Ricin and Abrin in Biosecurity: Detection Technologies and Strategic Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
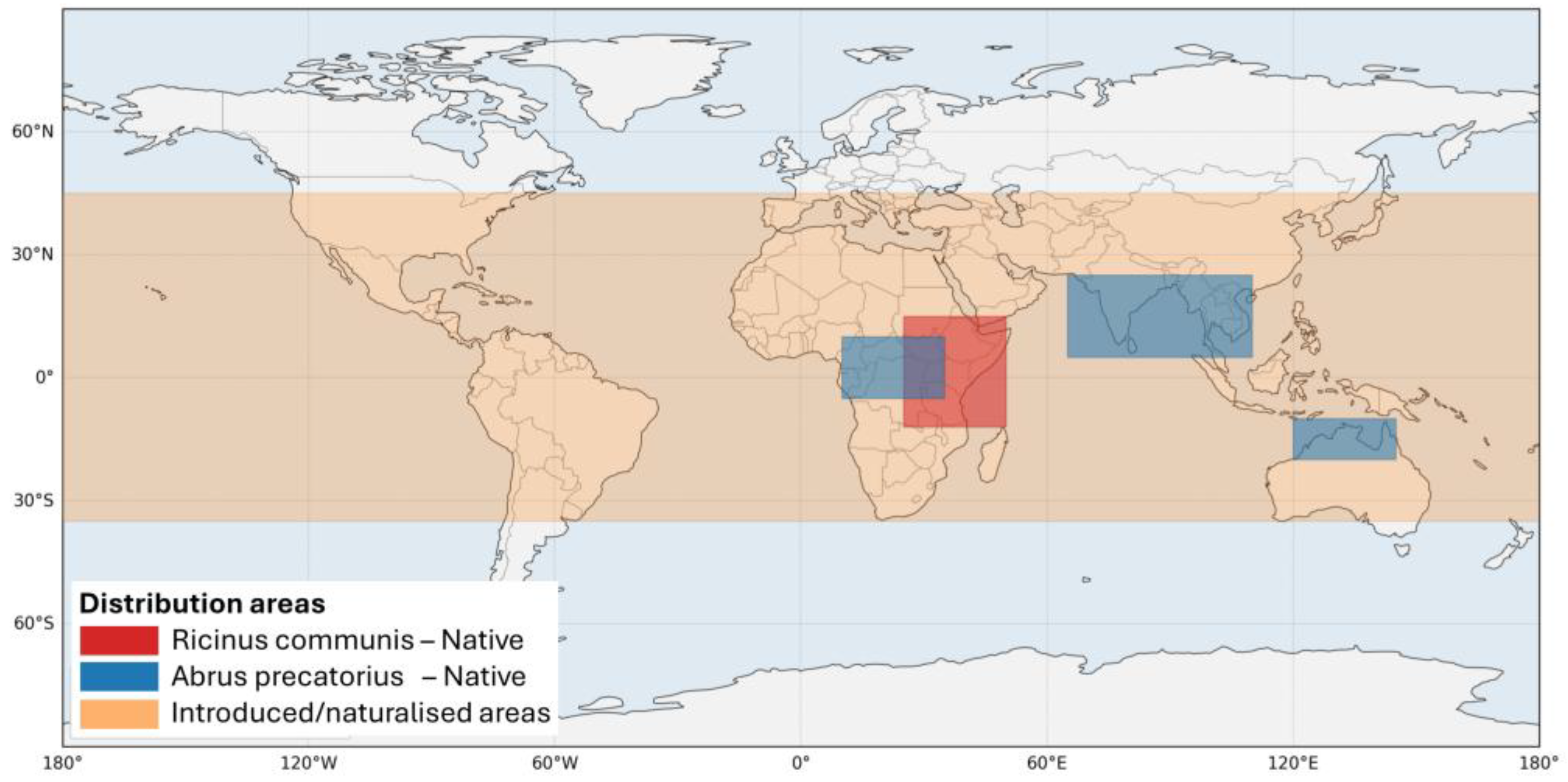
2. Source, Distribution, and Epidemiology
3. Molecular Architecture
4. Cytotoxic Mechanism
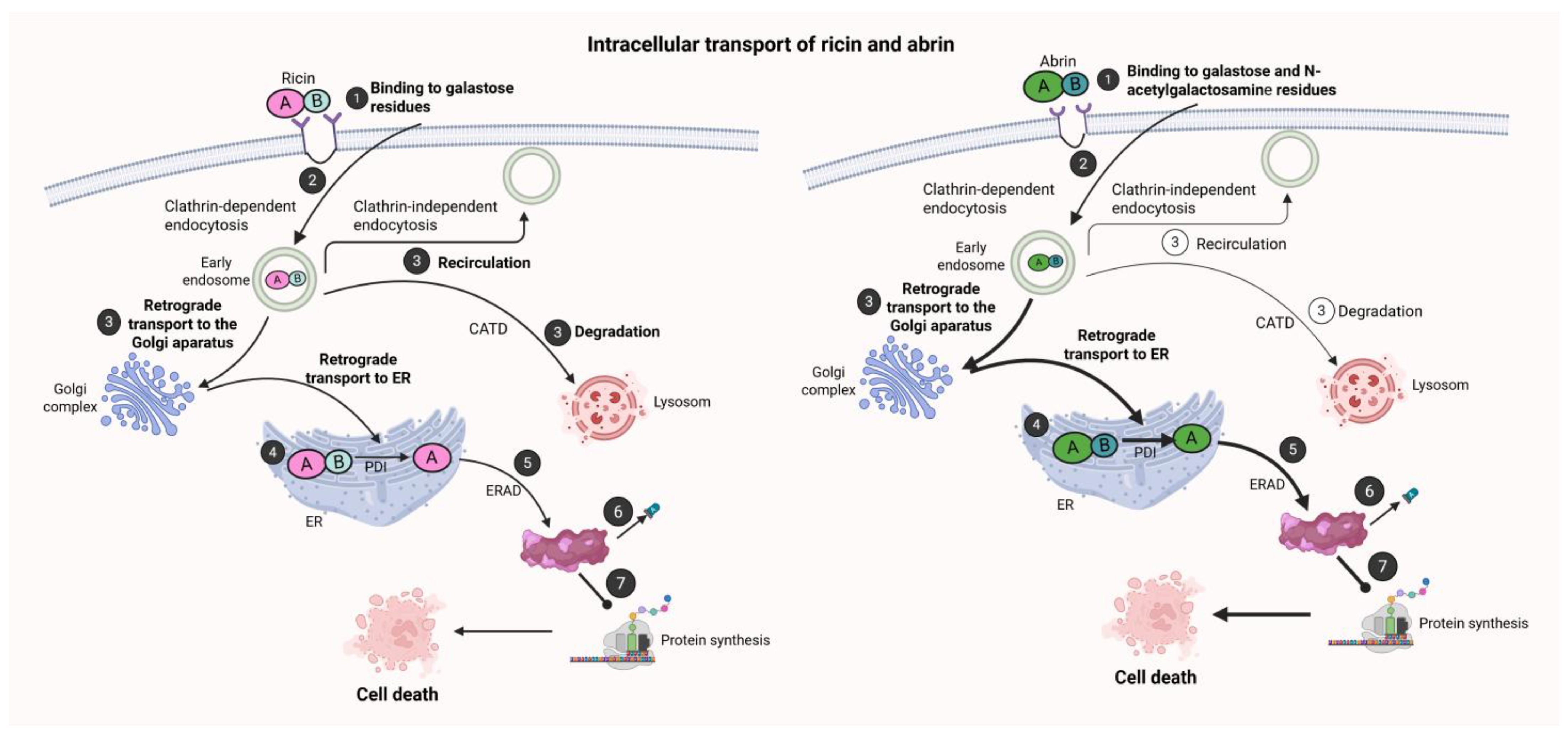
4.1. Cellular Binding and Endocytosis
4.2. Intracellular Trafficking and ER Translocation
4.3. Ribosome Inactivation and Cytotoxicity
4.4. Therapeutic Implications
5. Toxicology and Stability of Abrin and Ricin
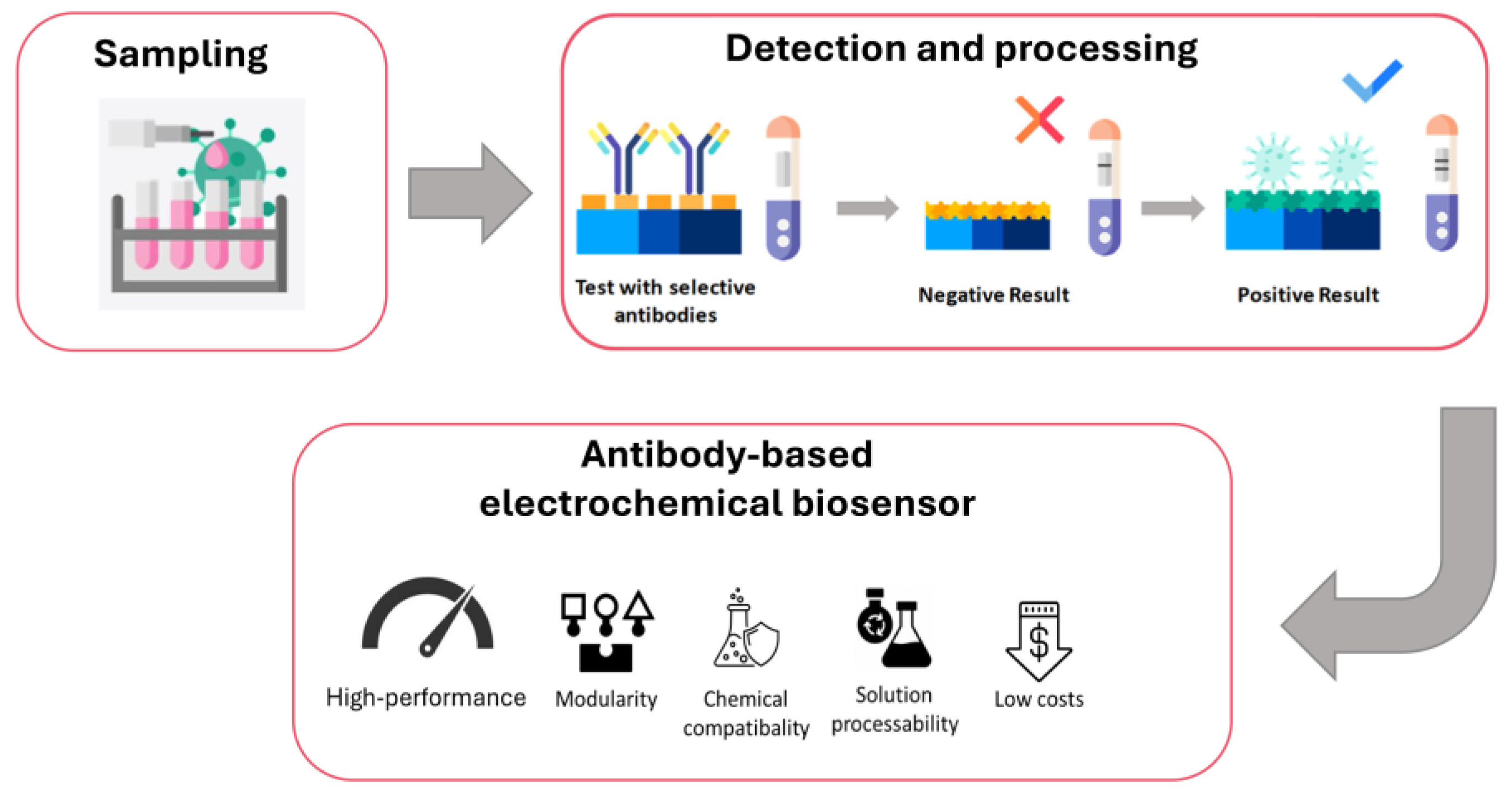
6. Detection
6.1. Immunoassay-Based Detection of Biotoxins: Ricin and Abrin
6.2. Mass Spectrometry for Biotoxin Detection: Ricin and Abrin
6.3. Biosensor Technologies for Ricin and Abrin Detection
6.4. Lateral Flow Assays (LFAs) for Ricin and Abrin Detection
7. Security Needs and Response Strategies
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| APCI | Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization |
| CBRN | Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear |
| CRM | Certified Reference Material |
| ECL-IA | Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| ERAD | Endoplasmic Reticulum-Associated Degradation |
| eEF | Eukaryotic Elongation Factor |
| FFPE | Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded |
| FTIR | Fourier-Transform Infrared |
| JAD | Jamaah Ansharud Daulah |
| LC-ESI-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray Ionization–Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| LFA | Lateral Flow Assay |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MALDI-TOF | Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight |
| MIRM | Multiple Isotopologue Reaction Monitoring |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MIP | Molecularly Imprinted Polymer |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| OPCW | Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PDI | Protein Disulfide Isomerase |
| RIP | Ribosome-Inactivating Protein |
| RCA120 | Ricinus communis Agglutinin 120 |
| RCSB | Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics |
| SRL | Sarcin–Ricin Loop |
| SPR | Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| TRF-IA | Time-Resolved Fluorescence Immunoassay |
References
- Sandvig, K.; van Deurs, B. Entry of ricin and Shiga toxin into cells: Molecular mechanisms and medical perspectives. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5943–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.Q.; Zhu, Z.N.; Zheng, Y.T.; Shaw, P.C. Engineering of Ribosome-inactivating Proteins for Improving Pharmacological Properties. Toxins 2020, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, D.J.; Mantis, N.J. Progress and challenges associated with the development of ricin toxin subunit vaccines. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasetti-Escargueil, C.; Avril, A. Medical Countermeasures against Ricin Intoxication. Toxins 2023, 15, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocyigit, E.; Kocaadam-Bozkurt, B.; Bozkurt, O.; Agagunduz, D.; Capasso, R. Plant Toxic Proteins: Their Biological Activities, Mechanism of Action and Removal Strategies. Toxins 2023, 15, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, S.; Boor, P. Oleander toxicity: An overview. Toxicon 1996, 34, 865–869. [Google Scholar]
