Functional and Proteomic Characterization of Acanthophis antarcticus Venom: Evidence of Fibrinogenolytic and Serine Peptidase Inhibitory Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Proteome of Acanthophis antarcticus Venom
2.1.1. Main Toxin Classes Identified
Three-Finger Toxins (3FTxs)
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2)
2.1.2. Less Abundant Toxins
2.2. Functional Activity of A. antarcticus Venom
2.3. Proteomics and Antivenomics
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Snake Venom Attainment
4.2. Fractionation of Crude Venom by Liquid Chromatography
4.2.1. Reverse-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
4.2.2. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC-HPLC)
4.3. Fingerprint Analysis of HILIC-HPLC Samples by Mass Spectrometry
4.4. Proteomic Analysis of RP-HPLC Samples by Mass Spectrometry
4.4.1. Sample Preparation: In-Solution Digestion
4.4.2. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4.4.3. Data Processing and Analysis
4.5. Biological Assays
4.5.1. Hyaluronidase Activity
4.5.2. Phospholipase A2 Activity
4.5.3. L-Amino Acid Oxidase Activity
4.5.4. Fibrinogenolytic Activity
4.5.5. Serine Peptidase Inhibitor
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- M’Coy, F. XVII.—Note on the Ancient and Recent Natural History of Victoria. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1862, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halford, G.B. Thoughts, Observations and Experiments on the Action of Snakes Venom on the Blood: With an Appendix; Stillwell: Melbourne, Australia, 1894. [Google Scholar]
- Fairley, N.H. The dentition and biting mechanism of Australian snakes. Med. J. Aust. 1929, 1, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, B.W. Half-Yearly Report on Toxicology, Forensic Medicine, and Public Hygiene. Br. Foreign Med. Chir. Rev. 1863, 31, 528. [Google Scholar]
- Macleay, W.J. Zoology of Australia. In Papers and Proceedings of the Royal Society of Tasmania; University of Tasmania: Tasmania, Australia, 1885; pp. 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoser, R. The Reptilian Magazine; Australasian Journal of Herpetology: Melbourne, Australia, 1995; pp. 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, W. Cyclopaedia of the Natural Sciences; Griffin: London, UK, 1858. [Google Scholar]
- Lea, I.; Carpenter, P.P.; Cope, E.D. Descriptions of Three New Species of Exotic Uniones. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila. 1859, 11, 331–353. [Google Scholar]
- Krefft, G. Two Papers on the Vertebrata of the Lower Murray and Darling, and on the Snakes of Sydney; Reading and Wellbank: Sydney, Australia, 1865. [Google Scholar]
- Slowinski, J.B.; Keogh, J.S. Phylogenetic Relationships of Elapid Snakes Based on Cytochrome b MtDNA Sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2000, 15, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wüster, W.; Da, M.; Salomão, G.; Butantan, I.; Quijada, A.; Thorpe, R.S. Origins and Evolution of the South American Pitviper Fauna: Evidence from Mitochondrial DNA Sequence Analysis. In Biology of the Vipers; Eagle Mountain Publishing: Eagle Mountain, UT, USA, 2002; pp. 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, H. The Death Adder’s Head. Ludgate 1900, 9, 502–515. [Google Scholar]
