Ion-Channel-Targeting Scorpion Recombinant Toxin as Novel Therapeutic Agent for Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Purification and Molecular Characterization of Fraction 43 from Chihuahuanus coahuilae Scorpion Venom
2.2. N-Terminal Sequencing and 3′ RACE
2.3. Construction of Vectors and Gene Cloning
2.4. Expression System
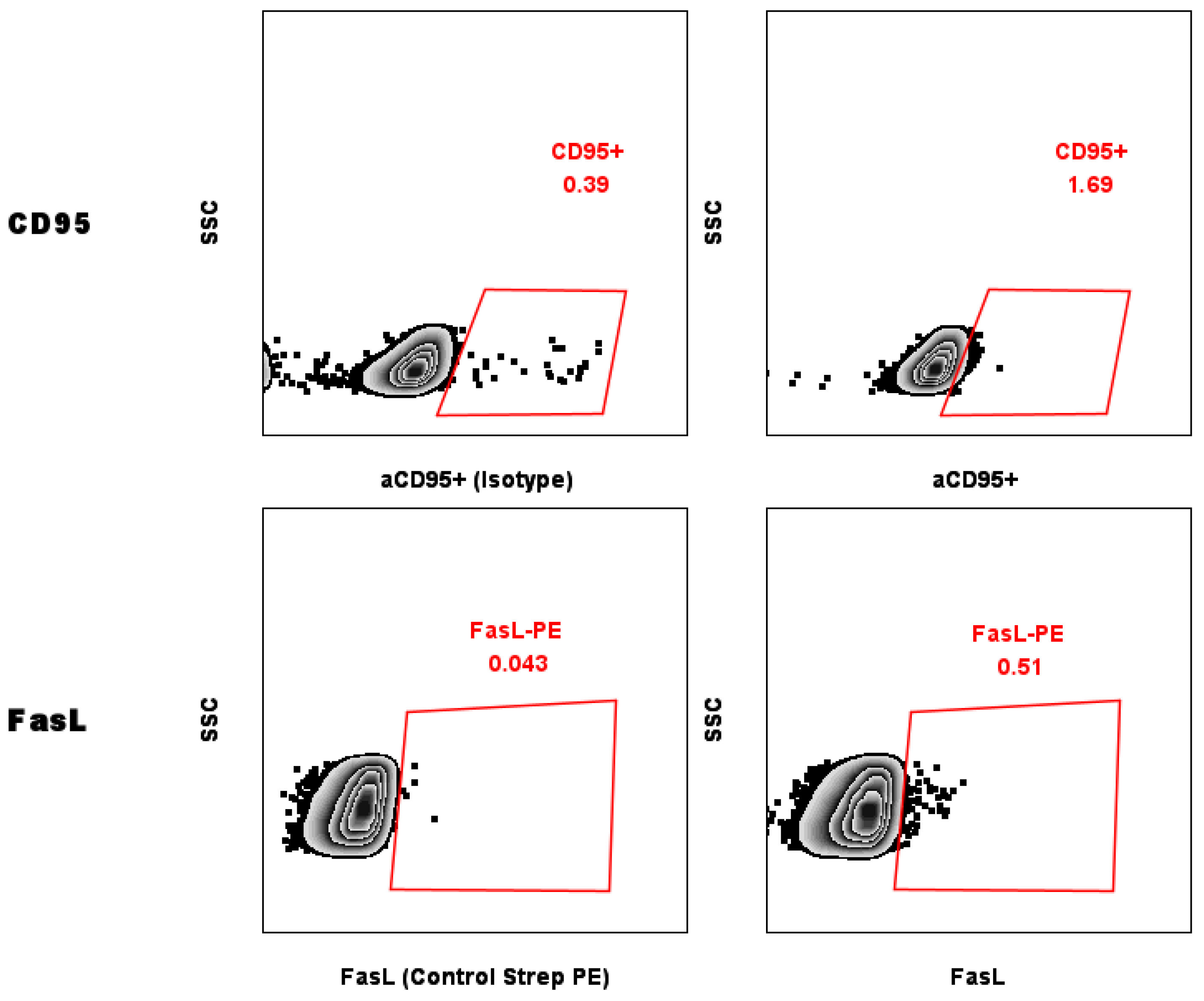
2.5. Evaluation of Levels of CD95 on the Surface of MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells
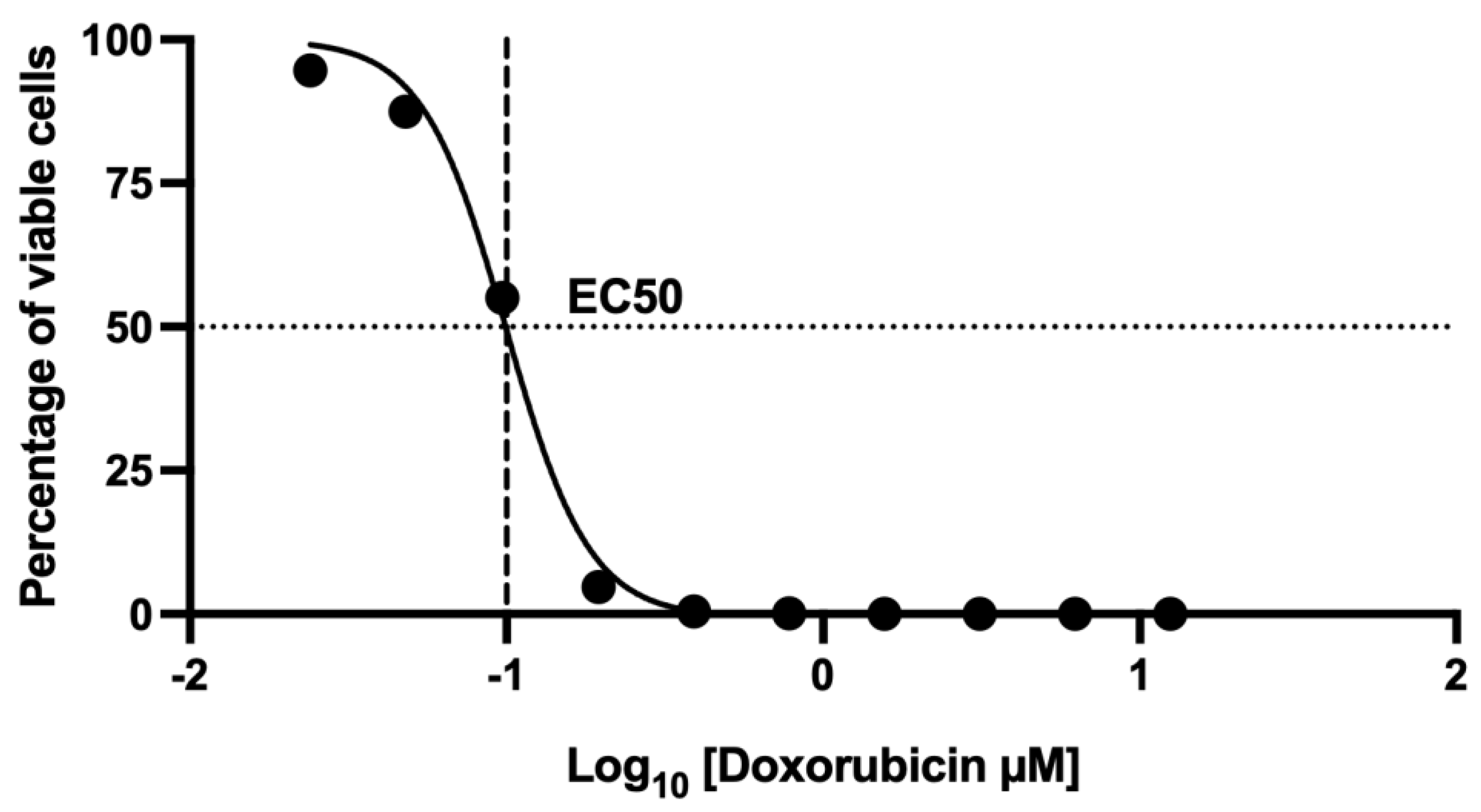
2.6. Assessment of Cell Death Using 7-AAD by Flow Cytometry: Dose–Response Curve of the Effect at 48 h Doxorubicin Exposure
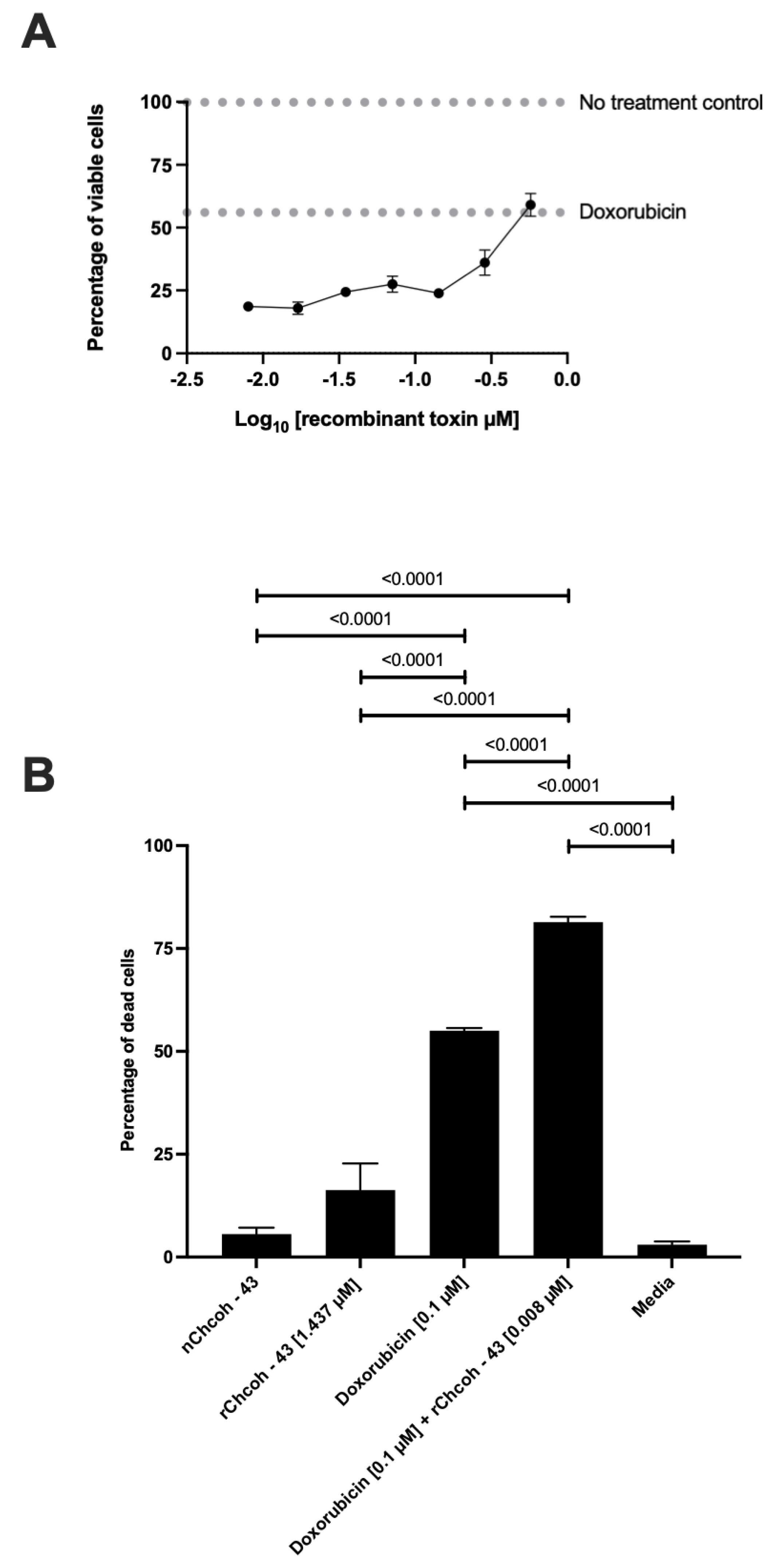
2.7. Dose–Response Curve of the Effect at 48 h Doxorubicin and Recombinant rChcoh43 Exposure in the MCF-7 Cell Line
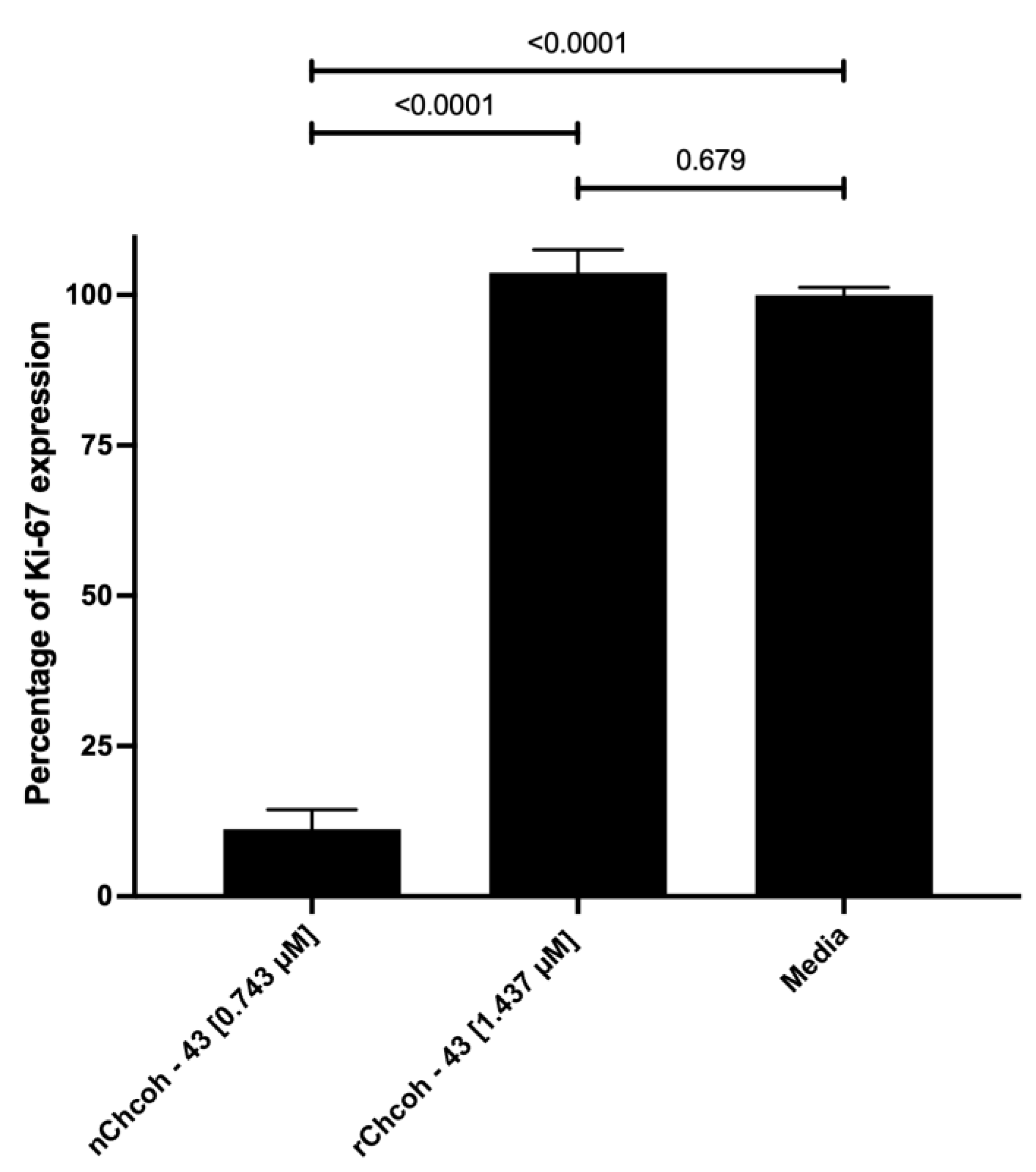
2.8. Evaluation of Ki-67 Expression by Flow Cytometry in the MCF-7 Cell Line After 48 h of Incubation with Native (n) and Recombinant (r) Chcoh43 Toxin and Doxorubicin
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
5.2. RNA Extraction from Chihuahuanus Species
5.3. cDNA Library Construction and Gene Cloning
5.4. Expression and Purification of the Recombinant Protein
5.5. Cell Culture
5.6. Detection of Fas/CD95 and FasL/CD178 Expression in MCF-7 Cells
5.7. Cytotoxicity and Proliferation Assays
