Regulation of FpvelC on Conidiation, Pathogenicity and Secondary Metabolism in Fusarium proliferatum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
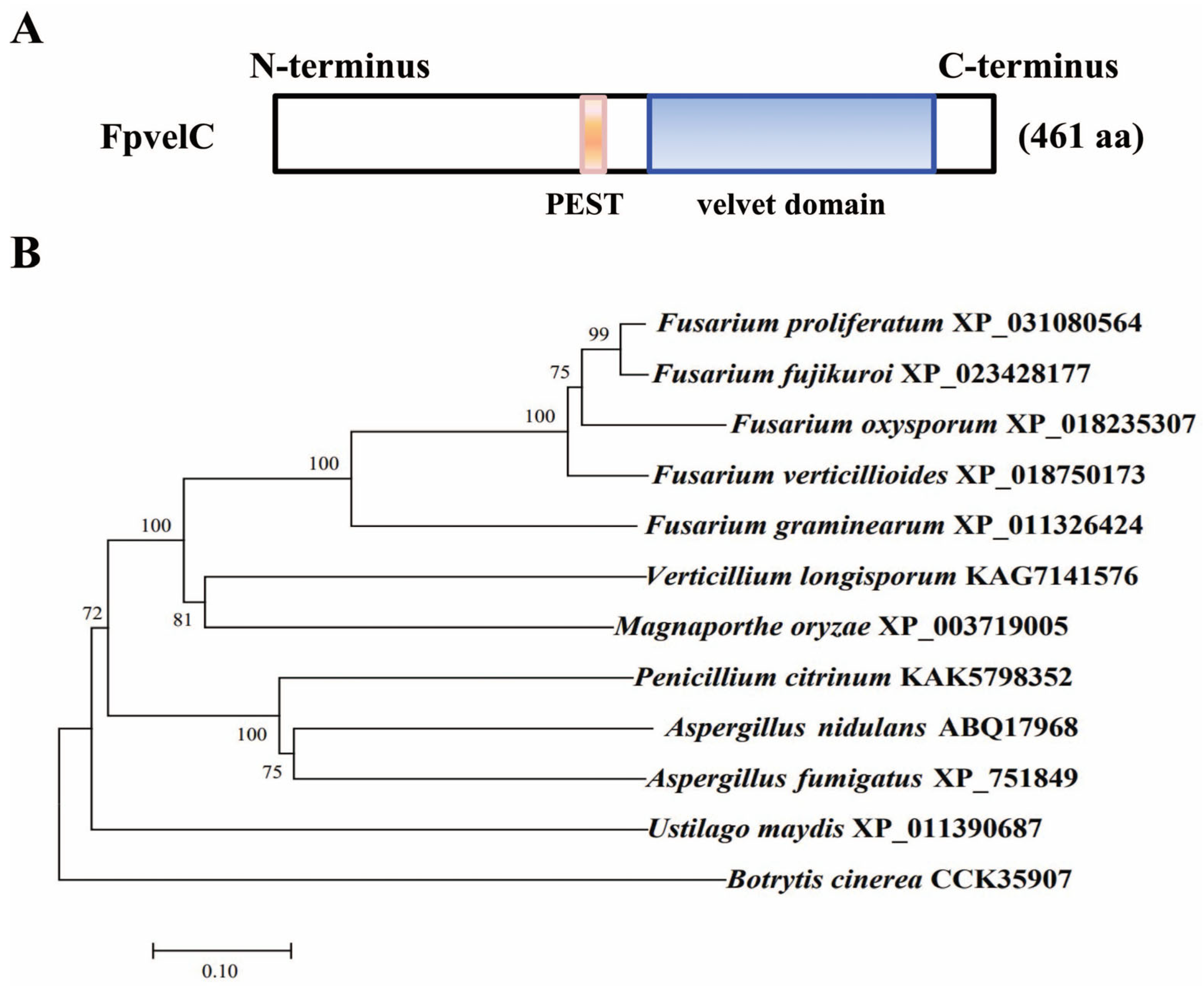
2.1. Identification and Deletion of FpvelC
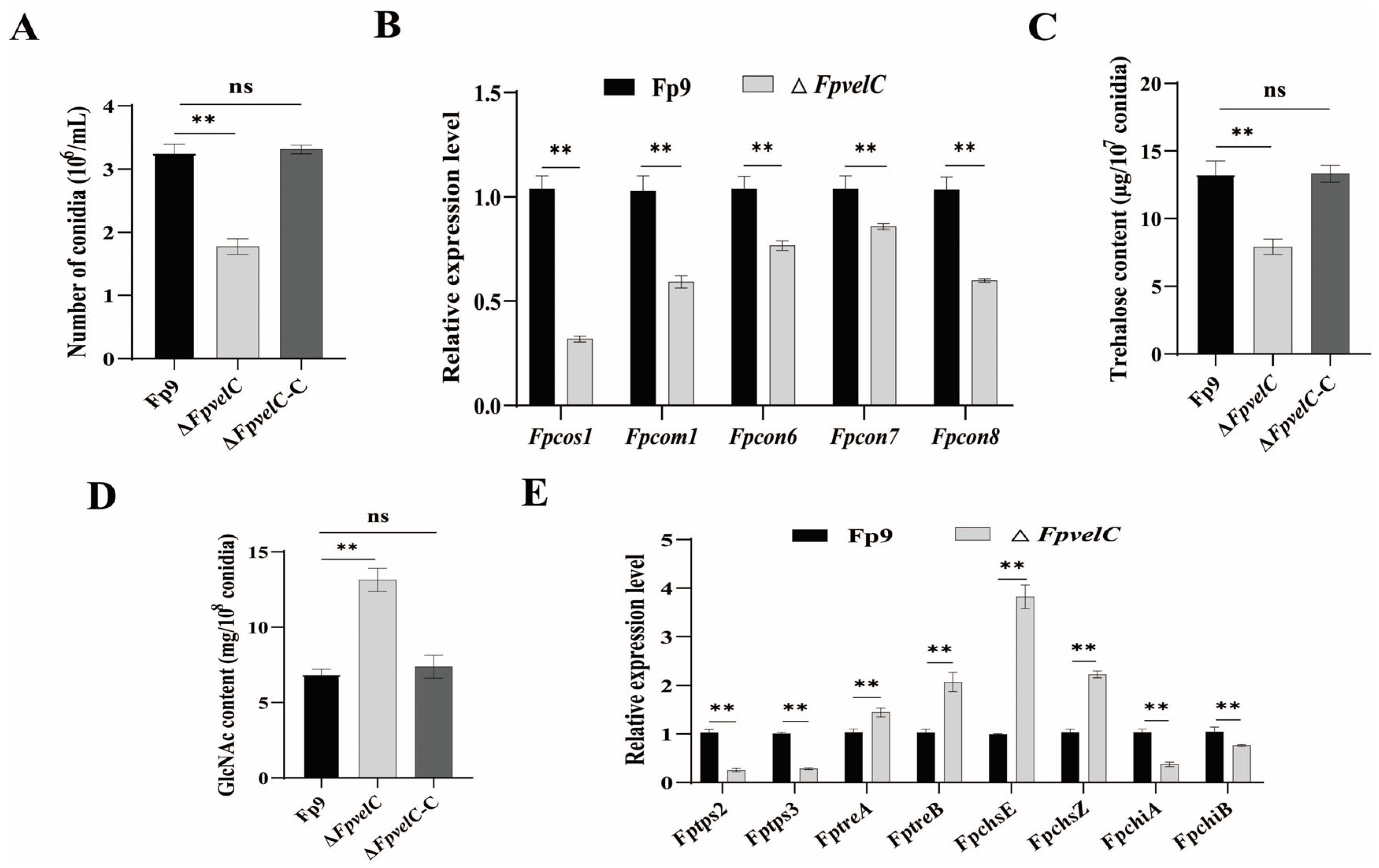
2.2. FpvelC Is Indispensable for Normal Conidiation
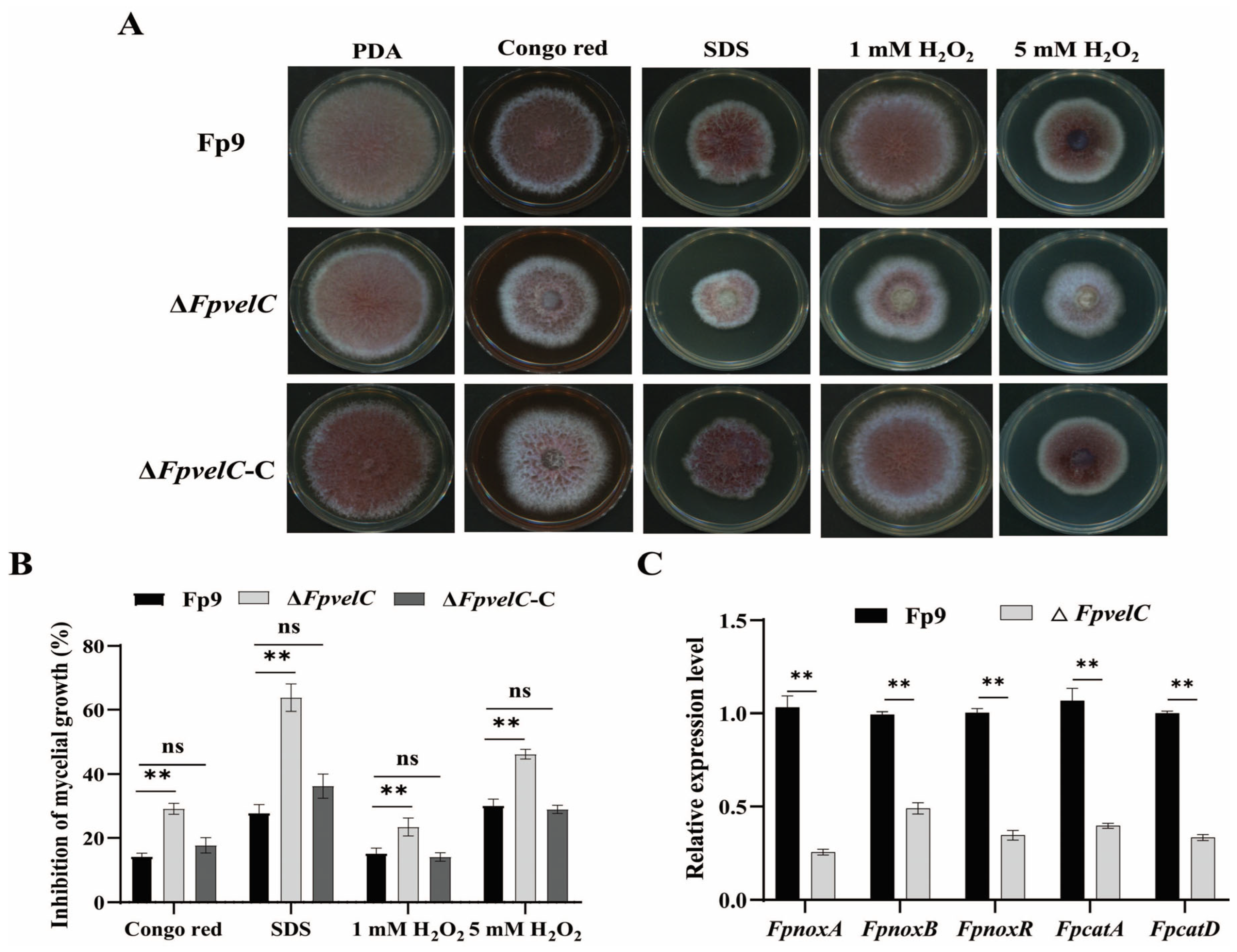
2.3. FpvelC Is Required for Responses to Stress Tolerance
2.4. FpvelC Plays an Important Role in Full Virulence
2.5. FpvelC Negatively Governs Production of Secondary Metabolites
2.6. FpvelC Is Involved in Nitrogen Metabolism
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Fungal Strains and Growth Conditions
5.2. Sequence Analysis of FpvelC
5.3. Gene Deletion and Complementation
5.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
5.5. Trehalose Assay
5.6. Chitin Assay
5.7. Stress Tolerance Analysis
5.8. Rice Infection Assay
5.9. Maize Infection Assay
5.10. Microscopy Observation
5.11. Determination of FB1 Production
5.12. Quantification of Fusaric Acid Production
5.13. Measurement of Intracellular Glutamine
5.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.; Hwang, S.F.; Strelkov, S.E. The host range of Fusarium proliferatum in western Canada. Pathogens 2024, 13, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.S.; Wink, M. Exposure, occurrence, and chemistry of fumonisins and their cryptic derivatives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 769–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce-García, N.; Serna-Saldivar, S.O.; Garcia-Lara, S. Fumonisins and their analogues in contaminated corn and its processed foods—A review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2018, 35, 2183–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Ye, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.-S.; Huang, C.; Sun, X. Occurrence, transformation, and toxicity of fumonisins and their covert products during food processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 3660–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anumudu, C.K.; Ekwueme, C.T.; Uhegwu, C.C.; Ejileugha, C.; Augustine, J.; Okolo, C.A.; Onyeaka, H. A review of the mycotoxin family of fumonisins, their biosynthesis, metabolism, methods of detection and effects on humans and animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 26, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamle, M.; Mahato, D.K.; Devi, S.; Lee, K.E.; Kang, S.G.; Kumar, P. Fumonisins: Impact on agriculture, food, and human health and their management strategies. Toxins 2019, 11, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Pfohl, K.; Karlovsky, P.; Dehne, H.