1. Introduction
Coral snakes represent the Elapidae family in America; they are constituted by three genera
Micrurus, Leptomicrurus, and
Micruroides [
1,
2], although the phylogenetic findings do not separate
Leptomicrurus from
Micrurus in a concluding way [
3].
Micrurus is the most abundant genus, with about 80 species distributed from the southern United States to Northern Argentina [
4].
M. dumerilii is a species widely distributed in Colombia, covering the west, center, and north of the country; additionally, it is found in northwestern Ecuador, Northwestern Venezuela, and southeastern Panama. The species has an average length between 50 to 70 cm and presents a combination of three colors along the body, such as rings of red, white, and black [
4].
Micrurus venoms are predominantly composed of Three-finger toxins (3FTxs) and Phospholipases A
2 (PLA
2s) [
5]. The snake venom secretory PLA
2 (svPLA
2s) found in coral snake venom belongs to group IA. In addition, one venom can contain several isoforms of these enzymes [
6]. The svPLA
2s are a group of calcium-dependent enzymes that can hydrolyze glycerophospholipids at the middle ester bond (sn-2) [
7]. According to Rey-Suárez et al. [
8], the venom of
M. dumerilii is mainly composed of PLA
2s (52%).
In addition, it was identified that MdumPLA
2 was the most abundant PLA
2 from
M. dumerilii venom [
9]. It is an enzymatically active acid protein, without lethal effect, and with a high myotoxicity in mice.
The svPLA
2s of coral snakes induce different pharmacological effects in victims such as neurotoxicity, myotoxicity, cytotoxicity, anticoagulant effects, cardiotoxicity, and edema, which are related to their capacity to hydrolyze membrane glycerophospholipids and multiple functional sites on its structure [
10]. Despite this, the conservation of their structures and the broad spectrum of severe pharmacological effects suggest that svPLA
2s represent a target for the production or enrichment of new antivenoms. In this way, the specific treatment for envenomation caused by snakebites is the intravenous administration of antivenoms produced from small doses of injected venom, mainly in horses [
11]. Nevertheless, the
Micrurus species produce a low quantity of venom and have serious issues surviving in captivity. In addition, they are difficult to find in the field, have ophiouphagus diets and semifossorial habits, and some species are relatively small [
12,
13].
It is known that antivenom production requires a high amount of venom to inject and produce an immune response in the animals selected [
14,
15]. Given the complexity of snake venoms, some of their components include toxins with different targets consequently resulting in diverse immunogenicity, thus generating antibodies targeting different antigens [
16]. In addition, some toxins act in an independent manner, whereas others act synergistically, contributing to an increase in their toxicity [
17,
18]. Therefore, it makes it more challenging to direct the antibodies of the most significant therapeutic interest toward snake venom toxins [
16]. Hence, getting high enough amounts of toxins from coral venom to produce antivenoms is a challenge that can be resolved by the recombinant expression of the target toxins into heterologous organisms. Although there are several systems to express recombinant proteins available,
Escherichia coli is the first option due to its ease of genetic manipulation, inexpensive culture conditions, and rapid growth, among many other advantages, compared to eukaryotic expression systems and other bacteria [
19].
In this context, Clement and colleagues [
20] expressed a metalloprotease and a serineproteinase in a recombinant way in
E. coli from mRNA transcripts of
Bothrops ammodytoides venom gland. Moreover, the same author obtained heterologous expression and antibody recognition of a Mlat, a neurotoxin from the Mexican coral snake
Micrurus laticorallis [
21]. In parallel, Russo’s team’s [
22] aim was to express two isoforms from the CB subunit from the crotoxin complex from
Crotalus durissus terrificus venom, by using a prokaryotic system. They optimized and cloned the sequences into a plasmid vector (pG21a) and reached the expression of a biologically active recombinant protein. Moreover, Shimokawa-Falcão et al. [
23] expressed Insularin, a disintegrin from the
Bothrops insularis, using the expression vector SUMO Tag in
E. coli strains.
Another important advance in this field was made by Wen-Li and colleagues [
24], who achieved the functional expression and the characterization of a recombinant phospholipase A
2 (PLA
2) from sea snake
Lapemis hardwickii as a soluble protein in
E. coli using the vector pTRX. Furthermore, Guerrero-Garzón et al. [
25] showed the heterologous expression of an α-neurotoxin (rD.H) from
Micrurus diastema in a bacterial system. Starting at thirty different 3FTx transcript sequences obtained from the venom glands of four species of
Micrurus, one transcript (D.H) encoded for short-chain α-neurotoxins was identified in the venom of
M. diastema. Likewise, de la Rosa et al. [
26] obtained a consensus sequence of an α-neurotoxin, using the sequences of species from elapid genera, including
Acanthophis,
Oxyuranus,
Walterinnesia,
Naja,
Dendroaspis, and
Micrurus. The consensus protein (ScNtx) was expressed in
E. coli cells by cloning into the expression vector pQE30.
Among the several expression systems, the pET System is a powerful system designed to express recombinant proteins in
E. coli BL21 strains upon the simple induction of the T7 RNA polymerase by IPTG [
27]. In pET28a, target genes are cloned downstream of, and in-frame with, a poly-histidine purification tag (His6) under the control of the T7 promoter. Additionally, pET28a contains a lac operator to suppress uninduced expression. These features confer advantages that leverage its use for protein expression in prokaryotic heterologous systems.
This study presents the heterologous expression of the major PLA2 from M. dumerilii, its biological activities, immunologic recognition, and its potential to be used as an immunogen to produce antivenom formulations.
3. Discussion
Snake venoms are complex mixtures of proteins, enzymes, peptides, non-enzymatic proteins, and inorganic components. These are rich sources of active compounds with a broad spectrum of biological activities [
28]. Indeed, several amino acid sequences and crystal structures of many snake venom PLA
2-isoforms have been reported, showing high identities and a conserved structural scaffold [
29,
30], but their biological effects differ [
31].
The PLA
2 are enzymes that occur in almost all venoms, including
Micrurus genus, and they play a vital role in the pharmacological effects observed in snakebites. The most abundant PLA
2 of
M. dumerilii was isolated and sequenced by Rey-Suarez et al. [
8]. This toxin induced myotoxicity and edema, but it was not lethal. This study produced it in a recombinant form and its potential to develop antivenoms was tested.
E. coli is a recombinant system that offers significant advantages such as the knowledge of its genetics, plasmids availability, a variety of inducible promoters, and low production costs [
32]. For this reason, a genetic construct that would allow overexpressing a protein in a prokaryote expression model was developed, using the optimization of sequences during the construct’s design process to increase its expression levels per se [
33].
