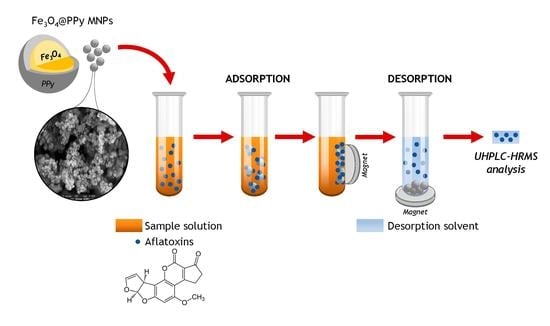
Dispersive Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction as a Novelty Sample Treatment for the Determination of the Main Aflatoxins in Paprika
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
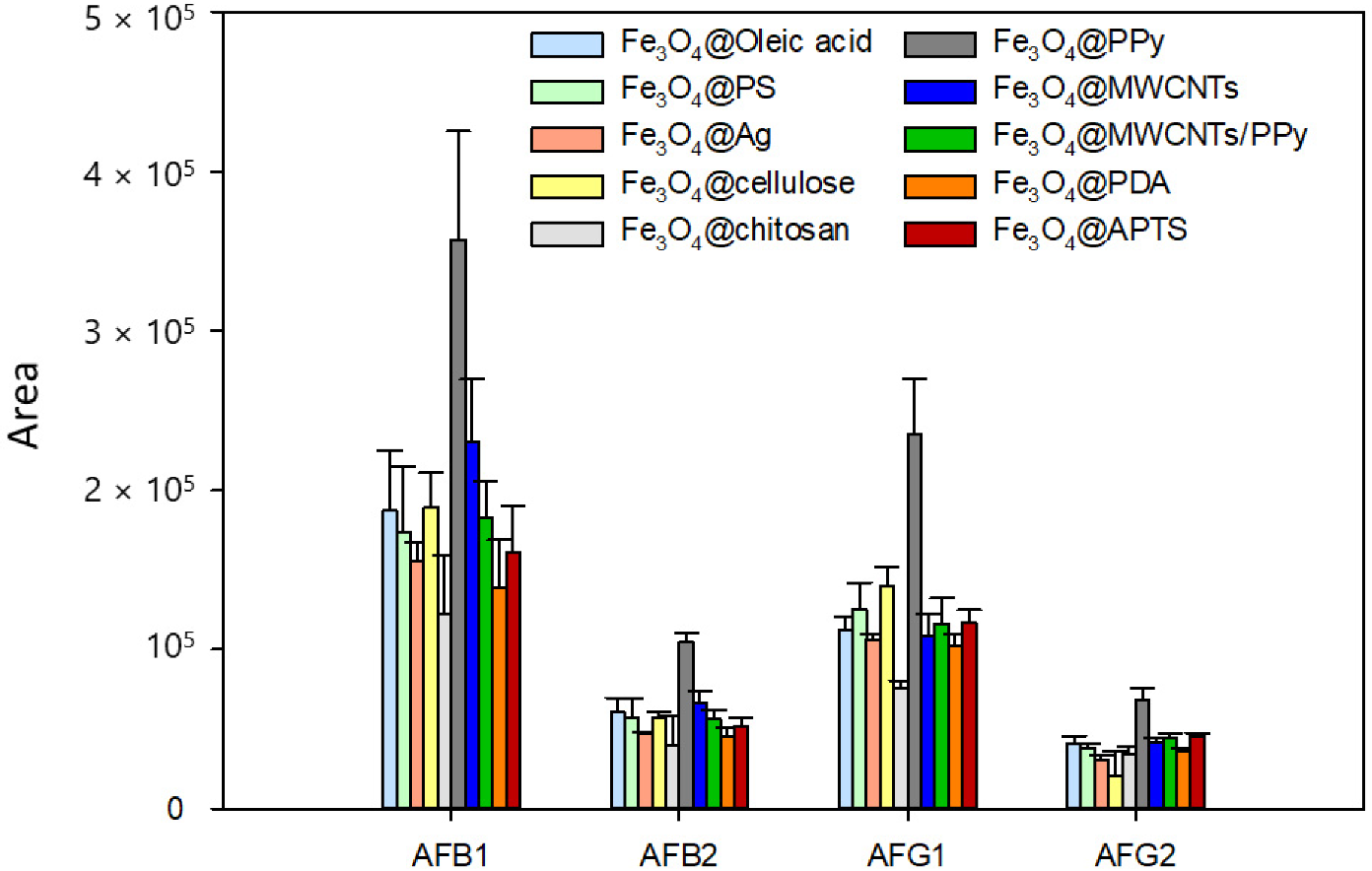
2.1. Characterization of Fe3O4@PPy Nanocomposite
2.2. DMSPE Procedure Optimization
2.3. Validation of the Analytical Method
2.4. Comparison with Other Methods
2.5. Commercial Paprika Samples Analysis
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Standards
4.2. Instrumentation and Software
4.3. Fe3O4@PPy Nanocomposite Synthesis
4.4. Samples
4.5. Sample Treatment
4.6. UHPLC-HRMS Analysis
4.7. HPLC-MS/MS Analysis
4.8. Method Validation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, P.; Tseng, M.; Su, A.; Chen, Y.; Lin, C. Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Small-Molecule Isolation, Identification, and Quantification. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5990–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhao, S.; Tchounwou, P.; Liu, Y.-M. A Nanoparticle-Based Solid Phase Extraction Method for Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometric Analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1166, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beiraghi, A.; Pourghazi, K.; Amoli-diva, M.; Razmara, A. Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction of Mefenamic Acid from Biological Samples Based on the Formation of Mixed Hemimicelle Aggregates on Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Prior to Its HPLC-UV Detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 945–946, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Synaridou, M.S.; Sakkas, V.A.; Stalikas, C.D.; Albanis, T.A. Evaluation of Magnetic Nanoparticles to Serve as Solid-Phase Extraction Sorbents for the Determination of Endocrine Disruptors in Milk Samples by Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1348, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimez, J.; Fente, C.A.; Vazquez, B.I.; Franco, C.M.; Cepeda, A.; Mahuzier, G.; Prognon, P. Application of the Assay of Aflatoxins by Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection in Food Analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 882, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, D.K.; Lee, K.E.; Kamle, M.; Devi, S.; Dewangan, K.N.; Kumar, P.; Kang, S.G. Aflatoxins in Food and Feed: An Overview on Prevalence, Detection and Control Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mccullum, C.; Tchounwou, P.; Ding, L.; Liao, X.; Liu, Y. Extraction of Aflatoxins from Liquid Foodstuff Samples with Polydopamine-Coated Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles for HPLC- MS/MS Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4261–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Taherimaslak, Z.; Rashidi, S. Enhanced Spectrofluorimetric Determination of Aflatoxin M1 in Liquid Milk after Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 128, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Bai, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G.; Yang, F. Multi-Mycotoxins Analysis in Liquid Milk by UHPLC-Q-Exactive HRMS after Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction Based on PEGylated Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 125429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Taherimaslak, Z. Determination of Aflatoxin M1 in Liquid Milk Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection after Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 33497–33506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Meng, Z.; Zhao, M.; Men, X.; Yang, J.; Li, J. Magnetic Hollow Bimetallic Zinc / Cobalt Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework as Sorbent for Efficiently Enriching Aflatoxins Combined with UHPLC-IT-MSn Determination. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ma, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, P. Determination of Aflatoxin B1 and B2 in Vegetable Oils Using Fe3O4/RGO Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Fluorescence with Post-Column Photochemical Derivatization. Toxins 2019, 11, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Adsorption of Aflatoxins and Ochratoxins in Edible Vegetable Oils with Dopamine-Coated Magnetic Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, A.; Fu, H.; Li, B.; Yang, M.; Wang, J.; Luan, Y. Affinity Capture of Aflatoxin B1 and B2 by Aptamer-Functionalized Magnetic Agarose Microspheres Prior to Their Determination by HPLC. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, M.; Allahyari, M.; Pourghazi, K.; Amoli-diva, M. Surfactant-Enhanced Spectrofluorimetric Determination of Total Aflatoxins from Wheat Samples after Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction Using Modified Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 146, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y. Simultaneous Determination of Aflatoxin B1 and Zearalenone by Magnetic Nanoparticles Filled Amino-Modified Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3353–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Taherimaslak, Z. Separation and Determination of Aflatoxins B1, B2, G1 and G2 in Pistachio Samples Based on the Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction Followed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 7663–7673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami-Osboo, R.; Ahmadpoor, F.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Maham, M. Polydopamine-Coated Magnetic Spirulina Nanocomposite for Efficient Magnetic Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of Aflatoxins in Pistachio. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 131967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Shao, Z.; Bao, X.; Yan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Determination of Aflatoxins in Milk Sample with Ionic Liquid Modified Magnetic Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1128, 121778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagher, M.; Hamid, S.; Ghasempour, R. Synthesis and Application of a Novel Functionalized Magnetic MIL-101(Cr) Nanocomposite for Determination of Aflatoxins in Pistachio Samples. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2020, 46, 4099–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alilou, S.; Amirzehni, M.; Eslami, P.A. A Simple Fluorometric Method for Rapid Screening of Aflatoxins after Their Extraction by Magnetic MOF-808/Graphene Oxide Composite and Their Discrimination by HPLC. Talanta 2021, 235, 122709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Tomé, M.; Jiménez, A.M.; Ruggieri, S.; Frega, N.; Strabbioli, R.; Murcia, M.A. Antioxidant Properties of Mediterranean Spices Compared with Common Food Additives. J. Food Prot. 2001, 64, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parliament, E.; Council, E.U. Regulation (EU) No 1151/2012 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 November 2012 on Quality Schemes for Agricultural Products and Foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2012, 343, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, J.; Rodríguez, R.; Garcia-Cela, E.; Medina, A.; Magan, N.; Lima, N.; Battilani, P.; Santos, C. Overview of Fungi and Mycotoxin Contamination in Capsicum Pepper and in Its Derivatives. Toxins 2019, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motloung, L.; De Saeger, S.; De Boevre, M.; Detavernier, C.; Audenaert, K.; Adebo, O.A.; Njobeh, P.B. Study on Mycotoxin Contamination in South African Food Spices. World Mycotoxin J. 2018, 11, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Nicolás, M.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Campillo, N.; Viñas, P. Cellulose-Ferrite Nanocomposite for Monitoring Enniatins and Beauvericins in Paprika by Liquid Chromatography and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Talanta 2021, 226, 122144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 2006, 5–24. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2006:364:0005:0024:EN:PDF (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Yu, X.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, C.; Sun, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Song, D. Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction of Five Pyrethroids from Environmental Water Samples Followed by Ultrafast Liquid Chromatography Analysis. Talanta 2012, 98, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-García, I.; Rengevicova, S.; Muñoz-Sandoval, M.J.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Speciation of Very Low Amounts of Antimony in Waters Using Magnetic Core-Modified Silver Nanoparticles and Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Talanta 2017, 162, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periyasamy, S.; Gopalakannan, V.; Viswanathan, N. Fabrication of Magnetic Particles Imprinted Cellulose Based Biocomposites for Chromium (VI) Removal. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharinezhad, A.A.; Ebrahimzadeh, H. Coextraction of Acidic, Basic and Amphiprotic Pollutants Using Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes/Magnetite Nanoparticles@polypyrrole Composite. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1412, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Lee, H.K. Study and Comparison of Polydopamine and Its Derived Carbon Decorated Nanoparticles in the Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction of Estrogens. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1414, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cong, L.; Meng, L.; Song, J.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, X. Preparation and Characterization of Magnetic Chitosan Microsphere Sorbent for Separation and Determination of Environmental Estrogens through SPE Coupled with HPLC. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukdasai, S.; Thomas, C.; Srijaranai, S. Analytical Methods Enhancement of Sensitivity for the Spectrophotometric Determination of Carbaryl Using Dispersive Liquid Microextraction Combined with Dispersive M-Solid Phase. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedé, J.L.; Chisvert, A.; Giokas, D.L.; Salvador, A. Development of Stir Bar Sorptive-Dispersive Microextraction Mediated by Magnetic Nanoparticles and Its Analytical Application to the Determination of Hydrophobic Organic Compounds in Aqueous Media. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1362, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wu, D.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, L. Polypyrrole-Modified Magnetic Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Based Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction Combined with Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by UHPLC-MS/MS for the Analysis of Sulfonamides in Environmental Water Samples. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 19578–19590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houshiar, M.; Zebhi, F.; Razi, Z.J.; Alidoust, A.; Askari, Z. Synthesis of Cobalt Ferrite (CoFe2O4) Nanoparticles Using Combustion, Coprecipitation, and Precipitation Methods: A Comparison Study of Size, Structural, and Magnetic Properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 371, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Qiao, K.; Li, L.; Liu, G.; Xu, X.; Lu, R.; Gao, H.; Xu, D. Preparation of a Magnetic Graphene/Polydopamine Nanocomposite for Magnetic Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of Benzoylurea Insecticides in Environmental Water Samples. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Mi, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Gao, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Lu, R. Preparation of Magnetic Attapulgite/Polypyrrole Nanocomposites for Magnetic Effervescence-Assisted Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of Pyrethroids from Honey Samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 2419–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Moreno, M.; Vargas-Ortiz, M.; Hernández-Camarillo, E.; Ruiz-Velasco, S.; Rojo-Callejas, F. Presence of Unreported Carcinogens, Aflatoxins and Their Hydroxylated Metabolites, in Industrialized Oaxaca Cheese from Mexico City. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esan, A.O.; Fapohunda, S.O.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Sulyok, M.; Krska, R. Distribution of Fungi and Their Toxic Metabolites in Melon and Sesame Seeds Marketed in Two Major Producing States in Nigeria. Mycotoxin Res. 2020, 36, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, J.; Chang, P.K.; Chen, Z.Y.; Bhatnagar, D.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Monitoring Metabolite Production of Aflatoxin Biosynthesis by Orbitrap Fusion Mass Spectrometry and a D-Optimal Mixture Design Method. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 14331–14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iram, W.; Anjum, T.; Iqbal, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Abbas, M. Mass Spectrometric Identification and Toxicity Assessment of Degraded Products of Aflatoxin B1 and B2 by Corymbia Citriodora Aqueous Extracts. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anjum, T.; Iram, W.; Iqbal, M.; Abbas, M.; Akram, W.; Li, G. Structure Elucidation and Toxicity Analysis of the Byproducts Formed after Biodegradation of Aflatoxins B1 and B2 Using Extracts of Mentha Arvensis. Toxins 2022, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 401/2006. Laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of the levels of mycotoxins in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 70, 12–34. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2006/401/oj (accessed on 20 January 2023).


| Mycotoxin | Equation | Linearity (μg kg−1) | Linearity R2 | LOD (μg kg−1) | LOQ (μg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1 | y = 5440x − 10,919 | 3.7–50 | 0.995 | 1.1 | 3.7 |
| AFB2 | y = 3636x − 11,161 | 3.9–50 | 0.993 | 1.2 | 3.9 |
| AFG1 | y = 5686x − 16,997 | 3.5–50 | 0.990 | 1.0 | 3.5 |
| AFG2 | y = 1982x − 15,273 | 4.7–50 | 0.998 | 1.4 | 4.7 |
| Repeatability, %RSD (n = 9) | Intermediate precision, %RSD (n = 12) | ||||
| 10 μg kg−1 | 25 μg kg−1 | 10 μg kg−1 | 25 μg kg−1 | ||
| AFB1 | 5.8 | 5.5 | 7.0 | 7.1 | |
| AFB2 | 7.6 | 7.1 | 7.2 | 7.7 | |
| AFG1 | 6.4 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 7.8 | |
| AFG2 | 5.3 | 5.9 | 5.6 | 5.3 | |
| Recoveries (%) (n = 9) | Matrix Effect (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mycotoxin | 10 μg kg−1 | 25 μg kg−1 | |
| AFB1 | 99.4 (0.7) | 81.9 (7.6) | 87.6 |
| AFB2 | 95.9 (4.8) | 98.7 (1.4) | 84.7 |
| AFG1 | 95.3 (4.6) | 96.9 (3.0) | 84.4 |
| AFG2 | 88.5 (10.0) | 88.8 (10.0) | 82.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Nicolás, M.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Viñas, P. Dispersive Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction as a Novelty Sample Treatment for the Determination of the Main Aflatoxins in Paprika. Toxins 2023, 15, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020160
García-Nicolás M, Arroyo-Manzanares N, Viñas P. Dispersive Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction as a Novelty Sample Treatment for the Determination of the Main Aflatoxins in Paprika. Toxins. 2023; 15(2):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020160
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Nicolás, María, Natalia Arroyo-Manzanares, and Pilar Viñas. 2023. "Dispersive Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction as a Novelty Sample Treatment for the Determination of the Main Aflatoxins in Paprika" Toxins 15, no. 2: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020160
APA StyleGarcía-Nicolás, M., Arroyo-Manzanares, N., & Viñas, P. (2023). Dispersive Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction as a Novelty Sample Treatment for the Determination of the Main Aflatoxins in Paprika. Toxins, 15(2), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020160