Characterization of Hottentotta judaicus Scorpion Venom: Toxic Effects and Neurobehavioral Modulation in Insect Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LC-ESI-MS Analysis of HjSV
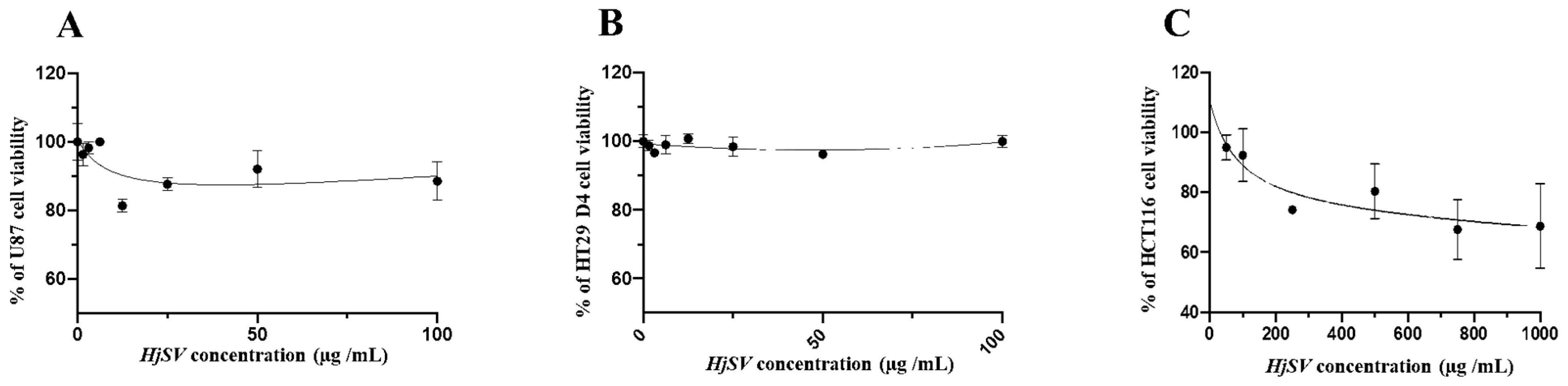
2.2. HjSV Exerts No Significant Cytotoxic Effect on U87, HT29 D4 and HTC116 Cancer Cells
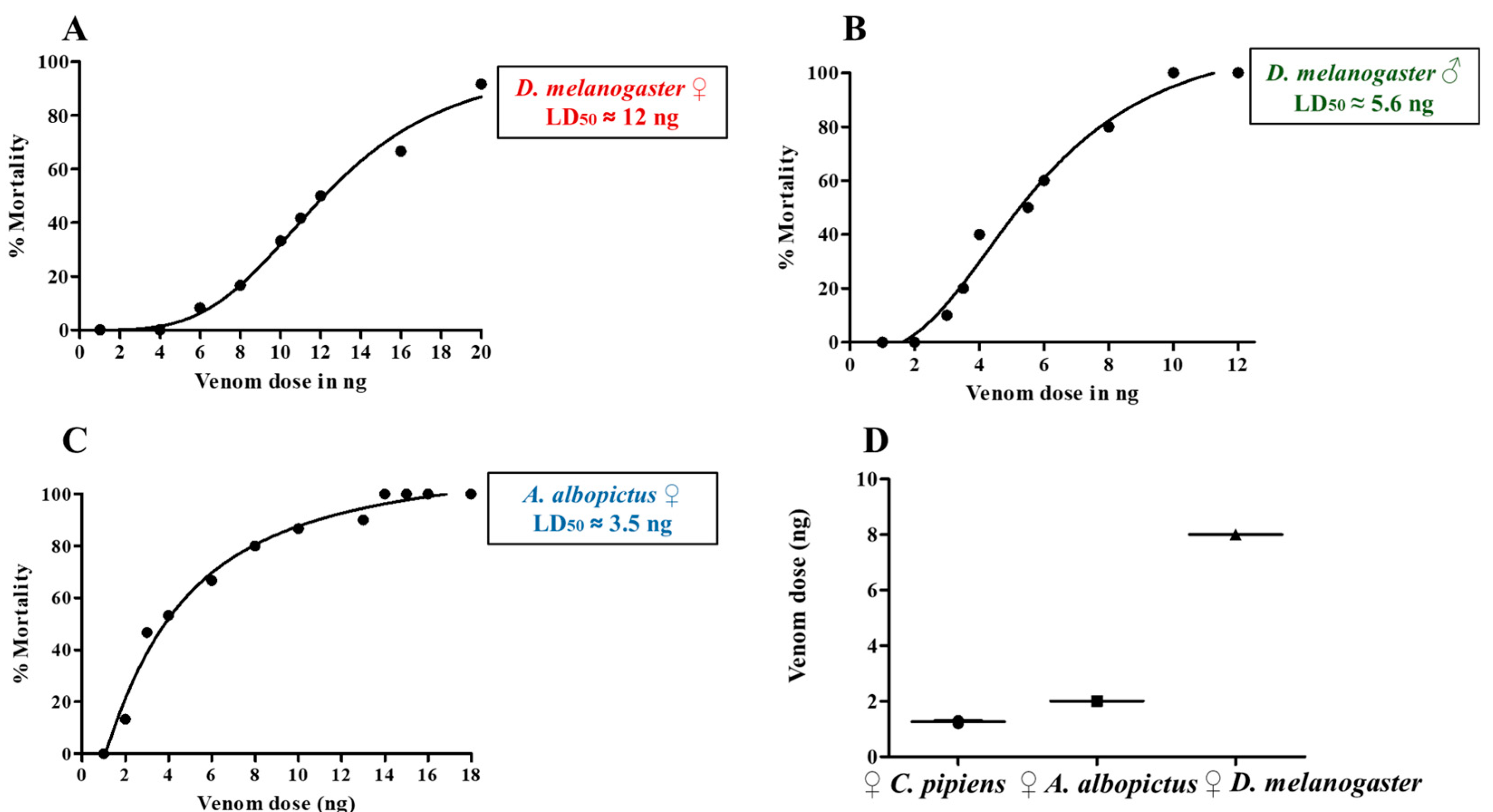
2.3. Effects of HjSV on D. melanogaster, A. albopictus and C. pipiens
2.4. Effects of HjSV on Locomotor Activity and Sleep Pattern in D. melanogaster
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. HjSV Preparation
4.2. Liquid Chromatography Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS) Analysis
4.3. Cell Culture and Cytotoxic Activity Assay
4.4. Mosquito and D. melanogaster Strains and Rearing
4.5. Venom Microinjection and Lethality Assessment
4.6. Drosophila Activity Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rafinejad, J.; Shahi, M.; Navidpour, S.; Jahanifard, E.; Hanafi-Bojd, A.A. Effect of climate change on spatial distribution of scorpions of significant public health importance in Iran. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2020, 13, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štundlová, J.; Šťáhlavský, F.; Opatova, V.; Stundl, J.; Kovařík, F.; Dolejš, P.; Šmíd, J. Molecular data do not support the traditional morphology-based groupings in the scorpion family Buthidae (Arachnida: Scorpiones). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2022, 173, 107511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibáñez-López, C.E.; Aharon, S.; Ballesteros, J.A.; Gainett, G.; Baker, C.M.; González-Santillán, E.; Harvey, M.S.; Hassan, M.K.; Almaaty, A.H.A.; Aldeyarbi, S.M.; et al. Phylogenomics of Scorpions Reveal Contemporaneous Diversification of Scorpion Mammalian Predators and Mammal-Active Sodium Channel Toxins. Syst. Biol. 2022, 71, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovařík, F. A Revision of the Genus Hottentotta Birula, 1908, with Descriptions of Four New Species (Scorpiones, Buthidae). Euscorpius 2007, 2007, 1–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyave-Muñoz, A.; van der Meijden, A.; Estrada-Gómez, S.; García, L.F. Linking toxicity and predation in a venomous arthropod: The case of Tityus fuhrmanni (Scorpiones: Buthidae), a generalist predator scorpion. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 28, e20210036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.M.; Tahir, H.M. Foraging Behaviour of Hottentotta tumulus (Fabricius, 1798) and Odontobuthus odonturus (Pocock, 1897). Pak. J. Zoolgy 2016, 48, 1811–1815. [Google Scholar]
- García, L.F.; Valenzuela-Rojas, J.C.; González-Gómez, J.C.; Lacava, M.; van der Meijden, A. Pinching or stinging? Comparing prey capture among scorpions with contrasting morphologies. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 28, e20210037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbister, G.K.; Bawaskar, H.S. Scorpion envenomation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubekeur, K.; L’Hadj, M.; Selmane, S. Demographic and epidemiological characteristics of scorpion envenomation and daily forecasting of scorpion sting counts in Touggourt, Algeria. Epidemiol. Health 2020, 42, e2020050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amr, Z.S.; Abu Baker, M.A.; Al-Saraireh, M.; Warrell, D.A. Scorpions and scorpion sting envenoming (scorpionism) in the Arab Countries of the Middle East. Toxicon 2021, 191, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Hernández, V.; Jiménez-Vargas, J.M.; Gurrola, G.B.; Valdivia, H.H.; Possani, L.D. Scorpion venom components that affect ion-channels function. Toxicon 2013, 76, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüddecke, T.; Dresler, J.; Hurka, S.; Wang, Y.; Pohler, T.; Simone, Y.; Krämer, J.; Vilcinskas, A.; Herzig, V. Venom gland transcriptomics of the Black Judaicus scorpion (Hottentotta judaicus) reveals its toxin arsenal and potential bioeconomic value. Toxicon 2025, 268, 108609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, L.C.; Viana, G.M.M.; Nencioni, A.L.A.; Pimenta, D.C.; Beraldo-Neto, E. Scorpion Peptides and Ion Channels: An Insightful Review of Mechanisms and Drug Development. Toxins 2023, 15, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, E.; Possani, L.D. The unfulfilled promises of scorpion insectotoxins. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevitz, M.; Gordon, D.; Barzilai, M.G.; Kahn, R.; Cohen, L.; Moran, Y.; Zilberberg, N.; Froy, O.; Altman-Gueta, H.; Turkov, M.; et al. Molecular Description of Scorpion Toxin Interaction with Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels; Scorpion Venoms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 471–491. [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron, Z.L.; Bingham, J.P. Scorpion toxins specific for potassium (K+) channels: A historical overview of peptide bioengineering. Toxins 2012, 4, 1082–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, D.; Rohde, B.H.; King, G.F.; Tal, T.; Sher, D.; Zlotkin, E. The tale of a resting gland: Transcriptome of a replete venom gland from the scorpion Hottentotta judaicus. Toxicon 2011, 57, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, T.; Potikha, T.; Sher, D.; Elazar, M.; Mao, W.; Tal, T.; Bosmans, F.; Tytgat, J.; Ben-Arie, N.; Zlotkin, E. BjαIT: A novel scorpion alpha-toxin selective for insects—Unique pharmacological tool. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 35, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotkin, E.; Gurevitz, M.; Fowler, E.; Adams, M.E. Depressant insect selective neurotoxins from scorpion venom: Chemistry, action, and gene cloning. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1993, 22, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiseh, M.; Gabikian, P.; Bahrami, S.B.; Veiseh, O.; Zhang, M.; Hackman, R.C.; Ravanpay, A.C.; Stroud, M.R.; Kusuma, Y.; Hansen, S.J.; et al. Tumor paint: A chlorotoxin:Cy5.5 bioconjugate for intraoperative visualization of cancer foci. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6882–6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroud, M.R.; Hansen, S.J.; Olson, J.M. In vivo bio-imaging using chlorotoxin-based conjugates. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 4362–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Xie, L.; Li, B.; Lv, X.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Z. Antimicrobial Potential of Scorpion-Venom-Derived Peptides. Molecules 2024, 29, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashmforoosh, N.; Baradaran, M. Peptides with Diverse Functions from Scorpion Venom: A Great Opportunity for the Treatment of a Wide Variety of Diseases. Iran. Biomed. J. 2023, 27, 84–99. [Google Scholar]
