Intravesical Botulinum Toxin Injection Plus Hydrodistention Is More Effective in Patients with Bladder Pain-Predominant Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Subjective and Objective Baseline Characteristics of Patients with NHIC
2.2. The Baseline Urine Biomarkers of Patients with NHIC
2.3. The Changes of Subjective and Objective Characteristics of Patients with NHIC after Intravesical Botulinum Toxin A Injection Treatment
2.4. An Analysis of the Factors Associated with Satisfactory Outcomes after Intravesical BoNT-A Injection Treatment in Patients with NHIC
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Patients
5.2. Assessments Questionnaires and Examination
5.3. Collection, Measurement, and Analysis of Inflammatory Cytokines and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Urine Biomarker Specimens
5.4. Videourodynamic Study Examination
5.5. Procedure of Intravesical Botulinum Toxin A Injection
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adelugba, I.; Siddiqui, S.; Aziz, A.; De, E.J.; Wolff, G. Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome: What Today’s Urologist Should Know. Curr. Bladder Dysfunct. Rep. 2023, 18, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, J.Q.; Erickson, D.R.; Varela, N.P.; Lai, H.H. Diagnosis and Treatment of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. J. Urol. 2022, 208, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anger, J.T.; Dallas, K.B.; Bresee, C.; De Hoedt, A.M.; Barbour, K.E.; Hoggatt, K.J.; Goodman, M.T.; Kim, J.; Freedland, S.J. National prevalence of IC/BPS in women and men utilizing veterans health administration data. Front. Pain Res. 2022, 3, 925834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, Y.; Luo, Y.; Hanno, P.M.; Maeda, D.; Homma, Y. Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: The evolving landscape, animal models and future perspectives. Int. J. Urol. 2020, 27, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Tomoe, H.; Furuta, A.; Ueda, T.; Maeda, D.; Lin, A.T.; Kuo, H.C.; Lee, M.H.; Oh, S.J. Clinical guidelines for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Int. J. Urol. 2020, 27, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majima, T.; Sassa, N. Organ cross-sensitization mechanisms in chronic diseases related to the genitourinary tract. J. Smooth Muscle Res. 2021, 57, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, M.; Dias, N.; Peng, Y.; Spitznagle, T.; Harris-Hayes, M.; Lai, H.H.; Zhang, Y. Gamma-band Inter-muscular Connectivity is Associated with Increased Neural Drive to Pelvic Floor Muscles in Women with Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. J. Urol. 2023, 210, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Nackley, A.; Huh, Y.; Terrando, N.; Maixner, W. Neuroinflammation and central sensitization in chronic and widespread pain. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbari, B.; Jabbari, B. Spence. In Botulinum Toxin Treatment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. FDA Approves Botox to Treat Overactive Bladder. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm336101.htm (accessed on 14 January 2024).
