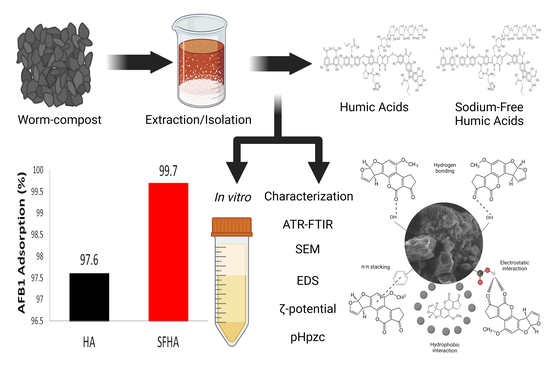
Humic Acids Preparation, Characterization, and Their Potential Adsorption Capacity for Aflatoxin B1 in an In Vitro Poultry Digestive Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization
2.1.1. ATR-FTIR
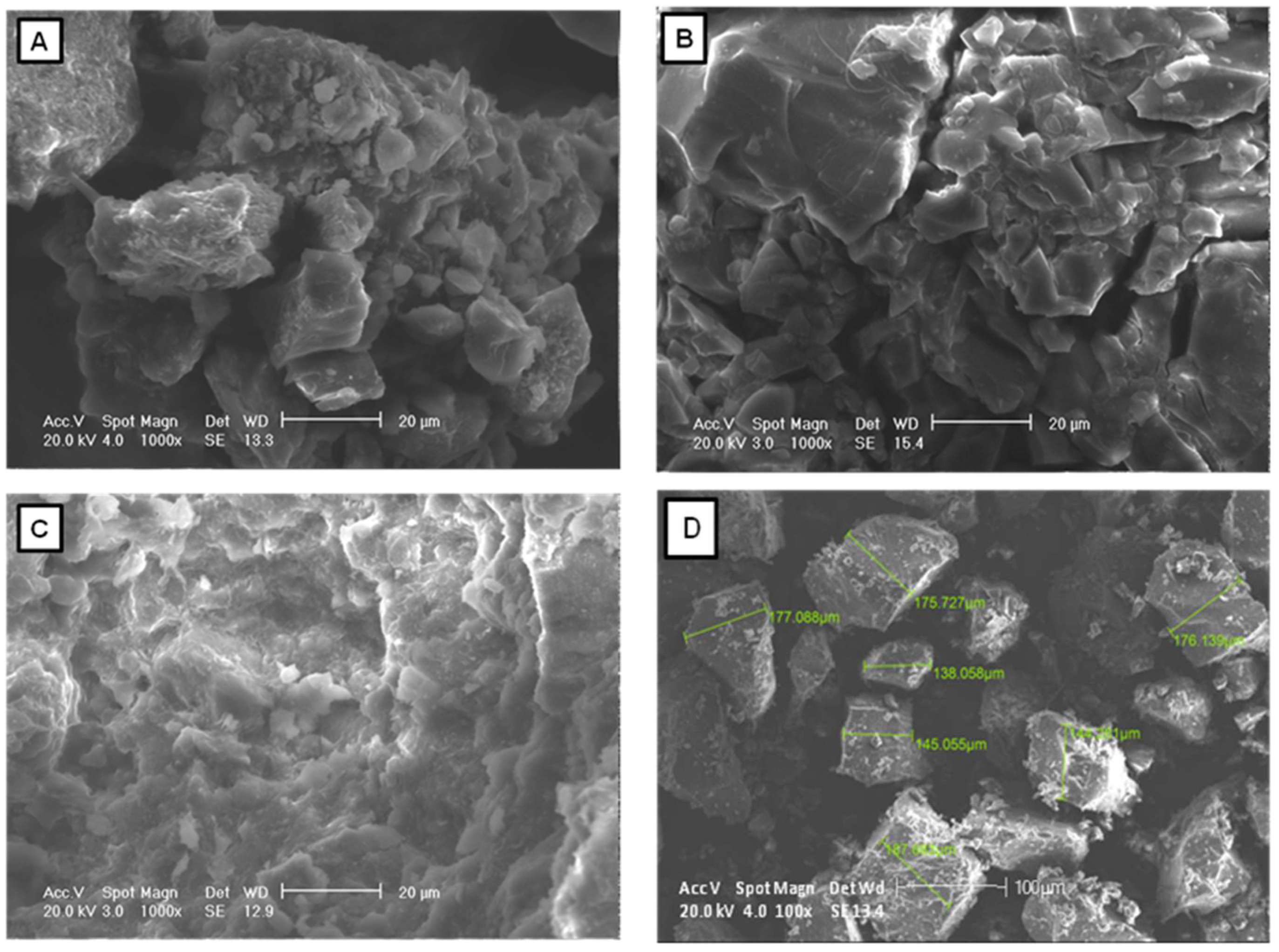
2.1.2. SEM
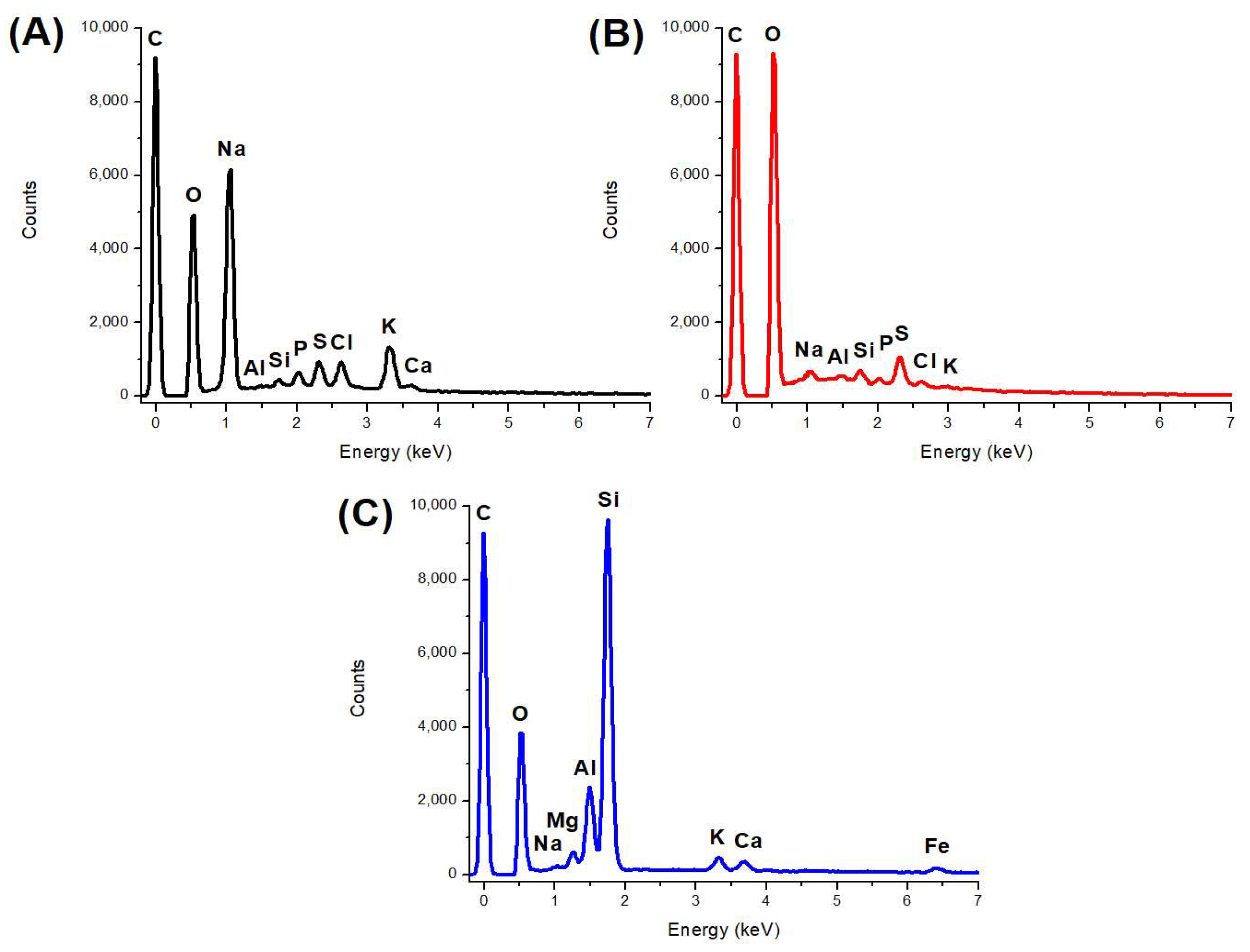
2.1.3. EDS
2.1.4. ζ-Potential
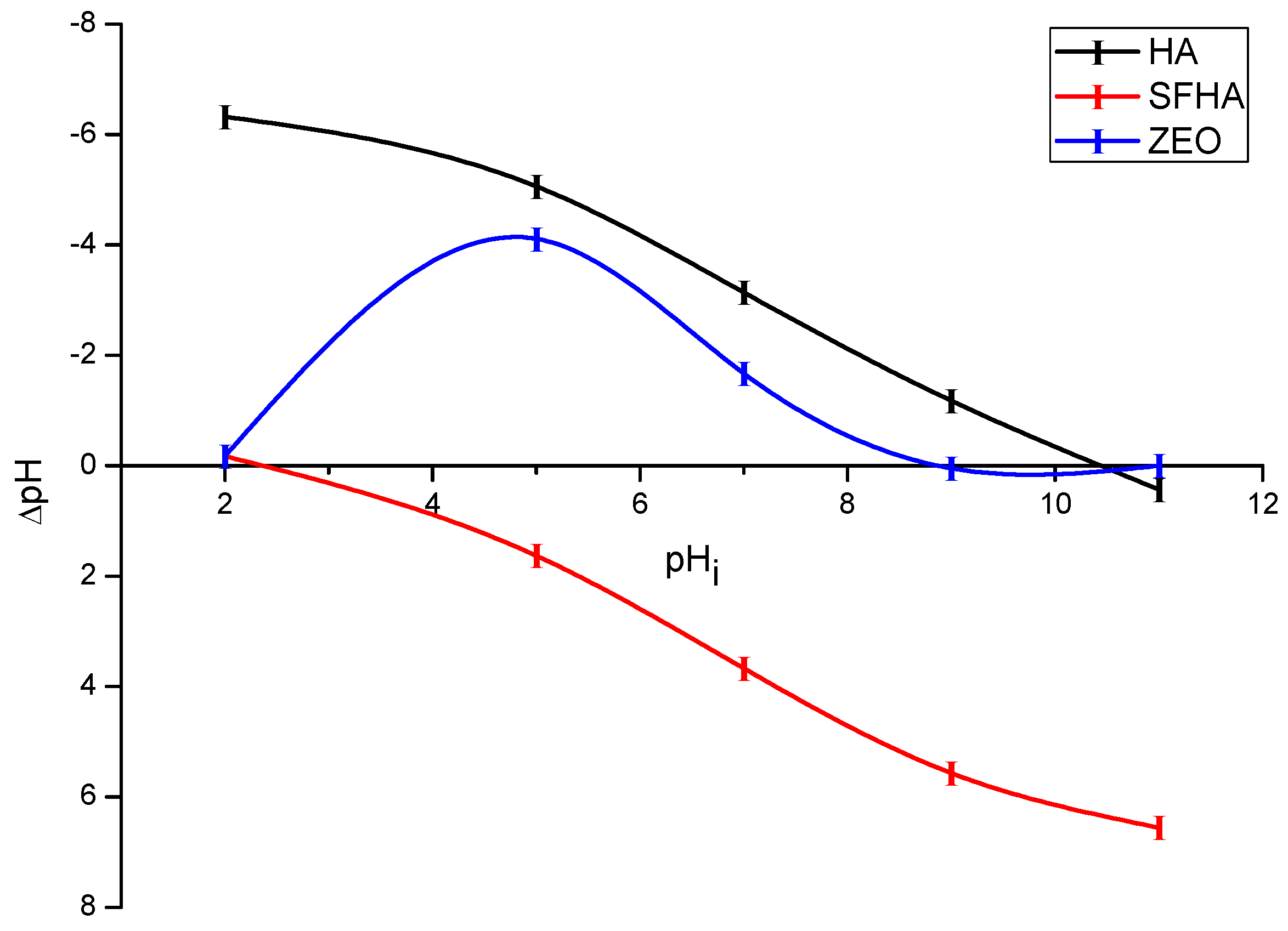
2.1.5. pHpzc
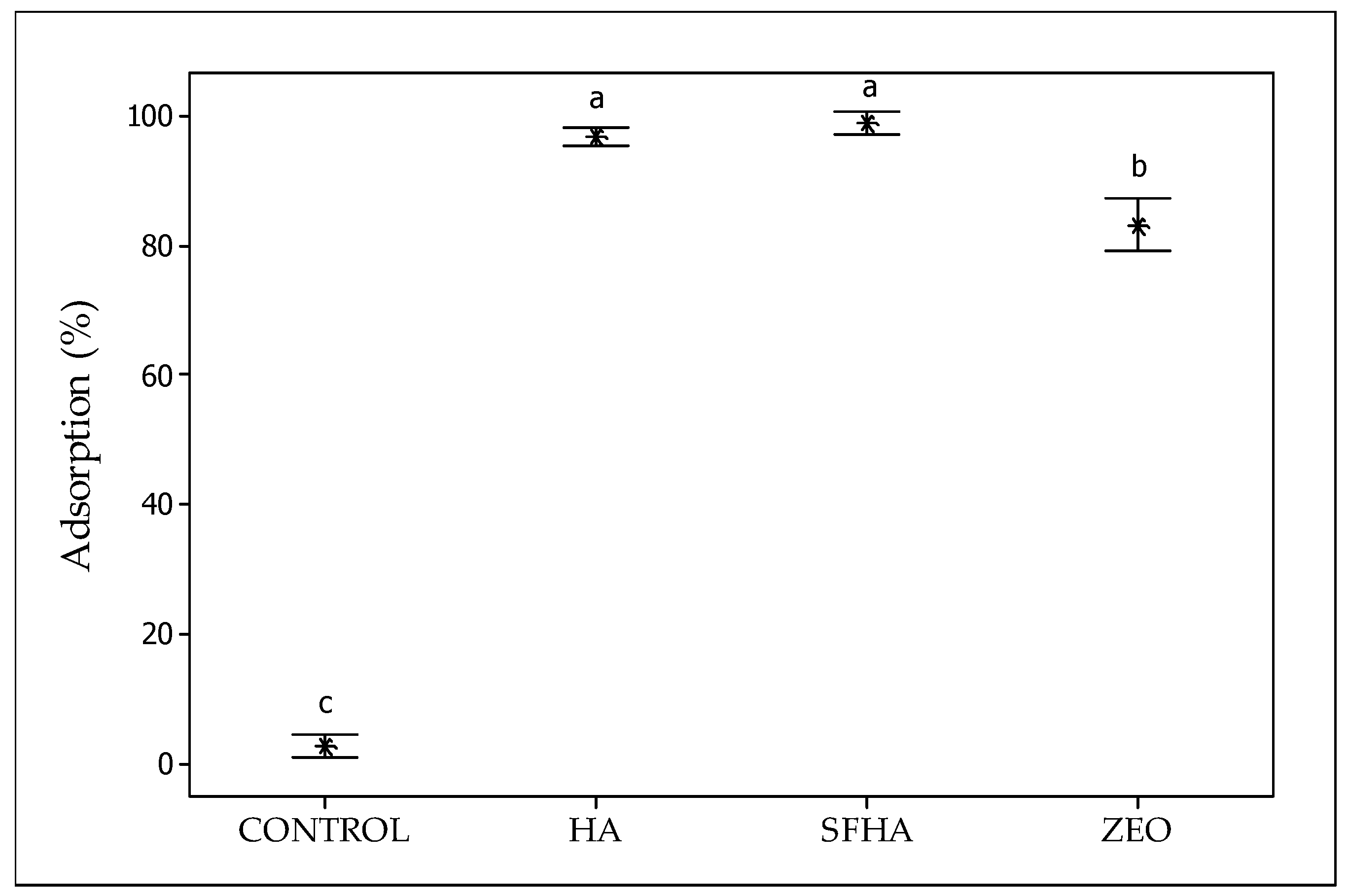
2.2. In Vitro Digestive Model
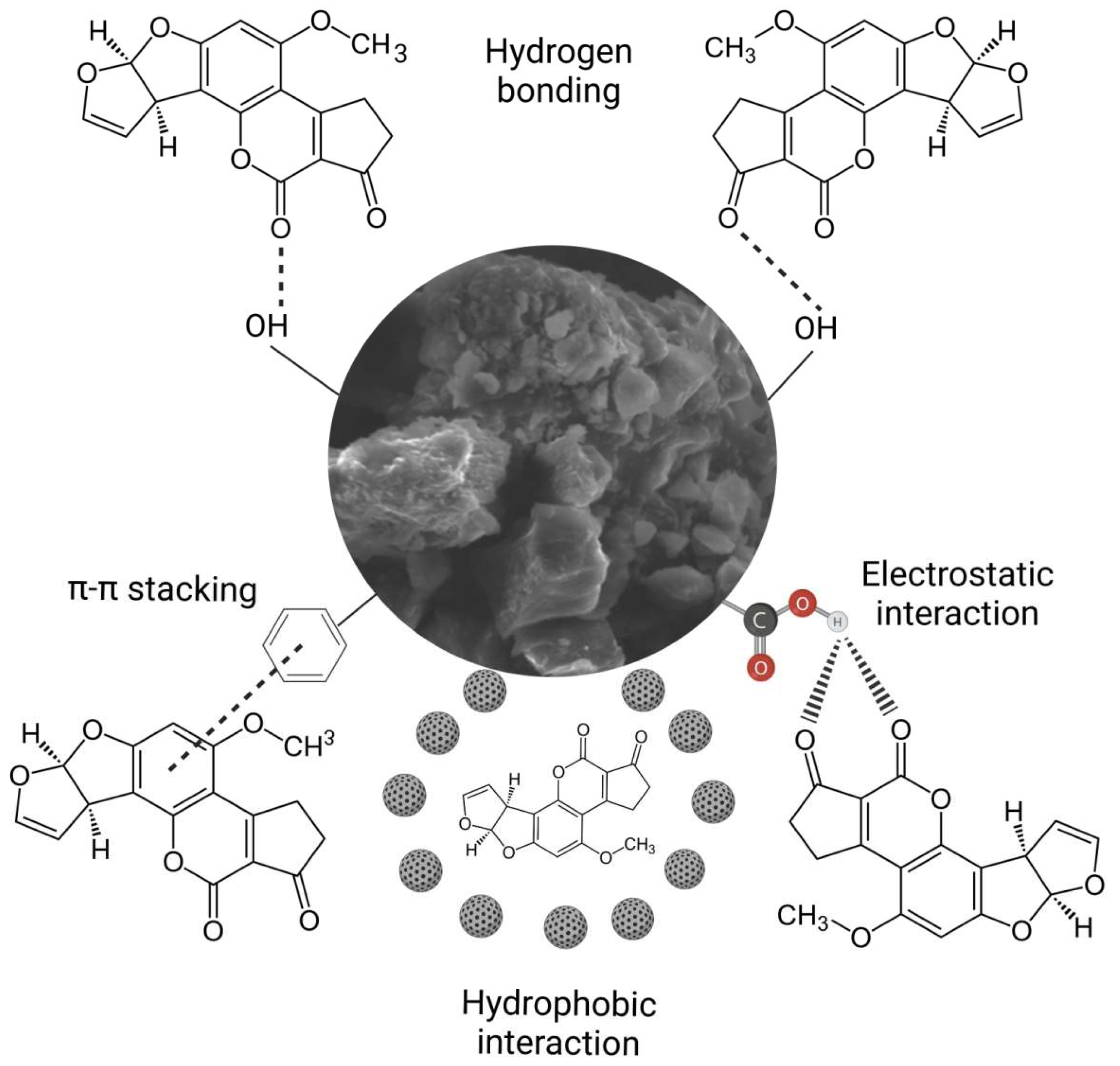
2.3. The Mechanism for AFB1 Adsorption onto HA
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Humic Acids
4.2. Characterization of HA
4.2.1. ATR-FTIR
4.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.2.3. Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
4.2.4. Zeta Potential (ζ-Potential)
4.2.5. Point of Zero Charge (pHpzc)
4.3. In Vitro Adsorption Studies
Preparation of the AFB1-Contaminated Diet
4.4. In Vitro Digestive Model
4.5. Aflatoxin Assay
4.6. Method Validation
4.7. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coulombe, R.A. Biological Action of Mycotoxins. J. Dairy Sci. 1993, 76, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, M.E. Impact of Mycotoxins on Humans and Animals. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2011, 15, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisvad, J.C.; Hubka, V.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Hong, S.-B.; Nováková, A.; Chen, A.J.; Arzanlou, M.; Larsen, T.O.; Sklenář, F.; Mahakarnchanakul, W.; et al. Taxonomy of Aspergillus Section Flavi and Their Production of Aflatoxins, Ochratoxins and Other Mycotoxins. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 93, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, S.; Kim, J.E.; Coulombe, R. Aflatoxin B1 in Poultry: Toxicology, Metabolism and Prevention. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 89, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, R.G.; Avramescu, S.; Marin, D.E.; Țăranu, I.; Georgescu, S.E.; Dinischiotu, A. The Reduction of the Combined Effects of Aflatoxin and Ochratoxin A in Piglet Livers and Kidneys by Dietary Antioxidants. Toxins 2021, 13, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Liu, M.; Zang, H.; Liu, X.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Alleviation of Oral Exposure to B1-Induced Renal Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Cell Apoptosis in Mice Kidney by Curcumin. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouad, A.; Ruan, D.; El-Senousey, H.; Chen, W.