Single Tri-Epitopic Antibodies (TeAbs) to Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotypes B, E, and F Recapitulate the Full Potency of a Combination of Three Monoclonal Antibodies in Toxin Neutralization
Abstract
1. Introduction
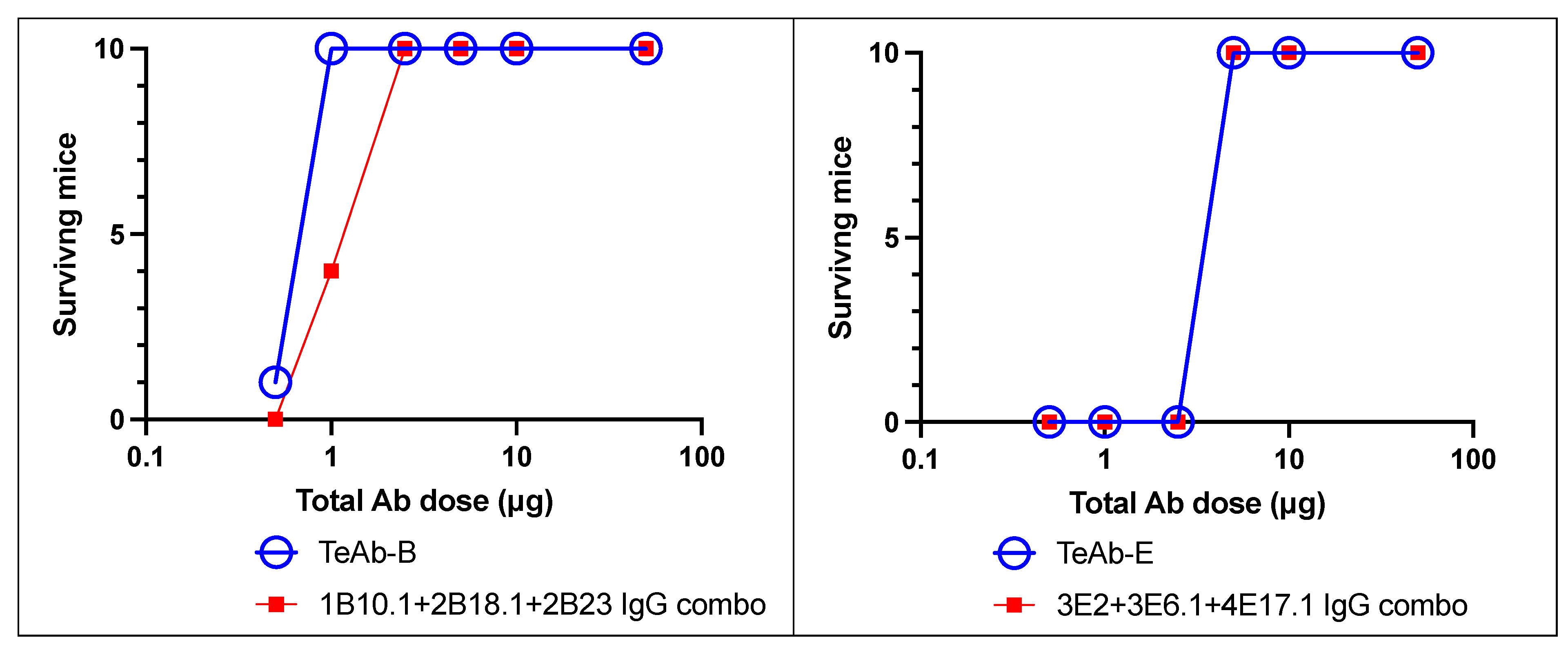
2. Results
TeAb Constructs
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Design, Cloning, Expression, and Purification of TeAbs
5.2. Protein Expression
5.3. Binding Affinity Determinations Using KinExA Analysis
5.4. Mouse Neutralization Assay (MNA) of BoNT/B1, BoNT/E3, or BoNT/F1 by IgG or TeAb
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dabritz, H.A.; Chung, C.H.; Read, J.S.; Khouri, J.M. Global Occurrence of Infant Botulism: 2007–2021. Pediatrics 2025, 155, e2024068791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñuelas, M.; Guerrero-Vadillo, M.; Valdezate, S.; Zamora, M.J.; Leon-Gomez, I.; Flores-Cuéllar, Á.; Carrasco, G.; Díaz-García, O.; Varela, C. Botulism in Spain: Epidemiology and Outcomes of Antitoxin Treatment, 1997–2019. Toxins 2022, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.-C.; Huang, Y.-C.; Huang, S.-H.; Yu, P.-C.; Wang, B.-L.; Lin, F.-H.; Chou, Y.-C.; Hsieh, C.-J.; Yu, C.-P. Epidemiology and risk factors for notifiable Clostridium botulinum infections in Taiwan from 2003 to 2020. Medicine 2022, 101, e31198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Tian, T.; Guo, W.; Liu, C.; Liang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Fu, P. Epidemiological Analysis of Foodborne Botulism Outbreaks—China, 2004–2020. China CDC Wkly. 2022, 4, 788–792. [Google Scholar]
- Learoyd, T.P. Underreporting or Failed Notification? Global Botulism Reporting, 2000–2022. Health Secur. 2024, 22, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.K.; Sobel, J.; Chatham-Stephens, K.; Luquez, C. Clinical Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Botulism, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021, 70, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangene. BAT® [Botulism Antitoxin Heptavalent (A, B, C, D, E, F, G)—(Equine)] Sterile Solution for Injection. 2013. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/approved-blood-products/bat-botulism-antitoxin-heptavalent-b-c-d-e-f-g-equine (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Arnon, S.S.; Schechter, R.; Maslanka, S.E.; Jewell, N.P.; Hatheway, C.L. Human botulism immune globulin for the treatment of infant botulism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankovich, T.L.; Arnon, S.S. Clinical trial of botulism immune globulin for infant botulism. West J. Med. 1991, 154, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Lonati, D.; Schicchi, A.; Crevani, M.; Buscaglia, E.; Scaravaggi, G.; Maida, F.; Cirronis, M.; Petrolini, V.M.; Locatelli, C.A. Foodborne Botulism: Clinical Diagnosis and Medical Treatment. Toxins 2020, 12, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, J.R.; Khouri, J.M.; Jewell, N.P.; Arnon, S.S. Efficacy of Human Botulism Immune Globulin for the Treatment of Infant Botulism: The First 12 Years Post Licensure. J. Pediatr. 