- Whitworth, R.P. Crushed: A Christmas Book; Baillière, F.F., Ed.; 1875. Available online: https://files02.sl.nsw.gov.au/fotoweb/pdf/1404/140452990.pdf (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Calmette, A. Le Venin Des Serpents: Physiologie de l’envenimation, Traitement Des Morsures Venimeuses Par Le Sérum Des Animaux Vaccinés. Available online: https://books.google.com.br/books?hl=pt-BR&lr=&id=JDFJAQAAMAAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA11&dq=Calmette,+Albert.+Le+venin+des+serpents:+Physiologie+de+l%27envenimation,+traitement+des+morsures+venimeuses+par+le+serum+des+animaux+vaccines.+Soci%C3%A9t%C3%A9+d%27%C3%A9ditions+scientifiques,+1896&ots=4wAO0R4Vcx&sig=SijdmqMn0mwGH39L5u7EWVegPyQ#v=snippet&q=acanthophis&f=false (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Kellaway, C.H. Observations on the Certainly Lethal Dose of the Venom of the Death Adder (Ancanthophis [Sic] Antarcticus) for the Common Laboratory Animals. Walter Eliza Hall. Inst. 1929, 1, 764–772. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, C.H. The Death Adder (Acanthopis Antarcticus); the Effect of the Bite and Its Treatment. Med. J. Aust. 1966, 2, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalloo, D.G.; Trevett, A.J.; Black, J.; Mapao, J.; Saweri, A.; Naraqi, S.; Owens, D.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Hutton, R.A.; Theakston, R.D.G.; et al. Neurotoxicity, Anticoagulant Activity and Evidence of Rhabdomyolysis in Patients Bitten by Death Adders (Acanthophis Sp.) in Southern Papua New Guinea. QJM Int. J. Med. 1996, 89, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramaratna, J.C.; Fry, B.G.; Hodgson, W.C. Species-Dependent Variations in the in Vitro Myotoxicity of Death Adder (Acanthophis) Venoms. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 74, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheumack, D.D.; Howden, M.E.H.; Spence, I. Isolation and Partial Characterisation of a Lethal Neurotoxin from the Venom of the Australian Death Adder (Acanthophis antarcticus). Toxicon 1979, 17, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheumack, D.D.; Spence, I.; Tyler, M.I.; Howden, M.E.H. The Complete Amino Acid Sequence of a Post-Synaptic Neurotoxin Isolated from the Venom of the Australian Death Adder Snake Acanthophis Antarcticus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1990, 95, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Tamiya, N. Isolation, Properties and Aminoacid Sequence of along-Chain Neurotoxin, Acanthophis Antarcticus b, from the Venom of an Australian Snake (the Common Death Adder, Acanthophis antarcticus). Biochem. J. 1981, 193, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Tamiya, N. The Amino Acid Sequence and Position of the Free Thiol Group of a Short-Chain Neurotoxin from Common-Death-Adder (Acanthophis antarcticus) Venom. Biochem. J. 1981, 199, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, M.I.; Retson-Yip, K.V.; Gibson, M.K.; Barnett, D.; Howe, E.; Stöcklin, R.; Turnbull, R.K.; Kuchel, T.; Mirtschin, P. Isolation and Amino Acid Sequence of a New Long-Chain Neurotoxin with Two Chromatographic Isoforms (Aa El and Ae E2) from the Venom of the Australian Death Adder (Acanthophis antarcticus). Toxicon 1997, 35, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Weyden, L.; Hains, P.; Morris’, M.; Broady’, K. Acanthoxin, a Toxic Phospholipase A2 from the Venom of the Common Death Adder (Acanthophis antarcticus). Toxicon 1997, 35, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, K.L. Purification