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, C. Harmful Effects and Control Strategies of Aflatoxin B1 Produced by Aspergillus Flavus and Aspergillus Parasiticus Strains on Poultry: Review. Toxins 2019, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabak, B.; Dobson, A.D.W.; Var, I. Strategies to Prevent Mycotoxin Contamination of Food and Animal Feed: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A. The Supramolecular Structure of Humic Substances: A Novel Understanding of Humus Chemistry and Implications in Soil Science. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 75, pp. 57–134. ISBN 978-0-12-000793-6. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Liu, H.; Wu, S. Humic Substances Developed during Organic Waste Composting: Formation Mechanisms, Structural Properties, and Agronomic Functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-González, M.A.; Álvarez, A.M.; Carral, P.; Almendros, G. Chemometric Assessment of Soil Organic Matter Storage and Quality from Humic Acid Infrared Spectra. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguey-Gonzalez, J.A.; Michel, M.A.; Baxter, M.F.A.; Solis-Cruz, B.; Hernandez-Patlan, D.; Merino-Guzman, R.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Latorre, J.D.; Hargis, B.M.; Tellez, G.; et al. Effects of Humic Acids on Recovery of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2018, 18, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguey-Gonzalez, J.A.; Michel, M.A.; Baxter, M.F.A.; Tellez, G.; Moore, P.A.; Solis-Cruz, B.; Hernández-Patlan, D.; Merino-Guzman, R.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Latorre, J.D.; et al. Effect of Humic Acids on Intestinal Viscosity, Leaky Gut and Ammonia Excretion in a 24 Hr Feed Restriction Model to Induce Intestinal Permeability in Broiler Chickens. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguey-González, J.A.; Gómez-Rosales, S.; de Lourdes Angeles, M.; López-Hernández, L.H.; Rodríguez-Hernández, E.; Solís-Cruz, B.; Hernández-Patlán, D.; Merino-Gúzman, R.; Téllez-Isaías, G. Effects of Humic Acids on the Recovery of Different Bacterial Strains in an in Vitro Chicken Digestive Model. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 145, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lourdes Angeles, M.; Gómez-Rosales, S.; Téllez-Isaias, G. Mechanisms of Action of Humic Substances as Growth Promoters in Animals. In Humus and Humic Substances—Recent Advances; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-1-80356-212-4. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Durán, A.; de Jesús Nava-Ramírez, M.; Téllez-Isaías, G.; Méndez-Albores, A. Removal of Aflatoxins Using Agro-Waste-Based Materials and Current Characterization Techniques Used for Biosorption Assessment. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 897302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dai, J.; Wang, R.; Li, F.; Wang, W. Adsorption and Desorption of Divalent Mercury (Hg2+) on Humic Acids and Fulvic Acids Extracted from Typical Soils in China. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 335, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozgawa, W.; Sitarz, M.; Rokita, M. Spectroscopic Studies of Different Aluminosilicate Structures. J. Mol. Struct. 1999, 511–512, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, J.J.; Filip, Z. Metal Binding in Estuarine Humic and Fulvic Acids: FTIR Analysis of Humic Acid-Metal Complexes. Environ. Technol. 1998, 19, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzak, A.; Kurşun, C.; Yıldız, Y. Characterization of Humic Acid Extracted from Aqueous Solutions with Polymer Inclusion Membranes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 81, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglieri, A.; Vindrola, D.; Gennari, M.; Negre, M. Chemical and Spectroscopic Characterization of Insoluble and Soluble Humic Acid Fractions at Different PH Values. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2014, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.S.; Ok, S.S.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. FTIR Tentative Characterization of Humic Acids Extracted from Organic Materials. Spectrosc. Lett. 2001, 34, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Negrete, A.; Gómez-Rosales, S.; Angeles, M.d.L.; López-Hernández, L.H.; Reis-de Souza, T.C.; López-García, Y.; Zavala-Franco, A.; Téllez-Isaias, G. Effect of the Addition of Humic Substances as Growth Promoter in Broiler Chickens Under Two Feeding Regimens. Animals 2019, 9, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupiasih, N.N.; Vidyasagar, P.B. Analytical Study of Humic Acid from Various Sources Commonly Used as Fertilizer: Emphasis on Heavy Metal Content. Int. J. Des. Nat. Ecodynamics 2009, 4, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Gu, Q.; Li, F. Adsorption Behavior of Herbicide Butachlor on Typical Soils in China and Humic Acids from the Soil Samples. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 285, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, A.W.P.; van Riemsdijk, W.H.; Koopal, L.K. Adsorption of Humic Acid to Mineral Particles. 1. Specific and Electrostatic Interactions. Langmuir 1998, 14, 2810–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Durán, A.; de Jesús Nava-Ramírez, M.; Hernández-Patlán, D.; Solís-Cruz, B.; Hernández-Gómez, V.; Téllez-Isaías, G.; Méndez-Albores, A. Potential of Kale and Lettuce Residues as Natural Adsorbents of the Carcinogen Aflatoxin B1 in a Dynamic Gastrointestinal Tract-Simulated Model. Toxins 2021, 13, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, A.G.S.; Pertusatti, J.; Nunes, A.R. Aspects of Protonation and Deprotonation of Humic Acid Surface on Molecular Conformation. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2011, 22, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, K.; Antonietti, M. A Hydrothermal Process to Turn Waste Biomass into Artificial Fulvic and Humic Acids for Soil Remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasevich, Y.I.; Dolenko, S.A.; Trifonova, M.Y.; Alekseenko, E.Y. Association and Colloid-Chemical Properties of Humic Acids in Aqueous Solutions. Colloid J. 2013, 75, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlaki, E.; Paghaleh, A.S.; Kianmehr, M.H.; Vakilian, K.A. Chemical, Spectral and Morphological Characterization of Humic Acids Extracted and Membrane Purified from Lignite. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2020, 14, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klučáková, M.; Věžníková, K. Micro-Organization of Humic Acids in Aqueous Solutions. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1144, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigorri, R.; Fuentes, M.; González-Gaitano, G.; García-Mina, J.M. Analysis of Molecular Aggregation in Humic Substances in Solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 302, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanela, M.; Crespo, J.S.; Antunes, M.; Adamatti, D.S.; Fernandes, A.N.; Barison, A.; da Silva, C.W.P.; Guégan, R.; Motelica-Heino, M.; Sierra, M.M.D. Chemical and Spectroscopic Characterization of Humic Acids Extracted from the Bottom Sediments of a Brazilian Subtropical Microbasin. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 981, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hou, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S. Hyperthermophilic Composting of Sewage Sludge Accelerates Humic Acid Formation: Elemental and Spectroscopic Evidence. Waste Manag. 2020, 103, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doskočil, L.; Burdíková-Szewieczková, J.; Enev, V.; Kalina, L.; Wasserbauer, J. Spectral Characterization and Comparison of Humic Acids Isolated from Some European Lignites. Fuel 2018, 213, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavala-Franco, A.; Hernández-Patlán, D.; Solís-Cruz, B.; López-Arellano, R.; Tellez-Isaias, G.; Vázquez-Durán, A.; Méndez-Albores, A. Assessing the Aflatoxin B1 Adsorption Capacity between Biosorbents Using an In Vitro Multicompartmental Model Simulating the Dynamic Conditions in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Poultry. Toxins 2018, 10, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Nava, C.; Olguín, M.T.; Solache-Ríos, M. Water Defluoridation by Mexican Heulandite–clinoptilolite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 3109–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrooumov, M.; Cappelletti, P.; de’Gennaro, R. Mineralogical Study of Zeolite from New Mexican Deposits (Cuitzeo Area, Michoacan, Mexico). Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 55, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.-Q.; Brixius, P.J.; Hubbuch, J.J.; Thömmes, J.; Kula, M.-R. Biomass/Adsorbent Electrostatic Interactions in Expanded Bed Adsorption: A Zeta Potential Study: Study of Zeta Potential in Expanded Bed Absorption. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 83, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, Z.; El-Hashash, M.; Aly, S.; Hathout, A.; Soto, E.; Sabry, B.; Ostroff, G. Preparation and Characterization of Yeast Cell Wall Beta-Glucan Encapsulated Humic Acid Nanoparticles as an Enhanced Aflatoxin B1 Binder. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Bai, R.B. Aminated Polyacrylonitrile Fibers for Humic Acid Adsorption: Behaviors and Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5799–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, C.A.; Yong, R.N. Humic Acid Preparation, Properties and Interactions with Metals Lead and Cadmium. Eng. Geol. 2006, 85, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loosli, F.; Le Coustumer, P.; Stoll, S. TiO2 Nanoparticles Aggregation and Disaggregation in Presence of Alginate and Suwannee River Humic Acids. PH and Concentration Effects on Nanoparticle Stability. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6052–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illés, E.; Tombácz, E. The Role of Variable Surface Charge and Surface Complexation in the Adsorption of Humic Acid on Magnetite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 230, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Garrido, J.J. Effect of PH on the Aggregation of a Gray Humic Acid in Colloidal and Solid States. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramales-Valderrama, R.; Vázquez-Durán, A.; Méndez-Albores, A. Biosorption of B-Aflatoxins Using Biomasses Obtained from Formosa Firethorn [Pyracantha Koidzumii (Hayata) Rehder]. Toxins 2016, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, B.G. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Aquatic Humus; Gjessing, E.T., Ed.; Ann Arbor Science Publishers Inc.: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giasuddin, A.B.M.; Kanel, S.R.; Choi, H. Adsorption of Humic Acid onto Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron and Its Effect on Arsenic Removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2022–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Shafea, Y. In vivo and in vitro evaluation of efficacy of humic acid against aflatoxins. Al-Azhar J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 49, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.-Q.; Lv, X.-Z.; Zhou, A.-G. In Vitro Evaluation of the Efficacy of Sodium Humate as an Aflatoxin B1 Adsorbent. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2009, 3, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.H. Humic Matter in Soil and the Environment: Principles and Controversies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-0-429-22322-8. [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonov, V.; Drozdova, O.; Karpukhin, M.; Demin, V. Participation of Cadmium (Ll) and Copper (Ll) Ions in Intermolecular Forces of Humic Acids in Solutions. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 368, 012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Morton, D.W.; Johnson, B.B.; Angove, M.J. Adsorption of Humic and Fulvic Acids onto a Range of Adsorbents in Aqueous Systems, and Their Effect on the Adsorption of Other Species: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 116949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Ouyang, S.; Ao, Z.; Sun, J.; Liu, G.; Hu, X. Integrating Biolayer Interferometry, Atomic Force Microscopy, and Density Functional Theory Calculation Studies on the Affinity between Humic Acid Fractions and Graphene Oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3773–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Durán, A.; Téllez-Isaías, G.; Hernández-Rodríguez, M.; Ruvalcaba, R.M.; Martínez, J.; Nicolás-Vázquez, M.I.; Aceves-Hernández, J.M.; Méndez-Albores, A. The Ability of Chlorophyll to Trap Carcinogen Aflatoxin B1: A Theoretical Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rensburg, C.J.; Van Rensburg, C.E.J.; Van Ryssen, J.B.J.; Casey, N.H.; Rottinghaus, G.E. In Vitro and In Vivo Assessment of Humic Acid as an Aflatoxin Binder in Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2006, 85, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghahri, H.; Habibian, R.; Fam, M.A. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Esterified Glucomannan, Sodium Bentonite, and Humic Acid to Ameliorate the Toxic Effects of Aflatoxin in Broilers. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2010, 34, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, R.Y.; Khan, S.H. Saima Evaluation of Humic Acid as an Aflatoxin Binder in Broiler Chickens. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2017, 17, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council; Board on Agriculture; Subcommittee on Poultry Nutrition. Nutrient Requirements of Poultry: Ninth Revised Edition, 1994; National Academies Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994; ISBN 978-0-309-04892-7. [Google Scholar]