Among the different procaryotic expression systems, one of the advantages of using pET vectors is their medium copy number, which makes it an efficient system to produce a large amount of the target protein in the competent cells of
E. coli. In addition, transcription of the inserted gene achieves when pET28a was inserted in BL21 (DE3), which carries the gene for T7 RNA polymerase. When induced, this gene plays a selective role, resulting in almost all the cell’s resources being focused on targeting gene expression [
34]. In this sense, after purification, the yield (10.1 mg/L) of His-rMdumPLA
2 showed a medium expression level, considering recovery yields of the recombinant protein in a range of 10–50 mg/L [
35,
36]. It is important to describe that pET, and other expression vectors have intrinsic features that can delimit the yield of the heterologous protein [
37]. Moreover,
E. coli strains express differentially heterologous genes because of specific genomic characteristics that can be a decisive factor in the high expression of recombinant proteins [
32].
Understanding the above, when we compare our results with other studies, the yield (10.1 mg/L) of His-rMdumPLA
2 after purification was superior to that of Wen-Li et al. [
24], who obtained a final yield of approximately 2.5 mg/L of pure rPLA
2-9 using the strain BL21 (DE3) but different expression vector. In the same way, our results contrast with those reported by Clement et al. [
20] and Guerrero-Garzón et al. [
25], who used the plasmid pQE30 and expressed in the strains
E. coli Origami, the recombinants rBamSP_1 (1 mg/L) and rBamMP_1 (1.8 mg/L), and the recombinant rD.H. (4.2 mg/L) after purification, respectively. Other researchers like Shimokawa-Falcão et al. [
23] obtained a yield of LgRec2 of about 24 mg/L of purified protein and 20 mg/L of the disintegrin Insularin. Both recombinant proteins were cloned on the pSUMOUlp1 vector and expressed in BL21 Star™ (DE3) cells
E. coli.
According to Woestenenk et al. [
38], high protein production levels could be mainly due to a high growth rate of the host cells, in this case, to a balanced exponential growth phase of BL21 (DE3)
E. coli. This growth, in turn, depends significantly on the overexpressed target protein. However, the essential factor in producing recombinant protein is the absolute amount of soluble protein per culture volume rather than the fraction of soluble protein per total protein. Even though the concentration soluble fraction is high, that does not mean high protein yields after purification. Additionally, high host cell growth levels combined with vector encoding N-His tag allowed total protein purification. Mohanty and colleagues [
39] have also postulated that the tag could confer more stability to the protein. Fundamentally, the sequences used in the design of genetic construct, the strategy of cloning, or the vector backbones should be considered when expressing the recombinant protein.
It is important to note that although His-rMdumPLA
2 is a cysteine-rich protein with seven disulfide bonds, which confer enzyme stability [
40], it was expressed as IBs. Thus, it was necessary to solubilize it with a denaturing agent. As the refolding process is a conformational change from the unfolded to the native protein state [
41], it implies a balance between aggregation and solubilization for achieving an active protein. However, it is known that during the refolding process can occur intermolecular and intramolecular interactions [
42], that may lead to a non-native structure which, in turn, may result in misfolding with the formation of non-native disulfides bonds [
41] and thus, in an incomplete folding [
43,
44]. Furthermore, impurities present in solubilized IBs can associate with the expressed protein and in some way interfere with its refolding [
42]. In this case, His-rMdumPLA
2 was able to adopt a stable soluble conformation but the exact architecture of the active site could be deficient; therefore, comparable activity with native protein was not obtained. Anyway, the solubilization of the His-rMdumPLA
2 IBs allowed a sufficiently flexible and disordered structure of protein that conferred biological activity with respect to native protein or the complete venom. In fact, in some proteins, it has been reported that IBs solubilization allows recovery of 50% or less of the bioactive product [
45] and no biologically active product in other cases [
46].
The mass of His-rMdumPLA
2 detected in SDS-PAGE was very close to the theoretical molecular mass of His-rMdumPLA
2 (~16 kDa). However, it differed from the native MdumPLA
2 which has a molecular mass of 13,288 Da [
8]. This difference was due to the 6His-tag, sequences coding to linker GS and the excision site of protease TEV. This was demonstrated when cutting the His tail using protease TEV, since the obtained molecular mass was comparable to the native MdumPLA
2.
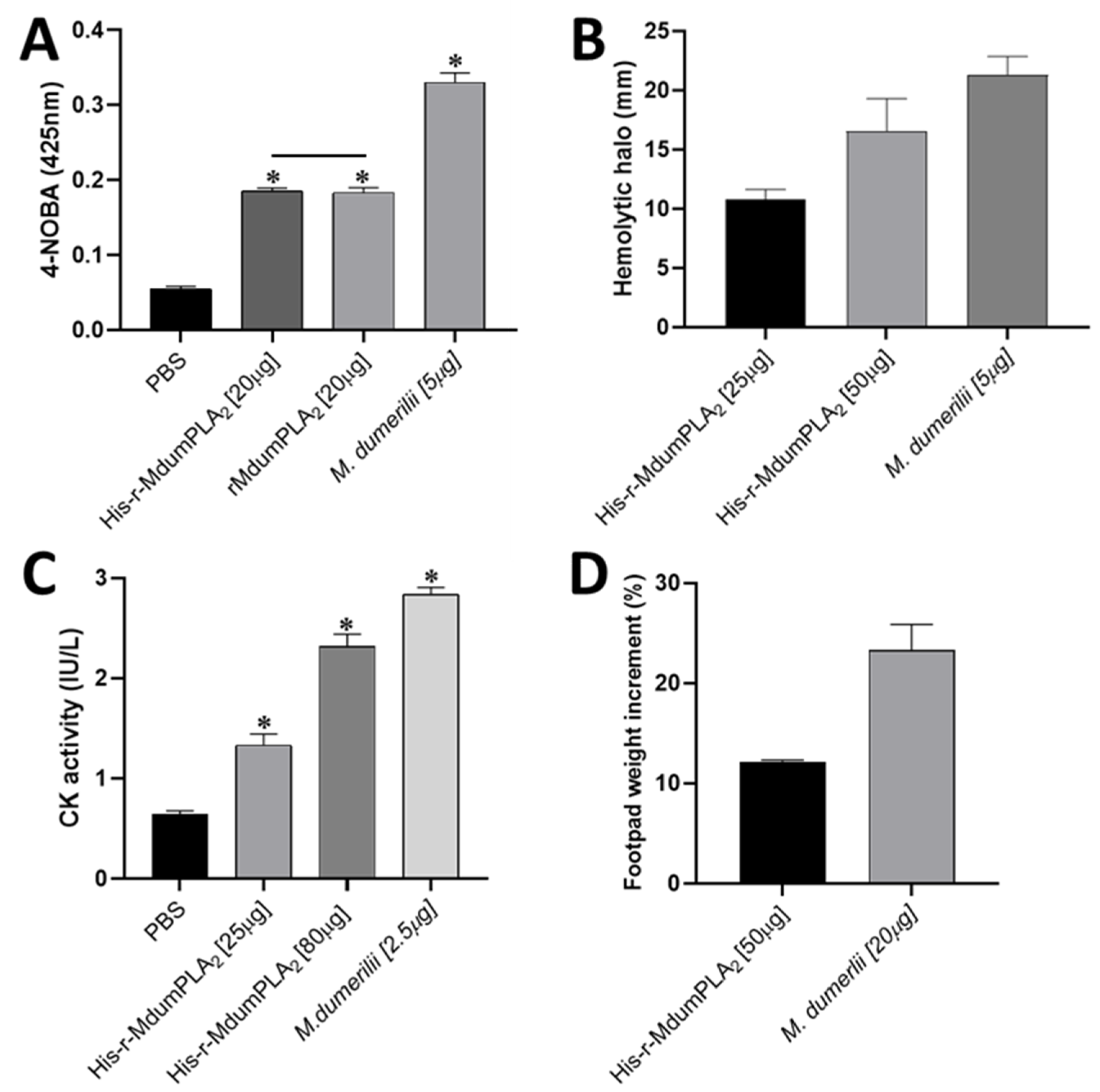
His-rMdumPLA2 was enzymatically active, as shown by its ability to hydrolyze the 4-NOBA synthetic substrate, and indirect hemolytic activity. In both cases, it did not display significant differences when we compared the enzymatic activity rMdumPLA2. This result allowed us to decide to continue using His-rMdumPLA2 since when the His tail is cut with the TEV protease, some amounts of the recombinant protein are lost, which results in a decrease in the quantity of rMdumPLA2 available for the rest of the assays.