6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OMS Cáncer. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Barzaman, K.; Karami, J.; Zarei, Z.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Kazemi, M.H.; Moradi-Kalbolandi, S.; Safari, E.; Farahmand, L. Breast Cancer: Biology, Biomarkers, and Treatments. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, E.J. Overview of Breast Cancer. JAAPA 2019, 32, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, L.; Gathani, T. Understanding Breast Cancer as a Global Health Concern. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20211033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-García, A.; Varela, D. Voltage-Gated K+/Na+ Channels and Scorpion Venom Toxins in Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, E.; Gurrola, G.B.; Schwartz, E.F.; Possani, L.D. Scorpion Venom Components as Potential Candidates for Drug Development. Toxicon 2015, 93, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran, M.; Pashmforoosh, N. Peptides with Diverse Functions from Scorpion Venom: A Great Opportunity for the Treatment of a Wide Variety of Diseases. Iran. Biomed. J. 2023, 27, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageitos, L.; Torres, M.D.T.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Biologically Active Peptides from Venoms: Applications in Antibiotic Resistance, Cancer, and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Gonzalez, C.; Clement, H.; Ballinas-Casarrubias, L.; Escarcega-Avila, A.; Arenas-Sosa, I.; Lopez-Contreras, K.S.; Zamudio, F.; Corzo, G.; Espino-Solis, G.P. Identification and Venom Characterization of Two Scorpions from the State of Chihuahua Mexico: Chihuahuanus Coahuliae and Chihuahuanus Crassimannus. Toxins 2023, 15, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Knerr, J.M.; Argemi, L.