2018, 193, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Gunn, R.A. Hypersensitivity reactions associated with botulinal antitoxin. Am. J. Med. 1980, 69, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrera, G.S.; Astacio, H.; Tunga, P.; Anderson, D.M.; Hall, C.L.; Richardson, J.S. Use of Botulism Antitoxin Heptavalent (A, B, C, D, E, F, G)—(Equine) (BAT®) in Clinical Study Subjects and Patients: A 15-Year Systematic Safety Review. Toxins 2022, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, National Botulism Surveillance Summary. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/botulism/php/national-botulism-surveillance/2019.html (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Nowakowski, A.; Wang, C.; Powers, D.B.; Amersdorfer, P.; Smith, T.J.; Montgomery, V.A.; Sheridan, R.; Blake, R.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. Potent neutralization of botulinum neurotoxin by recombinant oligoclonal antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11346–11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Razai, A.; Geren, I.N.; Lou, J.; Conrad, F.; Wen, W.-H.; Farr-Jones, S.; Smith, T.J.; Brown, J.L.; Skerry, J.C.; et al. A Three Monoclonal Antibody Combination Potently Neutralizes Multiple Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype E Subtypes. Toxins 2018, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.U.; Griffiss, J.M.; McKenzie, R.; Fuchs, E.J.; Jurao, R.A.; An, A.T.; Ahene, A.; Tomic, M.; Hendrix, C.W.; Zenilman, J.M. Safety and pharmacokinetics of XOMA 3AB, a novel mixture of three monoclonal antibodies against botulinum toxin A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5047–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guptill, J.T.; Raja, S.M.; Juel, V.C.; Walter, E.B.; Cohen-Wolkowiez, M.; Hill, H.; Sendra, E.; Hauser, B.; Jackson, P.; Swamy, G.K. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of NTM-1632, a novel mixture of three monoclonal antibodies against botulinum toxin B. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0232920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.M.; Guptill, J.T.; Juel, V.C.; Walter, E.B.; Cohen-Wolkowiez, M.; Hill, H.; Sendra, E.; Hauser, B.; Jackson, P.; Tomic, M.; et al. First-in-human clinical trial to assess the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of single doses of NTM-1633, a novel mixture of monoclonal antibodies against botulinum toxin E. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e01732-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, D.M.; Riling, K.; Kimbler, A.; Espinoza, Y.; Wong, D.; Pham, K.; Martinez, Z.; Kraus, C.N.; Conrad, F.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of a four monoclonal antibody combination against botulinum C and D neurotoxins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01270-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Lou, J.; Wen, W.; Conrad, F.; Zhai, W.; Smith, T.J.