Clostridioides difficile Toxins: Host Cell Interactions and Their Role in Disease Pathogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of C. difficile’s Toxins
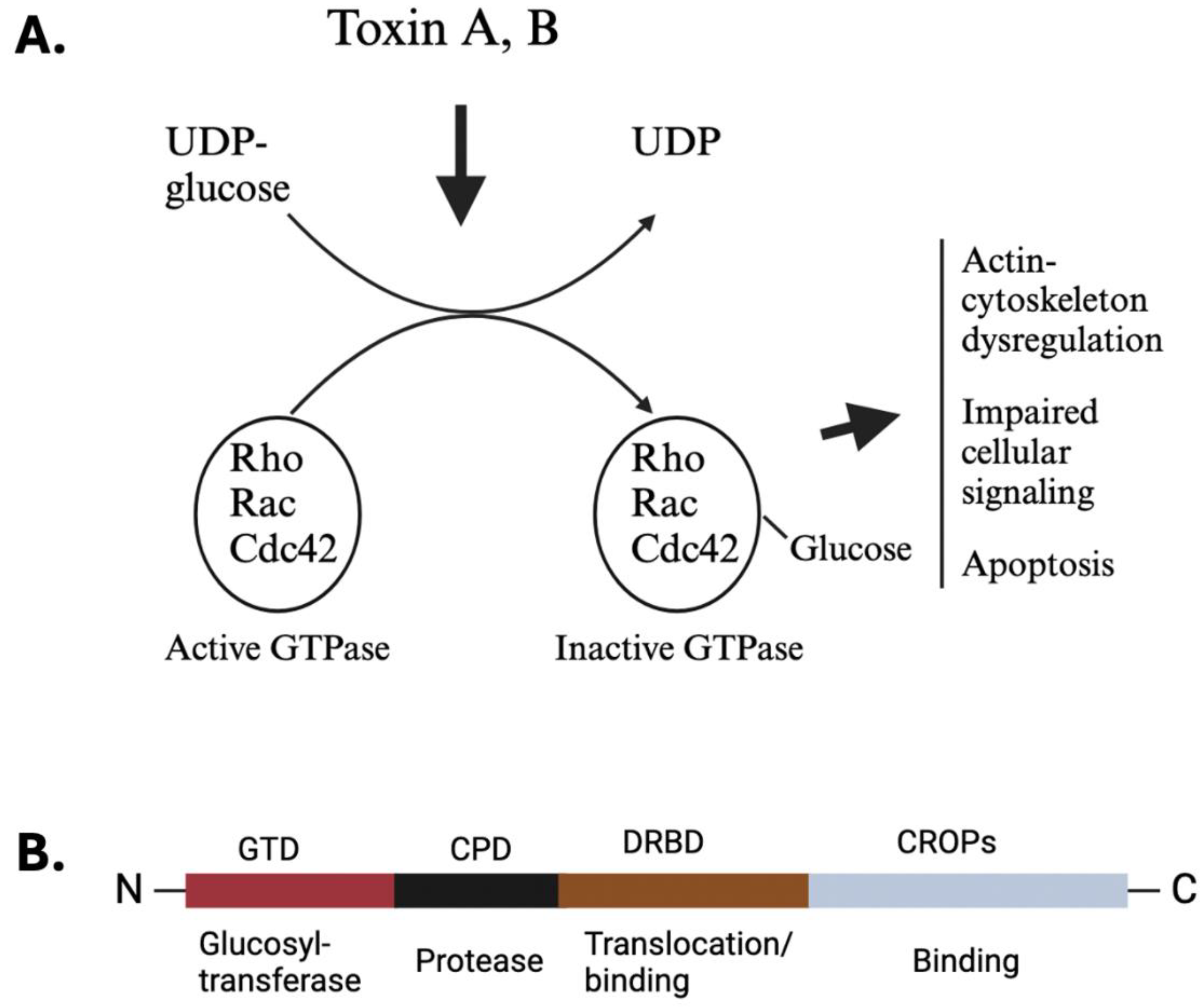
2.1. Toxin Structure
2.2. Regulation of Toxin Production
2.3. Toxin Receptors and Toxin’s Effect on Disease Pathogenesis
2.4. Role of Toxin-Mediated Inflammation in CDI Outcomes
3. Binary Toxin: C. difficile Transferase Toxin (CDT)
3.1. Overview of CDT
3.2. Structure of CDT
3.3. Receptors and Effect of CDT on Host Cells
4. Toxin-Based Strategies for Treating and Preventing C. difficile Infection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lessa, F.C.; Winston, L.G.; McDonald, L.C. Burden of Clostridium difficile Infection in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2369–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guh, A.Y.; Mu, Y.; Winston, L.G.; Johnston, H.; Olson, D.; Farley, M.M.; Wilson, L.E.; Holzbauer, S.M.; Phipps, E.C.; Dumyati, G.K.; et al. Trends in U.S. Burden of Clostridioides Difficile Infection and Outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razavi, B.; Apisarnthanarak, A.; Mundy, L.M. Clostridium difficile: Emergence of Hypervirulence and Fluoroquinolone Resistance. Infection 2007, 35, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheknis, A.; Johnson, S.; Chesnel, L.; Petrella, L.; Sambol, S.; Dale, S.E.; Nary, J.; Sears, P.; Citron, D.M.; Goldstein, E.J.C.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Clostridioides (Clostridium) difficile Strains Recovered from Clinical Trials in the US, Canada and Europe from 2006–2009 to 2012–2015. Anaerobe 2018, 53, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, T.; Li, W.; Yang, L.-L.; Yang, S.-M.; He, Q.; He, H.-Y.; Sun, D.-L. Systematic Review of Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Clostridioides Difficile Infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 926482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamo, Z.; Azrad, M.; Nitzan, O.; Peretz, A. Characterization of the Immune Response during Infection Caused by Clostridioides difficile. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.H.; Kim, Y.S. Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection: Risk Factors, Treatment, and Prevention. Gut Liver 2019, 13, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, L.; Rees, W.D.; Wong, M.Q.; Peters, H.; Levings, M.K.; Steiner, T.S. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Recurrent Clostridioides Difficile Infection Enhances Adaptive Immunity to C. difficile Toxin B. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2155–2158.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupnik, M.; Wilcox, M.H.; Gerding, D.N. Clostridium difficile Infection: New Developments in Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.; Martins, D.; Henriques, A.O. Clostridioides Difficile Sporulation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2024, 1435, 273–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.P.; Kyne, L. The Host Immune Response to Clostridium difficile. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). European Surveillance of Clostridium difficile Infections; Surveillance Protocol Version 2.2; ECDC: Solna, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa, M.; Baharav, N.; Melzer, E.; Regev-Yochay, G.; Yahav, D. Screening for Asymptomatic Clostridioides Difficile Carriage Among Hospitalized Patients: A Narrative Review. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2023, 12, 2223–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Khanna, S. Community-Acquired Clostridium difficile Infection: An Increasing Public Health Threat. Infect. Drug Resist. 