Analysis of the Proteome and Biochemistry of Venom from Tityus confluens, a Scorpion That Can Be Involved in Severe Envenomation Cases in Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
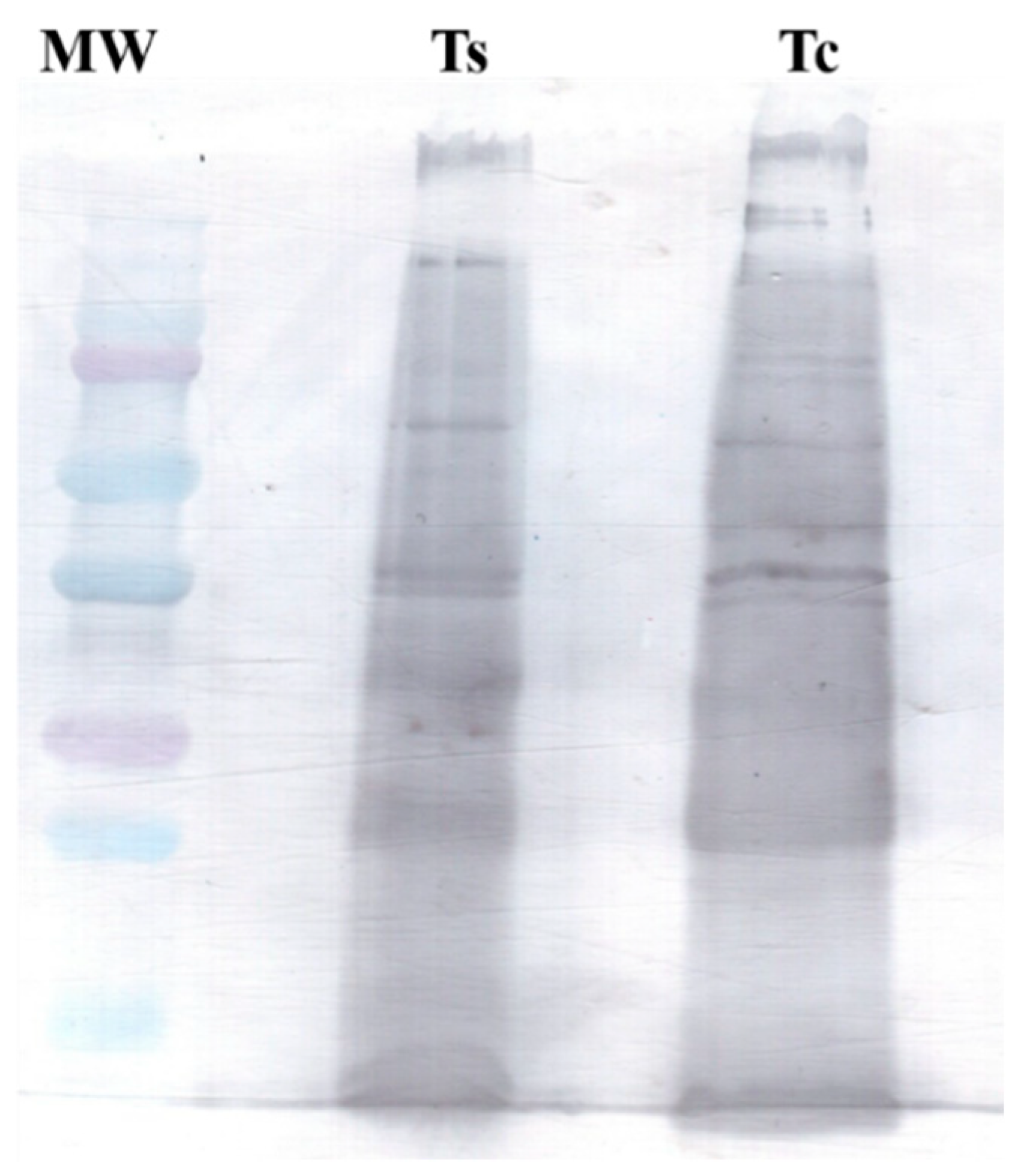
2.1. Electrophoretic Profile
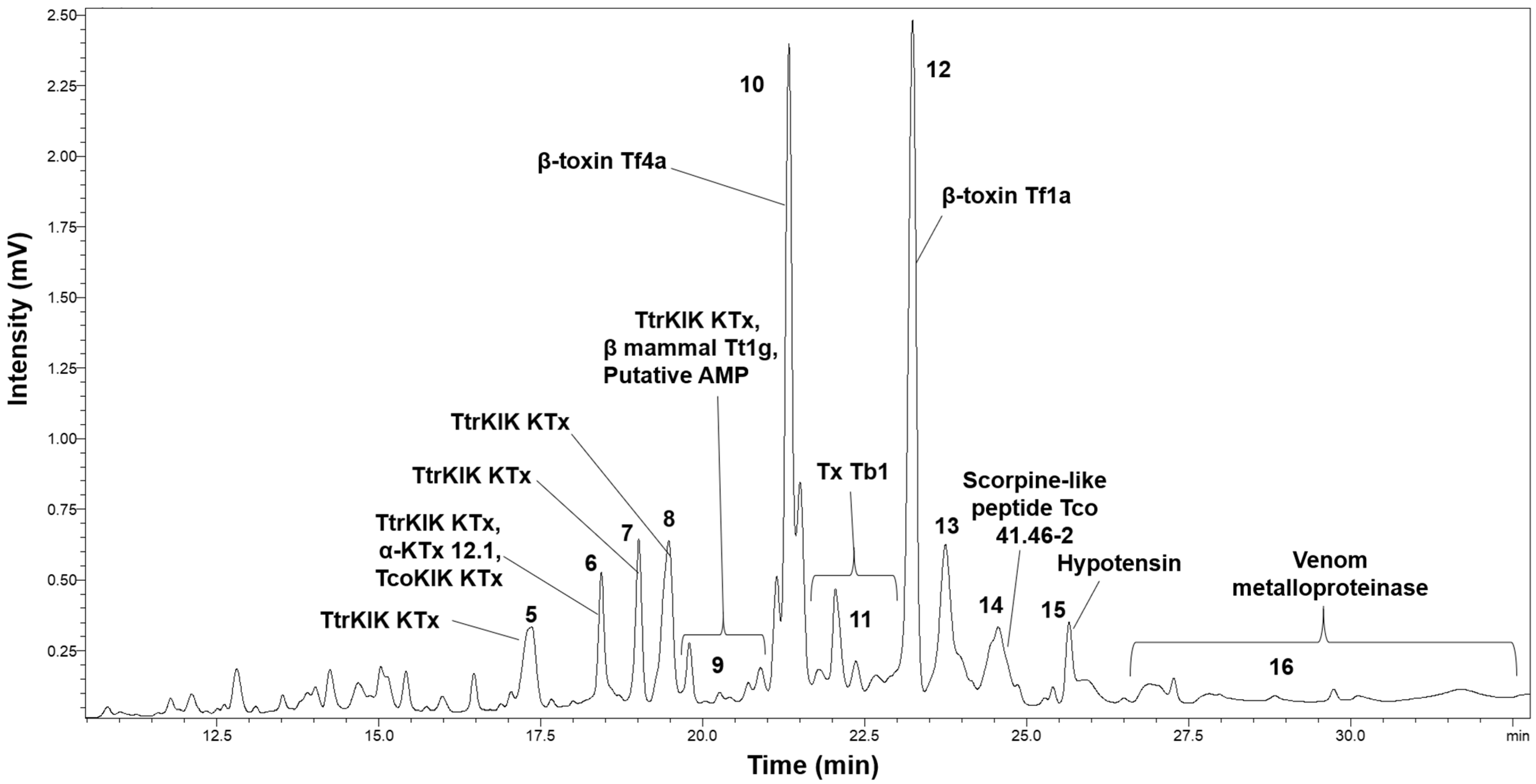