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Arantes, E.C.; Çalışkan, F.; Laustsen, A.H. Scorpion Venom: Detriments and Benefits. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Asgari, S.; Komijani, S.; Sadat, S.N.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Nasrabadi, D.; Pooshang Bagheri, K.; Shahbazzadeh, D.; Akbari Eidgahi, M.R.; De Waard, M.; et al. Discovery of Leptulipin, a New Anticancer Protein from TheIranian Scorpion, Hemiscorpius Lepturus. Molecules 2022, 27, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crusca, E.; Basso, L.G.M.; Altei, W.F.; Marchetto, R. Biophysical Characterization and Antitumor Activity of Synthetic Pantinin Peptides from Scorpion’s Venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes 2018, 1860, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezianian, S.; Zargan, J.; Goudarzi, H.R.; Haji Noormohamadi, A.; Mousavi, M.; Keshavarz Alikhani, H.; Johari, B. In-Vitro Study of Hottentotta Schach Crude Venom Anticancer Effects on MCF-7 and Vero Cell Lines. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargan, J.; Umar, S.; Sajad, M.; Naime, M.; Ali, S.; Khan, H.A. Scorpion Venom (Odontobuthus Doriae) Induces Apoptosis by Depolarization of Mitochondria and Reduces S-Phase Population in Human Breast Cancer Cells (MCF-7). Toxicol. In Vitro 2011, 25, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, J.; Mao, W. Inhibition Effects of Scorpion Venom Extracts (<I>Buthus Matensii</I> Karsch) on the Growth of Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-García, A.; Ruiz-Fuentes, J.L.