Aflatoxin M1 Determination in Whole Milk with Immersible Silicon Photonic Immunosensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Matrix Effect
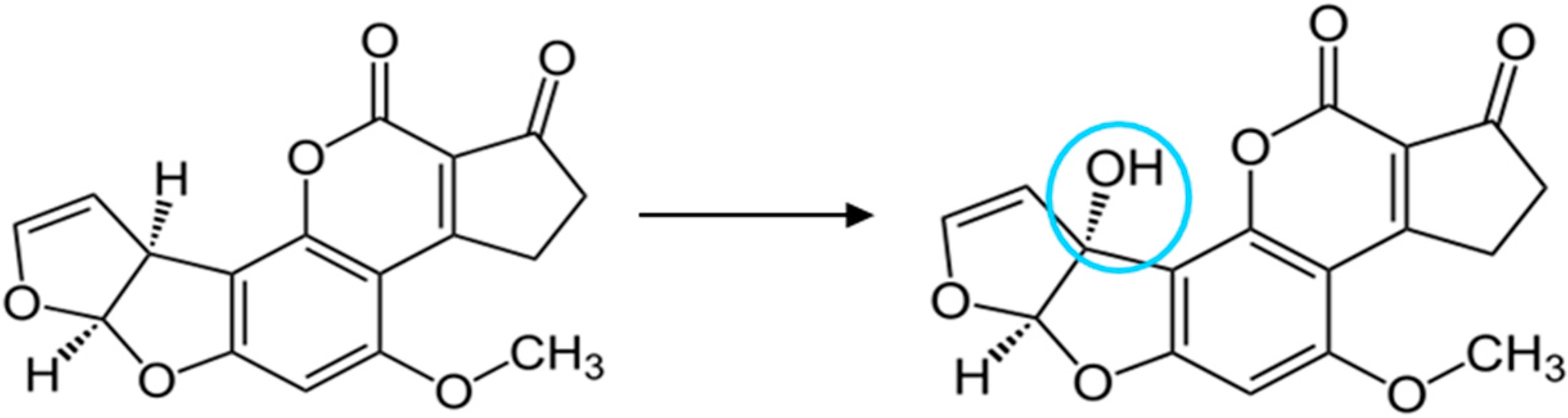
2.2. Chemical Activation of the Chip
2.3. Assay Parameter Optimization
2.4. Analytical Characteristics
2.5. Regeneration and Stability of the Sensor
2.6. Comparison with Label-Free Biosensors Reported in the Literature for AFM1 Detection in Dairy Products
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
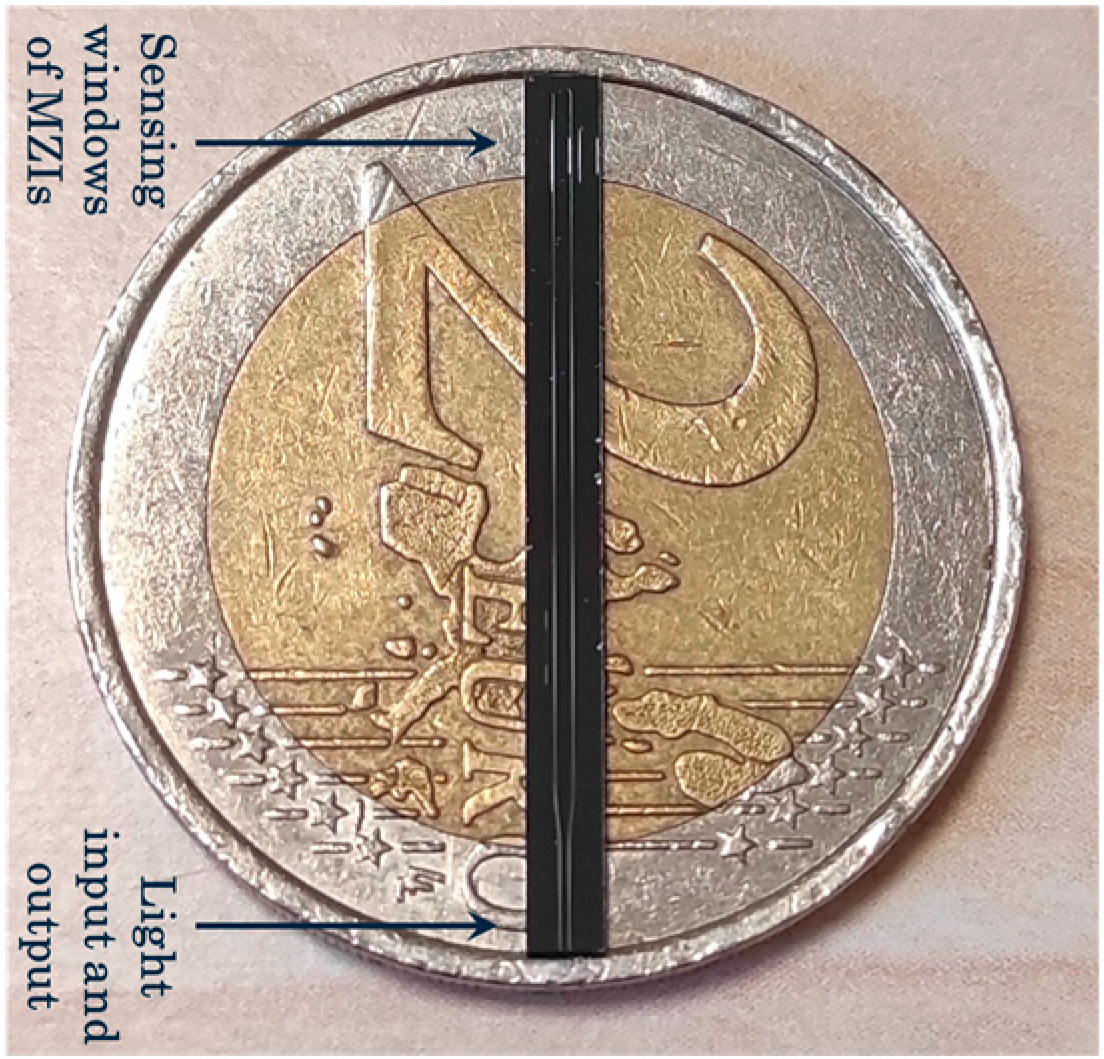
4.2. Instrumentation
4.3. Chemical Functionalization of the Sensor
4.3.1. Modification with APTES
4.3.2. Treatment with HF and Glutaraldehyde
4.4. Determination of the Amine Content of the Chemically Functionalized Surfaces
4.5. Biological Functionalization of the Sensor
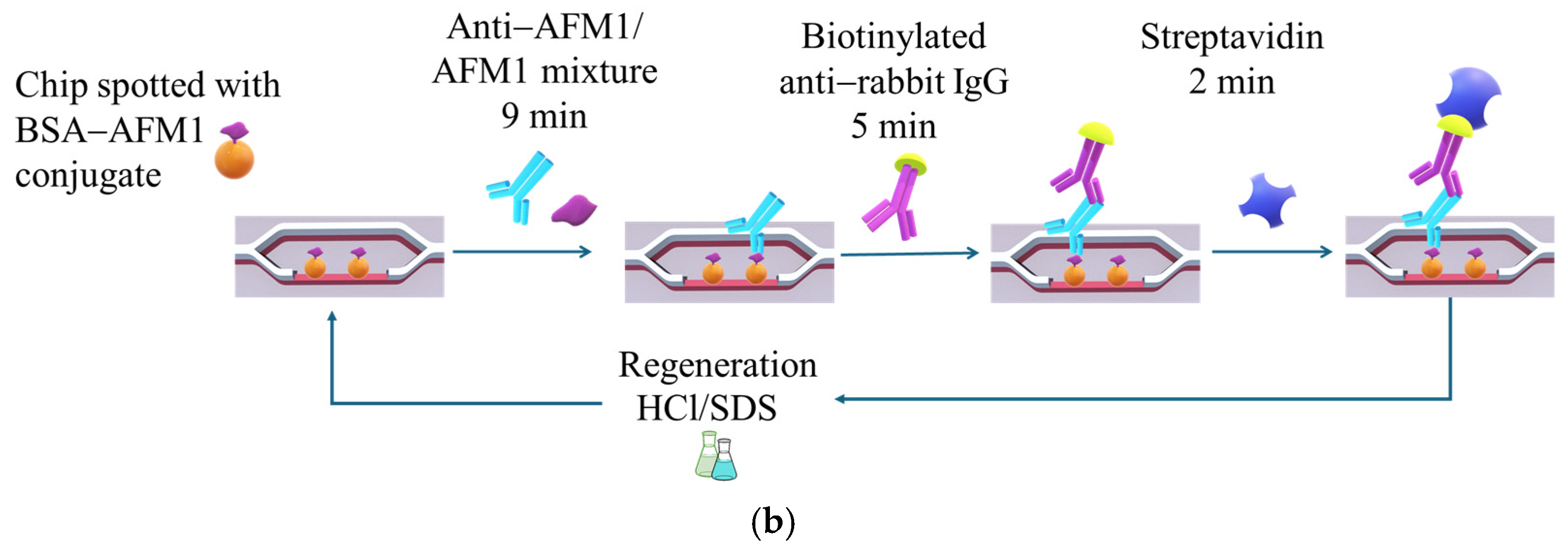
4.6. Assay for Detection of AFM1 with the Sensor
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boshra, M.H.; El-Housseiny, G.S.; Farag, M.M.S.; Aboshanab, K.M. Innovative Approaches for Mycotoxin Detection in Various Food Categories. AMB Express 2024, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovati, L.; Magliani, W.; Ciociola, T.; Santinoli, C.; Conti, S.; Polonelli, L. AFM1 in Milk: Physical, Biological, and Prophylactic Methods to Mitigate Contamination. Toxins 2015, 7, 4330–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, B.D.; Falco, A.; Ibba, P.; Cantarella, G.; Petti, L.; Lugli, P. Development of Flexible Dispense-Printed Electrochemical Immunosensor for Aflatoxin M1 Detection in Milk. Sensors 2019, 19, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Commission of the European Communities. European Commission (EC) Commission Regulation (EU) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contamination in Foodstuffs as Regards Aflatoxin. Off. J. EUL 2006, 59, 15–16. [Google Scholar]
- Rabie, M.; Movassaghghazani, M.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R. HPLC-FLD Determination of Aflatoxins M1 and M2 in Raw Cow Milk Samples Using in-Syringe Gas-Controlled Density Tunable Solidification of a Floating Organic Droplet-Based Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Method. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 5077–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Ramos, J.A.; Marín-Sáez, J.; Sanchis, V.; Gámiz-Gracia, L.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Hernández-Mesa, M.; Cano-Sancho, G. Simultaneous Detection of Mycotoxins and Pesticides in Human Urine Samples: A 24-h Diet Intervention Study Comparing Conventional and Organic Diets in Spain. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 188, 114650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Hay, M.E.S.I.; Shendy, A.H.; Aboalhassen, A.E.D.F.A.; Gomaa, A.M.; Ismail, E.H. Development and Validation of a Simple Solid-Liquid Extraction Protocol Coupled with LC-ESI-MS/MS for the Determination of Aflatoxin M1 in Products of Colostrum-Based Supplements and Whey Protein-Based Sports Food. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 126, 105933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarannum, N.; Nipa, M.N.; Das, S.; Parveen, S. Aflatoxin M1 Detection by ELISA in Raw and Processed Milk in Bangladesh. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Liu, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Development of a Toxin-Free Competitive Immunoassay for Aflatoxin M1 Based on a Nanobody as Surrogate Calibrator. LWT 2023, 182, 114829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjahan, T.; Javed, B.; Sharma, V.; Tian, F. Overview of Various Components of Lateral-Flow Immunochromatography Assay for the Monitoring of Aflatoxin and Limit of Detection in Food Products: A Systematic Review. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Meng, M.; Li, W.; Xiong, Y.; Fang, Y.; Lin, Q. Emerging Biosensors to Detect Aflatoxin M1 in Milk and Dairy Products. Food Chem. 2022, 398, 133848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evtugyn, G.; Hianik, T. Electrochemical Immuno- and Aptasensors for Mycotoxin Determination. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancelliere, R.; Paialunga, E.; Grattagliano, A.; Micheli, L. Label-free electrochemical immunosensors: A practical guide. Trend Anal. Chem. 2024, 180, 117949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.H.; Tran, L.D.; Do, Q.P.; Nguyen, H.L.; Tran, N.H.; Nguyen, P.X. Label-free detection of aflatoxin M1 with electrochemical Fe3O4/polyaniline-based aptasensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karapetis, S.; Nikolelis, D.; Hianik, T. Label-Free and Redox Markers-Based Electrochemical Aptasensors for Aflatoxin M1 Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolko, V.; Shurpik, D.; Porfireva, A.; Evtugyn, G.; Stoikov, I.; Hianik, T. Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Poly(Neutral Red) and Carboxylated Pillar[5]arene for Sensitive Determination of Aflatoxin M1. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Du, C.; Guo, T.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Ma, L. Ratiometric Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Split Aptamer and Au-RGO for Detection of Aflatoxin M1. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 2748–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Hui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; He, C.; Zhao, A.; Wei, L.; Wang, B. Novel Dual-Recognition Electrochemical Biosensor for the Sensitive Detection of AFM1 in Milk. Food Chem. 2024, 433, 137362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalian, S.H.; Ramezani, M.; Danesh, N.M.; Alibolandi, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. A novel electrochemical aptasensor for detection of aflatoxin M1 based on target-induced immobilization of gold nanoparticles on the surface of electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; Bhardwaj, N.; Deep, A. Selective and sensitive electrochemical sensor for aflatoxin M1 with a molybdenum disulfide quantum dot/metal–organic framework nanocomposite. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 17600–17608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacher, G.; Pal, S.; Kanungo, L.; Bhand, S. A Label-Free Silver Wire Based Impedimetric Immunosensor for Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2012, 168, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larou, E.; Yiakoumettis, I.; Kaltsas, G.; Petropoulos, A.; Skandamis, P.; Kintzios, S. High Throughput Cellular Biosensor for the Ultra-Sensitive, Ultra-Rapid Detection of Aflatoxin M1. Food Control 2013, 29, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Petrou, P.; Kakabakos, S. Advances in Interferometric Sensors for the Detection of Food Contaminants. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2024, 175, 117714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Guo, G.; Fu, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, T.; Li, T. A Fluorescent Aptasensor Based on Functional Graphene Oxide and FRET Strategy Simultaneously Detects Aflatoxins B1 and Aflatoxins M1. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2024, 52, 100408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Liang, D.; Tang, K.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Miao, M.; Zhao, Y. SERS and MRS Signals Engineered Dual-Mode Aptasensor for Simultaneous Distinguishment of Aflatoxin Subtypes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 462, 132810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaelpourfarkhani, M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. CRISPR-Cas12a-Based Colorimetric Aptasensor for Aflatoxin M1 Detection Based on Oxidase-Mimicking Activity of Flower-like MnO2 Nanozymes. Talanta 2024, 271, 125729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, W.; Nteppe Nteppe, E.L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, H. Fiber Optic LSPR Sensing AFM1 in Milk with Enhanced Sensitivity by the Hot Spot Effect Based on Nanogap Construction. Micromachines 2024, 15, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanim Al-Rubaye, A.; Nabok, A.; Catanante, G.; Marty, J.