and Preliminary Characterisation of Praelongin Phospholipases, Antiplatelet Agents from the Snake Venom of Acanthophis Praelongus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 1998, 1379, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Weyden, L.; Hains, P.G.; Broady, K.W. Characterisation of the Biochemical and Biological Variations from the Venom of the Death Adder Species (Acanthophis antarcticus, A. praelongus and A. pyrrhus). Toxicon 2000, 38, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Wickramaratna, J.C.; Jones, A.; Alewood, P.F.; Hodgson, W.C. Species and Regional Variations in the Effectiveness of Antivenom against the in Vitro Neurotoxicity of Death Adder (Acanthophis) Venoms. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 175, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawade, S.P. Snake Venom Neurotoxins: Pharmacological Classification. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2004, 23, 37–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacklow, B.; Konstantakopoulos, N.; Hodgson, W.C.; Nicholson, G.M. Presence of Presynaptic Neurotoxin Complexes in the Venoms of Australo-Papuan Death Adders (Acanthophis Spp.). Toxicon 2010, 55, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blacklow, B.; Escoubas, P.; Nicholson, G.M. Characterisation of the Heterotrimeric Presynaptic Phospholipase A2 Neurotoxin Complex from the Venom of the Common Death Adder (Acanthophis antarcticus). Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blacklow, B.; Kornhauser, R.; Hains, P.G.; Loiacono, R.; Escoubas, P.; Graudins, A.; Nicholson, G.M. α-Elapitoxin-Aa2a, a Long-Chain Snake α-Neurotoxin with Potent Actions on Muscle (A1)2βγδ Nicotinic Receptors, Lacks the Classical High Affinity for Neuronal A7 Nicotinic Receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Wickramaratna, J.C.; Hodgson, W.C.; Alewood, P.F.; Kini, R.M.; Ho, H.; Wüster, W. Electrospray Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Fingerprinting of Acanthophis (Death Adder) Venoms: Taxonomic and Toxinological Implications. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 16, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrell, G.W.; Earl, S.T.; Wallis, T.P.; Masci, P.P.; de Jersey, J.; Gorman, J.J.; Lavin, M.F. The Diversity of Bioactive Proteins in Australian Snake Venoms. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, T.N.W.; Sunagar, K.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Koludarov, I.; Chan, A.H.C.; Sanders, K.; Ali, S.A.; Hendrikx, I.; Dunstan, N.; Fry, B.G. Venom down under: Dynamic Evolution of Australian Elapid Snake Toxins. Toxins 2013, 5, 2621–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, G.; Subburaju, S.; Kini, R.M. Purification, Characterization, and Amino Acid Sequence Determination of Acanthins, Potent Inhibitors of Platelet Aggregation from Acanthophis antarcticus (Common Death Adder) Venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 354, 232–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hains, P.G.; Ramsland, P.A.; Broady, K.W. Modeling of Acanthoxin A1, a PLA2 Enzyme from the Venom of the Common Death Adder (Acanthophis antarcticus). Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 1999, 35, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falla, M.V.; Lebrun, I.; Pudenzi, M.A.; Oliveira, L.A.; Almeida, H.F.; Santos, N.G.