Experimental Bothrops atrox Envenomation: Blood Plasma Proteome Effects after Local Tissue Damage and Perspectives on Thromboinflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
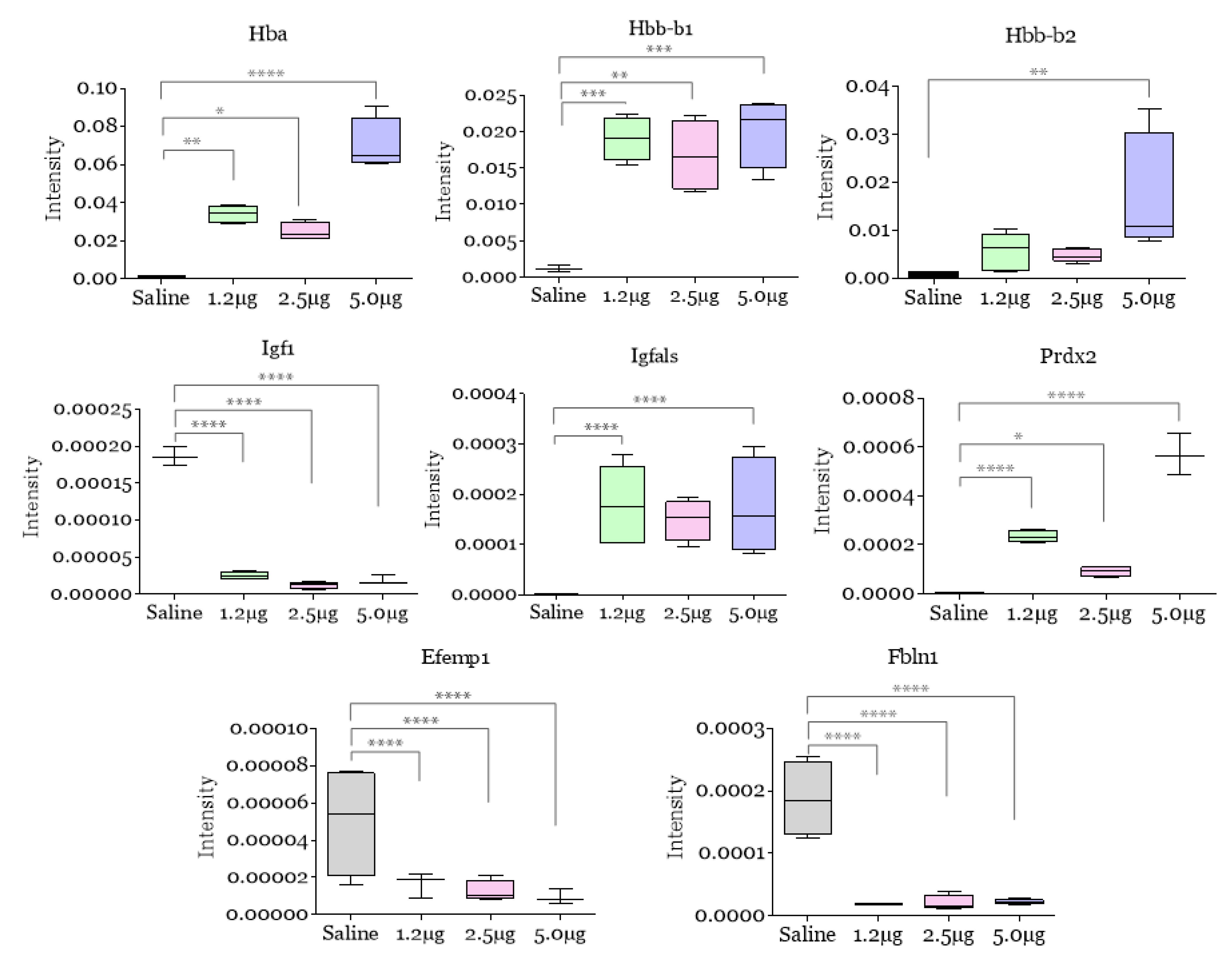
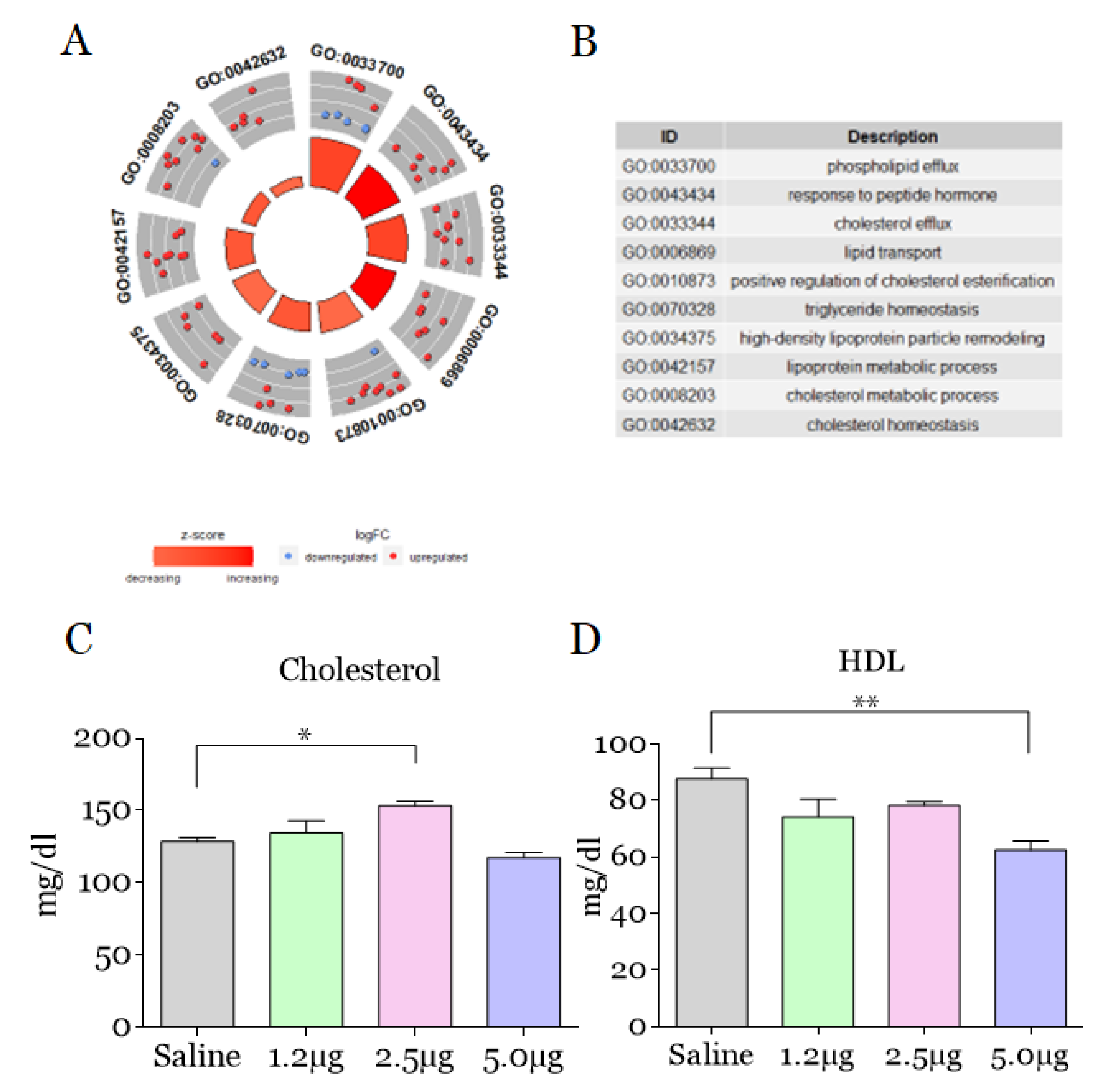
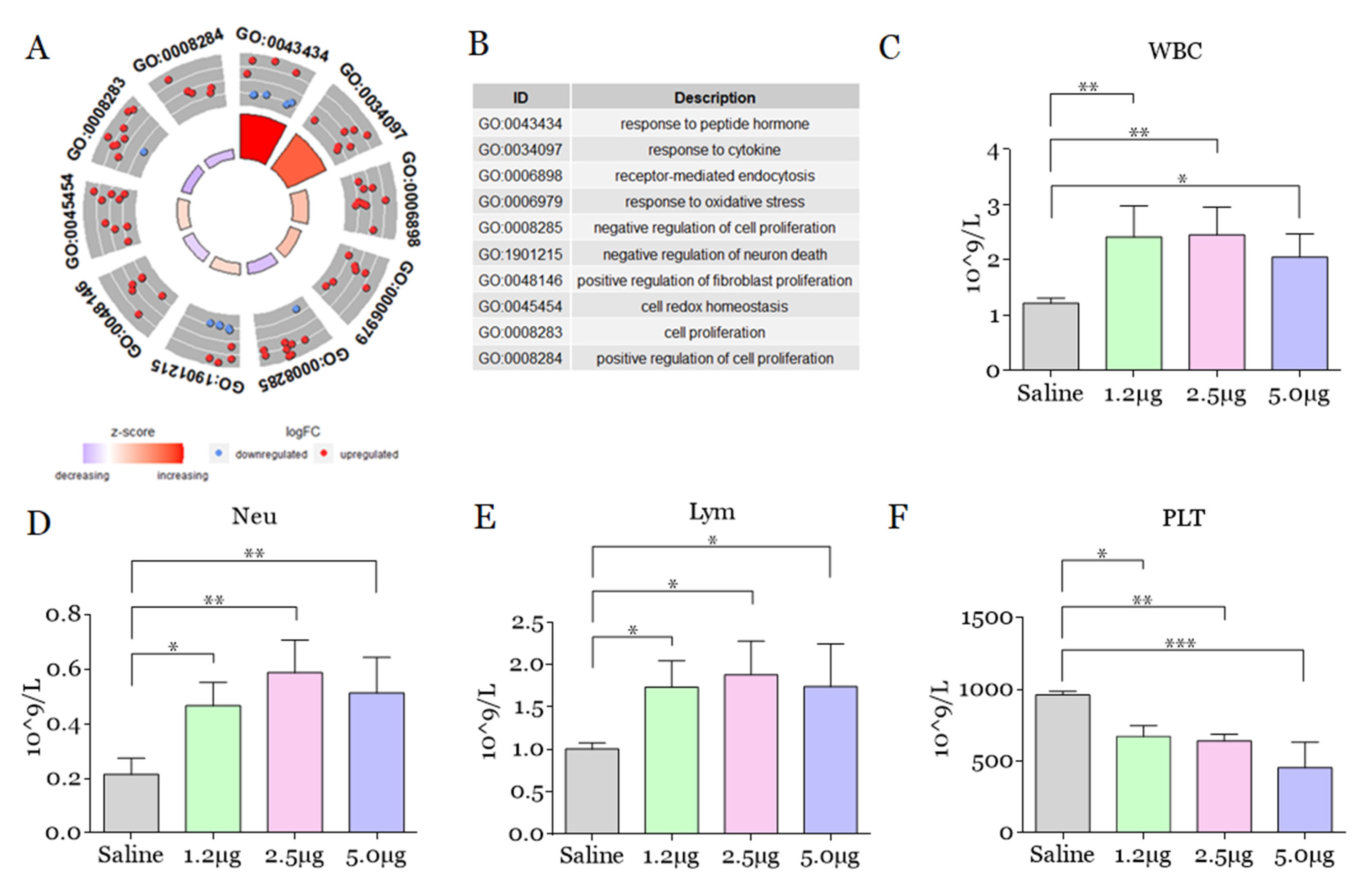
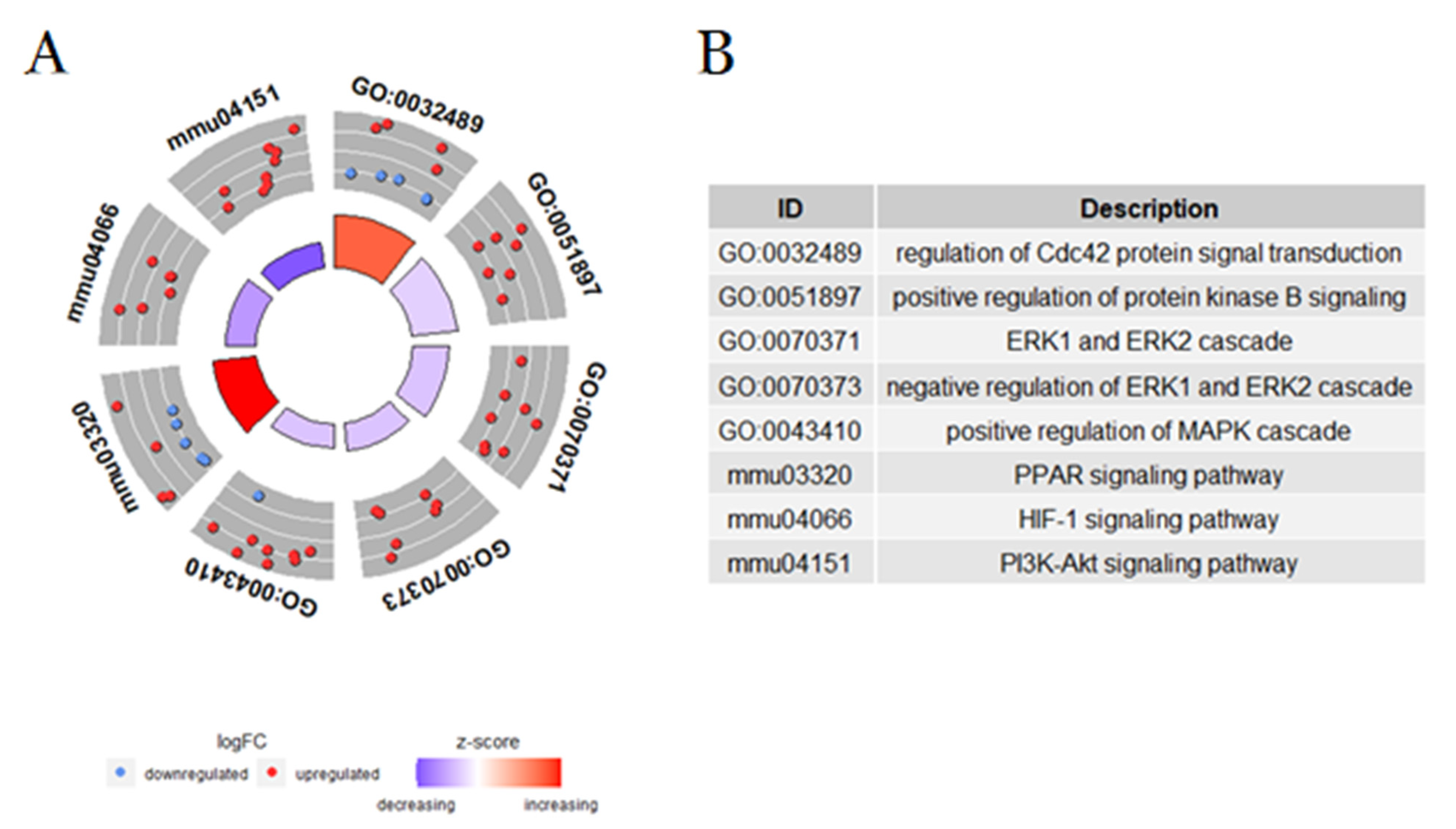
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Snake Venom Bothrops atrox
4.2. Animals and Experimental Envenomation
4.3. Hematologic and Lipidic Analysis
4.4. Collection, Selection, and Grouping of Plasma Samples
4.5. LC-MS/MS Analyses and Data Processing
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, A.M.D.; Colombini, M.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Souza, R.M.D.; Monteiro, W.M.; Bernarde, P.S. Epidemiological and clinical aspects of snakebites in the upper Juruá River region, western Brazilian Amazonia. Acta Amaz. 2019, 50, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, W.M.; Contreras-Bernal, J.C.; Bisneto, P.F.; Sachett, J.; Mendonça da Silva, I.; Lacerda, M.; Guimarães da Costa, A.; Val, F.; Brasileiro, L.; Sartim, M.A.; et al. Bothrops atrox, the most important snake involved in human envenomings in the amazon: How venomics contributes to the knowledge of snake biology and clinical toxinology. Toxicon X 2020, 23, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, L.F.; Portes-Junior, J.A.; Nicolau, C.A.; Bernardoni, J.L.; Nishiyama, M.Y., Jr.; Amazonas, D.R.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Functional proteomic analyses of Bothrops atrox venom reveals phenotypes associated with habitat variation in the Amazon. J. Proteom. 2017, 159, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G.K. A Review and Database of Snake Venom Proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, J.D.S.; Nogueira Júnior, F.A.; Bezerra-Jorge, R.J.; Almeida, C. Pain modulated by Bothrops snake venoms: Mechanisms of nociceptive signaling and therapeutic perspectives. Toxicon 2021, 201, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, S.S.; Alves, E.C.; Santos, A.S.; Nascimento, E.F.; Pereira, J.P.T.; Silva, I.M.; Sachett, J.A.G.; Sarraff, L.K.S.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Colombini, M.; et al. Bleeding Disorders in Bothrops atrox Envenomations in the Brazilian Amazon: Participation of Hemostatic Factors and the Impact of Tissue Factor. Toxins 2020, 12, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibiapina, H.N.S.; Costa, A.G.; Sachett, J.A.G.; Silva, I.M.; Tarragô, A.M.; Neves, J.C.F.; Monteiro, W.M. An immunological stairway to severe tissue complication assembly in Bothrops atrox snakebites. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.S.; Ibiapina, H.N.S.; Neves, J.C.F.; Coelho, K.F.; Barbosa, F.B.A.; Lacerda, M.V.G.; Sachett, J.A.G.; Malheiro, A.; Monteiro, W.M.; Costa, A.G. Severe tissue complications in patients of Bothrops snakebite at a tertiary health unit in the Brazilian Amazon: Clinical characteristics and associated factors. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2021, 54, e0374–e2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickler, P.E. Amplification of snake venom toxicity by endogenous signaling pathways. Toxins 2020, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, C.R.; Arrahman, A.; Xie, C.; Casewell, N.R.; Lewis, R.J.; Kool, J.; Cardoso, F.C. Multifunctional toxins in snake venoms and therapeutic implications: From pain to hemorrhage and necrosis. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, C.; Fernandes, C.M.; Leiguez, E.; Chudzinski-Tavassi, A.M. Inflammation induced by platelet-activating viperid snake venoms: Perspectives on thromboinflammation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, J.D.S.; de Almeida, C.A.S.; Clasen, M.A.; da Silva, E.L.; de Barros, L.C.; Marinho, A.D.; Rossini, B.C.; Marino, C.L.; Carvalho, P.C.; Jorge, R.J.B.; et al. A fingerprint of plasma proteome alteration after local tissue damage induced by Bothrops leucurus snake venom in mice. J. Proteom. 2021, 253, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luciano, P.M.; Silva, G.E.B.; Azevedo-Marques, M.M. Acidente botrópico fatal. Medicina 2009, 42, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graciano, A.R.; de Carvalho, K.C.N. Syndrome associated to snake bite of the Bothrops gender: Case report. Rev. Pesqui. Saúde 2018, 18, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Valle, L.A.; Silva, D.D.F.R.; Magalhães, P.H.; Mattos, P.A.; Leal, J.A. Amputação bilateral de extremidades inferiores após acidente botrópico grave: Relato de um caso. Arq. Médicos Hosp. Fac. Ciências Médicas St. Casa São Paulo 2018, 53, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen, C.; Jürgensen, J.A.; Føns, S.; Haack, A.M.; Friis, R.U.W.; Dam, S.H.; Bush, S.P.; White, J.; Laustsen, A.H. Snakebite Envenoming Diagnosis and Diagnostics. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 661457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Barreto, G.N.L.; de Oliveira, S.S.; Dos Anjos, I.V.; Chalkidis, H.D.M.; Mourão, R.H.V.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Gonçalves, L.R.D.C. Experimental Bothrops atrox envenomation: Efficacy of antivenom therapy and the combination of Bothrops antivenom with dexamethasone. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senise, L.V.; Yamashita, K.M.; Santoro, M.L. Bothrops jararaca envenomation: Pathogenesis of hemostatic disturbances and intravascular hemolysis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucaretchi, F.; Pimenta, M.M.B.; Borrasca-Fernandes, C.F.; Prado, C.C.; Capitani, E.M.D.; Hyslop, S. Thrombotic microangiopathy following Bothrops jararaca snakebite: Case report. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaque, C.M.S.; Duayer, I.F.; Santoro, M.L. Acute kidney injury induced by thrombotic microangiopathy in two cases of Bothrops envenomation. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, S.M.B.; Albuquerque, P.L.M.M.; Silva Júnior, G.B.D.; Daher, E.D.F. Thrombotic microangiopathy due to Bothrops erythromelas: A case report in Northeast Brazil. Rev. Do Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2020, 62, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, G.B.; Alves, L.S.; De Oliveira, R.; Dutra, F.F.; Rodrigues, D.; Fernandez, P.L.; Souto-Padron, T.; Rosa, M.J.; Kelliher, M.; Golenbock, D.; et al. Heme induces programmed necrosis on macrophages through autocrine TNF and ROS production. Blood 2012, 119, 2368–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krzyszczyk, P.; Schloss, R.; Palmer, A.; Berthiaume, F. The role of macrophages in acute and chronic wound healing and interventions to promote pro-wound healing phenotypes. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Chen, I.; Chen, Y.; Alkam, D.; Wang, Y.; Semenza, G.L. PRDX2 and PRDX4 are negative regulators of hypoxia-inducible factors under conditions of prolonged hypoxia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 6379–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobotta, M.C.; Liou, W.; Stöcker, S.; Talwar, D.; Oehler, M.; Ruppert, T.; Scharf, A.N.D.; Dick, T.P. Peroxiredoxin-2 and STAT3 form a redox relay for H 2 O 2 signaling. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Kim, S.U.; Yu, S.L.; Kim, S.H.; Park, D.S.; Moon, H.B.; Dho, S.H.; Kwon, K.S.; Kwon, H.J.; Han, Y.H.; et al. Peroxiredoxin II is essential for sustaining life span of erythrocytes in mice. Blood 2003, 101, 5033–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.J.; Cho, M.J.; Ko, N.Y.; Kim, S.; Jung, I.H.; Min, J.K.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.G.; Oh, G.T. Deficiency of peroxiredoxin 2 exacerbates angiotensin II-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1587–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.G.; Chae, H.Z.; Kim, K. Peroxiredoxins: A historical overview and speculative preview of novel mechanisms and emerging concepts in cell signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, W.L. Chronic Elevated Levels of Factor VIII and Other Coagulation Factors. In Transfusion Medicine and Hemostasis, 3rd ed.; Beth, S.H., Hillyer, C.D., Gil, M.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Alpharetta, GA, USA, 2019; pp. 907–908. [Google Scholar]
- Leiguez, E.; Giannotti, K.C.; Viana, M.D.N.; Matsubara, M.H.; Fernandes, C.M.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Lomont, B.; Teixeira, C. A Snake Venom-Secreted Phospholipase A2 Induces Foam Cell Formation Depending on the Activation of Factors Involved in Lipid Homeostasis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 2547918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.; Dos-Santos, M.C.; Nascimento, N.G.; da Silva, H.B.; Fernandes, C.M.; Lima, M.R.D.I.; Teixeira, C. Local inflammatory events induced by Bothrops atrox snake venom and the release of distinct classes of inflammatory mediators. Toxicon 2012, 60, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerio, A.D.P.; Sorgi, C.A.; Sadikot, R.; Carlo, T. The role of lipids mediators in inflammation and resolution. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 605959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esser-von Bieren, J. Eicosanoids in tissue repair. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamashita, K.M.; Nogueira, T.O.; Senise, L.V.; Cirillo, M.C.; Gonçalves, L.R.D.C.; Sano-Martins, I.S.; Giorgi, R.; Santoro, M.L. Involvement of circulating platelets on the hyperalgesic response evoked by carrageenan and Bothrops jararaca snake venom. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, M.L.; Sano-Martins, I.S. Platelet dysfunction during Bothrops jararaca snake envenomation in rabbits. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 92, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Amazonas, D.R.; Sousa, L.F.; Sant’Anna, S.S.; Nishiyama, M.Y., Jr.; Serrano, S.M.T.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.M.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Mourão, R.H.V. Comparison of venoms from wild and long-term captive Bothrops atrox snakes and characterization of Batroxrhagin, the predominant class PIII metalloproteinase from the venom of this species. Biochimie 2015, 118, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, E.F.; Schneider, F.S.; Yarleque, A.; Borges, M.H.; Richardson, M.; Figueiredo, S.G.; Evangelista, K.S.; Eble, J.A. The novel metalloproteinase atroxlysin-I from Peruvian Bothrops atrox (Jergón) snake venom acts both on blood vessel ECM and platelets. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 496, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.S.; Estevão-Costa, M.I.; Alvarenga, V.G.; Vivas-Ruiz, D.E.; Yarleque, A.; Lima, A.M.; Cavaco, A.; Sanchez, E.F. Atroxlysin-III, A metalloproteinase from the venom of the Peruvian pit viper snake Bothrops atrox (jergón) induces glycoprotein VI shedding and impairs platelet function. Molecules 2019, 24, 3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewiarowski, S.; Kirby, E.P.; Brudzynski, T.M.; Stocker, K. Thrombocytin, a serine protease from Bothrops atrox venom. 2. Interaction with platelets and plasma-clotting factors. Biochemistry 1979, 18, 3570–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.M.; Antonucci, G.A.; Paiva, H.H.; Cintra, A.C.O.; Franco, J.J.; Mendonça-Franqueiro, E.P.; Dorta, D.J.; Giglio, J.R.; Rosa, J.C.; Fuly, A.L.; et al. Evidence of caspase-mediated apoptosis induced by L-amino acid oxidase isolated from Bothrops atrox snake venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiology. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2008, 151, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliani, J.P.; Soares, A.M.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Polymorphonuclear neutrophil leukocytes in snakebite envenoming. Toxicon 2020, 187, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavers, W.N.; Skaar, E.P. Neutrophil-generated oxidative stress and protein damage in Staphylococcus aureus. Path. Dis. 2016, 