Abstract
The cockle Cerastoderma edule is a commercially important species in many European Countries. It can accumulate okadaic acid (OA) and other toxins in its group, which makes it unsuitable for human consumption, producing harvesting bans to avoid intoxications. The duration of those bans depends in part on the depuration kinetics of the toxin in this species. In this work, this kinetics was studied by means of fitting different models to depuration data experimentally obtained, using naturally contaminated cockles. Cockles depurated OA faster than most other bivalve species studied. Models that include Michaelis-Menten kinetics describe the depuration better than those using a first order exponential decrease to describe the first (or the only) compartment. One-compartment models were not able to describe the final part of the depuration curve, in which OA was depurated very slowly. Therefore, two-compartment models were needed. Esters were depurated at a much faster rate than the free form of the toxin; however, no significant esterification was detected during the process. The slow depuration rate suggests that other bivalve species could be used as sentinels to monitor cockle populations, but caution should be taken when toxin concentrations are very high.
Key Contribution:
OA depuration in the cockle follows two-compartment Michaelis-Menten kinetics. The depuration is faster than in most other bivalves; and esters are eliminated faster than free OA.
1. Introduction
Okadaic acid (OA) and dinophysistoxins (DTX) are compounds produced by several species of marine dinoflagellates and accumulated by other organisms, mainly bivalves. These toxins, when consumed by humans and other mammals, produce a syndrome known as diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP). In benthic environments, several Prorocentrum species can produce these toxins [1,2,3,4]. In plankton, the main producers are species of Dinophysis, which can contain OA, DTX1, DTX2, some isomers, some derivatives, such as diol- and triol-esters [5,6,7,8,9], and occasionally the groups of compounds known as DTX4 and DTX5 (up to now not described in Dinophysis but found in some OA-producing benthic species) [10,11]. Dinophysis species are distributed worldwide and DSP intoxications by mollusk consumption have been reported from many countries [6]. After the discovery of DSP by Yasumoto et al. [12] and the development of an assay to quantify it, the detection of this toxicity was progressively incorporated into shellfish monitoring systems. Later, the development of analytical methods to quantify these toxins allowed for the creation of reference levels for their maximum content in bivalve soft tissues, which cannot be surpassed to consider the shellfish safe for consumption. Currently, in the European Union [13] and most other countries, this level has been established at 160 µg of OA-equivalents kg−1, a level which was established from an acute reference dose of 0.3 µg of OA kg−1 of body weight obtained from epidemiological data [14]. In many areas, the recorded toxin concentrations led to frequent bans of mollusk harvesting, which represent an important economic and social problem.
Mollusk, and especially bivalves, are appreciated as a source of food for humans and, consequently, their fisheries are commercially important. The cockle Cerastoderma edule, among the non-cultured mollusks, is one of the economically most important species in Europe. Its production between 2014 and 2017 ranged from 14,651 to 26,125 t, with the UK as the top producer and Spain the second [15]. In Galicia (NW Spain) the annual production is around 600 t [16], and represents an important resource for the people who gather shellfish from the intertidal zone (a regulated activity). Bans can produce significant economic losses in the productive sector, which are dependent on their duration.
Ban duration depends on the amount of toxins that the bivalves can ingest, which in turn depends on the abundance of toxic cells, the toxin contents of the cells, the time during which the toxic populations persist, and the depuration kinetics of the bivalve [17]. Banning periods could be substantially shortened for the species that depurates faster. For C. edule, OA depuration rate has only been roughly estimated but seems to be faster than that of the mussels M. galloprovincialis and M. edulis [18,19], and some clams and oysters (reviewed in [17]). Its depuration kinetics has not been studied, making it difficult to precisely predict the time course of its reduction of toxicity.
In this work, the depuration kinetics of OA (free and esterified form) in C. edule has been determined by means of the implementation and fitting of different models to the data obtained using cockles naturally contaminated with the toxin.
2. Results
Okadaic acid was present in cockles mainly esterified with fatty acids. Initially, only 1.8% of the toxin was in free form, but attained 18.7% after 19 days of depuration, decreasing thereafter to 2.9% on day 33. In the experiment, free OA constituted 8.1% of the total toxin, on average. There was not a lineal trend of the percentage of free OA during the course of the experiment, nor was there any relationship with the change in body weight.