- Frohne, D.; Pfänder, H. Poisonous Plants: A Handbook for Doctors, Pharmacists, Toxicologists, Biologists and Veterinarians, 2nd ed.; Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, W.; Elvin-Lewis, M. Medical Botany: Plants Affecting Human Health, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, J.M.; Roberts, L.M.; Robertus, J.D. Ricin: Structure, mode of action, and some current applications. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Tsurugi, K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 8128–8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, S.; Day, P.J.R. Primary Sequence and Three-Dimensional Structural Comparison between Malanin and Ricin, a Type II Ribosome-Inactivating Protein. Toxins 2024, 16, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrini, M.S.; Katayama, M.; Nakase, I.; Vago, R. Plant Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins: Progesses, Challenges and Biotechnological Applications (and a Few Digressions). Toxins 2017, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Russo, R.; Landi, N.; Valletta, M.; Chambery, A.; Di Maro, A.; Bolognesi, A.; Ferreras, J.M.; Citores, L. Structure and Biological Properties of Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins and Lectins from Elder (Sambucus nigra L.) Leaves. Toxins 2022, 14, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW). Chemical Weapons Convention: Article I—General Obligations. Available online: https://www.opcw.org/chemical-weapons-convention/articles (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Bagchi, M.; Zafra-Stone, S.; Lau, F.C.; Bagchi, D. Ricin and Abrin. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Crompton, R.; Gall, D. Georgi Markov--death in a pellet. Med. Leg. J. 1980, 48, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Homeland Security. Biological Threats: A Resource Guide; U.S. Department of Homeland Security: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- FBIRicin Letter Investigation. Available online: https://www.fbi.gov/news/pressrel/press-releases/fbi-response-to-reports-of-suspicious-letters-received-at-mail-facilities (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Flade, F. The June 2018 Cologne Ricin Plot: A New Threshold in Jihadi Bio Terror. Available online: https://ctc.westpoint.edu/june-2018-cologne-ricin-plot-new-threshold-jihadi-bio-terror (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- German Prosecutors Arrest Man Over Alleged Ricin Attack Plot. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2018/jun/14/german-prosecutors-arrest-man-over-plot-to-launch-ricin-attack (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- nltimes.nl. Swedish Man Planned Poison Attack on Eurovision in Rotterdam in 2020. Available online: https://nltimes.nl/2025/07/22/swedish-man-planned-poison-attack-eurovision-rotterdam-2020 (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- US Department of Justice. Texas Man Sentenced for Possessing a Toxin for Use as a Weapon. 