OnabotulinumtoxinA to Prevent Chronic Migraine with Comorbid Bruxism: Real-World Data from the GRASP Study Group
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Sample
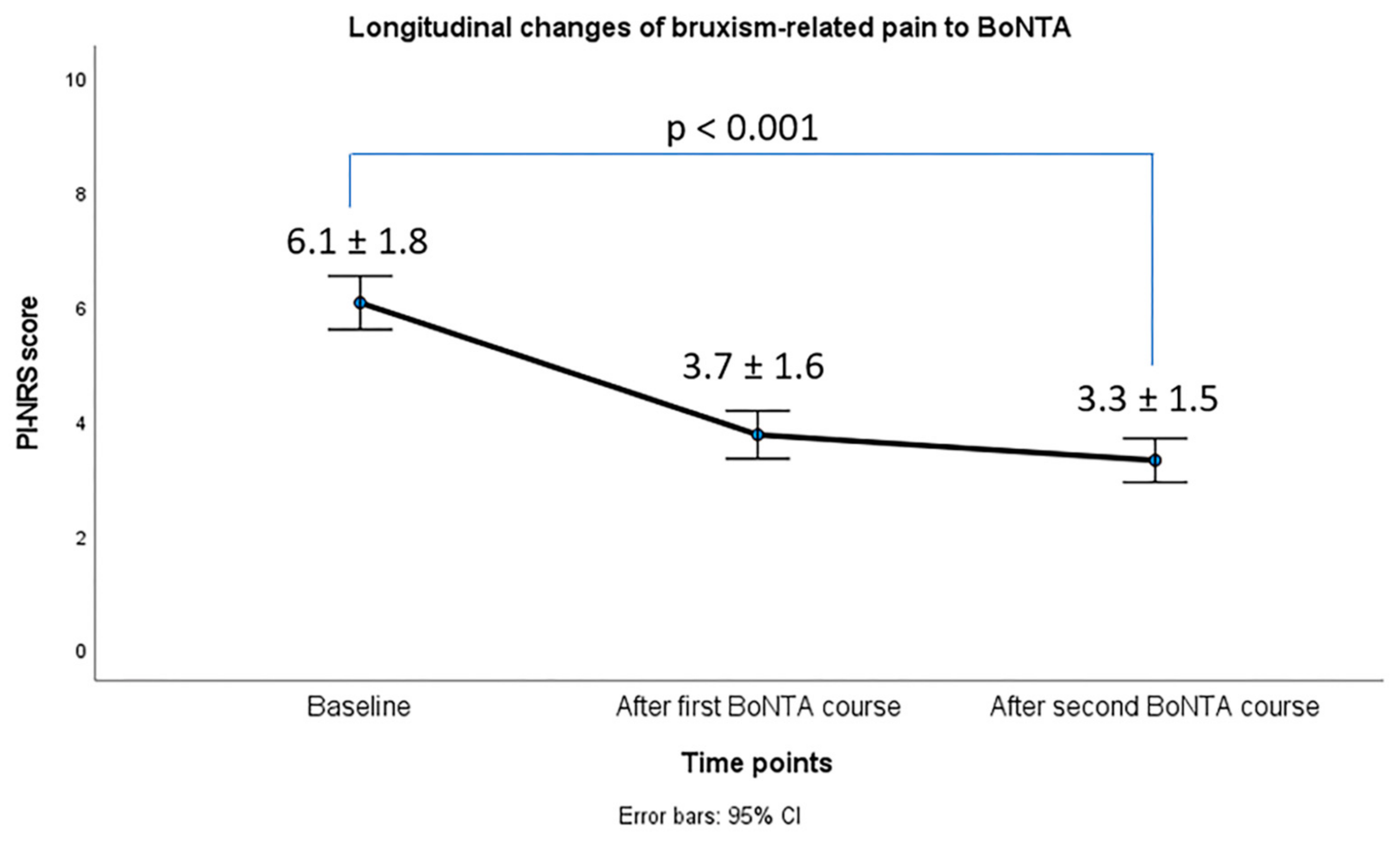
2.2. Effects of BoNTA on Bruxism Phenotype
2.3. Responder Rates and Effects of BoNTA on CM Efficacy and Disability Outcomes
2.4. Safety Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study Design and Patients’ Selection
5.2. Primary and Secondary Objectives
5.3. BoNTA Safety Evaluation
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quintela, E.; Castillo, J.; Muñoz, P.; Pascual, J. Premonitory and resolution symptoms in migraine: A prospective study in 100 unselected patients. Cephalalgia 2006, 26, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, M.; Raggi, A. A narrative review on the burden of migraine: When the burden is the impact on people’s life. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, R.B.; Buse, D.C.; Nahas, S.J.; Tietjen, G.E.; Martin, V.T.; Löf, E.; Brevig, T.; Cady, R.; Diener, H.C. Risk factors for migraine disease progression: A narrative review for a patient-centered approach. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 5692–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, G.L. Migraine overview and summary of current and emerging treatment options. Am. J. Manag. Care 2019, 25 (Suppl. S2), S23–S34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lipton, R.B.; Seng, E.K.; Chu, M.K.; Reed, M.L.; Fanning, K.M.; Adams, A.M.; Buse, D.C. The Effect of Psychiatric Comorbidities on Headache-Related Disability in Migraine: Results From the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes (CaMEO) Study. Headache 2020, 60, 1683–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Reed, M.L.; Fanning, K.M.; Bostic, R.; Dodick, D.W.; Schwedt, T.J.; Munjal, S.; Singh, P.; Lipton, R.B. Comorbid and co-occurring conditions in migraine and associated risk of increasing headache pain intensity and headache frequency: Results of the migraine in America symptoms and treatment (MAST) study. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voß, L.C.; Basedau, H.; Svensson, P.; May, A. Bruxism, temporomandibular disorders, and headache: A narrative review of correlations and causalities. Pain 2024, 165, 2409–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Reyes, M.; Bassiur, J.P. Temporomandibular Disorders, Bruxism and Headaches. Neurol. Clin. 2024, 42, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teruel, A.; Romero-Reyes, M. Interplay of Oral, Mandibular, and Facial Disorders and Migraine. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2022, 26, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.A.; Oliveira-Souza, A.I.S.; Hahn, G.; Bähr, L.; Armijo-Olivo, S.; Ferreira, A.P.L. Effectiveness of Biofeedback in Individuals with Awake Bruxism Compared to Other Types of Treatment: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussadori, S.K.; Motta, L.J.; Horliana, A.C.R.T.; Santos, E.M.; Martimbianco, A.L.C. The Current Trend in Management of Bruxism and Chronic Pain: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 2413–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodick, D.W.; Turkel, C.C.; DeGryse, R.E.; Aurora, S.K.; Silberstein, S.D.; Lipton, R.B.; Diener, H.C.; Brin, M.F.; PREEMPT Chronic Migraine Study Group. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Pooled results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phases of the PREEMPT clinical program. Headache 2010, 50, 921–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurora, S.K.; Winner, P.; Freeman, M.C.; Spierings, E.L.; Heiring, J.O.; DeGryse, R.E.; VanDenburgh, A.M.; Nolan, M.E.; Turkel, C.C. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Pooled analyses of the 56-week PREEMPT clinical program. Headache 2011, 51, 1358–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaterian, N.; Shaterian, N.; Ghanaatpisheh, A.; Abbasi, F.; Daniali, S.; Jahromi, M.J.; Sanie, M.S.; Abdoli, A. Botox (OnabotulinumtoxinA) for Treatment of Migraine Symptoms: A Systematic Review. Pain Res. Manag. 2022, 2022, 3284446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozo-Rosich, P.; Alpuente, A.; Silberstein, S.D.; Burstein, R. Insights from 25 years of onabotulinumtoxinA in migraine—Mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyriou, A.A.; Mitsikostas, D.D.; Mantovani, E.; Vikelis, M.; Tamburin, S. Beyond chronic migraine: A systematic review and expert opinion on the off-label use of botulinum neurotoxin type-A in other primary headache disorders. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2021, 21, 923–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, M.F.; Burstein, R. Botox (onabotulinumtoxinA) mechanism of action. Medicine 2023, 102 (Suppl. S1), e32372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbanti, P.; Egeo, G.; Fofi, L.; Aurilia, C.; Piroso, S. Rationale for use of onabotulinum toxin A (BOTOX) in chronic migraine. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 36 (Suppl S1), 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikelis, M.; Argyriou, A.A.; Dermitzakis, E.V.; Spingos, K.C.; Mitsikostas, D.D. Onabotulinumtoxin-A treatment in Greek patients with chronic migraine. J. Headache Pain 2016, 17, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikelis, M.; Argyriou, A.A.; Dermitzakis, E.V.; Spingos, K.C.; Makris, N.; Kararizou, E. Sustained onabotulinumtoxinA therapeutic benefits in patients with chronic migraine over 3 years of treatment. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyriou, A.A.; Dermitzakis, E.V.; Vlachos, G.S.; Vikelis, M. Long-term adherence, safety, and efficacy of repeated onabotulinumtoxinA over five years in chronic migraine prophylaxis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2022, 145, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Bae, T.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, C.; Kang, Y.N.; Chiu, W.K. Effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin Injection on Bruxism: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2023, 47, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcangi, G.; Patano, A.; Pezzolla, C.; Riccaldo, L.; Mancini, A.; Di Pede, C.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Inchingolo, F.; Bordea, I.R.; Dipalma, G.; et al. Bruxism and Botulinum Injection: Challenges and Insights. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réus, J.C.; Polmann, H.; Mendes Souza, B.D.; Flores-Mir, C.; Trevisol Bittencourt, P.C.; Winocur, E.; Okeson, J.; De Luca Canto, G. Association Between Primary Headache and Bruxism: An Updated Systematic Review. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2021, 35, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengi, A.; Uygunoglu, U. Impact of temporomandibular disorder comorbidity on pain, quality of life, sleep, and functional outcomes in chronic migraine patients not using preventive treatment: A cross-sectional study. Neurol. Res. 2025, 47, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Hay, I.; Bender, S.D. Bruxism and oro-facial pain not related to temporomandibular disorder conditions: Comorbidities or risk factors? J. Oral Rehabil. 2024, 51, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.S.; Almoyad, M.A.A.; Binduhayyim, R.I.H.; Quadri, S.A.; Gurumurthy, V.; Bavabeedu, S.S.; Kuruniyan, M.S.; Naseef, P.P.; Mosaddad, S.A.; Heboyan, A. The effectiveness of botulinum toxin for temporomandibular disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0300157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaman, G.; Kahraman, N.; Köseoğlu, B.G.; Bilgiç, B.; Matur, Z.; Ertaş, M.; Gülşen, Y.; Baykan Baykal, B. Evaluation of OnabotulinumtoxinA Treatment in Patients with Concomitant Chronic Migraine and Temporomandibular Disorders. Arch. Neuropsychiatry 2018, 55, 330–336. [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld, A.M.; Silberstein, S.D.; Dodick, D.W.; Aurora, S.K.; Brin, M.F.; Binder, W.J. Insights into the Functional Anatomy Behind the PREEMPT Injection Paradigm: Guidance on Achieving Optimal Outcomes. Headache 2017, 57, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.L.; Gonçalves, D.A.; Castanharo, S.M.; Speciali, J.G.; Bigal, M.E.; Camparis, C.M. Migraine is the most prevalent primary headache in individuals with temporomandibular disorders. J. Orofac. Pain 2010, 24, 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Exposto, C.R.; Mansoori, M.; Bech, B.H.; Baad-Hansen, L. Prevalence of Painful Temporomandibular Disorders and Overlapping Primary Headaches Among Young Adults. Eur. J. Pain 2025, 29, e70013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerman, S.; Romero-Reyes, M. Preclinical studies investigating the neural mechanisms involved in the co-morbidity of migraine and temporomandibular disorders: The role of CGRP. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 5555–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandão de Almeida, A.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Simão, C.; de Araújo, R.P.; Figueiredo, J. Prevalence of Sleep Bruxism Reported by Parents/Caregivers in a Portuguese Pediatric Dentistry Service: A Retrospective Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracci, A.; Lobbezoo, F.; Häggman-Henrikson, B.; Colonna, A.; Nykänen, L.; Pollis, M.; Ahlberg, J.; Manfredini, D.; International Network for Orofacial Pain And Related Disorders Methodology, INfORM. Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives on Awake Bruxism Assessment: Expert Consensus Recommendations. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colonna, A.; Bracci, A.; Manfredini, D. Bracing: The hidden side of the moon. Cranio. 2025, 43, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracutu, O.I.; Pollis, M.; Guarda-Nardini, L.; Bracci, A.; Manfredini, D. Family history of bruxism: A case-control study based on the ecological momentary assessment of awake bruxism. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2025, 39, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Reyes, M.; Akerman, S.; Rapoport, A.M. Optimising combined treatment for migraine and temporomandibular disorders (TMDs). Cephalalgia 2025, 45, 3331024251368882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.; Cardoso, J.A.; Mehta, S. A systematic review of botulinum toxin in the management of patients with temporomandibular disorders and bruxism. Br. Dent. J. 2019, 226, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val, M.; Delcanho, R.; Ferrari, M.; Guarda Nardini, L.; Manfredini, D. Is Botulinum Toxin Effective in Treating Orofacial Neuropathic Pain Disorders? A Systematic Review. Toxins 2023, 15, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberstein, S.D.; Dodick, D.W.; Aurora, S.K.; Diener, H.C.; DeGryse, R.E.; Lipton, R.B.; Turkel, C.C. Per cent of patients with chronic migraine who responded per onabotulinumtoxinA treatment cycle: PREEMPT. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobbezoo, F.; Ahlberg, J.; Verhoeff, M.C.; Aarab, G.; Bracci, A.; Koutris, M.; Nykänen, L.; Thymi, M.; Wetselaar, P.; Manfredini, D. The bruxism screener (BruxScreen): Development, pilot testing and face validity. J. Oral Rehabil. 2024, 51, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustrell-Barral, M.; Zamora-Olave, C.; Khoury-Ribas, L.; Rovira-Lastra, B.; Martinez-Gomis, J. The BruxChecker System for Quantitatively Assessing Sleep Bruxism at the Dental Level: Reliability, Reference Values and Methodological Considerations. J. Oral Rehabil. 2025, 52, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, D.; Ahlberg, J.; Aarab, G.; Bracci, A.; Durham, J.; Emodi-Perlman, A.; Ettlin, D.; Gallo, L.M.; Häggman-Henrikson, B.; Koutris, M.; et al. The development of the Standardised Tool for the Assessment of Bruxism (STAB): An international road map. J. Oral Rehabil. 2024, 51, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeff, M.C.; Lobbezoo, F.; Ahlberg, J.; Bender, S.; Bracci, A.; Colonna, A.; Dal Fabbro, C.; Durham, J.; Glaros, A.G.; Häggman-Henrikson, B.; et al. Updating the Bruxism Definitions: Report of an International Consensus Meeting. J. Oral Rehabil. 2025, 52, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, R.H.; Turk, D.C.; Wyrwich, K.W.; Beaton, D.; Cleeland, C.S.; Farrar, J.T.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Jensen, M.P.; Kerns, R.D.; Ader, D.N.; et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of treatment outcomes in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. J. Pain 2008, 9, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, D.; Ahlberg, J.; Aarab, G.; Bender, S.; Bracci, A.; Cistulli, P.A.; Conti, P.C.; De Leeuw, R.; Durham, J.; Emodi-Perlman, A.; et al. Standardised Tool for the Assessment of Bruxism. J. Oral Rehabil. 2024, 51, 29–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, W.F.; Lipton, R.B.; Kolodner, K.; Liberman, J.; Sawyer, J. Reliability of the migraine disability assessment score in a population-based sample of headache sufferers. Cephalalgia 1999, 19, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinski, M.; Bayliss, M.S.; Bjorner, J.B.; Ware, J.E., Jr.; Garber, W.H.; Batenhorst, A.; Cady, R.; Dahlöf, C.G.; Dowson, A.; Tepper, S. A six-item short-form survey for measuring headache impact: The HIT-6. Qual. Life Res. 2003, 12, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomidi, T.; Vikelis, M.; Artemiadis, A.; Chrousos, G.P.; Darviri, C. Reliability and Validity of the Greek Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) Questionnaire. PharmacoEconomics-Open 2018, 2, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, H.; Bolton, J. Assessing the clinical significance of change scores recorded on subjective outcome measures. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2004, 27, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Participants n = 58 Variable | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender Females Males | 53 (91.4) 5 (8.6) |
