Comparative Ecotoxicological Effects of Cyanobacterial Crude Extracts on Native Tropical Cladocerans and Daphnia magna
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cyanobacterial Abundance and Microcystin-LR Concentration in the FCHAB
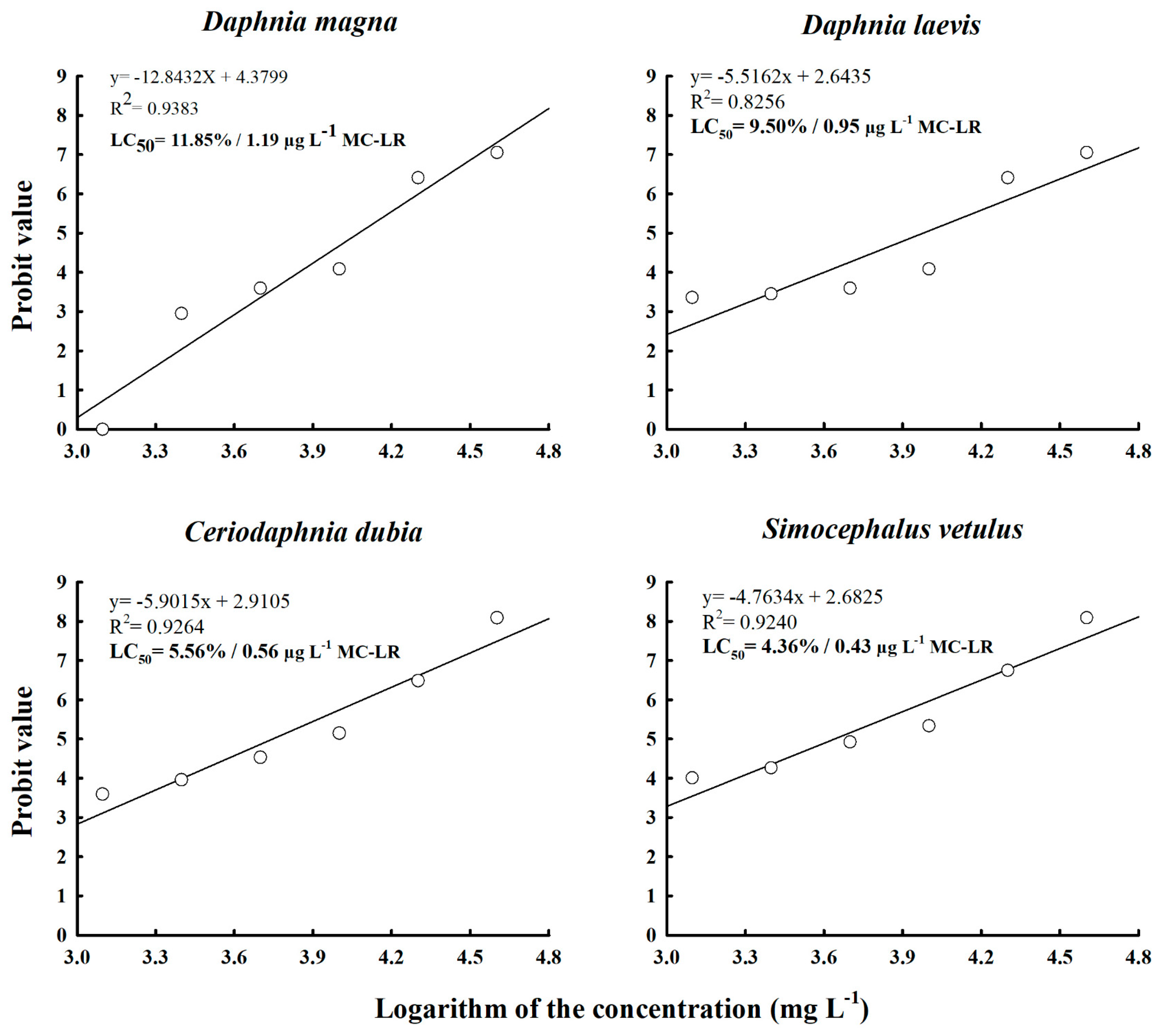
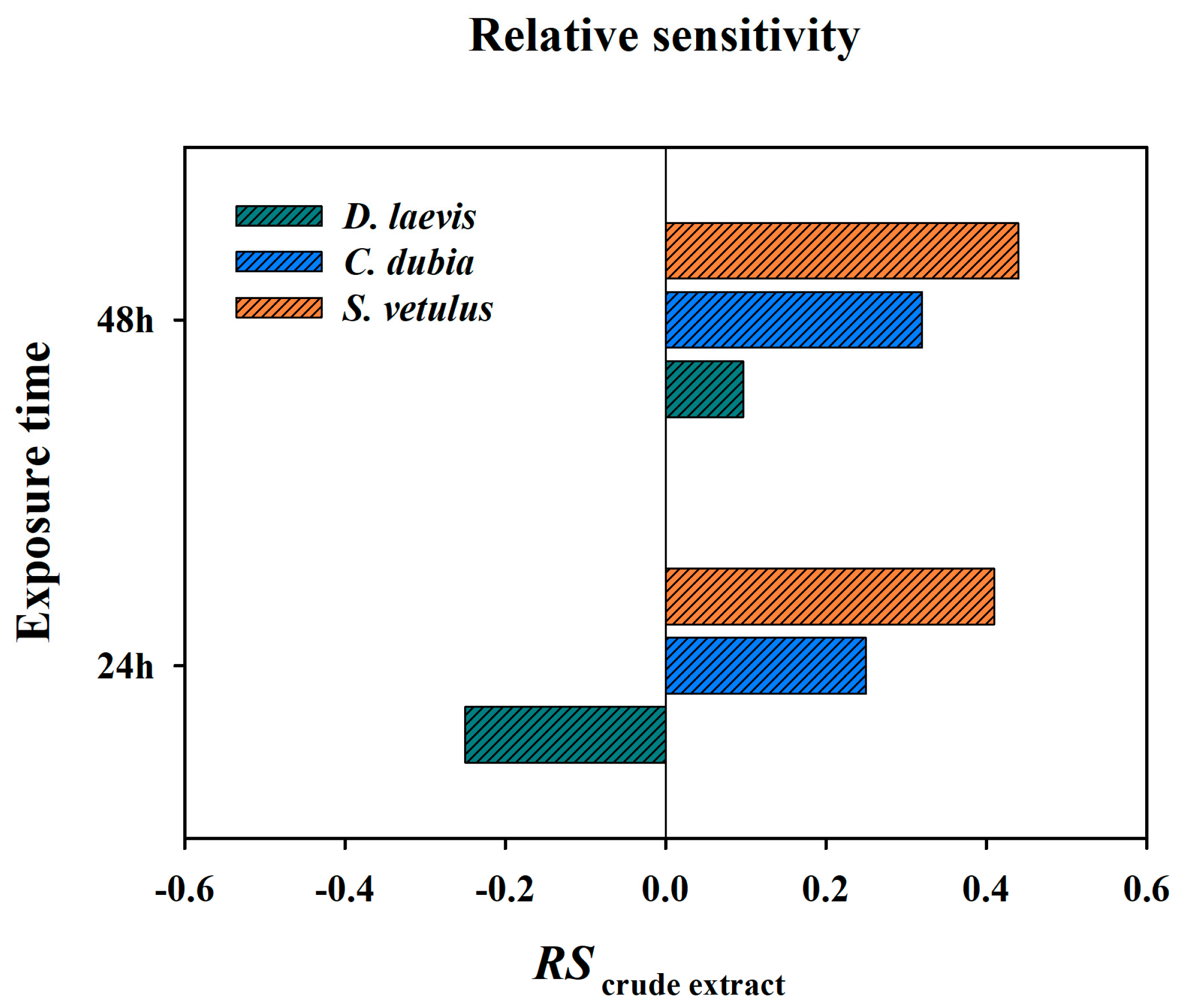
2.2. Acute Toxicity and Relative Sensitivity of Native Cladocerans
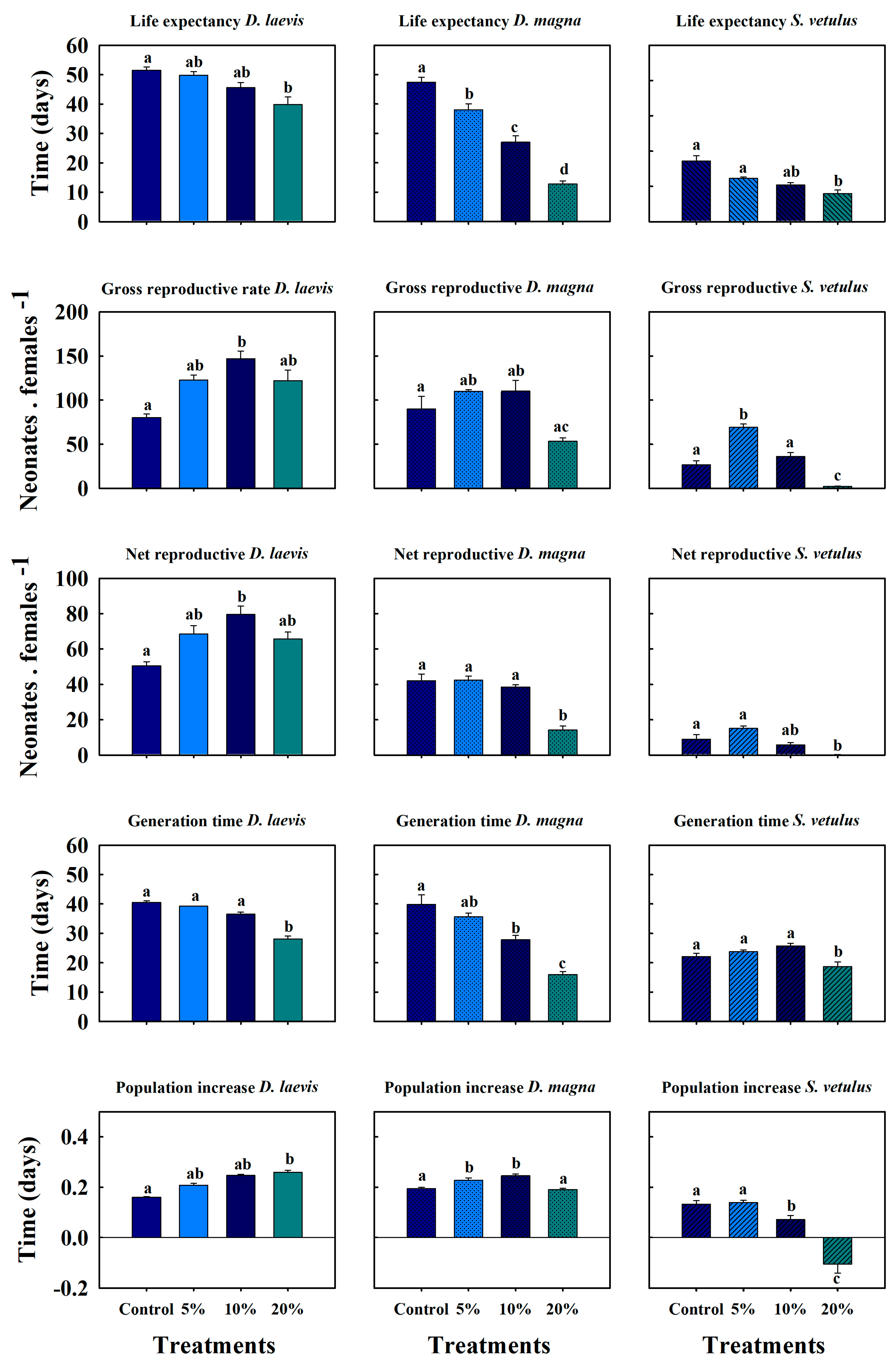
2.3. Sublethal Effects of Native Cladocerans and D. magna
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Isolation and Maintenance of Bioassay Organisms
5.2. Preparation of the Crude Extract of the Cyanobacterial Bloom
5.3. Identification and Quantification of Cyanobacteria
5.4. Acute Toxicity Tests
5.5. Chronic Toxicity Test (Life Table)
5.6. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RS | Relative sensitivity |
| FCHABs | Freshwater cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms |
| LC50 | Median Lethal concentration |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
References
- Ger, K.A.; Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Frost, P.C.; Hansson, L.A.; Sarnelle, O.; Wilson, A.E.; Lürling, M. The interaction between cyanobacteria and zooplankton in a more eutrophic world. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churro, C.; Azevedo, J.; Vasconcelos, V.; Silva, A. Detection of a Planktothrix agardhii bloom in Portuguese marine coastal waters. Toxins 2017, 9, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmgren, R.; Larsson, U. Nitrogen and the Baltic Sea: Managing nitrogen in relation to phosphorus. Sci. World J. 2001, 1, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W. Mitigating toxic planktonic cyanobacterial blooms in aquatic ecosystems facing increasing anthropogenic and climatic pressures. Toxins 2018, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Nagelkerken, I.; Goldenberg, S.U.; Fordham, D.A. Climate change could drive marine food web collapse through altered trophic flows and cyanobacterial proliferation. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2003446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Carey, C.C.; Hamilton, D.P.; Huisman, J.; Paerl, H.W.; Wood, S.A.; Wulff, A. Perspective: Advancing the research agenda for improving understanding of cyanobacteria in a future of global change. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.; Wienhues, G.; Misra, P.; Tylmann, W.; Lami, A.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Matthews, B. Anthropogenic eutrophication drives major food web changes in Mwanza Gulf, Lake Victoria. Ecosystems 2024, 27, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.R.; Pinto, E.; Torres, M.A.; Dörr, F.