In the same way, His-rMdumPLA2 induced a dose-dependent increase of plasma CK activity after (i.m.) injection into the gastrocnemius muscle of mice. Herein, the forming of incorrectly folded proteins and insoluble aggregates in the reducing environment of bacterial cytoplasm, and low recovery of the bioactive product might be related to a decreased myotoxic effect. Furthermore, the complex process of refolding protein in the presence of the 6His tag may cause differences in structural motifs. However, this subject requires further studies.
PLA
2s trigger the synthesis of lipid regulatory molecules at the inflammation site. These molecules are fatty acids, their derivatives (prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxanes), and phospholipid platelet-activating factor (PAF) [
29]. Considering that PLA
2s are venom components implicated either directly or indirectly in the induction of edema [
47,
48], we found that His-rMdumPLA
2 induced weak edema in the mouse footpad. Low recovery of the bioactive product from solubilized IBs, even with a medium level of expression of recombinant protein, as mentioned above may affect edematogenic activity. Nevertheless, this finding could be important from the point of view of animal welfare because it contributes to maximizing the host antibody response and minimizing the inflammatory lesions associated with the nature of the antigen [
49].
According to anticoagulant abilities, PLA
2 enzymes may be strong, weak, and non-anticoagulant enzymes [
50]. His-rMdumPLA
2 had a weak anticoagulant effect because it showed this activity in doses higher than 15 μg/mL [
50]. Nevertheless, the weaker anticoagulant activity of His-rMdumPLA
2 might be explained by possible structural differences to native PLA
2, especially in anticoagulant region (pharmacological site) that binds to a coagulation Factor Xa and inactivates it [
51]. However, these discrepancies were not tested in this study, thus, they should be addressed in further studies.
In general, we obtained a functional His-rMdumPLA
2 protein. Nevertheless, its bioactivity was different in comparison to native PLA
2 [
8]. These results might be due, in part, to misfolding of protein, given that during the refolding process, the presence of the His tag may cause negative effects on the tertiary structure or in the biological activity of the chimeric protein, such as it was reported by Khan et al. for MSP1(42) protein [
52]. Nevertheless, those structural changes may not affect the active site, interfacial binding surface and hydrophobic channel, which are involved in the catalytic mechanism of PLA
2s [
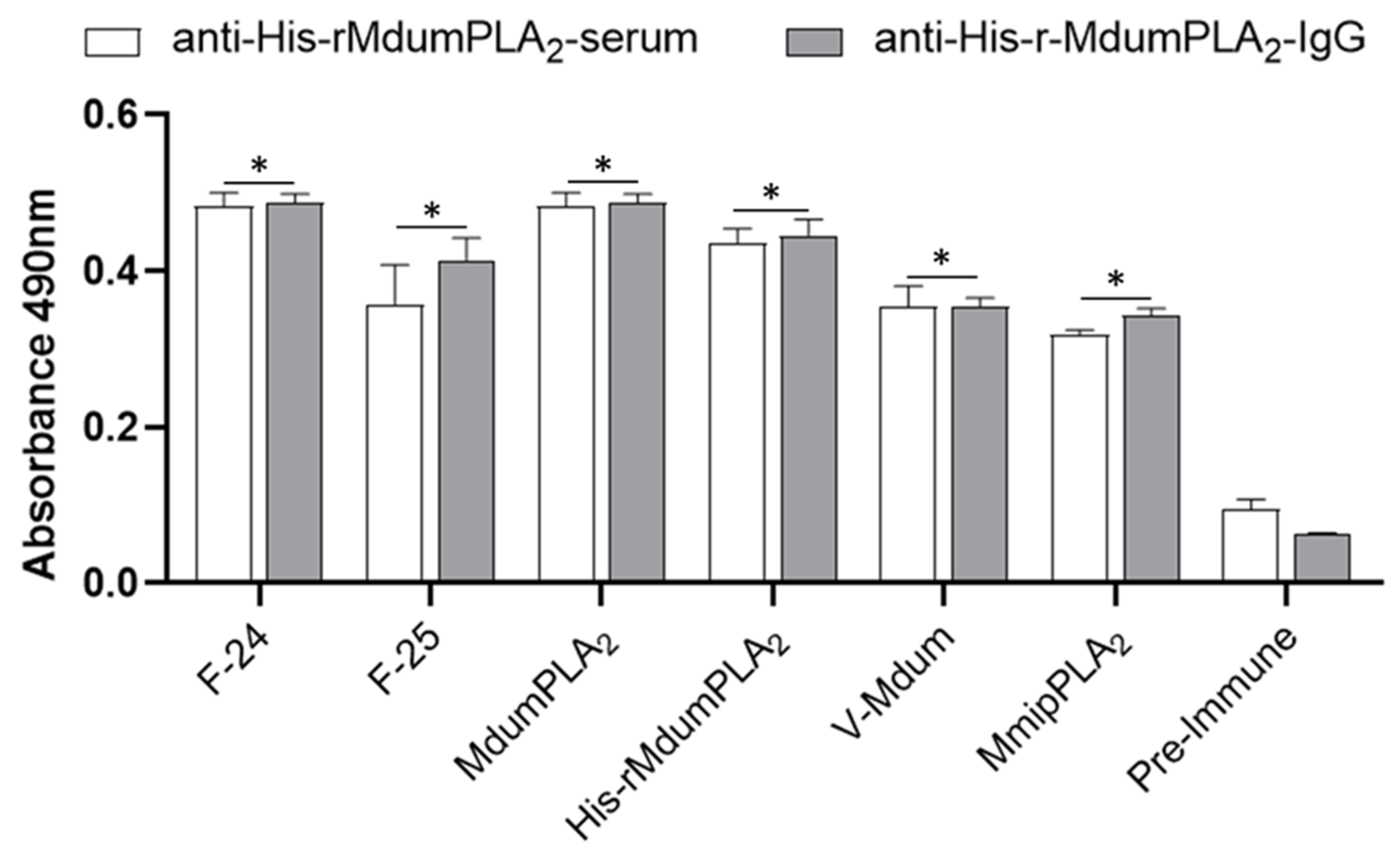
31], but this hypothesis should be addressed in further studies. Despite that, rabbit polyclonal antibodies generated against His-rMdumPLA
2 recognized both
M. dumerlii venom, native Mdum-PLA
2, the 24 and 25 fractions of the phospholipases region from the proteome of
M. dumerilii and MmipPLA
2. It is possible that some conformational epitopes have been recognized by some of anti-His-rMdumPLA
2 antibodies generated by the rabbit’s immune system.