-L.; Takács, E.; Székács, A. Label-free optical detection of mycotoxins using specific aptamers immobilized on gold nanostructures. Toxins 2018, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y. Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering-Based Lateral Flow Immunosensor for Sensitive Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1128, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczmarczyk, A.; Dubiak-Szepietowska, M.; Vorobii, M.; Rodriguez-Emmenegger, C.; Dostálek, J.; Feller, K.H. Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Utilizing Enhanced SPR and p(HEMA) Brushes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indyk, H.E.; Chetikam, S.; Gill, B.D.; Wood, J.E.; Woollard, D.C. Development and application of an optical biosensor immunoassay for Aflatoxin M1 in bovine milk. Food Anal. Method 2019, 12, 2630–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsounidi, D.; Koukouvinos, G.; Petrou, P.; Misiakos, K.; Zisis, G.; Goustouridis, D.; Raptis, I.; Kakabakos, S.E. Rapid and Sensitive Label-Free Determination of Aflatoxin M1 Levels in Milk through a White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy Immunosensor. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2019, 282, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalyan, T.; Potrich, C.; Schreuder, E.; Falke, F.; Pasquardini, L.; Pederzolli, C.; Heideman, R.; Pavesi, L. AFM1 detection in milk by fab’ functionalized Si3N4 asymmetric mach-Zehnder interferometric biosensors. Toxins 2019, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Kourti, D.; Misiakos, K.; Economou, A.; Petrou, P.; Kakabakos, S. Mach-Zehnder Interferometric Immunosensor for Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk, Chocolate Milk, and Yogurt. Biosensors 2023, 13, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A.; García, M.; Castro Grijalba, A. Development of Gold Nanoparticles Decorated Molecularly Imprinted–Based Plasmonic Sensor for the Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Samples. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, M.; Tsounidi, D.; Petrou, P.S.; Beltsios, K.G.; Kakabakos, S.E. Functionalization of silicon dioxide and silicon nitride surfaces with aminosilanes for optical biosensing applications. Med. Devices Sens. 2020, 3, e10072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañuls, M.