Kirkiin: A New Toxic Type 2 Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from the Caudex of Adenia kirkii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
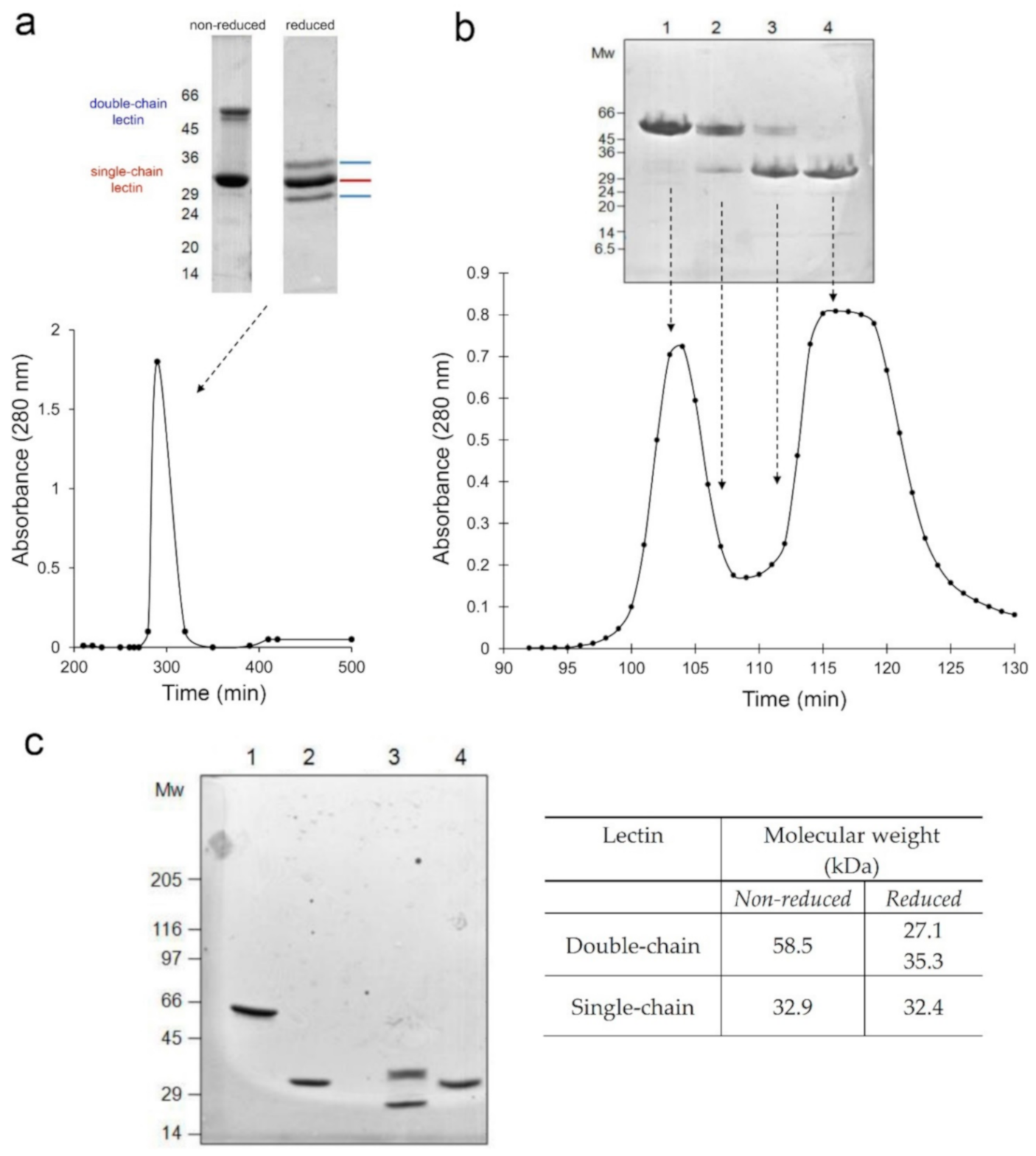
2.1. Purification and Characterization of Adenia Kirkii Lectins
2.2. Enzymatic Properties of Kirkiin
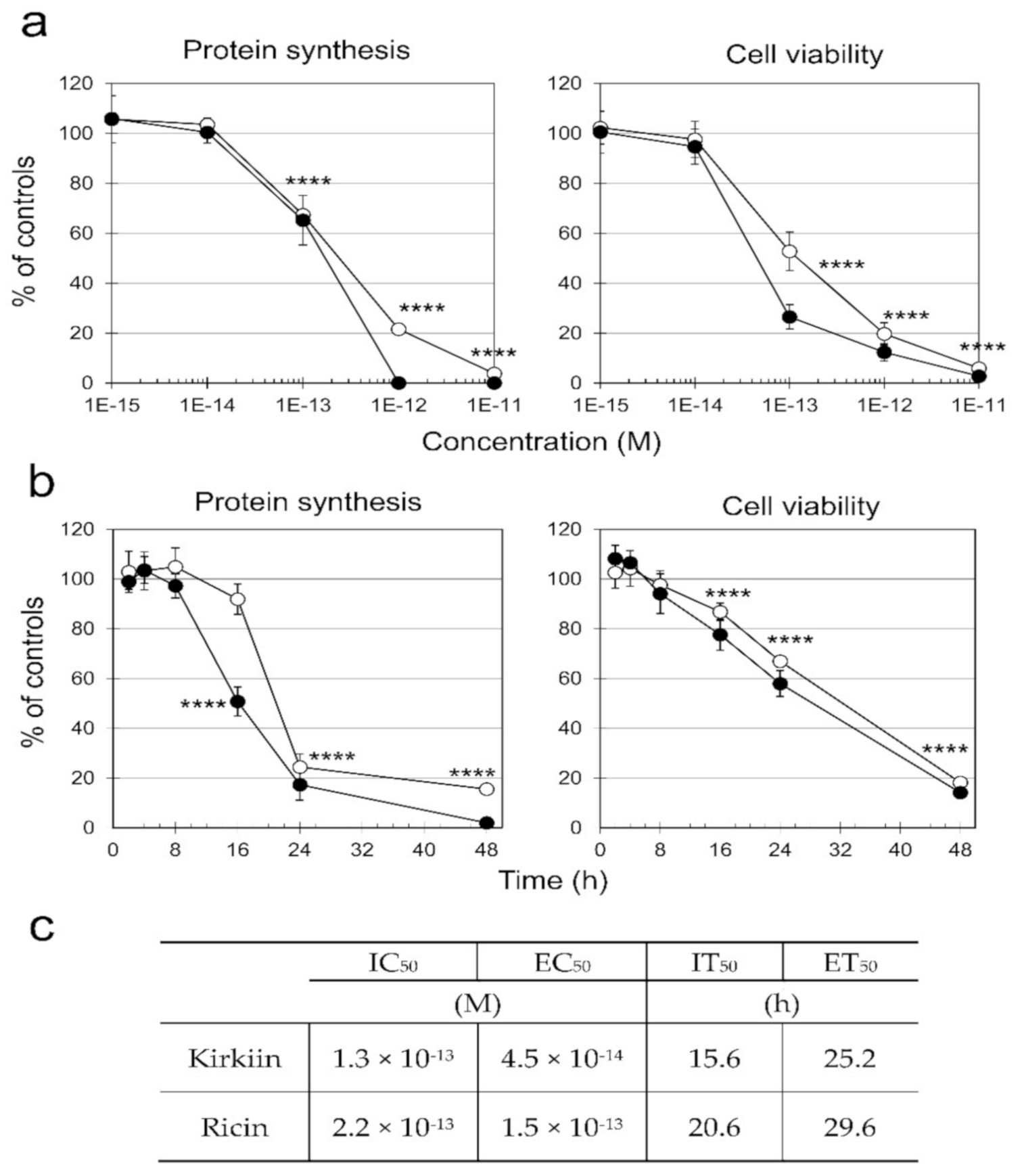
2.2.1. Effect on Protein Synthesis
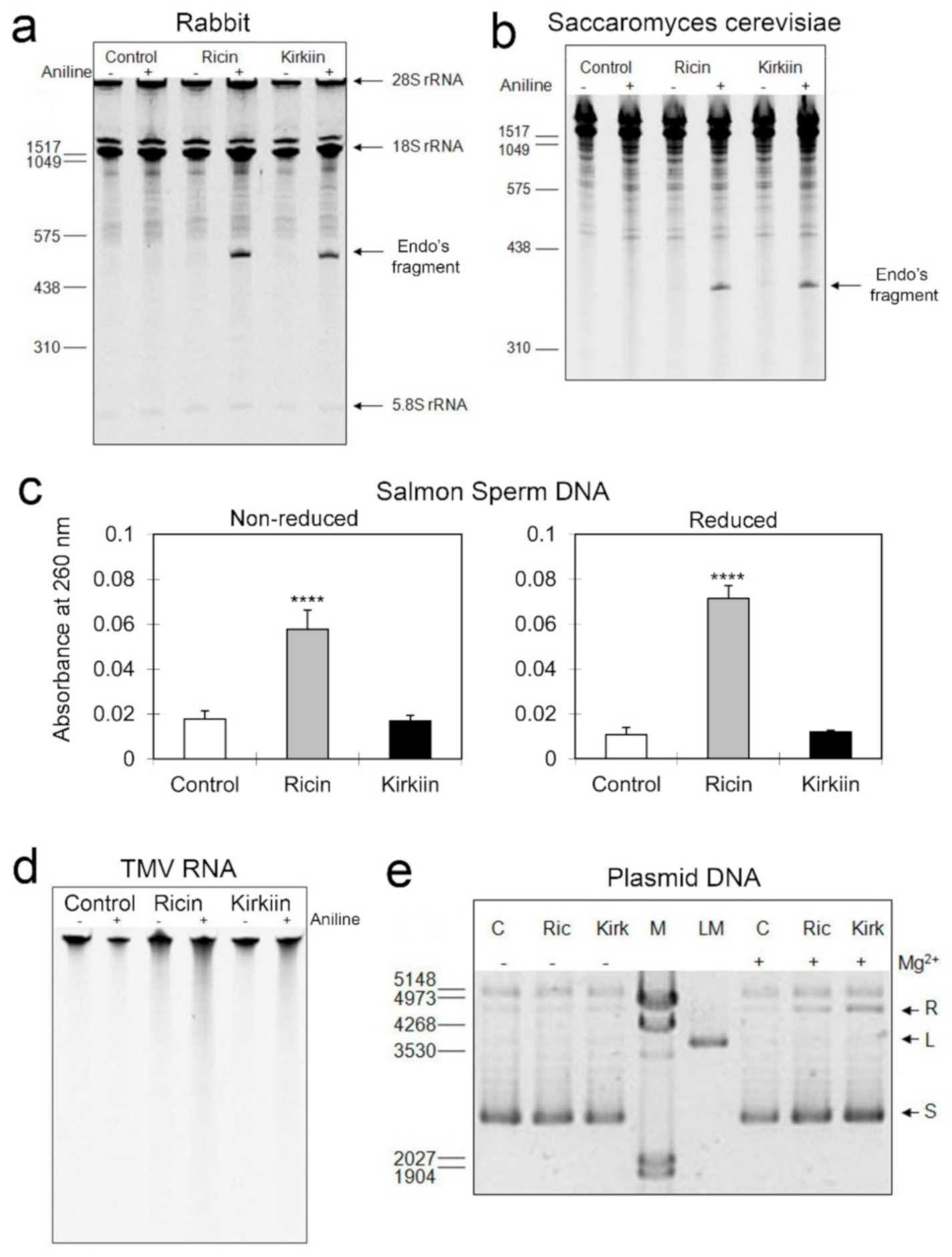
2.2.2. rRNA N-Glycosylase Activity on Mammalian and Yeast Ribosomes
2.2.3. DNA and RNA Adenine Polynucleotide Glycosylase Activity
2.2.4. Endonuclease Activity on Supercoiled Plasmid DNA
2.3. Immunological Properties
2.4. Cytotoxic Effects
2.4.1. Effect of Kirkiin on NB100 Protein Synthesis and Cell Viability
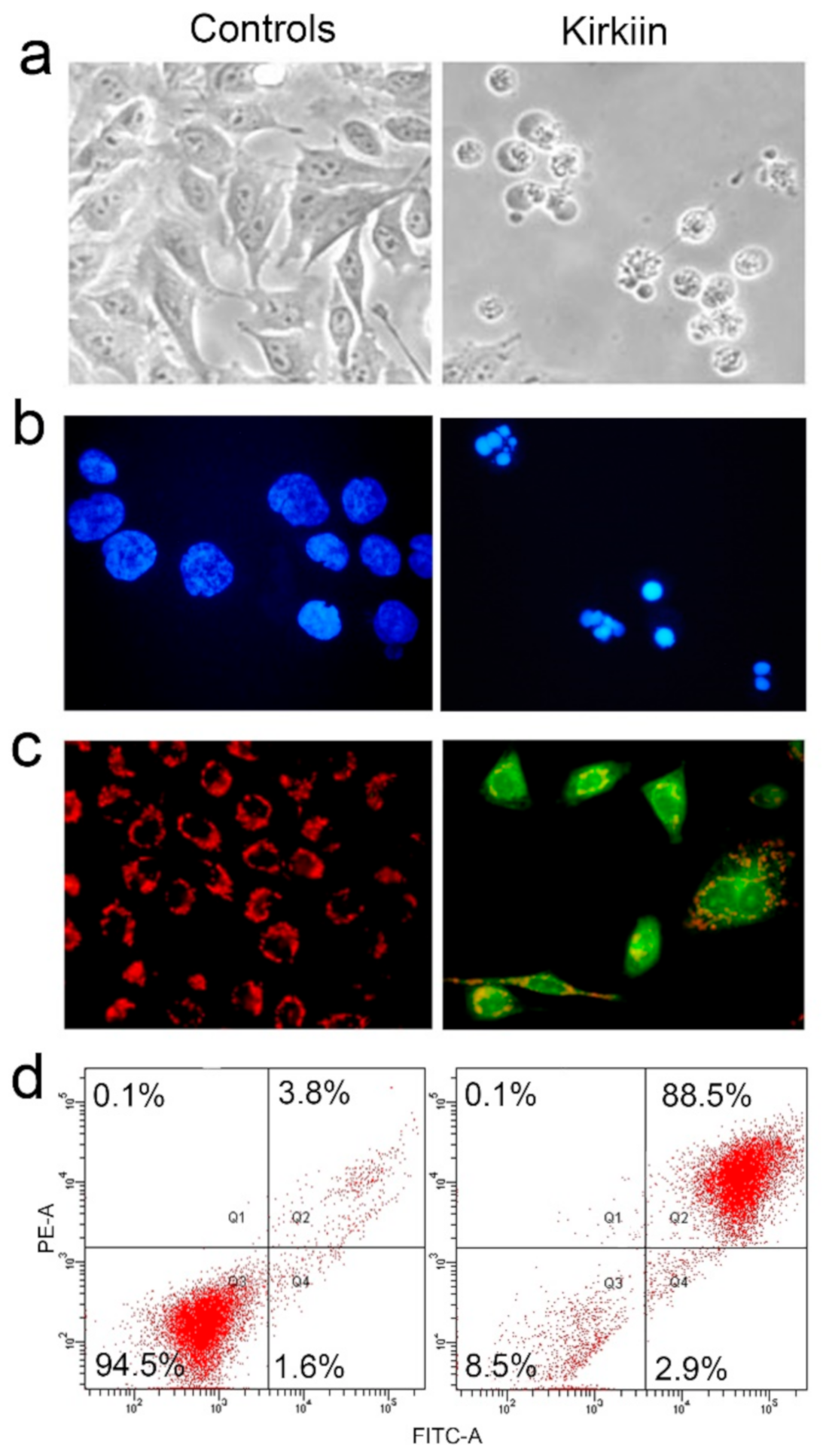
2.4.2. Evaluation of Apoptosis Induced by Kirkiin in NB100 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Methods
5.2.1. Adenia Kirkii Lectin Purification
5.2.2. Cell Free Protein Synthesis Inhibition
5.2.3. Hemagglutinating Activity
5.2.4. rRNA Glycosylase Activity
5.2.5. Adenine Polynucleotide Glycosylase Activity on Salmon Sperm DNA and on Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) RNA
5.2.6. Endonuclease Activity on Supercoiled Plasmid DNA
5.2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
5.2.8. Cell Protein Synthesis Inhibition and Viability Assay
5.2.9. Evaluation of Apoptosis
5.2.10. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolognesi, A.; Bortolotti, M.; Maiello, S.; Battelli, M.G.; Polito, L. Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins from Plants: A Historical Overview. Molecules 2016, 21, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrot, J.; Weng, A.; Melzig, M.F. Ribosome-inactivating and related proteins. Toxins 2015, 7, 1556–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.H.; Bao, H.; Ng, T.B.; Chan, H.H.L.; Ng, C.C.W.; Man, G.C.W.; Wang, H.; Guan, S.; Zhao, S.; Fang, E.F.; et al. New ribosome-inactivating proteins and other proteins with protein synthesis-inhibiting activities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 4211–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Maiello, S.