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, H.; Fraga Castro, J.A. Rhopalurus Junceus Scorpion Venom Induces Apoptosis in the Triple Negative Human Breast Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB-231. J. Venom. Res. 2017, 8, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Possani, L.D.; Becerril, B.; Delepierre, M.; Tytgat, J. Scorpion Toxins Specific for Na + -channels. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Hausdorff, S.F.; Miller, C. Design, Synthesis, and Functional Expression of a Gene for Charybdotoxin, a Peptide Blocker of K+ Channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2046–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez de la Vega, R.C.; Possani, L.D. Overview of Scorpion Toxins Specific for Na+ Channels and Related Peptides: Biodiversity, Structure–Function Relationships and Evolution. Toxicon 2005, 46, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.; Karbat, I.; Ilan, N.; Cohen, L.; Kahn, R.; Gilles, N.; Dong, K.; Stühmer, W.; Tytgat, J.; Gurevitz, M. The Differential Preference of Scorpion α-Toxins for Insect or Mammalian Sodium Channels: Implications for Improved Insect Control. Toxicon 2007, 49, 452–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Hernández, V.; Jiménez-Vargas, J.M.; Gurrola, G.B.; Valdivia, H.H.; Possani, L.D. Scorpion Venom Components That Affect Ion-Channels Function. Toxicon 2013, 76, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driffort, V.; Gillet, L.; Bon, E.; Marionneau-Lambot, S.; Oullier, T.; Joulin, V.; Collin, C.; Pagès, J.-C.; Jourdan, M.