Real-World Use of Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin Injections: A Population-Based Study from France
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
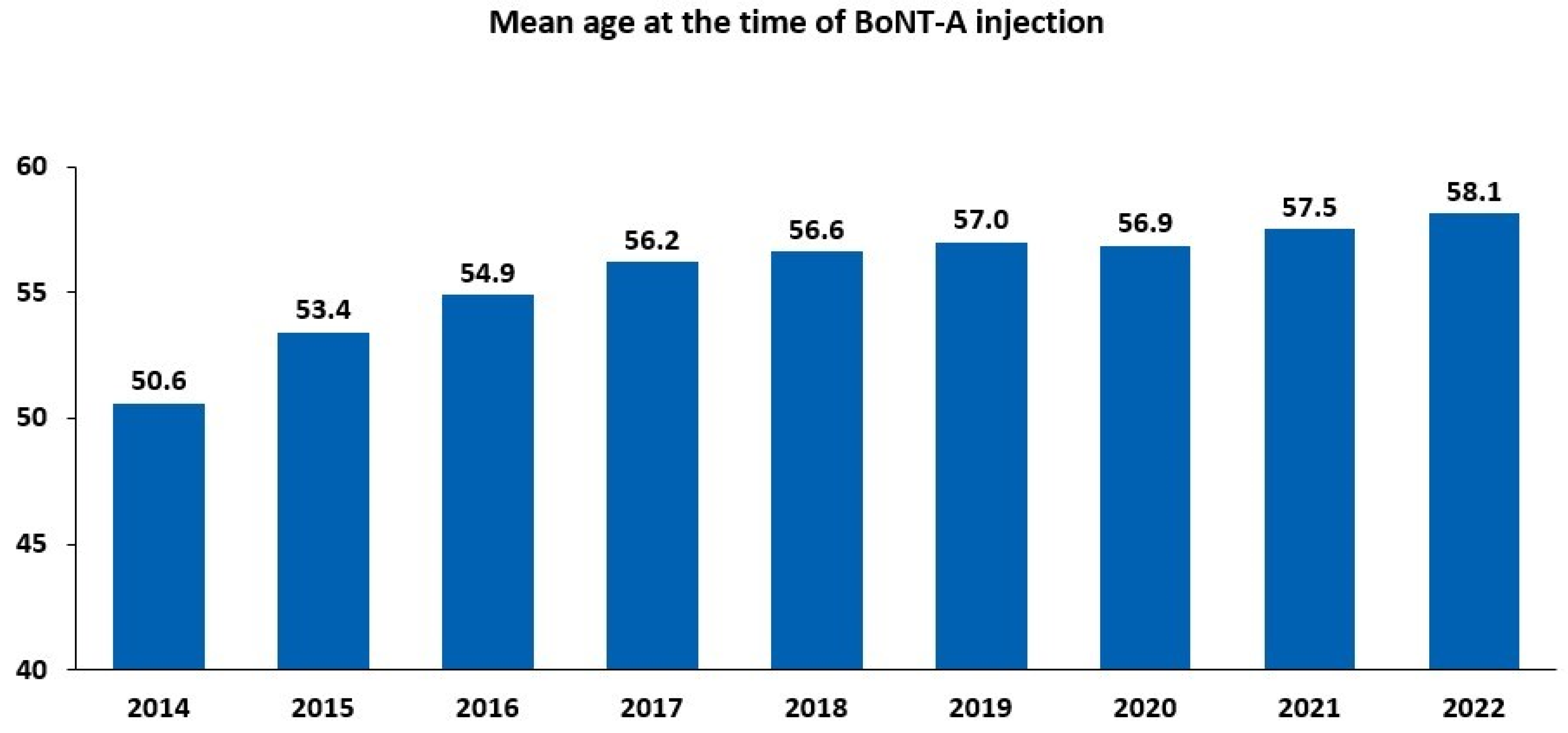
2.1. Overall Trends in Intradetrusor BoNT-A Use
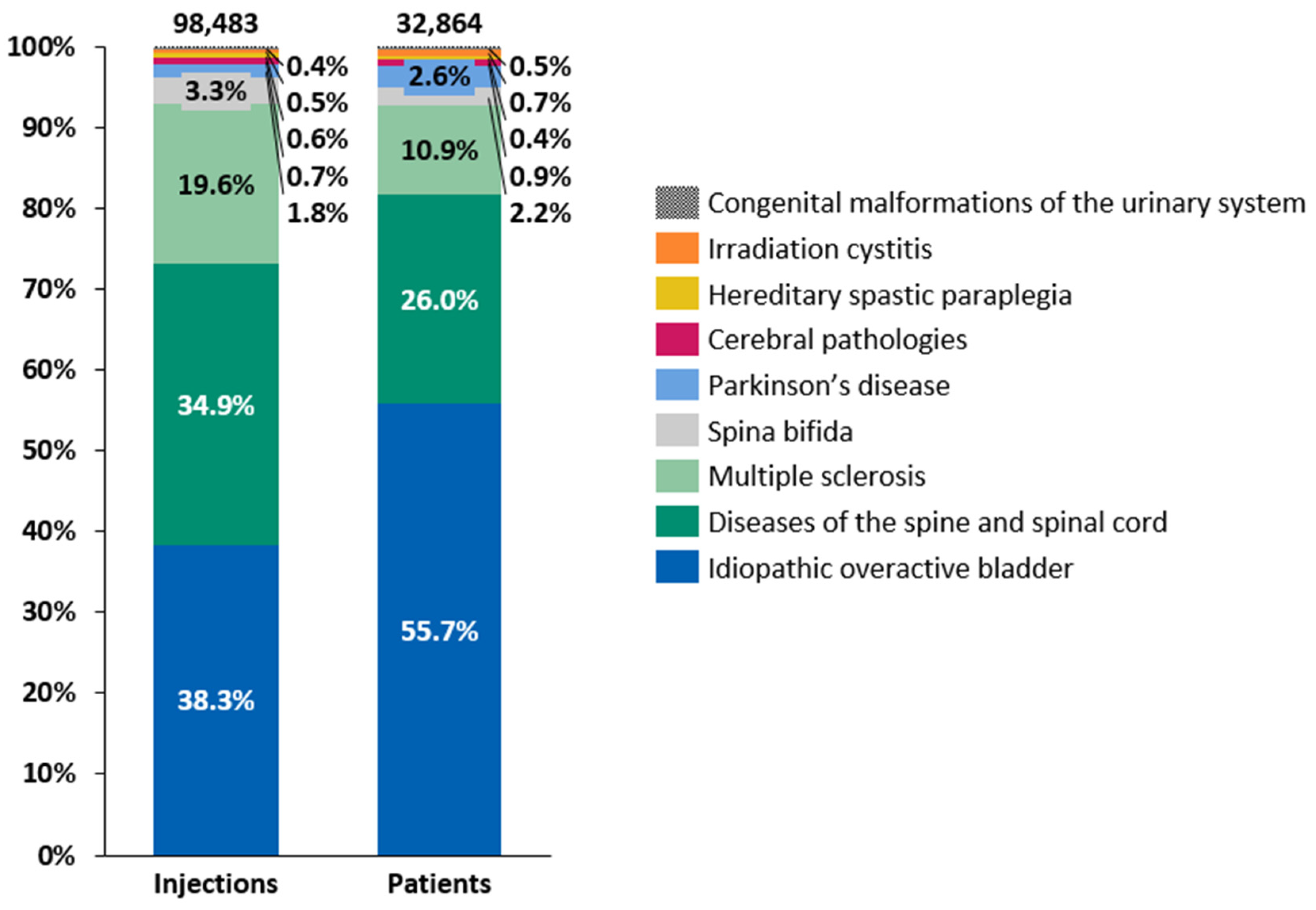
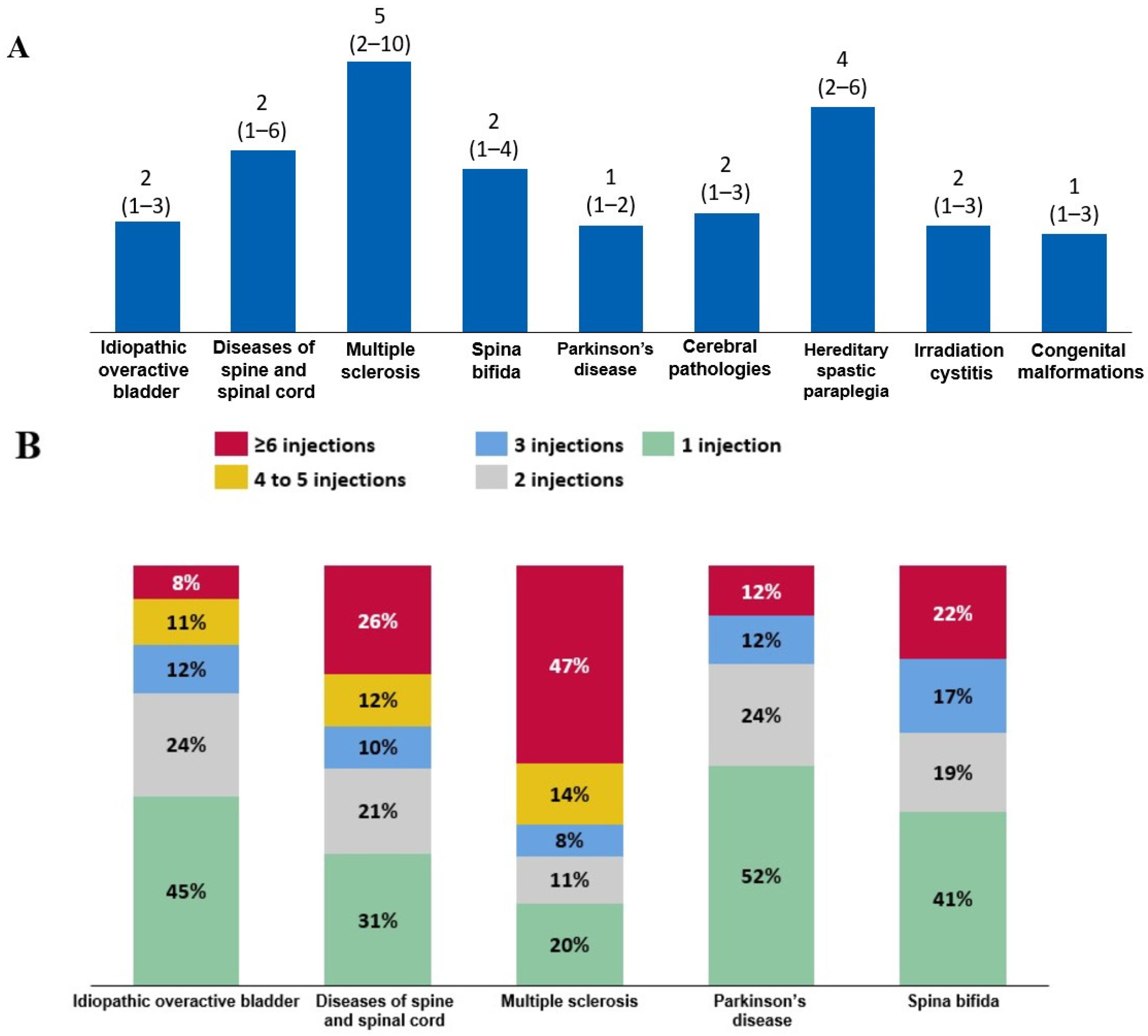
2.2. Indications for the Administration of Intradetrusor BoNT-A Injections
2.3. Safety of Intradetrusor BoNT-A
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study Design and Data Source
5.2. Study Population
5.3. Outcomes
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linsenmeyer, T.A. Use of botulinum toxin in individuals with neurogenic detrusor overactivity: State of the art review. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2013, 36, 402–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuepfer, S.; Juenemann, K.P. Experience with botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity in clinical practice. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2014, 6, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, P.; Cardozo, L.; Fall, M.; Griffiths, D.; Rosier, P.; Ulmsten, U.; van Kerrebroeck, P.; Victor, A.; Wein, A. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: Report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2002, 21, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.F.; Chiu, H.C.; Chen, K.C.; Chang, C.H.; Chou, E.C. Botulinum toxin A for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder. Toxins 2016, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsenty, G.; Reitz, A.; Lindemann, G.; Boy, S.; Schurch, B. Persistence