Functional and Immunological Studies Revealed a Second Superantigen Toxin in Staphylococcal Enterotoxin C Producing Staphylococcus aureus Strains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Purified SEC and SEL Stimulates Proliferation of MNCs
2.2. Western Blot Confirms Contamination of SEC Containing Staphylococcal Supernatant with SEL
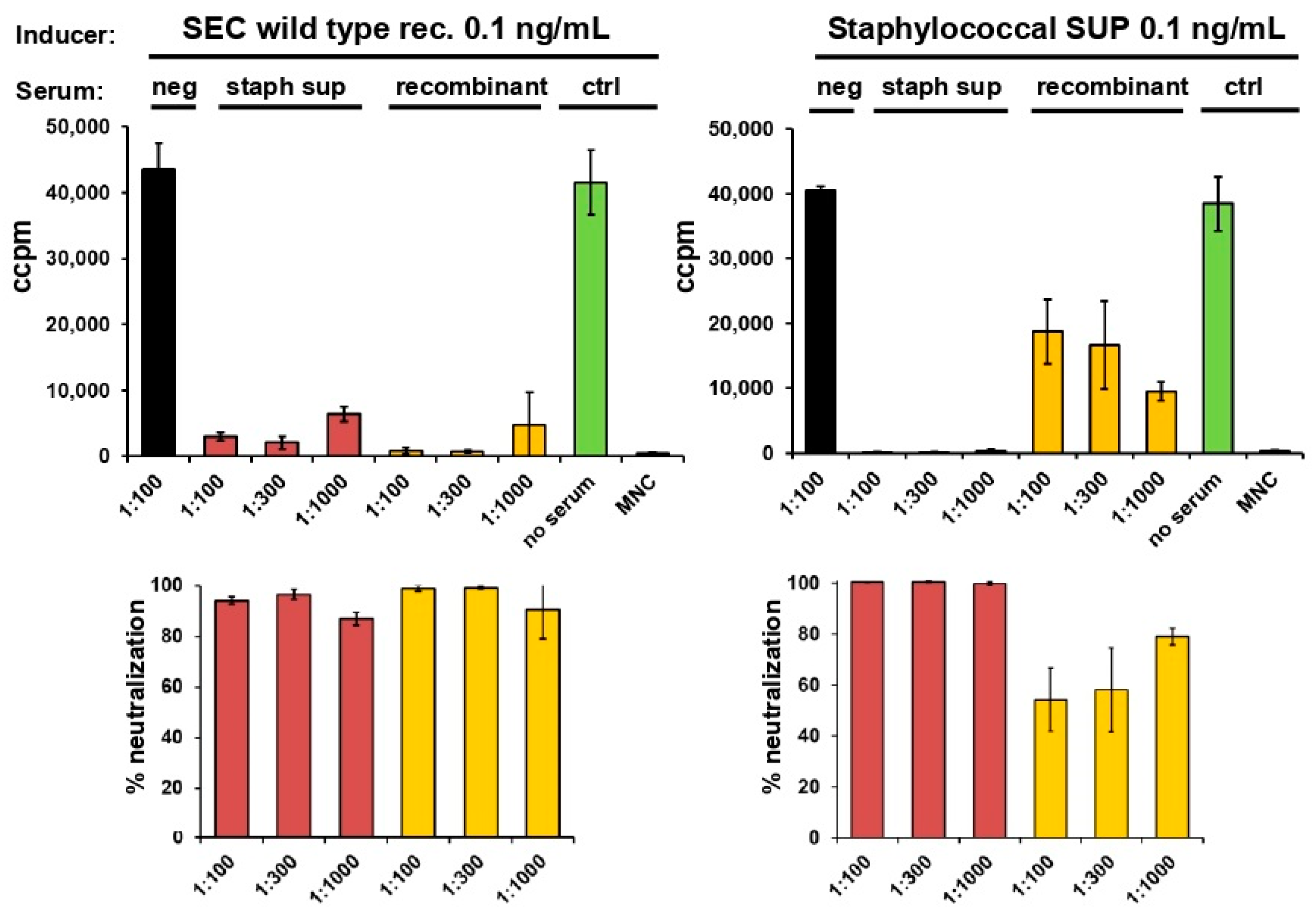
2.3. Neutralisation of Staphylococcal Supernatant and Recombinant SEC
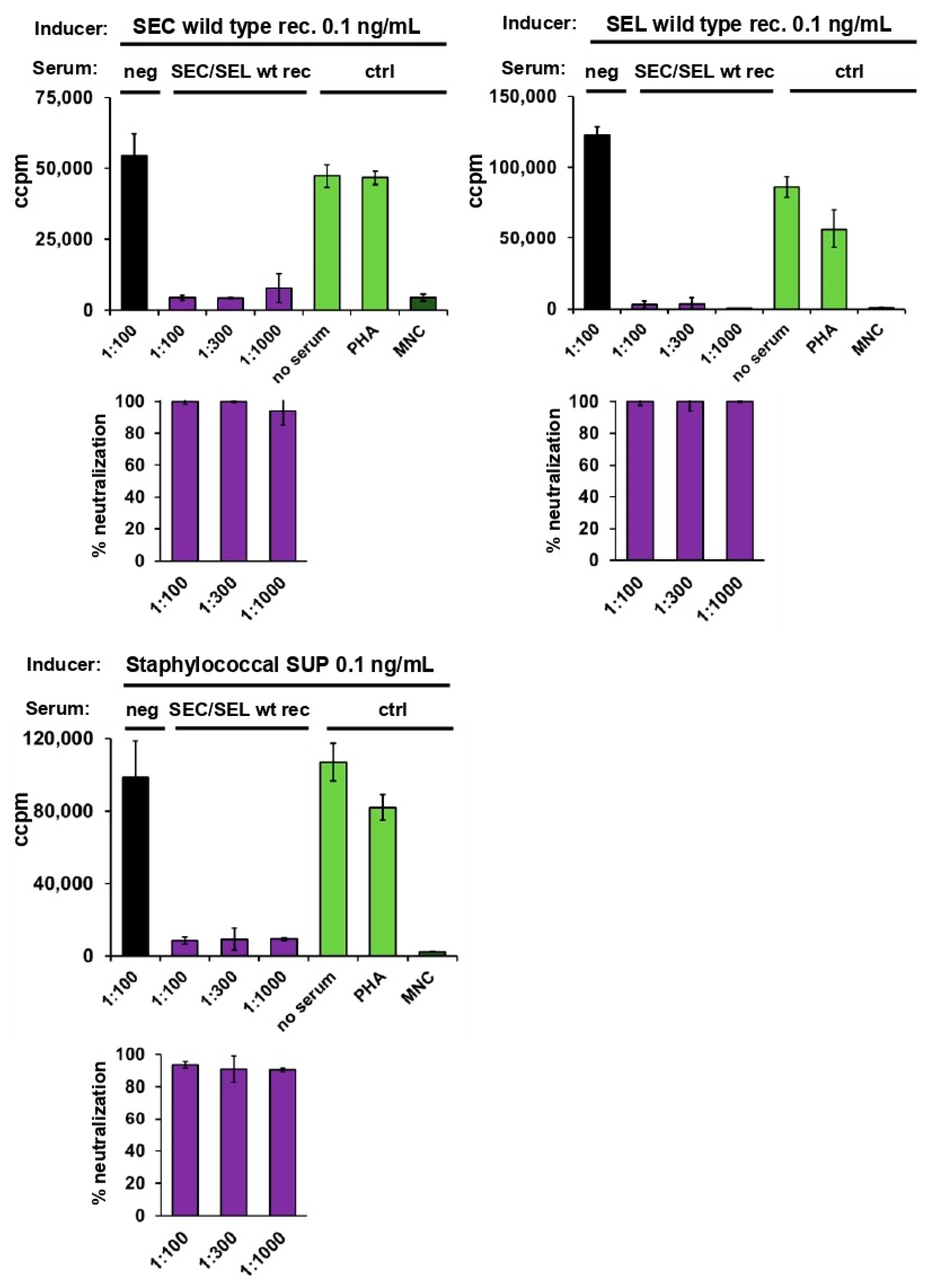
2.4. Neutralisation of Staphylococcal Supernatant and Recombinant SEC and SEL
2.5. Assessment of Antibody Titres against Wild-Type and Toxoid SEC by ELISA
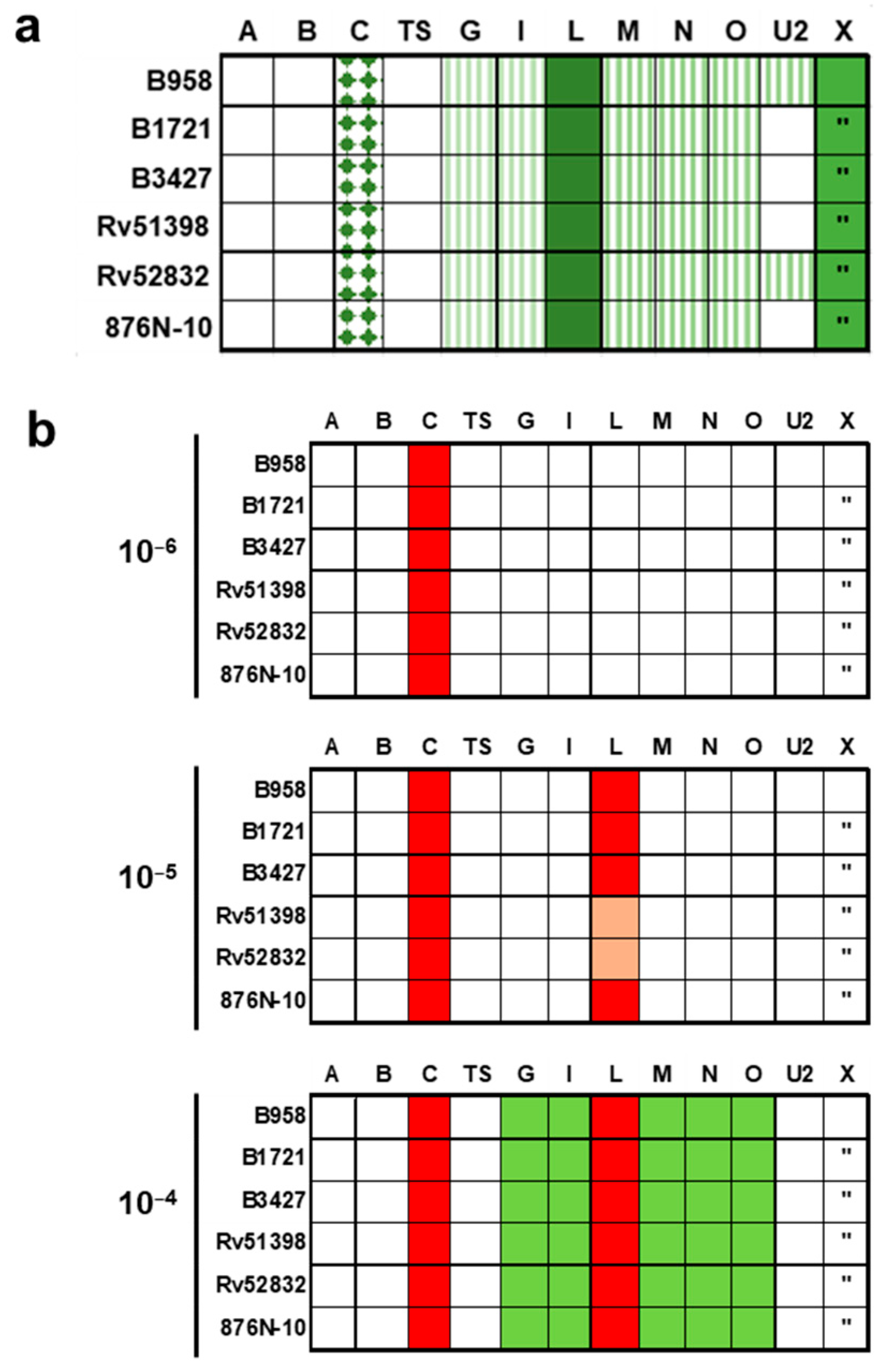
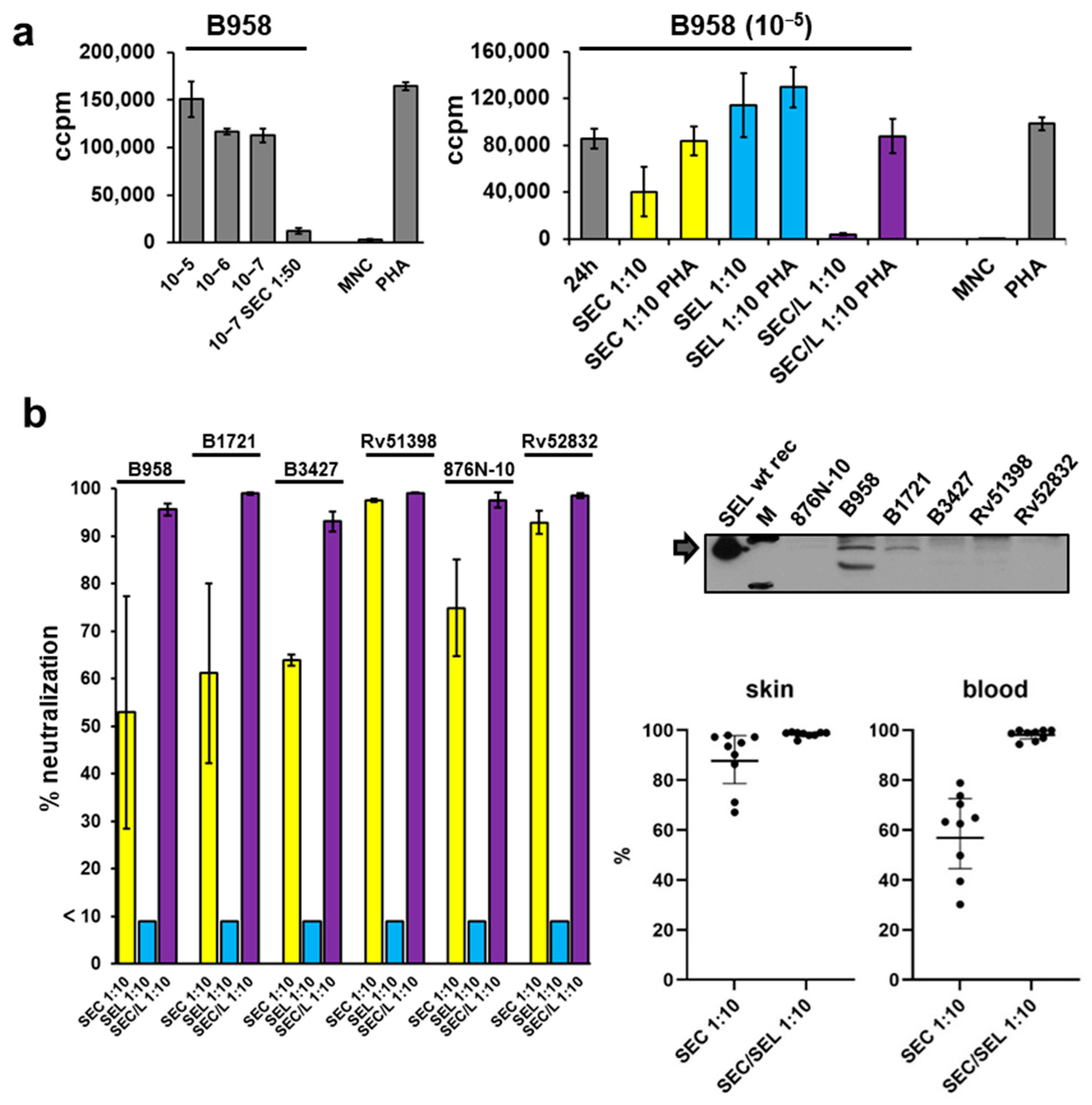
2.6. Proliferation of Mononuclear Cells Induced by Six Different Staphylococcal Strains Could Be Neutralised by a Combination of Antisera Raised against Single Superantigens
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of Supernatants
4.2. Purification of Native Staphylococcal SEC
4.3. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Proteins
4.4. Western Blot Analyses
4.5. Lymphocyte Proliferation Assay
4.6. Immunisation of Rabbits
4.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.8. Neutralisation
4.9. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mulcahy, M.E.; McLoughlin, R.M. Host-Bacterial Crosstalk Determines Staphylococcus aureus Nasal Colonization. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 872–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laux, C.; Peschel, A.; Krismer, B. Staphylococcus aureus Colonization of the Human Nose and Interaction with Other Microbiome Members. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertheim, H.F.; Melles, D.C.; Vos, M.C.; van Leeuwen, W.; van Belkum, A.; Verbrugh, H.A.; Nouwen, J.L. The role of nasal carriage in Staphylococcus aureus infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.Y.