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. A three monoclonal antibody combination potently neutralizes multiple botulinum neurotoxin serotype F subtypes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvin, S.C.; Ganguly, S.; Weiss, R.; Elango, C.; Zhong, X.; Mao, Y.; Yan, H.; Li, N.; Sumner, G.; Turner, K.C.; et al. REGEN-COV® antibody cocktail bioanalytical strategy: Comparison of LC-MRM-MS and immunoassay methods for drug quantification. Bioanalysis 2021, 13, 1827–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, D.; Winter, G.; Svilenov, H.L. It is Never Too Late for a Cocktail—Development and Analytical Characterization of Fixed-dose Antibody Combinations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, J.; Wen, W.; Conrad, F.; Meng, Q.; Dong, J.; Sun, Z.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Farr-Jones, S.; Cheng, L.W.; Henderson, T.D.; et al. A single tri-epitopic antibody virtually recapitulates the potency of a combination of three monoclonal antibodies in neutralization of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. Toxins 2018, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Du, P.; Yu, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. A human bispecific antibody neutralizes botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.-H.; Tremblay, J.M.; Vazquez-Cintron, E.; Perry, K.; Ondeck, C.; Webb, R.P.; McNutt, P.M.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Jin, R. Structural Insights into Rational Design of Single-Domain Antibody-Based Antitoxins against Botulinum Neurotoxins. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 2526–2539.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godakova, S.A.; Noskov, A.N.; Vinogradova, I.D.; Ugriumova, G.A.; Solovyev, A.I.; Esmagambetov, I.B.; Tukhvatulin, A.I.; Logunov, D.Y.; Naroditsky, B.S.; Shcheblyakov, D.V.; et al. Camelid VHHs Fused to Human Fc Fragments Provide Long Term Protection Against Botulinum Neurotoxin A in Mice. Toxins 2019, 11, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, J.; Ondeck, C.A.; Tremblay, J.M.; Archer, J.; Debatis, M.; Foss, A.; Awata, J.; Erasmus, J.H.; McNutt, P.M.; Shoemaker, C.B. Intramuscular delivery of formulated RNA encoding six linked nanobodies is highly protective for exposures to three Botulinum neurotoxin serotypes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, S.-I.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Dong, M. Delivery of single-domain antibodies into neurons using a chimeric toxin-based platform is therapeutic in mouse models of botulism. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaaz4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.A.; Tchao, C.; Prystajecky, N.; Weedmark, K.; Tcholakov, Y.; Lefebvre, M.; Austin, J.W. Foodborne Botulism, Canada, 2006–2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Barash, J.R.; Lou, J.; Conrad, F.; Marks, J.D.; Arnon, S.S. Immunological Characterization and Neutralizing Ability of Monoclonal Antibodies Directed Against Botulinum Neurotoxin Type H. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamant, E.; Lachmi, B.-E.; Keren, A.; Barnea, A.; Marcus, H.; Cohen, S.; David, A.B.; Zichel, R. Evaluating the synergistic neutralizing effect of anti-botulinum oligoclonal antibody preparations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamant, E.; Torgeman, A.; Ozeri, E.; Zichel, R. Monoclonal Antibody Combinations that Present Synergistic Neutralizing Activity: A Platform for Next-Generation Anti-Toxin Drugs. Toxins 2015, 7, 1854–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasetti-Escargueil, C.; Avril, A.; Miethe, S.; Mazuet, C.; Derman, Y.; Selby, K.; Thullier, P.; Pelat, T.; Urbain, R.; Fontayne, A.; et al. The European AntibotABE Framework Program and Its Update: Development of Innovative Botulinum Antibodies. Toxins 2017, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Conrad, F.; Wen, W.; Zhao, L.; Lou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Farr-Jones, S.; Marks, J.D. Multicolor fluorescence activated cell sorting to generate humanized monoclonal antibody binding seven subtypes of BoNT/F. PLoS ONE. 2022, 17, e0273512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Dong, J.; Lou, J.; Wen, W.; Conrad, F.; Geren, I.N.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Smith, T.J.; Smith, L.A.; Ho, M.; et al. Monoclonal antibodies that inhibit the proteolytic activity of botulinum neurotoxin serotype/B. Toxins 2015, 7, 3405–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ying, H.; Grinnell, C.; Bryant, S.; Miller, R.; Clabbers, A.; Bose, S.; McCarthy, D.; Zhu, R.-R.; Santora, L.; et al. Simultaneous targeting of multiple disease mediators by a dual-variable-domain immunoglobulin. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Yan, S.; Geren, I.N.; Knopp, K.A.; Dong, J.; Sun, Z.; Lou, J.; Conrad, F.; Wen, W.-H.; Farr-Jones, S.; et al. A Four-Monoclonal Antibody Combination Potently Neutralizes Multiple Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotypes C and D. Toxins 2021, 13, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddie, M.L.; Kirpotin, D.B.; Kohli, N.; Kornaga, T.; Boll, B.; Razlog, M.; Drummond, D.C.; Lugovskoy, A.A. Development of disulfide-stabilized Fabs for targeting of antibody-directed nanotherapeutics. MAbs 2022, 14, 2083466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Levy, R.; Arndt, J.W.; Forsyth, C.M.; Razai, A.; Lou, J.; Geren, I.; Stevens, R.C.; Marks, J.D. Molecular evolution of antibody cross-reactivity for two subtypes of type A botulinum neurotoxin. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; Geren, I.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Forsyth, C.M.; Wen, W.; Knopp, K.; Brown, J.; Smith, T.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. Affinity maturation of human botulinum neurotoxin antibodies by light chain shuffling via yeast mating. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2010, 23, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razai, A.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Lou, J.; Geren, I.; Forsyth, C.; Robles, Y.; Tsai, R.; Smith, T.; Smith, L.; Siegel, R.; et al. Molecular evolution of antibody affinity for sensitive detection of botulinum neurotoxin type A. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 351, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, R.C., II; Pavlov, A.R.; Blake, D.A. Automated kinetic exclusion assays to quantify protein binding interactions in homogeneous solution. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 272, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

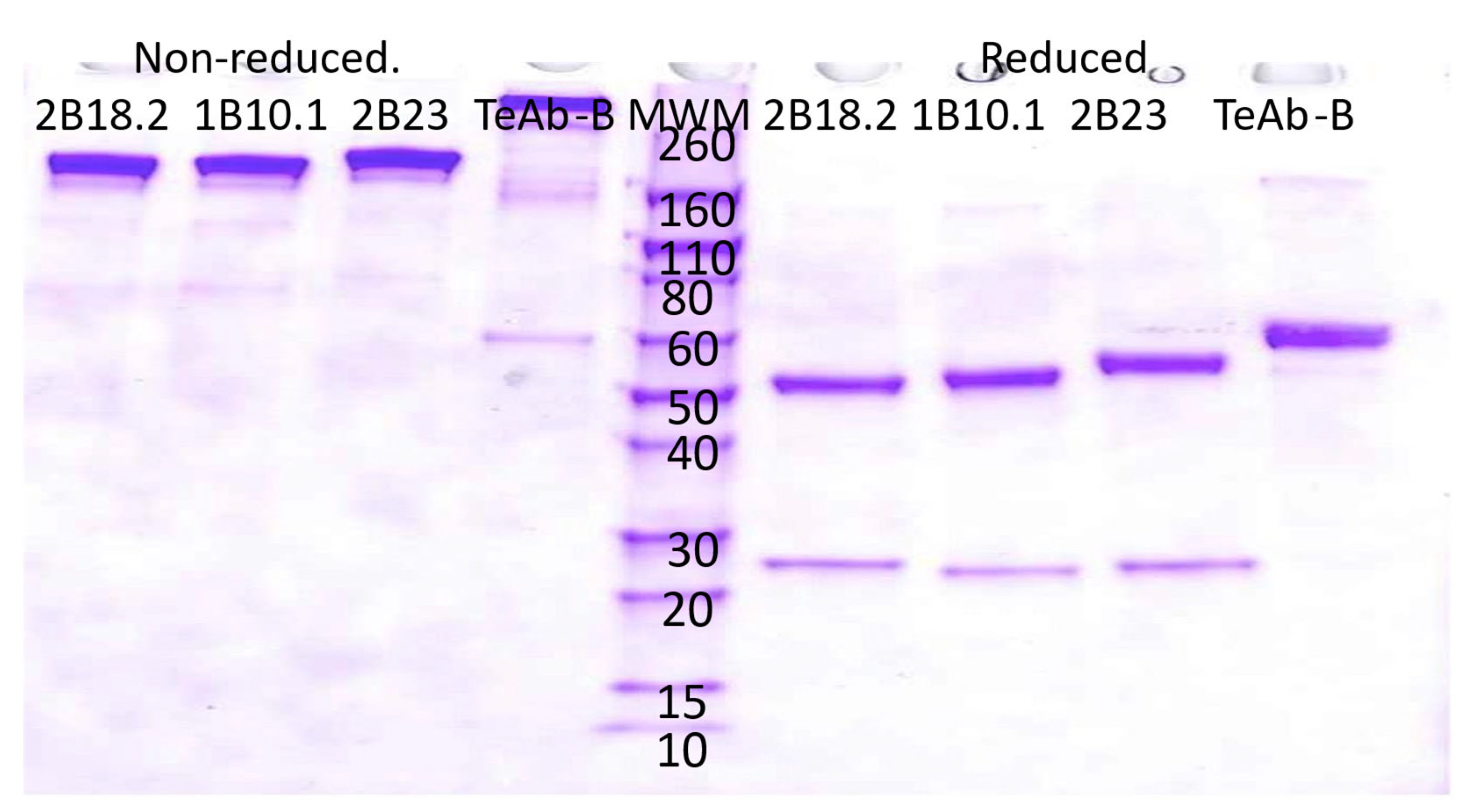


| BoNT/B1 Domain | BoNT/B1 Holotoxin | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAb | KD (pM) (95% Confidence Interval) | kon (106 M−1s−1) (95% Confidence Interval) | koff (10−6 s−1) | KD (pM) (95% Confidence Interval) | kon (106 M−1 s−1) (95% Confidence Interval) | koff (10−6 s−1) |
| LC-HN (1B10.1 epitope) | ||||||
| 1B10.1 | 0.473 (0.906–0.202) | 2.324 (4.040–1.078) | 1.099 | 0.331 (1.180–0.038) | 1.903 (2.026–1.788) | 0.630 |
| TeAb-B | 0.965 (1.960–0.449) | 0.414 (0.437–0.392) | 0.399 | 0.402 (0.846–0.143) | 0.875 (0.940–0.811) | 0.352 |
| LC-HN (2B18.2 epitope) | ||||||
| 2B18.2 | 5.12 (8.05–3.22) | 3.036 (4.149–2.101) | 15.54 | 56.88 (69.68–45.94) | 1.267 (1.368–1.174) | 72.09 |
| TeAb-B | 20.53 (24.56–16.52) | 0.691 (0.749–0.636) | 14.186 | 92.84 (214.16–20.05) | 1.146 (1.217–1.078) | 106.4 |
| LC-HN (2B23.1 epitope) | ||||||
| 2B23.1 | 38.45 (48.60–30.91) | 1.783 (2.270–1.348) | 68.54 | 38.07 (52.12–24.62) | 0.679 (0.707–0.651) | 25.83 |
| TeAb-B | 18.46 (23.22 –14.40) | 0.505 (0.525–0.485) | 9.325 | 0.254 (0.628–0.049) | 1.458 (1.621–1.313) | 0.370 |
| BoNT/E3 Domain | BoNT/E3 Holotoxin | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAb | KD (pM) (95% Confidence Interval) | kon (M−1s−1) (95% Confidence Interval) | koff (s−1) | KD (pM) (95% Confidence Interval) | kon (M−1s−1) (95% Confidence Interval) | koff (s−1) |
| LC-HN (3E2 epitope) | ||||||
| 3E2 | 22.09 (30.26–14.20) | 3.954 (6.450–2.429) | 87.35 | 2.28 (2.71–1.89) | 1.080 (1.253–0.927) | 2.461 |
| TeAb-E | 7.48 (21.60–3.82) | 0.186 (0.257–0.109) | 1.391 | 1.18 (2.99–0.256) | 0.3195 (0.3469–0.2937) | 0.377 |
| LC-HN (4E17.1 epitope) | ||||||
| 4E17.1 | 115.63 (136.72–88.91) | 5.737 (8.527–4.364) | 663.4 | 239.58 (281.13–181.42) | 0.797 (0.886–0.715 | 190.9 |
| TeAb-E | 18.15 (51.22–9.53) | 0.083 (0.089–0.077) | 1.506 | 0.428 (1.21–0.042) | 0.283 (0.299–0.268) | 0.121 |
| LC-HN (3E6.2 epitope) | ||||||
| 3E6.2 | 6.71 (9.28–4.62) | 8.314 (11.58–6.083) | 55.79 | 8.55 (14.32–4.5) | 2.136 (2.705–1.687) | 18.27 |
| TeAb-E | 13.87 (42.39–7.52) | 0.089 (0.094–0.086) | 1.246 | 0.851 (1.58–0.439) | 0.329 (0.339–0.319) | 0.28 |
