Two-Dimensional Blue Native/SDS Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis for Analysis of Brazilian Bothrops Snake Venoms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
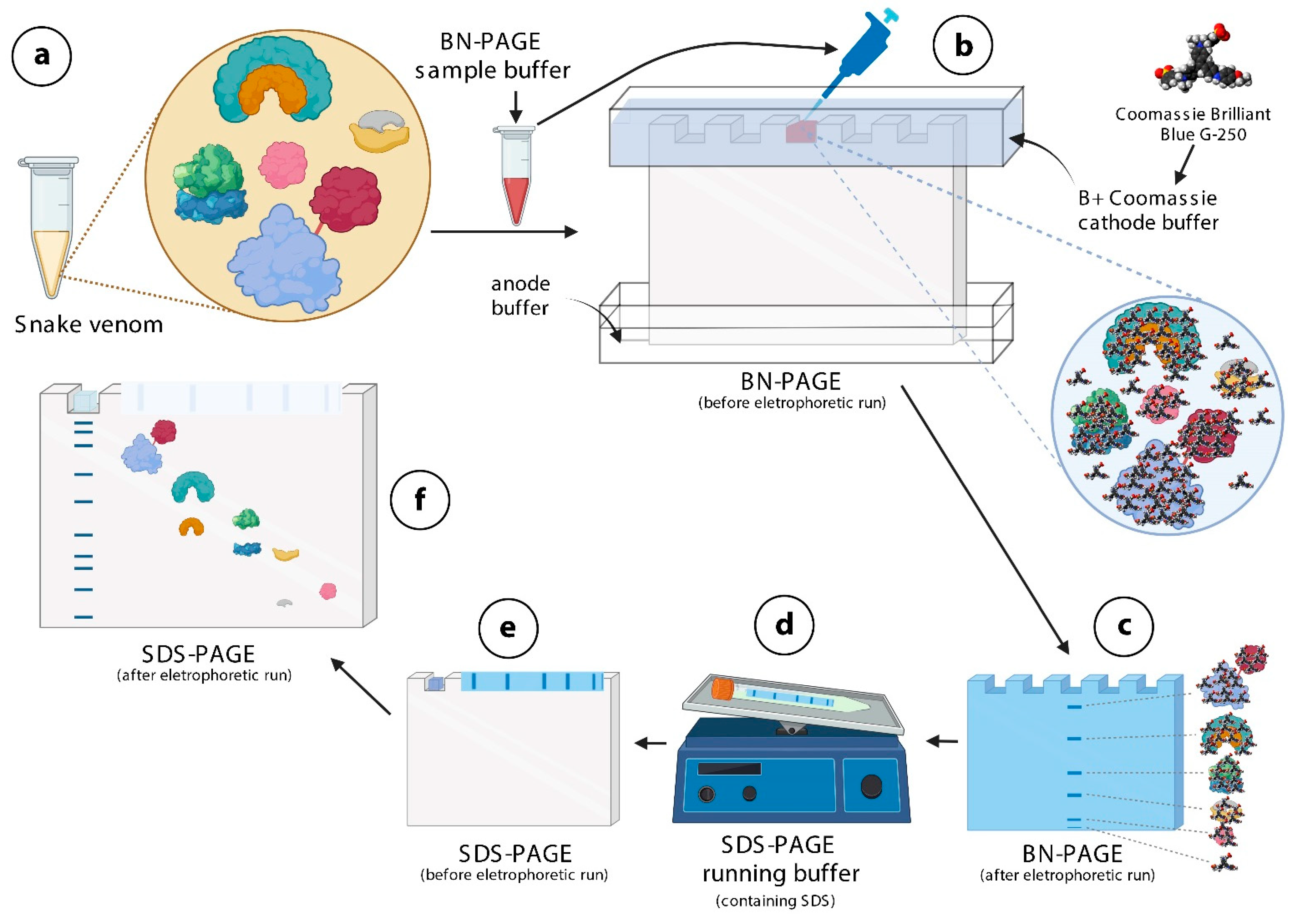
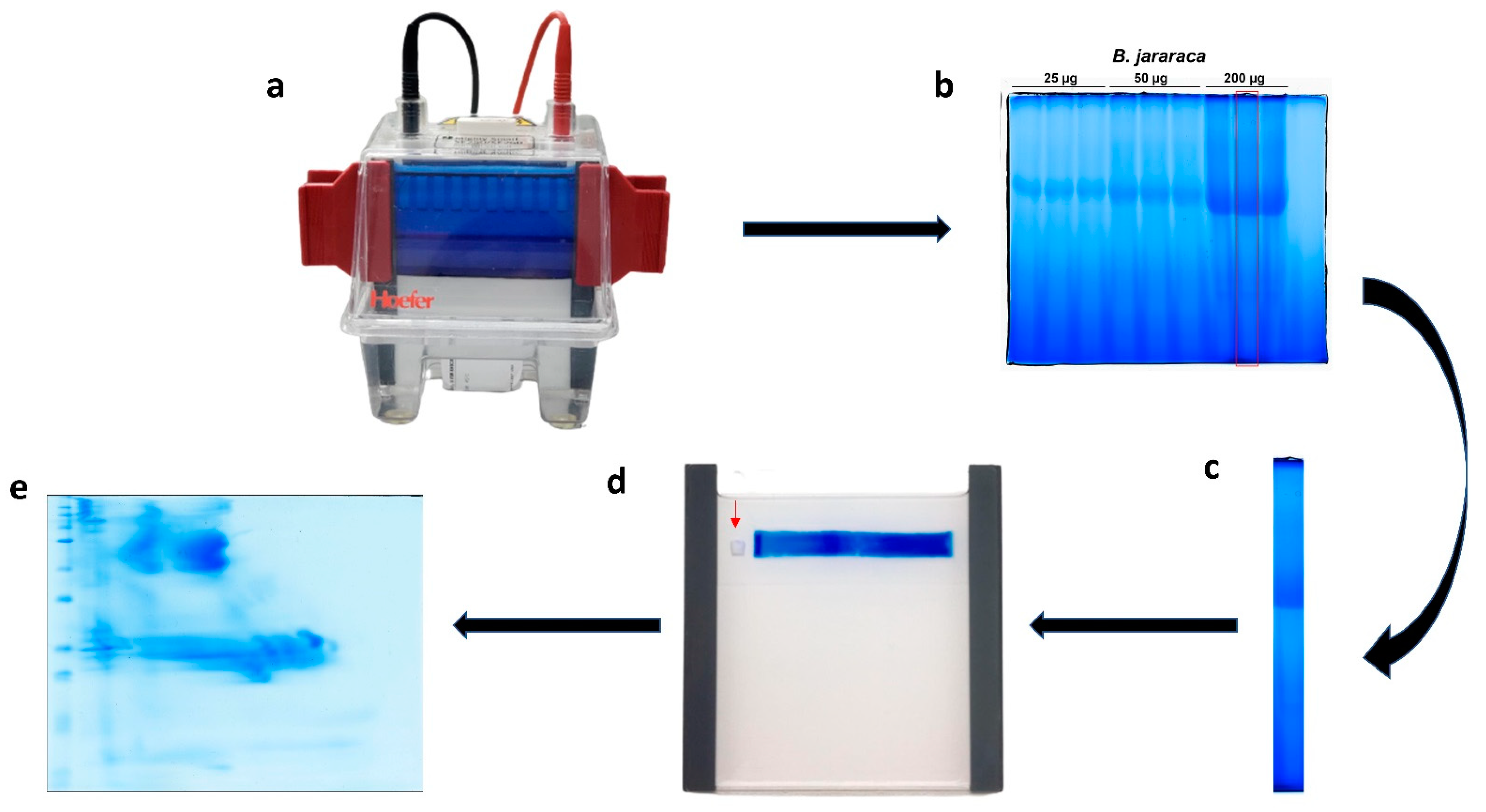
2.1. First-Dimension Electrophoresis (BN-PAGE)
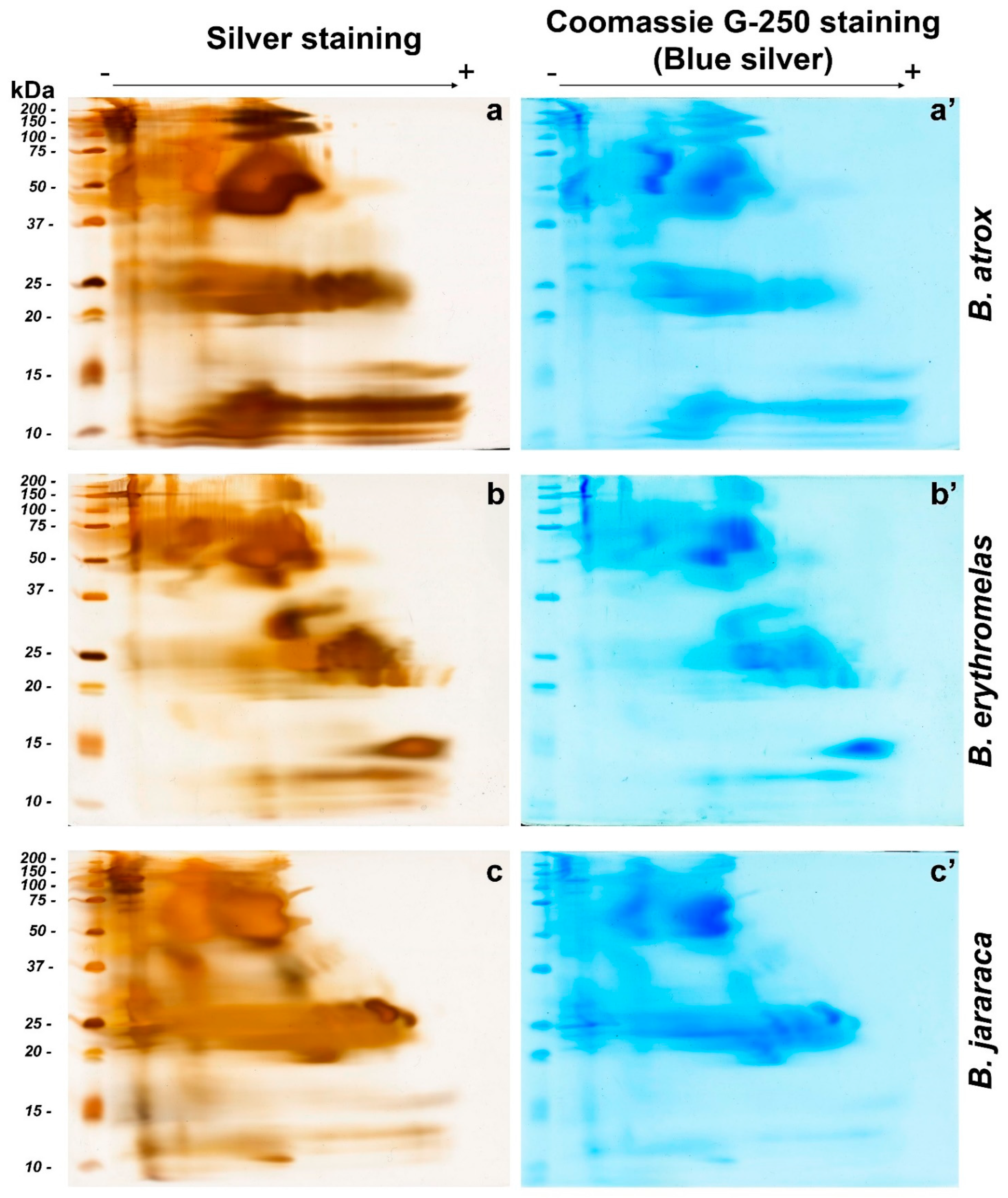
2.2. Profiles of Protein Spots in Venoms Analyzed by BN/SDS-PAGE
2.3. Mass Spectrometry
2.4. Zymography
2.4.1. Amidolytic Activity
2.4.2. Gelatinolytic Activity
2.5. Western Blotting
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Venoms
4.2. Reagents
4.3. BN/SDS-PAGE
4.4. Zymography
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Mass Spectrometry (MS) Identification
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sistema de Informação de Agravos de Notificação (Sinan). Available online: www.saude.gov.br/sinanweb (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Campbell, J.A.; Lamar, W.W. The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere; Comstock Publishing Associates: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2004; Volume I, p. 870. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, M.L.; Sousa-e-Silva, M.C.; Gonçalves, L.R.; Almeida-Santos, S.M.; Cardoso, D.F.; Laporta-Ferreira, I.L.; Saiki, M.; Peres, C.A.; Sano-Martins, I.S. Comparison of the biological activities in venoms from three subspecies of the south american rattlesnake (crotalus durissus terrificus, c. Durissus cascavella and c. Durissus collilineatus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1999, 122, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, T.C.; Yamashita, K.M.; Barbaro, K.C.; Saiki, M.; Santoro, M.L. Comparative analysis of newborn and adult bothrops jararaca snake venoms. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1443–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acunha, T.; Nardini, V.; Faccioli, L.H. A lipidomics approach reveals new insights into crotalus durissus terrificus and bothrops moojeni snake venoms. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Briones, A.; Aird, S.D. Organic and peptidyl constituents of snake venoms: The picture is vastly more complex than we imagined. Toxins 2018, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eble, J.A. Structurally robust and functionally highly versatile-c-type lectin (-related) proteins in snake venoms. Toxins 2019, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Kowalski, P.; Lopez, I. Using yeast two-hybrid system and molecular dynamics simulation to detect venom protein-protein interactions. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 2, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siigur, E.; Aaspollu, A.; Trummal, K.; Tonismagi, K.; Tammiste, I.; Kalkkinen, N.; Siigur, J. Factor x activator from vipera lebetina venom is synthesized from different genes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1702, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breithaupt, H. Neurotoxic and myotoxic effects of crotalus phospholipase a and its complex with crotapotin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1976, 292, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G.K. A review and database of snake venom proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, D.M.; Tasima, L.J.; Bravo-Tobar, C.A.; Serino-Silva, C.; Tashima, A.K.; Rodrigues, C.F.B.; Aguiar, W.D.S.; Galizio, N.D.C.; de Lima, E.O.V.; Kavazoi, V.K.; et al. Venom complexity of bothrops atrox (common lancehead) siblings. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 26, e20200018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, V.; Cid, P.; Sanz, L.; De La Torre, P.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics and antivenomics of bothrops atrox venoms from colombia and the amazon regions of brazil, peru and ecuador suggest the occurrence of geographic variation of venom phenotype by a trend towards paedomorphism. J. Proteom. 2009, 73, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves-Machado, L.; Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Jorge, R.J.; Leitão-De-Araujo, M.; Alves, M.L.; Alvares, D.J.; De Miranda, J.; Nowatzki, J.; de Morais-Zani, K.; et al. Combined venomics, venom gland transcriptomics, bioactivities, and antivenomics of two bothrops jararaca populations from geographic isolated regions within the brazilian atlantic rainforest. J. Proteom. 2015, 135, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, C.A.; Carvalho, P.C.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.; Teixeira-Ferreira, A.; Junqueira, M.; Perales, J.; Neves-Ferreira, A.G.; Valente, R.H. An in-depth snake venom proteopeptidome characterization: Benchmarking bothrops jararaca. J. Proteom. 2017, 151, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, R.J.; Monteiro, H.S.; Goncalves-Machado, L.; Guarnieri, M.C.; Ximenes, R.M.; Borges-Nojosa, D.M.; Luna, K.P.; Zingali, R.B.; Correa-Netto, C.; Gutierrez, J.M.; et al. Venomics and antivenomics of bothrops erythromelas from five geographic populations within the caatinga ecoregion of northeastern brazil. J. Proteom. 2014, 114C, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, C.A.; Ainsworth, S.; Albulescu, L.O.; Casewell, N.R. Snake venom metalloproteinases. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles, 2nd ed.; Mackessy, S.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 363–379. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.W.; Serrano, S.M. Structural considerations of the snake venom metalloproteinases, key members of the m12 reprolysin family of metalloproteinases. Toxicon 2005, 45, 969–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathan, L.O.; Staggers, S.L. Ancrod: The use of snake venom in the treatment of patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting: Nursing management. Heart Lung 1996, 25, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.; Song, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, B.; Meng, R. Use of batroxobin in central and peripheral ischemic vascular diseases: A systematic review. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 716778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.D.; Stack, S.; Markland, F.S., Jr. Snake venom phospholipase a2 toxins. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles, 2nd ed.; Mackessy, S.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 389–411. [Google Scholar]
- Calvete, J.J.; Sanz, L.; Perez, A.; Borges, A.; Vargas, A.M.; Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Mourao, R.H.; et al. Snake population venomics and antivenomics of bothrops atrox: Paedomorphism along its transamazonian dispersal and implications of geographic venom variability on snakebite management. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, F.T.; Eble, J.A. C-type lectin-like proteins from snake venoms. Toxicon 2012, 60, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeya, H.; Nishida, S.; Miyata, T.; Kawada, S.; Saisaka, Y.; Morita, T.; Iwanaga, S. Coagulation factor x activating enzyme from russell’s viper venom (rvv-x): A novel metalloproteinase with disintegrin (platelet aggregation inhibitor)-like and c-type lectin-like domains. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 14109–14117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, D.; Morita, T. Purification and characterization of a Ca2+ -dependent prothrombin activator, multactivase, from the venom of echis multisquamatus. J. Biochem. 1997, 122, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovjov, D.A.; Platonova, T.N.; Ugarova, T.P. Purification and characterization of ecamulin—A prothrombin activator from the venom of multi-scaled viper (echis multisquamatus). Ukr Biokhim Zh 1978 1996, 68, 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Petrovan, R.J.; Govers-Riemslag, J.W.; Nowak, G.; Hemker, H.C.; Rosing, J.; Tans, G. Purification and characterization of multisquamase, the prothrombin activator present in echis multisquamatus venom. Thromb. Res. 1997, 88, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, D.; Sekiya, F.; Morita, T. Isolation and characterization of carinactivase, a novel prothrombin activator in echis carinatus venom with a unique catalytic mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 5200–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Orefice, A.; Potter, A.; Evers, F.; Hevler, J.F.; Guerrero-Castillo, S. Complexome profiling-exploring mitochondrial protein complexes in health and disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 796128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobucci, I.; Monaco, V.; Cozzolino, F.; Monti, M. From classical to new generation approaches: An excursus of -omics methods for investigation of protein-protein interaction networks. J. Proteom. 2021, 230, 103990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Farrell, P.H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1975, 250, 4007–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasserre, J.P.; Ménard, A. Two-dimensional blue native/SDS gel electrophoresis of multiprotein complexes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 869, 317–337. [Google Scholar]