Both esterified and total toxin decreased quickly during the first 12 days of depuration—they were, at day 5, below 30% of the initial level and below 1% at day 12—but the decreasing velocity slowed down during subsequent days. The trend was similar for free toxin, but the transition was softer and the depuration velocity smaller (Figure 1).
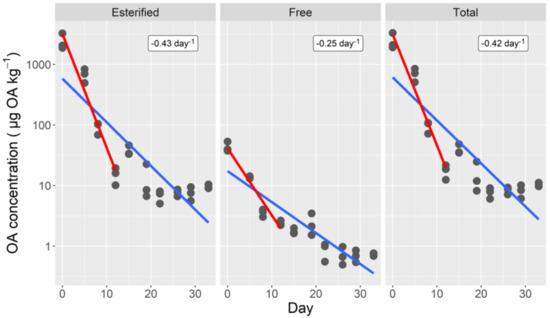
Figure 1.
Depuration curves of esterified, free, and total okadaic acid of the cockle. The lines correspond to fitting a simple exponential decrease to all data (blue line), and to the first 12 depuration days (red line). The numbers in the upper right corners are the estimated depuration rates for the first 12 days.
The depuration kinetics of the total toxin, clearly, did not follow an exponential decay. A one-compartment model does not fit the obtained data correctly. It overestimates the middle part of the curve and underestimates the final part, as can be observed from the depart of linearity of the logarithmically transformed data (Figure 1). All attempts to fit a two-compartment model with exponential kinetics were unsuccessful, because the fitted parameters, in fact, reverted it to a one-compartment model (Figure 2). By assuming that the depuration followed Michaelis-Menten kinetics, the model fit the initial and middle part of the curve much better, but the toxin content of the final part, when the toxin content was very low, was substantially underestimated, even when the differences were quantitatively small (only noticed in the logarithmically transformed data (Figure 2). A final model that combines Michaelis-Menten kinetics for the first compartment and exponential kinetics for both the transfer between compartments and the depuration from compartment 2, fit the data much better, even in the final part of the curve (Figure 2).
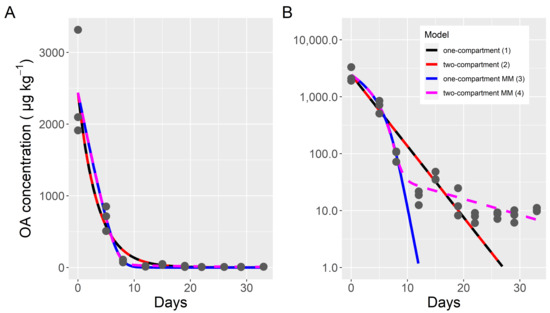
Figure 2.
Fitting of four models to the total okadaic acid depuration data of the cockle, in untransformed (A) and logarithmically transformed (B) scale. Dots are the observed data and lines are the outputs of the fitted models. MM indicates that the model used Michaelis-Menten kinetics for the first compartment (models 3 and 4).
The two-compartment Michaelis-Menten model also fit the data for esterified and free OA well (Figure 3). The fitted parameters, however, were not the same for the two forms. As could be expected by its high contribution to the total toxin, the parameters obtained for esterified okadaic acid were very similar to those for total toxin, but both Vmax and Km were slightly higher. Contrarily, some of the parameters obtained for free OA were very different. Those corresponding to the first compartment (Michaelis-Menten kinetics) were substantially lower, with Vmax and Km being only 1.6% and 1.2% of the corresponding rates for esterified OA, respectively. The estimated transfer rate between compartments 1 and 2 was six times higher for free than for esterified OA. The depuration rates of the second compartment were practically the same for the two OA forms.
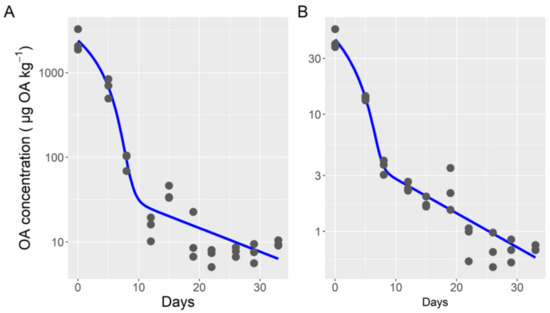
Figure 3.
