Reduced Cross-Sectional Muscle Growth Six Months after Botulinum Toxin Type-A Injection in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
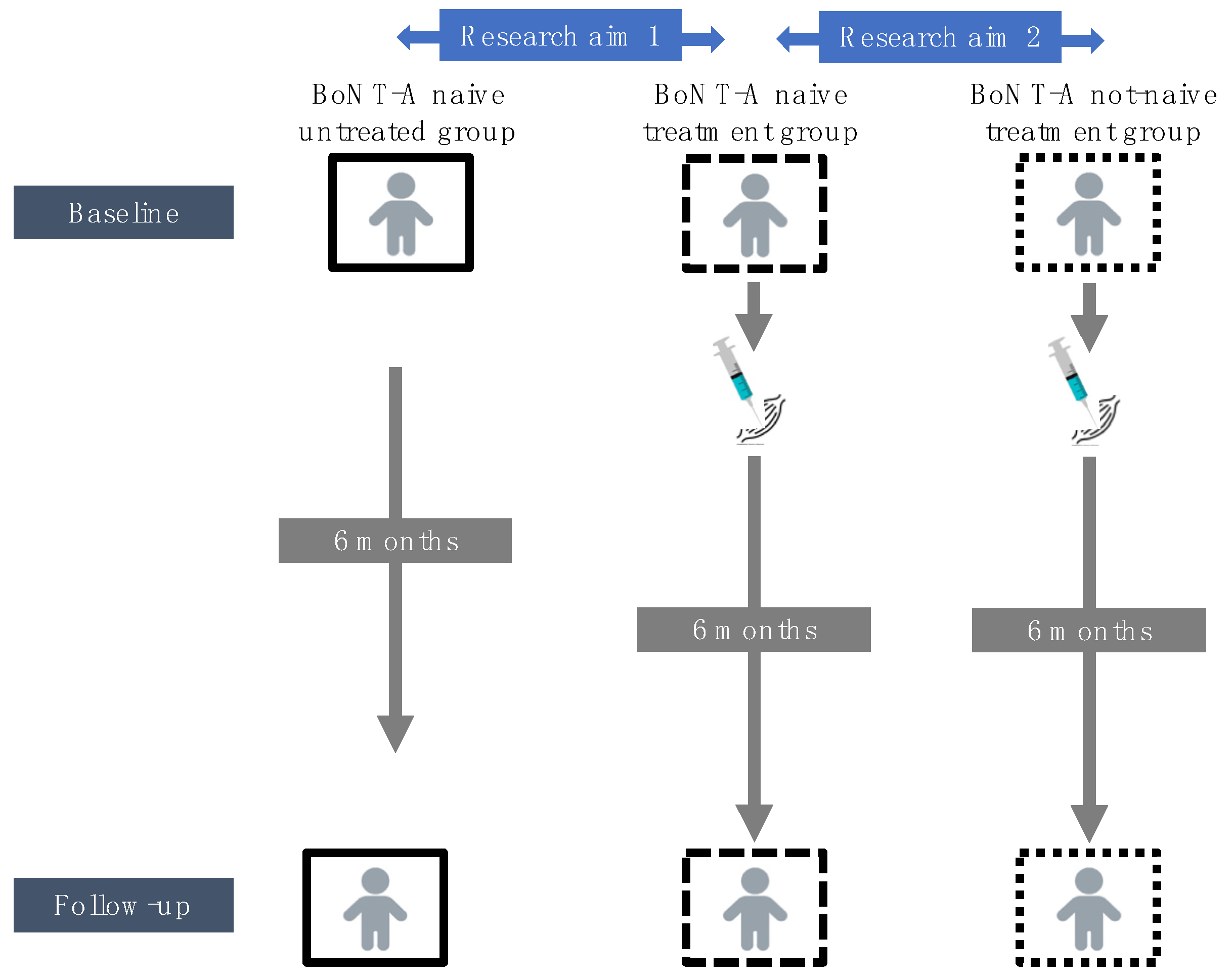
2.1. Characteristics of the BoNT-A Treatment Groups and the Untreated Group
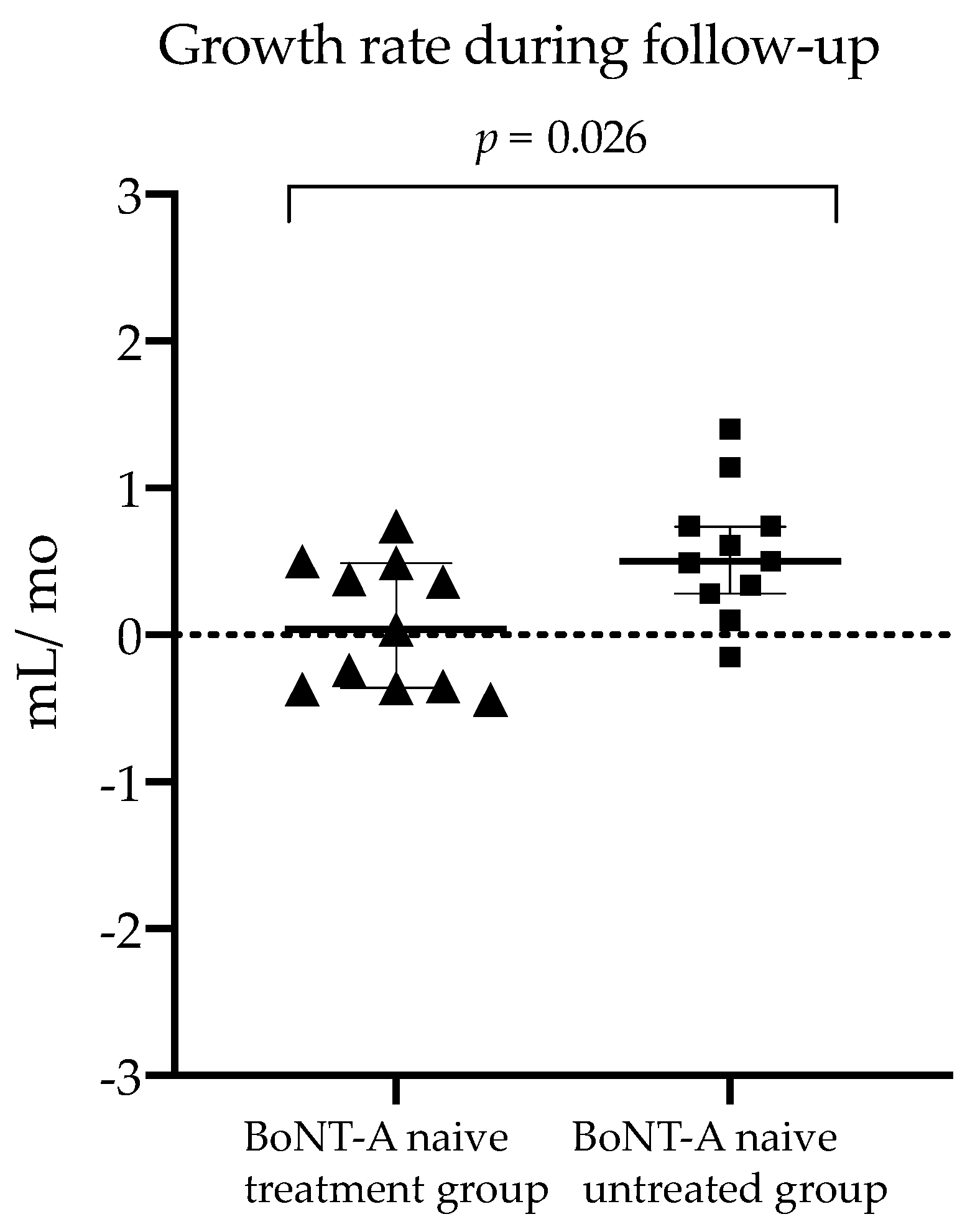
2.2. Comparison of BoNT-A Naive Treatment Group vs. Untreated Group (Research Aim 1)
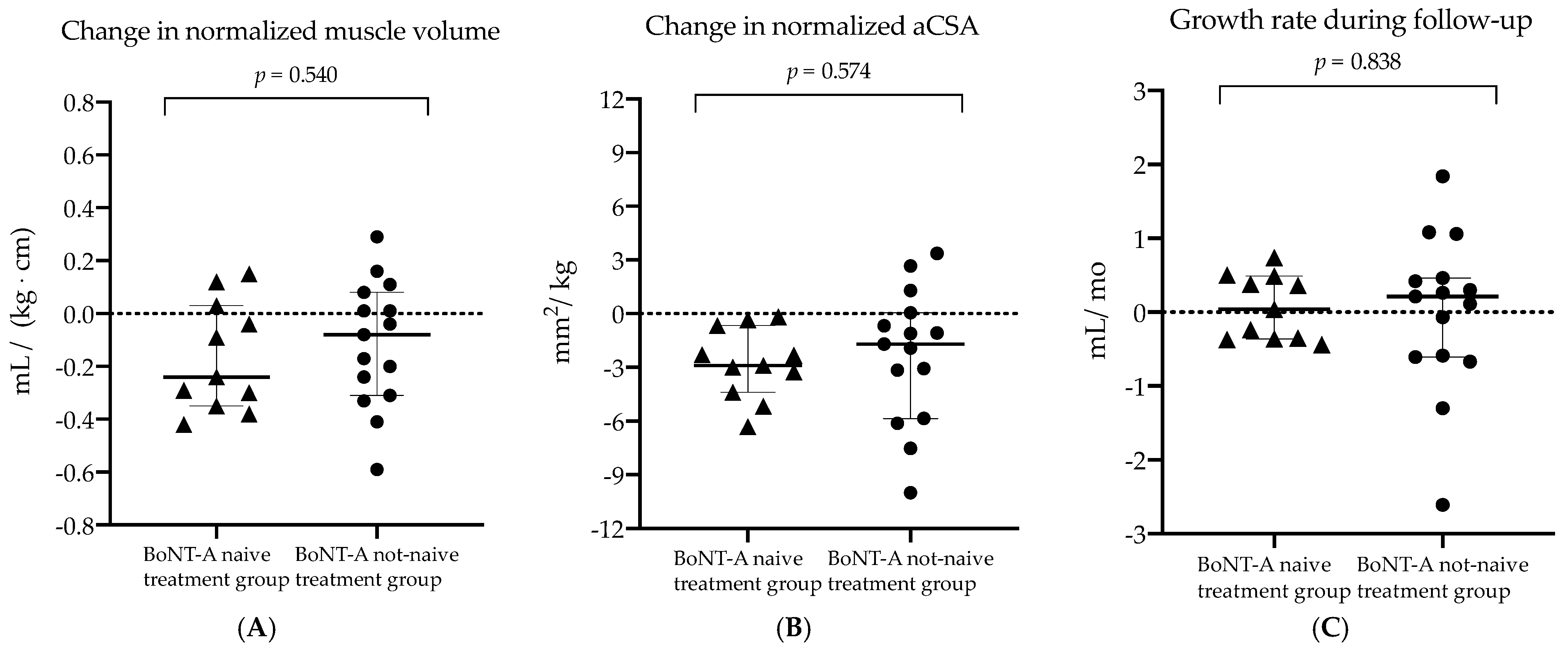
2.3. Comparison of BoNT-A Naive Treatment Group vs. Not-Naive Treatment Group (Research Aim 2)
3. Discussion
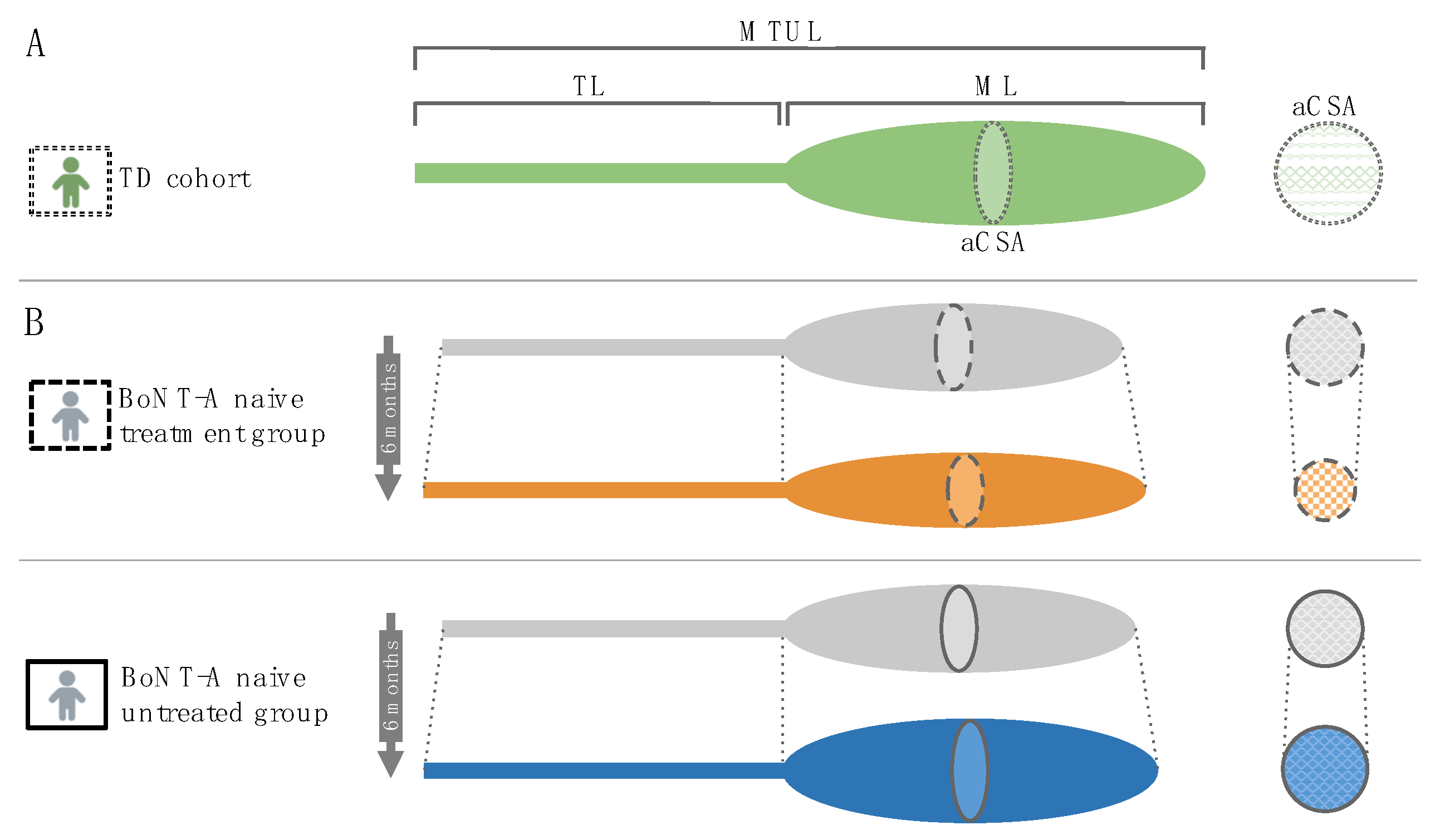
3.1. Hampered Growth in Muscle Volume Six Months after BoNT-A Injection
3.2. Preserved Growth in Muscle Lengths Six Months after BoNT-A Injection
3.3. Reduced Anatomical Cross-Sectional Area Six Months after BoNT-A Injection
3.4. Increased Echo-Intensity Values Six Months after BoNT-A Injection
3.5. Muscle Growth Rates following BoNT-A Injection
3.6. Clinical Implications
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Participants
5.2. Procedure
5.3. Assessment
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herskind, A.; Ritterband-Rosenbaum, A.; Willerslev-Olsen, M.; Lorentzen, J.; Hanson, L.; Lichtwark, G.; Nielsen, J.B. Muscle Growth Is Reduced in 15-Month-Old Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willerslev-Olsen, M.; Choe Lund, M.; Lorentzen, J.; Barber, L.; Kofoed-Hansen, M.; Nielsen, J.B. Impaired Muscle Growth Precedes Development of Increased Stiffness of the Triceps Surae Musculotendinous Unit in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.; Hastings-Ison, T.; Baker, R.; Barrett, R.; Lichtwark, G. Medial Gastrocnemius Muscle Volume and Fascicle Length in Children Aged 2 to 5 Years with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2011, 53, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schless, S.-H.; Hanssen, B.; Cenni, F.; Bar-On, L.; Aertbeliën, E.; Molenaers, G.; Desloovere, K. Estimating Medial Gastrocnemius Muscle Volume in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy: A Cross-Sectional Investigation. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, H.K.; Selber, P. Musculoskeletal Aspects of Cerebral Palsy. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Ser. B 2003, 85, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, H.K.; Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Dan, B.; Lin, J.-P.; Damiano, D.L.; Becher, J.G.; Gaebler-Spira, D.; Colver, A.; Reddihough, D.S.; et al. Cerebral Palsy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 15082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinen, F.; Desloovere, K.; Schroeder, A.S.; Berweck, S.; Borggraefe, I.; van Campenhout, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Aydin, R.; Becher, J.G.; Bernert, G.; et al. The Updated European Consensus 2009 on the Use of Botulinum Toxin for Children with Cerebral Palsy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2010, 14, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, S.C.; Novak, I.; Kentish, M.; Desloovere, K.; Heinen, F.; Molenaers, G.; Flaherty, S.O.