2018. Available online: https://www.justice.gov/usao-wdtx/pr/texas-man-sentenced-over-6-years-federal-prison-supplying-firearms-sinaloa-cartel (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Arianti, V. Biological Terrorism in Indonesia. Available online: https://thediplomat.com/2019/11/biological-terrorism-in-indonesia/ (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Li, Z.; Ma, B.; Gong, M.; Guo, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Xie, J. Sensitive Detection and Differentiation of Biologically Active Ricin and Abrin in Complex Matrices via Specific Neutralizing Antibody-Based Cytotoxicity Assay. Toxins 2024, 16, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscotti, F.; Bortolotti, M.; Fala, F.; Di Maro, A.; Bolognesi, A.; Polito, L. Ricin Toxicity to Intestinal Cells Leads to Multiple Cell Death Pathways Mediated by Oxidative Stress. Toxins 2025, 17, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramothloa, T.P.; Mkolo, N.M.; Motshudi, M.C.; Mphephu, M.M.; Makhafola, M.A.; Naidoo, C.M. Phytochemical Composition and Multifunctional Applications of Ricinus communis L.: Insights into Therapeutic, Pharmacological, and Industrial Potential. Molecules 2025, 30, 3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, H.; Wang, T.; Xiao, X.; Huang, B. The Traditional Uses, Nutrition, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology of the Medicinal Abrus Species: A Comprehensive Review. Chem. Biodivers. 2025, e00182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinkard, K.K.; Barr, J.R.; Kalb, S.R. Mass Spectrometric Detection and Differentiation of Enzymatically Active Abrin and Ricin Combined with a Novel Affinity Enrichment Technique. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2024, 37, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, R.; Lord, J. How ricin and Shiga toxin reach the cytosol. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 357, 19–40. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Song, T.; Zou, X.; Li, L.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, P. Gaps in forensic toxicological analysis: The veiled abrin. Toxicon 2024, 242, 107684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balint, G. Ricin: The toxic protein of castor oil plant. Toxicology 1974, 2, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, H.; Meier, M.A.R. Castor oil as a renewable resource for the chemical industry. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, P.; Amalnath, D. Rosary Pea Poisoning. Indian. J. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 21, 455–457. [Google Scholar]
- Hennigan, W.J. Pentagon Mail Quarantined After Traces of Deadly Poison Found on Envelopes. Available online: https://time.com/5412993/pentagon-mail-quarantined-after-traces-of-deadly-poison-found-on-envelopes (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Pilch, R. The Threat and Control of Ricin as a Weapon. Available online: https://nonproliferation.org/the-threat-and-control-of-ricin-as-a-weapon/ (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- DHS DHS’ 2025 Homeland Threat Assessment Indicates the