Depuration curve (dots) and output of the two-compartment model (model 4) with Michaelis-Menten kinetics for the first compartment (lines), for esterified (A) and free (B) okadaic acid.
This model also fits the ratio of free/total toxin reasonably well when the data of day 15, which were atypically low, were removed (Figure 4). When an esterification rate was included in the model (model 5), the fit to the data did not improve.
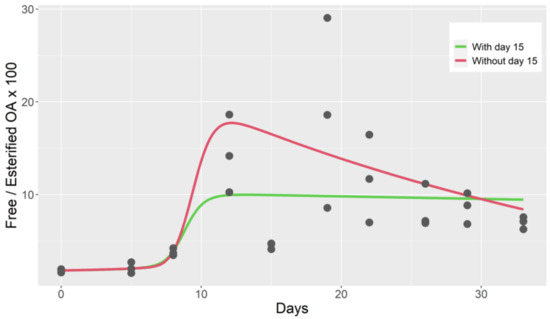
Figure 4.
Observed free/esterified OA ratio during the depuration of cockle (dots), computed from the output of a two-compartment model with Michaelis-Menten kinetics for the first compartment (model 4).
In order to be able to compare the observed depuration rates with other species, an exponential decay (model 1) was assumed for the first 12 days (in most cases in the available literature, depuration rates are computed assuming a first order exponential decay, or the data obtained are not enough to re-compute them to fit a more complex model). In such a case, rates of 0.42, 0.43, and 0.26 day−1 were obtained for the total, esterified, and free toxin, respectively (Figure 1), which correspond to 1.7, 1.6, and 2.7 days of semi-depuration period (time required to reduce the toxin concentration by 1/2).
3. Discussion
Cockles depurate most of their OA content faster than other studied bivalve species. They can reduce their toxin content by a half in 1.7 days. The rates observed in the mussels M. galloprovincialis and M. edulis are substantially lower than those found in this study, ranging from 0.05 to 0.19 day−1 [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26] (reviewed in Blanco [17]). This is also the case with different infaunal bivalve species such as Spisula solida [27] and Donax trunculus [26,27]. Vale et al. [19] also found higher depuration rates of OA and DTX2 in cockles (0.22 day−1, recomputed from the fastest decay of the depuration curve) than in mussels (0.09 day−1).
The better fitting of the models, which include the Michaelis-Menten kinetics in relation to those using an exponential decay, suggests that a saturable transporter should be involved in the process. Consequently, when the amount of toxin accumulated is very high, the depuration is slower, in relation to the toxin concentration, than when the concentration is lower. This kind of response seems to also be present in the depuration data obtained by Vale et al. [19], but it is not frequent among bivalves, whose depuration usually follows an exponential decay [17]. The need of a second compartment, with very low depuration and transfer rates, in the models of total toxin indicates that there is a small amount of nearly residual toxin that could persist in cockles for a long time. The amount of this nearly residual toxin is very low and does not pose any risk for consumer health. The presence of a small second compartment for OA is frequent among bivalves [17].
Most toxin was found to be in esterified form. Esterification of xenobiotics with fatty acids seems to be a frequent step in depuration, and has been shown to take place with okadaic acid and analogs [28] and with steroids [29]. Most bivalves quickly esterify okadaic acid, making esters constitute more that 90% of the total toxin [17].