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Plants Producing Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins in Traditional Medicine. Molecules 2016, 21, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Polito, L. Momordica charantia, a Nutraceutical Approach for Inflammatory Related Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, Y.; Mitsui, K.; Motizuki, M.; Tsurugi, K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 5908–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.J.; Dodd, J.E.; Hautbergue, G.M. Ribosome-inactivating proteins. Virulence 2013, 4, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, L.; Valbonesi, P.; Bonora, E.; Gorini, P.; Bolognesi, A.; Stirpe, F. Polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase activity of ribosome-inactivating proteins: Effect on DNA, RNA and poly(A). Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battelli, M.G.; Barbieri, L.; Bolognesi, A.; Buonamici, L.; Valbonesi, P.; Polito, L.; Van Damme, E.J.M.; Peumans, W.J.; Stirpe, F. Ribosome-inactivating lectins with polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase activity. FEBS Lett. 1997, 408, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, A.; Polito, L.; Lubelli, C.; Barbieri, L.; Parente, A.; Stirpe, F. Ribosome-inactivating and adenine polynucleotide glycosylase activities in Mirabilis jalapa L. tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 13709–13716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Battelli, M.G.; Calafato, G.; Bolognesi, A. Ricin: An Ancient Story for a Timeless Plant Toxin. Toxins 2019, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spooner, R.A.; Lord, J.M. Ricin trafficking in cells. Toxins 2015, 7, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grela, P.; Szajwaj, M.; Horbowicz-Drożdżal, P.; Tchórzewski, M. How Ricin Damages the Ribosome. Toxins 2019, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Zaeytijd, J.; Van Damme, E.J. Extensive Evolution of Cereal Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins Translates into Unique Structural Features, Activation Mechanisms, and Physiological Roles. Toxins 2017, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirpe, F.; Barbieri, L.; Abbondanza, A.; Falasca, A.I.; Brown, A.N.; Sandvig, K.; Olsnes, S.; Pihl, A. Properties of volkensin, a toxic lectin from Adenia volkensii. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 14589–14595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperi-Campani, A.; Barbieri, L.; Lorenzoni, E.; Montanaro, L.; Sperti, S.; Bonetti, E.; Stirpe, F. Modeccin, the toxin of Adenia digitata. Purification, toxicity and inhibition of protein synthesis in vitro. Biochem. J. 1978, 174, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirpe, F.; Bolognesi, A.; Bortolotti, M.; Farini, V.; Lubelli, C.; Pelosi, E.; Polito, L.; Dozza, B.; Strocchi, P.; Chambery, A.; et al. Characterization of highly toxic type 2 ribosome-inactivating proteins from Adenia lanceolata and Adenia stenodactyla (Passifloraceae). Toxicon 2007, 50, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battelli, M.G.; Scicchitano, V.; Polito, L.; Farini, V.; Barbieri, L.; Bolognesi, A. Binding and intracellular routing of the plant-toxic lectins, lanceolin and stenodactylin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1800, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, R.G.; Kline IV, R.H. Neuronal lesioning with axonally transported toxins. J. Neurosci. Methods 2000, 103, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, B.; D’Alessandro, C.; Farini, V.; Bolognesi, A.; Polazzi, E.; Contestabile, A.; Stirpe, F.; Battelli, M.G. In vitro and in vivo toxicity of type 2 ribosome-inactivating proteins lanceolin and stenodactylin on glial and neuronal cells. Neurotoxicology 2007, 28, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangalos, M.N.; Francis, P.T.; Pearson, R.C.; Middlemiss, D.N.; Bowen, D.M. Destruction of a sub-population of cortical neurones by suicide transport of volkensin, a lectin from Adenia volkensii. J. Neurosci. Methods 1991, 40, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, A.; Partridge, L.J.; Davletov, B.; Hautbergue, G.M. The Use of Plant-Derived Ribosome Inactivating Proteins in Immunotoxin Development: Past, Present and Future Generations. Toxins 2017, 9, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Djemil, A.; Bortolotti, M. Plant Toxin-Based Immunotoxins for Cancer Therapy: A Short Overview. Biomedicines 2016, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzo, E.; Di Maro, A. A new age for biomedical applications of Ribosome Inactivating Proteins (RIPs): From bioconjugate to nanoconstructs. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Pedrazzi, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Apoptosis and necroptosis induced by stenodactylin in neuroblastoma cells can be completely prevented through caspase inhibition plus catalase or necrostatin-1. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercatelli, D.; Bortolotti, M.; Andresen, V.; Sulen, A.; Polito, L.; Gjertsen, B.T.; Bolognesi, A. Early Response to the Plant Toxin Stenodactylin in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Involves Inflammatory and Apoptotic Signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Pérez, Y.; de Torre, C.; Ferreras, J.M.; Antolín, P.; Jiménez, P.; Rojo, M.A.; Méndez, E.; Girbés, T. Molecular characterization and systemic induction of single-chain ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) leaves. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Citores, L.; Di Maro, A.; Ferreras, J.M. Biological activities of the antiviral protein BE27 from sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Planta 2015, 241, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggli, U.; Newton, L.E. Etymological Dictionary of Succulent Plant. Names, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 3, p. 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrini, M.S.; Katayama, M.; Nakase, I.; Vago, R. Plant Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins: Progesses, Challenges and Biotechnological Applications (and a Few Digressions). Toxins 2017, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, E.; Lubelli, C.; Polito, L.; Barbieri, L.; Bolognesi, A.; Stirpe, F. Ribosome-inactivating proteins and other lectins from Adenia (Passifloraceae). Toxicon 2005, 46, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, J.; Gillet, D. Ribosome Inactivating Proteins: From Plant Defense to Treatments against Human Misuse or Diseases. Toxins 2018, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, Y.; Tsurugi, K. The RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. The characteristics of the enzymatic activity of ricin A-chain with ribosomes and with rRNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 8735–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhou, Y.K.; Ji, Z.L.; Chen, X.R. The Plant Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins Play Important Roles in Defense against Pathogens and Insect Pest Attacks. Front. Plant. Sci. 2018, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, B.A.; Tumer, N.E. Antiviral activity of ribosome inactivating proteins in medicine. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 523–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, L.; Ciani, M.; Girbés, T.; Liu, W.Y.; Van Damme, E.J.; Peumans, W.J.; Stirpe, F. Enzymatic activity of toxic and non-toxic type 2 ribosome-inactivating proteins. FEBS Lett. 2004, 563, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, L.; Valbonesi, P.; Righi, F.; Zuccheri, G.; Monti, F.; Gorini, P.; Samorí, B.; Stirpe, F. Polynucleotide:Adenosine glycosidase is the sole activity of ribosome-inactivating proteins on DNA. J. Biochem. 2000, 128, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilabert-Oriol, R.; Weng, A.; von Mallinckrodt, B.; Melzig, M.F.; Fuchs, H.; Thakur, M. Immunotoxins constructed with ribosome-inactivating proteins and their enhancers: A lethal cocktail with tumor specific efficacy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 6584–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Saporin-S6: A useful tool in cancer therapy. Toxins 2013, 5, 1698–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Q.; Zhu, Z.N.; Zheng, Y.T.; Shaw, P.C. Engineering of Ribosome-inactivating Proteins for Improving Pharmacological Properties. Toxins 2020, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Surendranath, K.; Bora, N.; Surolia, A.; Karande, A.A. Ribosome inactivating proteins and apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Farini, V.; Battelli, M.G.; Barbieri, L.; Bolognesi, A. Saporin induces multiple death pathways in lymphoma cells with different intensity and timing as compared to ricin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikriwal, D.; Ghosh, P.; Batra, J.K. Ribosome inactivating protein saporin induces apoptosis through mitochondrial cascade, independent of translation inhibition. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 2880–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, A.L.; Kempen, C.G.; McCaig, W.D.; Parker, C.A.; Mantis, N.J.; LaRocca, T.J. TNF Family Cytokines Induce Distinct Cell Death Modalities in the A549 Human Lung Epithelial Cell Line when Administered in Combination with Ricin Toxin. Toxins 2019, 11, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polito, L.; Mercatelli, D.; Bortolotti, M.; Maiello, S.; Djemil, A.