Rapid and Efficient Enrichment of Snake Venoms from Human Plasma Using a Strong Cation Exchange Tip Column to Improve Snakebite Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Differences in pI Values between High-Abundance Human Plasma Proteins and Snake Venom Proteins
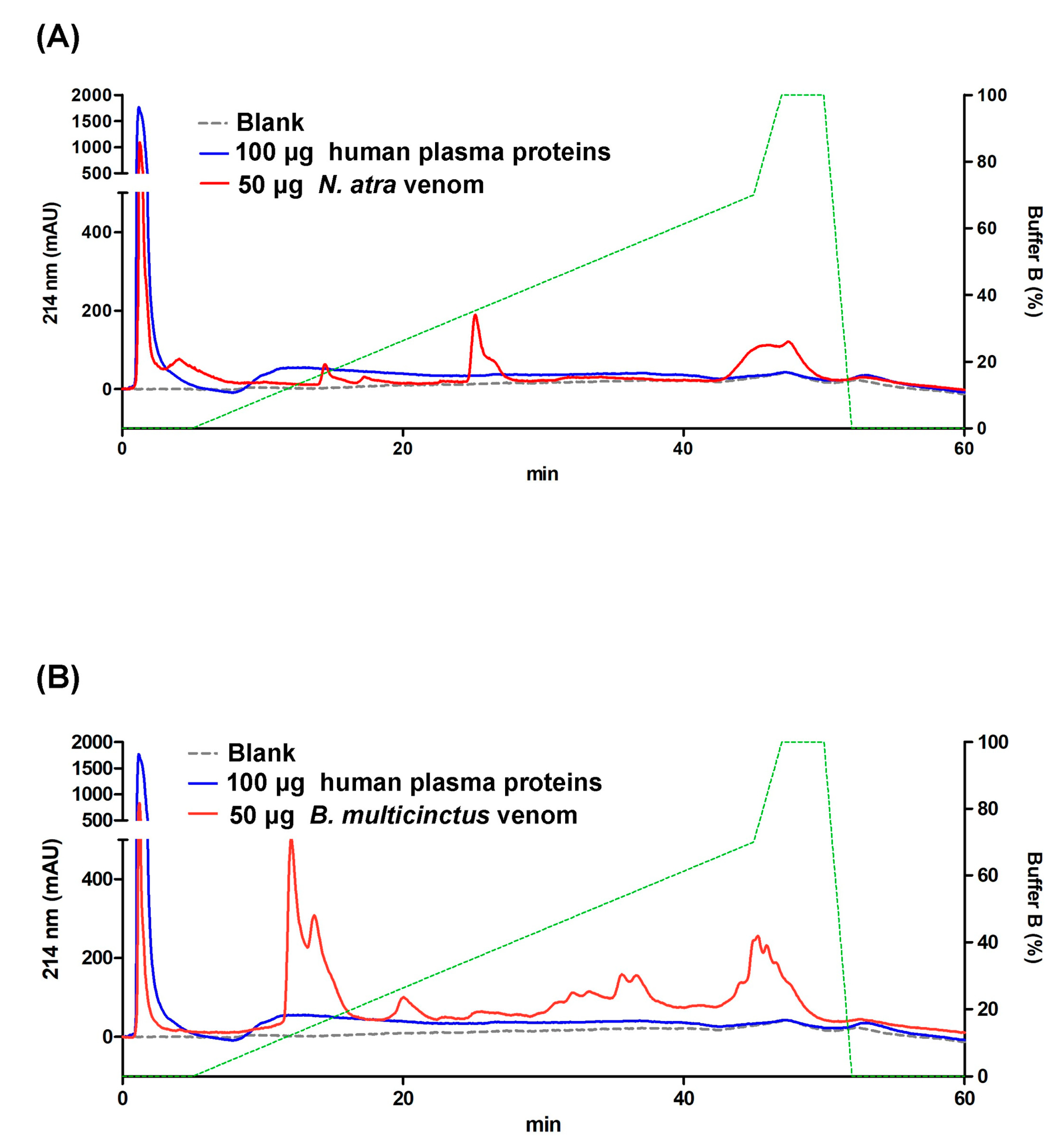
2.2. SCX-HPLC for Separating Venom Proteins from Human Plasma Proteins
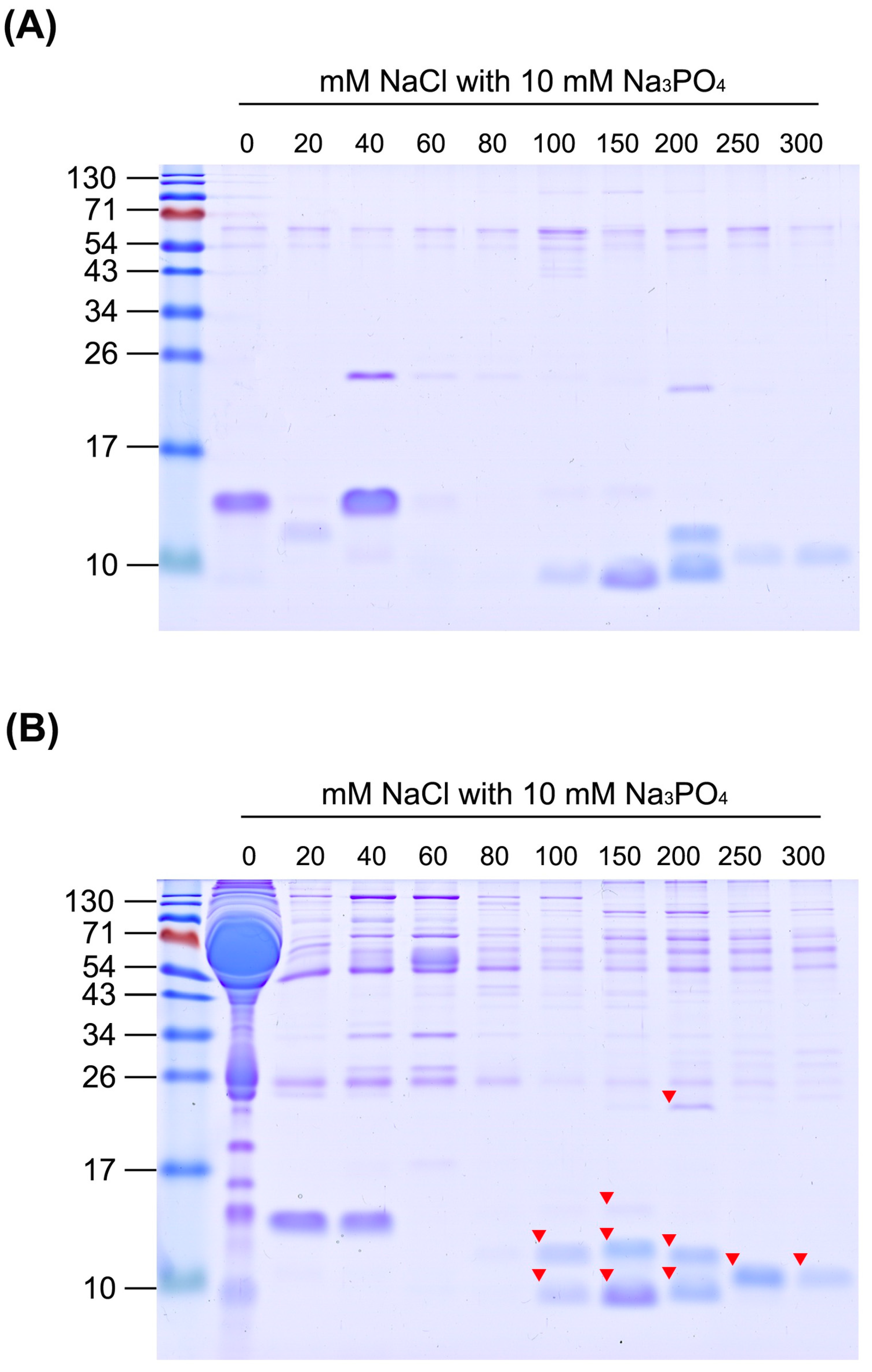
2.3. Development of Methodology for Efficient Enrichment of Snake Venom Proteins from Human Plasma
2.4. Identification of SCX Tip Column-Enriched Snake Venom Proteins
2.5. Evaluation of Venom Protein Enrichment Efficiency Via the SCX Tip Column
2.6. Combination of SCX-Tip Column Enrichment with Snakebite Detection Assays
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Snake Venom
5.2. Strong Cation Exchange High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (SCX-HPLC)
5.3. Separation of Venom and Plasma Proteins Using the Strong Cation Exchange (SCX) Tip Column
5.4. Acetone Precipitation
5.5. In-Gel Tryptic Digestion
5.6. LC-MS/MS Analysis
5.7. Database Searches and Bioinformatics Analysis
5.8. Venom Detection with Lateral Flow Strips
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. The global burden of snakebite: A literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.C.; Liaw, S.J.; Bullard, M.J.; Chiu, T.F. Treatment of poisonous snakebites in northern Taiwan. J. Formos Med. Assoc. 2000, 99, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, T.P.; Wu, C.S. Clinico-pathological studies on snakebites in Taiwan. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi 1972, 71, 447–466. [Google Scholar]
- Liau, M.Y.; Huang, R.J. Toxoids and antivenoms of venomous snakes in Taiwan. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 1997, 16, 163–175. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.C.; Liu, P.Y.; Chiang, L.C.; Lai, C.S.; Lai, K.L.; Ho, C.H.; Wang, T.H.; Yang, C.C. Naja atra snakebite in Taiwan. Clin. Toxicol. 2018, 56, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.P.; Yu, Y.J.; Hung, D.Z. Sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Taiwan cobra venom. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 2002, 44, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hung, D.Z.; Liau, M.Y.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y. The clinical significance of venom detection in patients of cobra snakebite. Toxicon 2003, 41, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, D.Z.; Lin, J.H.; Mo, J.F.; Huang, C.F.; Liau, M.Y. Rapid diagnosis of Naja atra snakebites. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Yu, J.S.; Wang, P.J.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Lai, P.F.; Hsu, C.P.; Fann, W.C.; Lin, C.C. Development of sandwich ELISA and lateral flow strip assays for diagnosing clinically significant snakebite in Taiwan. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0007014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawade, B.S.; Salvi, N.C.; Shaikh, I.K.; Waghmare, A.B.; Jadhav, N.D.; Wagh, V.B.; Pawade, A.S.; Waykar, I.G.; Potnis-Lele, M. Rapid and selective detection of experimental snake envenomation—Use of gold nanoparticle based lateral flow assay. Toxicon 2016, 119, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; You, Y.; Li, X.; Robinson, M.A. Detection and confirmation of alpha-cobratoxin in equine plasma by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1533, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, M.; Ganio, K.; Steel, R. Extraction of alpha-neurotoxins from equine plasma by receptor based affinity purification. Drug Test Anal. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, S.L.; Acosta, G.; Avila, L.; Giudicessi, S.L.; Camperi, S.A.; Albericio, F.; Cascone, O.; Martinez Ceron, M.C. Use of a phosphopeptide as a ligand to purify phospholipase A2 from the venom of Crotalus durisuss terrificus by affinity chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1146, 122070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theakston, R.D.; Laing, G.D. Diagnosis of snakebite and the importance of immunological tests in venom research. Toxins 2014, 6, 1667–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, G.; Copic, A.; Le Porrier, S.; Gubensek, F.; Bon, C.; Krizaj, I. Crotoxin