Õ. Botulinum Toxin Assessment, Intervention and after-Care for Lower Limb Spasticity in Children with Cerebral Palsy: International Consensus Statement. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 9–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenaers, G.; Fagard, K. Botulinum Toxin A Treatment of the Lower Extremities in Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Child. Orthop. 2013, 7, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryll, U.; Bastiaenen, C.; De Bie, R.; Staal, B. Effects of Leg Muscle Botulinum Toxin A Injections on Walking in Children with Spasticity-Related Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2011, 53, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumetti, F.; Belloti, J.; Tamaoki, M.; Pinto, J. Botulinum Toxin Type A in the Treatment of Lower Limb Spasticity in Children with Cerebral Palsy (Review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019, 10, CD001408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, M.; Fairhurst, C.; Shortland, A.P. Botulinum Toxin and Cerebral Palsy: Time for Reflection? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 48, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multani, I.; Manji, J.; Hastings-ison, T.; Khot, A.; Graham, K. Botulinum Toxin in the Management of Children with Cerebral Palsy. Pediatr. Drugs 2019, 21, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.S.; Ertl-Wagner, B.; Britsch, S.; Schröder, J.M.; Nikolin, S.; Weis, J.; Müller-Felber, W.; Koerte, I.; Stehr, M.; Berweck, S.; et al. Muscle Biopsy Substantiates Long-Term MRI Alterations One Year after a Single Dose of Botulinum Toxin Injected into the Lateral Gastrocnemius Muscle of Healthy Volunteers. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.H.; Song, C.W.; Kim, Y.B.; Ha, C.S.; Yang, G.H.; Woo, H.D.; Jung, H.H.; Koh, W.S. Skeletal Muscle Atrophy Induced by Intramuscular Repeated Dose of Botulinum Toxin Type A in Rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 30, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuna, R.; Aurélio Vaz, M.; Rehan Youssef, A.; Longino, D.; Herzog, W. Changes in Contractile Properties of Muscles Receiving Repeat Injections of Botulinum Toxin (Botox). J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.R.; Minamoto, V.B.; Suzuki, K.P.; Hulst, J.B.; Bremner, S.N.; Lieber, R.L. Recovery of Rat Muscle Size but Not Function More than 1 Year after a Single Botulinum Toxin Injection. Muscle Nerve 2018, 57, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.; Elliott, C.; Valentine, J.; Stannage, K.; Bear, N.; Donnelly, C.J.; Shipman, P.; Reid, S. Muscle Volume Alterations after First Botulinum Neurotoxin A Treatment in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A 