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Two Saporin-Containing Immunotoxins Specific for CD20 and CD22 Show Different Behavior in Killing Lymphoma Cells. Toxins 2017, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowa-Rogozińska, N.; Sominka, H.; Nowakowska-Gołacka, J.; Sandvig, K.; Słomińska-Wojewódzka, M. Intracellular Transport and Cytotoxicity of the Protein Toxin Ricin. Toxins 2019, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, M.; Kaur, I.; Perugini, M.A.; Gupta, R.C. Ribosome-inactivating proteins: Current status and biomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, L.; Falasca, A.I.; Stirpe, F. Volkensin, the toxin of Adenia volkensii (kilyambiti plant). FEBS Lett. 1984, 171, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, G.L.; Blaustein, J.; Etzler, M.E. Characterization of two plant lectins from Ricinus communis and their quantitative interaction with a murine lymphoma. Biochemistry 1974, 13, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, L.; Stoppa, C.; Bolognesi, A. Large scale chromatographic purification of ribosome-inactivating proteins. J. Chromatogr. 1987, 408, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strocchi, P.; Barbieri, L.; Stirpe, F. Immunological properties of ribosome-inactivating proteins and of a saporin-IgG conjugate. J. Immunol. Methods 1992, 155, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalb, V.F., Jr.; Bernlohr, R.W. A new spectrophotometric assay for protein in cell extracts. Anal. Biochem. 1977, 82, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Mancuso, R.; Baruzzi, G.; Faedi, W.; Bolognesi, A. Protein synthesis inhibition activity by strawberry tissue protein extracts during plant life cycle and under biotic and abiotic stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 15532–15545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, R.; Citores, L.; Ragucci, S.; Russo, R.; Di Maro, A.; Ferreras, J.M. Biological and antipathogenic activities of ribosome-inactivating proteins from Phytolacca dioica L. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Maro, A.; Chambery, A.; Daniele, A.; Casoria, P.; Parente, A. Isolation and characterization of heterotepalins, type 1 ribosome-inactivating proteins from Phytolacca heterotepala leaves. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Adenia Species | Cell Free IC50 (μg/mL) | Agglutinating Activity 1 (μg/mL) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Red. | Red. | |||