2.2. HPLC Analysis
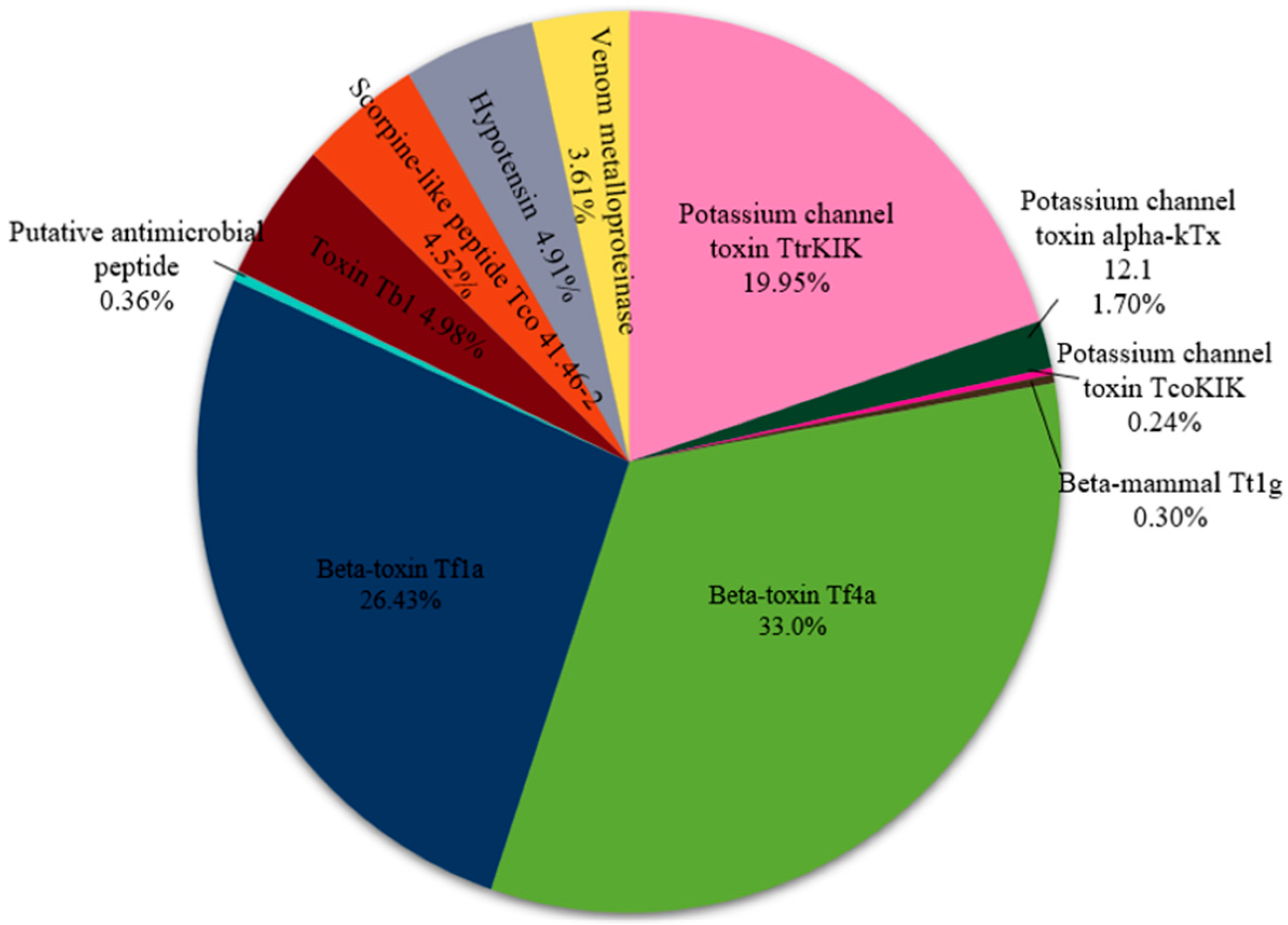
2.3. Proteomic Analysis
2.4. Western Blotting Analysis
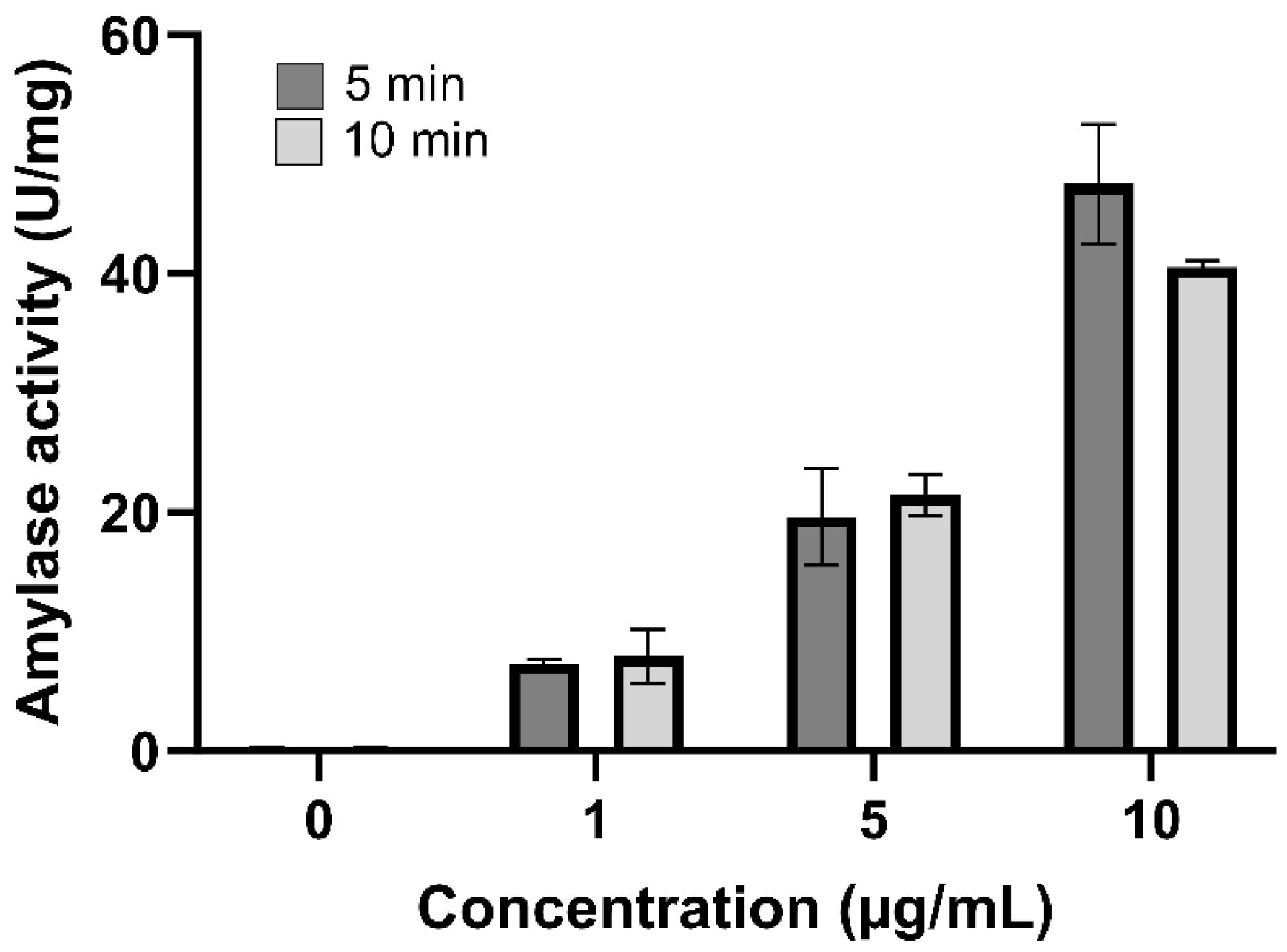
2.5. Amylolytic Activity
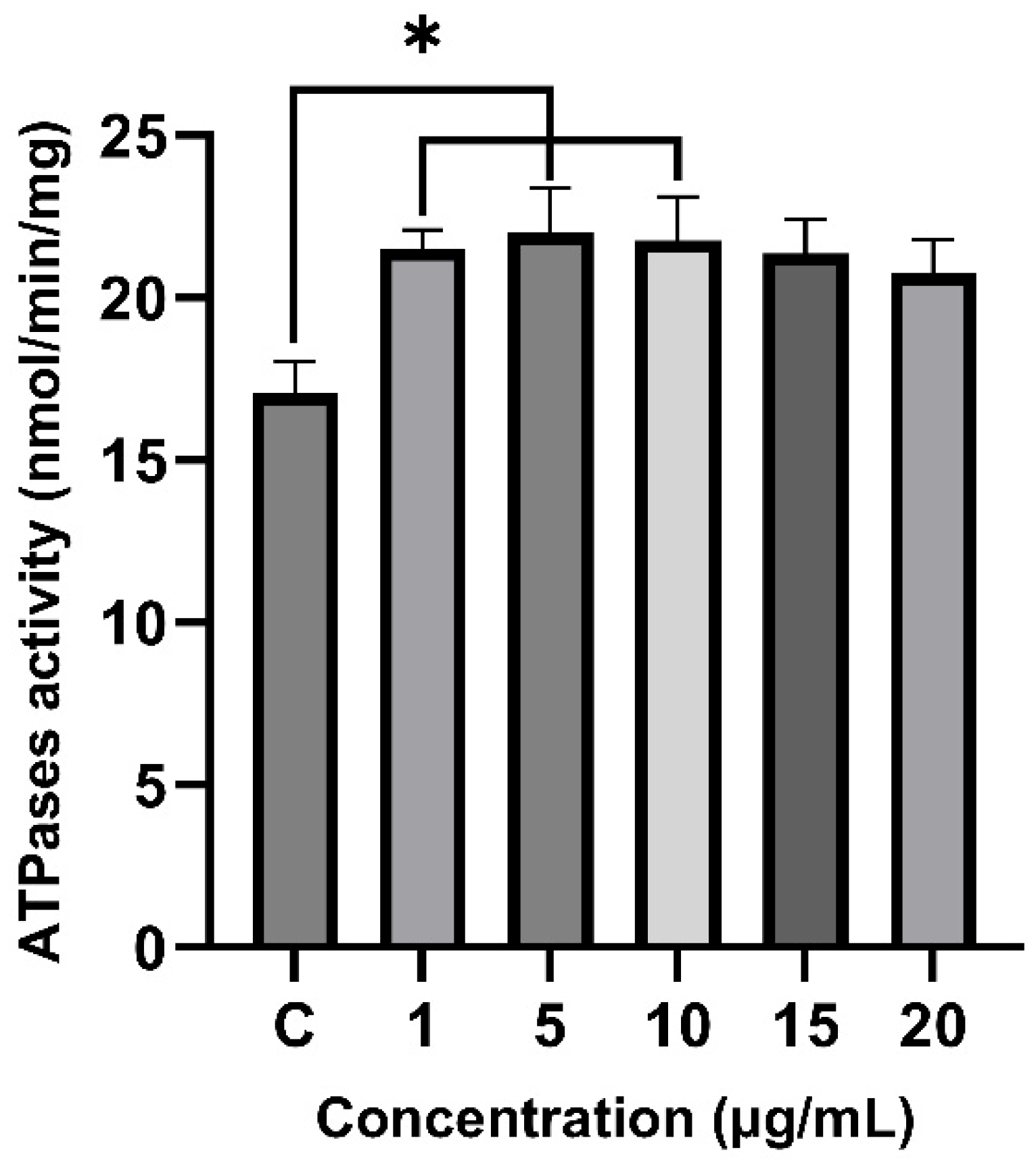
2.6. Effect of Venom on Total ATPase Activity
2.7. Cytotoxicity
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Specimen Collection and Storage
5.2. Venom Extraction
5.3. Protein Quantification
5.4. Electrophoretic Profile
5.5. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic (HPLC) Analysis
5.6. Mass Spectrometry Analyses
5.7. Data Analysis
- Rp = relative protein quantity;
- Af = chromatographic peak area (fraction area, UV chromatogram);
- At = total chromatographic Area (total UV chromatogram integration);
- PUp = protein Unique peptides (integer number of);
- TUp = total Unique peptides (integer number of).
