The Curious Case of the “Neurotoxic Skink”: Scientific Literature Points to the Absence of Venom in Scincidae
Abstract
1. Introduction
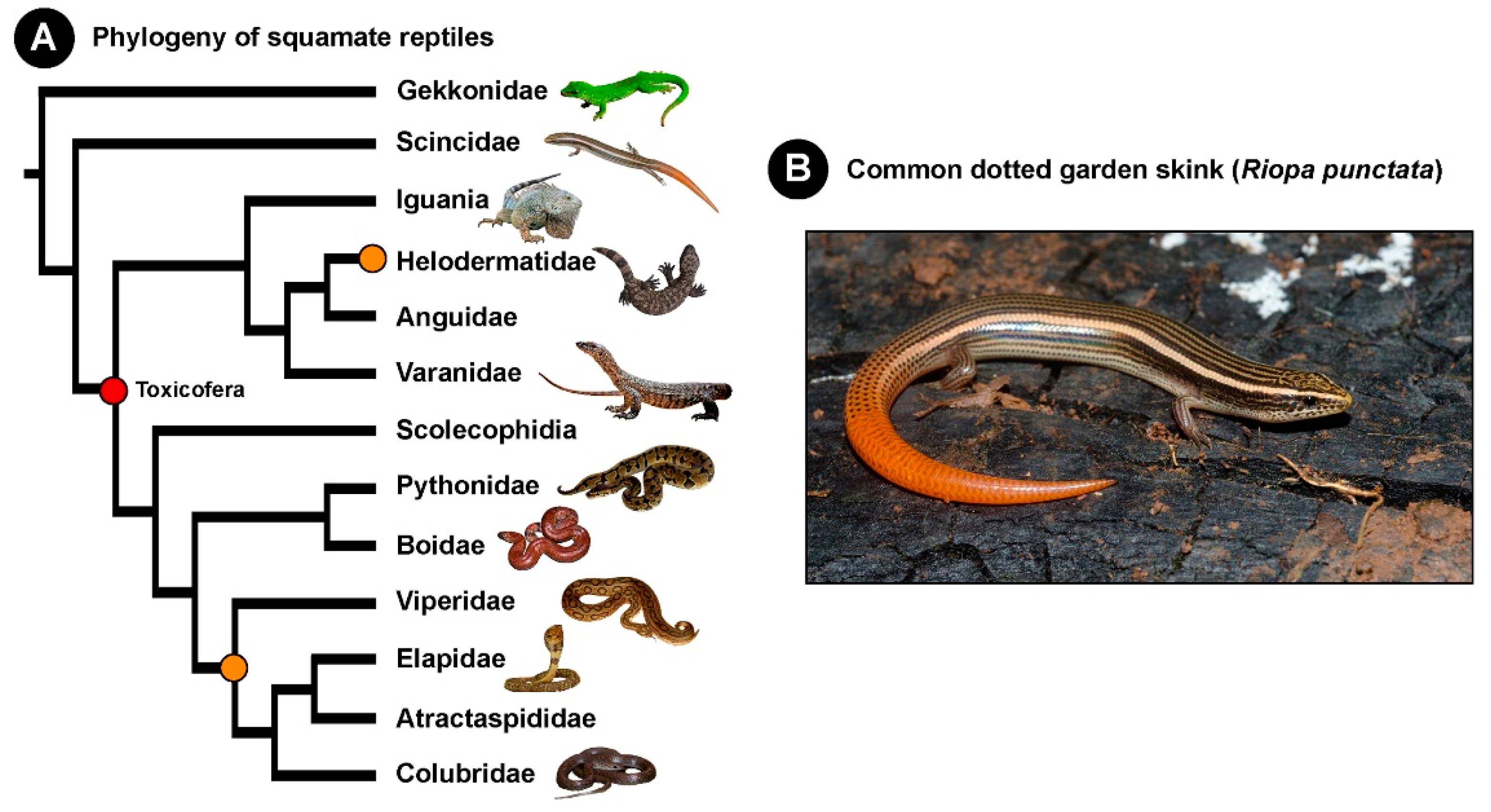
2. The Evolutionary Origin of “Toxicofera” Venom Systems
3. Evidence Supports the Lack of Venom in Scincidae
4. Potential Causes of the Observed Neurotoxic Envenoming
5. A Typical Case of “Early Morning Neuroparalytic Syndrome”
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Modica, M.V.; Sunagar, K.; Holford, M.; Dutertre, S. Editorial: Diversity and Evolution of Animal Venoms: Neglected Targets, Ecological Interactions, Future Perspectives. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daltry, J.C.; Wuster, W.; Thorpe, R.S. Diet and snake venom evolution. Nature 1996, 379, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, H.L.; Sanz, L.; Chiucchi, J.E.; Farrell, T.M.; Calvete, J.J. Proteomic analysis of ontogenetic and diet-related changes in venom composition of juvenile and adult Dusky Pigmy rattlesnakes (Sistrurus miliarius barbouri). J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 2169–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zancolli, G.; Calvete, J.J.; Cardwell, M.D.; Greene, H.W.; Hayes, W.K.; Hegarty, M.J.; Herrmann, H.W.; Holycross, A.T.; Lannutti, D.I.; Mulley, J.F.; et al. When one phenotype is not enough: Divergent evolutionary trajectories govern venom variation in a widespread rattlesnake species. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20182735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casewell, N.R.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Laustsen, A.H.; Sunagar, K. Causes and Consequences of Snake Venom Variation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxme, R.R.S.; Khochare, S.; de Souza, H.F.; Ahuja, B.; Suranse, V.; Martin, G.; Whitaker, R.; Sunagar, K. Beyond the ‘big four’: Venom profiling of the medically important yet neglected Indian snakes reveals disturbing antivenom deficiencies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Fry, B.G.; Kini, R.M. Eggs-only diet: Its implications for the toxin profile changes and ecology of the marbled sea snake (Aipysurus eydouxii). J. Mol. Evol. 2005, 60, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackessy, S.P.; Sixberry, N.M.; Heyborne, W.H.; Fritts, T. Venom of the Brown Treesnake, Boiga irregularis: Ontogenetic shifts and taxa-specific toxicity. Toxicon 2006, 47, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Wroe, S.; Teeuwisse, W.; van Osch, M.J.; Moreno, K.; Ingle, J.; McHenry, C.; Ferrara, T.; Clausen, P.; Scheib, H.; et al. A central role for venom in predation by Varanus komodoensis (Komodo Dragon) and the extinct giant Varanus (Megalania) priscus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8969–8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, R.; Abinaya. A Rare Neurotoxic Red-tailed-skink Bite. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2020, 68, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Kochva, E. Oral glands of the Reptilia. Biol. Reptil. 1978, 8, 43–162. [Google Scholar]