| A. kirkii | 9.2 | 4.7 | 4.0 | |
| A. stenodactyla | 5.6 | 0.5 | 49.9 | [17] |
| A. lanceolate | 5.2 | 1.1 | 230.9 | [17] |
| A. volkensii | 7.5 | 0.7 | 15.6 | [15,17] |
| Purification Step | Protein (mg/mL) | Total Protein (mg) | Total Protein (%) | IC50 (µg/mL) 1 | Agglutinating Activity 2 (μg/mL) | Specific Activity (U/mg) 3 | Total Activity (U) | Yeld (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Red. | Red. | ||||||||
| Crude extract | 3.46 | 1730.0 | 100.0 | 55.0 | 21.2 | 45.1 | 18.2 | 31,454.5 | 100.0 |
| Sepharose CL-6B Eluate | 2.84 | 107.9 | 6.2 | 9.2 | 4.7 | 4.0 | 108.7 | 4130.4 | 13.1 |
| Sephacryl S-100 peak 1 | 1.43 | 24.2 | 1.4 | 7.4 | 1.0 | 175.0 | 135.1 | 3270.2 | 10.4 |
| Sephacryl S-100 peak 2 | 1.49 | 62.4 | 3.6 | >50 | >50 | 2.9 | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bortolotti, M.; Maiello, S.; Ferreras, J.M.; Iglesias, R.; Polito, L.; Bolognesi, A. Kirkiin: A New Toxic Type 2 Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from the Caudex of Adenia kirkii. Toxins 2021, 13, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020081
Bortolotti M, Maiello S, Ferreras JM, Iglesias R, Polito L, Bolognesi A. Kirkiin: A New Toxic Type 2 Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from the Caudex of Adenia kirkii. Toxins. 2021; 13(2):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020081
Chicago/Turabian StyleBortolotti, Massimo, Stefania Maiello, José M. Ferreras, Rosario Iglesias, Letizia Polito, and Andrea Bolognesi. 2021. "Kirkiin: A New Toxic Type 2 Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from the Caudex of Adenia kirkii" Toxins 13, no. 2: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020081
APA StyleBortolotti, M., Maiello, S., Ferreras, J. M., Iglesias, R., Polito, L., & Bolognesi, A. (2021). Kirkiin: A New Toxic Type 2 Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from the Caudex of Adenia kirkii. Toxins, 13(2), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020081