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Szubert, K.; Janssen, E.M.L. CyanoMetDB, a comprehensive public database of secondary metabolites from cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2021, 196, 117017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testai, E.; Scardala, S.; Vichi, S.; Buratti, F.M.; Funari, E. Risk to human health associated with the environmental occurrence of cyanobacterial neurotoxic alkaloids anatoxins and saxitoxins. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2016, 46, 385–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, M.C.; Rodrigues, T.F.; Silva, L.O.; Pacheco, A.B.F.; Ferrão-Filho, A.S.; Azevedo, S.M. Ecophysiological aspects and sxt genes expression underlying induced chemical defense in STX-producing Raphidiopsis raciborskii (cyanobacteria) against the zooplankter Daphnia gessneri. Toxins 2021, 13, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazdova, I.; Keremidarska-Markova, M.; Chichova, M.; Uzunov, B.; Nikolaev, G.; Mladenov, M.; Gagov, H.S. Review of Cyanotoxicity Studies Based on Cell Cultures. J. Toxicol. 2022, 2022, 5647178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontanillo, M.; Köhn, M. Microcystins: Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationship Studies Toward PP1 and PP2A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus, I.; Welker, M. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2021; p. 858. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora-Barrios, C.A.; Nandini, S.; Sarma, S.S.S. Review of Potentially Harmful Cyanobacteria. Tecnol. Cienc. Agua 2023, 14, 250–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandini, S.; Sarma, S.S.S. Experimental studies on zooplankton-toxic cyanobacteria interactions: A review. Toxics 2023, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, K.G. Integrating the Microbial Loop and the Classic Food Chain into a Realistic Planktonic Food Web. In Food Webs: Integration of Patterns & Dynamics; Polis, G.A., Winemiller, K.O., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Medrano, G.E.; Rico-Martínez, R. Acute Sensitivity Comparison Among Daphnia magna Straus, 1820, Daphnia pulex Leydig, 1860 and Simocephalus vetulus Müller, 1776, Exposed to Nine Toxicants. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 19, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, E.C.; Rocha, O. Acute Toxicity Tests with the Tropical Cladoceran Pseudosida ramosa: The Importance of Using Native Species as Test Organisms. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 60, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Rodríguez, C.A.; Jiménez-Santos, M.A.; Martínez-Miranda, D.M.; Piedra-Ibarra, E.; Rivera-De la Parra, L.; Lugo-Vázquez, A. Daphnia magna (Crustacea: Anomopoda) in Central Mexico Wetlands: Implications of Escape from Ecotoxicological Laboratories. Biol. Invasions 2024, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, J.S.; Codd, G.A. Co-occurrence of cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins with other environmental health hazards: Impacts and implications. Toxins 2020, 12, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, V.; Martins, A.; Vale, M.; Antunes, A.; Azevedo, J.; Welker, M.; Montejano, G. First report on the occurrence of microcystins in planktonic cyanobacteria from Central Mexico. Toxicon 2010, 56, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Sánchez, M.A.; Nandini, S.; Sarma, S.S.S. Zooplankton community structure in relation to microcystins in the eutrophic Lake Zumpango (State of Mexico). Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2020, 196, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Safe Recreational Water Environments: Coastal and Fresh Waters; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlack, T.; Christoffersen, K.; Dittmann, E.; Nogueira, I.; Vasconcelos, V.; Börner, T. Ingestion of microcystins by Daphnia: Intestinal uptake and toxic effects. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandini, S.; Sarma, S.S.S.; Ramírez-García, P. Life table demography and population growth of Daphnia laevis (Cladocera, Anomopoda) under different densities of Chlorella vulgaris and Microcystis aeruginosa. Crustaceana 2000, 73, 1273–1286. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/20106399 (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Ferrão-Filho, A.; de Abreu, S.; Silva, D.; de Oliveira, T.A.; de Magalhães, V.F.; Pflugmacher, S.; da Silva, E.M. Single and combined effects of microcystin- and saxitoxin-producing cyanobacteria on the fitness and antioxidant defenses of cladocerans. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlik-Skowrońska, B.; Toporowska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H. Effects of secondary metabolites produced by different cyanobacterial populations on the freshwater zooplankters Brachionus calyciflorus and Daphnia pulex. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 11793–11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, R.; Nandini, S.; Sarma, S.S.S. A comparative study on the ability of tropical micro-crustaceans to feed and grow on cyanobacterial diets. J. Plankton Res. 2012, 34, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krantzberg, G. Metal accumulation by chironomid larvae: The effects of age and body weight on metal body burdens. In Environmental Bioassay Techniques and their Application: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference, Lancaster, UK, 11–14 July 1988; Wells, P.G., Lee, K., Blaise, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokul, T.; Kumar, K.R.; Veeramanikandan, V.; Arun, A.; Balaji, P.; Faggio, C. Impact of particulate pollution on aquatic invertebrates. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 100, 104146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, P. Variables affecting body burdens of lead, zinc and cadmium in a roadside population of the snail Cepaea hortensis Müller. Oecologia 1980, 44, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dölger, J.; Kiørboe, T.; Andersen, A. Dense dwarfs versus gelatinous giants: The trade-offs and physiological limits determining the body plan of planktonic filter feeders. Am. Nat. 2019, 194, E30–E40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macke, E.; Callens, M.; De Meester, L.; Decaestecker, E. Host-genotype dependent gut microbiota drives zooplankton tolerance to toxic cyanobacteria. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lyu, K.; Yang, Z. Size-specific sensitivity of cladocerans to freshwater salinization: Evidences from the changes in life history and population dynamics. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 296, 118770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulot, F.D.; Carmignac, D.; Legendre, S.; Yepremian, C.; Bernard, C. Effects of microcystin-producing and microcystin-free strains of Planktothrix agardhii on long-term population dynamics of Daphnia magna. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Limnol. 2012, 48, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.S.; Do-Hong, L.C.; Wiegand, C. Chronic effects of cyanobacterial toxins on Daphnia magna and their offspring. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacArthur, R.H. Geographical Ecology: Patterns in the Distribution of Species; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgher, S.; Espíndola, E.L.G.; Lombardi, A.T. Suitability of Daphnia similis as an alternative organism in ecotoxicological tests: Implications for metal toxicity. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkaczyk, A.; Bownik, A.; Dudka, J.; Kowal, K.; Ślaska, B. Daphnia magna model in the toxicity assessment of pharmaceuticals: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 143038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feniova, I.Y.; Brzeziński, T.; Bednarska, A.; Dzialowski, A.R.; Petrosyan, V.G.; Zilitinkevich, N.; Dawidowicz, P. Effects of cyanobacteria on competitive interactions between different-sized cladoceran species. Water 2025, 17, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, N.A.; Elser, J.J. Nutrient recycling by Daphnia reduces N₂ fixation by cyanobacteria. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declerck, S.A.; de Senerpont Domis, L.N. Contribution of freshwater metazooplankton to aquatic ecosystem services: An overview. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 2795–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitzka, M.A.; Borowitzka, L.J. (Eds.) Dunaliella. In Microalgal Biotechnology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988; pp. 27–58. [Google Scholar]
- Pietsch, C.; Wiegand, C.; Amé, M.V.; Nicklisch, A.; Wunderlin, D.; Pflugmacher, S. The effects of a cyanobacterial crude extract on different aquatic organisms: Evidence for cyanobacterial toxin modulating factors. Environ. Toxicol. 2001, 16, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J.; Johansen, J.R. Filamentous cyanobacteria. In Freshwater Algae of North America; Whitton, B.A., Potts, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 135–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von der Ohe, P.C.; Liess, M. Relative sensitivity distribution of aquatic invertebrates to organic and metal compounds. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, C.J. Ecology: The Experimental Analysis of Distribution and Abundance, 3rd ed.; Harper and Row: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamora-Barrios, C.A.; Rodríguez, M.E.F.; Nandini, S.; Sarma, S.S.S. Comparative Ecotoxicological Effects of Cyanobacterial Crude Extracts on Native Tropical Cladocerans and Daphnia magna. Toxins 2025, 17, 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060277
Zamora-Barrios CA, Rodríguez MEF, Nandini S, Sarma SSS. Comparative Ecotoxicological Effects of Cyanobacterial Crude Extracts on Native Tropical Cladocerans and Daphnia magna. Toxins. 2025; 17(6):277. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060277
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamora-Barrios, Cesar Alejandro, Marcos Efrén Fragoso Rodríguez, S. Nandini, and S. S. S. Sarma. 2025. "Comparative Ecotoxicological Effects of Cyanobacterial Crude Extracts on Native Tropical Cladocerans and Daphnia magna" Toxins 17, no. 6: 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060277
APA StyleZamora-Barrios, C. A., Rodríguez, M. E. F., Nandini, S., & Sarma, S. S. S. (2025). Comparative Ecotoxicological Effects of Cyanobacterial Crude Extracts on Native Tropical Cladocerans and Daphnia magna. Toxins, 17(6), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060277