74, ftw060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manda-Handzlik, A.; Demkow, U. Neutrophils: The role of oxidative and nitrosative stress in health and disease. In Pulmonary Infection, 1st ed.; Pokorski, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortaz, E.; Alipoor, S.D.; Adcock, I.M.; Mumby, S.; Koenderman, L. Update on neutrophil function in severe inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naegelen, I.; Beaume, N.; Plançon, S.; Schenten, V.; Tschirhart, E.J.; Bréchard, S. Regulation of neutrophil degranulation and cytokine secretion: A novel model approach based on linear fitting. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 21, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, M.; Khan, M.A.; Palaniyar, N. Neutrophil extracellular trap formation: Physiology, pathology, and pharmacology. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, C. Neutrophil: A cell with many roles in inflammation or several cell types? Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Neutrophils in tissue injury and repair. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 371, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, B.; Chu, J.Y.; Vermeren, S. Cross-talk between Rho GTPases and PI3K in the neutrophil. Small GTPases 2019, 10, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczur, K.; Xu, H.; Atkinson, S.; Zheng, Y.; Filippi, M.D. Rho GTPase CDC42 regulates directionality and random movement via distinct MAPK pathways in neutrophils. Blood 2006, 108, 4205–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tackenberg, H.; Möller, S.; Filippi, M.D.; Laskay, T. The small GTPase Cdc42 Is a major regulator of neutrophil effector functions. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F. RhoA and Cdc42 in T cells: Are they targetable for T cell-mediated inflammatory diseases? Precis. Clin. Med. 2021, 4, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, Y.D.; Seger, R. The MEK/ERK cascade: From signaling specificity to diverse functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.J. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolch, W. Coordinating ERK/MAPK signalling through scaffolds and inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagnol, S.; Chambard, J.C. ERK and cell death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death–apoptosis, autophagy and senescence. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Lopez, N.; Singh, R. ATGs: Scaffolds for MAPK/ERK signaling. Autophagy 2014, 10, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, S.; Choy, P.M.; Bubici, C. The ERK and JNK pathways in the regulation of metabolic reprogramming. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2223–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Malemud, C.J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase: A regulator of cell growth, inflammation, chondrocyte and bone cell receptor-mediated gene expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, W.Z.; Liu, T.; Feng, X.; Yang, N.; Zhou, H.F. Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2015, 35, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.K.; Joshi, M.B.; Ullah, A.; Masood, R.; Biligiri, S.G.; Arni, R.K.; Satyamoorthy, K. Serine proteinases from Bothrops snake venom activates PI3K/Akt mediated angiogenesis. Toxicon 2016, 124, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Ko, J.; Ju, C.; Eltzschig, H.K. Hypoxia signaling in human diseases and therapeutic targets. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiang, D.; Zhang, H.; Yao, H.; Wang, Y. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1: A potential target to treat acute lung injury. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8871476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Wang, X.M.; Qian, D.H.; Qin, Z.X.; Jin, J.; Xu, Q.; Yuan, Q.Y.; Li, X.J.; Si, L.Y. Induction of oxidative stress by oxidized LDL via meprinα-activated epidermal growth factor receptor in macrophages. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 97, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troib, A.; Azab, A.N. Effects of psychotropic drugs on nuclear factor kappa B. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Chalothorn, D.; Jackson, L.F.; Lee, D.C.; Faber, J.E. Transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor mediates catecholamine-induced growth of vascular smooth muscle. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Veleeparambil, M.; Poddar, D.; Abdulkhalek, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K.; Fensterl, V.; Sen, G.C. EGFR kinase activity is required for TLR4 signaling and the septic shock response. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Shan, P.; Zhong, P.; Khan, Z.; Wang, J.; Fang, Q.; Liang, G.; et al. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor attenuates atherosclerosis via decreasing inflammation and oxidative stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Oliveira, C.; Vasconcelos, B.M.; Vilela, D.; Melo, L.; Ambrósio, L.; da Silva, A.; Murback, L.; Kurissio, J.; Cavalcante, J.; et al. Good management practices of venomous snakes in captivity to produce biological venom-based medicines: Achieving replicability and contributing to pharmaceutical industry. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 2021, 24, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, P.C.; Lima, D.B.; Leprevost, F.V.; Santos, M.D.; Fischer, J.S.; Aquino, P.F.; Moresco, J.J.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Barbosa, V.C. Integrated analysis of shotgun proteomic data with PatternLab for proteomics 4.0. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavalcante, J.S.; Brito, I.M.d.C.; De Oliveira, L.A.; De Barros, L.C.; Almeida, C.; Rossini, B.C.; Sousa, D.L.; Alves, R.S.; Jorge, R.J.B.; Santos, L.D.d. Experimental Bothrops atrox Envenomation: Blood Plasma Proteome Effects after Local Tissue Damage and Perspectives on Thromboinflammation. Toxins 2022, 14, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090613
Cavalcante JS, Brito IMdC, De Oliveira LA, De Barros LC, Almeida C, Rossini BC, Sousa DL, Alves RS, Jorge RJB, Santos LDd. Experimental Bothrops atrox Envenomation: Blood Plasma Proteome Effects after Local Tissue Damage and Perspectives on Thromboinflammation. Toxins. 2022; 14(9):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090613
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavalcante, Joeliton S., Ingrid Mayara da Cunha Brito, Laudicéia Alves De Oliveira, Luciana Curtolo De Barros, Cayo Almeida, Bruno Cesar Rossini, Duaran Lopes Sousa, Renata Sousa Alves, Roberta Jeane Bezerra Jorge, and Lucilene Delazari dos Santos. 2022. "Experimental Bothrops atrox Envenomation: Blood Plasma Proteome Effects after Local Tissue Damage and Perspectives on Thromboinflammation" Toxins 14, no. 9: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090613
APA StyleCavalcante, J. S., Brito, I. M. d. C., De Oliveira, L. A., De Barros, L. C., Almeida, C., Rossini, B. C., Sousa, D. L., Alves, R. S., Jorge, R. J. B., & Santos, L. D. d. (2022). Experimental Bothrops atrox Envenomation: Blood Plasma Proteome Effects after Local Tissue Damage and Perspectives on Thromboinflammation. Toxins, 14(9), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090613