It is important to note that the pattern of the group I PLA
2s from elapid venoms is conserved between MmipPLA
2 and MdumPLA
2 according to the study of Rey-Suarez et al. [
8], and furthermore when the amino acid sequences of both toxins were compared, they shared 65% identity [
8]. In this regard, and in concordance with the mentioned above, immunological cross recognition of antibodies against His-rMdumPLA
2 might be the result of a conserved structural scaffold of both MdumPLA
2 and MmipPLA
2.
On the other hand, anti-His-rMdumPLA
2-IgG did not neutralize the lethal activity of the
M. dumerilii venom; moreover, these antibodies neutralized 100% of the PLA
2 activity of itself and a moderated percentage of the myotoxicity activity of
M. dumerilii venom. These results could be explained by the presence of other lethal components or other strongly toxic PLA
2 in
M. dumerilii venom. It is known that toxins and other components of snake venom can act independently or synergistically, to cause a broad spectrum of toxic effects such as local or systemic damage [
53]. In addition, due to the presence of the “pharmacological sites” in the three-dimensional structure of the PLA
2s, neutralizing catalytic activity does not ensure the inhibition of the biological effects, such as myotoxicity or edema-forming [
30]. Likewise, it has been reported that low molecular mass proteins, such as PLA
2 generate a low immune response compared to high molecular mass proteins [
5,
54,
55]. Thus, it is to be expected that MdumPLA
2 or the whole
M. dumerilii venom was not neutralized by anti-His-rMdumPLA
2-IgG. Unfortunately, because we did not have enough anti-His-rMdumPLA
2-IgG, it was impossible to test other doses or carry out more assays.
The use of most abundant toxins involved in envenoming not only of
M. dumerilii (in this case) but of different coral snake species with clinical relevance [
56], and whose availability is reduced by other factors such as survival captivity and a low venom production [
12], is key to antivenom development. The results of His-rMdumPLA
2 suggest that this recombinant toxin could be included in the mix of venoms and other toxins used to produce antivenoms against different species of elapids.
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
Restriction enzymes NcoI, XbaI, NotI, XhoI and EcoRV, and T4 DNA ligase were purchased from New England Biolabs (NEB) (Ipswich, MA, USA). Escherichia coli DH5α (Invitrogen) strain was used for gene cloning and plasmid propagation meanwhile E. coli strain BL21(DE3) (Stratagene, San Diego, CA, USA) was used for protein expression. The plasmid pET28a (Novogene, Cambridge, UK) was used as an episomal vector to produce the fusion construct as described below.
5.2. Venoms and Animals
M. dumerilii venom (lyophilized) was provided by the Serpentarium of the University of Antioquia and obtained from adult specimens collected in Antioquia, Colombia. Swiss-Webster mice of both sexes with 18–20 g of body weight were utilized in all in vivo experiments under the ethics committee of Antioquia University (license No. 110 of 2017). New Zealand white rabbits (2.15 kg) were utilized in vivo immunizations experiments according to the ethics committee above.
5.3. Optimization and Genetic Construction
The amino acidic sequence C0HKB8 of phospholipase A
2 (MdumPLA
2) of
M. dumerilii from the database UniProt “
https://www.uniprot.org (accessed on 10 May 2019)”was loaded in the OPTIMIZER tool “
http://genomes.urv.es/OPTIMIZER/ (accessed on 20 September 2019)”, using the preferential codon usage according to Kazusa database “
http://www.kazusa.or.jp/codon/ (accessed on 20 September 2019)”. The open reading frame (ORF) of the optimized sequence was verified by in silico translation using the ExPASy tool “
https://www.expasy.org/ (accessed on 20 September 2019)”. Finally, the optimized sequence was fused with an N-terminal polyhistidine tag (6HisTag) followed by a glycine-serine linker and a TEV protease recognition site, right in front of the Met-ini of the PLA
2 ORF. For cloning into the MCS pET28a, we set a 5′ NcoI site in front of the 6HisTag at the 5′ end and a 3′ NotI site downstream of the stop codon. The construct synthesis was made by General Biosystems and delivered in the commercial cloning vector pUC57_BsaI_Free. A short name HisrMdumPLA
2 was assigned to the plasmid product (
Figure 1A).