Esters are depurated from the cockle at a much higher rate than free toxin. This difference was also found in a previous study with the same species in Portugal [19], and was also the case in the mussels M. galloprovincialis [19] and M. edulis, but not in the oyster Ostrea edulis in Norway [30]. However, Lindegarth et al. [31], also from Norway, reported that free forms were depurated from mussels and oysters faster than the esters. Notwithstanding, an approximate re-computation from their plots using only the first two depuration weeks shows that the esterified forms depurate at a much higher rate (nearly 2x) than the free toxin in both species. The fact that the fit to the data did not improve when esterification of the free OA was included in the model suggests that this process had low importance during cockle depuration. This is surprising because it is known that free OA is easily esterified in bivalves [28,32,33] and, during four years of monitoring in Galicia, the percentage of free OA in cockle was nearly always below 5% of the total toxin [34], which would not be possible if the esterification was not very fast. One explanation for this is that most OA was already esterified at the beginning of the experiment (more than 98% of the OA), making it difficult to estimate the model parameters precisely. Another possible explanation would be that the esterification rate follows a sigmoid curve, with low esterification rates when the concentration of free OA is also low (due to inhibition by the product or other causes). Rossignoli et al. found that most OA was depurated from the mussel M. galloprovincialis in esterified form [35], even when the proportion of free form in that species is high, which suggests that free OA should be esterified before being excreted from the digestive gland cells. This would explain why the second compartment is relatively more important for free that for esterified OA.
The fast depuration rate observed suggests that cockles represent a smaller risk than other bivalves and, consequently, that other less valued species, such as mussels, can be used as sentinels to carry out an efficient monitoring system. However, some precaution should be taken when very high toxin concentrations are attained because, in those cases, with the observed kinetics, cockles can depurate the toxin slower than mussels and other species whose depuration follows a first-order exponential decay.
The identification of the membrane transporter most likely involved could allow for selecting fast depurating cockles or for the creation of design-specific treatments to accelerate depuration in the future.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Material and Experimental Design
Cockles C. edule were obtained from the Baldaio, A Coruña, Spain (43°17′ N, 8°39′ W), where they had accumulated OA from a bloom of Dinophysis acuminata. They (120 individuals) were placed in a 50 L tank with running seawater at a temperature of approximately 18 °C and maintained there until the end of the experiment (33 days). A mixture of Tetraselmis, Isochrysis, Pavlova, and Chaetoceros was supplied daily, and the flow was stopped for two hours. At days 0, 5, 8, 12, 15, 19, 22, 26, 29, and 33, three samples of three cockles each were obtained randomly. The shells were removed, and the soft tissues of each 3-cockle sample were weighed and subjected to toxin extraction.
4.2. Chemicals and Reference Materials
Acetonitrile (LC-MS grade) and methanol (HPLC grade quality) were purchased from Scharlab (Sentmenat, Spain) and VWR (Llinars del Vallés, Spain), respectively. Ultrapure water was obtained from a Milli-Q gradient system fed with an Elix Advantage-10 (Millipore Ibérica, Spain). Ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH, 25%) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH > 99%) were obtained from Merck (Barcelona, Spain), and hydrochloric acid (HCl, 37%) from Panreac (Barcelona, Spain).
The OA certified solution was acquired from the Institute for Marine Biosciences, National Research Council (NRC), Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada.
4.3. Toxin Extraction and Hydrolysis
Toxins from cockle tissues were extracted in methanol MeOH (1:4 w:v) with an Ultraturrax T25 (IKA, Staufen, Germany) homogenizer. Solids were removed by centrifugation at 18,000× g, and the supernatant was kept at −20 °C until analysis. Before the analysis, the possible precipitates were removed by filtration through 0.22 µm polyethersulphone PES syringe filters (Membrane Solutions,, from Jasco Analítica, Madrid, Spain).
To determine free OA, the extracts were analyzed without additional processing. To quantify total OA (free + esterified), aliquots of the extracts were subjected to an alkaline hydrolysis, following the procedure established in the SOP of the European Community Reference Laboratory of Marine Biotoxins [36], which consist of adding NaOH 2.5 M, heat at 76 °C for 40 min, and neutralizing the solution with HCl 2.5 M.
