Palytoxin Signal in LC-MS and UV: Preliminary Investigation on the Effect of Solvent and Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
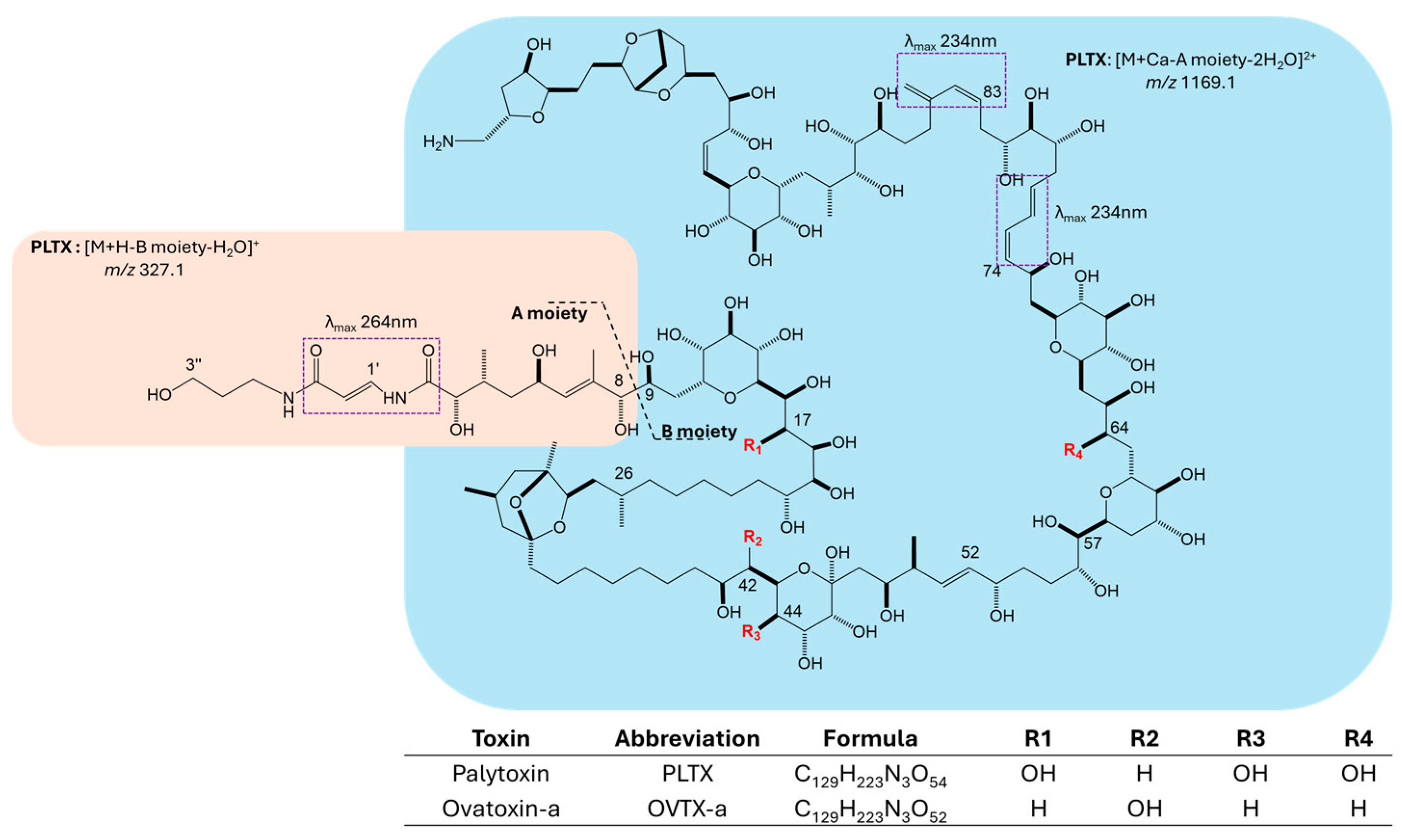
2. Results
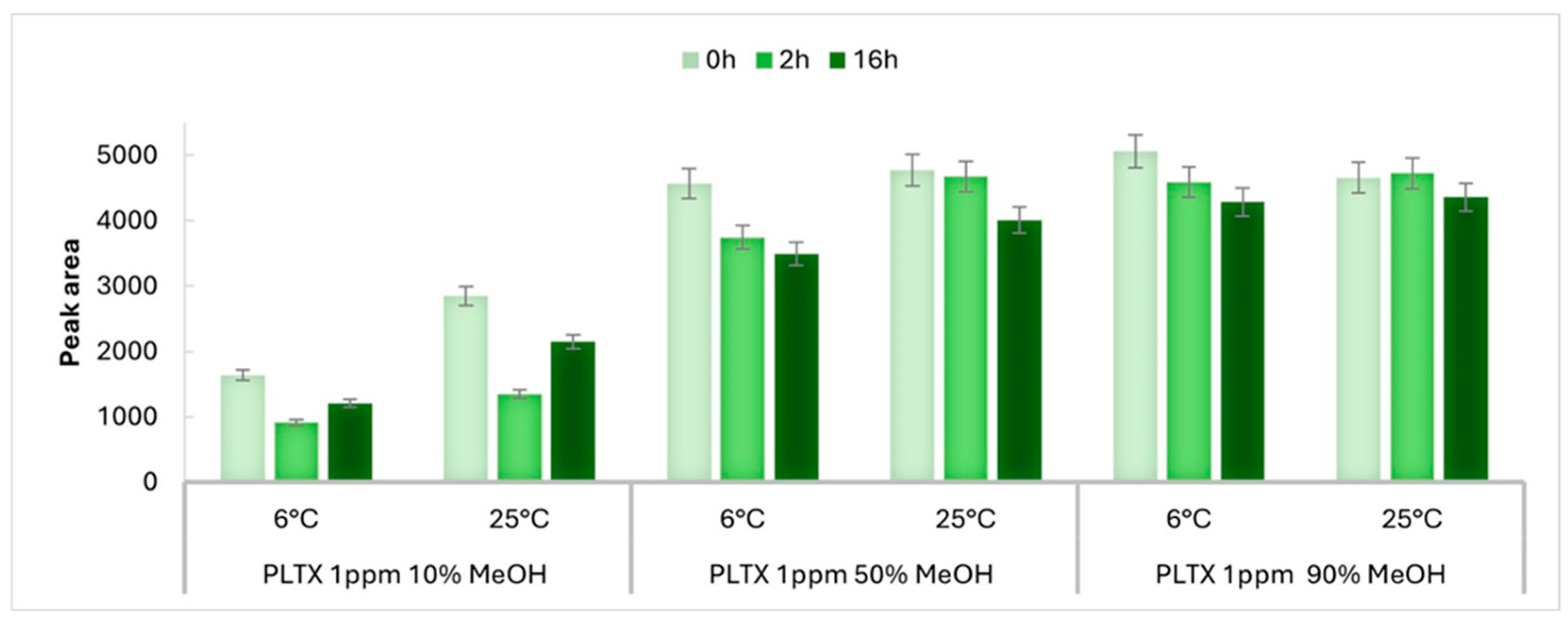
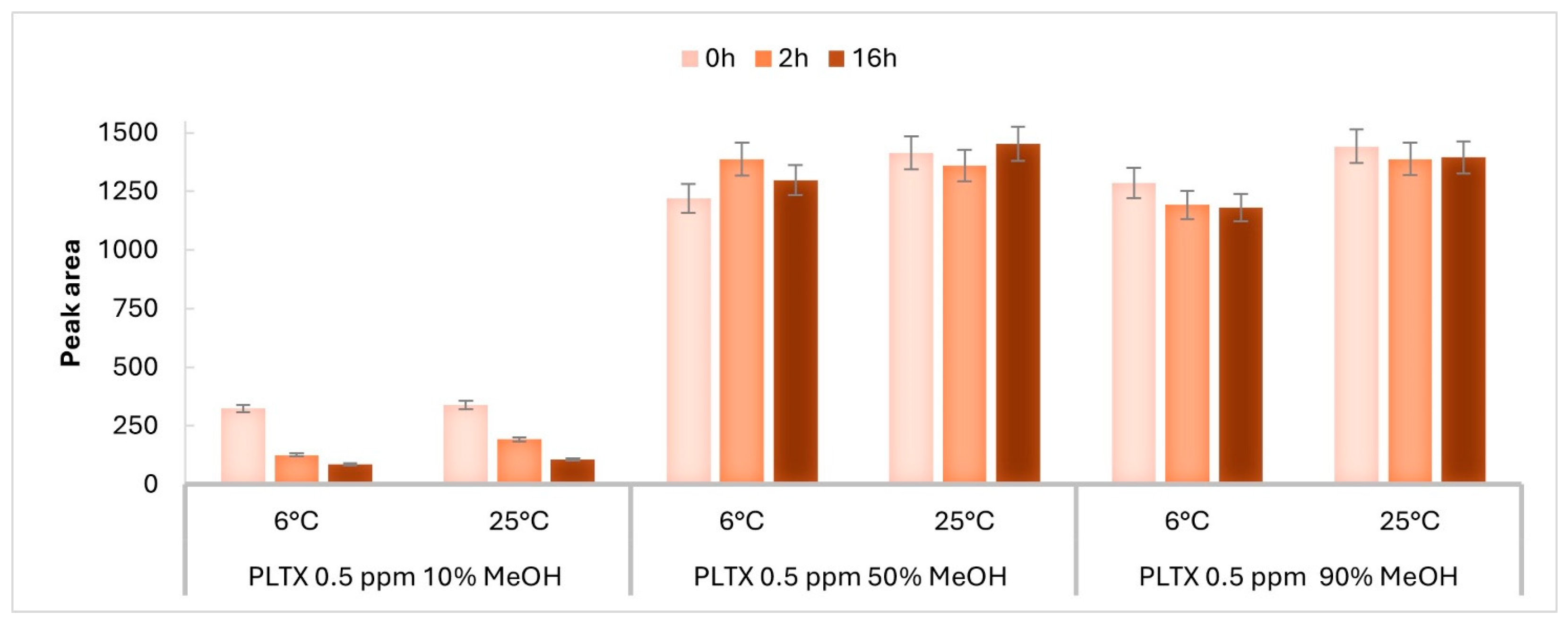
2.1. Stability of LC-MRM-MS Signal Response
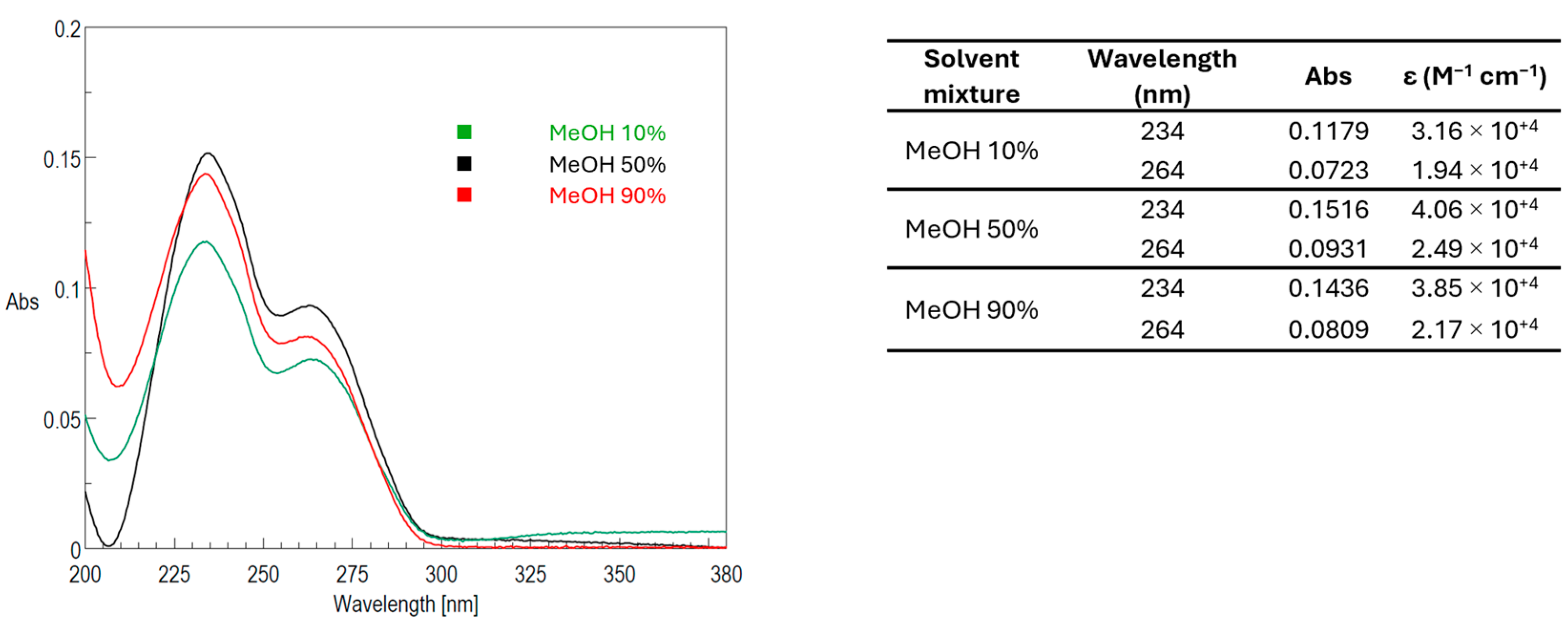
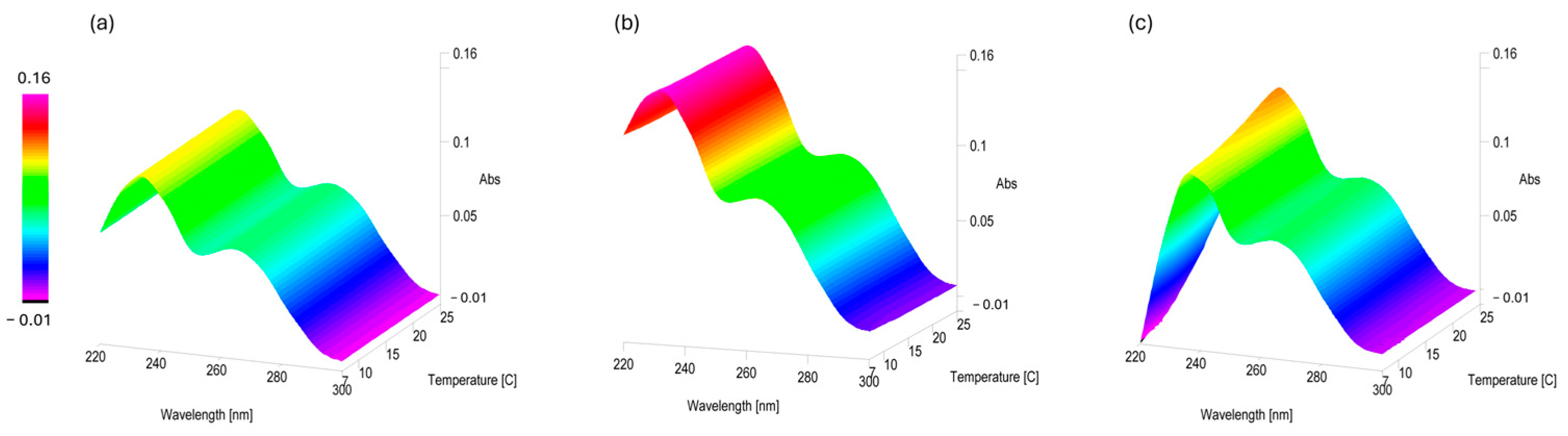
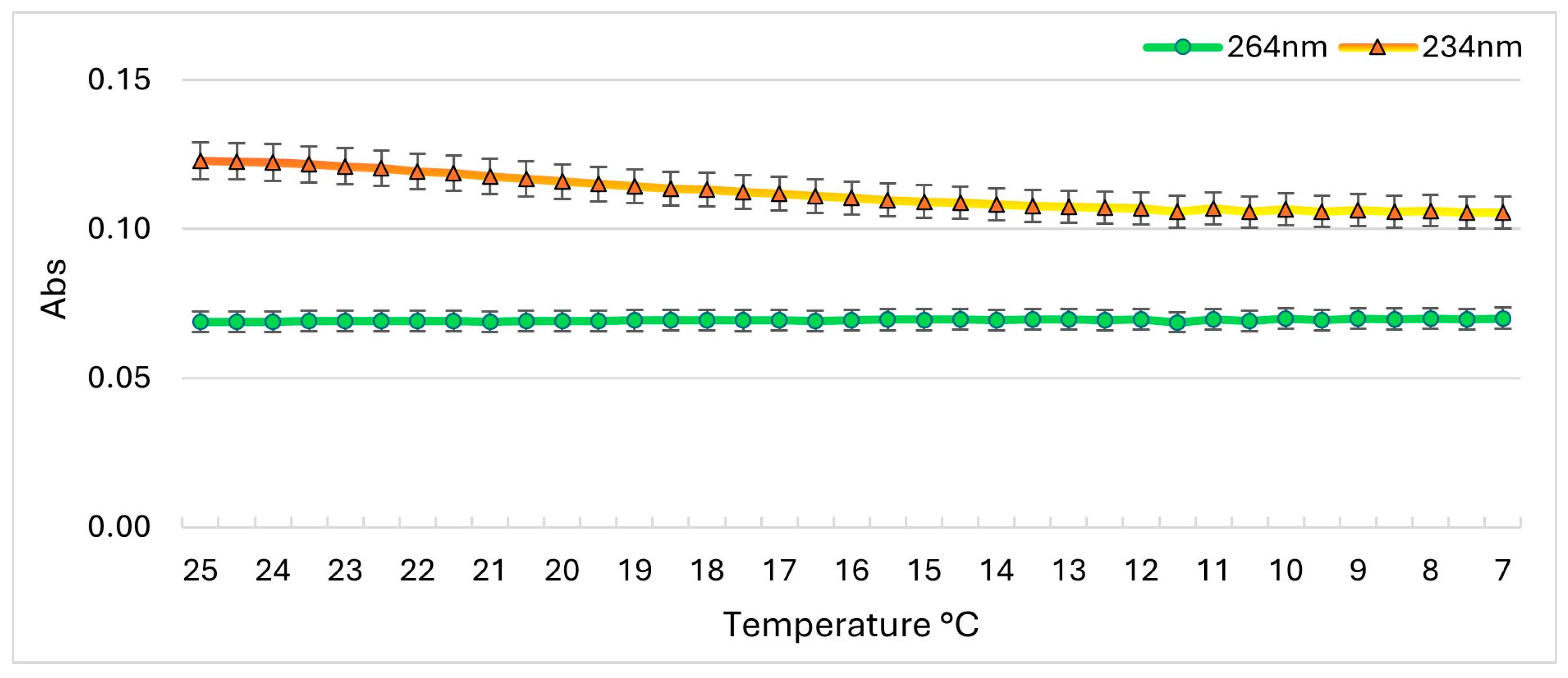
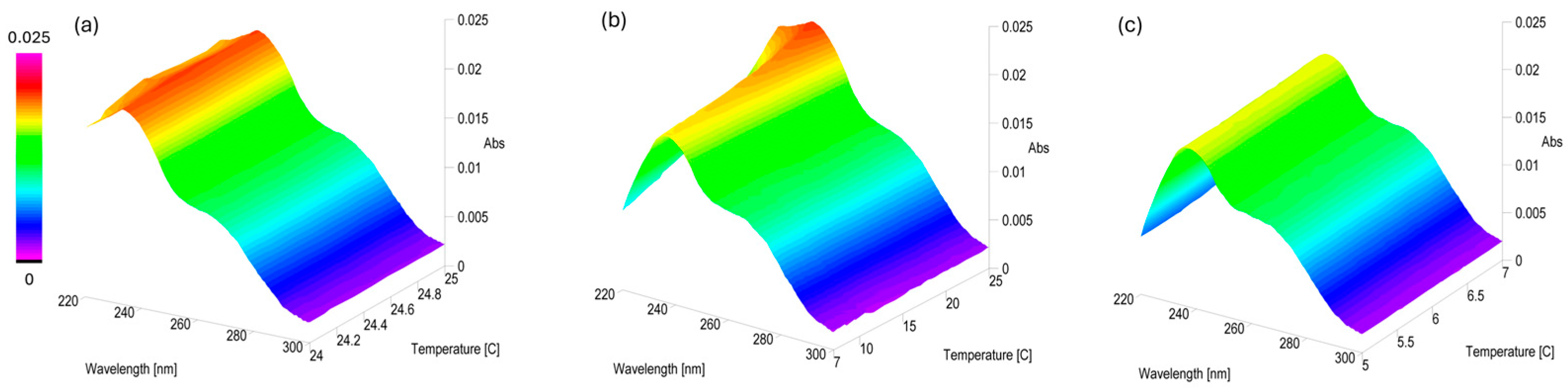
2.2. Stability of PLTX UV-Vis Spectrophotometric Signal
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
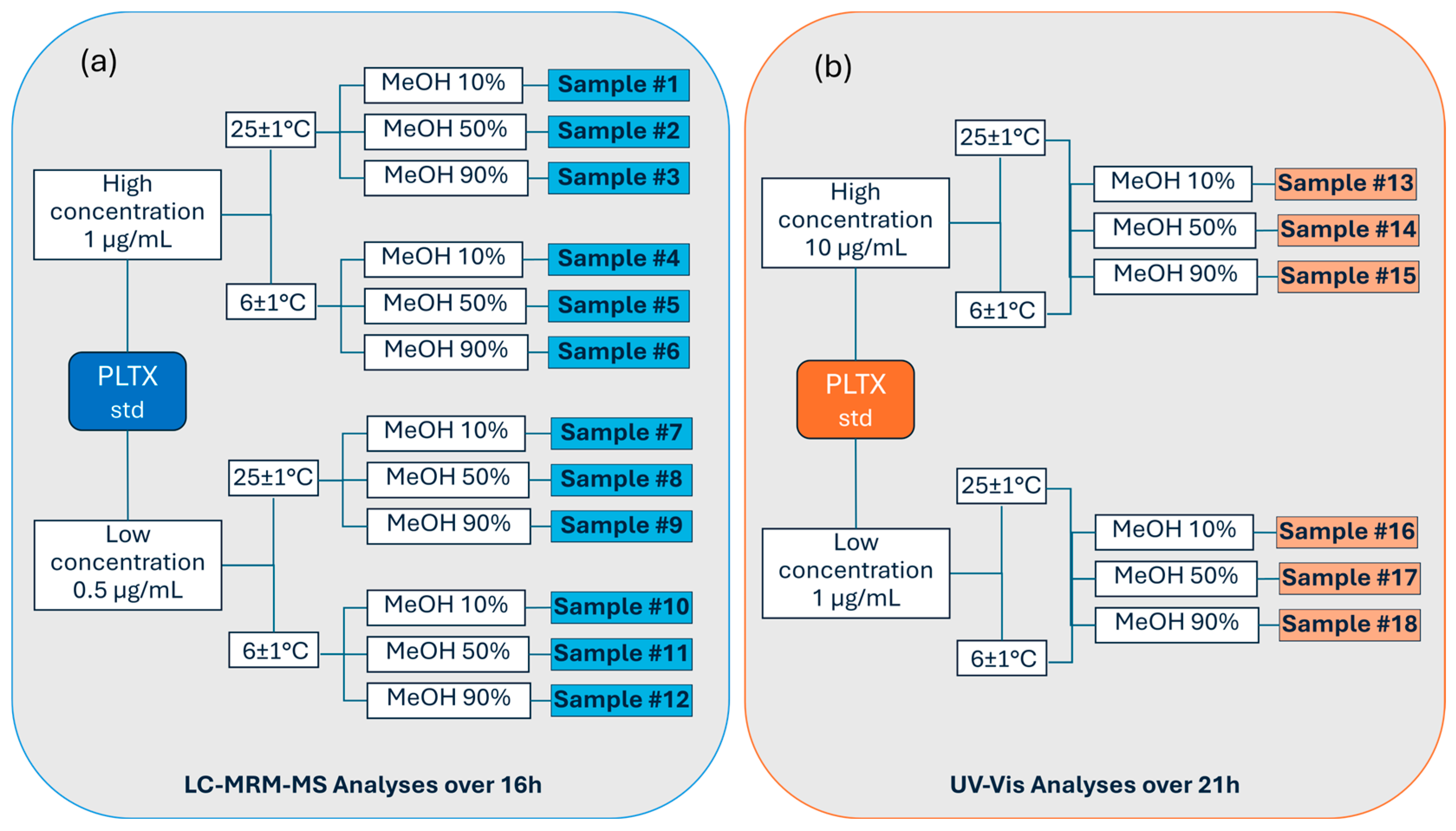
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Sample Preparation for LC-MRM-MS Analyses
5.3. LC-MRM-MS Method
5.4. Samples Preparation for UV-Vis Analyses
5.5. UV-Vis Spectrophotometry Method
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | Acetic acid |
| Abs | Absorption |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| CID | Collision-Induced Dissociation |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority |
| LC | Liquid chromatography |
| LC-MS-MS | Liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| MRM | Multiple-reaction monitoring mode |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| OVTX | Ovatoxin |