2014, 7, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, A.C.A.; Magalhães, R.J.S.; Tatem, A.J.; Paterson, D.L.; Riley, T.V. Clostridium difficile PCR Ribotype 027: Assessing the Risks of Further Worldwide Spread. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janezic, S.; Rupnik, M. Genomic Diversity of Clostridium difficile Strains. Res. Microbiol. 2015, 166, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, R.; Lacy, D.B. The Role of Toxins in Clostridium difficile Infection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktories, K.; Papatheodorou, P.; Schwan, C. Binary Clostridium difficile Toxin (CDT)—A Virulence Factor Disturbing the Cytoskeleton. Anaerobe 2018, 53, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktories, K.; Schwan, C.; Jank, T. Clostridium difficile Toxin Biology. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 281–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orrell, K.E.; Melnyk, R.A. Large Clostridial Toxins: Mechanisms and Roles in Disease. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e0006421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. The Role of Rho GTPases in Toxicity of Clostridium difficile Toxins. Toxins 2015, 7, 5254–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerding, D.N.; Johnson, S.; Rupnik, M.; Aktories, K. Clostridium difficile Binary Toxin CDT: Mechanism, Epidemiology, and Potential Clinical Importance. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, C.S.; Costa, D.V.S.; Lima, B.B.; Leitäo, R.F.C.; Freire, G.E.; Silva, G.F.M.; Pacífico, D.M.; Abreu, J.G.; Brito, G.A.C. Clostridioides Difficile Toxin A-Induced Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Inhibition Is Mediated by Rac1 Glucosylation. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.B.; Carter, R.A.; Ling, L.; Leiner, I.; Taur, Y.; Kamboj, M.; Dubberke, E.R.; Xavier, J.; Pamer, E.G. Pathogenicity Locus, Core Genome, and Accessory Gene Contributions to Clostridium difficile Virulence. mBio 2017, 8, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monot, M.; Eckert, C.; Lemire, A.; Hamiot, A.; Dubois, T.; Tessier, C.; Dumoulard, B.; Hamel, B.; Petit, A.; Lalande, V.; et al. Clostridium difficile: New Insights into the Evolution of the Pathogenicity Locus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Sorg, J.A.; Sun, X. Clostridioides Difficile Biology: Sporulation, Germination, and Corresponding Therapies for C. difficile Infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, R.; Ngo, P.A.; Martínez-Sánchez, L.D.; Neurath, M.F.; López-Posadas, R. Rho GTPases as Key Molecular Players within Intestinal Mucosa and GI Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genisyuerek, S.; Papatheodorou, P.; Guttenberg, G.; Schubert, R.; Benz, R.; Aktories, K. Structural Determinants for Membrane Insertion, Pore Formation and Translocation of Clostridium difficile Toxin B. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 79, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, P.; Tian, S.; Zeng, J.; Perry, K.; Dong, M.; Jin, R. Structural Basis for Selective Modification of Rho and Ras GTPases by Clostridioides Difficile Toxin B. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Liu, Z.; Perry, K.; Jin, R. Structure of the Glucosyltransferase Domain of TcdA in Complex with RhoA Provides Insights into Substrate Recognition. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.M.; Frisbee, A.L.; Leslie, J.L.; Buonomo, E.L.; Cowardin, C.A.; Ma, J.Z.; Simpson, M.E.; Scully, K.W.; Abhyankar, M.M.; Petri, W.A.J. Colitis-Induced Th17 Cells Increase the Risk for Severe Subsequent Clostridium difficile Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 756–765.