-W.; Altincicek, B.; Marion-Poll, F. Dissemination of Fusarium proliferatum by mealworm beetle Tenebrio molitor. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, D.; Segorbe, D.; López-Berges, M.S.; De Curtis, F.; Lima, G.; Di Pietro, A.; Turrà, D. Alkaline pH, low iron availability, poor nitrogen sources and CWI MAPK signaling are associated with increased fusaric acid production in Fusarium oxysporum. Toxins 2023, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.K.; Bacon, C.W.; Wray, E.M.; Hagler, W.M. Fusaric acid in Fusarium moniliforme cultures, corn, and feeds toxic to livestock and the neurochemical effects in the brain and pineal gland of rats. Nat. Toxins 1995, 3, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, E.S.; Rakhmankulova, M.; Kucera, K.; de Sena Filho, J.G.; Portero, C.E.; Narváez-Trujillo, A.; Holley, S.A.; Strobel, S.A. Fusaric acid induces a notochord malformation in zebrafish via copper chelation. BioMetals 2015, 28, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.T.; Yao, C.P.; Liu, W.H.; Cao, W.Y.; Shao, W.; Liao, S.Q.; Yu, T.; Zhu, Q.F.; Chen, Z.; Zang, Y.J.; et al. An fusaric acid-based CRISPR library screen identifies MDH2 as a broad-spectrum regulator of Fusarium toxin-induced cell death. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamur, S.; Ünal, F.; Yılmaz, S.; Erikel, E.; Yüzbaşıoğlu, D. Evaluation of the cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of mycotoxin fusaric acid. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 43, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, Ö.; Braus, G.H. Coordination of secondary metabolism and development in fungi: The VELVET family of regulatory proteins. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, Ö.; Krappmann, S.; Ni, M.; Bok, J.W.; Helmstaedt, K.; Valerius, O.; Braus-Stromeyer, S.; Kwon, N.; Keller, N.P.; Yu, J.; et al. VelB/VeA/LaeA complex coordinates light signal with fungal development and secondary metabolism. Science 2008, 320, 1504–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Pei, R.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, Y.; He, B. Light regulation of secondary metabolism in fungi. J. Biol. Eng. 2023, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, N.; Yue, Q.; An, Z.; Bills, G.F. Apc.LaeA and Apc.VeA of the velvet complex govern secondary metabolism and morphological development in the echinocandin-producing fungus Aspergillus pachycristatus. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 47, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, T.J.; Moon, H.; Yu, J.H.; Park, H.S. Characterization of the velvet regulators in Aspergillus flavus. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, E.; Ma, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. Requirement of LaeA, VeA, and VelB on asexual development, ochratoxin A biosynthesis, and fungal virulence in Aspergillus ochraceus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estiarte, N.; Lawrence, C.; Sanchis, V.; Ramos, A.; Crespo-Sempere, A. LaeA and VeA are involved in growth morphology, asexual development, and mycotoxin production in Alternaria alternata. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 238, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merhej, J.; Urban, M.; Dufresne, M.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Richard-Forget, F.; Barreau, C. The velvet gene, FgVe1, affects fungal development and positively regulates trichothecene biosynthesis and pathogenicity in Fusarium graminearum. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Yun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Z. FgVELB is associated with vegetative differentiation, secondary metabolism and virulence in Fusarium graminearum. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2012, 49, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Han, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Kong, L. Velvet family protein FpVelB affects virulence in association with secondary metabolism in Fusarium pseudograminearum. Cells 2024, 13, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Zong, Y.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Long, M.; Tian, S. Dissection of patulin biosynthesis, spatial control and regulation mechanism in Penicillium expansum. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 1124–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhou, S.; Tang, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, Z. The velvet proteins CsVosA and CsVelB coordinate growth, cell wall integrity, sporulation, conidial viability and pathogenicity in the rubber anthracnose fungus Colletotrichum siamense. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 268, 127290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Ge, S.; Liang, W.; Liao, W.; Li, W.; Jiao, G.; Wei, X.; Shao, G.; Xie, L.; et al. Genomic footprints related with adaptation and fumonisins production in Fusarium proliferatum. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1004454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Fei, Y.J.; Wu, Y.B.; Luo, D.L.; Chen, M.; Sun, K.; Zhang, W.; Dai, C.C. Endophytic fungus reshapes spikelet microbiome to reduce mycotoxin produced by Fusarium proliferatum through altering rice metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 11350–11364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ge, S.; Liang, W.; Liao, W.; Li, W.; Jiao, G.; Wei, X.; Shao, G.; Xie, L.; Sheng, Z.; et al. Genome-wide characterization reveals variation potentially involved in pathogenicity and mycotoxins biosynthesis of Fusarium proliferatum causing spikelet rot disease in rice. Toxins 2022, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, J.A.F.; Orso, P.B.; Bordin, K.; Hara, R.V.; Luciano, F.B. Toxicological effects of fumonisin B1 in combination with other Fusarium toxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 121, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsehaye, H.; Brurberg, M.B.; Sundheim, L.; Assefa, D.; Tronsmo, A.; Tronsmo, A.M. Natural occurrence of Fusarium species and fumonisin on maize grains in Ethiopia. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 147, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Yu, J.H. Genetic control of asexual sporulation in filamentous fungi. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruger-Herreros, C.; Corrochano, L.M. Conidiation in Neurospora crassa: Vegetative reproduction by a model fungus. Int. Microbiol. 2020, 23, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Son, S.H.; Chen, W.; Son, Y.E.; Lee, I.; Yu, J.H.; Park, H.S. Regulation of conidiogenesis in Aspergillus flavus. Cells 2022, 11, 2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, S.; Guo, C.; Wei, H.; He, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, X. The C2H2 transcription factor Con7 regulates vegetative growth, cell wall integrity, oxidative stress, asexual sporulation, appressorium and hyphopodium formation, and pathogenicity in Colletotrichum graminicola and Colletotrichum siamense. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höfer, A.M.; Harting, R.; Aßmann, N.F.; Gerke, J.; Schmitt, K.; Starke, J.; Bayram, Ö.; Tran, V.-T.; Valerius, O.; Braus-Stromeyer, S.A.; et al. The velvet protein Vel1 controls initial plant root colonization and conidia formation for xylem distribution in Verticillium wilt. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Song, T.; Yu, J.; Cao, H.; Pan, X.; Qi, Z.; Du, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y. UvVelC is important for conidiation and pathogenicity in the rice false smut pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens. Virulence 2024, 15, 2301243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Han, J.-H.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.