- Akiyama, Y. Update on the pathophysiology of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Curr. Bladder Dysfunct. Rep. 2020, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-H.; Jhang, J.-F.; Kuo, H.-C. The clinical application of intravesical botulinum toxin A injection in patients with overactive bladder and interstitial cystitis. Tzu-Chi Med. J. 2023, 35, 31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simpson, L.L. Kinetic studies on the interaction between botulinum toxin type A and the cholinergic neuromuscular junction. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1980, 212, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Giannantoni, A.; Gubbiotti, M.; Bini, V. Botulinum neurotoxin A intravesical injections in interstitial cystitis/bladder painful syndrome: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Toxins 2019, 11, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeler, D.A.P.B.; Berghmans, B.; Birch, J.; Borovicka, J.; Cottrell, A.M.; Dinis-Oliveira, P.; Elneil, S.; Hughes, J.; Messelink, E.J.; Pinto, R.A.; et al. EAU Guidelines on Chronic Pelvic Pain; European Association of Urology: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Schachar, J.; Evans, R.J.; Matthews, C.A.; Badlani, G.; Walker, S.J. Hydrodistention does not alter bladder gene expression profiles in patients with non-Hunner lesion interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2021, 40, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plair, A.; Evans, R.J.; Langefeld, C.D.; Matthews, C.A.; Badlani, G.; Walker, S.J. Anesthetic bladder capacity is a clinical biomarker for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome subtypes. Urology 2021, 158, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, M.B. Fibromyalgia and overlapping disorders: The unifying concept of central sensitivity syndromes. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 36, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.H.; Gardner, V.; Ness, T.J.; Gereau IV, R.W. Segmental hyperalgesia to mechanical stimulus in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Evidence of central sensitization. J. Urol. 2014, 191, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, L.; Erickson, A.; Brierley, S.M. Visceral pain. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 261–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohleder, N. Stress and inflammation–The need to address the gap in the transition between acute and chronic stress effects. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 105, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Gianferante, D.; Hanlin, L.; Fiksdal, A.; Breines, J.G.; Thoma, M.V.; Rohleder, N. HPA-axis and inflammatory reactivity to acute stress is related with basal HPA-axis activity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 78, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, K.J.; Van Ooteghem, K.; McIlroy, W.E. Emotional state as a modulator of autonomic and somatic nervous system activity in postural control: A review. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1188799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.S.; Apple, C.G.; Kannan, K.B.; Funk, Z.M.; Plazas, J.M.; Efron, P.A.; Mohr, A.M. Chronic stress induces persistent low-grade inflammation. Am. J. Surg. 2019, 218, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.B.S.; Meng, J.; Zhang, J. Does low grade systemic inflammation have a role in chronic pain? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 785214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Jhang, J.F.; Birder, L.A.; Kuo, H.C. Sensory Receptor, Inflammatory, and Apoptotic Protein Expression in the Bladder Urothelium of Patients with Different Subtypes of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Du, L.; Liu, S.; Lan, Z.; Zang, K.; Feng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Xie, Z.; Wang, P.L. A TRPV4-dependent neuroimmune axis in the spinal cord promotes neuropathic pain. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e161507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, N.; Pan, L.; Wang, B. TRP (transient receptor potential) ion channel family: Structures, biological functions and therapeutic interventions for diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denaro, S.; Pasquinucci, L.; Turnaturi, R.; Alberghina, C.; Longhitano, L.; Giallongo, S.; Costanzo, G.; Spoto, S.; Grasso, M.; Zappalà, A. Sigma-1 Receptor Inhibition Reduces Mechanical Allodynia and Modulate Neuroinflammation in Chronic Neuropathic Pain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacković, Z. Botulinum Toxin and Pain; Whitcup, S.M., Hallett, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 263, pp. 251–264. [Google Scholar]
- Lucioni, A.; Bales, G.T.; Lotan, T.L.; McGehee, D.S.; Cook, S.P.; Rapp, D.E. Botulinum toxin type A inhibits sensory neuropeptide release in rat bladder models of acute injury and chronic inflammation. BJU Int. 2008, 101, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.E.; Werbel, T.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C.C.; Yaksh, T.L.; Di Nardo, A. Botulinum toxin blocks mast cells and prevents rosacea like inflammation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 93, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhu, X.; Yang, G.; Shen, J.; Xie, P.; Zuo, X.; Xia, L.; Han, Q.; Zhao, Y. The efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A in treatment of trigeminal neuralgia and peripheral neuropathic pain: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.A.; Nelson, M.; Wickware, C.; Choi, S.; Moon, G.; Xiong, E.; Orta, L.; Brideau-Andersen, A.; Brin, M.F.; Broide, R.S. OnabotulinumtoxinA effects on trigeminal nociceptors. Cephalalgia 2023, 43, 03331024221141683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Jhang, J.F.; Lee, Y.K.; Kuo, H.C. Low-energy shock wave plus intravesical instillation of botulinum toxin A for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Pathophysiology and preliminary result of a novel minimally invasive treatment. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewski, P.; Słomko, J.; Zawadka-Kunikowska, M. Autonomic dysfunction and chronic disease. Br. Med. Bull. 2018, 128, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.G.; Nadruz Jr, W.; Mónica, F.Z. Endothelial and vascular smooth muscle dysfunction in hypertension. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 205, 115263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, B.M.; Campbell, S.E.; Vizzard, M.A. Stress-induced symptom exacerbation: Stress increases voiding frequency, somatic sensitivity, and urinary bladder inflammation when combined with low concentration cyclophosphamide treatment in mice. Front. Urol. 2023, 3, 1079790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanno, P.M.; Erickson, D.; Moldwin, R.; Faraday, M.M. Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: AUA guideline amendment. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.F.; Viseux, F.J.; Salm, D.C.; Ribeiro, A.C.A.; da Silva, H.K.L.; Seim, L.A.; Bittencourt, E.B.; Bianco, G.; Moré, A.O.O.; Reed, W.R. The role of the vagus nerve in fibromyalgia syndrome. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 131, 1136–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Tyagi, S.; Chermansky, C.; Kanai, A.; Beckel, J.; Hashimoto, M.; Cho, K.J.; Chancellor, M.; Kaufman, J.; Yoshimura, N. Treating Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Older Adults: Intravesical Options. Drugs Aging 2023, 40, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Kuo, H.C. Clinical application of intravesical botulinum toxin type A for overactive bladder and interstitial cystitis. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2020, 61, S33–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanno, P.M.; Landis, J.R.; Matthews-cook, Y.; Kusek, J. The diagnosis of interstitial cystitis revisited: Lessons learned from the National Institutes of Health Interstitial Cystitis Database study. J. Urol. 1999, 161, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Merwe, J.P.; Nordling, J.; Bouchelouche, P.; Bouchelouche, K.; Cervigni, M.; Daha, L.K.; Elneil, S.; Fall, M.; Hohlbrugger, G.; Irwin, P. Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: An ESSIC proposal. Eur. Urol. 2008, 53, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinberg, K.; Sela, Y.; Nissanholtz-Gannot, R. New Insights about Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawker, G.A.; Mian, S.; Kendzerska, T.; French, M. Measures of adult pain: Visual analog scale for pain (vas pain), numeric rating scale for pain (nrs pain), mcgill pain questionnaire (mpq), short-form mcgill pain questionnaire (sf-mpq), chronic pain grade scale (cpgs), short form-36 bodily pain scale (sf-36 bps), and measure of intermittent and constant osteoarthritis pain (icoap). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.R.; Jiang, Y.H.; Jhang, J.F.; Kuo, H.C. Use of Urinary Biomarkers in Discriminating Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome from Male Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunctions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, P.; Cardozo, L.; Fall, M.; Griffiths, D.; Rosier, P.; Ulmsten, U.; Van Kerrebroeck, P.; Victor, A.; Wein, A. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: Report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 187, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Jhang, J.F.; Kuo, H.C. Revisiting the role of potassium sensitivity testing and cystoscopic hydrodistention for the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.D.; Chiu, B.; Kuo, H.C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Wang, C.C.; Guan, Z.; Chancellor, M.B. Transabdominal ultrasonography of detrusor wall thickness in women with overactive bladder. BJU Int. 2010, 105, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Total (n = 220) | Unsatisfactory Outcome GRA ≤ 1 (n = 124) | Satisfactory Outcome GRA ≥ 2 (n = 96) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 53.64 ± 13.19 | 52.88 ± 14.35 | 54.63 ± 11.52 | 0.318 | |
| Gender | Male | 42 (19.1%) | 26 (19.7%) | 16 (16.7%) | 0.349 |
| Female | 178 (80.9%) | 98 (80.3%) | 80 (83.3%) | ||
| IC duration | 13.51 ± 10.02 | 14.07 ± 10.63 | 12.80 ± 9.19 | 0.356 | |
| Comorbidities | 2.83 ± 2.25 | 2.88 ± 2.22 | 2.77 ± 2.08 | 0.713 | |
| Numerical rating pain scale | 4.93 ± 2.65 | 4.55 ± 2.73 | 5.44 ± 2.47 | 0.004 * | |
| IC symptoms index | 12.51 ± 3.74 | 12.06 ± 3.67 | 13.10 ± 3.76 | 0.043 * | |
| IC problem index | 11.91 ± 3.32 | 11.30 ± 3.17 | 12.71 ± 3.37 | 0.002 * | |
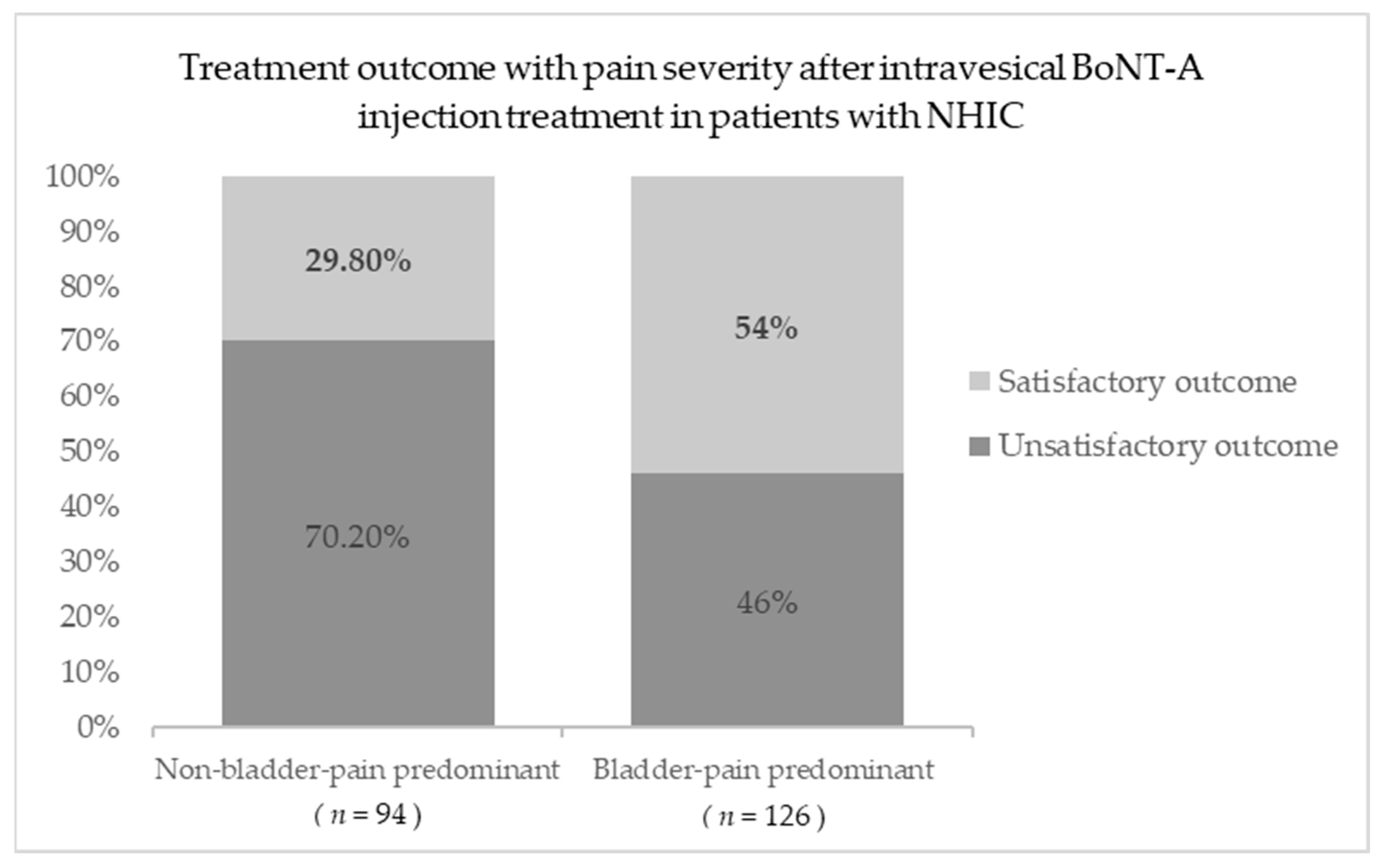
| Bladder pain-predominant phenotype | 126 (57.3%) | 58 (46.8%) | 68 (70.8%) | <0.001 * | |
| Variable | Total (n = 220) | Unsatisfactory Outcome GRA ≤ 1 (n = 124) | Satisfactory Outcome GRA ≥ 2 (n = 96) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSF (mL) | 120.32 ± 51.88 | 120.82 ± 51.39 | 119.67 ± 52.78 | 0.871 | |
| FS (mL) | 186.25 ± 71.96 | 186.99 ± 73.92 | 185.29 ± 69.74 | 0.863 | |
| CBC (mL) | 284.85 ± 110.12 | 278.17 ± 102.70 | 293.47 ± 110.01 | 0.308 | |
| PdetQmax (cm H2O) | 21.20 ± 12.88 | 21.02 ± 12.79 | 21.43 ± 13.07 | 0.821 | |
| Qmax (mL/s) | 12.50 ± 5.82 | 12.15 ± 5.69 | 12.95 ± 5.98 | 0.318 | |
| Voided volume (mL) | 258.93 ± 119.13 | 248.8 ± 113.17 | 272.02 ± 125.81 | 0.152 | |
| PVR (mL) | 26.44 ± 51.64 | 28.31 ± 53.91 | 22.99 ± 48.86 | 0.426 | |
| KCl test—Pain (%) | 170 (77.3%) | 92 (75.4%) | 74 (78.7%) | 0.342 | |