6-Month Prospective Cohort Study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egenolf, P.; Duran, I.; Stark, C.; Martakis, K.; Hamacher, S.; Schoenau, E.; Semler, O. Development of Disorder-Specific Normative Data for Growth in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modlesky, C.M.; Zhang, C. Complicated Muscle-Bone Interactions in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2020, 18, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.; Hastings-Ison, T.; Baker, R.; Kerr Graham, H.; Barrett, R.; Lichtwark, G. The Effects of Botulinum Toxin Injection Frequency on Calf Muscle Growth in Young Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy: A 12-Month Prospective Study. J. Child. Orthop. 2013, 7, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, M.; Shortland, A.P. Could Muscle Deformity in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy Be Related to an Impairment of Muscle Growth and Altered Adaptation? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2012, 54, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, N.; Van Campenhout, A.; Hanssen, B.; Cenni, F.; Schless, S.H.; Van den Broeck, C.; Desloovere, K.; Bar-On, L. Joint and Muscle Assessments of the Separate Effects of Botulinum NeuroToxin-A and Lower-Leg Casting in Children With Cerebral Palsy. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.S.; Sim, E.; Rha, D.; Jung, S. Architectural Changes of the Gastrocnemius Muscle after Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Yonsei Med. J. 2014, 55, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kawano, A.; Yanagizono, T.; Kadouchi, I.; Umezaki, T.; Chosa, E. Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Changes in the Muscle Architecture of the Gastrocnemius with Botulinum Toxin Treatment for Lower Extremity Spasticity in Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Orthop. Sci. 2018, 23, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schless, S.H.; Cenni, F.; Bar-On, L.; Hanssen, B.; Kalkman, B.; O’brien, T.; Aertbeliën, E.; Van Campenhout, A.; Molenaers, G.; Desloovere, K. Medial Gastrocnemius Volume and Echo-Intensity after Botulinum Neurotoxin A Interventions in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 61, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, N.R.; Gough, M.; Shortland, A.P. Three-Dimensional Realisation of Muscle Morphology and Architecture Using Ultrasound. Gait Posture 2004, 20, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obst, S.J.; Boyd, R.; Read, F.; Barber, L. Quantitative 3-D Ultrasound of the Medial Gastrocnemius Muscle in Children with Unilateral Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 2814–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Campenhout, A.; Verhaegen, A.; Pans, S.; Molenaers, G. Botulinum Toxin Type A Injections in the Psoas Muscle of Children with Cerebral Palsy: Muscle Atrophy after Motor End Plate-Targeted Injections. Res. Dev. Disab. 