- Schägger, H.; Cramer, W.A.; von Jagow, G. Analysis of molecular masses and oligomeric states of protein complexes by blue native electrophoresis and isolation of membrane protein complexes by two-dimensional native electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 217, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittig, I.; Braun, H.P.; Schagger, H. Blue native page. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, G.J.; Schamel, W.W.; Blumenthal, B. Blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (bn-page) for analysis of multiprotein complexes from cellular lysates. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 24, e2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisinger, V.; Eichacker, L.A. How to analyze protein complexes by 2d blue native sds-page. Proteomics 2007, 7 (Suppl. 1), 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schägger, H.; von Jagow, G. Blue native electrophoresis for isolation of membrane protein complexes in enzymatically active form. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 199, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candiano, G.; Bruschi, M.; Musante, L.; Santucci, L.; Ghiggeri, G.M.; Carnemolla, B.; Orecchia, P.; Zardi, L.; Righetti, P.G. Blue silver: A very sensitive colloidal coomassie g-250 staining for proteome analysis. Electrophoresis 2004, 25, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfoli, I.; Calzia, D.; Santucci, L.; Ravera, S.; Bruschi, M.; Candiano, G. A blue dive: From ’blue fingers’ to ’blue silver’: A comparative overview of staining methods for in-gel proteomics. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2012, 9, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, H.; Beier, H.; Gross, H.J. Improved silver staining of plant proteins, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 1987, 8, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharahdaghi, F.; Weinberg, C.R.; Meagher, D.A.; Imai, B.S.; Mische, S.M. Mass spectrometric identification of proteins from silver-stained polyacrylamide gel: A method for the removal of silver ions to enhance sensitivity. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Huang, K.F.; Tsai, I.H. Snake venom glutaminyl cyclases: Purification, cloning, kinetic study, recombinant expression, and comparison with the human enzyme. Toxicon 2014, 86, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Y.N.; Wu, H. Glutaminyl cyclase, diseases, and development of glutaminyl cyclase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 6549–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Fujimura, Y.; Usami, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Miura, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Makita, K.; Taniuchi, Y.; Hirano, K.; Titani, K. Complete amino acid sequence and identification of the platelet glycoprotein ib-binding site of jararaca gpib-bp, a snake venom protein isolated from bothrops jararaca. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 10635–10639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Hori, A.; Hamako, J.; Matsushita, F.; Ozeki, Y.; Sakurai, Y.; Hayakawa, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimura, Y. Mutant botrocetin-2 inhibits von willebrand factor-induced platelet agglutination. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Shirai, T.; Tsukiji, N.; Otake, S.; Tamura, S.; Ichikawa, J.; Osada, M.; Satoh, K.; Ozaki, Y.; Suzuki-Inoue, K. Functional characterization of recombinant snake venom rhodocytin: Rhodocytin mutant blocks clec-2/podoplanin-dependent platelet aggregation and lung metastasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polgár, J.; Clemetson, J.M.; Kehrel, B.E.; Wiedemann, M.; Magnenat, E.M.; Wells, T.N.C.; Clemetson, K.J. Platelet activation and signal transduction by convulxin, a c-type lectin from crotalus durissus terrificus (tropical rattlesnake) venom via the p62/gpvi collagen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 13576–13583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, N.; Hayashi, M.A.; Ohi, H.; Ferreira, L.A.F.; Hermann, V.V.; Saito, H.; Fujita, Y.; Higuchi, S.; Fernandes, B.L.; Yamane, T.; et al. Cloning and sequence analysis of a bothrops jararaca cdna encoding a precursorof seven bradykinin-potentiating peptides and a c-type natriuretic peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguiura, N.; Correa, P.G.; Rosmino, I.L.; de Souza, A.O.; Pasqualoto, K.F.M. Antimicrobial activity of snake beta-defensins and derived peptides. Toxins 2021, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomate, P.R.; Jadhav, B.R.; Giri, A.P.; Hivrale, V.K. Alterations in the helicoverpa armigera midgut digestive physiology after ingestion of pigeon pea inducible leucine aminopeptidase. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, M.F.D.; Maruyama, M.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Antonio, L.C. Comparative study of nine bothrops snake venoms from adult female snakes and their offspring. Toxicon 1991, 29, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.L.; do Carmo, T.; Cunha, B.H.; Alves, A.F.; Zelanis, A.; Serrano, S.M.; Grego, K.F.; Sant’Anna, S.S.; Barbaro, K.C.; Fernandes, W. Ontogenetic variation in biological activities of venoms from hybrids between bothrops erythromelas and bothrops neuwiedi snakes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotto, N.P.; de Albuquerque Modesto, J.C.; Sant’Anna, S.S.; Grego, K.F.; Guarnieri, M.C.; Lira-da-Silva, R.M.; Santoro, M.L.; Oguiura, N. The absence of thrombin-like activity in bothrops erythromelas venom is due to the deletion of the snake venom thrombin-like enzyme gene. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes Leme, A.F.; Prezoto, B.C.; Yamashiro, E.T.; Bertholim, L.; Tashima, A.K.; Klitzke, C.F.; Camargo, A.C.; Serrano, S.M. Bothrops protease a, a unique highly glycosylated serine proteinase, is a potent, specific fibrinogenolytic agent. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, O.B.; Lavras, A.A.C.; Fichman, M.; Mandelbaum, F.R.; Henriques, S.B. The proteolytic activity of the venom of bothrops jararaca. Biochem. J. 1958, 68, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaqueo, K.D.; Kayano, A.M.; Simoes-Silva, R.; Moreira-Dill, L.S.; Fernandes, C.F.; Fuly, A.L.; Maltarollo, V.G.; Honorio, K.M.; da Silva, S.L.; Acosta, G.; et al. Isolation and biochemical characterization of a new thrombin-like serine protease from bothrops pirajai snake venom. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 595186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaqueo, K.D.; Kayano, A.M.; Domingos, T.F.; Moura, L.A.; Fuly, A.L.; da Silva, S.L.; Acosta, G.; Oliveira, E.; Albericio, F.; Zanchi, F.B.; et al. Bbrzsp-32, the first serine protease isolated from bothrops brazili venom: Purification and characterization. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2016, 195, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.K.; Joshi, M.B.; Ullah, A.; Masood, R.; Biligiri, S.G.; Arni, R.K.; Satyamoorthy, K. Serine proteinases from bothrops snake venom activates pi3k/akt mediated angiogenesis. Toxicon 2016, 124, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, M.; Mackessy, S.P. An aqueous endpoint assay of snake venom phospholipase a2. Toxicon 1996, 34, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Avila, C.; Rojas, E.; Cerdas, L. An alternative in vitro method for testing the potency of the polyvalent antivenom produced in costa rica. Toxicon 1988, 26, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomazini, C.M.; Sachetto, A.T.A.; Albuquerque, C.Z.; Mattaraia, V.G.M.; de Oliveira, A.K.; Serrano, S.M.T.; Lebrun, I.; Barbaro, K.C.; Santoro, M.L. Involvement of von willebrand factor and botrocetin in the thrombocytopenia induced by bothrops jararaca snake venom. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009715. [Google Scholar]
- Lira, M.S.; Furtado, M.F.; Martins, L.M.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Santoro, M.L.; Barbaro, K.C. Enzymatic and immunochemical characterization of bothrops insularis venom and its neutralization by polyspecific bothrops antivenom. Toxicon 2007, 49, 982–994. [Google Scholar]