5.8. Western Blotting
5.9. Amylolytic Activity
5.10. Effect of the Venom on the Total ATPase Activity
5.11. Cytotoxicity Assay
5.12. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sinan Sistema de Informação de Agravos de Notificação. Available online: https://datasus.saude.gov.br/acesso-a-informacao/doencas-e-agravos-de-notificacao-de-2007-em-diante-sinan/ (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Guerra-Duarte, C.; Saavedra-Langer, R.; Matavel, A.; Oliveira-Mendes, B.B.R.; Chavez-Olortegui, C.; Bittencourt Paiva, A.L. Scorpion Envenomation in Brazil: Current Scenario and Perspectives for Containing an Increasing Health Problem. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucca, M.B.; Cavalcante, J.S.; Jati, S.R.; Cerni, F.A.; Ferreira, R.S.; Arantes, E.C. Scorpions Are Taking over: The Silent and Escalating Public Health Crisis in Brazil. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1573767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardes-Oliveira, E.; Farias, K.J.S.; Gomes, D.L.; de Araújo, J.M.G.; Da Silva, W.D.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Donadi, E.A.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.D.F.; Crispim, J.C.D.O. Tityus Serrulatus Scorpion Venom Induces Apoptosis in Cervical Cancer Cell Lines. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 5131042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covali-Pontes, H.R.; Lima Fernandes, M.M.; Corrêa de Lima, L.; Rodrigues Macedo, M.L.; Giannesi, G.C.; Bastos de Oliveira, M.A.; Teixeira Ferreira, A.M.; Farias Frihling, B.E.; Migliolo, L.; Pereira dos Santos, N.G.; et al. Tityus paraguayensis, a Scorpion from the Brazilian Cerrado: First Assessment of Venom and Hemolymph Composition and Biological Activity. Toxicon 2025, 258, 108332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laraba-Djebari, F.; Sonia Adi-Bessalem, S.; Hammoudi-Triki, D. Scorpion Venoms: Pathogenesis and Biotherapies. In Scorpion Venoms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 63–85. [Google Scholar]
- Santibáñez-López, C.E.; Francke, O.F.; Ureta, C.; Possani, L.D. Scorpions from Mexico: From species diversity to venom complexity. Toxins 2015, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.C.M.; Campos, G.P.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Parrela, A.F.B.; Rodrigues, B.S.S.L.; Melo-Braga, M.N.; Junior, A.N.R.; Siqueira-Batista, R. Escorpiões do Gênero Tityus no Brasil: Biologia, Bioquímica da Peçonha e Fisiopatologia do Escorpionismo. Sci. Vitae 2022, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Goldoni, P.A.M.; Iniesta, L.F.M.; Marques-da-Silva, E.; Brescovit, A.D. Adding a Puzzle Piece to the Scorpion Distribution: Expanding the Records of Tityus (Tityus) confluens Borelli, 1899 (Scorpiones, Buthidae) in Southern Brazil. Bol. Mus. Para. Emílio Goeldi–Ciências Nat. 2025, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, J.O. The Scorpion Files. Available online: https://www.ntnu.no/ub/scorpion-files/ (accessed on 13 February 2022).
- Carvalho, L.S.; Brescovit, A.D.; Souza, C.A.R.; Raizer, J. Checklist Dos Escorpiões (Arachnida, Scorpiones) Do Mato Grosso Do Sul, Brasil. Iheringia Ser. Zool. 2017, 107, e2025-1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, W.R.; Cabral, B.C.; Ramos, E.C.B. Confirmation of Tityus confluens Borelli, 1899 (Scorpiones, Buthidae) in Brazil and description of a new subspecies from the State of Mato Grosso do Sul. Bol. Soc. Entomol. Aragonesa 2004, 34, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ojanguren-Affilastro, A.; Bizzotto, C.; Lanari, L.C.; Remes-Lenicov, M.; de Roodt, A.R. The Presence of Tityus Confluens Borelli in Buenos Aires City and the Expansion of the Distribution of the Medically Important Species of Tityus (Scorpiones; Buthidae) in Argentina. Rev. Mus. Argent. Cienc. Nat. Nueva Ser. 2019, 21, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; Rojas de Arias, A.; Montaño, A.M.; de Souza, C.M.V. Scorpion Envenoming as an Emerging Public Health Problem in Paraguay, Bolivia, and Midwest Brazil: Involvement of Tityus Confluens and the Need for a Panregional Evaluation of Available Antivenoms. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2024, 111, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde. Guia de Animais Peçonhentos do Brasil; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2024; p. 106. [Google Scholar]
- de Roodt, A.R.; Lago, N.R.; Salomón, O.D.; Laskowicz, R.D.; Neder de Román, L.E.; López, R.A.; Montero, T.E.; Vega, V.d.V. A New Venomous Scorpion Responsible for Severe Envenomation in Argentina: Tityus Confluens. Toxicon 2009, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Portilho, R.; Brito, I.L.; Santos, A.N.; Moreschi, B.P.; de Lucena, M.N.; Otsubo Jaques, J.A. First Evidence of Tityus Confluens Borelli, 1899 (Buthidae) Venom Altering Purine Metabolism in Rat Blood Cells. Purinergic Signal 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Âa, A.; Pessini, C.; Ãnia, T.; Takao, T.; Ãngela, E.; Cavalheiro, C.; Vichnewski, W.; Sampaio, S.V.; Giglio, J.Â.R.; Arantes, E.C. A Hyaluronidase from Tityus Serrulatus Scorpion Venom: Isolation, Characterization and Inhibition by flavonoid. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar]