2013, 34, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.A.; Reid, S.; Elliott, C.; Shipman, P.; Valentine, J. Muscle Volume Alterations in Spastic Muscles Immediately Following Botulinum Toxin Type-A Treatment in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, J.; Stannage, K.; Fabian, V.; Ellis, K.; Reid, S.; Pitcher, C.; Elliott, C. Muscle Histopathology in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy Receiving Botulinum Toxin Type A. Muscle Nerve 2016, 53, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitcher, C.A.; Elliott, C.M.; Williams, S.A.; Licari, M.K.; Kuenzel, A.; Shipman, P.J.; Valentine, J.P.; Reid, S.L. Childhood Muscle Morphology and Strength: Alterations over Six Months of Growth. Muscle Nerve 2012, 46, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, S.L.; Pitcher, C.A.; Williams, S.A.; Licari, M.K.; Valentine, J.P.; Shipman, P.J.; Elliott, C.M. Does Muscle Size Matter? The Relationship between Muscle Size and Strength in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2015, 37, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handsfield, G.G.; Meyer, C.H.; Hart, J.M.; Abel, M.F.; Blemker, S.S. Relationships of 35 Lower Limb Muscles to Height and Body Mass Quantified Using MRI. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handsfield, G.G.; Meyer, C.H.; Abel, M.F.; Blemker, S.S. Heterogeneity of Muscle Sizes in the Lower Limbs of Children with Cerebral Palsy. Muscle Nerve 2016, 53, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palisano, R.J.; Rosenbaum, P.; Bartlett, D.; Livingston, M.H. Content Validity of the Expanded and Revised Gross Motor Function Classification System. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2008, 50, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindén, O.; Hägglund, G.; Rodby-Bousquet, E.; Wagner, P. The Development of Spasticity with Age in 4,162 Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Register-Based Prospective Cohort Study. Acta Orthop. 2019, 90, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, R.L.; Fridén, J. Functional and Clinical Significance of Skeletal Muscle Architecture. Muscle Nerve 2000, 23, 1647–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.J.; Herzog, W.; Howard, J.J. Skeletal Muscle in Cerebral Palsy: From Belly to Myofibril. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathewson, M.A.; Lieber, R.L. Pathophysiology of Muscle Contractures in Cerebral Palsy. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 26, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, R.S.; Lichtwark, G.A. Gross Muscle Morphology and Structure in Spastic Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, I.; Reid, L.; Stott, N.S.; Valentine, J.; Elliott, C. Measuring Skeletal Muscle Morphology and Architecture with Imaging Modalities in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Scoping Review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 63, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, B.; Peeters, N.; Dewit, T.; Hugyhe, E.; Dan, B.; Molenaers, G.; Van Campenhout, A.; Bar-On, L.; Van den Broeck, C.; Calders, P.; et al. Comprehensive Reliability of 3D Freehand Ultrasound to Assess Lower Limb Muscles in Spastic Cerebral Palsy and Typical Development. Eur. J. Ultrasound, 2022; to be submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher, C.A.; Elliott, C.M.; Valentine, J.P.; Stannage, K.; Williams, S.A.; Shipman, P.J.; Reid, S.L. Muscle Morphology of the Lower Leg in Ambulant Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Muscle Nerve 2018, 58, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillen, S.; Tak, R.O.; Zwarts, M.J.; Lammens, M.M.Y.; Verrijp, K.N.; Arts, I.M.P.; van der Laak, J.A.; Hoogerbrugge, P.M.; van Engelen, B.G.M.; Verrips, A. Skeletal Muscle Ultrasound: Correlation Between Fibrous Tissue and Echo Intensity. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, H.J.; Jenkins, N.T.; Zhao, Q.; Mccully, K.K. Measurement of Intramuscular Fat by Muscle Echo Intensity. Muscle Nerve 2015, 52, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingel, J.; Nielsen, M.S.; Lauridsen, T.; Rix, K.; Bech, M.; Alkjaer, T.; Andersen, I.T.; Nielsen, J.B.; Feidenhansl, R. Injection of High Dose Botulinum-Toxin A Leads to Impaired Skeletal Muscle Function and Damage of the Fibrilar and Non-Fibrilar Structures. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multani, I.; Manji, J.; Tang, M.J.; Herzog, W.; Howard, J.J.; Graham, H.K. Sarcopenia, Cerebral Palsy, and Botulinum Toxin Type A. JBJS Rev. 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenaers, G.; Schörkhuber, V.; Fagard, K.; Van Campenhout, A.; De Cat, J.; Pauwels, P.; Ortibus, E.; De Cock, P.; Desloovere, K. Long-Term Use of Botulinum Toxin Type A in Children with Cerebral Palsy: Treatment Consistency. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2009, 13, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, N.G.; Falvo, M.J.; Damiano, D.L. Rapid Force Generation Is Impaired in Cerebral Palsy and Is Related to Decreased Muscle Size and Functional Mobility. Gait Posture 2012, 35, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenaers, G.; Desloovere, K.; Fabry, G.; De Cock, P. The Effects of Quantitative Gait Assessment and Botulinum Toxin A on Musculoskeletal Surgery in Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Ser. A 2006, 88, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, P.; Willoughby, K.; Graham, H.K. Orthopaedic assessment. In Cerebral Palsy: Science and Clinical Practice; Mac Keith Press: London, UK, 2014; pp. 287–312. [Google Scholar]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Smith, M.B. Interrater Reliability of a Modified Ashworth Scale of Muscle Spasticity. Phys. Ther. 1987, 67, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, R.N.; Graham, H.K. Objective Measurement of Clinical Findings in the Use of Botulinum Toxin Type A for the Management of Children with Cerebral Palsy. Eur. J. Neurol. 