5.4. Cloning His-rMdumPLA2
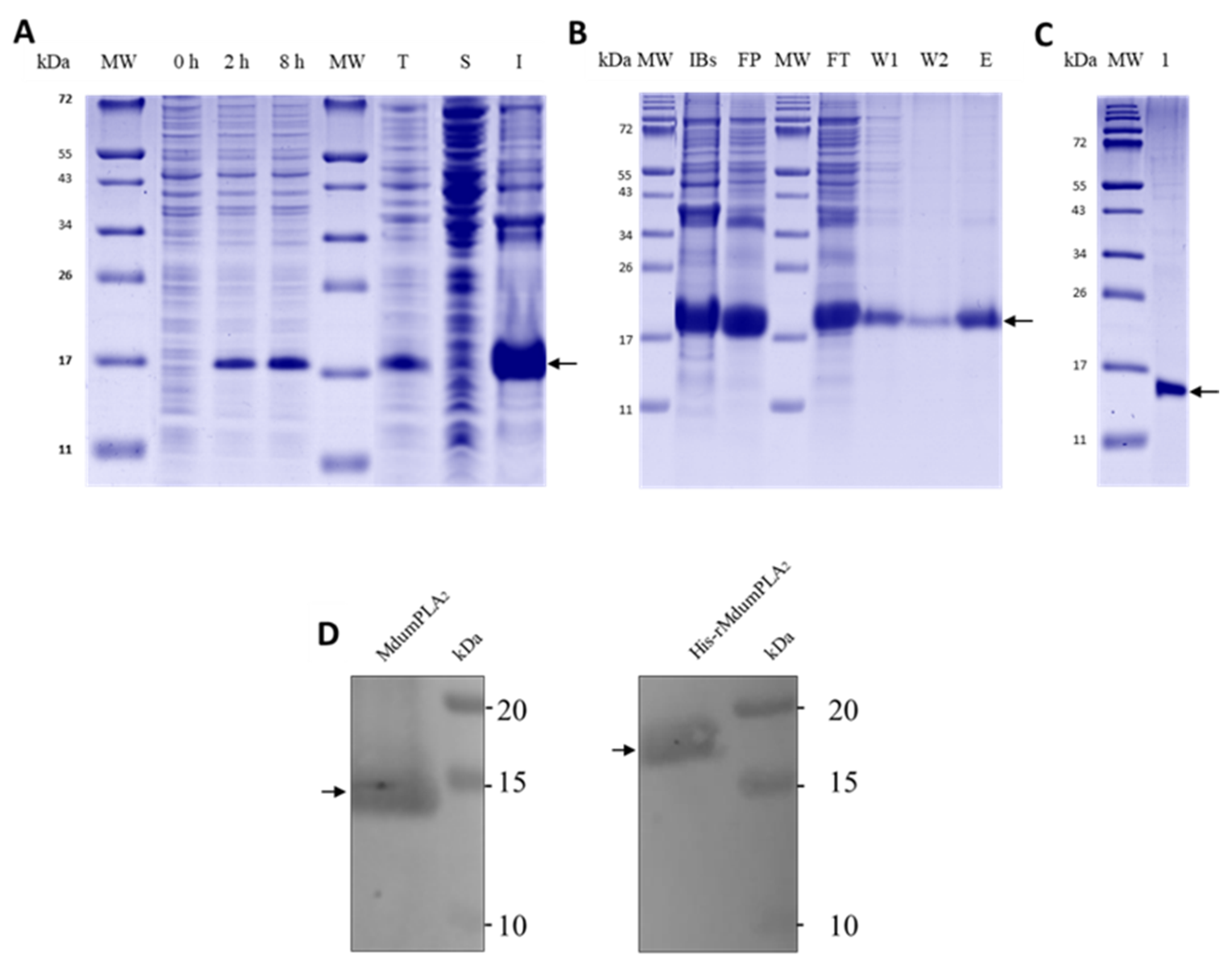
First, the plasmid pUC57-His-rMdumPLA2 was propagated in competent cells of E. coli strain DH5α by standard heat shock transformation and selection in LB media containing 100 μg/mL of ampicillin. Three clones were selected and grown overnight in LB medium with ampicillin. The plasmid DNA of each clone was recovered using FavorPrep Plasmid Extraction Mini Kit (FAVORGEN Biotech Corporation). The integrity of the plasmid DNA was assessed by 1% agarose electrophoresis and quantified using the Thermo Scientific™ NanoDrop 2000 from Thermo Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). The same procedure was applied to the empty pET28 vector using kanamycin as the selection antibiotic. The plasmid DNA and the pET28a expression vector were digested with specific restriction enzymes NcoI and NotI in the 5′ and 3′ positions, respectively. The digestion reaction (50 µL) was incubated for 3 h at 37 °C and the digestion products were analyzed on a 1% agarose gel. The bands with the expected size for the insert and linearized vector were cut from the gel and purified using the GeneJet Plasmid kit from Thermo Scientific, following the manufacturer’s instructions. For the insertion of the construct into pET28a, a ligation reaction (20 µL) was set using a 3:1 excess of insert and T4 DNA ligase. The reaction was incubated at room temperature for 2 h. A total of 5 µL of the ligation reaction was transformed in DH5α cells and incubated overnight in selection LB media containing 50 μg/mL kanamycin. Final propagation and recovery were made as described above. Clones and the directionality of the insert were checked by XhoI and EcoRV digestion and agarose gel analysis. EcoRV cuts after position 158, and XhoI cuts after position 1573 on pET28a.
5.5. Expression of pET28a-His-rMdumPLA2
As mentioned above, one clone of the recombinant plasmid pET28a-His-rMdumPLA2 was used to transform BL21 (DE3) cells by heat shock. Transformed cells were selected in LB-Kanamycin [50 mg/mL]. One single colony was used for propagation and protein induction each time. For protein expression, 1 L of LB medium was enriched with 5 mL of the overnight pre-culture. Then, the culture flask was grown at 37 °C and 180 rpm until it reached OD 600 nm = 0.6–0.7, and protein expression was induced with 0.5 mM IPTG (isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside) at 37 °C for eight hours. Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 32,000× g at 4 °C for 30 min. The cell pellet was washed with PBS 1X buffer pH 7.4 and centrifuged at 13,000× g for 30 min at 4 °C. Finally, the cell pellet was stored at −20 °C until use or until six months as the maximum storage period.
5.6. Protein Purification and Refolding
The protocol mentioned above delivered HisrMdumPLA2 chimeric protein as inclusion bodies which were purified as follows. The cell pellet was thawed on ice and resuspended in lysis buffer [100 mM Tris pH 8.5, 10 mM EDTA] and sonicated 7 min, 2 sec ON, and 2 sec OFF at 22 °C and 20% power in Ultrasonic Cell Disruptor (BIOBASE Biodustry, Jinan, Shandong, China). The lysate was centrifuged at 32,000× g at 4 °C for 30 min. The insoluble fraction or inclusion bodies were dissolved in solubilization buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 10 mM EDTA, 8 M urea) at 180 rpm, at room temperature overnight. The solubilized protein was clarified by centrifugation at 32,000× g at 4 °C for 30 min, and the supernatant was transferred to a SPECTRA/Por MWCO: 3.5 kDa tubbing membrane. Refolding of the denatured His-rMdumPLA2 was achieved by stepwise removal of the urea by dialysis against refolding buffer (200 mM Tris pH 8.5, 10 mM EDTA) containing reduced concentrations of urea from 4 M to 0 M, making exchanges of the refolding buffer every 12 h in constant agitation (110 rpm) at 4 °C. Once urea 0 M concentration was reached, the protein was centrifuged at 32,000× g at 4 °C for 30 min and the supernatant or the recombinant solubilized protein was recovered.