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Spencer, P.J.; Rocha, M.M.; Pimenta, D.C.; et al. Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Coupled to High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HILIC-LC-HRMS): An Approach to Study Natural Peptides in Viperidae Snake Venom. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1743, 465715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G.K. A Review and Database of Snake Venom Proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-S. Genetic Diversity in Snake Venom Three-Finger Proteins and Phospholipase A2 Enzymes. Toxin 2007, 26, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doley, R.; Kini, R.M. Protein Complexes in Snake Venom. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 2851–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kini, R.M. Excitement Ahead: Structure, Function and Mechanism of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 Enzymes. Toxicon 2003, 42, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kini, R.M.; Doley, R. Structure, Function and Evolution of Three-Finger Toxins: Mini Proteins with Multiple Targets. Toxicon 2010, 56, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, Y.N. Last Decade Update for Three-Finger Toxins: Newly Emerging Structures and Biological Activities. World J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 10, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Wüster, W.; Kini, R.M.; Brusic, V.; Khan, A.; Venkataraman, D.; Rooney, A.P. Molecular Evolution and Phylogeny of Elapid Snake Venom Three-Finger Toxins. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 57, 110–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beraldo-Neto, E.; Vigerelli, H.; Coelho, G.R.; da Silva, D.L.; Nencioni, A.L.A.; Pimenta, D.C. Unraveling and Profiling Tityus Bahiensis Venom: Biochemical Analyses of the Major Toxins. J. Proteom. 2023, 274, 104824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, A.; Ali, S.A.; Akrem, A.; Betzel, C. Snake Venom Peptides: Tools of Biodiscovery. Toxins 2018, 10, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, T.; Tamiya, N. Current View on the Structure-Function Relationship of Postsynaptic Neurotoxins from Snake Venoms. Pharmacol. Ther. 1987, 34, 403–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, K.; Dodakallanavar, J.; Sampat, G.H.; Patil, V.S.; Harish, D.R.; Chavan, R.; Hegde, H.V.; Roy, S. Three Finger Toxins of Elapids: Structure, Function, Clinical Applications and Its Inhibitors. Mol. Divers. 2023, 28, 3409–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.S.; Dennis, M.S.; Louie, A.; Shuster, M.; Mulkerrin, M.G. Mambin, a Potent Glycoprotein IIb-IIIa Antagonist and Platelet Aggregation Inhibitor Structurally Related to the Short Neurotoxins. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 4766–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, X.C.; Wong, P.T.H.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. A Novel Analgesic Toxin (Hannalgesin) from the Venom of King Cobra (Ophiophagus Hannah). Toxicon 1995, 33, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.J.; Chang, C.C.; Cfutvc, C.C. Presynaptic Effects of Snake Venom Toxins Which Have Phospholipase A2 Activity (β-Bungarotoxin, Taipoxin, Crotoxin). Toxicon 1964, 22, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bon, C.; Changeux, J.-P.; Jeng, T.-W.; Fraenkl-conrat, H. Postsynaptic Effects of Crotoxin and of Its Isolated Subunits. Eur. J. Biochem. 