- Pough, F.H.; Andrews, R.M.; Cadle, J.E.; Crump, M.L.; Savitzky, A.H.; Wells, K.D. Herpetology, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, A.D.; Swain, M.T.; Logan, D.W.; Mulley, J.F. Testing the Toxicofera: Comparative transcriptomics casts doubt on the single, early evolution of the reptile venom system. Toxicon 2014, 92, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Vidal, N.; Norman, J.A.; Vonk, F.J.; Scheib, H.; Ramjan, S.F.; Kuruppu, S.; Fung, K.; Hedges, S.B.; Richardson, M.K.; et al. Early evolution of the venom system in lizards and snakes. Nature 2006, 439, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Undheim, E.A.; Ali, S.A.; Jackson, T.N.; Debono, J.; Scheib, H.; Ruder, T.; Morgenstern, D.; Cadwallader, L.; Whitehead, D.; et al. Squeezers and leaf-cutters: Differential diversification and degeneration of the venom system in toxicoferan reptiles. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 1881–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, J.S.; Zdenek, C.N.; Hay, C.; Violette, A.; Fourmy, R.; Cochran, C.; Fry, B.G. Varanid Lizard Venoms Disrupt the Clotting Ability of Human Fibrinogen through Destructive Cleavage. Toxins 2019, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebs, D.; Lomonte, B.; Fernández, J.; Calvete, J.J.; Sanz, L.; Mahlow, K.; Müller, J.; Köhler, G.; Zollweg, M. The earless monitor lizard Lanthanotus borneensis—A venomous animal? Toxicon 2021, 189, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Ashokan, R.; Ramasamy, K.; Nattamaisundar, K.; Jeyaraj, A.; Chandran, V.; Gajjeraman, P.; Baksh, M.F.; Gibbins, J.M.; et al. Snakebite and its socio-economic impact on the rural population of Tamil Nadu, India. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, R.; Subramanian, S.; Ponniah, T. Snakebites in Tamil Nadu, India. In Clinical Toxinology: Clinical Toxinology; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Faiz, S.M.A., Gnanathasan, C.A., Habib, A.G., Fernando, R., Yang, C.-C., Vogel, C.W., Tambourgi, D.V., Seifert, S.A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, A.P.; Periyasamy, R.; Parthiban, D.A. A Comprehensive Study of Patients Admitted with Snakebite in Tirunelveli Medical College Hospital. Int. J. Sci. Stud. 2019, 7. Available online: http://repository-tnmgrmu.ac.in/id/eprint/11202 (accessed on 2 February 2021).