-L.; Chevalier, S.; et al. Ranolazine Inhibits NaV1.5-Mediated Breast Cancer Cell Invasiveness and Lung Colonization. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroui, S.; Ram, N.; Appaix, F.; Ronjat, M.; Kenani, A.; Pirollet, F.; De Waard, M. Maurocalcine as a Non Toxic Drug Carrier Overcomes Doxorubicin Resistance in the Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB 231. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Kozminski, D.J.; Wold, L.A.; Modak, R.; Calhoun, J.D.; Isom, L.L.; Brackenbury, W.J. Therapeutic Potential for Phenytoin: Targeting Nav1.5 Sodium Channels to Reduce Migration and Invasion in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 134, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, S.P.; Diss, J.K.J.; Chioni, A.-M.; Mycielska, M.E.; Pan, H.; Yamaci, R.F.; Pani, F.; Siwy, Z.; Krasowska, M.; Grzywna, Z.; et al. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Expression and Potentiation of Human Breast Cancer Metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5381–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komi; Lassila. Toremifene Increases the Expression of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1) on MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells and Jurkat Cells. Scand. J. Immunol. 2000, 51, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, S.; Gillet, L.; Le Guennec, J.-Y.; Besson, P. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels and Cancer: Is Excitability Their Primary Role? Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, H.; Corzo, G.; Neri-Castro, E.; Arenas, I.; Hajos, S.; de Roodt, A.R.; Villegas, E. CDNA Cloning, Heterologous Expression, Protein Folding and Immunogenic Properties of a Phospholipase A2 from Bothrops Ammodytoides Venom. Protein Expr. Purif. 2019, 154, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herberich, E.; Sikorski, J.; Hothorn, T. A Robust Procedure for Comparing Multiple Means under Heteroscedasticity in Unbalanced Designs. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Toxin | Amino Acid Sequence | No. Amino Acids | MW Theoretic | MW Experiment | No. Cys |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rChcoh43 | MRGSHHHHHHGSIEGRKKDGYPVNKYGEVSNCVMGMLIGDNTFCKSICRSRGGSGYCYFFACWCEGINDDVKIWKKG**LQ | 77 | 8697.90 | 8690.31 | 6 |
| Database ID | Name | Sequence | (MW) Da |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCD31427.1 | Scorpion Toxin To10 precursor | MNYSTLIAVASLLTAGTESKKDGYPVEGSCAFPCGYDNAYCDKLCKERKADSGYCYWVNILCYCYGLPDNAAIKGYGRCKPGKK | 9186.54 |
| C9X4K6 | Toxin TdNa8 | MNYLTLIAAASLLTAGTESKKDGYPVKEGDCAFPCGYDNAYCDKLCKERKADSGYCYWGNILCYCYGLPDKAAIKGYGRCRPGKK | 9341 |
| CCD31433.1 | scorpion toxin Tpa4 precursor | MNYFVLIAVACLLTAGTESKKDGYPLEYDNCAYDCLGYDNKKCDKLCKDKKADSGYCYWAHILCYCYGLPDNEPIKTSGRCRPGKK | 9725.2 |
| P84810.1 | Lipolysis-activating peptide 1-alpha chain | MMKLVLFGIIVILFSLIGSIHGISGNYPLNPYGGYYYCTILGENEYCKKICRIHGVRYGYCYDSACWCETLKDEDVSVWNAVKKHCKNPYL | 10,457 |
| 2LJM_A | Beta-mammal toxin Css2 | KEGYLVSKSTGCKYECLKLGDNDYCLRECKQQYGKSSGGYCYAFACWCTHLYEQAVVWPLPNKTCN | 7537.6 |
| Name | Sequence 5-3′ |
|---|---|
| Forward | GAGGATCCATCGAGGGACGCAAAAAGGATGGCTATCCTGTGAAT |