| PLTX | Palytoxin |
| RM | Reference Material |
| UHPLC | Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography |
| UV-Vis | Ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry |
| W | MilliQ water |
References
- Boente-Juncal, A.; Vale, C.; Camiña, M.; Cifuentes, J.M.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Reevaluation of the acute toxicity of palytoxin in mice: Determination of lethal dose 50 (LD50) and No-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL). Toxicon 2020, 177, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gémin, M.-P.; Lanceleur, R.; Meslier, L.; Hervé, F.; Réveillon, D.; Amzil, Z.; Ternon, E.; Thomas, O.P.; Fessard, V. Toxicity of palytoxin, purified ovatoxin-a, ovatoxin-d and extracts of Ostreopsis cf. ovata on the Caco-2 intestinal barrier model. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 94, 103909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, H.L.; Roy, C.J. History and Toxinology of Palytoxins. Toxins 2024, 16, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglione, L.; Dello Iacovo, E.; Mazzeo, A.; Casabianca, S.; Ciminiello, P.; Penna, A.; Dell’Aversano, C. Variability in Toxin Profiles of the Mediterranean Ostreopsis cf. ovata and in Structural Features of the Produced Ovatoxins. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13920–13928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; Abohbell, H.; Elfituri, A.; Dalhum, E.G.; Omran, A.S.B.; Badr, H.A. First record of Ostreopsis cf. ovata bloom and its ovatoxins in Libyan Mediterranean coastal waters. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2025, 10, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Iacovo, E.D.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Tartaglione, L.; Benedettini, G.; Onorari, M.; Serena, F.; Battocchi, C. First finding of Ostreopsis cf. ovata toxins in marine aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3532–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeds, J.R.; Schwartz, M.D. Human risk associated with palytoxin exposure. Toxicon 2010, 56, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissard, C.; Herrenknecht, C.; Séchet, V.; Hervé, F.; Pisapia, F.; Harcouet, J.; Lémée, R.; Chomérat, N.; Hess, P.; Amzil, Z. Complex Toxin Profile of French Mediterranean Ostreopsis cf. ovata Strains, Seafood Accumulation and Ovatoxins Prepurification. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2851–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangialajo, L.; Bertolotto, R.