- Solís-Cruz, B.; Hernández-Patlán, D.; Beyssac, E.; Latorre, J.D.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Merino-Guzman, R.; Tellez, G.; López-Arellano, R. Evaluation of Chitosan and Cellulosic Polymers as Binding Adsorbent Materials to Prevent Aflatoxin B1, Fumonisin B1, Ochratoxin, Trichothecene, Deoxynivalenol, and Zearalenone Mycotoxicoses Through an In Vitro Gastrointestinal Model for Poultry. Polymers 2017, 9, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, J.D.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Kuttappan, V.A.; Wolfenden, R.E.; Vicente, J.L.; Wolfenden, A.D.; Bielke, L.R.; Prado-Rebolledo, O.F.; Morales, E.; Hargis, B.M.; et al. Selection of Bacillus Spp. for Cellulase and Xylanase Production as Direct-Fed Microbials to Reduce Digesta Viscosity and Clostridium Perfringens Proliferation Using an in Vitro Digestive Model in Different Poultry Diets. Front. Vet. Sci. 2015, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Ramírez, J.O.; Merino-Guzmán, R.; Téllez-Isaías, G.; Vázquez-Durán, A.; Méndez-Albores, A. Mitigation of AFB1-Related Toxic Damage to the Intestinal Epithelium in Broiler Chickens Consumed a Yeast Cell Wall Fraction. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 677965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, L.; Hill, A.; Holland, P.T.; Lantos, J.; Lee, S.M.; MacNeil, J.D.; O’Rangers, J.; van Zoonen, P.; Ambrus, A. Guidelines for single-laboratory validation of analytical methods for trace-level concentrations of organic chemicals. In Principles and Practices of Method Validation; Fajgelj, A., Ambrus, Á., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 179–187. ISBN 978-0-85404-783-3. [Google Scholar]
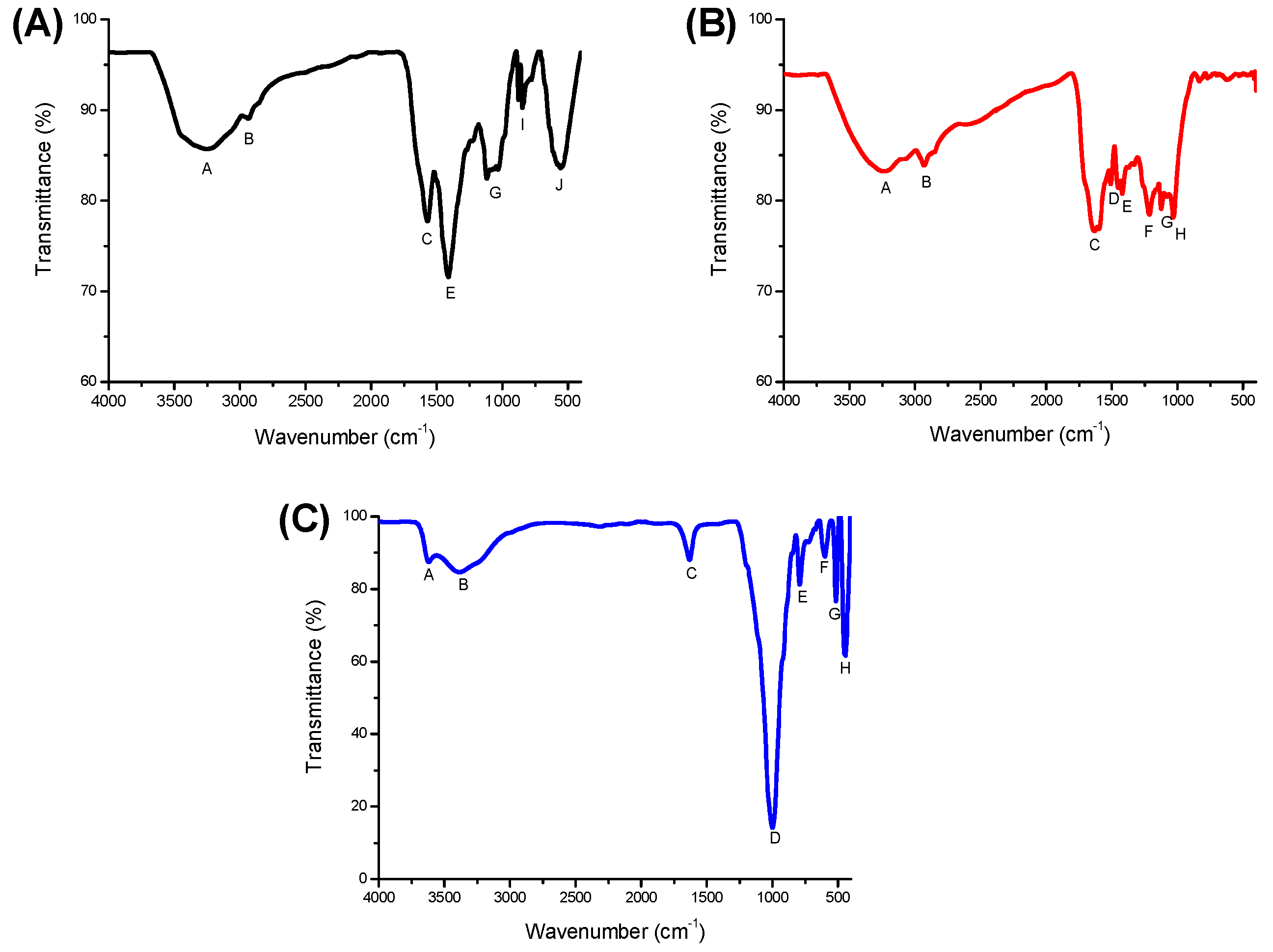

| Band | Wavenumber (cm−1) | Associated Functional Group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HA | SFHA | ||
| A | 3267 | 3238 | O-H stretching vibrations and partially N-H stretch |
| B | 2926 | 2927 | Aliphatic CH2 and CH3 |
| C | 1571 | 1597 | COO−, amides (NH2 of NH bonding) |
| D | 1508 | C=O of carboxylic groups and amide; N–H stretch; aromatic C=C | |
| E | 1412 | 1420 | COO− C=C stretch (aromatic ring), O–H and C–O of phenolic; C–N; C–H of CH3, CH2 and CH |
| F | 1215 | C–O and O–H stretch of COOH and phenol | |
| G | 1120 | 1123 | C–O stretch of alcohols, carbonyl, esters and ethers, O-H of phenol and carbohydrates |
| H | 1030 | Aromatic ethers, C-O of carbohydrates; Si-O of silicate | |
| I | 846 | Aromatic groups | |
| J | 620 | Aliphatic –CH2 | |
| Zeolite | |||
| A | 3621 | O-H stretching (Al3+-OH) | |
| B | 3387 | O-H stretching vibrations | |
| C | 1630 | H-O-H bending (water) | |
| D | 1000 | Si-O-Si antisymmetric stretch | |
| E | 793 | Si-O-Si stretching symmetric | |
| F | 600 | SiO4 and AlO4 tetrahedral | |
| G | 515 | Si-O bending vibration | |
| H | 444 | Si-O bending mode (-SiO4−) | |
| Element | Adsorbent | SEM | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA | SFHA | Zeolite | |||
| C | 35.42 b | 43.13 a | 31.99 c | 0.20 | <0.0001 |
| O | 20.32 b | 46.43 a | 14.13 c | 0.61 | <0.0001 |
| Na | 27.68 a | 1.78 b | 0.25 c | 0.11 | <0.0001 |
