Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Symmetry and Emotions in Facial Palsy Patients After Botulinum Toxin A Injections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Cohort
2.2. Amount and Site of BoNT-A Injection
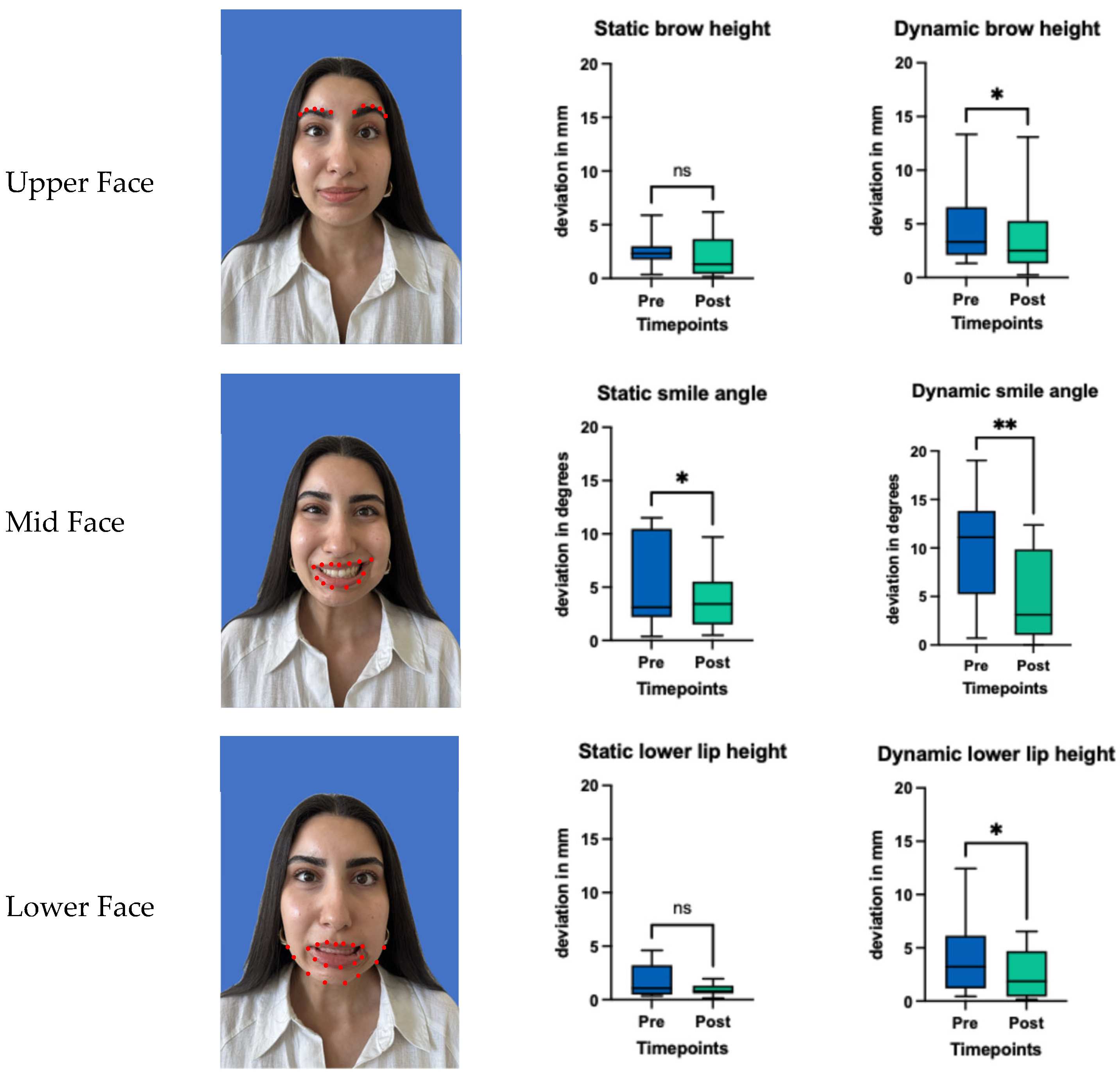
2.3. Facial Symmetry, Emotrics®
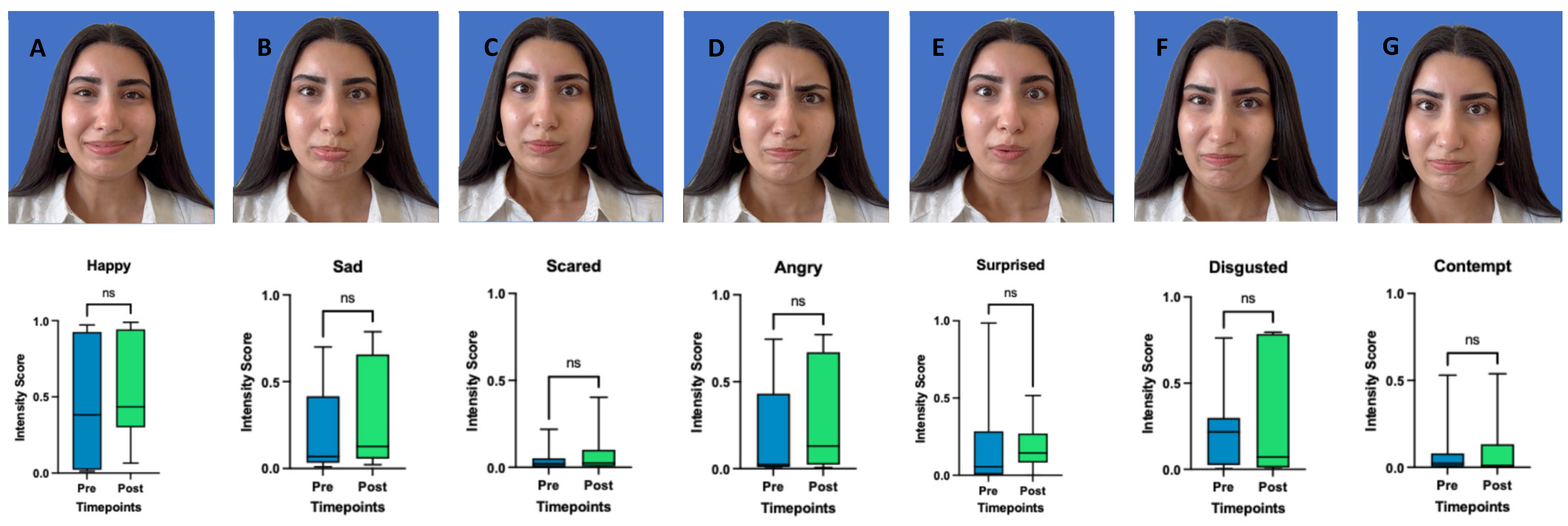
2.4. Emotion Recognition, FaceReader™
2.5. PROMs
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| BoNT-A | Botulinum toxin Type A |
| eFACE | Electronic Facial Clinimetric Evaluation |
| FACE-Q | Facial Aesthetic and Cosmetic Questionnaire |
| FDI | Facial Disability Index |
| GCP | Good Clinical Practice |
| HBGS | House–Brackmann Grading Scale |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| IU | Injection Units |
| PROMs | Patient-Reported Outcome Measures |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
References
- Hohman, M.H.; Hadlock, T.A. Etiology, diagnosis, and management of facial palsy: 2000 patients at a facial nerve center. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, E283–E293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncaliano, M.C.; Ding, P.; Goshe, J.M.; Genther, D.J.; Ciolek, P.J.; Byrne, P.J. Clinical features, evaluation, and management of ophthalmic complications of facial paralysis: A review. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2023, 87, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamil, E.; Noriega, M.; Moin, S.; Ko, T.K.; Tan, D.J.Y.; Meller, C.; Andrews, P.; Lekakis, G. Psychological Aspects of Facial Palsy. Facial Plast. Surg. 2024, 40, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotton, M.; Huggons, E.; Hamlet, C.; Shore, D.; Johnson, D.; Norris, J.H.; Kilcoyne, S.; Dalton, L. The psychosocial impact of facial palsy: A systematic review. Br. J. Health Psychol. 2020, 25, 695–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellis, J.C.; Ishii, M.; Byrne, P.J.; Boahene, K.D.O.; Dey, J.K.; Ishii, L.E. Association Among Facial Paralysis, Depression, and Quality of Life in Facial Plastic Surgery Patients. JAMA Facial Plast. Surg. 2017, 19, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Prengel, J.; Cohen, O.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Vander Poorten, V.; Ronen, O.; Shaha, A.; Ferlito, A. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy of facial synkinesis: A systematic review and clinical practice recommendations by the international head and neck scientific group. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1019554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.Q.; Hadlock, T.A. Beyond Botox: Contemporary Management of Nonflaccid Facial Palsy. Facial Plast. Surg. Aesthet. Med. 2020, 22, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipo, R.; Spahiu, I.; Covelli, E.; Nicastri, M.; Bertoli, G.A. Botulinum toxin in the treatment of facial synkinesis and hyperkinesis. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sanctis Pecora, C.; Shitara, D. Botulinum Toxin Type A to Improve Facial Symmetry in Facial Palsy: A Practical Guideline and Clinical Experience. Toxins 2021, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.B.; Gliklich, R.E.; Boyev, K.P.; Stewart, M.G.; Metson, R.B.; McKenna, M.J. Validation of a patient-graded instrument for facial nerve paralysis: The FaCE scale. Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanSwearingen, J.M.; Brach, J.S. The Facial Disability Index: Reliability and validity of a disability assessment instrument for disorders of the facial neuromuscular system. Phys. Ther. 1996, 76, 1288–1298; discussion 98–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmire, N.M.; Wong Riff, K.W.Y.; O’Hara, J.L.; Aggarwala, S.; Allen, G.C.; Bulstrode, N.W.; Forrest, C.R.; French, B.M.; Goodacre, T.E.; Marucci, D.; et al. Development of a New Module of the FACE-Q for Children and Young Adults with Diverse Conditions Associated with Visible and/or Functional Facial Differences. Facial Plast. Surg. 2017, 33, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, J.W.; Brackmann, D.E. Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 1985, 93, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, B.G.; Fradet, G.; Nedzelski, J.M. Development of a sensitive clinical facial grading system. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 1996, 114, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, S.E.; Croxson, G.R.; Adams, R.D.; O’Dwyer, N.J. Reliability of the “Sydney,” “Sunnybrook,” and “House Brackmann” facial grading systems to assess voluntary movement and synkinesis after facial nerve paralysis. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2005, 132, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, C.A.; Bhama, P.K.; Park, J.; Hadlock, C.R.; Hadlock, T.A. Clinician-Graded Electronic Facial Paralysis Assessment: The eFACE. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 136, 223e–230e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boochoon, K.; Mottaghi, A.; Aziz, A.; Pepper, J.P. Deep Learning for the Assessment of Facial Nerve Palsy: Opportunities and Challenges. Facial Plast. Surg. 2023, 39, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadlock, T.A.; Urban, L.S. Toward a universal, automated facial measurement tool in facial reanimation. Arch. Facial Plast. Surg. 2012, 14, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarin, D.L.; Dusseldorp, J.; Hadlock, T.A.; Jowett, N. A Machine Learning Approach for Automated Facial Measurements in Facial Palsy. JAMA Facial Plast. Surg. 2018, 20, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyl MJd. The FaceReader™: Online facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of Measuring Behavior; Kuilenburg, H.V., Ed.; Wageningen: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 589–590. [Google Scholar]
- Dorante, M.I.; Kollar, B.; Obed, D.; Haug, V.; Fischer, S.; Pomahac, B. Recognizing Emotional Expression as an Outcome Measure After Face Transplant. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1919247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollar, B.; Schneider, L.; Horner, V.K.; Zeller, J.; Fricke, M.; Brugger, Z.; Gentz, M.; Kiefer, J.; Eisenhardt, S.U. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Video Analysis for Novel Outcome Measures After Smile Reanimation Surgery. Facial Plast. Surg. Aesthet. Med. 2022, 24, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonipat, T.; Asaad, M.; Lin, J.; Glass, G.E.; Mardini, S.; Stotland, M. Using Artificial Intelligence to Measure Facial Expression following Facial Reanimation Surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 146, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witmanowski, H.; Błochowiak, K. The whole truth about botulinum toxin—A review. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2020, 37, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, L.; Lui, M.; Nduka, C. Botulinum toxin treatment for facial palsy: A systematic review. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2017, 70, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jongh, F.W.; Schaeffers, A.W.M.A.; Kooreman, Z.E.; Ingels, K.J.A.O.; van Heerbeek, N.; Beurskens, C.; Monstrey, S.J.; Pouwels, S. Botulinum toxin A treatment in facial palsy synkinesis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 280, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento Remigio, A.F.; Salles, A.G.; de Faria, J.C.M.; Ferreira, M.C. Comparison of the efficacy of onabotulinumtoxinA and abobotulinumtoxinA at the 1:3 conversion ratio for the treatment of asymmetry after long-term facial paralysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monini, S.; De Carlo, A.; Biagini, M.; Buffoni, A.; Volpini, L.; Lazzarino, A.I.; Barbara, M. Combined protocol for treatment of secondary effects from facial nerve palsy. Acta Otolaryngol. 2011, 131, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodic, G.; Bartley, M.; Slattery, W.; Glasscock, M.; Johnson, E.; Malazio, C.; Goodnough, M.; Acquadro, M.; McKenna, M. Botulinum toxin for aberrant facial nerve regeneration: Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial using subjective endpoints. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 116, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, A.; Zito, F.; Menapace, G.; Zannoni, C.; Bergonzani, M.; Perlangeli, G.; Bianchi, B. Optimizing the results of facial animation surgery: Botulinum toxin injection into free functional gracilis flap transfer. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2023, 83, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Glowka, T.R.; Angelov, D.N.; Irintchev, A.; Neiss, W.F. Improved functional recovery after facial nerve reconstruction by temporary denervation of the contralateral mimic musculature with botulinum toxin in rats. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2011, 25, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, N.; Singh, S.; DeBoulle, K.; Rahman, E. A Review of Complications Due to the Use of Botulinum Toxin A for Cosmetic Indications. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2021, 45, 1210–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarin, D.L.; Yunusova, Y.; Taati, B.; Dusseldorp, J.R.; Mohan, S.; Tavares, J.; van Veen, M.M.; Fortier, E.; Hadlock, T.A.; Jowett, N. Toward an Automatic System for Computer-Aided Assessment in Facial Palsy. Facial Plast. Surg. Aesthet. Med. 2020, 22, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Kollar, B.; Weber, J.; Eisenhardt, S.U.; Weiss, J.B.W. Assessment of Facial Synkinesis Treatment with Botulinum Toxin Using Automated Analysis of Facial Expression: A Pilot Study. Facial Plast. Surg. Aesthet. Med. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.L.C.; Pfister, P.; Menzi, N.; Muller, L.; Klein, H.J.; Schweizer, R.; Lee, Z.-H.; Kollar, B.; Eisenhardt, S.U.; Schaefer, D.J.; et al. Artificial Intelligence in Facial Palsy Treatment: A Systematic Review and Recommendations. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2025, 156, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacolucci, C.M.; Banks, C.; Jowett, N.; Kozin, E.D.; Bhama, P.K.; Barbara, M.; Hadlock, T.A. Development and validation of a spontaneous smile assay. JAMA Facial Plast. Surg. 2015, 17, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishay, M.; Preston, K.; Strafuss, M.; Page, G.; Turcot, J.; Mavadati, M. (Eds.) AFFDEX 2.0: A Real-Time Facial Expression Analysis Toolkit. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 17th International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Waikoloa Beach, HI, USA, 5 January 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Santosa, K.B.; Fattah, A.; Gavilán, J.; Hadlock, T.A.; Snyder-Warwick, A.K. Photographic Standards for Patients With Facial Palsy and Recommendations by Members of the Sir Charles Bell Society. JAMA Facial Plast. Surg. 2017, 19, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Mean age, years (SD, range) | 50.1 (18, 24.5–84.9) |
| Male/Female sex | 1/10 |
| Median BMI, kg/m2 (IQR, range) | 23.1 (22.3–26.95, 18–38.6) |
| Smoking | 2 |
| Facial palsy etiology | 5 Idiopathic 3 Herpes zoster 1 Iatrogenic, 1 Postpartum 1 Tumor |
| Region | Condition | Timepoint | Photo | Median | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Face | Brow height difference (mm) | Before | Rest | 2.31 mm | 1.057 to 1.90 | 0.365 |
| After | Rest | 1.33 mm | ||||
| Before | Brows elevated | 3.32 mm | 0.07 to 2.44 | 0.032 | ||
| After | Brows elevated | 2.51 mm | ||||
| Mid Face | Smile angle deviation (degree) | Before | Rest | 3.11 mm | 0.12 to 3.34 | 0.024 |
| After | Rest | 3.42 mm | ||||
| Before | Smiling showing teeth | 11.11 mm | 1.06 to 8.69 | 0.005 | ||
| After | Smiling showing teeth | 3.12 mm | ||||
| Lower Face | Lower lip height difference (mm) | Before | Rest | 1.07 mm | −0.459 to 1.80 | 0.240 |
| After | Rest | 0.78 mm | ||||
| Before | Showing lower teeth | 3.76 mm | 0.06 to 3.32 | 0.042 | ||
| After | Showing lower teeth | 2.38 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Müller, S.L.C.; Zeier, C.; Pfister, P.; Menzi, N.; Tafrishi, B.; Schaefer, D.J.; Plock, J.A.; Ismail, T.; Klein, H.J. Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Symmetry and Emotions in Facial Palsy Patients After Botulinum Toxin A Injections. Toxins 2025, 17, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120597
Müller SLC, Zeier C, Pfister P, Menzi N, Tafrishi B, Schaefer DJ, Plock JA, Ismail T, Klein HJ. Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Symmetry and Emotions in Facial Palsy Patients After Botulinum Toxin A Injections. Toxins. 2025; 17(12):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120597
Chicago/Turabian StyleMüller, Seraina L. C., Chantal Zeier, Pablo Pfister, Nadia Menzi, Bita Tafrishi, Dirk J. Schaefer, Jan A. Plock, Tarek Ismail, and Holger J. Klein. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Symmetry and Emotions in Facial Palsy Patients After Botulinum Toxin A Injections" Toxins 17, no. 12: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120597
APA StyleMüller, S. L. C., Zeier, C., Pfister, P., Menzi, N., Tafrishi, B., Schaefer, D. J., Plock, J. A., Ismail, T., & Klein, H. J. (2025). Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Symmetry and Emotions in Facial Palsy Patients After Botulinum Toxin A Injections. Toxins, 17(12), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17120597