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Staphylococcus aureus infections: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaulding, A.R.; Salgado-Pabon, W.; Kohler, P.L.; Horswill, A.R.; Leung, D.Y.; Schlievert, P.M. Staphylococcal and streptococcal superantigen exotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 422–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumba, P.; Mairpady Shambat, S.; Siemens, N. The Role of Streptococcal and Staphylococcal Exotoxins and Proteases in Human Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections. Toxins 2019, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.; Priest, E.; Naglik, J.R.; Richardson, J.P. Fungal Toxins and Host Immune Responses. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 643639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, G.; Bohach, G.A.; Nair, S.P.; Hiramatsu, K.; Jouvin-Marche, E.; Mariuzza, R.; International Nomenclature Committee for Staphylococcal Superantigens. Standard nomenclature for the superantigens expressed by Staphylococcus. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 2334–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etter, D.; Schelin, J.; Schuppler, M.; Johler, S. Staphylococcal Enterotoxin C-An Update on SEC Variants, Their Structure and Properties, and Their Role in Foodborne Intoxications. Toxins 2020, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuffs, S.W.; Haeryfar, S.M.M.; McCormick, J.K. Manipulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity by Staphylococcal Superantigens. Pathogens 2018, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaler, C.R.; Choi, J.; Rudak, P.T.; Memarnejadian, A.; Szabo, P.A.; Tun-Abraham, M.E.; Rossjohn, J.; Corbett, A.J.; McCluskey, J.; McCormick, J.K.; et al. MAIT cells launch a rapid, robust and distinct hyperinflammatory response to bacterial superantigens and quickly acquire an anergic phenotype that impedes their cognate antimicrobial function: Defining a novel mechanism of superantigen-induced immunopathology and immunosuppression. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2001930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, F.E.; Borgogna, T.R.; Patel, D.M.; Sward, E.W.; Voyich, J.M. Epic Immune Battles of History: Neutrophils vs. Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, T. Staphylococcal Superantigens: Pyrogenic Toxins Induce Toxic Shock. Toxins 2019, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Jiang, J.; Chen, T.; Xu, D.; Hou, F.; Huang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Ye, C.; Hu, D.L.; Fang, R. Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin 1 Induces Immune Response via the Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome. Toxins 2021, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, L.; Cooper, A.; Fantino, C.; Altmann, D.M.; Sriskandan, S. The mechanism of superantigen-mediated toxic shock: Not a simple Th1 cytokine storm. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 6870–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandberg, K.L.; Rotschafer, J.H.; Vetter, S.M.; Buonpane, R.A.; Kranz, D.M.; Schlievert, P.M. Staphylococcal superantigens cause lethal pulmonary disease in rabbits. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skov, L.; Olsen, J.V.; Giorno, R.; Schlievert, P.M.; Baadsgaard, O.; Leung, D.Y. Application of Staphylococcal enterotoxin B on normal and atopic skin induces up-regulation of T cells by a superantigen-mediated mechanism. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nienaber, J.J.; Sharma Kuinkel, B.K.; Clarke-Pearson, M.; Lamlertthon, S.; Park, L.; Rude, T.H.; Barriere, S.; Woods, C.W.; Chu, V.H.; Marin, M.; et al. Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis isolates are associated with clonal complex 30 genotype and a distinct repertoire of enterotoxins and adhesins. J. Infect Dis. 2011, 204, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Principato, M.; Qian, B.F. Staphylococcal enterotoxins in the etiopathogenesis of mucosal autoimmunity within the gastrointestinal tract. Toxins 2014, 6, 