Threat of Domestic and Foreign Terrorism in the Homeland Remains High. Available online: https://www.dhs.gov/archive/news/2024/10/02/dhs-2025-homeland-threat-assessment-indicates-threat-domestic-and-foreign-terrorism (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Audi, J.; Belson, M.; Patel, M.; Schier, J.; Osterloh, J. Ricin poisoning: A comprehensive review. JAMA 2005, 294, 2342–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsnes, S.; Pihl, A. Different biological properties of the two constituent peptide chains of ricin, a toxic protein inhibiting protein synthesis. Biochemistry 1973, 12, 3121–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, J.M.; Spooner, R.A. Ricin trafficking and cytotoxicity. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 6599–6606. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Qiu, J.; Yang, R.; Zhou, L. Rapid detection of abrin in foods with an up-converting phosphor technology-based lateral flow assay. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BioRender: Scientific Image and Illustration Software. Available online: https://BioRender.com/7yvr5l1 (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Sowa-Rogozinska, N.; Sominka, H.; Nowakowska-Golacka, J.; Sandvig, K.; Slominska-Wojewodzka, M. Intracellular Transport and Cytotoxicity of the Protein Toxin Ricin. Toxins 2019, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verollet, C.; Colombie, N.; Daubon, T.; Bourbon, H.M.; Wright, M.; Raynaud-Messina, B. Drosophila melanogaster gamma-TuRC is dispensable for targeting gamma-tubulin to the centrosome and microtubule nucleation. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.A.; Silva, P.N.; Pereira, A.C.; De Sousa, L.P.; Ferreira, P.C.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Kroon, E.G.; Ropert, C.; Bonjardim, C.A. The vaccinia virus-stimulated mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is required for virus multiplication. Biochem. J. 2004, 381, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Khade, P.K.; Sanbonmatsu, K.Y.; Joseph, S. Functional role of the sarcin-ricin loop of the 23S rRNA in the elongation cycle of protein synthesis. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 419, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.W.; Tang, Y.S.; Sze, S.Y.; Zhu, Z.N.; Wong, K.B.; Shaw, P.C. Crystal Structure of Ribosome-Inactivating Protein Ricin A Chain in Complex with the C-Terminal Peptide of the Ribosomal Stalk Protein P2. Toxins 2016, 8, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.C.; Henderson, T.D.; Stanker, L.H.; He, X.; Cheng, L.W. Abrin Toxicity and Bioavailability after Temperature and pH Treatment. Toxins 2017, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansia, H.; Bagaria, S.; Karande, A.A.; Ramakumar, S. Structural basis for neutralization of cytotoxic abrin by monoclonal antibody D6F10. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 1003–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słomińska-Wojewódzka, M.; Sandvig, K. Ricin and Ricin-Containing Immunotoxins: Insights into Intracellular Transport and Mechanism of action in Vitro. Antibodies 2013, 2, 236–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, P.R.; Reisler, R.B.; Lindsey, C.Y.; Guerena, F.; Rivard, R.; Clizbe, D.P.; Chambers, M.; Norris, S.; Smith, L.A. Safety and immunogenicity of ricin vaccine, RVEc, in a Phase 1 clinical trial. Vaccine 2015, 33, 7299–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, C.J.; Ehrbar, D.; Van Slyke, G.; Doering, J.; Didier, P.J.; Doyle-Meyers, L.; Donini, O.; Vitetta, E.S.; Mantis, N.J. Serum antibody profiling identifies vaccine-induced correlates of protection against aerosolized ricin toxin in rhesus macaques. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falach, R.; Sapoznikov, A.; Alcalay, R.; Aftalion, M.; Ehrlich, S.; Makovitzki, A.; Agami, A.; Mimran, A.; Rosner, A.; Sabo, T.; et al. Generation of Highly Efficient Equine-Derived Antibodies for Post-Exposure Treatment of Ricin Intoxications by Vaccination with Monomerized Ricin. Toxins 2018, 10, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequesne, L.; Dano, J.; Rouaix, A.; Kropp, C.; Plaisance, M.; Gelhaye, S.; Lequesne, M.L.; Piquet, P.; Avril, A.; Becher, F.; et al. A Monoclonal Antibody with a High Affinity for Ricin Isoforms D and E Provides Strong Protection against Ricin Poisoning. Toxins 2024, 16, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Ma, B.; Luo, L.; Guo, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Xie, J. Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody, mAb 10D8, Is an Effective Detoxicant against Abrin-a Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Toxins 2022, 14, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgens, D.W.; Chan, C.; Kane, A.J.; Weir, N.R.; Li, A.; Dubreuil, M.M.; Tsui, C.K.; Hess, G.T.; Lavertu, A.; Han, K.; et al. Retro-2 protects cells from ricin toxicity by inhibiting ASNA1-mediated ER targeting and insertion of tail-anchored proteins. Elife 2019, 8, e48434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phatak, P.; Nagar, D.P.; Saxena, N. Dose dependent acute toxicity of abrin in Balb/c mice after intraperitoneal administration. Toxicon 2019, 167, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.G.; Yin, J.; Chau, D.; Negrych, L.M.; Cherwonogrodzky, J.W. Humanization and characterization of an anti-ricin neutralization monoclonal antibody. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, O.; Sugendran, K.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Oxidative stress associated hepatic and renal toxicity induced by ricin in mice. Toxicon 2003, 41, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamor, M.; Gharbi, E.; Bouzid, S.; Chakroun-Walha, O.; Rekik, N. Ricin poisoning after oral ingestion of castor beans: A case report and literature review. Afr. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 10, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audi, J. Stability of Ricin. In Ricin and Other Plant Toxins; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal, P.; Kumar, O.; Kameswararao, M.; Ravindran, J.; Khan, M.; Sharma, S.