| KCl test—Urge (%) | 66 (30%) | 41 (33.6%) | 25 (26.6%) | 0.169 | |
| MBC (mL) | 672.59 ± 188.82 | 647.50 ± 189.21 | 705 ± 184.26 | 0.025 * | |
| Glomerulation grade | Grade 1 | 93 (42.3%) | 48 (38.7%) | 45 (46.9%) | 0.420 |
| Grade 2 | 97 (44.1%) | 59 (47.6%) | 38 (39.6%) | ||
| Grade 3 | 30 (13.6%) | 17 (13.7%) | 13 (13.5%) | ||
| Variable | Total (n = 220) | Unsatisfactory Outcome GRA ≤ 1 (n = 124) | Satisfactory Outcome GRA ≥ 2 (n = 96) | p-Value | Control (n = 31) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urine Biomarkers | |||||
| IL-8 | 25.58 ± 74.36 | 21.63 ± 44.63 | 31.02 ± 102.32 | 0.495 | 12.44 ± 20.97 |
| CXCL 10 | 17.59 ± 45.04 | 20.41 ± 49.95 | 13.71 ± 37.39 | 0.421 | 13.81 ± 18.42 |
| MCP-1 | 316.37 ± 447.38 | 310.68 ± 492.59 | 324.18 ± 381.32 | 0.871 | 147.13 ± 109.73 * |
| NGF | 0.17 ± 0.0692 | 0.18 ± 0.08 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.557 | 0.26 ± 0.07 * |
| BDNF | 1.56 ± 9.80 | 2.28 ± 12.87 | 0.59 ± 0.16 | 0.351 | 0.54 ± 0.11 |
| Eotaxin | 6.97 ± 7.47 | 6.49 ± 6.20 | 7.62 ± 8.95 | 0.413 | 4.97 ± 3.7 * |
| IL-2 | 0.21 ± 0.1823 | 0.22 ± 0.23 | 0.2071 ± 0.07 | 0.560 | 0.80 ± 0.18 * |
| IL-6 | 9.09 ± 55.91 | 10.98 ± 71.45 | 6.50 ± 21.14 | 0.666 | 1.29 ± 1.35 |
| MIP-1β | 1.71 ± 4.0471 | 1.35 ± 2.48 | 2.19 ± 5.51 | 0.283 | 2.52 ± 1.81 |
| RANTES | 11.14 ± 64.04 | 16.82 ± 87.06 | 5.43 ± 7.35 | 0.405 | 6.04 ± 5.15 |
| TNF-α | 7.46 ± 37.26 | 11.23 ± 48.64 | 2.27 ± 4.48 | 0.695 | 0.81 ± 0.32 |
| PGE2 | 319.72 ± 349.93 | 346.27 ± 336.51 | 283.27 ± 367.80 | 0.130 | 161.37 ± 105.15 * |
| 8-OHdG | 34.68 ± 27.05 | 36.48 ± 30.10 | 32.05 ± 22.21 | 0.375 | 18 ± 13.73 * |
| 8-Isoprostane | 88.77 ± 202.29 | 120.47 ± 260.04 | 45.87 ± 46.48 | 0.022 * | 16.78 ± 11.74 * |
| TAC | 1171.75 ± 1175.36 | 1061.15 ± 1096.02 | 1314.88 ± 1267.41 | 0.249 | 1077.91 ± 925 |
| Variable | Total (n = 220) | Unsatisfactory Outcome GRA ≤ 1 (n = 124) | Satisfactory Outcome GRA ≥ 2 (n = 96) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ ICSI | −4.14 ± 4.72 | −3.12 ± 4.38 | −5.46 ± 4.84 | 0.001 * |
| Δ ICPI | −3.81 ± 4.93 | −3.32 ± 4.57 | −6.83 ± 5.06 | <0.001 * |
| Δ NRS | −1.87 ± 3.20 | −1.09 ± 2.98 | −2.89 ± 3.21 | <0.001 * |
| Δ Qmax | 3.03 ± 7.97 | 2.95 ± 7.60 | 3.15 ± 8.47 | 0.858 |
| Δ Voided volume | −26.84 ± 148.24 | −19.38 ± 138.82 | −36.48 ± 159.87 | 0.415 |
| Δ PVR | 26.44 ± 51.64 | 21.10 ± 73.55 | 12.10 ± 58.06 | 0.343 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, W.-R.; Jhang, J.-F.; Kuo, H.-C. Intravesical Botulinum Toxin Injection Plus Hydrodistention Is More Effective in Patients with Bladder Pain-Predominant Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Toxins 2024, 16, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16020074
Yu W-R, Jhang J-F, Kuo H-C. Intravesical Botulinum Toxin Injection Plus Hydrodistention Is More Effective in Patients with Bladder Pain-Predominant Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Toxins. 2024; 16(2):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16020074
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Wan-Ru, Jia-Fong Jhang, and Hann-Chorng Kuo. 2024. "Intravesical Botulinum Toxin Injection Plus Hydrodistention Is More Effective in Patients with Bladder Pain-Predominant Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome" Toxins 16, no. 2: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16020074
APA StyleYu, W.-R., Jhang, J.-F., & Kuo, H.-C. (2024). Intravesical Botulinum Toxin Injection Plus Hydrodistention Is More Effective in Patients with Bladder Pain-Predominant Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Toxins, 16(2), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16020074