- Amorim-Carmo, B.; Parente, A.M.S.; Souza, E.S.; Silva-Junior, A.A.; Araújo, R.M.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F. Antimicrobial Peptide Analogs From Scorpions: Modifications and Structure-Activity. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 887763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoub, T.; Rima, M.; Karam, M.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Fajloun, Z. Antimicrobials from Venomous Animals: An Overview. Molecules 2020, 25, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, L.; Chender, A.; Roufayel, R.; Accary, C.; Borges, A.; Sabatier, J.M.; Fajloun, Z.; Karam, M. Effect of Hottentotta judaicus Scorpion Venom on Nociceptive Response and Inflammatory Cytokines in Mice Using Experimental Hyperalgesia. Molecules 2025, 30, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeibmann, A.; Paulus, W. Drosophila melanogaster as a model organism of brain diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 407–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rand, M.D.; Tennessen, J.M.; Mackay, T.F.C.; Anholt, R.R.H. Perspectives on the Drosophila melanogaster Model for Advances in Toxicological Science. Curr. Protoc. 2023, 3, e870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obradovic, Z.; Smjecanin, E.; Pindzo, E.; Omerovic, H.; Cibo, N. A Literature Review on Vector Borne Diseases. Int. J. Med. Rev. Case Rep. 2022, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmana, H.; Mediannikov, O. Mosquito-Borne Diseases Emergence/Resurgence and How to Effectively Control It Biologically. Pathogens 2020, 9, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasegaran, K.; Lahondère, C.; Escobar, L.E.; Vinauger, C. Linking Mosquito Ecology, Traits, Behavior, and Disease Transmission. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; Lomonte, B.; de Arias, A.R.; Fernández, J. Proteomic characterization and lethality of the venom of the Black Judean scorpion, Hottentotta judaicus (Buthidae): Expanded toxin diversity and revisited toxicological significance. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 99, 5105–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-García, A.; Morier-Díaz, L.; Frión-Herrera, Y.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, H.; Caballero-Lorenzo, Y.; Mendoza-Llanes, D.; Riquenes-Garlobo, Y.; Fraga-Castro, J.A. In vitro anticancer effect of venom from Cuban scorpion Rhopalurus junceus against a panel of human cancer cell lines. J. Venom Res. 2013, 4, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nosouhian, M.; Rastegari, A.A.; Shahanipour, K.; Ahadi, A.M.; Sajjadieh, M.S. Anticancer potentiality of Hottentotta saulcyi scorpion curd venom against breast cancer: An in vitro and in vivo study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, S.; Knerr, J.M.; Argemi, L.