-J.; González-Pedro, V.; Barrios, C.A.; Puchades, R.; Maquieira, A. Selective chemical modification of silicon nitride/silicon oxide nanostructures to develop label-free biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakabakos, S.E.; Tyllianakis, P.E.; Evangelatos, G.P.; Ithakissios, D.S. Colorimetric determination of reactive solid-supported primary and secondary amino groups. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarría, G.; Molina, A.; Leiva, A.; Méndez, G.; Wong-González, E.; Cortés-Muñoz, M.; Rodríguez, C.; Granados-Chinchilla, F. Distribution, stability, and protein interactions of Aflatoxin M1 in fresh cheese. Food Control 2017, 73, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancelliere, R.; Di Tinno, A.; Cataldo, A.; Bellucci, S.; Kumbhat, S.; Micheli, L. Nafion-based label-free immunosensor as a reliable warning system: The case of AFB1 detection in cattle feed. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourti, D.; Angelopoulou, M.; Makarona, E.; Economou, A.; Petrou, P.; Misiakos, K.; Kakabakos, S. Photonic Dipstick Immunosensor to Detect Adulteration of Ewe, Goat, and Donkey Milk with Cow Milk through Bovine κ-Casein Detection. Sensors 2024, 24, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



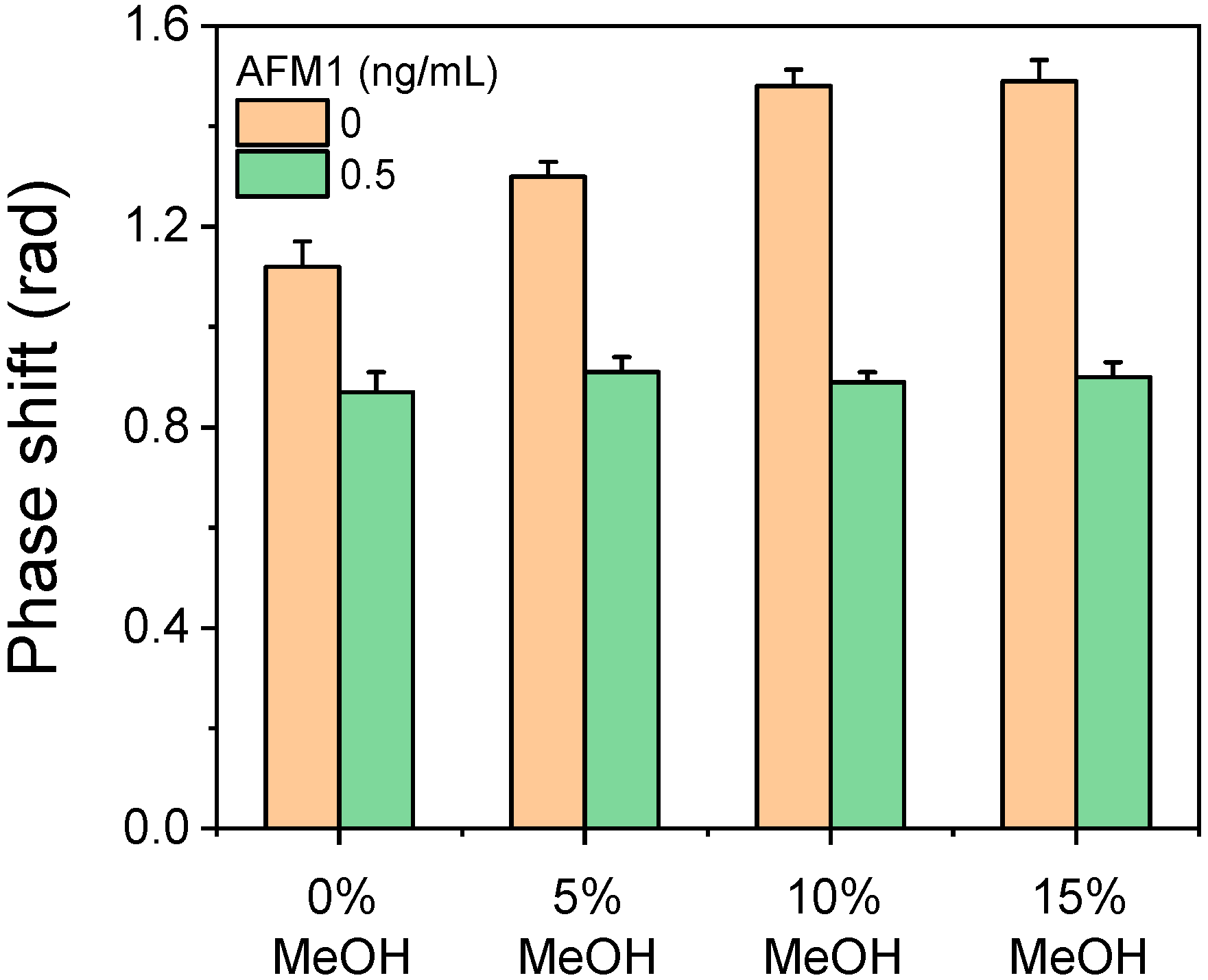



| Sample | Amount Added (ng/mL) | Amount Determined * (ng/mL) | %Recovery ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cow milk | 0.15 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 107 ± 6.7 |
| 0.40 | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 90.0 ± 5.0 | |
| 1.5 | 1.4 ± 0.05 | 93.3 ± 3.3 | |
| Sheep milk | 0.15 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 93.3 ± 6.7 |
| 0.40 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 105 ± 2.5 | |
| 1.5 | 1.6 ± 0.07 | 107 ± 4.7 | |
| Goat milk | 0.15 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 86.7 ± 6.7 |
| 0.40 | 0.45 ± 0.03 | 112 ± 7.5 | |
| 1.5 | 1.4 ± 0.10 | 93.3 ± 6.7 |
| Detection Principle | Biorecognition Element/Assay Type | Sample | LOD (pg/mL) | Assay Duration (min) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical sensors | |||||
| Fe3O4/polyaniline film on IDE | Aptamer/direct binding | Buffer | 1.98 | 60 | [14] |
| Dendrimer layer on a gold platform | Aptamer/direct binding | Milk (pretreatment required) | 8.47 | 60 | [15] |
| Neutravidin layer on a gold platform | Biotinylated aptamer/direct binding | 8.52 | |||