5.7. Purification of His-rMdumPLA2
The first purification step of His-rMdumPLA
2 was performed by affinity chromatography using Ni-NTA agarose resin. The recombinant refolded fraction protein was applied twice to a 2 mL bed of resin (Qiagen™ Ni-NTA Superflow) by gravity flow previously equilibrated with refolding buffer without urea [20 mM Tris pH 8.5, 100 mM NaCl]. Next, the first wash with equilibrium buffer was performed. Then, two washes with 20 mM imidazole and 500 mM NaCl were applied each time to eliminate cellular debris and nonspecific proteins. Finally, a 360 mM imidazole buffer was applied to elution the target protein. The concentration of protein (in mg/mL) was determined by the Bradford protein assay [
57] using the equation
y = 0.6625
x − 0.0535 with an R-squared value of 0.9978, where
y is absorbance and
x is concentration. In addition, only to check the molecular mass approximate of rMdumPLA
2, we cut the 6His-Tag with [10 mg/mL] TEV protease by dialysis, using buffer [20 mM Tris pH 8.5, 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM 2-Mercaptoethanol (Sigma, Saint Louis, MO, USA)] at pH 8.5 and a SPECTRA/Por MWCO: 3.5 kDa tubbing membrane. The TEV cut was analyzed with 14% Tris-Tricine SDS-PAGE gel, described by Laemmli [
58] with modifications of Schägger and Gebhard [
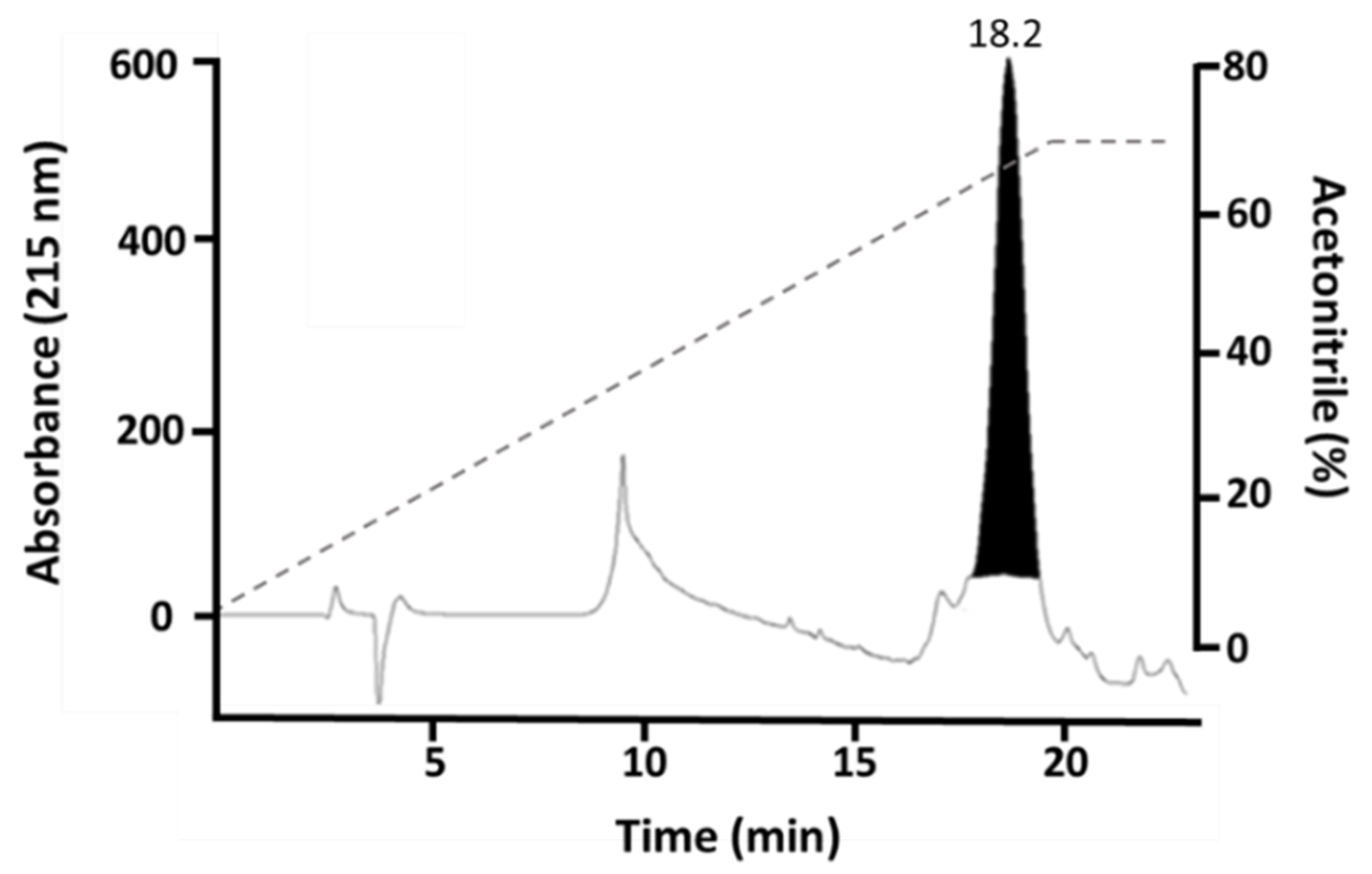
59] under reducing conditions. Subsequently, in a second purification step of His-rMdumPLA
2, the sample was centrifuged and applied to reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) C18 column (250 × 10 mm, 5 µm particle: Restek, Bellefonte, PA, USA), using a Shimadzu Prominence-20A chromatograph. Elution was performed at 1 mL/min by applying solution B (acetonitrile + 0.1% TFA) as lineal gradient 0 to 70% B over 35 min. The elution profile was monitored at 215 nm in a UV/VIS photodiode array detector (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The sample was vacuum dried in a Vacufuge Plus Complete System (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) at 30 °C and resuspended into Milli-Q water to be analyzed by 14% Tris-Tricine SDS-PAGE and to confirm its molecular mass by mass spectrometry. The heterologous expression of His-rMdumPLA
2 was confirmed by western-blot assay following the protocol of Lomonte et al. [
55]. An anti-MdumPLA
2 native antibody coupled to peroxidase (obtained from rabbit inoculated with MdumPLA
2), was used for this. Additionally, a nitrocellulose membrane (0.45 mm) in a TRANS-BLOT SD (BIO-RAD, California, United States) system, and a transference buffer (192 mM Glycine, 25 mM Tris, 20% Methanol, and pH 8.3) were used. Membrane blockade was performed with 1% BSA/1% casein and the washes with 1:10 dilution of the blocking solution. Color development was performed using 6.5 mM 4-Cl-1 naphthol in 0.02 M Tris buffer at pH 7.5 in the presence of H
2O
2.
5.8. Mass Spectrometry
Intact mass of the His-rMdumPLA
2 was determined by direct infusion ESI-MS in a Q-Exactive Plus
® instrument (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Proteins were dissolved in 50% acetonitrile/water containing 0.1% formic acid at 50–100 μg/mL and infused at 5 μL/min into a HESI source, to acquire a full MS scan in the 800–2000
m/
z range, at resolution of 140,000 (at
m/
z 240), in positive mode. The acquired MS spectra of the multiply charged ion series were deconvoluted using Freestyle
® v.1.5 (Thermo, Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) to obtain monoisotopic masses [
60].