1979, 99, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrington, P.L.; Soons, K.R.; Rosenbergt, P. Cardiotoxicity of Naja Nigricollis Phospholipase A2 Is Not Due to Alterations in Prostaglandin Synthesis. Toxicon 1986, 24, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Jackson, S.P.; Mitchell, C.A.; Salem, H.H. Purification and Characterisation of a Snake Venom Phospholipase A2: A Potent Inhibitor of Platelet Aggregation. Research 1993, 70, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, S.; Moreno, J.J.; MoRENo Oedema, J.J. Edema Formation and Degranulation of Mast Cells by Phospholipase A2 Purified from Porcine Pancreas and Snake Venoms. Toxicon 1993, 31, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G. Structure-Function Properties of Venom Components from Australian Elapids. Toxicon 1999, 37, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.Y.; Wang, C.E.; Li, Y.N.; Bao, J. Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation and Blood Coagulation by a P-III Class Metalloproteinase Purified from Naja Atra Venom. Toxicon 2020, 187, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, T.G.; dos Santos, J.L.; Alvarenga, V.G.d.; Santos, J.S.C.; Leclercq, S.Y.; Faria, C.D.; Oliveira, M.A.A.; Bemquerer, M.P.; Sanchez, E.O.F.; de Lima, M.E.; et al. Biochemical and Functional Properties of a New L-Amino Acid Oxidase (LAAO) from Micrurus Lemniscatus Snake Venom. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunagar, K.; Fry, B.G.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Casewell, N.R.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Vidal, N.; Ali, S.A.; King, G.F.; Vasudevan, K.; Vasconcelos, V.; et al. Molecular Evolution of Vertebrate Neurotrophins: Co-Option of the Highly Conserved Nerve Growth Factor Gene into the Advanced Snake Venom Arsenalf. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, S.D. Ophidian Envenomation Strategies and the Role of Purines. Toxicon 2002, 40, 335–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, R.; Mukherjee, A.K. Pathophysiological Significance and Therapeutic Applications of Snake Venom Protease Inhibitors. Toxicon 2017, 131, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitz, H.; Vigne, P.; Moinier, D.; Frelin, C.; Lazdunski, M. A New Member of the Natriuretic Peptide Family Is Present in the Venom of the Green Mamba (Dendroaspis Angusticeps). J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 13928–13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Wickramaratana, J.C.; Lemme, S.; Beuve, A.; Garbers, D.; Hodgson, W.C.; Alewood, P. Novel Natriuretic Peptides from the Venom of the Inland Taipan (Oxyuranus Microlepidotus): Isolation, Chemical and Biological Characterisation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 327, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Yamazaki, Y.; Brown, R.L.; Fujimoto, Z.; Morita, T.; Mizuno, H. Structures of Pseudechetoxin and Pseudecin, Two Snake-Venom Cysteine-Rich Secretory Proteins That Target Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Ion Channels: Implications for Movement of the C-Terminal Cysteine-Rich Domain. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2008, 64, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.H.; Ponnudurai, G. A Comparative Study of the Biological Properties of Australian Elapid Venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. Pharmacol. 