| Al | 0.26 c | 0.78 b | 7.46 a | 0.17 | <0.0001 |
| Si | 0.82 c | 1.60 b | 40.93 a | 0.08 | <0.0001 |
| K | 6.66 a | 0.17 c | 1.80 b | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| P | 1.53 a | 0.59 b | ND | 0.24 | 0.02 |
| S | 3.00 b | 4.80 a | ND | 0.21 | 0.004 |
| Cl | 3.77 a | 0.71 b | ND | - | - |
| Mg | ND | ND | 1.12 a | - | - |
| Ca | 0.54 b | ND | 1.45 a | - | 0.02 |
| Fe | ND | ND | 0.87 | - | - |
| Ingredient | % |
|---|---|
| Maize | 55.07 |
| Soybean meal | 36.94 |
| Vegetable oil | 3.32 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 1.58 |
| Calcium phosphate | 1.44 |
| Salt | 0.35 |
| DL-Methionine | 0.25 |
| Choline chloride 60% | 0.20 |
| L-Lysine HCL | 0.10 |
| Vitamin premix 1 | 0.30 |
| Mineral premix 2 | 0.30 |
| Antioxidant 3 | 0.15 |
| Protein | 19.5% |
| Metabolizable energy | 13 MJ/kg |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maguey-González, J.A.; Nava-Ramírez, M.d.J.; Gómez-Rosales, S.; Ángeles, M.d.L.; Solís-Cruz, B.; Hernández-Patlán, D.; Merino-Guzmán, R.; Hernández-Velasco, X.; Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.d.D.; Vázquez-Durán, A.; et al. Humic Acids Preparation, Characterization, and Their Potential Adsorption Capacity for Aflatoxin B1 in an In Vitro Poultry Digestive Model. Toxins 2023, 15, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020083
Maguey-González JA, Nava-Ramírez MdJ, Gómez-Rosales S, Ángeles MdL, Solís-Cruz B, Hernández-Patlán D, Merino-Guzmán R, Hernández-Velasco X, Figueroa-Cárdenas JdD, Vázquez-Durán A, et al. Humic Acids Preparation, Characterization, and Their Potential Adsorption Capacity for Aflatoxin B1 in an In Vitro Poultry Digestive Model. Toxins. 2023; 15(2):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020083
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaguey-González, Jesús Adonai, María de Jesús Nava-Ramírez, Sergio Gómez-Rosales, María de Lourdes Ángeles, Bruno Solís-Cruz, Daniel Hernández-Patlán, Rubén Merino-Guzmán, Xóchitl Hernández-Velasco, Juan de Dios Figueroa-Cárdenas, Alma Vázquez-Durán, and et al. 2023. "Humic Acids Preparation, Characterization, and Their Potential Adsorption Capacity for Aflatoxin B1 in an In Vitro Poultry Digestive Model" Toxins 15, no. 2: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020083
APA StyleMaguey-González, J. A., Nava-Ramírez, M. d. J., Gómez-Rosales, S., Ángeles, M. d. L., Solís-Cruz, B., Hernández-Patlán, D., Merino-Guzmán, R., Hernández-Velasco, X., Figueroa-Cárdenas, J. d. D., Vázquez-Durán, A., Hargis, B. M., Téllez-Isaías, G., & Méndez-Albores, A. (2023). Humic Acids Preparation, Characterization, and Their Potential Adsorption Capacity for Aflatoxin B1 in an In Vitro Poultry Digestive Model. Toxins, 15(2), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020083