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Arantes, E.C.; Çalışkan, F.; Laustsen, A.H. Scorpion Venom: Detriments and Benefits. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, S.; Borges, A.; Sahyoun, C.; Nasr, R.; Roufayel, R.; Legros, C.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Fajloun, Z. Scorpion Venom as a Source of Antimicrobial Peptides: Overview of Biomolecule Separation, Analysis and Characterization Methods. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Lei, Y.; Qin, H.; Cao, Z.; Kwok, H.F. Deciphering Scorpion Toxin-Induced Pain: Molecular Mechanisms and Ion Channel Dynamics. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2025, 21, 2921–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoobdel, M.; Zahraei-Salehi, T.; Nayeri-Fasaei, B.; Khosravi, M.; Omidian, Z.; Motedayen, M.H.; Akbari, A. Purification of the Immunogenic Fractions and Determination of Toxicity in Mesobuthus eupeus (Scorpionida: Buthidae) Venom. J. Arthropod Borne Dis. 2013, 7, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- El-Qassas, J.; Abd El-Atti, M.; El-Badri, N. Harnessing the potency of scorpion venom-derived proteins: Applications in cancer therapy. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2024, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotkin, E.; Kadouri, D.; Gordon, D.; Pelhate, M.; Martin, M.F.; Rochat, H. An excitatory and a depressant insect toxin from scorpion venom both affect sodium conductance and possess a common binding site. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1985, 240, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezellou, P.; Jakob, K.; Atashi, J.; Ghassempour, A.; Spengler, B. Mass-Spectrometry-Based Lipidome and Proteome Profiling of Hottentotta saulcyi (Scorpiones: Buthidae) Venom. Toxins 2022, 14, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Luccio, E.; Azulay, D.-O.; Regaya, I.; Fajloun, Z.; Sandoz, G.; Mansuelle, P.; Kharrat, R.; Fathallah, M.; Carrega, L.; Estève, E.; et al. Parameters affecting in vitro oxidation/folding of maurotoxin, a four-disulphide-bridged scorpion toxin. Biochem. J. 2001, 358, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Barek, S.; Lopez-Gonzalez, I.; Andreotti, N.; di Luccio, E.; Visan, V.; Grissmer, S.; Judge, S.; El Ayeb, M.; Darbon, H.; Rochat, H.; et al. A maurotoxin with constrained standard disulfide bridging: Innovative strategy of chemical synthesis, pharmacology, and docking on K+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 31095–31104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezianian, S.; Zargan, J.; Goudarzi, H.R.; Haji Noormohamadi, A.; Mousavi, M.; Alikhani, H.K.; Johari, B. In-vitro Study of Hottentotta Schach Crude Venom Anticancer Effects on MCF-7 and Vero Cell Lines. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 192–202. [Google Scholar]