of therapeutic effect after repeated injections of botulinum toxin type A to treat incontinence due to neurogenic detrusor overactivity. Urology 2006, 68, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Kuo, H.C. Will repeated botulinum toxin A improve detrusor overactivity and bladder compliance in patients with chronic spinal cord injury? Tzu Chi Med. J. 2021, 33, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse, J.; Kramer, G.; Stöhrer, M. Success of repeat detrusor injections of botulinum a toxin in patients with severe neurogenic detrusor overactivity and incontinence. Eur. Urol. 2005, 47, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, D.; Gousse, A.; Keppenne, V.; Sievert, K.D.; Thompson, C.; Lam, W.; Brin, M.F.; Jenkins, B.; Haag-Molkenteller, C. Phase 3 efficacy and tolerability study of onabotulinumtoxinA for urinary incontinence from neurogenic detrusor overactivity. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, P.; Castaño Botero, J.C.; Vita Nunes, R.L.; Wachs, B.; Mendes Gomes, C.; Krivoborodov, G.; Tu, L.M.; Del-Popolo, G.; Thompson, C.; Vilain, C.; et al. AbobotulinumtoxinA is effective in patients with urinary incontinence due to neurogenic detrusor overactivity regardless of spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis etiology: Pooled analysis of two phase III randomized studies (CONTENT1 and CONTENT2). Neurourol. Urodyn. 2023, 42, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y. Overactive Bladder Symptoms Within Nervous System: A Focus on Etiology. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 747144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Zeng, F.; Niu, J.; Qi, L.; Chen, H. Botulinum toxin-A injections for idiopathic overactive bladder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Urol. Int. 2013, 91, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreisler, A. A French overview of botulinum toxin injection practices in neurological indications. Prat. Neurol. FMC 2023, 14, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.; Karam, P.; Forestier, A.; Loze, J.Y.; Bensmail, D. Botulinum toxin use in patients with post-stroke spasticity: A nationwide retrospective study from France. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1245228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C. Clinical Application of Botulinum Neurotoxin in Lower-Urinary-Tract Diseases and Dysfunctions: Where Are We Now and What More Can We Do? Toxins 2022, 14, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eapen, R.S.; Radomski, S.B. Review of the epidemiology of overactive bladder. Res. Rep. Urol. 2016, 8, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsenty, G.; Denys, P.; Amarenco, G.; De Seze, M.; Gamé, X.; Haab, F.; Kerdraon, J.; Perrouin-Verbe, B.; Ruffion, A.; Saussine, C.; et al. Botulinum toxin A (Botox) intradetrusor injections in adults with neurogenic detrusor overactivity/neurogenic overactive bladder: A systematic literature review. Eur. Urol. 2008, 53, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, M.; Aublé, A.; Paret, F.; Pfister, C.; Cornu, J.N. Long-term follow-up reveals a low persistence rate of abobotulinumtoxinA injections for idiopathic overactive bladder. Prog. Urol. 2020, 30, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Sakakibara, R.; Yamamoto, T.; Ito, T.; Yamaguchi, C.; Awa, Y.; Yanagisawa, M.; Higuchi, Y.; Sato, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; et al. Urinary dysfunction in early and untreated Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 1382–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, R.; Tateno, F.; Kishi, M.; Tsuyuzaki, Y.; Uchiyama, T.; Yamamoto, T. Pathophysiology of bladder dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensmail, D.; Karam, P.; Forestier, A.; Loze, J.Y.; Lévy, J. Trends in Botulinum Toxin Use among Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Population-Based Study. Toxins 2023, 15, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orasanu, B.; Mahajan, S.T. The use of botulinum toxin for the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome. Indian J. Urol. 2013, 29, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.S.; Kim, K.H. Botulinum toxin in spinal cord injury patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2016, 12, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrar, M.; Pindoria, N.; Malde, S.; Chancellor, M.; DeRidder, D.; Sahai, A. Predictors of Poor Response and Adverse Events Following Botulinum Toxin A for Refractory Idiopathic Overactive Bladder: A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. Focus 2021, 7, 1448–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD). 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/standards/classifications/classification-of-diseases (accessed on 9 September 2024).


