Role of the IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Axis in the Protective Effect of Selenomethionine Against Zearalenone-Induced Hepatic Inflammatory Injury in Rabbits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
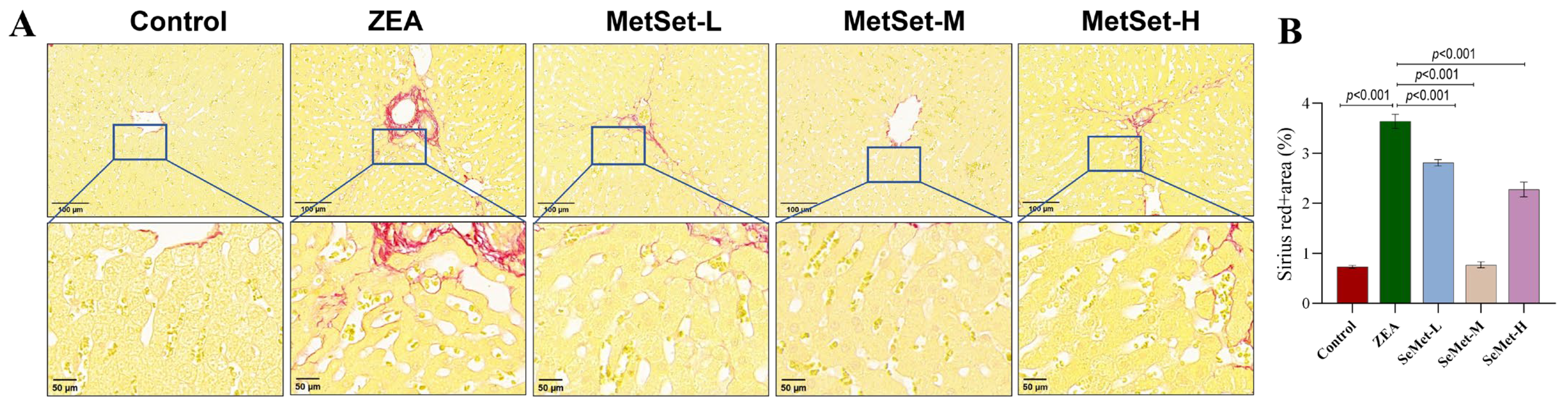
2.1. Effect of SeMet on Morphological Structure of Liver Tissue in Rabbits Exposed to ZEA
2.2. Effect of SeMet on Inflammatory Injury of Liver Tissue Induced by ZEA
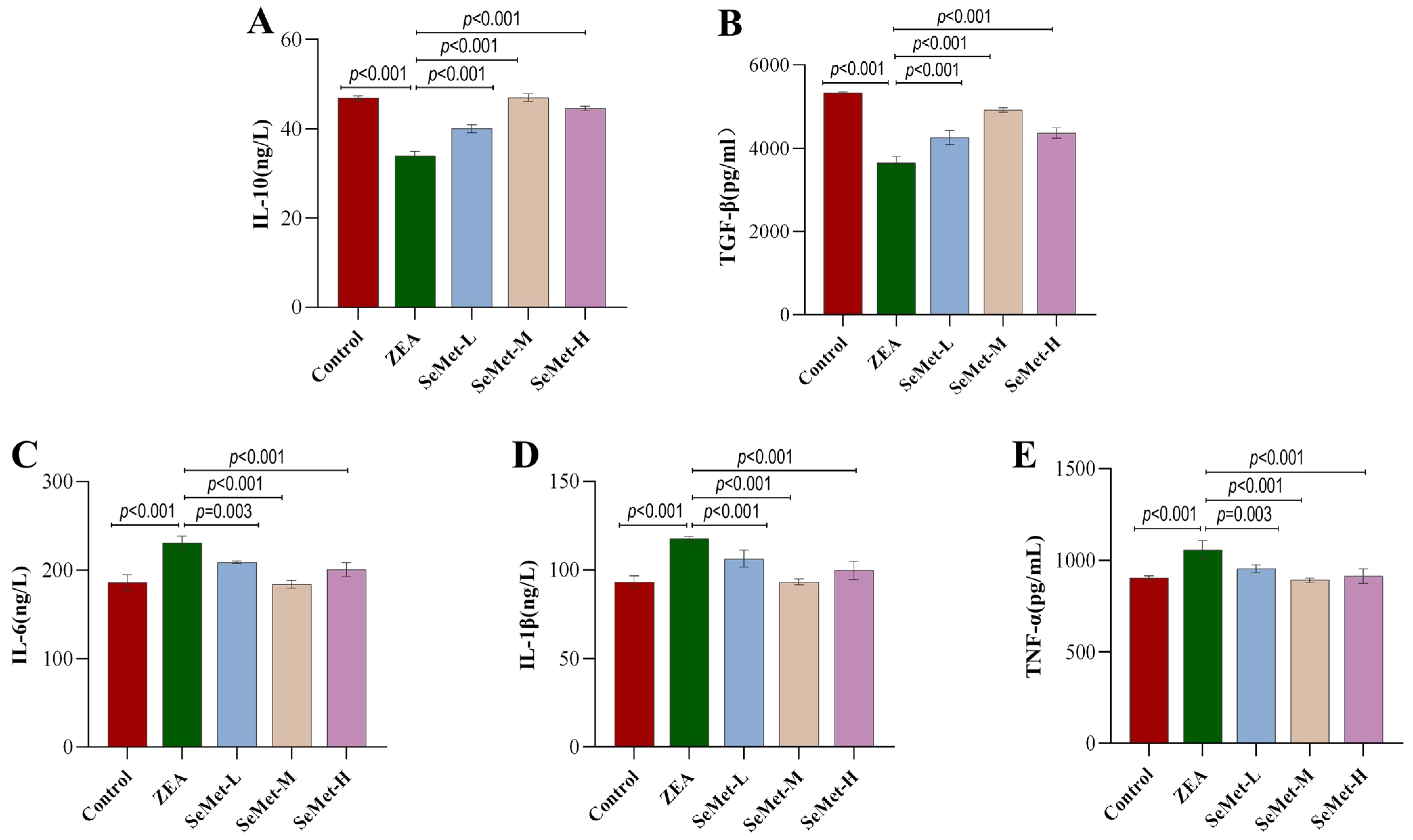
2.3. Effect of SeMet on Levels of Hepatic Inflammatory Cytokines in ZEA-Exposed Rabbits
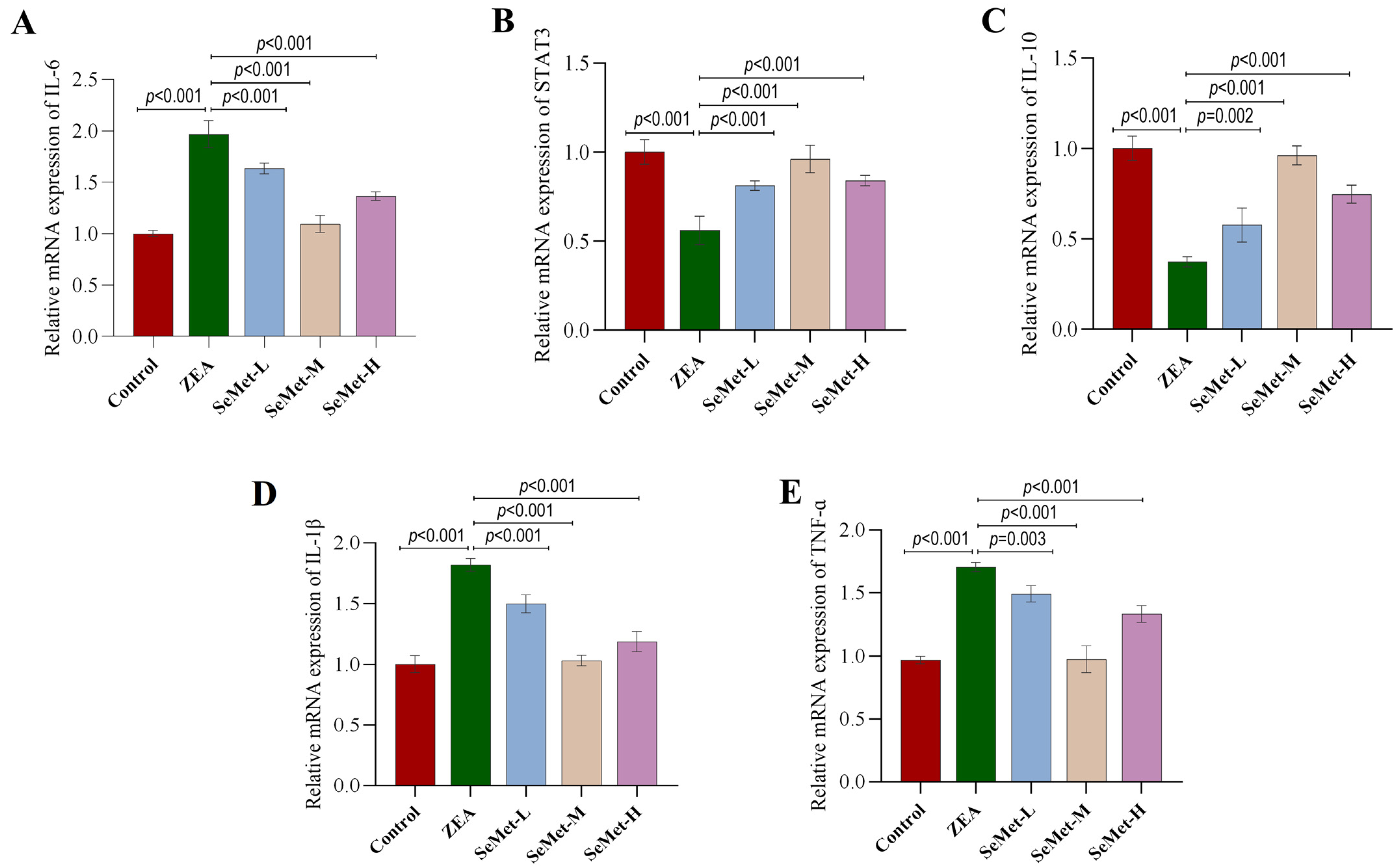
2.4. Effect of SeMet on the Expressions of IL-6/STAT3 Pathway-Related Genes in ZEA-Exposed Rabbit Livers
2.5. Effects of SeMet on Expression and Location of Hepatic IL-6/STAT3 Pathway-Involved Proteins in ZEA-Exposed Rabbits
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemical Reagents
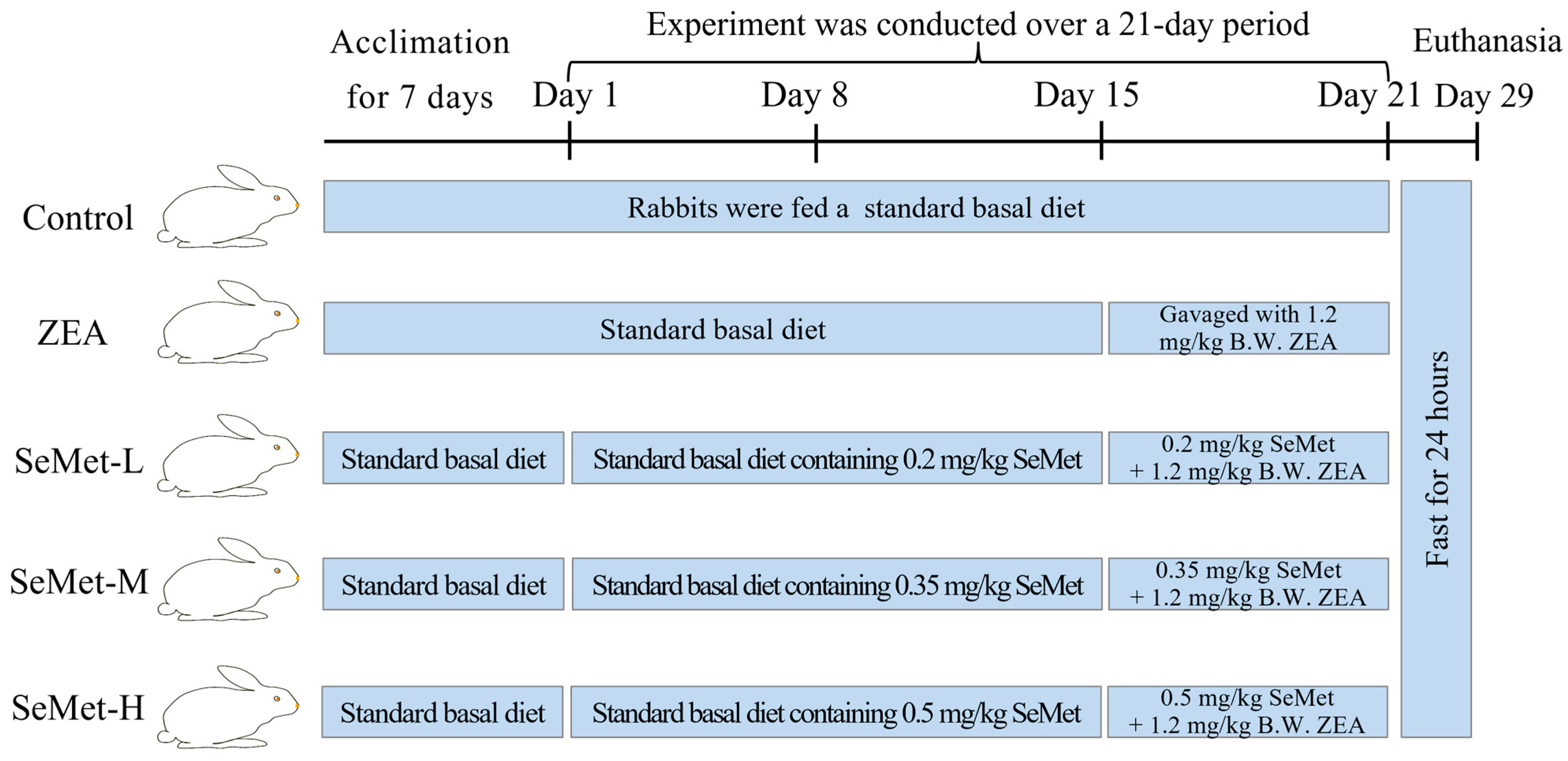
5.2. Animal Grouping and Treatment
5.3. Collection of Liver Tissue Samples
5.4. Serum Biochemical Analysis
5.5. HE and Sirius Red Staining for Hepatic Histopathology Analysis
5.6. ELISA Detection of Inflammation Markers
5.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
5.8. Immunohistochemical Detection of IL-6 and STAT3 Protein Expression
5.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ropejko, K.; Twarużek, M. Zearalenone and Its Metabolites-General Overview, Occurrence, and Toxicity. Toxins 2021, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinton, P.; Tsybulskyy, D.; Lucioli, J.; Laffitte, J.; Callu, P.; Lyazhri, F.; Grosjean, F.; Bracarense, A.P.; Kolf-Clauw, M.; Oswald, I.P. Toxicity of deoxynivalenol and its acetylated derivatives on the intestine: Differential effects on morphology, barrier function, tight junction proteins, and mitogen-activated protein kinases. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 130, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, D.E.; Pistol, G.C.; Neagoe, I.V.; Calin, L.; Taranu, I. Effects of zearalenone on oxidative stress and inflammation in weanling piglets. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obremski, K.; Gonkowski, S.; Wojtacha, P. Zearalenone-induced changes in the lymphoid tissue and mucosal nerve fibers in the porcine ileum. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 18, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistol, G.C.; Braicu, C.; Motiu, M.; Gras, M.A.; Marin, D.E.; Stancu, M.; Calin, L.; Israel-Roming, F.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Taranu, I. Zearalenone mycotoxin affects immune mediators, MAPK signalling molecules, nuclear receptors and genome-wide gene expression in pig spleen. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.-L.; Li, N.; Wang, H.; Ma, J.-M.; Shen, W.; Li, L. Zearalenone Exposure Induces the Apoptosis of Porcine Granulosa Cells and Changes Long Noncoding RNA Expression To Promote Antiapoptosis by Activating the JAK2-STAT3 Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12117–12128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Su, X.; Tang, Y.; Koci, M.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Q.; et al. Rutin, a natural flavonoid glycoside, ameliorates zearalenone induced liver inflammation via inhibiting lipopolysaccharide gut leakage and NF-κB signaling pathway in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 191, 114887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Yan, C.; Gu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zou, H.; Liu, Z.; Bian, J. Resveratrol Alleviates Zearalenone-Induced Intestinal Dysfunction in Mice through the NF-κB/Nrf2/HO-1 Signalling Pathway. Foods 2024, 13, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsouloufi, T.K. An overview of mycotoxicoses in rabbits. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2024, 36, 638–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yi, J.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Mehmood, K.; Hussain, R.; Tang, Z.; et al. Zearalenone exposure mediated hepatotoxicity via mitochondrial apoptotic and autophagy pathways: Associated with gut microbiome and metabolites. Toxicology 2021, 462, 152957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, F.; Tang, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Liu, S.; Han, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, B. Quercetagetin