1990, 97, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Tasoulis, T.; Dunstan, N.; Isbister, G.K. Anticoagulant Activity in Australasian Elapid Snake Venoms and Neutralisation with Antivenom and Varespladib. Toxicon 2024, 247, 107836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasoulis, T.; Lee, M.S.Y.; Ziajko, M.; Dunstan, N.; Sumner, J.; Isbister, G.K. Activity of Two Key Toxin Groups in Australian Elapid Venoms Show a Strong Correlation to Phylogeny but Not to Diet. BMC Evol. Biol. 2020, 20, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottrall, J.L.; Madaras, F.; Biven, C.D.; Venning, M.G.; Mirtschin, P.J. Proteolytic Activity of Elapid and Viperid Snake Venoms and Its Implication to Digestion. J. Venom Res. 2010, 1, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Wüster, W.; Dumbrell, A.J.; Hay, C.; Pook, C.E.; Williams, D.J.; Fry, B.G. Snakes across the Strait: Trans-Torresian Phylogeographic Relationships in Three Genera of Australasian Snakes (Serpentes: Elapidae: Acanthophis, Oxyuranus, and Pseudechis). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzig, V.; Kohler, M.; Grund, K.F.; Reeve, S.; Smith, A.I.; Hodgson, W.C. Analysis of Intraspecific Variation in Venoms of Acanthophis antarcticus Death Adders from South Australia. J. Venom Res. 2013, 4, 13. [Google Scholar]
- O’Leary, M.A.; Isbister, G.K. Commercial Monovalent Antivenoms in Australia Are Polyvalent. Toxicon 2009, 54, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steuten, J.; Winkel, K.; Carroll, T.; Williamson, N.A.; Ignjatovic, V.; Fung, K.; Purcell, A.W.; Fry, B.G. The Molecular Basis of Cross-Reactivity in the Australian Snake Venom Detection Kit (SVDK). Toxicon 2007, 50, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, H.R.; Vassão, R.C.; de Roodt, A.R.; Santos e Silva, E.C.; Mirtschin, P.; Ho, P.L.; Spencer, P.J. Cross Neutralization of Coral Snake Venoms by Commercial Australian Snake Antivenoms. Clin. Toxicol. 2017, 55, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; León, G.; Alape-Girón, A.; Flores-Díaz, M.; Sanz, L.; Angulo, Y.; Calvete, J.J. Snake Venomics and Antivenomics: Proteomic Tools in the Design and Control of Antivenoms for the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming. J. Proteom. 2009, 72, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Escolano, J.; Sanz, L. Snake Venomics of Bitis Species Reveals Large Intragenus Venom Toxin Composition Variation: Application to Taxonomy of Congeneric Taxa. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 2732–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirtschin, P.J.; Dunstan, N.; Hough, B.; Hamilton, E.; Klein, S.; Lucas, J.; Millar, D.; Madaras, F.; Nias, T. Venom Yields from Australian and Some Other Species of Snakes. Ecotoxicology 2006, 15, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, E.B.; Coelho, G.R.; Sciani, J.M.; Pimenta, D.C. Proteomic Characterization of Naja Mandalayensis Venom. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 27, e20200125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukrittayakamee, S.; Warrell, D.A.; Desakorn, V.; McMichael, A.J.; White, N.J.; Bunnag, D. The Hyaluronidase Activities of Some Southeast Asian Snake Venoms. Toxicon 1988, 26, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, M.; Mackessy, S.P. An Aqueous Endpoint Assay of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2. Toxicon 1996, 34, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, M.; Takahashi, T. A Spectrophotometric Microplate Assay for L-Amino Acid Oxidase. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 298, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peichoto, M.E.; Teibler, P.; Mackessy, S.P.; Leiva, L.; Acosta, O.; Gonçalves, L.R.C.; Tanaka-Azevedo, A.M.; Santoro, M.L. Purification and Characterization of Patagonfibrase, a Metalloproteinase Showing α-Fibrinogenolytic and Hemorrhagic Activities, from Philodryas Patagoniensis Snake Venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2007, 1770, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
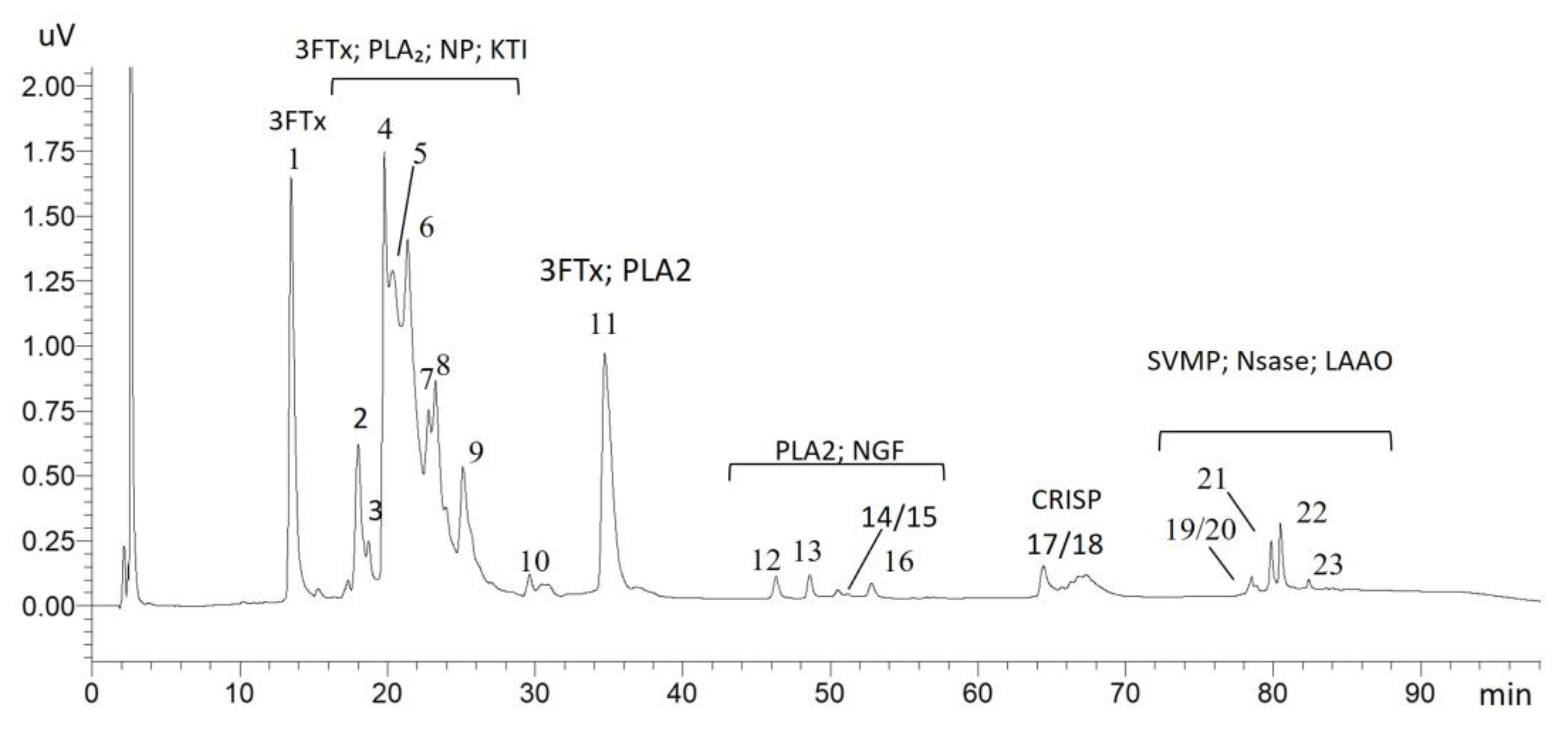
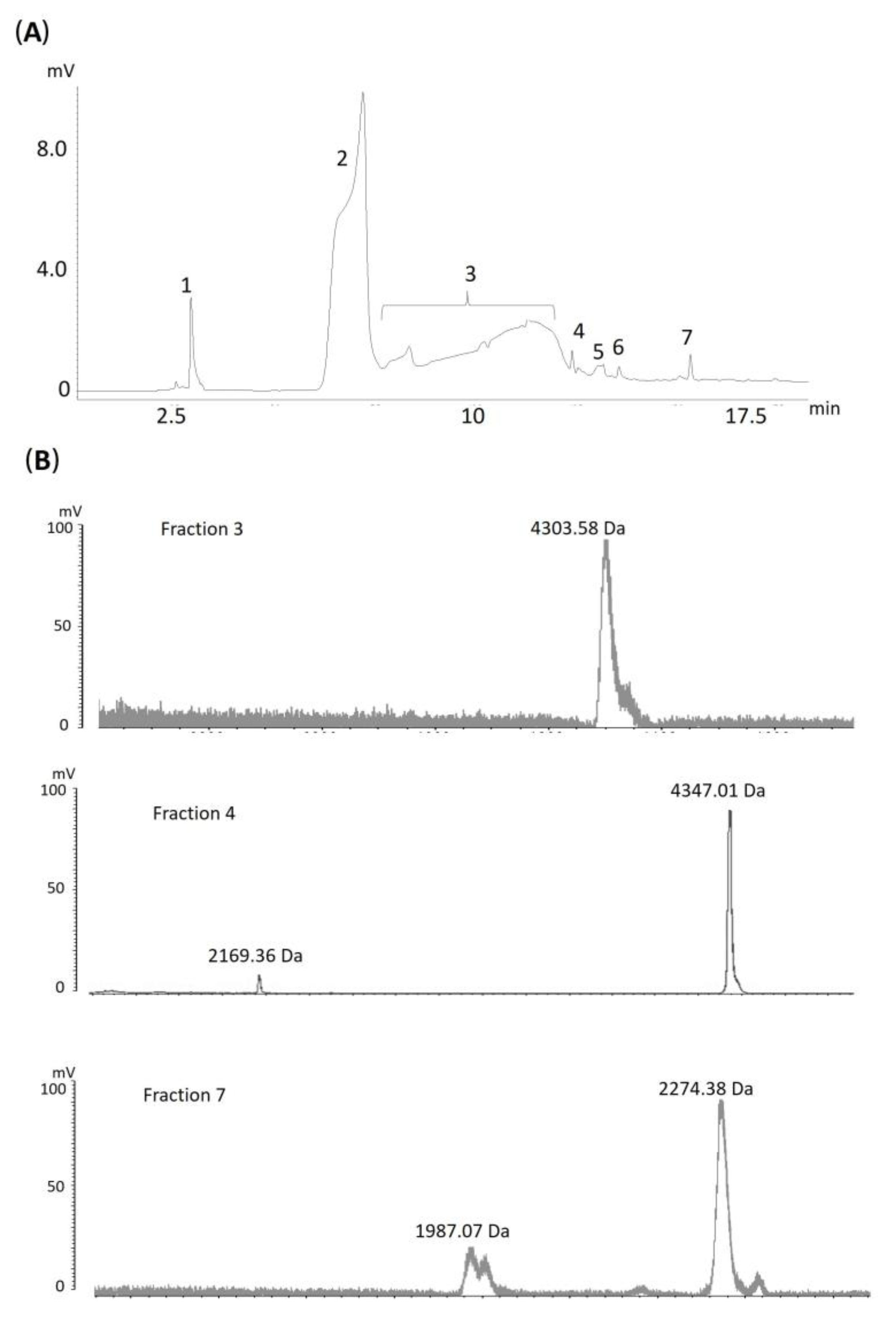
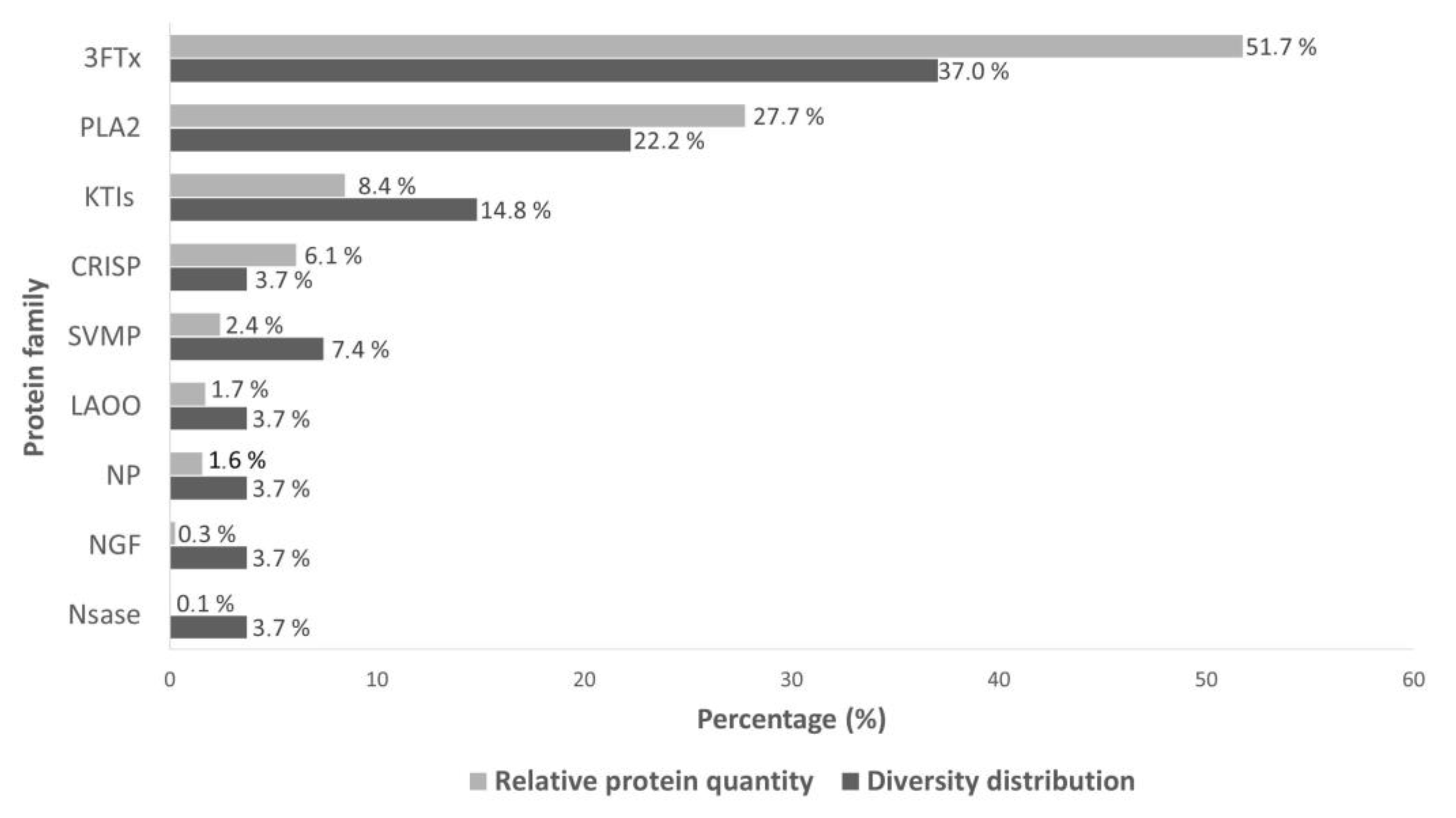
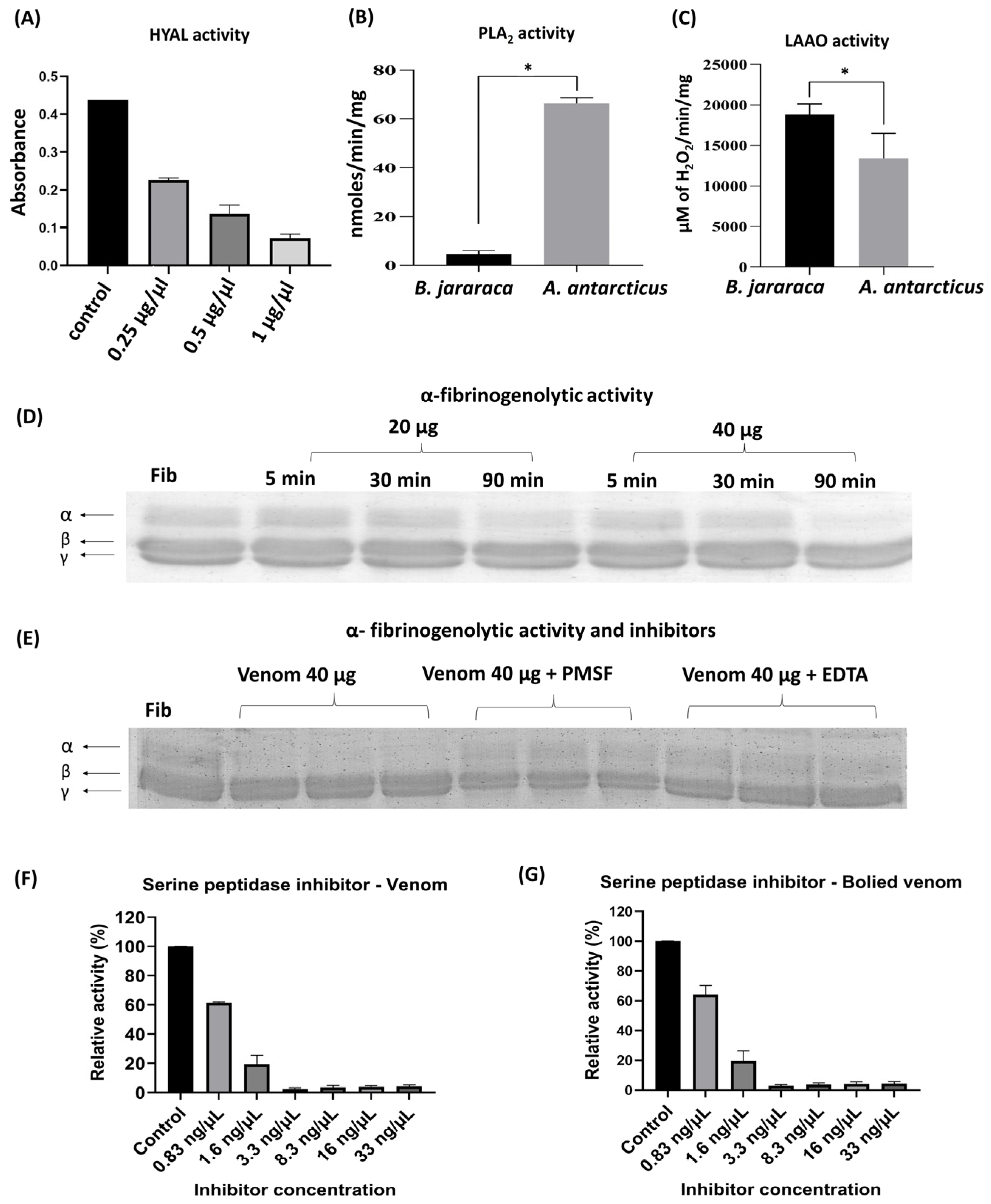
| Peaks | Protein Class | Description | Taxon Homology | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Three-finger toxins | Short neurotoxin 1 | Acanthophis antarcticus | P01434 |
| 2 | Three-finger toxins | 3FTxs-Aca-57 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D8 |
| 3FTxs-Aca-55 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4FI70 | ||
| Alpha-elapitoxin-Aa2a | Acanthophis antarcticus | P86522 | ||
| Short neurotoxin 1 | Acanthophis antarcticus | P01434 | ||
| Phospholipase A2 | PLA2 -Aca-2 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4FI60 | |
| Natriuretic peptide | NP-Aca-7 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G7E4 | |
| 3 | Phospholipase A2 | PLA2 -Aca-2 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4FI60 |
| Three-finger toxins | Alpha-elapitoxin-Aa2a (Fragment) | Acanthophis antarcticus | P86522 | |
| 3FTxs-Aca-57 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D8 | ||
| 4 | Three-finger toxins | 3FTxs-Aca-57 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D8 |
| 3FTxs-Aca-27 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D9 | ||
| Phospholipase A2 | Basic phospholipase A2 acanthin-2 | Acanthophis antarcticus | P81237 | |
| Basic phospholipase A2 acanthin-1 | Acanthophis antarcticus | P81236 | ||
| Basic phospholipase A2 PA-13 | Acanthophis wellsi | P04057 | ||
| 5 | Three-finger toxins | Alpha-elapitoxin-Aa2b | Acanthophis antarcticus | P01385 |
| Alpha-elapitoxin-Nss2a | Notechis scutatus scutatus | P01384 | ||
| 3FTxs-Aca-30 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G7E8 | ||
| 3FTxs-Aca-57 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D8 | ||
| 6 | Three-finger toxins | 3FTxs-Aca-30 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G7E8 |
| Kunitz inhibitor | Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor 18 | Drysdalia coronoides | F8J2F6 | |
| 7 | Three-finger toxins | 3FTxs-Aca-27 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D9 |
| 3FTxs-Aca-108 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2P2 | ||
| 8 | Three-finger toxins | Alpha-elapitoxin-Aa2b | Acanthophis antarcticus | P01385 |
| 3FTxs-Aca-27 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D9 | ||
| 9 | Three-finger toxins | 3FTxs-Aca-108 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2P2 |
| Alpha-elapitoxin-Aa2b | Acanthophis antarcticus | P01385 | ||
| Kunitz inhibitor | KP-Aca-8 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D6 | |
| Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor superbin-2 | Austrelaps superbus | B5KL39 | ||