4.4. LC-MS/MS Method
The analyses have been carried out on an Exion LC AD™ System (SCIEX, Framingham, MA, USA) coupled to a Qtrap 6500+ mass spectrometer (SCIEX) through an IonDrive Turbo V interface in electrospray mode. The chromatographic separation [37] was made in a Phenomenex (Alcobendas, Spain) Kinetex EVO C18 column 50 mm × 2.1 mm, 2.6 µm using a gradient of water (phase A) and acetonitrile MeCN 90% (phase B), both containing 6.7 mM NH4OH (pH 11) [38]. The gradient started with 22% B, (held for 0.1 min), followed by a linear increment to reach 95% B at minute 1.8, and holding this composition until minute 2.90. The proportion was then returned to 22% B in 0.20 min and held for 0.5 min before the next injection. The flow rate, the injection volume, and the column temperature were 1000 µL min−1, 1 µL, and 40 °C, respectively.
The mass spectrometer parameters were optimized by direct infusion using toxin standards, when available, and were set to: Ion source Gas 1, 75 (arbitrary units); Ion source Gas 2, 75 (arbitrary units); and −4500 V. The transitions 803.5 > 255.1 and 803.5 > 563.4, with collision energies of −62 and −60 v, were used as quantifier and qualifier, respectively.
The OA in the extracts was quantified by the external standard method using dilutions of a certified solution of OA in MeOH.
4.5. Modelling
Models were implemented using the R [39] package deSolve [40] and fitted to the observed data with the package FME [41]. The results were plotted with the R package ggplot2 [42].
Five models were fitted. Model 1 was a simple exponential decay:
where K is the depuration rate.
dOA/dt = −K·OA
Model 2 also used the simple exponential decay of the toxin but from two compartments, depurating the first one faster than the second, and transferring a part of its toxin content to the second compartment.
where subscripts indicate the compartment and T12 is the transfer rate from compartment 1 to 2.
dOA1/dt = −K1·OA1 − T12·OA1
dOA2/dt = −K2·OA1 + T12
OAT = OA1 + OA2
The third and fourth models are analogs of the first and second, respectively, but the rate of the exponential decay in the unique (model 3) or the first (model 4) compartment was replaced by the Michaelis-Menten parameters.
Model 3:
where Vmax is the maximum depuration velocity and Km is the Michaelis-Menten constant.
dOA/dt = −Vmax·OA/(Km + OA)
Model 4:
dOA1/dt =−Vmax·OA1/(Km + OA1) − T12·OA1
dOA2/dt = −K2·OA1 + T12·OA1
OAT = OA1 + OA2
Model 5:
where “free” or “est” indicate if the toxin is in free or esterified form, and Kest is the rate of esterification of the free toxin (only in compartment 1).
dOAest1/dt = −Vmaxest·OAest1/(Kmest + OAest1) − Test12·OAest1 + Kest·OAfree1
dOAest2/dt = -Kest2·OA1 + Test12·OAest1
dOAfree1/dt =−Kfree1·OAfree2 − Tfree12·OAfree1 − Kest·OAfree1
dOAfree2/dt = −Kfree2·OAfree2 + Tfree12·OAfree1
OAestT = OAest1 + OAest2
OAfreeT = OAfree1 + OAfree2
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.B. and A.E.R.; software, J.B.; validation, J.B. and A.E.R.; investigation, J.B., A.E.R., H.M. and C.M.; writing—original draft preparation, J.B.; writing—review and editing, J.B. and A.E.R.; project administration, C.M.; funding acquisition, A.E.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Consellería do Mar, Xunta de Galicia, Acción de Investigación TOXEMER, grant number CIMA 21/01 TOXEMER.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data used in this study are available from the article.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the Biotoxin department of Intecmar by supplying the toxic biological material for this work, and India Laina Kirssin for English Language editing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, J.S.; Igarashi, T.; Fraga, S.; Dahl, E.; Hovgaard, P.; Yasumoto, T. Determination of diarrhetic shellfish toxins in various dinoflagellate species. J. Appl. Phycol. 1989, 1, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Identification of Okadaic Acid As a Toxic Component of a Marine Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum Lima. Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 1982, 48, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, R.W.; Bobzin, S.C.; Faulkner, D.J.; Bencsath, F.A.; Andrzejewski, D. Identification of okadaic acid from a Caribbean dinoflagellate, Prorocentrum Concavum. Toxicon 1990, 28, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, S.L.; Moeller, P.D.R.; Young, K.A.; Lanoue, G. Okadaic acid production from the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum belizeanum Faust isolated from the Belizean coral reef ecosystem. Toxicon 1988, 36, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Beuzenberg, V.; Mackenzie, L.; Quilliam, M.A. Discovery of okadaic acid esters in the toxic dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuta from New Zealand using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2004, 18, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, B.