alleviates zearalenone-induced liver injury in rabbits through Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1271384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbuZahra, H.M.; Rajendran, P.; Ismail, M.B. Zerumbone Exhibit Protective Effect against Zearalenone Induced Toxicity via Ameliorating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Induced Apoptosis. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.-C.; Lee, H.-C.; Liao, C.-C.; Chou, A.-H.; Yu, H.-P. Role of NADPH Oxidase-Derived ROS-Mediated IL-6/STAT3 and MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Protective Effect of Corilagin against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. Biology 2023, 12, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaura, S.; Chauhan, P.; Chandra, H.; Bhardwaj, N. Aflatoxin B1 administration induces reactive oxygen species production and apoptosis of erythrocytes in mice. Toxicon 2023, 221, 106963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, G.-Y.; Cheng, J.-Y.; Wan, H.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Li, H.-J. Hinokiflavone exerts dual regulation on apoptosis and pyroptosis via the SIX4/Stat3/Akt pathway to alleviate APAP-induced liver injury. Life Sci. 2024, 354, 122968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żybura, A.; Jedziniak, P. The efficiency of mycotoxin binding by sorbents in the in vitro model using a naturally contaminated animal feed. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 68, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Chu, H.; Wei, J.; Yan, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Yang, F. Astaxanthin Alleviates Hepatic Lipid Metabolic Dysregulation Induced by Microcystin-LR. Toxins 2024, 16, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ge, C.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y. Graveoline attenuates D-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver injury via inhibition of JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 117163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, M.; Bernhoft, A.; Reinoso-Maset, E.; Salbu, B.; Lebed, P.; Framstad, T.; Fuhrmann, H.; Oropeza-Moe, M. Beneficial antioxidant status of piglets from sows fed selenomethionine compared with piglets from sows fed sodium selenite. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 58, 126439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Zhu, G.-Y.; Sheng, X.-H.; Xing, K.; Venema, K.; Wang, X.-G.; Xiao, L.-F.; Guo, Y.; Ni, H.-M.; Zhu, N.-H.; et al. Dietary supplementation with selenomethionine enhances antioxidant capacity and selenoprotein gene expression in layer breeder roosters. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Bu, D.; Liu, S.; Zhang, K. Hydroxy-selenomethionine: A novel organic selenium source that improves antioxidant status and selenium concentrations in milk and plasma of mid-lactation dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 9602–9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Xi, Y.; Liu, X. A Comprehensive Comparison of Different Selenium Supplements: Mitigation of Heat Stress and Exercise Fatigue-Induced Liver Injury. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 917349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Lin, L.; Li, P.; Tian, H.; Shen, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Tang, C. Selenomethionine protects the liver from dietary deoxynivalenol exposure via Nrf2/PPARγ-GPX4-ferroptosis pathway in mice. Toxicology 2024, 501, 153689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, A.; Zhao, B.; Xia, Y.; He, Y.; Xue, H.; Li, S. Dietary selenomethionine reduced oxidative stress by resisting METTL3-mediated m(6)A methylation level of Nrf2 to ameliorate LPS-induced liver necroptosis in laying hens. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 125, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Ammar, R.B.; Al-Saeedi, F.J.; Mohamed, M.E.; ElNaggar, M.A.; Al-Ramadan, S.Y.; Bekhet, G.M.; Soliman, A.M. Kaempferol Inhibits Zearalenone-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt-Mediated Nrf2 Signaling Pathway: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Y.; Yang, P.; Hua, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, X.; Han, X.; Pang, X.; Xu, S.; Jiang, X.; Lin, Y.; et