Shear Wave Velocity to Evaluate the Effect of Botulinum Toxin on Post-Stroke Spasticity of the Lower Limb
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Population Characteristics
2.2. Changes after BoNT-A Injection and Correlations between SWV and Clinical Examinations
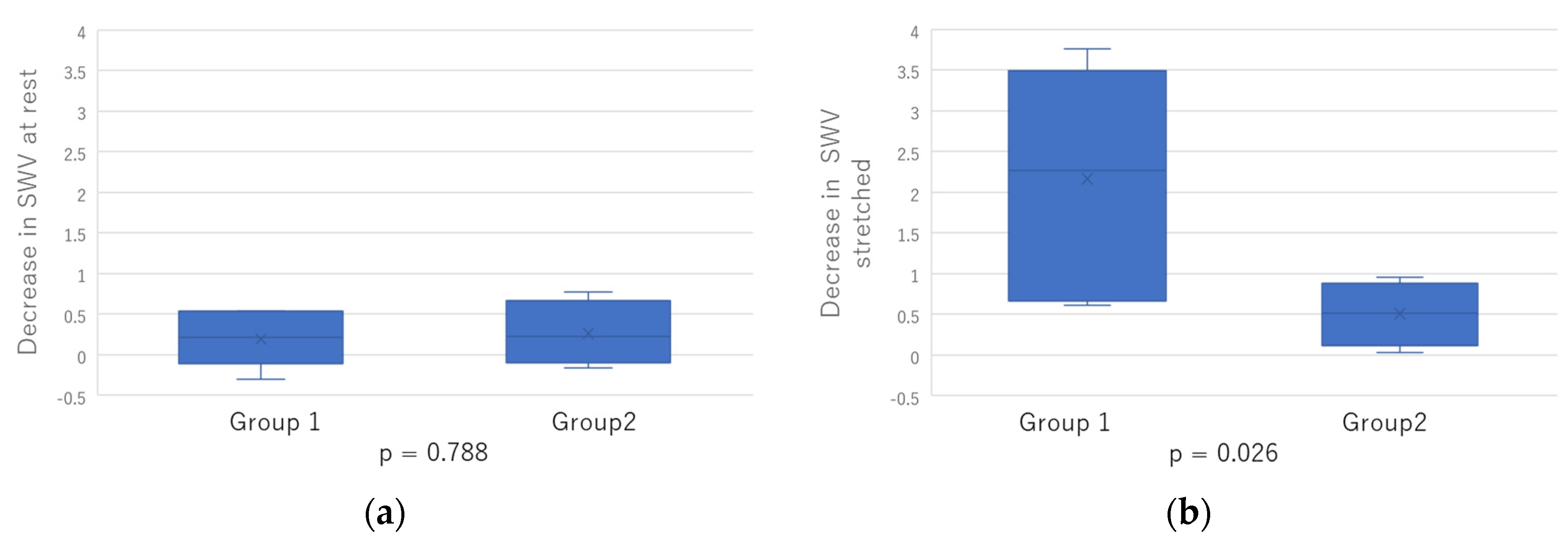
2.3. Comparison between Two Groups
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Participants
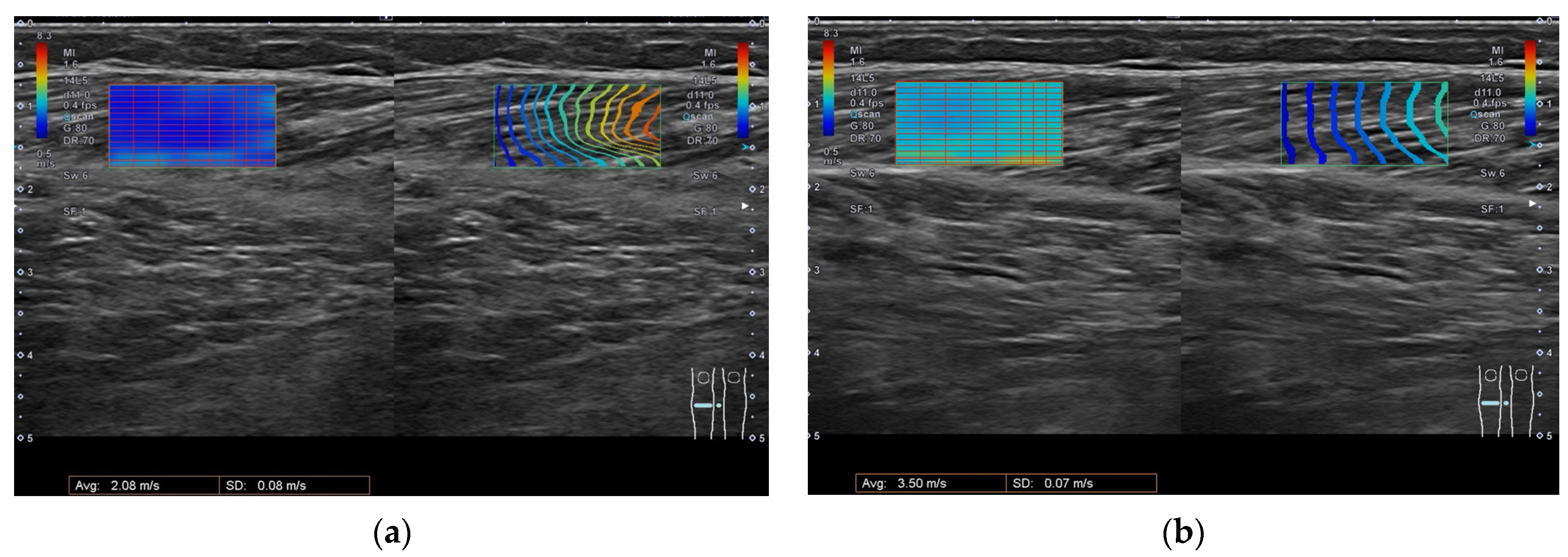
5.2. Ultrasonography
5.3. BoNT-A Treatment
5.4. Clinical Examination
5.5. Statistical Analysis
5.6. Equations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayer, N.H. Clinicophysiologic concepts of spasticity and motor dysfunction in adults with an upper motoneuron lesion. Muscle Nerve 1997, 20 (Suppl. S6), 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, D.K.; Eek, E.U.; Svensson, A.K.; Holmqvist, L.W.; von Arbin, M.H. Spasticity after stroke: Its occurrence and association with motor impairments and activity limitations. Stroke 2004, 35, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watkins, C.L.; Leathley, M.J.; Gregson, J.M.; Moore, A.P.; Smith, T.L.; Sharma, A.K. Prevalence of spasticity post stroke. Clin. Rehabil. 2002, 16, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinwelski, M.; Sławek, J. Prevalence of spasticity following stroke and its impact on quality of life with emphasis on disability in activities of daily living. Systematic review. Neurol. I Neurochir. Pol. 2010, 44, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, A.; Abo, M.; Kawate, N.; Osako, Y.; Suyama, K.; Maeda, T.; Uechi, Y.; Iwasaki, M. Efficacy and Safety of Botulinum Toxin Type A in treating Lower Limb Spasticity in Post-stroke Patients: A Multicenter, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Trial followed by an Open-label Trial. Jpn. J. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 47, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burbaud, P.; Wiart, L.; Dubos, J.L.; Gaujard, E.; Debelleix, X.; Joseph, P.A.; Mazaux, J.M.; Bioulac, B.; Barat, M.; Lagueny, A. A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial of botulinum toxin in the treatment of spastic foot in hemiparetic patients. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1996, 61, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanikawa, H.; Kagaya, H.; Saitoh, E.; Ozaki, K.; Hirano, S.; Itoh, N.; Yamada, J.; Kanada, Y. Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin A Treatment for Pes Varus during Gait. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 2416–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brin, M.F. Botulinum toxin: Chemistry, pharmacology, toxicity, and immunology. Muscle Nerve 1997, 20 (Suppl. S6), 146–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.N.; Pliatsios, V.; Starr, R.; Wolfe, R.; Graham, H.K. Biomechanical transformation of the gastroc-soleus muscle with botulinum toxin A in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2000, 42, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, A.E.; Filippini, G.; Calandrella, D.; Albanese, A. Botulinum Neurotoxin for Post-Stroke Spasticity in Adults: A Systematic Review. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, R.L.; Chua-Yap, A.S. Evidence-based systematic review on the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin-A therapy in post-stroke spasticity. J. Neural Transm. 2008, 115, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Smith, M.B. Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Phys. Ther. 1987, 67, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, M.; Albanese, A.; Heinen, F.; Molenaers, G.; Relja, M. Safety and efficacy of botulinum toxin type A following long-term use. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, M.F.; Brashear, A.; Elovic, E.; Kassicieh, D.; Marciniak, C.; Liu, J.; Turkel, C.; BOTOX Poststroke Spasticity Study Group. Repeated dosing of botulinum toxin type A for upper limb spasticity following stroke. Neurology 2004, 63, 1971–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, T.; Momosaki, R.; Niimi, M.; Yamada, N.; Hara, H.; Abo, M. Botulinum Toxin Therapy Combined with Rehabilitation for Stroke: A Systematic Review of Effect on Motor Function. Toxins 2019, 11, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleuren, J.F.; Voerman, G.E.; Erren-Wolters, C.V.; Snoek, G.J.; Rietman, J.S.; Hermens, H.J.; Nene, A.V. Stop using the Ashworth Scale for the assessment of spasticity. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balci, B.P. Spasticity Measurement. Arch. Neuropsychiatry 2018, 55 (Suppl. S1), S49–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrholz, J.; Wagner, K.; Meissner, D.; Grundmann, K.; Zange, C.; Koch, R.; Pohl, M. Reliability of the Modified Tardieu Scale and the Modified Ashworth Scale in adult patients with severe brain injury: A comparison study. Clin. Rehabil. 2005, 19, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.P.; Johnson, G.R. Upper Motor Neurone Syndrome and Spasticity: Clinical Management and Neurophysiology, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Akpinar, P.; Atici, A.; Ozkan, F.U.; Aktas, I.; Kulcu, D.G.; Sarı, A.; Durmus, B. Reliability of the Modified Ashworth Scale and Modified Tardieu Scale in patients with spinal cord injuries. Spinal Cord 2017, 55, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, N.N.; Naghdi, S.; Hasson, S.; Azarsa, M.H.; Azarnia, S. The Modified Tardieu Scale for the measurement of elbow flexor spasticity in adult patients with hemiplegia. Brain Inj. 2008, 22, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreta, M.C.; Fleet, A.; Reebye, R.; McKernan, G.; Berger, M.; Farag, J.; Munin, M.C. Reliability and Validity of the Modified Heckmatt Scale in Evaluating Muscle Changes With Ultrasound in Spasticity. Arch. Rehabil. Res. Clin. Transl. 2020, 2, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picelli, A.; Bonetti, P.; Fontana, C.; Barausse, M.; Dambruoso, F.; Gajofatto, F.; Girardi, P.; Manca, M.; Gimigliano, R.; Smania, N. Is spastic muscle echo intensity related to the response to botulinum toxin type A in patients with stroke? A cohort study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aşkın, A.; Kalaycı, Ö.; Bayram, K.B.; Tosun, A.; Demirdal, Ü.; Atar, E.; İnci, M.F. Strain sonoelastographic evaluation of biceps muscle intrinsic stiffness after botulinum toxin-A injection. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2017, 24, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Rubin, J.M.; Chen, J.; O’Dell, M. Ultrasound Elastography to Assess Botulinum Toxin A Treatment for Post-stroke Spasticity: A Feasibility Study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, J.E.; Eby, S.F.; Song, P.; Zhao, H.; Brault, J.S.; Chen, S.; An, K.N. Ultrasound elastography: The new frontier in direct measurement of muscle stiffness. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Creze, M.; Nordez, A.; Soubeyrand, M.; Rocher, L.; Maître, X.; Bellin, M.F. Shear wave sonoelastography of skeletal muscle: Basic principles, biomechanical concepts, clinical applications, and future perspectives. Skelet. Radiol. 2018, 47, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dağ, N.; Cerit, M.N.; Şendur, H.N.; Zinnuroğlu, M.; Muşmal, B.N.; Cindil, E.; Oktar, S. The utility of shear wave elastography in the evaluation of muscle stiffness in patients with cerebral palsy after botulinum toxin A injection. J. Med. Ultrason. 2020, 47, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.Y.; Kwon, D.R. Sonoelastographic evaluation of medial gastrocnemius muscles intrinsic stiffness after rehabilitation therapy with botulinum toxin a injection in spastic cerebral palsy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 2085–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, W.; Corazza, A.; Puce, L.; Privitera, L.; Pedrini, R.; Mori, L.; Boccuni, L.; Turtulici, G.; Trompetto, C.; Marinelli, L. Shear wave elastography combined with electromyography to assess the effect of botulinum toxin on spastic dystonia following stroke: A pilot study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 980746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Ho, Y.C.; Hsiao, M.Y.; Chen, W.S.; Wang, T.G. Evaluation of Post-Stroke Spastic Muscle Stiffness Using Shear Wave Ultrasound Elastography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picelli, A.; Tamburin, S.; Cavazza, S.; Scampoli, C.; Manca, M.; Cosma, M.; Berto, G.; Vallies, G.; Roncari, L.; Melotti, C.; et al. Relationship between ultrasonographic, electromyographic, and clinical parameters in adult stroke patients with spastic equinus: An observational study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 1564–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picelli, A.; Filippetti, M.; Melotti, C.; Guerrazzi, F.; Modenese, A.; Smania, N. Does Botulinum Toxin Treatment Affect the Ultrasonographic Characteristics of Post-Stroke Spastic Equinus? A Retrospective Pilot Study. Toxins 2020, 12, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.K.; Hug, F. Factors that influence muscle shear modulus during passive stretch. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 3539–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.S.; Spear, S.; Rymer, W.Z. Quantifying changes in material properties of stroke-impaired muscle. Clin. Biomech. 2015, 30, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.M.; Jakubowski, K.L.; Spear, S.C.; Rymer, W.Z. Response to Letter to the Editor for Manuscript “Muscle material properties in passive and active stroke-impaired muscle”. J. Biomech. 