acceptor protein isolated from Torpedo electric organ: Binding properties to crotoxin by surface plasmon resonance. Toxicon 2003, 41, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.N.; Konwar, B.; Kaur, S.; Doley, R.; Mondal, B. Study on Snake Venom Protein-Antibody Interaction by Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy. Photonic Sens. 2018, 8, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.R.; Valdes, J.J.; Eldefrawi, M.E. Effects of receptor concentration, media pH and storage on nicotinic receptor-transmitted signal in a fiber-optic biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1991, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Tan, K.Y.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, N.H. Venom-gland transcriptome and venom proteome of the Malaysian king cobra (Ophiophagus hannah). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Lomonte, B.; Lohse, B.; Fernandez, J.; Gutierrez, J.M. Unveiling the nature of black mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis) venom through venomics and antivenom immunoprofiling: Identification of key toxin targets for antivenom development. J. Proteom. 2015, 119, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, W.M.; Contreras-Bernal, J.C.; Bisneto, P.F.; Sachett, J.; Mendonca da Silva, I.; Lacerda, M.; Guimaraes da Costa, A.; Val, F.; Brasileiro, L.; Sartim, M.A.; et al. Bothrops atrox, the most important snake involved in human envenomings in the amazon: How venomics contributes to the knowledge of snake biology and clinical toxinology. Toxicon X 2020, 6, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; You, C.H.; Wang, P.J.; Yu, J.S.; Huang, G.J.; Liu, C.H.; Hsieh, W.C.; Lin, C.C. Analysis of the efficacy of Taiwanese freeze-dried neurotoxic antivenom against Naja kaouthia, Naja siamensis and Ophiophagus hannah through proteomics and animal model approaches. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Chou, Y.S.; Chen, C.Y.; Liu, K.L.; Huang, G.J.; Yu, J.S.; Wu, C.J.; Liaw, G.W.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chen, C.K. Pathogenesis of local necrosis induced by Naja atra venom: Assessment of the neutralization ability of Taiwanese freeze-dried neurotoxic antivenom in animal models. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, R.; Bonilla, F.; Sasa, M.; Dwyer, Q.; Fernandez, J.; Lomonte, B. Proteomic profiling, functional characterization, and immunoneutralization of the venom of Porthidium porrasi, a pitviper endemic to Costa Rica. Acta Trop. 2019, 193, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Species | Sample | Accession | Description | Coverage (%) 1 | Peptides 2 | PSMs 3 | MW [kDa] | pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N. atra | 100mM-1 | P60304 | Cytotoxin 1 | 35.8 | 4 | 10 | 9.0 | 8.7 |
| 100mM-2 | P60304 | Cytotoxin 1 | 71.6 | 11 | 229 | 9.0 | 8.7 | |
| P80245 | Cytotoxin 6 | 58.0 | 8 | 103 | 9.0 | 8.9 | ||
| P01442 | Cytotoxin 2 | 51.9 | 7 | 86 | 9.0 | 8.9 | ||
| P01443 | Cytotoxin 4 | 51.9 | 7 | 86 | 9.1 | 9.0 | ||
| 150 mM-1 | P60304 | Cytotoxin 1 | 35.8 | 5 | 12 | 9.0 | 8.7 | |
| P80245 | Cytotoxin 6 | 43.2 | 5 | 10 | 9.0 | 8.9 | ||
| 150 mM-2 | O93422 | Long neurotoxin homolog | 22.1 | 2 | 6 | 9.8 | 8.7 | |
| Q9YGI2 | Probable weak neurotoxin NNAM1 | 22.1 | 2 | 6 | 9.8 | 8.5 | ||
| Q9YGI4 | Probable weak neurotoxin NNAM2 | 25.6 | 2 | 10 | 9.9 | 8.6 | ||
| 150 mM-3 | P60304 | Cytotoxin 1 | 71.6 | 11 | 356 | 9.0 | 8.7 | |
| P80245 | Cytotoxin 6 | 71.6 | 12 | 164 | 9.0 | 8.9 | ||
| P01442 | Cytotoxin 2 | 59.3 | 9 | 124 | 9.0 | 8.9 | ||
| P01443 | Cytotoxin 4 | 59.3 | 9 | 124 | 9.1 | 9.0 | ||
| 200 mM-1 | Q7ZZN8 | Cysteine-rich venom protein natrin-2 | 33.6 | 9 | 63 | 26.2 | 8.7 | |
| 200 mM-2 | Q9YGI2 | Probable weak neurotoxin NNAM1 | 36.1 | 4 | 99 | 9.8 | 8.5 | |
| O93422 | Long neurotoxin homolog | 36.1 | 4 | 99 | 9.8 | 8.7 | ||
| Q9YGI4 | Probable weak neurotoxin NNAM2 | 25.6 | 2 | 37 | 9.9 | 8.6 | ||
| 200 mM-3 | P60301 | Cytotoxin 3 | 60.5 | 9 | 178 | 9.0 | 9.0 | |
| P60304 | Cytotoxin 1 | 65.4 | 9 | 161 | 9.0 | 8.7 | ||
| P80245 | Cytotoxin 6 | 58.0 | 9 | 115 | 9.0 | 8.9 | ||
| 250 mM-1 | P62375 | Cytotoxin A5 | 45.8 | 4 | 44 | 9.3 | 9.0 | |
| 300 mM-1 | P62375 | Cytotoxin A5 | 46.0 | 6 | 17 | 9.3 | 9.0 | |
| B. multicinctus | 150 mM-1 | P00617 | Basic phospholipase A2 beta-bungarotoxin A1 chain | 21.1 | 2 | 5 | 16.2 | 7.5 |