5.9. Myotoxic Activity
Groups of three mice were injected intramuscular (i.m.) route with 50 µg and 80 µg of recombinant toxin, and another group was 2.5 µg M. dumerilii venom diluted in 100 µL of saline solution (SS). A control group received 100 µL of SS alone. At 3 h, the animals were caudal veins bleeding and blood was collected into heparinized capillary tubes, and plasma creatine kinase (CK; EC 2.7.3.2) activity was determined by a kinetic assay (CK-NAC UV AA Kit) from Weiner Lab (Boston, MA, USA). Triplicate measurements were performed on each sample in a UV-1700 PharmaSpec Spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) and CK activity was expressed in U/L.
5.10. Edema-Forming Activity
Groups of three mice received a subcutaneous (s.c.) injection of 50 µg of recombinant toxin or 20 µg
M. dumerilii venom dissolved in 50 µL SS, into the right footpad. A similar volume of SS was injected into the left footpad in both groups as a negative control. After 2 h, mice were sacrificed by isoflurane inhalation, both feet were cut and weighed, as described by Gutierrez et al. [
61], and the percentage increment in weight with respect to negative control was determined.
5.11. PLA2 Activity
PLA
2 activity of His-rMdumPLA
2 and rMdumPLA
2 was evaluated in vitro using synthetic monodisperse substrate 4-NOBA (4-nitro-3-octanoyloxy-benzoic acid) [
62] for 96-well plates. For this, 20 µg of the recombinant toxin dissolved in 10 mM Tris pH 8.0, 0.1 M NaCl, and 10 mM CaCl
2 buffer in presence of NOBA (1 mg/mL in acetonitrile), the mix was added in 96 wells microplates (Falcon TM) and incubated at 37 °C for 60 min [
63]. The absorbances were recorded at 425 nm on a Multiskan Sky Microplate Spectrophotometer from Thermo Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). Wells containing only the buffer were used as a blank. All samples were assayed in triplicate. Additionally, indirect hemolysis method using agarose-erythrocyte-egg yolk gels [
64] was also used to PLA
2 activity evaluate, to them doses of recombinant toxin (25 and 50 µg) or five µg of
M. dumerilii venom diluted in 16 µL of SS were added into of each well. The assay was performed by triplicate, and measurements of the hemolytic halo diameter of each sample were in millimeters (mm). The erythrocytes were donated by the “Clínica León XIII” blood bank of the Universidad de Antioquia.
5.12. Anticoagulant Activity
A total of 25 µg of His-rMdumPLA2 dissolved in 50 µL PBS (0.12 M NaCl, 0.04 M sodium phosphate, pH 7.2) were preincubated for 10 min at 37 °C with 200 µL of citrated human plasma obtained from the “Clínica León XIII” blood bank of The Universidad de Antioquia. After that, 100 µL of 0.25 M CaCl2 was added, and clotting times were recorded. PBS was used as a negative control. Both negative control and samples were assayed in triplicate.
5.13. Lethal Activity
To determine the lethality of recombinant toxin, a dose 100 µg/mouse (6 µg/g body weight) of His-rMdumPLA2 in 300 µL of SS was injected by the intraperitoneal (i.p.) route in two mice. A control group received SS alone. After, deaths were recorded within the following 24 h.
5.14. Antibodies Anti-His-rMdumPLA2 Production
One New Zealand white rabbit was immunized by subcutaneous route with a first dose (325 µg) of the recombinant His-rMdumPLA2 protein diluted in 600 µL of saline solution and emulsified with 600 µL of incomplete Freund’s adjuvant (IFA). Then, rabbit was boosted 21, 42, 63, 84, 105, 133 and 162 days with 488, 732, 1098, 1647, 1647, 1647 and 2470 µg of His-rMdumPLA2, respectively. The rabbit was bled on the first day (pre-immune) and after of first, third, fifth and seventh boosted.
5.15. Antibodies Anti-His-rMdumPLA2 Titers and Immunological Recognition in Serum by ELISA
For measuring the antibody titers, two assays by ELISA were performed: First, a tittering curve using different dilutions of the sera obtained from the bleedings, and second, an assay of the immunological recognition of His-rMdumPLA2 for specific rabbit serum using the dilution with the higher antibody titer. Firstly, bleedings were centrifuged at 6500× g for 10 min at 4 °C, and the supernatants (sera) were recovered. Afterward, several centrifugations were performed under the same conditions until the sera were clarified. A curve of different sera dilutions was assayed (1:10, 1:100, 1:1000, 1:5000, and 1:10,000), and two controls (serum pre-immune as negative control and M. dumerilii venom as positive control) were included. Next, a 96-well plate (Falcon TM) was covered with a 100 µL solution [1 µg/mL] of His-rMdumPLA2 or of complete M. dumerilii venom in coating buffer (0.1 M Tris, 0.15 M NaCl, pH 9.0) by overnight incubation. After five washes for 5 min each with wash buffer (0.05M Tris, 0.15M NaCl, 20 mM ZnCl2, 1mM MgCl2, pH 7.4), wells were blocked with 100 µL of blocking buffer (PBS containing 2% BSA), for 60 min, and decanted. Then, 100 µL of each dilution of rabbit immune serum, or a serum from a non-immunized rabbit, were identically diluted in PBS-BSA and added for 1.5 h. Subsequently, five washes with PBS for 5 min each were performed, followed by adding 100 µL of antirabbit immunoglobulins–Peroxidase conjugate (Sigma, Saint Louis, MO, USA), diluted 1:8000 in PBS-BSA, for 1.5 h. Finally, five washes for 5 min each with PBS were performed, and color was developed with 100 µL/well of o-Phenylenediamine (OPD) [2 mg/mL] in sodium citrate buffer (C6H5Na3O7-2H2O), pH 5.0. All samples were assessed in triplicate, and absorbances were recorded at 490 nm on a Multiskan Sky Microplate Spectrophotometer from Thermo Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). Secondly, we followed the protocol above in another 96 wells microplate and used the same controls. Still, this time, 100 µL of the dilution 1:1000 of rabbit immune serum in PBS-BSA was added for 1.5 h, and the rest of the steps were followed, as mentioned above.
5.16. Anti-His-rMdumPLA2-IgG Purification
To obtain the IgG of serum anti-His-rMdumPLA
2, fractionation with caprylic acid (Sigma, Saint Louis, MO, USA) was performed [
65]. For this, small amounts of caprylic acid were added to each serum until reaching 6% of the total volume of the serum. The solution was kept under constant and vigorous stirring for 1 h. The precipitated was separated by centrifugation at 4500×
g for 5 min, and the supernatant was dialyzed on Fisherbrand cellulose membranes (3500 MWCO) with PBS and distilled water for two days. Finally, it was lyophilized in a LABCONCO (Kansas, MO, USA) lyophilizer using a range of temperature changes during processing (−40 °C to 10 °C) and stored at −20 °C.