2019, 93, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, K.L.; Terman, A.; Santana, R.V.C.; Lee, S.S.M. Passive material properties of stroke-impaired plantarflexor and dorsiflexor muscles. Clin. Biomech. 2017, 49, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, J.E.; Eby, S.F.; Song, P.; Kingsley-Berg, S.; Bamlet, W.; Sieck, G.C.; An, K.N. Quantifying passive muscle stiffness in children with and without cerebral palsy using ultrasound shear wave elastography. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Xiao, Y.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, Z.; Ren, J.; Zheng, R.; Zheng, H.; Chen, Z. Reliability and diagnostic accuracy of corrected slack angle derived from 2D-SWE in quantitating muscle spasticity of stroke patients. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2022, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernak, L.A.; DeWall, R.J.; Lee, K.S.; Thelen, D.G. Length and activation dependent variations in muscle shear wave speed. Physiol. Meas. 2013, 34, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puce, L.; Currà, A.; Marinelli, L.; Mori, L.; Capello, E.; Di Giovanni, R.; Bodrero, M.; Solaro, C.; Cotellessa, F.; Fattapposta, F.; et al. Spasticity, spastic dystonia, and static stretch reflex in hypertonic muscles of patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2021, 6, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.S.; Ertl-Wagner, B.; Britsch, S.; Schröder, J.M.; Nikolin, S.; Weis, J.; Müller-Felber, W.; Koerte, I.; Stehr, M.; Berweck, S.; et al. Muscle biopsy substantiates long-term MRI alterations one year after a single dose of botulinum toxin injected into the lateral gastrocnemius muscle of healthy volunteers. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidensteiner, C.; Madoerin, P.; Deligianni, X.; Haas, T.; Bieri, O.; Akinci D’Antonoli, T.; Bracht-Schweizer, K.; Romkes, J.; De Pieri, E.; Santini, F.; et al. Quantification and Monitoring of the Effect of Botulinum Toxin A on Paretic Calf Muscles of Children With Cerebral Palsy With MRI: A Preliminary Study. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 630435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vola, E.A.; Albano, M.; Di Luise, C.; Servodidio, V.; Sansone, M.; Russo, S.; Corrado, B.; Servodio Iammarrone, C.; Caprio, M.G.; Vallone, G. Use of ultrasound shear wave to measure muscle stiffness in children with cerebral palsy. J. Ultrasound 2018, 21, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilgici, M.C.; Bekci, T.; Ulus, Y.; Ozyurek, H.; Aydin, O.F.; Tomak, L.; Selcuk, M.B. Quantitative assessment of muscular stiffness in children with cerebral palsy using acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) ultrasound elastography. J. Med. Ultrason. 2018, 45, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallemant-Dudek, P.; Vergari, C.; Dubois, G.; Forin, V.; Vialle, R.; Skalli, W. Ultrasound shearwave elastography to characterize muscles of healthy and cerebral palsy children. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eby, S.; Zhao, H.; Song, P.; Vareberg, B.J.; Kinnick, R.; Greenleaf, J.F.; An, K.N.; Chen, S.; Brown, A.W. Quantitative Evaluation of Passive Muscle Stiffness in Chronic Stroke. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 95, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; He, W.; Du, L.J.; Chen, J.; Park, D.; Wells, M.; Fowlkes, B.; O’Dell, M. Quantitative Ultrasound Imaging to Assess the Biceps Brachii Muscle in Chronic Post-Stroke Spasticity: Preliminary Observation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathevon, L.; Michel, F.; Aubry, S.; Testa, R.; Lapole, T.; Arnaudeau, L.F.; Fernandez, B.; Parratte, B.; Calmels, P. Two-dimensional and shear wave elastography ultrasound: A reliable method to analyse spastic muscles? Muscle Nerve 2018, 57, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, J.E.; Eby, S.F.; Song, P.; Bamlet, W.R.; Sieck, G.C.; An, K.N. Quantifying Effect of Onabotulinum Toxin A on Passive Muscle Stiffness in Children with Cerebral Palsy Using Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 97, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, K.; Takahashi, H. Influence of pennation angle on measurement of shear wave elastography: In vivo observation of shear wave propagation in human pennate muscle. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 115003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunnstrom, S. Motor testing procedures in hemiplegia: Based on sequential recovery stages. Phys. Ther. 1966, 46, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naghdi, S.; Ansari, N.N.; Mansouri, K.; Hasson, S. A neurophysiological and clinical study of Brunnstrom recovery stages in the upper limb following stroke. Brain Inj. 2010, 24, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, M. Principle of Ultrasound Elastography Based on Shear Wave Propagation. Med. Imaging Technol. 2014, 32, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Subject Demographics | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | |
| mean (SD) | 62.7 (8.7) |
| Gender (n) | |
| male/female | 7/3 |
| Time since stroke onset (years) | |
| mean (SD) | 13.4 (3.9) |
| Stroke etiology (n) | |
| ischemic/hemorrhagic | 1/9 |
| ROM changes after treatment: (Group 1) no change; (Group 2) change. | |
| Group1/2 | 6/4 |
| Age | Sex | Stroke Hemisphere | Etiology | Period | Dose GCM/GCL/Sol | Timing | MHS | MAS | MTS X | MTS R1 | MTS R2 | SWV at Rest | SWV Stretched | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | before | 56 | F | L | H | 12.2 | 50/30/50 | 30 | 4 | 2 | 2 | −15 | 0 | 2.49 | 5.01 |
| after | 2 | 2 | −15 | 0 | 2.46 | 2.82 | |||||||||
| 2 | before | 60 | M | R | H | 10.4 | 30/30/60 | 28 | 4 | 3 | 2 | −30 | −20 | 2.28 | 6.77 |
| after | 3 | 2 | −30 | −20 | 2.32 | 3.01 | |||||||||
| 3 | before | 77 | M | L | H | 10 | 40/40/40 | 29 | 2 | 2 | 3 | −10 | 0 | 2.6 | 7.6 |
| after | 1.5 | 2 | −5 | 0 | 2.9 | 5.25 | |||||||||
| 4 | before | 72 | M | L | H | 16.3 | 40/40/40 | 28 | 3 | 2 | 2 | −40 | −35 | 2.23 | 3.63 |
| after | 2 | 2 | −35 | −25 | 2.16 | 3.6 | |||||||||
| 5 | before | 66 | F | R | H | 21.8 | 40/40/50 | 34 | 3 | 3 | 3 | −25 | −20 | 2.78 | 3.86 |
| after | 2 | 3 | −20 | −15 | 2.41 | 2.9 | |||||||||
| 6 | before | 62 | M | R | I | 11.7 | 40/0/40 | 28 | 2 | 3 | 2 | −40 | −35 | 2.54 | 2.93 |
| after | 2 | 2 | −30 | −20 | 1.77 | 2.53 | |||||||||
| 7 | before | 50 | M | R | H | 12.1 | 40/30/40 | 33 | 3 | 2 | 2 | −30 | −25 | 2.17 | 3.56 |