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Prasad, G.B. Differential toxicity profile of ricin isoforms correlates with their glycosylation levels. Toxicology 2011, 282, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EuroBioTox; European Commission. Europejski program ustanawiania zatwierdzonych procedur wykrywania i identyfikacji toksyn biologicznych (EuroBioTox). Available online: https://www.eurobiotox.eu/index.html# (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Chen, H.Y.; Tran, H.; Foo, L.Y.; Sew, T.W.; Loke, W.K. Development and validation of an ELISA kit for the detection of ricin toxins from biological specimens and environmental samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5157–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.C.; Cheng, L.W.; He, X.; Merrill, P.; Hodge, D.; Stanker, L.H. A Monoclonal-Monoclonal Antibody Based Capture ELISA for Abrin. Toxins 2017, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, J. Time-Resolved Fluorescence Immunochromatographic Assay Developed Using Two Idiotypic Nanobodies for Rapid, Quantitative, and Simultaneous Detection of Aflatoxin and Zearalenone in Maize and Its Products. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11520–11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalb, S.R.; Barr, J.R. Mass spectrometric detection of ricin and its activity in food and clinical samples. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2037–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worbs, S.; Skiba, M.; Soderstrom, M.; Rapinoja, M.L.; Zeleny, R.; Russmann, H.; Schimmel, H.; Vanninen, P.; Fredriksson, S.A.; Dorner, B.G. Characterization of Ricin and R. communis Agglutinin Reference Materials. Toxins 2015, 7, 4906–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Tang, J.; Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Guo, L.; Xie, J. Identification and quantification of ricin in biomedical samples by magnetic immunocapture enrichment and liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5147–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zendong, Z.; McCarron, P.; Herrenknecht, C.; Sibat, M.; Amzil, Z.; Cole, R.B.; Hess, P. High resolution mass spectrometry for quantitative analysis and untargeted screening of algal toxins in mussels and passive samplers. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1416, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.L.H.; T Maher, S. Portable Instrumentation for Ambient Ionization and Miniature Mass Spectrometers. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2024, 17, 69–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ai, J.; Cai, L.; Yan, Y.; Wang, B.; Ma, H.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Huo, X. Deep learning enabled miniature mass spectrometer for rapid qualitative and quantitative analysis of pesticides on vegetable surfaces. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 180, 114000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Cooks, R. Miniature mass spectrometers for field detection of chemical and biological threats. Trends Anal. Chem. (TrAC) 2022, 148, 116536. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Lv, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Kang, L.; Xin, W. Establishment and Comparison of Detection Methods for Ricin and Abrin Based on Their Depurination Activities. Toxins 2025, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, L. Determination of Patulin in Apple Juice and Apple-Derived Products Using a Robotic Sample Preparation System and LC-APCI-MS/MS. Toxins 2024, 16, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Taylor, K.; Gu, H.; Santockyte, R.; Wang, X.T.; McCarty, J.; Adelakun, O.; Zhang, Y.J.; Pillutla, R.; Zeng, J. Antipeptide Immunocapture with In-Sample Calibration Curve Strategy for Sensitive and Robust LC-MS/MS Bioanalysis of Clinical Protein Biomarkers in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tumor Tissues. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 14713–14722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetter, L.; Richards, J.; Daniel, J.; Roon, L.; Rowland, T.J.; Bonham, A.J. Electrochemical aptamer scaffold biosensors for detection of botulism and ricin toxins. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15137–15140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Hu, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wan, W.; Jin, Z.; Li, Y.; Xin, W.; Kang, L.; et al. A Self-Driven Microfluidic Chip for Ricin and Abrin Detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Guo, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; et al. Label-free differentiation and quantification of ricin, abrin from their agglutinin biotoxins by surface plasmon resonance. Talanta 2022, 238, 122860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, T.H.; Thangavel, B.; Sharipov, M.; Chen, K.; Shin, J.H. Smartphone-Based Portable Bio-Chemical Sensors: Exploring Recent Advancements. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, E.A.; He, L.; Warriner, K.; Labuza, T.P.; Sreevatsan, S. A single DNA aptamer functions as a biosensor for ricin. Analyst 2011, 136, 3884–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Hu, W.; Hua, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, T.; Hu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhu, A. A dual-fluorescence analytical strategy using nano fiber probe mediated optofluidic dual-laser biosensor for simultaneous and sensitive detection of ricin and abrin. Talanta 2025, 298, 128843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tong, Z.; Mu, X.; Liu, B.; Du, B.; Liu, Z.; Gao, C. Detection of Abrin by Electrochemiluminescence Biosensor Based on Screen Printed Electrode. Sensors 2018, 18, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, J.G.; Prentice, K.W.; Morse, S.A.; Carter, A.J.; Datta, S.; Drumgoole, R.; Gargis, S.R.; Griffin-Thomas, L.; Hastings, R.; Masri, H.P.; et al. Comprehensive laboratory evaluation of a specific lateral flow assay for the presumptive identification of abrin in suspicious white powders and environmental samples. Biosecurity Bioterrorism: Biodefense Strat. Pr. Sci. 2014, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, R.; Dindal, A.; Willenberg, Z.; Riggs, K. Environmental Technology Verification Report. Available online: https://archive.epa.gov/nrmrl/archive-etv/web/pdf/01_vr_biothreat.pdf (accessed on 19 September 2025).