1471–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlievert, P.M.; Shands, K.N.; Dan, B.B.; Schmid, G.P.; Nishimura, R.D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 1981, 143, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizkallah, M.F.; Tolaymat, A.; Martinez, J.S.; Schlievert, P.M.; Ayoub, E.M. Toxic shock syndrome caused by a strain of Staphylococcus aureus that produces enterotoxin C but not toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. Am. J. Dis. Child 1989, 143, 848–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, H.; Smith, D.; Turner, C.E.; Game, L.; Pichon, B.; Hope, R.; Hill, R.; Kearns, A.; Sriskandan, S. Clinical and Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome in the United Kingdom. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kravitz, G.R.; Dries, D.J.; Peterson, M.L.; Schlievert, P.M. Purpura fulminans due to Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang-Smith, O.N.; Schlievert, P.M. Staphylococcal Enterotoxin C Subtypes Are Differentially Associated with Human Infections and Immunobiological Activities. mSphere 2021, 6, e01153-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudin, M.A.; Mendoza, M.C.; Rodicio, M.R. Food poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 1751–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roetzer, A.; Haller, G.; Beyerly, J.; Geier, C.B.; Wolf, H.M.; Gruener, C.S.; Model, N.; Eibl, M.M. Genotypic and phenotypic analysis of clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus revealed production patterns and hemolytic potentials unlinked to gene profiles and source. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwin, P.M.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Leung, D.Y.; Gutierrez, J.A.; Bohach, G.A.; Schlievert, P.M. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin L. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2916–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoe, K.; Hu, D.L.; Ono, H.K.; Shimizu, S.; Takahashi-Omoe, H.; Nakane, A.; Uchiyama, T.; Shinagawa, K.; Imanishi, K. Emetic potentials of newly identified staphylococcal enterotoxin-like toxins. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3627–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.K.; Hirose, S.; Naito, I.; Sato’o, Y.; Asano, K.; Hu, D.L.; Omoe, K.; Nakane, A. The emetic activity of staphylococcal enterotoxins, SEK, SEL, SEM, SEN and SEO in a small emetic animal model, the house musk shrew. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 61, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bania, J.; Dabrowska, A.; Bystron, J.; Korzekwa, K.; Chrzanowska, J.; Molenda, J. Distribution of newly described enterotoxin-like genes in Staphylococcus aureus from food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 108, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banaszkiewicz, S.; Calland, J.K.; Mourkas, E.; Sheppard, S.K.; Pascoe, B.; Bania, J. Genetic Diversity of Composite Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus epidermidis Pathogenicity Islands. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 3498–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhusoodanan, J.; Seo, K.S.; Remortel, B.; Park, J.Y.; Hwang, S.Y.; Fox, L.K.; Park, Y.H.; Deobald, C.F.; Wang, D.; Liu, S.; et al. An Enterotoxin-Bearing Pathogenicity Island in Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, J.R.; Monday, S.R.; Foster, T.J.; Bohach, G.A.; Hartigan, P.J.; Meaney, W.J.; Smyth, C.J. Characterization of a putative pathogenicity island from bovine Staphylococcus aureus encoding multiple superantigens. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, M.; Ohta, T.; Uchiyama, I.; Baba, T.; Yuzawa, H.; Kobayashi, I.; Cui, L.; Oguchi, A.; Aoki, K.; Nagai, Y.; et al. Whole genome sequencing of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet 2001, 357, 1225–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibayov, B.; Zdenkova, K.; Sykorova, H.; Demnerova, K. Molecular analysis of Staphylococcus aureus pathogenicity islands (SaPI) and