- Oukkache, N.; Chgoury, F.; Lalaoui, M.; Cano, A.A.; Ghalim, N. Comparison between Two Methods of Scorpion Venom Milking in Morocco. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.; Patra, A.; Mukherjee, A.K. Correlation of Venom Toxinome Composition of Indian Red Scorpion (Mesobuthus Tamulus) with Clinical Manifestations of Scorpion Stings: Failure of Commercial Antivenom to Immune-Recognize the Abundance of Low Molecular Mass Toxins of This Venom. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez de la Vega, R.C.; Possani, L.D. Novel Paradigms on Scorpion Toxins That Affects the Activating Mechanism of Sodium Channels. Toxicon 2007, 49, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, K.N.; Pavana, D.; Shruthi, B.R.; Thippeswamy, N.B. Protein Profile of Scorpion Venom from Hottentotta Rugiscutis and Its Immunogenic Potential in Inducing Long Term Memory Response. Toxicon 2022, 205, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valikangas, T.; Suomi, T.; Elo, L.L. A comprehensive evaluation of popular proteomics software workflows for label-free proteome quantification and imputation. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1344–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauniyar, N.; Yates, J.R. Isobaric labeling-based relative quantification in shotgun proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 5293–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gstaiger, M.; Aebersold, R. Applying mass spectrometry–based proteomics to genetics, genomics and network biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics: From the inventory of toxins to biology. Toxicon 2013, 75, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, F.C.; Lewis, R.J. Sodium Channels and Pain: From Toxins to Therapies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 2138–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Mata, É.C.G.; Mourão, C.B.F.; Rangel, M.; Schwartz, E.F. Antiviral Activity of Animal Venom Peptides and Related Compounds. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, E.B.; de Freitas, L.A.; Pimenta, D.C.; Lebrun, I.; Nencioni, A.L.A. Tb1, a Neurotoxin from Tityus Bahiensis Scorpion Venom, Induces Epileptic Seizures by Increasing Glutamate Release. Toxins 2020, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantegazza, M.; Cestèle, S. β-Scorpion Toxin Effects Suggest Electrostatic Interactions in Domain II of Voltage-Dependent Sodium Channels. J. Physiol. 2005, 568, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipold, E.; DeBiasi, S.; Borchardt, T.; Heinemann, S.H. Scorpion β-Toxin Interference with Na Channel Voltage Sensor Gives Rise to Excitatory and Depressant Modes. J. Gen. Physiol. 2012, 139, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbat, I.; Ilan, N.; Zhang, J.Z.; Cohen, L.; Kahn, R.; Benveniste, M.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A.; Gordon, D.; Gurevitz, M. Partial Agonist and Antagonist Activities of a Mutant Scorpion β-Toxin on Sodium Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 30531–30538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, Z.L.; Bingham, J.P. Scorpion Toxins Specific for Potassium (K+) Channels: A Historical Overview of Peptide Bioengineering. Toxins 2012, 4, 1082–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartok, A.; Panyi, G.; Varga, Z. Potassium Channel Blocking Peptide Toxins from Scorpion Venom. In Scorpion Venoms; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 4, pp. 493–528. ISBN 978-94-007-6403-3. [Google Scholar]
- Coronas, F.V.; De Roodt, A.R.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Zamudio, F.Z.; Batista, C.V.F.; Gómez-Lagunas, F.; Possani, L.D. Disulfide Bridges and Blockage of Shaker B K+-Channels by Another Butantoxin Peptide Purified from the Argentinean Scorpion Tityus Trivittatus. Toxicon 2003, 41, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holaday, S.K.; Martin, B.M.; Fletcher, P.L.; Krishna, N.R. NMR Solution Structure of Butantoxin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 379, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalapothakis, Y.; Miranda, K.; Aragão, M.; Larangote, D.; Braga-Pereira, G.; Noetzold, M.; Molina, D.; Langer, R.; Conceição, I.M.; Guerra-Duarte, C.; et al. Divergence in Toxin Antigenicity and Venom Enzymes in Tityus Melici, a Medically Important Scorpion, despite Transcriptomic and Phylogenetic Affinities with Problematic Brazilian Species. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, J.C.; Arantes, E.C.; Varanda, W.A.; Oliveira, B.; Giglio, J.R.; Rgio Marangoni, S. TsTX-IV, a Short Chain Four-Disulfide-Bridged Neurotoxin from Tityus Serrulatus Venom Which Acts on Ca2+-Activated K+ Channels. Toxicon 1999, 37, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diego-García, E.; Batista, C.V.F.; García-Gómez, B.I.; Lucas, S.; Candido, D.M.; Gómez-Lagunas, F.; Possani, L.D. The Brazilian Scorpion Tityus Costatus Karsch: Genes, Peptides and Function. Toxicon 2005, 45, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Assis, D.R.R.; Pimentel, P.M.; dos Reis, P.V.M.; Rabelo, R.A.N.; Vitor, R.W.A.; Cordeiro, M.; Felicori, L.F.; Olórtegui, C.D.C.; Resende, J.M.; Teixeira, M.M.; et al. Tityus Serrulatus (Scorpion): From the Crude Venom to the Construction of Synthetic Peptides and Their Possible Therapeutic Application Against Toxoplasma Gondii Infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 706618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verano-Braga, T.; Figueiredo-Rezende, F.; Melo, M.N.; Lautner, R.Q.; Gomes, E.R.M.; Mata-Machado, L.T.; Murari, A.; Rocha-Resende, C.; Elena de Lima, M.; Guatimosim, S.; et al. Structure-Function Studies of Tityus Serrulatus Hypotensin-I (TsHpt-I): A New Agonist of B2 Kinin Receptor. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettinger, K.; Cohen, G.; Momic, T.; Lazarovici, P. The Effects of a Chactoid Scorpion Venom and Its Purified Toxins on Rat Blood Pressure and Mast Cells Histamine Release. Toxins 2013, 5, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verano-Braga, T.; Martins, A.L.V.; Motta-Santos, D.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J.; Santos, R.A.S. ACE2 in the Renin–Angiotensin System. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 3063–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, P.L.; Fletcher, M.D.; Weninger, K.; Anderson, T.E.; Martin, B.M. Vesicle-Associated Membrane Protein (VAMP) Cleavage by a New Metalloprotease from the Brazilian Scorpion Tityus Serrulatus. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7405–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazón, J.; Guerrero, B.; D’Suze, G.; Sevcik, C.; Arocha-Piñango, C.L. Fibrin(Ogen)Olytic Enzymes in Scorpion (Tityus Discrepans) Venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 168, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Knerr, J.M.; Argemi, L.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Arantes, E.C.; Çalişkan, F.; Laustsen, A.H. Scorpion Venom: Detriments and Benefits. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horta, C.C.R.; Magalhães, B.F.; Oliveira-Mendes, B.B.R.; do Carmo, A.O.; Duarte, C.G.; Felicori, L.F.; Machado-de-Ávila, R.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C.; Kalapothakis, E. Identification, Cloning and Functional Characterization of a Hyaluronidase from the Venom of the Brazilian Scorpion Tityus serrulatus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.D.; Scortecci, K.C.; Kobashi, L.S.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.D.L.M.; Pimenta, D.C.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F.; Kalapothakis, E. Profiling the Resting Venom Gland of the Scorpion Tityus stigmurus through a Transcriptomic Survey. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.M.; Pimenta, A.M.; de Figueiredo, S.G.; Santoro, M.M.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Diniz, C.R.; de Lima, M.E. Enzymes with Gelatinolytic Activity Can Be Found in Tityus bahiensis and Tityus serrulatus Venoms. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, N.B.; de Souza, B.M.; Cocchi, F.K.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Dorce, V.A.C.; Palma, M.S. Profiling the Short, Linear, Non-Disulfide Bond-Containing Peptidome from the Venom of the Scorpion Tityus obscurus. J. Proteom. 2018, 170, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, W.M.; Gomes, J.; Fé, N.; Silva, I.M.; Lacerda, M.; Alencar, A.; Farias, A.S.; Val, F.; Sampaio, V.S.; Melo, G.C.; et al. Perspectives and Recommendations towards Evidence-Based Health Care for Scorpion Sting Envenoming in the Brazilian Amazon: A Comprehensive Review. Toxicon 2019, 169, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, F.H.; Monteiro, W.M.; Moura da Silva, A.M.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Mendonça da Silva, I.; Sampaio, V.S.; dos Santos, M.C.; Sachett, J.; Ferreira, L.C.L.; Kalil, J.; et al. Snakebites and Scorpion Stings in the Brazilian Amazon: Identifying Research Priorities for a Largely Neglected Problem. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, A.K.; Caricati, C.P.; Lima, M.L.; Santos, M.C.; Kipnis, T.L.; Eickstedt, Z.V.; Knysar, I.; Da, M.H.; Higashi, H.G.; Dias Silva, W.D. Antigenic cross-reactivity among the venoms from several species of Brazilian scorpions. Toxicon 1994, 32, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid-Uribe, J.I.; Veytia-Bucheli, J.I.; Romero-Gutierrez, T.; Ortiz, E.; Possani, L.D. Scorpion Venomics: A 2019 Overview. Expert. Rev. Proteom. 2020, 17, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, A.C.M.; de Santana, C.J.C.; Melani, R.D.; Domont, G.B.; Castro, M.S.; Fontes, W.; Roepstorff, P.; Júnior, O.R.P. Exploring the Biological Activities and Proteome of Brazilian Scorpion Rhopalurus Agamemnon Venom. J. Proteom. 2021, 237, 104119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y. Mode of Inhibitory Action of Melittin on Na+-K+-ATPase Activity of the Rat Synaptic Membrane. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1985, 34, 2335–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera Córdova, W.H.; Leitão, S.G.; Cunha-Filho, G.; Bosch, R.A.; Alonso, I.P.; Pereda-Miranda, R.; Gervou, R.; Touza, N.A.; Quintas, L.E.M.; Noël, F. Bufadienolides from Parotoid Gland Secretions of Cuban Toad Peltophryne Fustiger (Bufonidae): Inhibition of Human Kidney Na+/K+-ATPase Activity. Toxicon 2016, 110, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa, L.Q.; da Conceição Machado, K.; de Carvalho Oliveira, S.F.; da Silva Araújo, L.; dos Santos Monção-Filho, E.; de Carvalho Melo-Cavalcante, A.A.; Vieira-Júnior, G.M.; Ferreira, P.M.P. Bufadienolides from Amphibians: A Promising Source of Anticancer Prototypes for Radical Innovation, Apoptosis Triggering and Na+/K+-ATPase Inhibition. Toxicon 2017, 127, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Linardi, A.; Rocha, E.; Silva, T.A.A.; Miyabara, E.H.; Franco-Penteado, C.F.; Cardoso, K.C.; Boer, P.A.; Moriscot, A.S.; Gontijo, J.A.R.; Joazeiro, P.P.; et al. Histological and Functional Renal Alterations Caused by Bothrops Alternatus Snake Venom: Expression and Activity of Na+/K+-ATPase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2011, 1810, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, F.G.; Longhim, H.T.; Cologna, C.T.; Degueldre, M.; Pauw, E.d.; Quinton, L.; Arantes, E.C. Proteome of Fraction from Tityus serrulatus Venom Reveals New Enzymes and Toxins. J. Venom Anim. Toxins Trop. Dis. 2019, 25, e148218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doley, R.; Kini, R.M. Protein Complexes in Snake Venom. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 2851–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, A.A.; Daniele-Silva, A.; Silva-Júnior, A.A.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F. Biology, Venom Composition, and Scorpionism Induced by Brazilian Scorpion Tityus stigmurus (Thorell, 1876) (Scorpiones: Buthidae): A Mini-Review. Toxicon 2020, 185, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schägger, H.; von Jagow, G. Tricine-Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis for the Separation of Proteins in the Range from 1 to 100 KDa. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 166, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, L.S.; Neto, E.B.; Francisco, A.F.; Alfonso, J.; Soares, A.; Pimenta, D.C.; Leiva, L.C. Fast Venomic Analysis of Crotalus Durissus Terrificus from Northeastern Argentina. Toxicon X 2020, 7, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beraldo-Neto, E.; Vigerelli, H.; Coelho, G.R.; da Silva, D.L.; Nencioni, A.L.A.; Pimenta, D.C. Unraveling and profiling Tityus bahiensis venom: Biochemical analyses of the major toxins. J. Proteom. 2023, 274, 104824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.L. Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skehan, P.; Storeng, R.; Scudiero, D.; Monks, A.; Mcmahon, J.; Vistica, D.; Warren, J.T.; Bokesch, H.; Kenney, S.; Boyd, M.R. New Colorimetric Cytotoxicity Assay for Anticancer-Drug Screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Peak | Access Number | Toxin | Coverage% | LogP | Species | Molecular Mass | Peptides | Unique |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | KBX2_TITTR | Potassium channel toxin TtrKIK | 44 | 140.35 | Tityus trivittatus | 10,067 | 9 | 9 |
| 6 | KBX2_TITTR | Potassium channel toxin TtrKIK | 43 | 162.13 | Tityus trivittatus | 10,067 | 13 | 7 |
| 6 | KA121_TITSE | Potassium channel toxin alpha-KTx 12.1 | 52 | 156.37 | Tityus serrulatus | 7083 | 12 | 7 |
| 6 | KBX2_TITCO | Potassium channel toxin TcoKIK | 72 | 120.04 | Tityus costatus | 5284 | 7 | 1 |
| 7 | KBX2_TITTR | Potassium channel toxin TtrKIK | 44 | 129.11 | Tityus trivittatus | 10,067 | 7 | 7 |
| 8 | KBX2_TITTR | Potassium channel toxin TtrKIK | 43 | 175.67 | Tityus trivittatus | 10,067 | 15 | 8 |
| 9 | KBX2_TITTR | Potassium channel toxin TtrKIK | 45 | 161.54 | Tityus trivittatus | 10,067 | 13 | 13 |
| 9 | SCX1_TITTR | Beta-mammal Tt1g | 44 | 116.13 | Tityus trivittatus | 9426 | 7 | 5 |
| 9 | A0A218QX30_TITSE | Putative antimicrobial peptide | 14 | 83.26 | Tityus serrulatus | 9496 | 6 | 6 |
| 10 | SCX4A_TITFA | Beta-toxin Tf4a | 83 | 198.46 | Tityus fasciolatus | 6964 | 21 | 19 |
| 11 | SCX1_TITBA | Toxin Tb1 | 60 | 132.95 | Tityus bahiensis | 9384 | 16 | 12 |
| 12 | SCX1A_TITFA | Beta-toxin Tf1a | 60 | 189.90 | Tityus fasciolatus | 9426 | 16 | 16 |
| 14 | KBX1_TITCO | Scorpine-like peptide Tco 41.46-2 | 36 | 155.09 | Tityus costatus | 9776 | 13 | 13 |
| 15 | A0AA49K9M8_9SCOR | Hypotensin | 47 | 117.50 | Tityus melici | 8033 | 5 | 2 |
| 16 | VMPA1_TITTR | Venom metalloproteinase | 14 | 130.70 | Tityus trivittatus | 43,062 | 9 | 4 |
| 16 | A0AA49K9T0_9SCOR | Venom metalloproteinase | 14 | 140.41 | Tityus melici | 44,596 | 7 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lima, L.C.; Covali-Pontes, H.R.; Leite, O.G.S.; Perdomo, R.T.; Moraes, L.F.R.N.d.; Migliolo, L.; Moyses, M.N.; Santos, N.G.P.d.; Pimenta, D.C.; Rodrigues, M.S.; et al. Analysis of the Proteome and Biochemistry of Venom from Tityus confluens, a Scorpion That Can Be Involved in Severe Envenomation Cases in Brazil. Toxins 2025, 17, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080406
Lima LC, Covali-Pontes HR, Leite OGS, Perdomo RT, Moraes LFRNd, Migliolo L, Moyses MN, Santos NGPd, Pimenta DC, Rodrigues MS, et al. Analysis of the Proteome and Biochemistry of Venom from Tityus confluens, a Scorpion That Can Be Involved in Severe Envenomation Cases in Brazil. Toxins. 2025; 17(8):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080406
Chicago/Turabian StyleLima, Laís Corrêa, Henrique Ranieri Covali-Pontes, Ohanna Gabriely Souza Leite, Renata Trentin Perdomo, Luiz Filipe Ramalho Nunes de Moraes, Ludovico Migliolo, Mauricio Nogueira Moyses, Natália Gabrielly Pereira dos Santos, Daniel Carvalho Pimenta, Mariana Soares Rodrigues, and et al. 2025. "Analysis of the Proteome and Biochemistry of Venom from Tityus confluens, a Scorpion That Can Be Involved in Severe Envenomation Cases in Brazil" Toxins 17, no. 8: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080406
APA StyleLima, L. C., Covali-Pontes, H. R., Leite, O. G. S., Perdomo, R. T., Moraes, L. F. R. N. d., Migliolo, L., Moyses, M. N., Santos, N. G. P. d., Pimenta, D. C., Rodrigues, M. S., Morais-Zani, K., Coelho, G. R., & Lucena, M. N. (2025). Analysis of the Proteome and Biochemistry of Venom from Tityus confluens, a Scorpion That Can Be Involved in Severe Envenomation Cases in Brazil. Toxins, 17(8), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17080406