al. Effects of Chronic Exposure to Diets Containing Moldy Corn or Moldy Wheat Bran on Growth Performance, Ovarian Follicular Pool, and Oxidative Status of Gilts. Toxins 2022, 14, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alassane-Kpembi, I.; Puel, O.; Oswald, I.P. Toxicological interactions between the mycotoxins deoxynivalenol, nivalenol and their acetylated derivatives in intestinal epithelial cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China, L.; Becares, N.; Rhead, C.; Tittanegro, T.; Freemantle, N.; O’Brien, A. Targeted Albumin Infusions Do Not Improve Systemic Inflammation or Cardiovascular Function in Decompensated Cirrhosis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, e00476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexa, E.; Dehelean, C.A.; Poiana, M.-A.; Radulov, I.; Cimpean, A.-M.; Bordean, D.-M.; Tulcan, C.; Pop, G. The occurrence of mycotoxins in wheat from western Romania and histopathological impact as effect of feed intake. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, S.; Longobardi, C.; Ferrara, G.; Piscopo, N.; Riccio, L.; Russo, V.; Meucci, V.; De Marchi, L.; Esposito, L.; Florio, S.; et al. Oxidative Status and Histological Evaluation of Wild Boars’ Tissues Positive for Zearalenone Contamination in the Campania Region, Southern Italy. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.P.; Medhi, S. Role of inflammasomes and cytokines in immune dysfunction of liver cirrhosis. Cytokine 2023, 170, 156347. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, J.-Y.; Wei, Y.; Gao, S.-L.; Wang, L.; Zheng, J.-Y.; Gu, M.; Qin, L.-Q. Protective Effect of Selenium-Enriched Green Tea on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 2233–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, L.; Gao, X.; Liu, W.; Zhu, X.; Huang, W.; Zhao, H.; Wei, Z.; Wang, K.; et al. Baicalin protects against zearalenone-induced chicks liver and kidney injury by inhibiting expression of oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines and caspase signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hao, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. Selenium-Enriched Yeast Relieves Hexavalent Chromium Toxicity by Inhibiting NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Broiler Spleens. Animals 2022, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Yin, J.; Xu, T.; Dai, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Fuling-Zexie formula attenuates hyperuricemia-induced nephropathy and inhibits JAK2/STAT3 signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319 Pt 2, 117262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassmann, S.; Schuster, I.; Walch, A.; Göbel, H.; Jütting, U.; Makowiec, F.; Hopt, U.; Werner, M. STAT3 mRNA and protein expression in colorectal cancer: Effects on STAT3-inducible targets linked to cell survival and proliferation. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 60, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edsbäcker, E.; Serviss, J.T.; Kolosenko, I.; Palm-Apergi, C.; De Milito, A.; Tamm, K.P. STAT3 is activated in multicellular spheroids of colon carcinoma cells and mediates expression of IRF9 and interferon stimulated genes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Müller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374 Pt 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Pardoll, D.; Jove, R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swetha, K.; Indumathi, M.C.; Kishan, R.; Siddappa, S.; Chen, C.-H.; Marathe, G.K. Selenium Mitigates Caerulein and LPS-induced Severe Acute Pancreatitis by Inhibiting MAPK, NF-κB, and STAT3 Signaling via the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z. Protective effect of selenomethionine on T-2 toxin-induced liver injury in New Zealand rabbits. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Grouping | Liver Function Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALB (g/L) | GLOB (g/L) | TBA (μmol/L) | TB (μmol/L) | A/G | |
| Control | 43.80 ± 3.44 b | 13.40 ± 0.10 c | 11.57 ± 0.14 b | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 3.74 ± 0.27 a |
| ZEA | 54.27 ± 0.15 a | 17.63 ± 1.70 a | 16.04 ± 1.05 a | 0.73 ± 1.10 | 2.95 ± 0.35 b |