| Reverse | CTACAGTTCTATACCTTTTTCCCGATTATCGACGTCCTCT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mata de los Rios, N.; Gastelum-Arellanez, A.; Clement, H.; Álvarez-Cruz, K.; Romero-Terrazas, D.; Alvarado-González, C.; Hinojos-Gallardo, L.C.; Corzo, G.; Espino-Solis, G.P. Ion-Channel-Targeting Scorpion Recombinant Toxin as Novel Therapeutic Agent for Breast Cancer. Toxins 2025, 17, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040166
Mata de los Rios N, Gastelum-Arellanez A, Clement H, Álvarez-Cruz K, Romero-Terrazas D, Alvarado-González C, Hinojos-Gallardo LC, Corzo G, Espino-Solis GP. Ion-Channel-Targeting Scorpion Recombinant Toxin as Novel Therapeutic Agent for Breast Cancer. Toxins. 2025; 17(4):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040166
Chicago/Turabian StyleMata de los Rios, Natalia, Argel Gastelum-Arellanez, Herlinda Clement, Karely Álvarez-Cruz, Diana Romero-Terrazas, Carolina Alvarado-González, Luis Carlos Hinojos-Gallardo, Gerardo Corzo, and Gerardo Pável Espino-Solis. 2025. "Ion-Channel-Targeting Scorpion Recombinant Toxin as Novel Therapeutic Agent for Breast Cancer" Toxins 17, no. 4: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040166
APA StyleMata de los Rios, N., Gastelum-Arellanez, A., Clement, H., Álvarez-Cruz, K., Romero-Terrazas, D., Alvarado-González, C., Hinojos-Gallardo, L. C., Corzo, G., & Espino-Solis, G. P. (2025). Ion-Channel-Targeting Scorpion Recombinant Toxin as Novel Therapeutic Agent for Breast Cancer. Toxins, 17(4), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040166