| Age ± SD (range) | 46.5 ± 8.3 (29–70) |
| Previous lines of prophylactic medications Median value (range) | 5 (3–8) |
| Years with migraine diagnosis Median value (range) Psychiatric comorbidities No Anxiety disorder Depression Mixed anxiety and depression disorder Fibromyalgia Yes No Medication overuse headache Yes No Aura Yes No Temporomandibular joint disorders Yes No Masseter hypertrophy Yes No | 26 (5–50) 28 (48.3) 14 (24.1) 10 (17.2) 6 (10.4) 5 (8.6) 53 (91.4) 55 (94.8) 3 (5.2) 11 (19.0) 47 (81.0) 5 (8.6) 53 (91.4) 46 (79.3) 12 (20.7) |
| Median (Minimum–Maximum) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Baseline | After Treatment with 2 BoNTA Cycles | z | p Value | Effect Size |
| Monthly headache days | 22 15–30 | 11 3–28 | −5.450 | <0.001 | 0.70 |
| Monthly days with peak headache intensity of at least 5/10 in VAS | 17 6–30 | 6 1–25 | −7.351 | <0.001 | 0.86 |
| Monthly days with intake of acute headache medication | 20 8–30 | 6 2–25 | −7.241 | <0.001 | 0.85 |
| MIDAS score | 77 36–168 | 34 10–168 | −6.944 | <0.001 | 0.83 |
| HIT-6 score | 72 63–78 | 63 42–76 | −5.398 | <0.001 | 0.65 |
| Response to BoNTA (%) | |||||
| <50% | 17 (29.3) | ||||
| >50% | 32 (55.2) | ||||
| >75% | 9 (15.5) | ||||
| 100% | 0 (0) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Argyriou, A.A.; Dermitzakis, E.V.; Chondrogianni, M.; Foska, A.; Rikos, D.; Xiromerisiou, G.; Soldatos, P.; Litsardopoulos, P.; Vikelis, M., on behalf of the Greek Research Alliance for the Study of Headache and Pain (GRASP) Study Group. OnabotulinumtoxinA to Prevent Chronic Migraine with Comorbid Bruxism: Real-World Data from the GRASP Study Group. Toxins 2025, 17, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110547
Argyriou AA, Dermitzakis EV, Chondrogianni M, Foska A, Rikos D, Xiromerisiou G, Soldatos P, Litsardopoulos P, Vikelis M on behalf of the Greek Research Alliance for the Study of Headache and Pain (GRASP) Study Group. OnabotulinumtoxinA to Prevent Chronic Migraine with Comorbid Bruxism: Real-World Data from the GRASP Study Group. Toxins. 2025; 17(11):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110547
Chicago/Turabian StyleArgyriou, Andreas A., Emmanouil V. Dermitzakis, Maria Chondrogianni, Aikaterini Foska, Dimitrios Rikos, Georgia Xiromerisiou, Panagiotis Soldatos, Pantelis Litsardopoulos, and Michail Vikelis on behalf of the Greek Research Alliance for the Study of Headache and Pain (GRASP) Study Group. 2025. "OnabotulinumtoxinA to Prevent Chronic Migraine with Comorbid Bruxism: Real-World Data from the GRASP Study Group" Toxins 17, no. 11: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110547
APA StyleArgyriou, A. A., Dermitzakis, E. V., Chondrogianni, M., Foska, A., Rikos, D., Xiromerisiou, G., Soldatos, P., Litsardopoulos, P., & Vikelis, M., on behalf of the Greek Research Alliance for the Study of Headache and Pain (GRASP) Study Group. (2025). OnabotulinumtoxinA to Prevent Chronic Migraine with Comorbid Bruxism: Real-World Data from the GRASP Study Group. Toxins, 17(11), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110547