| SeMet-L | 52.10 ± 1.44 a | 16.07 ± 0.76 a,b | 13.82 ± 1.14 a,b | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 3.16 ± 0.46 a,b |
| SeMet-M | 43.97 ± 1.69 b | 14.53 ± 0.47 b,c | 12.03 ± 0.47 b | 0.57 ± 0.81 | 3.77 ± 0.25 a |
| SeMet-H | 51.23 ± 1.43 a | 15.20 ± 0.75 b,c | 13.53 ± 2.17 b | 0.13 ± 0.06 | 3.37 ± 0.26 a,b |
| Gene | Sequence (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|
| β-Actin | F: CGTGCGGGACATCAAGGAG R: AGGAAGGAGGGCTGGAAGAG |
| IL-6 | F: ACCTGCCTGCTGAGAATCAC R: TCGTCACTCCTGAACTTGGC |
| STAT3 | F: CAGCCTGTCTGCAGAGTTCA R: AAGGTGATCAGGTGCAGCTC |
| IL-1β | F: AAGACGATAAACCTACCCTGC R: GACTCAAATTCCAGCTTGTCC |
| TNF-α | F: AAGAGTCCCCAAACAACCTCC R: CTCCACTTGCGGGTTTGCTAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Wei, W.; Li, H.; Xu, W.; Lv, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Role of the IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Axis in the Protective Effect of Selenomethionine Against Zearalenone-Induced Hepatic Inflammatory Injury in Rabbits. Toxins 2025, 17, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060275
Chen X, Wei W, Li H, Xu W, Lv Q, Liu Y, Zhang Z. Role of the IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Axis in the Protective Effect of Selenomethionine Against Zearalenone-Induced Hepatic Inflammatory Injury in Rabbits. Toxins. 2025; 17(6):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060275
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaoguang, Wenjuan Wei, Haonan Li, Wenjing Xu, Qiongxia Lv, Yumei Liu, and Ziqiang Zhang. 2025. "Role of the IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Axis in the Protective Effect of Selenomethionine Against Zearalenone-Induced Hepatic Inflammatory Injury in Rabbits" Toxins 17, no. 6: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060275
APA StyleChen, X., Wei, W., Li, H., Xu, W., Lv, Q., Liu, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Role of the IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Axis in the Protective Effect of Selenomethionine Against Zearalenone-Induced Hepatic Inflammatory Injury in Rabbits. Toxins, 17(6), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17060275