-H. Comparative functional analysis of the velvet gene family reveals unique roles in fungal development and pathogenicity in Magnaporthe oryzae. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014, 66, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Nam, T.Y.; Han, K.H.; Kim, S.C.; Yu, J.H.; Yun, S.H. VelC positively controls sexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopke, K.; Hoff, B.; Bloemendal, S.; Katschorowski, A.; Kamerewerd, J.; Kück, U. Members of the Penicillium chrysogenum velvet complex play functionally opposing roles in the regulation of penicillin biosynthesis and conidiation. Eukaryot. Cell 2013, 12, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Berges, M.S.; Hera, C.; Sulyok, M.; Schäfer, K.; Capilla, J.; Guarro, J.; Di Pietro, A. The velvet complex governs mycotoxin production and virulence of Fusarium oxysporum on plant and mammalian hosts. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 87, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, J.; Farkaš, V.; Sanz, A.B.; Cabib, E. Strengthening the fungal cell wall through chitin-glucan cross-links: Effects on morphogenesis and cell integrity. Cell. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, D.; Chen, T.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, G.; Tian, S. Production, signaling, and scavenging mechanisms of reactive oxygen species in fruit–pathogen interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.M.; Wilson, R.A. Reactive oxygen species metabolism and plant-fungal interactions. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2018, 110, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, N.; Zhang, H.; Hu, C.; Wang, W.; Calvo, A.M.; Harris, S.D.; Chen, S.; Li, S. Coordinated and distinct functions of velvet proteins in Fusarium verticillioides. Eukaryot. Cell 2014, 13, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camejo, D.; Guzmán-Cedeño, Á.; Moreno, A. Reactive oxygen species, essential molecules, during plant-pathogen interactions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, N.; Leroch, M.; Schumacher, J.; Zimmer, D.; Könnel, A.; Klug, K.; Leisen, T.; Scheuring, D.; Sommer, F.; Mühlhaus, T.; et al. Investigations on VELVET regulatory mutants confirm the role of host tissue acidification and secretion of proteins in the pathogenesis of Botrytis cinerea. New Phytol. 2018, 219, 1062–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Hou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liang, M.; Gao, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, S. Infection and colonization of pathogenic fungus Fusarium proliferatum in rice spikelet rot disease. Rice Sci. 2019, 26, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, V.; Vélëz, H.; Tzelepis, G. The role of glycoside hydrolases in phytopathogenic fungi and Oomycetes virulence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, N.; González, M.A.; González, C.; Brito, N. Simultaneous silencing of xylanase genes in Botrytis cinerea. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, N.; Li, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Short, D.P.G.; Li, L.; Guo, W.; et al. Verticillium dahliae manipulates plant immunity by glycoside hydrolase 12 proteins in conjunction with carbohydrate-binding module 1. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1914–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, M. Regulation of kojic acid production in Aspergillus oryzae. JSM Mycotoxins 2022, 72, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, S. Effects of disruption of five FUM genes on fumonisin biosynthesis and pathogenicity in Fusarium proliferatum. Toxins 2019, 11, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niehaus, E.-M.; Münsterkötter, M.; Proctor, R.H.; Brown, D.W.; Sharon, A.; Idan, Y.; Oren-Young, L.; Sieber, C.M.; Novák, O.; Pěnčík, A.; et al. Comparative “omics” of the Fusarium fujikuroi species complex highlights differences in genetic potential and metabolite synthesis. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 3574–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhang, T.L.; Yu, Q.; Liu, L.M.; Huang, S.W.; Wang, L. Effects of nitrogen-regulating gene AreA on growth, pathogenicity, and fumonisin synthesis of Fusarium proliferatum. Rice Sci. 2024, 31, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, M.; Schothorst, J.; Kankipati, H.N.; Van Zeebroeck, G.; Rubio-Texeira, M.; Thevelein, J.M. Nutrient sensing and signaling in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 254–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S.; Battistuzzi, F.U. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Ge, S.; Sheng, Z.; Hu, S.; Jiao, G.; Shao, G.; Xie, L.; Tang, S.; Hu, P. The role of FpfetC from Fusarium proliferatum in iron acquisition, fumonisin B1 production, and virulence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.H.; Hamari, Z.; Han, K.H.; Seo, J.A.; Reyes-Domínguez, Y.; Scazzocchio, C. Double-joint PCR: A PCR-based molecular tool for gene manipulations in filamentous fungi. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2004, 41, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Ni, M.; Jeong, K.