| 150 mM-2 | P00987 | Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor homolog beta-bungarotoxin B1 chain | 28.2 | 3 | 17 | 9.6 | 8.7 | |
| 200 mM-1 | P00617 | Basic phospholipase A2 beta-bungarotoxin A1 chain | 61.9 | 9 | 44 | 16.2 | 7.5 | |
| 200 mM-2 | P00987 | Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor homolog beta-bungarotoxin B1 chain | 48.2 | 5 | 26 | 9.6 | 8.7 | |
| 250 mM-1 | P00617 | Basic phospholipase A2 beta-bungarotoxin A1 chain | 53.1 | 7 | 17 | 16.2 | 7.5 | |
| 250 mM-2 | P00987 | Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor homolog beta-bungarotoxin B1 chain | 30.6 | 3 | 9 | 9.6 | 8.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.-C.; Yang, Y.-H.; Hsiao, Y.-C.; Wang, P.-J.; Liu, J.-C.; Liu, C.-H.; Hsieh, W.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Yu, J.-S. Rapid and Efficient Enrichment of Snake Venoms from Human Plasma Using a Strong Cation Exchange Tip Column to Improve Snakebite Diagnosis. Toxins 2021, 13, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020140
Liu C-C, Yang Y-H, Hsiao Y-C, Wang P-J, Liu J-C, Liu C-H, Hsieh W-C, Lin C-C, Yu J-S. Rapid and Efficient Enrichment of Snake Venoms from Human Plasma Using a Strong Cation Exchange Tip Column to Improve Snakebite Diagnosis. Toxins. 2021; 13(2):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020140
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chien-Chun, Ya-Han Yang, Yung-Chin Hsiao, Po-Jung Wang, Jo-Chuan Liu, Chien-Hsin Liu, Wen-Chin Hsieh, Chih-Chuan Lin, and Jau-Song Yu. 2021. "Rapid and Efficient Enrichment of Snake Venoms from Human Plasma Using a Strong Cation Exchange Tip Column to Improve Snakebite Diagnosis" Toxins 13, no. 2: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020140
APA StyleLiu, C.-C., Yang, Y.-H., Hsiao, Y.-C., Wang, P.-J., Liu, J.-C., Liu, C.-H., Hsieh, W.-C., Lin, C.-C., & Yu, J.-S. (2021). Rapid and Efficient Enrichment of Snake Venoms from Human Plasma Using a Strong Cation Exchange Tip Column to Improve Snakebite Diagnosis. Toxins, 13(2), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020140