- WHO Public Health Response to Biological and Chemical Weapons: WHO Guidance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/public-health-response-to-biological-and-chemical-weapons-who-guidance-(2004) (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Bevilacqua, V.L.; Nilles, J.M.; Rice, J.S.; Connell, T.R.; Schenning, A.M.; Reilly, L.M.; Durst, H.D. Ricin activity assay by direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry detection of adenine release. Anal Chem 2010, 82, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EuroBioTox. European Programme for the Establishment of Validated Procedures for the Detection and Identification of Biological Toxins. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/article/id/446825-expert-institutions-network-to-reduce-threat-of-bioterrorism (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Yue, W.-Q.; Tan, Z.; Li, X.-P.; Liu, F.-F.; Wang, C. Micro/nanofluidic technologies for efficient isolation and detection of circulating tumor cells. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 117, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardy-Fontan, S.; Brieudes, V.; Lalere, B.; Candido, P.; Couturier, G.; Budzinski, H.; Lavison-Bompard, G. For more reliable measurements of pharmaceuticals in the environment: Overall measurement uncertainty estimation, QA/QC implementation and metrological considerations. A case study on the Seine River. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 77, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, K. Natural Enemies. Available online: https://www.cbp.gov/frontline/natural-enemies-how-cbp-battles-bioterrorism-and-biohazards (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- DHS First Responder Technologies. Available online: https://www.dhs.gov/archive/science-and-technology/first-responder-technologies (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Paramedic Standing Orders and Policies for Chemical Terrorism, Bioterrorism, Radiation Injury and Pandemic Illness. Available online: https://dhss.delaware.gov/wp-content/uploads/sites/10/dph/pdf/2018ChemicalBioterrorismRadiationProtocolsigned2023.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- MODEX; E Field Exercises for Water-Related, Forest Firefighting and CBRN "Cycle 12". Available online: https://civil-protection-knowledge-network.europa.eu/projects/field-exercises-water-related-forest-firefighting-and-cbrn-cycle-12 (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Interpol. Proficiency Testing; Interpol: Lyon, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. CBRN Exercises; EC DG HOME: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Accessibility | Plants producing ricin and abrin are widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions and can be cultivated with minimal expertise. |
| Ease of extraction | Simple mechanical or aqueous extraction methods can yield crude toxins with high biological activity [24]. |
| Lack of detection infrastructure | Many security screening systems are not equipped to detect biotoxins unless specifically targeted. |
| Stability | These toxins remain stable under various environmental conditions, enhancing their persistence and effectiveness during dissemination. |
| Detection Method | Sensitivity | Selectivity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | 0.09–0.28 ng/mL in PBS/blood | Antibody-dependent; potential cross-reactivity (e.g., RCA120) | [42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75] |
| ECL-IA/TRF-IA | femtomolar–sub-ng/mL | High * | [45] |
| LC-MS/MS | <0.1 ng/mL after immuno/lectin capture ** | Excellent (confirmatory) | [42,48,49,50] |
| Biosensors | 10 pg/mL–0.1 ng/mL depending on platform | Recognition-element dependent | [52,53,54,55,56,57] |
| LFAs | 1–10 ng/mL | Moderate; antibody-based | [58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zajaczkowski, W.; Bojarska, E.; Furtak, E.; Bijak, M.; Szelenberger, R.; Niemcewicz, M.; Podogrocki, M.; Stela, M.; Cichon, N. Ricin and Abrin in Biosecurity: Detection Technologies and Strategic Responses. Toxins 2025, 17, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100494
Zajaczkowski W, Bojarska E, Furtak E, Bijak M, Szelenberger R, Niemcewicz M, Podogrocki M, Stela M, Cichon N. Ricin and Abrin in Biosecurity: Detection Technologies and Strategic Responses. Toxins. 2025; 17(10):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100494
Chicago/Turabian StyleZajaczkowski, Wojciech, Ewelina Bojarska, Elwira Furtak, Michal Bijak, Rafal Szelenberger, Marcin Niemcewicz, Marcin Podogrocki, Maksymilian Stela, and Natalia Cichon. 2025. "Ricin and Abrin in Biosecurity: Detection Technologies and Strategic Responses" Toxins 17, no. 10: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100494
APA StyleZajaczkowski, W., Bojarska, E., Furtak, E., Bijak, M., Szelenberger, R., Niemcewicz, M., Podogrocki, M., Stela, M., & Cichon, N. (2025). Ricin and Abrin in Biosecurity: Detection Technologies and Strategic Responses. Toxins, 17(10), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100494