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Chiantore, M.; Grillo, C.; Lemee, R.; Melchiorre, N.; Moretto, P.; Povero, P.; Ruggieri, N. The toxic benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis ovata: Quantification of proliferation along the coastline of Genoa, Italy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdalet, E.; Pavaux, A.-S.; Abós-Herràndiz, R.; Travers, M.; Appéré, G.; Vila, M.; Thomas, J.; De Haro, L.; Estrada, M.; Medina-Pérez, N.I. Environmental, human health and socioeconomic impacts of Ostreopsis spp. blooms in the NW Mediterranean. Harmful Algae 2022, 119, 102320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyo, Y. Taxonomical study on benthic dinoflagellates collected in coral reefs. Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 1981, 47, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; Berdalet, E. Climate change and harmful benthic microalgae. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibiriçá, C.E.J.; Leite, I.P.; Batista, T.V.; Fernandes, L.F.; Chomérat, N.; Herve, F.; Hess, P.; Mafra, L.L., Jr. Ostreopsis cf. ovata bloom in Currais, Brazil: Phylogeny, toxin profile and contamination of mussels and marine plastic litter. Toxins 2019, 11, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Watanabe, R.; Uchida, H.; Matsushima, R.; Nagai, H.; Yasumoto, T.; Yoshimatsu, T.; Sato, S.; Adachi, M. LC-MS/MS analysis of novel ovatoxin isomers in several Ostreopsis strains collected in Japan. Harmful Algae 2012, 20, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Yasumura, D.; Ohizumi, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Alcala, A.C.; Alcala, L.C. Palytoxin in two species of xanthid crab from the Philippines. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1986, 50, 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Watanabe, R.; Matsushima, R.; Ishihara, K.; Uchida, H.; Kikutsugi, S.; Harada, T.; Nagai, H.; Adachi, M.; Yasumoto, T. LC-MS/MS analysis of palytoxin analogues in blue humphead parrotfish Scarus ovifrons causing human poisoning in Japan. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, S.M.; França, J.V.; Gonçalves, J.E.; Ferreira, C.E. Ostreopsis cf. ovata (Dinophyta) bloom in an equatorial island of the Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.; Wang, Y.; Derrien, A.; Hervé, F.; Wang, N.; Pransilpa, M.; Lim, P.T.; Leaw, C.P. Two toxigenic Ostreopsis species, O. cf. ovata and O. siamensis (Dinophyceae), from the South China Sea, tropical Western Pacific. Harmful Algae 2022, 113, 102206. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, S.M.; Neves, R.A.; De’Carli, G.A.; Borsato, G.T.; da Silva, R.A.; Melo, G.A.; de Morais, A.M.; Cockell, T.C.; Fraga, S.; Menezes-Salgueiro, A.D. Ostreopsis cf. ovata (Dinophyceae) molecular phylogeny, morphology, and detection of ovatoxins in strains and field samples from Brazil. Toxins 2020, 12, 70.s. [Google Scholar]
- Phua, Y.H.; Tejeda, J.; Roy, M.C.; Husnik, F.; Wakeman, K.C. Bacterial communities and toxin profiles of Ostreopsis (Dinophyceae) from the Pacific island of Okinawa, Japan. Eur. J. Protistol. 2023, 89, 125976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Magno, G.S.; Tartaglione, L.; Grillo, C.; Melchiorre, N. The Genoa 2005 outbreak. Determination of putative palytoxin in Mediterranean Ostreopsis o vata by a new liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 6153–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Dello Iacovo, E.; Forino, M.; Tartaglione, L. Liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry for palytoxins in mussels. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, M.; Ruiz-Olvera, P.; Nalca, A.; Ruiz, S.; Livingston, V.; Frick, O.; Dyer, D.; Schellhase, C.; Raymond, J.; Kulis, D. Toxicity and pathophysiology of palytoxin congeners after intraperitoneal and