| Year | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | n (%) | 2567 (44.5) | 2982 (39.4) | 3363 (37.2) | 3851 (36.2) | 4183 (35.7) | 4523 (34.8) | 4292 (35.5) | 4891 (34.0) | 5326 (34.8) |
| Women | n (%) | 3201 (55.5) | 4579 (60.6) | 5681 (62.8) | 6773 (63.8) | 7521 (64.3) | 8486 (65.2) | 7802 (64.5) | 9497 (66.0) | 9971 (65.2) |
| Total number of patients | 5768 | 7561 | 9044 | 10,624 | 11,704 | 13,009 | 12,094 | 14,388 | 15,297 | |
| Condition | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | Percentage Change between 2014 and 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congenital malformations of urinary system | 30 | 33 (+10%) | 33 (0%) | 30 (−9%) | 50 (+67%) | 44 (−12%) | 37 (−16%) | 59 (+59%) | 36 (−39%) | +20% |
| Irradiation cystitis | 20 | 40 (+100%) | 66 (+65%) | 71 (+8%) | 69 (−3%) | 68 (−1%) | 58 (−15%) | 63 (+9%) | 68 (+8%) | +240% |
| Hereditary spastic paraplegia | 54 | 49 (−9%) | 53 (+8%) | 50 (−6%) | 58 (+16%) | 71 (+22%) | 70 (−1%) | 76 (+9%) | 84 (+11%) | +56% |
| Cerebral pathology | 40 | 52 (+30%) | 76 (+46%) | 97 (+28%) | 85 (−12%) | 87 (+2%) | 74 (−15%) | 91 (+23%) | 72 (−21%) | +80% |
| Parkinson’s disease | 73 | 113 (+55%) | 156 (+38%) | 205 (+31%) | 252 (+23%) | 270 (+7%) | 206 (−24%) | 236 (+15%) | 259 (+10%) | +255% |
| Spina bifida | 372 | 292 (−22%) | 310 (+6%) | 304 (−2%) | 324 (+7%) | 381 (+18%) | 336 (−12%) | 438 (+30%) | 459 (+5%) | +23% |
| Multiple sclerosis | 1303 | 1589 (+22%) | 1813 (+14%) | 2094 (+16%) | 2259 (+8%) | 2573 (+14%) | 2100 (−18%) | 2718 (+29%) | 2851 (+5%) | +119% |
| Diseases of the spine and spinal cord | 2617 | 2968 (+13%) | 3314 (+12%) | 3790 (+14%) | 3980 (+5%) | 4265 (+7%) | 3928 (−8%) | 4594 (+17%) | 4898 (+7%) | +87% |
| Idiopathic overactive bladder | 1227 | 2384 (+94%) | 3192 (+34%) | 3941 (+23%) | 4579 (+16%) | 5171 (+13%) | 4667 (−10%) | 6052 (+30%) | 6516 (+8%) | +431% |
| Total | 5736 | 7520 (+31%) | 9013 (+20%) | 10,582 (+17%) | 11,656 (+10%) | 12,930 (+11%) | 11,476 (−11%) | 14,327 (+25%) | 15,243 (+6%) | +166% |
| Condition | ICD-10 Code | |
|---|---|---|
| List of main etiologies | ||
| Multiple sclerosis | G35 | |
| Spina bifida | Q05 | |
| Other congenital malformations of the urinary system | Q64 | |
| Hereditary spastic paraplegia | G11.4 | |
| Irradiation cystitis | N30.4 | |
| Diseases of the spine and spinal cord | Other and unspecified diseases of the spinal cord | G95 |
| Sequelae of injuries of the neck and trunk | T91 | |
| Injury of nerves and the spinal cord at the neck level | S14 | |
| Injury of nerves and the spinal cord at the thorax level | S24 | |
| Injury of the lumbar and sacral spinal cord and nerves at the abdomen, lower back, and pelvis levels | S34 | |
| Nerve-root and plexus compressions in diseases classified elsewhere | G55 | |
| Spinal stenosis | M480 | |
| Hemiplegia and hemiparesis | G81 | |
| Paraplegia and quadriplegia | G82 | |
| Other paralytic syndromes | G83 | |
| Symptoms or less defined etiologies | ||
| Parkinson’s disease | G20 | |
| Cerebral palsy | G80 | |
| Sequelae of cerebrovascular disease | I69 | |
| Idiopathic overactive bladder | Uninhibited neuropathic bladder not classified elsewhere | N31.0 |
| Reflex neuropathic bladder not classified elsewhere | N31.1 | |
| Flaccid neuropathic bladder not classified elsewhere | N31.2 | |
| Other neuromuscular dysfunctions of the bladder | N31.8 | |
| Unspecified neuromuscular dysfunction of the bladder | N31.9 | |
| Unspecified urinary incontinence | R32 | |
| Stress incontinence | N39.3 | |
| Other specified urinary incontinence | N39.4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruffion, A.; Karam, P.; Forestier, A.; Denys, P. Real-World Use of Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin Injections: A Population-Based Study from France. Toxins 2024, 16, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16100423
Ruffion A, Karam P, Forestier A, Denys P. Real-World Use of Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin Injections: A Population-Based Study from France. Toxins. 2024; 16(10):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16100423
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuffion, Alain, Pierre Karam, Anne Forestier, and Pierre Denys. 2024. "Real-World Use of Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin Injections: A Population-Based Study from France" Toxins 16, no. 10: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16100423
APA StyleRuffion, A., Karam, P., Forestier, A., & Denys, P. (2024). Real-World Use of Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin Injections: A Population-Based Study from France. Toxins, 16(10), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16100423