| Poly(neutral red) and carboxylated pillar[5]arene on GCE | Aptamer/direct binding | Cow/Sheep milk Kefir (pretreatment required) | 40 | 60 | [16] |
| MoS2/UiO-66-modified screen-printed carbon electrodes | Antibody/direct binding | Milk (pretreatment required) | 60 | 10 | [20] |
| Silver wire electrode | Antibody/direct binding | Milk (pretreatment required) | 1 | 20 | [21] |
| Optical sensors | |||||
| LSPR | Aptamer/direct binding | Milk (pretreatment required) | 40 | 60 | [27] |
| LSPR based on TIRE | Aptamer/competitive with Au nanoparticles labeled secondary antibody | Buffer | 10 | 15 | [30] |
| Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) | BSA–AFM1 conjugate/competitive immunoassay | Milk/ Milk powder (pretreatment required) | 100 | 10 | [31] |
| White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy | BSA–AFM1 conjugate/competitive with biotinylated secondary antibody and streptavidin | Milk | 6 | 25 | [32] |
| Fab’ functionalized asymmetric MZIs | Antibody/direct binding | Milk (pretreatment required) | 16.8 | 1.5 | [33] |
| Broad-band MZIs | BSA–AFM1 conjugate/competitive with biotinylated secondary antibody and streptavidin | Milk Chocolate milk (pretreatment required) Yogurt (pretreatment required) | 5 5 10 | 15 | [34] |
| Immersible photonic chip | BSA–AFM1 conjugate/competitive with biotinylated secondary antibody and streptavidin | Milk | 20 | 20 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kourti, D.; Angelopoulou, M.; Makarona, E.; Economou, A.; Petrou, P.; Misiakos, K.; Kakabakos, S. Aflatoxin M1 Determination in Whole Milk with Immersible Silicon Photonic Immunosensor. Toxins 2025, 17, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040165
Kourti D, Angelopoulou M, Makarona E, Economou A, Petrou P, Misiakos K, Kakabakos S. Aflatoxin M1 Determination in Whole Milk with Immersible Silicon Photonic Immunosensor. Toxins. 2025; 17(4):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040165
Chicago/Turabian StyleKourti, Dimitra, Michailia Angelopoulou, Eleni Makarona, Anastasios Economou, Panagiota Petrou, Konstantinos Misiakos, and Sotirios Kakabakos. 2025. "Aflatoxin M1 Determination in Whole Milk with Immersible Silicon Photonic Immunosensor" Toxins 17, no. 4: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040165
APA StyleKourti, D., Angelopoulou, M., Makarona, E., Economou, A., Petrou, P., Misiakos, K., & Kakabakos, S. (2025). Aflatoxin M1 Determination in Whole Milk with Immersible Silicon Photonic Immunosensor. Toxins, 17(4), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040165