- Ó’Fágáin, C.; Cummins, P.M.; O’Connor, B.F. Gel-filtration chromatography. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1485, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Low, T.Y.; Syafruddin, S.E.; Mohtar, M.A.; Vellaichamy, A.; NS, A.R.; Pung, Y.F.; Tan, C.S.H. Recent progress in mass spectrometry-based strategies for elucidating protein-protein interactions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 5325–5339. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wu, R.; Lu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y.D. Protein-protein interaction networks as miners of biological discovery. Proteomics 2022, 22, e2100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage t4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, M.C.; Furtado, M.F.; Travaglia-Cardoso, S.R.; Camargo, A.C.; Serrano, S.M. Sex-based individual variation of snake venom proteome among eighteen bothrops jararaca siblings. Toxicon 2006, 47, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Božić, N.; Vujčić, Z. Detection and quantification of leucyl aminopeptidase after native electrophoresis using leucine-p-nitroanilide. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 2476–2480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomazini, C.M.; Soares, R.P.S.; da Rocha, T.R.F.; Sachetto, A.T.A.; Santoro, M.L. Optimization of von willebrand factor multimer analysis in vertical mini-gel electrophoresis systems: A rapid procedure. Thromb. Res. 2019, 175, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukac, L.A.; Carter, J.E.; Morrison, K.S.; Karnovsky, M.J. Enhancement of diaminobenzidine colorimetric signal in immunoblotting. Biotechniques 1997, 23, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, M.L.; Barbaro, K.C.; da Rocha, T.R.F.; Torquato, R.J.S.; Hirata, I.Y.; Sano-Martins, I.S. Simultaneous isolation of platelet factor 4 and glycoprotein iib-iiia complex from rabbit platelets, and characterization of specific chicken antibodies to assay them. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 284, 55–72. [Google Scholar]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havlis, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira de Oliveira, N.; Sachetto, A.T.A.; Santoro, M.L. Two-Dimensional Blue Native/SDS Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis for Analysis of Brazilian Bothrops Snake Venoms. Toxins 2022, 14, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100661
Ferreira de Oliveira N, Sachetto ATA, Santoro ML. Two-Dimensional Blue Native/SDS Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis for Analysis of Brazilian Bothrops Snake Venoms. Toxins. 2022; 14(10):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100661
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira de Oliveira, Natacha, Ana Teresa Azevedo Sachetto, and Marcelo Larami Santoro. 2022. "Two-Dimensional Blue Native/SDS Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis for Analysis of Brazilian Bothrops Snake Venoms" Toxins 14, no. 10: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100661
APA StyleFerreira de Oliveira, N., Sachetto, A. T. A., & Santoro, M. L. (2022). Two-Dimensional Blue Native/SDS Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis for Analysis of Brazilian Bothrops Snake Venoms. Toxins, 14(10), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14100661