aerosol administration in rats. Toxicon 2018, 150, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubaro, A.; Durando, P.; Del Favero, G.; Ansaldi, F.; Icardi, G.; Deeds, J.; Sosa, S. Case definitions for human poisonings postulated to palytoxins exposure. Toxicon 2011, 57, 478–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.W.; e Silva, M.M.O.; Bandeira, A.C.; Silva, R.B.; Prates, A.P.P.B.; Soares, E.n.S.; Silva, J.J.M.; de Souza, L.J.R.; da Silva Souza, M.M.; Muhana, M.A. Haff Disease in Salvador, Brazil, 2016–2021: Attack rate and detection of toxin in fish samples collected during outbreaks and disease surveillance. Lancet Reg. Health–Am. 2022, 5, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuma, Y.; Satake, M.; Ukena, T.; Roux, J.; Chanteau, S.; Rasolofonirina, N.; Ratsimaloto, M.; Naoki, H.; Yasumoto, T. Identification of putative palytoxin as the cause of clupeotoxism. Toxicon 1999, 37, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, J.E. Review of clupeotoxism, an often fatal illness from the consumption of clupeoid fishes. Pac. Sci. 2005, 59, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 Laying Down Specific Hygiene Rules for Food of Animal Origin. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2004, 139, 55–205.