- Chauhan, V.; Thakur, S. Painless Krait Bite in a Sleeping Victim: Delayed Diagnosis and High Mortality. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2017, 65, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Luu, V.Q.; Ha, N.V. Bungarus fasciatus (Banded Krait) Diet. Herpetol. Rev. 2018, 49, 543. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, D.P.; Bhattarai, P.; Piya, R.C. Food Spectrum of Common Kraits (Bungarus caeruleus): An Implication for Snakebite Prevention and Snake Conservation. J. Herpetol. 2020, 54, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R. Practical approach to the patient with acute neuromuscular weakness. World J. Clin. Cases 2017, 5, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranawaka, U.K.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. Neurotoxicity in snakebite--the limits of our knowledge. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, R.; Kharbanda, P.S.; Bhalla, A.; Rajan, R.; Prabhakar, S. Acute Flaccid paralysis in adults: Our experience. J. Emerg. Trauma Shock. 2014, 7, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO/Regional Office for South-East Asia. Guidelines for the Management of Snakebites, 2nd ed.; Warrell, D.A., Ed.; World Health Organization: New Delhi, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ariaratnam, C.A.; Sheriff, M.H.; Arambepola, C.; Theakston, R.D.; Warrell, D.A. Syndromic approach to treatment of snake bite in Sri Lanka based on results of a prospective national hospital-based survey of patients envenomed by identified snakes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 81, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolon, I.; Durso, A.M.; Mesa, S.B.; Ray, N.; Alcoba, G.; Chappuis, F.; de Castaneda, R.R. Identifying the snake: First scoping review on practices of communities and healthcare providers confronted with snakebite across the world. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrell, D.A. Snake bite. Lancet 2010, 375, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Singh, S.; Sharma, S.; Rampal, V.; Manhas, A.S.; Gupta, V.K. Snake bite poisoning presenting as early morning neuroparalytic syndrome in jhuggi dwellers. J. Assoc. Physicians India 1986, 34, 415–417. [Google Scholar]
- Samprathi, M.; Gupta, V.; Jayashree, M.; Bansal, A.; Baranwal, A.; Nallasamy, K. Epidemiology and Outcomes of Early Morning Neuroparalytic Syndrome Following Snake Bite-A Retrospective Study. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2020, 66, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Dogra, V.; Sharma, G.; Chauhan, V. Mass awareness regarding snake bite induced early morning neuroparalysis can prevent many deaths in North India. Int. J. Crit. Illn. Inj. Sci. 2016, 6, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikrant, S.; Verma, B.S. Monitor lizard bite-induced acute kidney injury—A case report. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 444–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.; Weinstein, S.A. Reply to Vikrant and Verma about “Monitor Lizard Envenoming”. Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sunagar, K.; Abraham, S.V. The Curious Case of the “Neurotoxic Skink”: Scientific Literature Points to the Absence of Venom in Scincidae. Toxins 2021, 13, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020114
Sunagar K, Abraham SV. The Curious Case of the “Neurotoxic Skink”: Scientific Literature Points to the Absence of Venom in Scincidae. Toxins. 2021; 13(2):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020114
Chicago/Turabian StyleSunagar, Kartik, and Siju V Abraham. 2021. "The Curious Case of the “Neurotoxic Skink”: Scientific Literature Points to the Absence of Venom in Scincidae" Toxins 13, no. 2: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020114
APA StyleSunagar, K., & Abraham, S. V. (2021). The Curious Case of the “Neurotoxic Skink”: Scientific Literature Points to the Absence of Venom in Scincidae. Toxins, 13(2), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13020114