1999, 6 (Suppl. S4), s23–s35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, H.K.; Harvey, A.; Rodda, J.; Nattrass, G.R.; Pirpiris, M. The Functional Mobility Scale. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2004, 24, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenni, F.; Schless, S.H.; Monari, D.; Bar-On, L.; Aertbeliën, E.; Bruyninckx, H.; Hanssen, B.; Desloovere, K. An Innovative Solution to Reduce Muscle Deformation during Ultrasonography Data Collection. J. Biomech. 2018, 77, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, B.; De Beukelaer, N.; Schless, S.H.; Cenni, F.; Bar-On, L.; Peeters, N.; Molenaers, G.; Van Campenhout, A.; Van den Broeck, C.; Desloovere, K. Reliability of Processing 3-D Freehand Ultrasound Data to Define Muscle Volume and Echo-Intensity in Pediatric Lower Limb Muscles with Typical Development or with Spasticity. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 2702–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treece, G.; Prager, R.; Gee, A.; Berman, L. Fast Surface and Volume Estimation from Non-Parallel Cross-Sections, for Freehand Three-Dimensional Ultrasound. Med. Image Anal. 1999, 3, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | BoNT-A Naive Treatment | BoNT-A Naive Untreated | BoNT-A Not-Naive Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 3.3 (1.2) | 2.8 (1.8) | 6.4 (2.5) |
| Topographic involvement | Bilateral, n = 7 Unilateral, n = 4 | Bilateral, n = 4 Unilateral, n = 7 | Bilateral, n = 8 Unilateral, n = 7 |
| Gender | Boy, n = 8 Girl, n = 3 | Boy, n = 4 Girl, n = 7 | Boy, n = 8 Girl, n = 7 |
| GMFCS level | I, n = 6 II, n = 1 III, n = 4 | I, n = 6, II, n = 1 III, n = 4 | I, n = 5 II, n = 8 III, n = 2 |
| Previous BoNT-A sessions | NA | NA | 1–2, n = 9 3–6, n = 6 |
| Time between two assessments (weeks) | 27.4 (3.4)/24–36 | 25 (2.5)/20–30 | 26.7 (3.6)/23–35 |
| BoNT-A Naive Treatment (a) | BoNT-A Naive Untreated (b) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Section 1: Baseline assessment | |||
| Age (years) | 3.3 (1.2) | 2.8 (1.8) | 0.401 |
| Body mass (kg) | 13.6 (1.3) | 14.5 (4.9) | 0.243 |
| Body length (cm) | 91.0 (9.2) | 97.0 (18.4) | 0.652 |
| Leg length (cm) | 44.2 (5.0) | 46.0 (9.5) | 0.797 |
| MV (mL) | 16.6 (8.80) | 22.8 (14.9) | 0.300 |
| nMV (mL/(kg·m)) | 1.47 (0.43) | 1.52 (0.45) | 0.478 |
| ML (mm) | 104.3 (19.0) | 111.0 (33.5) | 0.652 |
| nML (%) | 23.6 (4.05) | 23.3 (5.83) | 0.949 |
| MTUL (mm) | 203.1 (25.8) | 207.8 (57.5) | 0.748 |
| nMTUL (%) | 45.8 (1.92) | 46.7 (5.55) | 0.438 |
| aCSA (mm2) | 245.7 (79.4) | 258.1 (94.3) | 0.652 |
| aCSAnorm (mm2/kg) | 16.7 (6.40) | 17.5 (4.15) | 0.797 |
| EI (bit) | 153.2 (12.1) | 158.5 (31.5) | 1.000 |