- European Food Safety Authority. A Scientific Opinion on Marine Biotoxins in Shellfish—Palytoxin Group. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, H.; Taira, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Structural elucidation of palytoxin analogs produced by the dinoflagellate Ostreopsis ovata IK2 strain by complementary use of positive and negative ion liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 27, 1999–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.; Christ, W.; Finan, J.; Fujioka, H.; Kishi, Y.; Klein, L.; Ko, S.; Leder, J.; McWhorter, W.; Pfaff, K. Stereochemistry of palytoxin. Part 4. Complete structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 7369–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Dello Iacovo, E.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Grauso, L.; Tartaglione, L. Stereochemical Studies on Ovatoxin-a. Chemistry 2012, 18, 16836–16843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, R. Palytoxin toxicology: Animal studies. Toxicon 2011, 57, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, E.; Yasumoto, T. Toxicological studies on palytoxin and ostreocin-D administered to mice by three different routes. Toxicon 2009, 54, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H. Palytoxin: Membrane mechanisms of action. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermann, E.; Hudel, M.; Dauzenroth, M.-E. Palytoxin promotes potassium outflow from erythrocytes, HeLa and bovine adrenomedullary cells through its interaction with Na+, K+-ATPase. Toxicon 1989, 27, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Qin, K.; Li, S.; Ren, S.; Jia, X.; Gao, Z. Potential threat of environmental toxin palytoxin to cerebral nerves: A mechanism study in vitro and in vivo. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 295, 118150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miele, V.; Varriale, F.; Melchiorre, C.; Varra, M.; Tartaglione, L.; Kulis, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Ricks, K.; Poli, M.; Dell’Aversano, C. Isolation of ovatoxin-a from Ostreopsis cf. ovata cultures. A key step for hazard characterization and risk management of ovatoxins. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1736, 465350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Dello Iacovo, E.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Grauso, L.; Tartaglione, L. High resolution LC-MSn fragmentation pattern of palytoxin as template to gain new insights into ovatoxin-a structure. The key role of calcium in MS behavior of palytoxins. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 23, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, A.; Varra, M.; Tartaglione, L.; Ciminiello, P.; Zendong, Z.; Hess, P.; Dell’Aversano, C. Toward isolation of palytoxins: Liquid chromatography coupled to low-or high-resolution mass spectrometry for the study on the impact of drying techniques, solvents and materials. Toxins 2021, 13, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Sugahara, K.; Maeda, M.; Shimamoto, K.; Iwashita, T.; Yamagaki, T. A truncated palytoxin analogue, palytoxin carboxylic acid, isolated as an insecticidal compound from the red alga, Chondria armata. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 4420–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.E.; Scheuer, P.J. Palytoxin: A new marine toxin from a coelenterate. Science 1971, 172, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usami, M.; Satake, M.; Ishida, S.; Inoue, A.; Kan, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Palytoxin analogs from the dinoflagellate Ostreopsis siamensis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 5389–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klijnstra, M.D.; Gerssen, A. A Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method for Palytoxin Using Lithium Cationization. Toxins 2018, 10, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunschel, D.S.; Valenzuela, B.R.; Kaiser, B.L.D.; Victry, K.; Woodruff, D. Method development for comprehensive extraction and analysis of marine toxins: Liquid-liquid extraction and tandem liquid chromatography separations coupled to electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2018, 187, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terajima, T.; Uchida, H.; Abe, N.; Yasumoto, T. Structure elucidation of ostreocin-A and ostreocin-E1, novel palytoxin analogs produced by the dinoflagellate Ostreopsis siamensis, using LC/Q-TOF MS. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, Y.; Uemura, D.; Ueda, K.; Takano, S. Several compounds from Palyfhoa tuberculosa (Coelenterata). Pure Appl. Chem. 1979, 51, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inuzuka, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Arimoto, H.; Uemura, D. Molecular shape of palytoxin in aqueous solution. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inuzuka, T.; Uemura, D.; Arimoto, H. The conformational features of palytoxin in aqueous solution. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 7718–7723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Seo, N.; Kim, H.W.; Yu, J.Y.; Oh, M.J.; An, H.J.; Jeon, Y.-J. Enhanced Chromatographic Separation for Quantitative Accuracy of Palytoxin. Ocean Sci. J. 2024, 59, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, L.; Gergov, G.; Petrov, V.; Kubista, M.; Nygren, J. UV–Vis spectroscopic and chemometric study on the aggregation of ionic dyes in water. Talanta 1999, 49, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagannathan, R.; Abraham, P.M.; Poddar, P. Temperature-Dependent Spectroscopic Evidences of Curcumin in Aqueous Medium: A Mechanistic Study of Its Solubility and Stability. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 14533–14540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melchiorre, C.; Varra, M.; Tegola, V.; Miele, V.; Dell’Aversano, C. Palytoxin Signal in LC-MS and UV: Preliminary Investigation on the Effect of Solvent and Temperature. Toxins 2025, 17, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060286
Melchiorre C, Varra M, Tegola V, Miele V, Dell’Aversano C. Palytoxin Signal in LC-MS and UV: Preliminary Investigation on the Effect of Solvent and Temperature. Toxins. 2025; 17(6):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060286
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelchiorre, Chiara, Michela Varra, Valeria Tegola, Valentina Miele, and Carmela Dell’Aversano. 2025. "Palytoxin Signal in LC-MS and UV: Preliminary Investigation on the Effect of Solvent and Temperature" Toxins 17, no. 6: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060286
APA StyleMelchiorre, C., Varra, M., Tegola, V., Miele, V., & Dell’Aversano, C. (2025). Palytoxin Signal in LC-MS and UV: Preliminary Investigation on the Effect of Solvent and Temperature. Toxins, 17(6), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060286