their superantigens combination of food samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 107, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roetzer, A.; Gruener, C.S.; Haller, G.; Beyerly, J.; Model, N.; Eibl, M.M. Enterotoxin Gene Cluster-Encoded SEI and SElN from Staphylococcus aureus Isolates are Crucial for the Induction of Human Blood Cell Proliferation and Pathogenicity in Rabbits. Toxins 2016, 8, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.Y.; Jarraud, S.; Lemercier, B.; Cozon, G.; Echasserieau, K.; Etienne, J.; Gougeon, M.L.; Lina, G.; Vandenesch, F. Staphylococcal enterotoxin-like toxins U2 and V, two new staphylococcal superantigens arising from recombination within the enterotoxin gene cluster. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4724–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stich, N.; Waclavicek, M.; Model, N.; Eibl, M.M. Staphylococcal superantigen (TSST-1) mutant analysis reveals that t cell activation is required for biological effects in the rabbit including the cytokine storm. Toxins 2010, 2, 2272–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupin, C.; Anderson, S.; Damais, C.; Alouf, J.E.; Parant, M. Toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 as an inducer of human tumor necrosis factors and gamma interferon. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 167, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado-Pabon, W.; Breshears, L.; Spaulding, A.R.; Merriman, J.A.; Stach, C.S.; Horswill, A.R.; Peterson, M.L.; Schlievert, P.M. Superantigens are critical for Staphylococcus aureus Infective endocarditis, sepsis, and acute kidney injury. mBio 2013, 4, e00494-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, E.L.; Otto, M.; Cheung, G.Y.C. Basis of Virulence in Enterotoxin-Mediated Staphylococcal Food Poisoning. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roetzer, A.; Jilma, B.; Eibl, M.M. Vaccine against toxic shock syndrome in a first-in-man clinical trial. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2017, 16, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.L.; McGinley, J.P.; Drysdale, S.B.; Pollard, A.J. Epidemiology and Immune Pathogenesis of Viral Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnquist, C.; Ryan, B.M.; Horikawa, I.; Harris, B.T.; Harris, C.C. Cytokine Storms in Cancer and COVID-19. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waclavicek, M.; Stich, N.; Rappan, I.; Bergmeister, H.; Eibl, M.M. Analysis of the early response to TSST-1 reveals Vbeta-unrestricted extravasation, compartmentalization of the response, and unresponsiveness but not anergy to TSST-1. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 85, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roetzer, A.; Model, N.; Laube, J.; Unterhumer, Y.; Haller, G.; Eibl, M.M. Functional and Immunological Studies Revealed a Second Superantigen Toxin in Staphylococcal Enterotoxin C Producing Staphylococcus aureus Strains. Toxins 2022, 14, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090595
Roetzer A, Model N, Laube J, Unterhumer Y, Haller G, Eibl MM. Functional and Immunological Studies Revealed a Second Superantigen Toxin in Staphylococcal Enterotoxin C Producing Staphylococcus aureus Strains. Toxins. 2022; 14(9):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090595
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoetzer, Andreas, Nina Model, Jakob Laube, Yvonne Unterhumer, Guenter Haller, and Martha M. Eibl. 2022. "Functional and Immunological Studies Revealed a Second Superantigen Toxin in Staphylococcal Enterotoxin C Producing Staphylococcus aureus Strains" Toxins 14, no. 9: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090595
APA StyleRoetzer, A., Model, N., Laube, J., Unterhumer, Y., Haller, G., & Eibl, M. M. (2022). Functional and Immunological Studies Revealed a Second Superantigen Toxin in Staphylococcal Enterotoxin C Producing Staphylococcus aureus Strains. Toxins, 14(9), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090595



