17] | <0.0001 |
| History of diabetes | 1.60 | [0.97–2.66] | 0.068 |
| Antidiabetic treatments | 1.76 | [1.06–2.92] | 0.029 |
| Multivariate analysis | |||
| IL-8 ≥ 40.26 pg/mL | 1.85 | [1.04–3.29] | 0.036 |
| MCP-1 (per 100 pg/mL increase) | 1.19 | [1.01–1.39] | 0.033 |
| Gender | 1.26 | [0.71–2.21] | 0.492 |
| Age > 71.2 years | 0.82 | [0.47–1.44] | 0.393 |
| AVG | 1.43 | [0.68–3.02] | 0.346 |
| Normal BMI 18.5–25 (Ref) | 0.082 | ||
| BMI < 18.5 | 0.68 | [0.15–3.01] | 0.612 |
| BMI 25–29.9 | 1.33 | [0.68–2.61] | 0.407 |
| BMI ≥ 30 | 2.33 | [1.16–4.64] | 0.017 |
| History of diabetes | 1.20 | [0.67–2.16] | 0.541 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chermiti, R.; Bataille, S.; Giaime, P.; Solignac, J.; Pedinielli, N.; McKay, N.; Bigey-Frau, D.; Lano, G.; Benjelloun, H.; Addi, T.; et al. From Uremic Toxins to Hemodialysis Access Failure: IL-8 and MCP-1 Chemokines as a Link Between Endothelial Activation and AV Access Complications. Toxins 2025, 17, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090434
Chermiti R, Bataille S, Giaime P, Solignac J, Pedinielli N, McKay N, Bigey-Frau D, Lano G, Benjelloun H, Addi T, et al. From Uremic Toxins to Hemodialysis Access Failure: IL-8 and MCP-1 Chemokines as a Link Between Endothelial Activation and AV Access Complications. Toxins. 2025; 17(9):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090434
Chicago/Turabian StyleChermiti, Rania, Stanislas Bataille, Philippe Giaime, Justine Solignac, Nathalie Pedinielli, Nathalie McKay, Dorian Bigey-Frau, Guillaume Lano, Hamza Benjelloun, Tawfik Addi, and et al. 2025. "From Uremic Toxins to Hemodialysis Access Failure: IL-8 and MCP-1 Chemokines as a Link Between Endothelial Activation and AV Access Complications" Toxins 17, no. 9: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090434
APA StyleChermiti, R., Bataille, S., Giaime, P., Solignac, J., Pedinielli, N., McKay, N., Bigey-Frau, D., Lano, G., Benjelloun, H., Addi, T., Mancini, J., Burtey, S., & Dou, L. (2025). From Uremic Toxins to Hemodialysis Access Failure: IL-8 and MCP-1 Chemokines as a Link Between Endothelial Activation and AV Access Complications. Toxins, 17(9), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090434