| 10 | Three-finger toxins | Alpha-elapitoxin-Aa2b | Acanthophis antarcticus | P01385 |
| Kunitz inhibitor | KP-Aca-1 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4FI64 | |
| Phospholipase A2 | Basic phospholipase A2 acanthin-2 | Acanthophis antarcticus | P81237 | |
| 11 | Phospholipase A2 | Basic phospholipase A2 acanthin-2 | Acanthophis antarcticus | P81237 |
| Three-finger toxins | 3FTxs-Aca-53 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4FI75 | |
| 12 | Phospholipase A2 | PLA2 -Aca-38 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G7E3 |
| 13 | Phospholipase A2 | Basic phospholipase A2 acanthin-2 | Acanthophis antarcticus | P81237 |
| 14/15 | Venom nerve growth factor | Venom nerve growth factor 3 | Notechis scutatus scutatus | Q3HXY5 |
| Phospholipase A2 | PLA2 -Aca-34 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D4 | |
| 16 | Phospholipase A2 | PLA2 -Aca-34 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D4 |
| 17/18 | Cysteine-rich protein | Cysteine-rich venom protein | Drysdalia coronoides | F8J2D4 |
| 19/20 | Metallopeptidase | SVMP-Aca-4 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D3 |
| Nucleotidase | Snake venom 5′-nucleotidase (Fragment) | Naja atra | A0A2I4HXH5 | |
| 21 | L-amino acid oxidase | L-amino acid oxidase | Pseudechis australis | Q4JHE1 |
| Metallopeptidase | SVMP-Aca-4 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D3 | |
| 22 | L-amino acid oxidase | L-amino acid oxidase | Pseudechis australis | Q4JHE1 |
| Metallopeptidase | SVMP-Aca-4 | Acanthophis wellsi | R4G2D3 | |
| 23 | L-amino acid oxidase | L-amino acid oxidase | Pseudechis australis | Q4JHE1 |
| Metallopeptidase | Textilease-1 | Pseudonaja textilis | B5KFV9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Falla, M.V.; Sousa, E.P.; Morais-Zani, K.d.; Valladão, R.; Santos, N.G.; Galizio, N.C.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Almeida, H.F.; Lopes, A.R.; Moises, M.N.; et al. Functional and Proteomic Characterization of Acanthophis antarcticus Venom: Evidence of Fibrinogenolytic and Serine Peptidase Inhibitory Activities. Toxins 2025, 17, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080405
Falla MV, Sousa EP, Morais-Zani Kd, Valladão R, Santos NG, Galizio NC, Rodrigues MS, Almeida HF, Lopes AR, Moises MN, et al. Functional and Proteomic Characterization of Acanthophis antarcticus Venom: Evidence of Fibrinogenolytic and Serine Peptidase Inhibitory Activities. Toxins. 2025; 17(8):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080405
Chicago/Turabian StyleFalla, Monica V., Enzo P. Sousa, Karen de Morais-Zani, Rodrigo Valladão, Natalia G. Santos, Nathalia C. Galizio, Mariana S. Rodrigues, Heloisa F. Almeida, Adriana R. Lopes, Mauricio N. Moises, and et al. 2025. "Functional and Proteomic Characterization of Acanthophis antarcticus Venom: Evidence of Fibrinogenolytic and Serine Peptidase Inhibitory Activities" Toxins 17, no. 8: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080405
APA StyleFalla, M. V., Sousa, E. P., Morais-Zani, K. d., Valladão, R., Santos, N. G., Galizio, N. C., Rodrigues, M. S., Almeida, H. F., Lopes, A. R., Moises, M. N., Lebrun, I., Spencer, P. J., Pimenta, D. C., & Coelho, G. R. (2025). Functional and Proteomic Characterization of Acanthophis antarcticus Venom: Evidence of Fibrinogenolytic and Serine Peptidase Inhibitory Activities. Toxins, 17(8), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080405