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Yu, J.H. The role, interaction and regulation of the velvet regulator VelB in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaggini, S.; Munro, C.A.; Paschoud, S.; Sanglard, D.; Gow, N.A.R. Independent regulation of chitin synthase and chitinase activity in Candida albicans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiology 2004, 150, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.W.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.M.; Tang, S.Q.; Zhu, D.F.; Savary, S. Rice spikelet rot disease in China—2. Pathogenicity tests, assessment of the importance of the disease, and preliminary evaluation of control options. Crop. Prot. 2011, 30, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, G.B.; de Castro Gome Vieira, C.M.; Orlando, R.M.; Faria, A.F. Simultaneous determination of fumonisins B1 and B2 in different types of maize by matrix solid phase dispersion and HPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Ling, J.; Li, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Xie, B.; Lai, D.; Li, Y. Insights into the pathogenic role of fusaric acid in Fusarium oxysporum infection of Brassica oleracea through the comparative transcriptomic, chemical, and genetic analyses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 9559–9569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bheemanapally, K.; Napit, P.R.; Ibrahim, M.M.H.; Briski, K.P. UHPLC–electrospray ionization–mass spectrometric analysis of brain cell-specific glucogenic and neurotransmitter amino acid content. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Tang, S.; Liao, W.; Sheng, Z.; Hu, S.; Jiao, G.; Shao, G.; Xie, L.; Hu, P. Regulation of FpvelC on Conidiation, Pathogenicity and Secondary Metabolism in Fusarium proliferatum. Toxins 2025, 17, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090433
Wang L, Tang S, Liao W, Sheng Z, Hu S, Jiao G, Shao G, Xie L, Hu P. Regulation of FpvelC on Conidiation, Pathogenicity and Secondary Metabolism in Fusarium proliferatum. Toxins. 2025; 17(9):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090433
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ling, Shaoqing Tang, Weiyang Liao, Zhonghua Sheng, Shikai Hu, Gui’ai Jiao, Gaoneng Shao, Lihong Xie, and Peisong Hu. 2025. "Regulation of FpvelC on Conidiation, Pathogenicity and Secondary Metabolism in Fusarium proliferatum" Toxins 17, no. 9: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090433
APA StyleWang, L., Tang, S., Liao, W., Sheng, Z., Hu, S., Jiao, G., Shao, G., Xie, L., & Hu, P. (2025). Regulation of FpvelC on Conidiation, Pathogenicity and Secondary Metabolism in Fusarium proliferatum. Toxins, 17(9), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17090433