| Growth rate (mL/mo) | 0.47 (0.25) | 0.51 (0.09) | 0.270 |
| Section 2: Changes over six-month follow-up | |||
| Interval (months) | 6.00 (1.00) | 6.00 (0.00) | 0.075 |
| Δ Body mass (kg) | 1.20 (1.20)/+8% | 1.10 (0.65)/+ 8% | 0.217 |
| Δ Body length (cm) | 5.60 (3.90)/+6% | 4.20 (3.20)/+ 4% | 0.365 |
| Δ Leg length (cm) | 2.80 (2.80)/+6% | 2.50 (2.20)/+5% | 0.847 |
| Δ MV (mL) | 0.23 (5.15)/+1% | 2.95 (2.78)/+13% | 0.045 |
| Δ nMV (mL/(kg⋅m)) | −0.24 (0.38)/−16% | 0.05 (0.19)/−3% | 0.020 |
| Δ ML (mm) | 8.50 (9.10)/+8% | 7.87 (9.00)/+7% | 0.870 |
| Δ nML (%) | 0.47 (2.67)/+2% | 0.78 (2.67)/+3% | 0.818 |
| Δ MTUL (mm) | 13.1 (9.40)/+7% | 8.90 (13.8)/+4% | 0.670 |
| Δ nMTUL (%) | −0.56 (3.63)/−1% | −0.82 (2.08)/−2% | 0.622 |
| Δ aCSA (mm2) | −14.2 (49.9)/−6% | 30.0 (23.1)/+12% | 0.003 |
| Δ aCSAnorm (mm2/kg) | −2.89 (3.72)/−17% | 0.72 (3.18)/+4% | <0.001 |
| Δ EI (bit) | 7.80 (23.7)/+5% | −5.30 (23.2)/−3% | 0.009 |
| Growth rate during follow-up (Δ mL/Δ mo) | 0.038 (0.85) | 0.498 (0.46) | 0.026 |
| BoNT-A Naive Treatment (a) | BoNT-A Naive Untreated (b) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Follow-Up | Median Differences | p | Baseline | Follow-Up | Median Differences | p | |
| Participants (n) | 11 | 11 | 15 | 15 | ||||
| Age | 3.3 (1.2) | 3.8 (1.0) | 0.60 | 0.003 | 2.8 (1.8) | 3.4 (1.8) | 0.60 | 0.003 |
| Body mass (kg) | 13.6 (1.3) | 14.7 (2.6) | 1.20 (+8%) | 0.003 | 14.5 (4.9) | 15.6 (4.3) | 1.10 (+8%) | 0.003 |
| Body length (cm) | 91.0 (9.2) | 99.0 (9.0) | 5.60 (+6%) | 0.003 | 97.0 (18.4) | 99.0 (14.9) | 4.20 (+4%) | 0.003 |
| Leg length (cm) | 44.2 (5.0) | 46.5 (8.0) | 2.80 (+6%) | 0.003 | 46.0 (9.5) | 49.0 (10.0) | 2.50 (+5%) | 0.003 |
| MV (mL) | 16.6 (8.80) | 16.6 (13.4) | +0.23 (+1%) | 0.375 | 22.8 (14.9) | 27.1 (12.6) | +2.95 (+13%) | 0.006 |
| nMV (mL/(kg⋅m)) | 1.47 (0.43) | 1.24 (0.43) | −0.24 (−16%) | 0.041 | 1.52 (0.45) | 1.49 (0.51) | −0.05 (−3%) | 0.155 |
| ML (mm) | 104.3 (19.0) | 107.5 (21.5) | +8.50 (+8%) | 0.013 | 111.0 (33.5) | 115.1 (29.4) | +7.87 (+7%) | 0.007 |
| nML (%) | 23.6 (4.05) | 23.5 (2.41) | +0.47 (+2%) | 0.534 | 23.3 (5.83) | 23.5 (5.23) | +0.78 (+3%) | 0.790 |
| MTUL (mm) | 203.1 (25.8) | 211.8 (35.2) | +13.1 (+7%) | 0.005 | 207.8 (57.5) | 221.2 (45.4) | +8.90 (+4%) | 0.008 |
| nMTUL (%) | 45.8 (1.92) | 45.2 (2.50) | −0.56 (−1%) | 0.859 | 46.7 (5.55) | 46.3 (6.04) | −0.82 (−2%) | 0.374 |
| aCSA (mm2) | 245.7 (79.4) | 224.9 (101.0) | −14.2 (−6%) | 0.075 | 258.1 (94.3) | 295.7 (142.1) | +30.0 (+12%) | 0.013 |
| aCSAnorm(mm2/kg) | 16.7 (6.40) | 13.5 (7.98) | −2.89 (−17%) | 0.003 | 17.5 (4.15) | 18.8 (5.82) | +0.72 (+4%) | 0.110 |
| EI (bit) | 153.2 (12.1) | 162.6 (18.8) | +7.80 (+5%) | 0.033 | 158.5 (31.5) | 153.1 (17.9) | −5.30 (−3%) | 0.131 |
| BoNT-A Naive Treatment (a) | BoNT-A Not-Naive Treatment (b) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Section 1: Baseline assessment | |||
| Age (years) | 3.3 (1.2) | 6.4 (2.5) | <0.001 |