| after | 2 | 1 | −30 | −25 | 1.64 | 2.95 | |||||||||
| 8 | before | 71 | F | R | H | 17.7 | 40/0/40 | 28 | 3 | 3 | 3 | −35 | −30 | 1.92 | 4.14 |
| after | 1.5 | 1.5 | −10 | 0 | 2.08 | 3.5 | |||||||||
| 9 | before | 59 | M | L | H | 12.9 | 20/0/40 | 29 | 4 | 3 | 2 | −30 | −10 | 2.76 | 6.78 |
| after | 1.5 | 2 | −25 | −10 | 2.36 | 3.38 | |||||||||
| 10 | before | 54 | M | R | H | 9.4 | 50/50/70 | 26 | 3 | 3 | 2 | −45 | −35 | 2.64 | 3.21 |
| after | 3 | 2 | −40 | −35 | 2.1 | 2.52 |
| Before BoNT-A Injection | After BoNT-A Injection | p-Value a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAS (Median (IQR)) | 3 (2–3) | 2 (1.5–3) | * 0.041 |
| MTS X (Median (IQR)) | 2 (2–3) | 2 (2–2) | 0.102 |
| R1 (o) (Median (IQR)) | −30 (−40–−22.5) | −27.5 (−31.3–−13.8) | * 0.014 |
| R2 (o) (Median (IQR)) | −22.5 (−35.0–−7.5) | −17.5 (−25.0–0.0) | 0.068 |
| SWV at rest (m/s) (Median (IQR)) | 2.52 (2.21–2.67) | 2.24 (2.00–2.42) | 0.093 |
| SWV stretched (m/s) (Median (IQR)) | 4.00 (3.47–6.77) | 2.98 (2.74–3.52) | * 0.005 |
| Age | Period | MTS R1 | MTS R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWV at rest | r | −0.106 | −0.089 | 0.227 | 0.364 |
| before BoNT-A injection | p | 0.77 | 0.806 | 0.528 | 0.301 |
| SWV at rest | r | 0.534 | −0.012 | 0.602 | 0.579 |
| after BoNT-A injection | p | 0.111 | 0.974 | 0.066 | 0.079 |
| SWV stretched | r | 0.283 | −0.325 | 0.663 | * 0.773 |
| before BoNT-A injection | p | 0.428 | 0.359 | 0.036 | * 0.009 |
| SWV stretched | r | 0.749 | −0.069 | 0.638 | 0.534 |
| after BoNT-A injection | p | 0.013 | 0.85 | 0.047 | 0.112 |
| MHS | MAS | MTS X | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWV at rest | ρ | −0.013 | 0.355 | 0.114 |
| before BoNT-A injection | p | 0.971 | 0.314 | 0.754 |
| SWV at rest | ρ | 0.243 | −0.23 | 0.634 |
| after BoNT-A injection | p | 0.498 | 0.522 | 0.049 |
| SWV stretched | ρ | 0.395 | −0.142 | 0.342 |
| before BoNT-A injection | p | 0.259 | 0.695 | 0.334 |
| SWV stretched | ρ | −0.072 | −0.632 | −0.201 |
| after BoNT-A injection | p | 0.843 | 0.051 | 0.577 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasegawa, Y.; Niimi, M.; Hara, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Soshi, S.; Udaka, J.; Abo, M. Shear Wave Velocity to Evaluate the Effect of Botulinum Toxin on Post-Stroke Spasticity of the Lower Limb. Toxins 2023, 15, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010014
Hasegawa Y, Niimi M, Hara T, Sakurai Y, Soshi S, Udaka J, Abo M. Shear Wave Velocity to Evaluate the Effect of Botulinum Toxin on Post-Stroke Spasticity of the Lower Limb. Toxins. 2023; 15(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasegawa, Yuki, Masachika Niimi, Takatoshi Hara, Yoshihiro Sakurai, Shigeru Soshi, Jun Udaka, and Masahiro Abo. 2023. "Shear Wave Velocity to Evaluate the Effect of Botulinum Toxin on Post-Stroke Spasticity of the Lower Limb" Toxins 15, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010014
APA StyleHasegawa, Y., Niimi, M., Hara, T., Sakurai, Y., Soshi, S., Udaka, J., & Abo, M. (2023). Shear Wave Velocity to Evaluate the Effect of Botulinum Toxin on Post-Stroke Spasticity of the Lower Limb. Toxins, 15(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010014