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Díaz, P.; Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.; Blanco, J. Dinophysis Toxins: Causative Organisms, Distribution and Fate in Shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 394–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, B.; Daranas, A.H.; Cruz, P.G.; Franco, J.M.; Norte, M.; Fernández, J.J. Identification of 19-epi-okadaic acid, a new diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxin, by liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry detection. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 489–495. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Hawkes, A.D.; Jensen, D.J.; Cooney, J.M.; Larsen, K.; Petersen, D.; Rise, F.; Beuzenberg, V.; MacKenzie, A.L. Isolation and identification of a cis-C-8-diol-ester of okadaic acid from Dinophysis acuta in New Zealand. Toxicon 2006, 48, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.T.; Krock, B.; Hansen, P.J. Production and excretion of okadaic acid, pectenotoxin-2 and a novel dinophysistoxin from the DSP-causing marine dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuta—Effects of light, food availability and growth phase. Harmful Algae 2013, 23, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Curtis, J.M.; Walter, J.A.; McLachlan, J.L.; Wright, J.L.C. Two new water-soluble dsp toxin derivatives from the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum maculosum: Possible storage and excretion products. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 9273–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; de Freitas, A.S.W.; Doyle, J.; Jackson, D.; Marr, J.; Nixon, E.; Pleasance, S.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. New dsp toxin derivatives isolated from toxic mussels and the dinoflagellates, Prorocentrum lima and Prorocentrum concavum. Toxic Phytoplankton Bloom. Sea 1993, 3, 507–512. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yamaguchi, M. Occurrence of a new type of shellfish poisoning in the Tohoku district. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1978, 44, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU. Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for on the hygiene of foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2004, 139, 55–205. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Marine biotoxins in shellfish-okadaic acid and analogues-Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food chain. EFSA J. 2008, 6, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carss, D.N.; Brito, A.C.; Chainho, P.; Ciutat, A.; de Montaudouin, X.; Fernandez Otero, R.M.; Filgueira, M.I.; Garbutt, A.; Goedknegt, M.A.; Lynch, S.A.; et al. Ecosystem services provided by a non-cultured shellfish species: The common cockle Cerastoderma edule. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 158, 104931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pescadegalicia. Estatísticas. Publicacións. Available online: https://www.pescadegalicia.gal/gl/publicacions (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Blanco, J. Accumulation of Dinophysis Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs. Toxins 2018, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svensson, S.; André, C.; Rehnstam-Holm, A.S.; Hansson, J. A case of consistent spatial differences in content of diarrhetic shellfish toxins (DST) among three bivalve species: Mytilus edulis, Ostrea edulis and Cerastoderma edule. J. Shellfish. Res. 2000, 19, 1017–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Vale, P. Differential Dynamics of Dinophysistoxins and Pectenotoxins Between Blue Mussel and Common Cockle: A Phenomenon Originating From the Complex Toxin Profile of Dinophysis acuta. Toxicon 2004, 44, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Fernández, M.L.; Míguez, A.; Moroño, A. Okadaic acid depuration in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis: One- and two-compartment models and the effect of environmental conditions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 176, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.L.; Míguez, A.; Moroño, A.; Cacho, E.; Martínez, A.; Blanco, J. Detoxification of low polarity toxins (DTX3) from mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis in Spain. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia and IOC of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1998; pp. 449–452. [Google Scholar]
- Moroño, A.; Arévalo, F.; Fernández, M.L.; Maneiro, J.; Pazos, Y.; Salgado, C.; Blanco, J. Accumulation and transformation of DSP toxins in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis LMK during a toxic episode caused by Dinophysis acuminata. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 62, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroño, A.; Fernández, M.L.; Franco, J.M.; Martínez, A.; Reyero, I.; Míguez, A.; Cacho, E.; Blanco, J. PSP and DSP detoxification kinetics in mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis: Effect of environmental parameters and body weight. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia and IOC of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1998; pp. 445–448. [Google Scholar]