| Body mass (kg) | 13.6 (1.3) | 20.0 (7.5) | <0.001 |
| Body length (cm) | 91.0 (9.20) | 114.0 (26.0) | <0.001 |
| Leg length (cm) | 44.2 (5.0) | 55.4 (15.5) | <0.001 |
| nMV (mL/(kg⋅m)) | 1.47 (0.43) | 1.39 (0.62) | 0.959 |
| nML (%) | 23.6 (4.05) | 23.4 (3.46) | 0.838 |
| nMTUL (%) | 45.8 (1.92) | 45.5 (1.49) | 0.384 |
| aCSAnorm (mm2/kg) | 16.7 (6.40) | 17.8 (5.56) | 0.721 |
| EI (bit) | 153.2 (12.1) | 175.3 (22.4) | 0.020 |
| Growth rate (mL/mo) | 0.47 (0.25) | 0.42 (0.21) | 0.959 |
| Section 2: Changes over six-month follow-up | |||
| Interval (months) | 6.00 (1.00) | 7.00 (1.00) | |
| Δ Body mass (kg) | 1.20 (1.20)/(+8%) | 1.20 (1.00)/(+6%) | 0.959 |
| Δ Body length (cm) | 5.60 (3.90)/(+6%) | 3.20 (2.30)/(+3%) | 0.097 |
| Δ Leg length (cm) | 2.80 (2.80)/(+6%) | 3.00 (1.10)/(+5%) | 1.000 |
| Δ nMV (mL/(kg⋅m)) | −0.24 (0.38)/−16% | −0.08 (0.39)/−6% | 0.540 |
| Δ nML (%) | 0.47 (2.67)/+2% | −0.15 (0.82)/−1% | 0.474 |
| Δ nMTUL (%) | -0.56 (3.63)/−1% | 0.02 (1.79)/0% | 1.000 |
| Δ aCSAnorm (mm2/kg) | −2.89 (3.72)/−17% | −1.69 (1.73)/−10% | 0.574 |
| Δ EI (bit) | 7.80 (23.7)/+5% | 9.20 (36.2)/+5% | 1.000 |
| Growth rate during follow-up (Δ mL/Δ mo) | 0.038 (0.85) | 0.210 (1.07) | 0.838 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Beukelaer, N.; Weide, G.; Huyghe, E.; Vandekerckhove, I.; Hanssen, B.; Peeters, N.; Uytterhoeven, J.; Deschrevel, J.; Maes, K.; Corvelyn, M.; et al. Reduced Cross-Sectional Muscle Growth Six Months after Botulinum Toxin Type-A Injection in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Toxins 2022, 14, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14020139
De Beukelaer N, Weide G, Huyghe E, Vandekerckhove I, Hanssen B, Peeters N, Uytterhoeven J, Deschrevel J, Maes K, Corvelyn M, et al. Reduced Cross-Sectional Muscle Growth Six Months after Botulinum Toxin Type-A Injection in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Toxins. 2022; 14(2):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14020139
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Beukelaer, Nathalie, Guido Weide, Ester Huyghe, Ines Vandekerckhove, Britta Hanssen, Nicky Peeters, Julie Uytterhoeven, Jorieke Deschrevel, Karen Maes, Marlies Corvelyn, and et al. 2022. "Reduced Cross-Sectional Muscle Growth Six Months after Botulinum Toxin Type-A Injection in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy" Toxins 14, no. 2: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14020139
APA StyleDe Beukelaer, N., Weide, G., Huyghe, E., Vandekerckhove, I., Hanssen, B., Peeters, N., Uytterhoeven, J., Deschrevel, J., Maes, K., Corvelyn, M., Costamagna, D., Gayan-Ramirez, G., Van Campenhout, A., & Desloovere, K. (2022). Reduced Cross-Sectional Muscle Growth Six Months after Botulinum Toxin Type-A Injection in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Toxins, 14(2), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14020139