- Elrayess, R.A.; Mohallal, M.E.; Mobarak, Y.M.; Ebaid, H.M.; Haywood-Small, S.; Miller, K.; Strong, P.N.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A. Scorpion Venom Antimicrobial Peptides Induce Caspase-1 Dependant Pyroptotic Cell Death. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 788874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, S.A.M.; Taylor-Wells, J.; Gross, A.D.; Bloomquist, J.R. Toxicity and Physiological Actions of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors to Aedes aegypti and Drosophila melanogaster. Insects 2017, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, O.V.; DeFoe, A.E.; Qi, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Weng, S.C.; Houri-Zeevi, L.; Lakhiani, P.; Morita, T.; Razzauti, J.; Rosas-Villegas, A.; et al. Mosquito Cell Atlas: A single-nucleus transcriptomic atlas of the adult Aedes aegypti mosquito. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nene, V.; Wortman, J.R.; Lawson, D.; Haas, B.; Kodira, C.; Tu, Z.; Loftus, B.; Xi, Z.; Megy, K.; Grabherr, M.; et al. Genome sequence of Aedes aegypti, a major arbovirus vector. Science 2007, 316, 1718–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, J.J. Ion channels to inactivate neurons in Drosophila. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2009, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotkin, E.; Devonshire, A.L.; Warmke, J.W. The pharmacological flexibility of the insect voltage gated sodium channel: Toxicity of AaIT to knockdown resistant (kdr) flies. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 29, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Meerloo, J.; Kaspers, G.J.; Cloos, J. Cell sensitivity assays: The MTT assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 731, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rifi, M.; Radwan, Z.; AlMonla, R.; Fajloun, Z.; Sabatier, J.M.; Kouzayha, A.; El-Sabban, M.; Mawlawi, H.; Dassouki, Z. The Lebanese Red Algae Jania rubens: Promising Biomolecules against Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wehbe, R.; Karaki, A.; Dassouki, Z.; Rima, M.; Borges, A.; Roufayel, R.; Legros, C.; Fajloun, Z.; Kambris, Z. Characterization of Hottentotta judaicus Scorpion Venom: Toxic Effects and Neurobehavioral Modulation in Insect Models. Toxins 2025, 17, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110546
Wehbe R, Karaki A, Dassouki Z, Rima M, Borges A, Roufayel R, Legros C, Fajloun Z, Kambris Z. Characterization of Hottentotta judaicus Scorpion Venom: Toxic Effects and Neurobehavioral Modulation in Insect Models. Toxins. 2025; 17(11):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110546
Chicago/Turabian StyleWehbe, Rim, Aline Karaki, Zeina Dassouki, Mohamad Rima, Adolfo Borges, Rabih Roufayel, Christian Legros, Ziad Fajloun, and Zakaria Kambris. 2025. "Characterization of Hottentotta judaicus Scorpion Venom: Toxic Effects and Neurobehavioral Modulation in Insect Models" Toxins 17, no. 11: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110546
APA StyleWehbe, R., Karaki, A., Dassouki, Z., Rima, M., Borges, A., Roufayel, R., Legros, C., Fajloun, Z., & Kambris, Z. (2025). Characterization of Hottentotta judaicus Scorpion Venom: Toxic Effects and Neurobehavioral Modulation in Insect Models. Toxins, 17(11), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110546