5.17. Cross Immunological Recognition by Anti-His-rMdumPLA2-Serum and Anti-His-rMdumPLA2-IgG by ELISA
Following the description of “
Section 5.15.” of Materials and methods, we performed an assay of cross immunological recognition by anti-His-rMdumPLA
2-serum and His-rMdumPLA
2-IgG in the presence of: (1)
M. dumerilii venom (V-Mdum). (2) Two fractions (F24 and F25) close to MdumPLA
2. These fractions were isolated from
M. dumerilii venom by RP-HPLC and belong to the region of PLA
2s obtained from its proteome [
9]. (3) MmipPLA
2, the most abundant PLA
2 from
M. mipartitus venom [
8].
5.18. Neutralizing Ability of Anti-His-rMdumPLA2-IgG
PLA2 activity: 3 mg anti-His-rMdumPLA2-IgG was mixed with 25 µg His-rMdumPLA2, the mixtures were incubated for 30 min to 37 °C and added to plates (Corning®, ref 3098) of agarose-erythrocyte-egg yolk gels and incubated 20 h. A total of 5 µg of M. dumerilii venom was used as a positive control. All assays were performed in triplicate, and measurements of the hemolytic halo diameter of each sample were expressed in millimeters (mm). The assays were performed in triplicate.
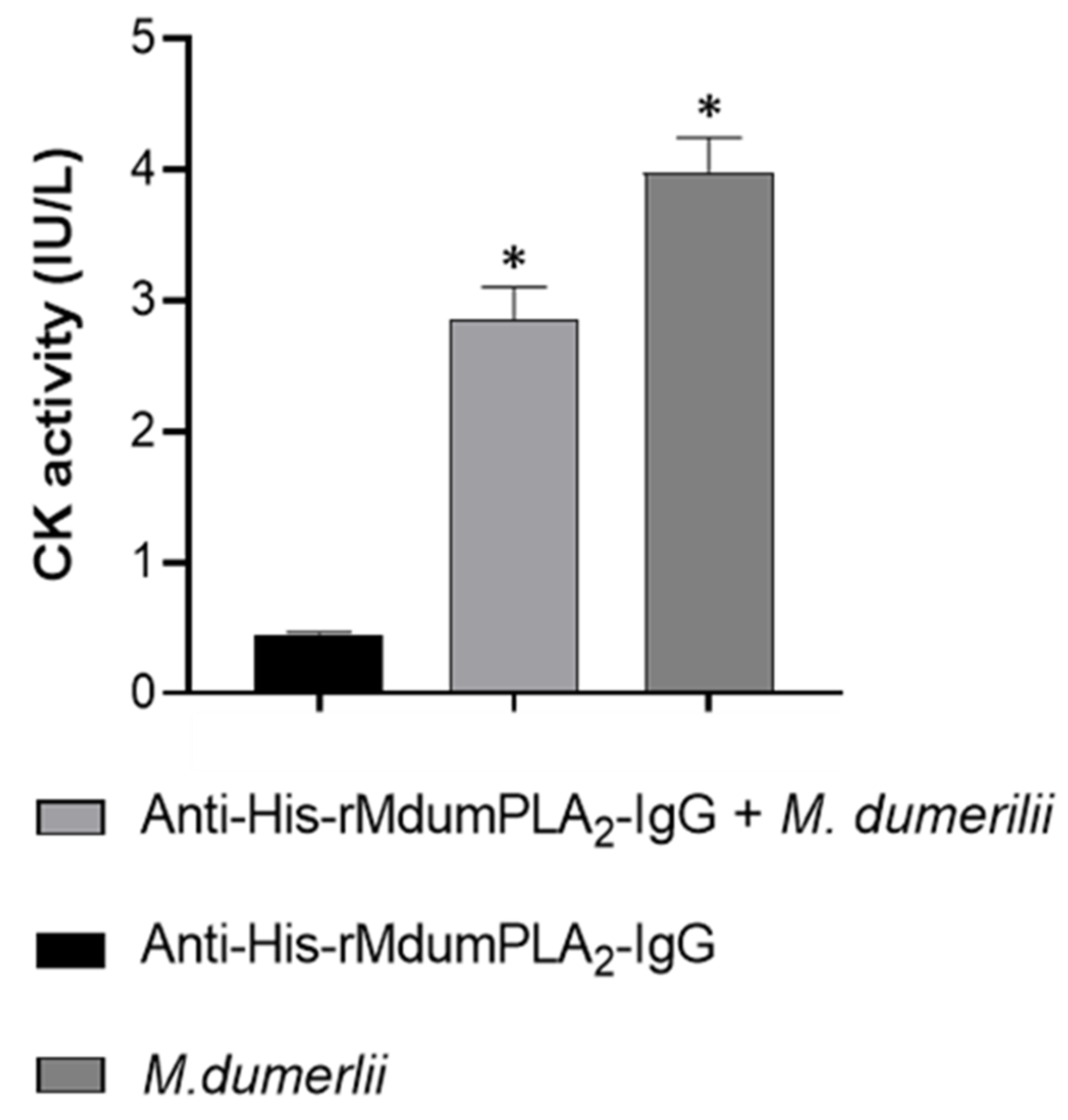
Myotoxic activity: 3 mg of anti-His-rMdumPLA2-IgG was mixed with 5 µg of M. dumerilii venom and diluted in 100 µL saline solution, incubated for 30 min to 37 °C, and injected intramuscular (i.m.) route to groups of three mice in the muscle gastrocnemius. A group with whole venom was used as a control. The CK activity was evaluated as previously described.
Lethal effect: 5 mg anti-His-rMdumPLA2-IgG was mixed with 1.5 LD50 (30 µg/mouse) of M. dumerilii venom in 300 µL of saline solution, incubated for 30 min at 37 °C and injected intraperitoneal (i.p.) route to two mice. A group with whole venom was used as a control. After 24 h later the number of deaths was recorded.
5.19. Statistical Analysis
The PLA2 activity, myotoxicity, anticoagulation, and edema induction experiments were performed in triplicate and the results were expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). The immunological cross-recognition experiment was carried out by ELISA test. In the PLA2 activity and myotoxicity experiments, as in the ELISA test, the significant differences between the His-rMdumPLA2 treatments and the controls were determined using the one-way ANOVA test, followed by the Bonferroni post-test. In the same way, the neutralization experiments were analyzed using a two-way ANOVA test. In the edema induction activity experiment, the significant differences between the His-rMdumPLA2 treatments and the controls were determined using the unpaired t-test. In all cases, differences were considered significant for p < 0.05.