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, M.C.; McKenney, P.T.; Pamer, E.G. Clostridium difficile Colitis: Pathogenesis and Host Defence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Yada, S.; Liu, M.Z.; Kamada, N.; Muñoz-Planillo, R.; Do, N.; Núñez, G.; Inohara, N. Interleukin-22 Regulates the Complement System to Promote Resistance against Pathobionts after Pathogen-Induced Intestinal Damage. Immunity 2014, 41, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Lam, K.-H.; Liu, Z.; Mindlin, F.A.; Chen, B.; Gutierrez, C.B.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hamza, T.; Feng, H.; et al. Structure of the Full-Length Clostridium difficile Toxin B. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminzadeh, A.; Larsen, C.E.; Boesen, T.; Jørgensen, R. High-Resolution Structure of Native Toxin A from Clostridioides Difficile. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e53597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Basak, S.; Chen, P.; Zhang, C.; Perry, K.; Tian, S.; Yu, C.; Dong, M.; Huang, L.; Bowen, M.E.; et al. Structure and Conformational Dynamics of Clostridioides Difficile Toxin A. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, e202201383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingle, T.; Wee, S.; Mulvey, G.L.; Greco, A.; Kitova, E.N.; Sun, J.; Lin, S.; Klassen, J.S.; Palcic, M.M.; Ng, K.K.S.; et al. Functional Properties of the Carboxy-Terminal Host Cell-Binding Domains of the Two Toxins, TcdA and TcdB, Expressed by Clostridium difficile. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govind, R.; Dupuy, B. Secretion of Clostridium difficile Toxins A and B Requires the Holin-like Protein TcdE. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.S.; Wee, B.Y.; Song, K.P. Evidence for Holin Function of tcdE Gene in the Pathogenicity of Clostridium difficile. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Tian, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Robinson-McCarthy, L.; Miyashita, S.-I.; Breault, D.T.; Gerhard, R.; Oottamasathien, S.; Whelan, S.P.J.; et al. Sulfated Glycosaminoglycans and Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor Contribute to Clostridium difficile Toxin A Entry into Cells. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares da Costa, D.; Reis, R.L.; Pashkuleva, I. Sulfation of Glycosaminoglycans and Its Implications in Human Health and Disorders. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöttelndreier, D.; Langejürgen, A.; Lindner, R.; Genth, H. Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein-1 (LRP1) Is Involved in the Uptake of Clostridioides Difficile Toxin A and Serves as an Internalizing Receptor. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 565465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothoulakis, C.; Gilbert, R.J.; Cladaras, C.; Castagliuolo, I.; Semenza, G.; Hitti, Y.; Montcrief, J.S.; Linevsky, J.; Kelly, C.P.; Nikulasson, S.; et al. Rabbit Sucrase-Isomaltase Contains a Functional Intestinal Receptor for Clostridium difficile Toxin A. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, X.; Kim, H.; Moyer, M.P.; Pothoulakis, C.; LaMont, J.T. Gp96 Is a Human Colonocyte Plasma Membrane Binding Protein for Clostridium difficile Toxin A. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 2862–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, P.; Zhang, H.; Cai, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; He, R.; Li, C.; Guo, S.; Li, S.; et al. Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan 4 Functions as the Cellular Receptor for Clostridium difficile Toxin B. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zeng, J.; Liu, Z.; Thaker, H.; Wang, S.; Tian, S.; Zhang, J.; Tao, L.; Gutierrez, C.B.; Xing, L.; et al. Structural Basis for CSPG4 as a Receptor for TcdB and a Therapeutic Target in Clostridioides difficile Infection. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöttelndreier, D.; Seeger, K.; Grassl, G.A.; Winny, M.R.; Lindner, R.; Genth, H. Expression and (Lacking) Internalization of the Cell Surface Receptors of Clostridioides difficile Toxin B. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFrance, M.E.; Farrow, M.A.; Chandrasekaran, R.; Sheng, J.; Rubin, D.H.; Lacy, D.B. Identification of an Epithelial Cell Receptor Responsible for Clostridium difficile TcdB-Induced Cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7073–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Zhang, J.; Meraner, P.; Tovaglieri, A.; Wu, X.; Gerhard, R.; Zhang, X.; Stallcup, W.B.; Miao, J.; He, X.; et al. Frizzled Proteins Are Colonic Epithelial Receptors for C. difficile Toxin B. Nature 2016, 538, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, L.; Zhan, X.; Zhou, Y.; He, L.; Li, D.; Jin, D.; et al. TFPI Is a Colonic Crypt Receptor for TcdB from Hypervirulent Clade 2 C. difficile. Cell 2022, 185, 980–994.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Xiong, X.; Zeng, J.; Wang, S.; Tremblay, B.J.-M.; Chen, P.; Chen, B.; Liu, M.; Chen, P.; Sheng, K.; et al. Identification of TFPI as a Receptor Reveals Recombination-Driven Receptor Switching in Clostridioides difficile Toxin B Variants. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.P.; Chakravorty, A.; Pham Nguyen, T.A.; Mileto, S.; Schreiber, F.; Li, L.; Howarth, P.; Clare, S.; Cunningham, B.; Sambol, S.P.; et al. Defining the Roles of TcdA and TcdB in Localized Gastrointestinal Disease, Systemic Organ Damage, and the Host Response during Clostridium difficile Infections. mBio 2015, 6, e00551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.J.; Ketley, J.M.; Haslam, S.C.; Stephen, J.; Burdon, D.W.; Candy, D.C.; Daniel, R. Effect of Toxin A and B of Clostridium difficile on Rabbit Ileum and Colon. Gut 1986, 27, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyerly, D.M.; Lockwood, D.E.; Richardson, S.H.; Wilkins, T.D. Biological Activities of Toxins A and B of Clostridium difficile. Infect. Immun. 1982, 35, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyerly, D.M.; Saum, K.E.; MacDonald, D.K.; Wilkins, T.D. Effects of Clostridium difficile Toxins given Intragastrically to Animals. Infect. Immun. 1985, 47, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drudy, D.; Fanning, S.; Kyne, L. Toxin A-Negative, Toxin B-Positive Clostridium difficile. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 11, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Olarte, E.; Löw, P.; Freer, E.; Norlin, T.; Weidmann, M.; von Eichel-Streiber, C.; Thelestam, M. A Novel Cytotoxin from Clostridium difficile Serogroup F Is a Functional Hybrid between Two Other Large Clostridial Cytotoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 11046–11052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savidge, T.C.; Pan, W.-H.; Newman, P.; O’brien, M.; Anton, P.M.; Pothoulakis, C. Clostridium difficile Toxin B Is an Inflammatory Enterotoxin in Human Intestine. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riegler, M.; Sedivy, R.; Pothoulakis, C.; Hamilton, G.; Zacherl, J.; Bischof, G.; Cosentini, E.; Feil, W.; Schiessel, R.; LaMont, J.T. Clostridium difficile Toxin B Is More Potent than Toxin A in Damaging Human Colonic Epithelium in Vitro. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 2004–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, M.H.; Gerding, D.N.; Poxton, I.R.; Kelly, C.; Nathan, R.; Birch, T.; Cornely, O.A.; Rahav, G.; Bouza, E.; Lee, C.; et al. Bezlotoxumab for Prevention of Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Gerding, D.N. Bezlotoxumab. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothoulakis, C.; Karmeli, F.; Kelly, C.P.; Eliakim, R.; Joshi, M.A.; O’Keane, C.J.; Castagliuolo, I.; LaMont, J.T.; Rachmilewitz, D. Ketotifen Inhibits Clostridium difficile Toxin A-Induced Enteritis in Rat Ileum. Gastroenterology 1993, 105, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fachi, J.L.; Sécca, C.; Rodrigues, P.B.; de Mato, F.C.P.; Di Luccia, B.; Felipe, J.d.S.; Pral, L.P.; Rungue, M.; Rocha, V.d.M.; Sato, F.T.; et al. Acetate Coordinates Neutrophil and ILC3 Responses against C. difficile through FFAR2. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarchum, I.; Liu, M.; Shi, C.; Equinda, M.; Pamer, E.G. Critical Role for MyD88-Mediated Neutrophil Recruitment during Clostridium difficile Colitis. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 2989–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Greenberg, A.; Stone, C.D. Outcomes of Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized Leukemia Patients: A Nationwide Analysis. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2015, 36, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.M.; Marini, B.L.; Frame, D.; Aronoff, D.M.; Nagel, J.L. Risk Factors for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2014, 16, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.P.; Becker, S.; Linevsky, J.K.; Joshi, M.A.; O’Keane, J.C.; Dickey, B.F.; LaMont, J.T.; Pothoulakis, C. Neutrophil Recruitment in Clostridium difficile Toxin A Enteritis in the Rabbit. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonomo, E.L.; Madan, R.; Pramoonjago, P.; Li, L.; Okusa, M.D.; Petri, W.A. Role of Interleukin 23 Signaling in Clostridium difficile Colitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manion, J.; Musser, M.A.; Kuziel, G.A.; Liu, M.; Shepherd, A.; Wang, S.; Lee, P.-G.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Marreddy, R.K.R.; et al. C. difficile Intoxicates Neurons and Pericytes to Drive Neurogenic Inflammation. Nature 2023, 622, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Huh, Y.; Ji, R.-R. Roles of Inflammation, Neurogenic Inflammation, and Neuroinflammation in Pain. J. Anesth. 2019, 33, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, H.; Aktories, K.; Popoff, M.R.; Stiles, B.G. Binary Bacterial Toxins: Biochemistry, Biology, and Applications of Common Clostridium and Bacillus Proteins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 373–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülke, I.; Pfeifer, G.; Liese, J.; Fritz, M.; Hofmann, F.; Aktories, K.; Barth, H. Characterization of the Enzymatic Component of the ADP-Ribosyltransferase Toxin CDTa from Clostridium difficile. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 6004–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Craig, J.A.; Putnam, C.D.; Carozzi, N.B.; Tainer, J.A. Evolution and Mechanism from Structures of an ADP-Ribosylating Toxin and NAD Complex. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1999, 6, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmasi, S.; Czulkies, B.A.; Schorch, B.; Veit, A.; Aktories, K.; Papatheodorou, P. Interaction of the Clostridium difficile Binary Toxin CDT and Its Host Cell Receptor, Lipolysis-Stimulated Lipoprotein Receptor (LSR). J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 14031–14044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesli, S.; Javorschi, S.; Bérard, A.M.; Landry, M.; Priddle, H.; Kivlichan, D.; Smith, A.J.H.; Yen, F.T.; Bihain, B.E.; Darmon, M. Distribution of the Lipolysis Stimulated Receptor in Adult and Embryonic Murine Tissues and Lethality of LSR-/- Embryos at 12.5 to 14.5 Days of Gestation. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 3103–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, T.; Tokuda, S.; Kitajiri, S.; Masuda, S.; Nakamura, H.; Oda, Y.; Furuse, M. Analysis of the “angulin” Proteins LSR, ILDR1 and ILDR2–Tricellulin Recruitment, Epithelial Barrier Function and Implication in Deafness Pathogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, F.T.; Mann, C.J.; Guermani, L.M.; Hannouche, N.F.; Hubert, N.; Hornick, C.A.; Bordeau, V.N.; Agnani, G.; Bihain, B.E. Identification of a Lipolysis-Stimulated Receptor That Is Distinct from the LDL Receptor and the LDL Receptor-Related Protein. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, S.; Oda, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Ikenouchi, J.; Higashi, T.; Akashi, M.; Nishi, E.; Furuse, M. LSR Defines Cell Corners for Tricellular Tight Junction Formation in Epithelial Cells. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.A.T.; Collier, R.J. Anthrax Toxin: Receptor Binding, Internalization, Pore Formation, and Translocation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 243–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, K.; Langer, S.; Kaiser, E.; Osseforth, C.; Michaelis, J.; Popoff, M.R.; Schwan, C.; Aktories, K.; Kahlert, V.; Malesevic, M.; et al. Cyclophilin-Facilitated Membrane Translocation as Pharmacological Target to Prevent Intoxication of Mammalian Cells by Binary Clostridial Actin ADP-Ribosylated Toxins. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 1224–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, G.; Leemhuis, J.; Tiemann, D.; Meyer, D.K.; Aktories, K.; Barth, H. The Host Cell Chaperone Hsp90 Is Essential for Translocation of the Binary Clostridium Botulinum C2 Toxin into the Cytosol. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 32266–32274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nölke, T.; Schwan, C.; Lehmann, F.; Østevold, K.; Pertz, O.; Aktories, K. Septins Guide Microtubule Protrusions Induced by Actin-Depolymerizing Toxins like Clostridium difficile Transferase (CDT). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7870–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwan, C.; Stecher, B.; Tzivelekidis, T.; van Ham, M.; Rohde, M.; Hardt, W.-D.; Wehland, J.; Aktories, K. Clostridium difficile Toxin CDT Induces Formation of Microtubule-Based Protrusions and Increases Adherence of Bacteria. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowardin, C.A.; Buonomo, E.L.; Saleh, M.M.; Wilson, M.G.; Burgess, S.L.; Kuehne, S.A.; Schwan, C.; Eichhoff, A.M.; Koch-Nolte, F.; Lyras, D.; et al. The Binary Toxin CDT Enhances Clostridium difficile Virulence by Suppressing Protective Colonic Eosinophilia. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonomo, E.L.; Cowardin, C.A.; Wilson, M.G.; Saleh, M.M.; Pramoonjago, P.; Petri, W.A.J. Microbiota-Regulated IL-25 Increases Eosinophil Number to Provide Protection during Clostridium difficile Infection. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.; Lavergne, V.; Skinner, A.M.; Gonzales-Luna, A.J.; Garey, K.W.; Kelly, C.P.; Wilcox, M.H. Clinical Practice Guideline by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA): 2021 Focused Update Guidelines on Management of Clostridioides Difficile Infection in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, L.C.; Gerding, D.N.; Johnson, S.; Bakken, J.S.; Carroll, K.C.; Coffin, S.E.; Dubberke, E.R.; Garey, K.W.; Gould, C.V.; Kelly, C.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Clostridium difficile Infection in Adults and Children: 2017 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, e1–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.F.; Lyerly, D.M.; Hill, J.E.; Monath, T.P. Evaluation of Formalin-Inactivated Clostridium difficile Vaccines Administered by Parenteral and Mucosal Routes of Immunization in Hamsters. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 4619–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babcock, G.J.; Broering, T.J.; Hernandez, H.J.; Mandell, R.B.; Donahue, K.; Boatright, N.; Stack, A.M.; Lowy, I.; Graziano, R.; Molrine, D.; et al. Human Monoclonal Antibodies Directed against Toxins A and B Prevent Clostridium difficile-Induced Mortality in Hamsters. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6339–6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kink, J.A.; Williams, J.A. Antibodies to Recombinant Clostridium difficile Toxins A and B Are an Effective Treatment and Prevent Relapse of C. difficile-Associated Disease in a Hamster Model of Infection. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 2018–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leav, B.A.; Blair, B.; Leney, M.; Knauber, M.; Reilly, C.; Lowy, I.; Gerding, D.N.; Kelly, C.P.; Katchar, K.; Baxter, R.; et al. Serum Anti-Toxin B Antibody Correlates with Protection from Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI). Vaccine 2010, 28, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyne, L.; Warny, M.; Qamar, A.; Kelly, C.P. Association between Antibody Response to Toxin A and Protection against Recurrent Clostridium difficile Diarrhoea. Lancet 2001, 357, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksi, J.; Anttila, V.-J.; Mattila, E. Treatment of Clostridioides (Clostridium) difficile Infection. Ann. Med. 2020, 52, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thandavaram, A.; Channar, A.; Purohit, A.; Shrestha, B.; Patel, D.; Shah, H.; Hanna, K.; Kaur, H.; Alazzeh, M.S.; Mohammed, L. The Efficacy of Bezlotoxumab in the Prevention of Recurrent Clostridium difficile: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e27979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remich, S.; Kitchin, N.; Peterson, J.; Li, P.; Pride, M.W.; Brock, L.; Anderson, A.S.; Gruber, W.C.; Jansen, K.U.; Lockhart, S.P.; et al. A Phase 2 Extension Study Evaluating the Immunogenicity, Safety, and Tolerability of 3 or 4 Doses of a Clostridioides Difficile Vaccine in Healthy US Adults Aged 65 to 85 Years. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 229, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raeisi, H.; Azimirad, M.; Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H.; Zarnani, A.-H.; Abdolalizadeh, J.; Yadegar, A.; Zali, M.R. Development and Characterization of Phage Display-Derived Anti-Toxin Antibodies Neutralizing TcdA and TcdB of Clostridioides Difficile. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0531022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieglitz, F.; Gerhard, R.; Hönig, R.; Giehl, K.; Pich, A. TcdB of Clostridioides Difficile Mediates RAS-Dependent Necrosis in Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alam, M.Z.; Madan, R. Clostridioides difficile Toxins: Host Cell Interactions and Their Role in Disease Pathogenesis. Toxins 2024, 16, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16060241
Alam MZ, Madan R. Clostridioides difficile Toxins: Host Cell Interactions and Their Role in Disease Pathogenesis. Toxins. 2024; 16(6):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16060241
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlam, Md Zahidul, and Rajat Madan. 2024. "Clostridioides difficile Toxins: Host Cell Interactions and Their Role in Disease Pathogenesis" Toxins 16, no. 6: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16060241
APA StyleAlam, M. Z., & Madan, R. (2024). Clostridioides difficile Toxins: Host Cell Interactions and Their Role in Disease Pathogenesis. Toxins, 16(6), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16060241