- Poletti, R.; Viviani, R.; Casadei, C.; Lucentini, L.; Giannetti, L.; Funari, E.; Draisci, R. Decontamination dynamics of mussels naturally contaminated with diarrhetic toxins relocated to a basin of the Adriatic Sea. In Harmful and Toxic Algal Blooms; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; IOC of UNESCO: Paris, France, 1996; pp. 429–432. [Google Scholar]
- Marcaillou-Le Baut, C.; Bardin, B.; Bardouil, M.; Bohec, M.; Le Dean, L.; Masselin, P.; Truquet, P. DSP depuration rates of mussels reared in a laboratory and an aquaculture pond. In Toxic Phytoplankton Blooms in the Sea; Smayda, T.J., Shimizu, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA; Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 531–535. [Google Scholar]
- Botelho, M.J.; Vale, C.; Joaquim, S.; Costa, S.T.; Soares, F.; Roque, C.; Matias, D. Combined effect of temperature and nutritional regime on the elimination of the lipophilic toxin okadaic acid in the naturally contaminated wedge shell Donax trunculus. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, P. Differential dynamics of dinophysistoxins and pectenotoxins, part II: Offshore bivalve species. Toxicon 2006, 47, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossignoli, A.E.; Fernández, D.; Regueiro, J.; Mariño, C.; Blanco, J. Esterification of okadaic acid in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 2011, 57, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janer, G.; Mesia-Vela, S.; Porte, C.; Kauffman, F.C. Esterification of vertebrate-type steroids in the Eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Steroids 2004, 69, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, T.; Sandvik, M.; Lundve, B.; Lindegarth, S. Profiles and levels of fatty acid esters of okadaic acid group toxins and pectenotoxins during toxin depuration. Part II: Blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) and flat oyster (Ostrea edulis). Toxicon 2008, 52, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindegarth, S.; Torgersen, T.; Lundve, B.; Sandvik, M. Differential Retention Of Okadaic Acid (Oa) Group Toxins And Pectenotoxins (Ptx) In The Blue Mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.), And European Flat Oyster, Ostrea Edulis (L.). J. Shellfish. Res. 2009, 28, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Martín, H.; Mariño, C.; Rossignoli, A.E. Simple Diffusion as the Mechanism of Okadaic Acid Uptake by the Mussel Digestive Gland. Toxins 2019, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konoki, K.; Onoda, T.; Watanabe, R.; Cho, Y.; Kaga, S.; Suzuki, T.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. In Vitro Acylation of Okadaic Acid in the Presence of Various Bivalves’ Extracts. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco, J.; Arévalo, F.; Correa, J.; Moroño, A. Lipophilic Toxins in Galicia (NW Spain) between 2014 and 2017: Incidence on the Main Molluscan Species and Analysis of the Monitoring Efficiency. Toxins 2019, 11, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escudeiro Rossignoli, A. Acumulación de Toxinas DSP en el Mejillón Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ph.D. Thesis, Santiago de Compostela University, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- EURLMB. EU-Harmonised Standard Operating Procedure for Determination of Lipophilic Marine Biotoxins in Molluscs by LC-MS/MS, Version 5. 2014. Available online: https://www.aesan.gob.es/AECOSAN/docs/documentos/laboratorios/LNRBM/ARCHIVO2EU-Harmonised-SOP-LIPO-LCMSMS_Version5.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Rossignoli, A.E.; Mariño, C.; Martín, H.; Blanco, J. Development of a Fast Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry Method (LC-MS/MS) to Determine Fourteen Lipophilic Shellfish Toxins Based on Fused–Core Technology: In-House Validation. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerssen, A.; Mulder, P.P.; McElhinney, M.A.; de Boer, J. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the detection of marine lipophilic toxins under alkaline conditions. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; Version 4.0.2; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 30 January 2022).
- Soetaert, K.; Petzoldt, T.; Setzer, R.W. Solving Differential Equations in R: Package deSolve. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soetaert, K.; Petzoldt, T. Inverse Modelling, Sensitivity and Monte Carlo Analysis in R Using Package FME. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; 260p. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).