| BoNT/F1 Domain | BoNT/F1 Holotoxin | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAb | KD (pM) (95% Confidence Interval) | kon (M−1s−1) (95% Confidence Interval) | koff (s−1) | KD (pM) (95% Confidence Interval) | kon (M−1s−1) (95% Confidence Interval) | koff (s−1) |
| LC-HN (Hu6F13.4 epitope) | ||||||
| Hu6F13.4 | 27.01 (49.76–14.96) | 4.062 (5.443–2.896) | 109.7 | 80.47 (139.24–13.40) | 4.129 (11.4–1.438) | 332.2 |
| TeAb-F | 1790 (2500–755.38) | 0.729 (0.963–0.579) | 1305 | 15.5 (35.52–3.48) | 52.86 (110.3 –47.65) | 819.3 |
| LC-HN (6F5.4 epitope) | ||||||
| 6F5.4 | 2.40 (3.52–1.48) | 18.37 (23.14–13.51) | 44.09 | 189.63 (497.81–99.31) | 0.973 (1.717–0.425) | 184.5 |
| TeAb-F | 4.41 (9.86–1.46) | 13.9 (59.7–3.82) | 61.31 | 26.6 (68.91–5.44) | 0.963 (1.141–0.806) | 25.61 |
| LC-HN (Hu6F11 epitope) | ||||||
| Hu6F11 | 25.1 (41.25–12.66) | 1.154 (1.693–0.711) | 28.95 | 0.348 (0.874–0.022) | 1.035 (1.068–1.003) | 0.360 |
| TeAb-F | 125.07 (181.2–80.1) | 2.373 (3.300–1.706) | 296.7 | 23.3 (65.15–3.01) | 0.952 (0.998–0.907) | 22.19 |
| Mabs Administered (50 µg/Mouse) | Amount of BoNT/F1 Administered (Mouse LD50) | Number of Mice Surviving/Number of Mice Treated |
|---|---|---|
| 3 IgG: 6F5.4, hu6F11, hu6F13.4 | 20,000 | 10/10 |
| 3 IgG:6F5.4, hu6F11, hu6F13.4 | 40,000 | 5/5 |
| TeAb-F | 40,000 | 5/5 |
| TeAb-F | 20,000 | 5/5 |
| TeAb-F | 10,000 | 5/5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lou, J.; Wen, W.H.; Conrad, F.; Tam, C.C.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Farr-Jones, S.; Marks, J.D. Single Tri-Epitopic Antibodies (TeAbs) to Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotypes B, E, and F Recapitulate the Full Potency of a Combination of Three Monoclonal Antibodies in Toxin Neutralization. Toxins 2025, 17, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060281
Lou J, Wen WH, Conrad F, Tam CC, Garcia-Rodriguez C, Farr-Jones S, Marks JD. Single Tri-Epitopic Antibodies (TeAbs) to Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotypes B, E, and F Recapitulate the Full Potency of a Combination of Three Monoclonal Antibodies in Toxin Neutralization. Toxins. 2025; 17(6):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060281
Chicago/Turabian StyleLou, Jianlong, Wei Hua Wen, Fraser Conrad, Christina C. Tam, Consuelo Garcia-Rodriguez, Shauna Farr-Jones, and James D. Marks. 2025. "Single Tri-Epitopic Antibodies (TeAbs) to Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotypes B, E, and F Recapitulate the Full Potency of a Combination of Three Monoclonal Antibodies in Toxin Neutralization" Toxins 17, no. 6: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060281
APA StyleLou, J., Wen, W. H., Conrad, F., Tam, C. C., Garcia-Rodriguez, C., Farr-Jones, S., & Marks, J. D. (2025). Single Tri-Epitopic Antibodies (TeAbs) to Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotypes B, E, and F Recapitulate the Full Potency of a Combination of Three Monoclonal Antibodies in Toxin Neutralization. Toxins, 17(6), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060281







