Molecular Characterization of the Enterohemolysin Gene (ehxA) in Clinical Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Isolates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Distribution of ehxA in the Clinical STEC Isolates
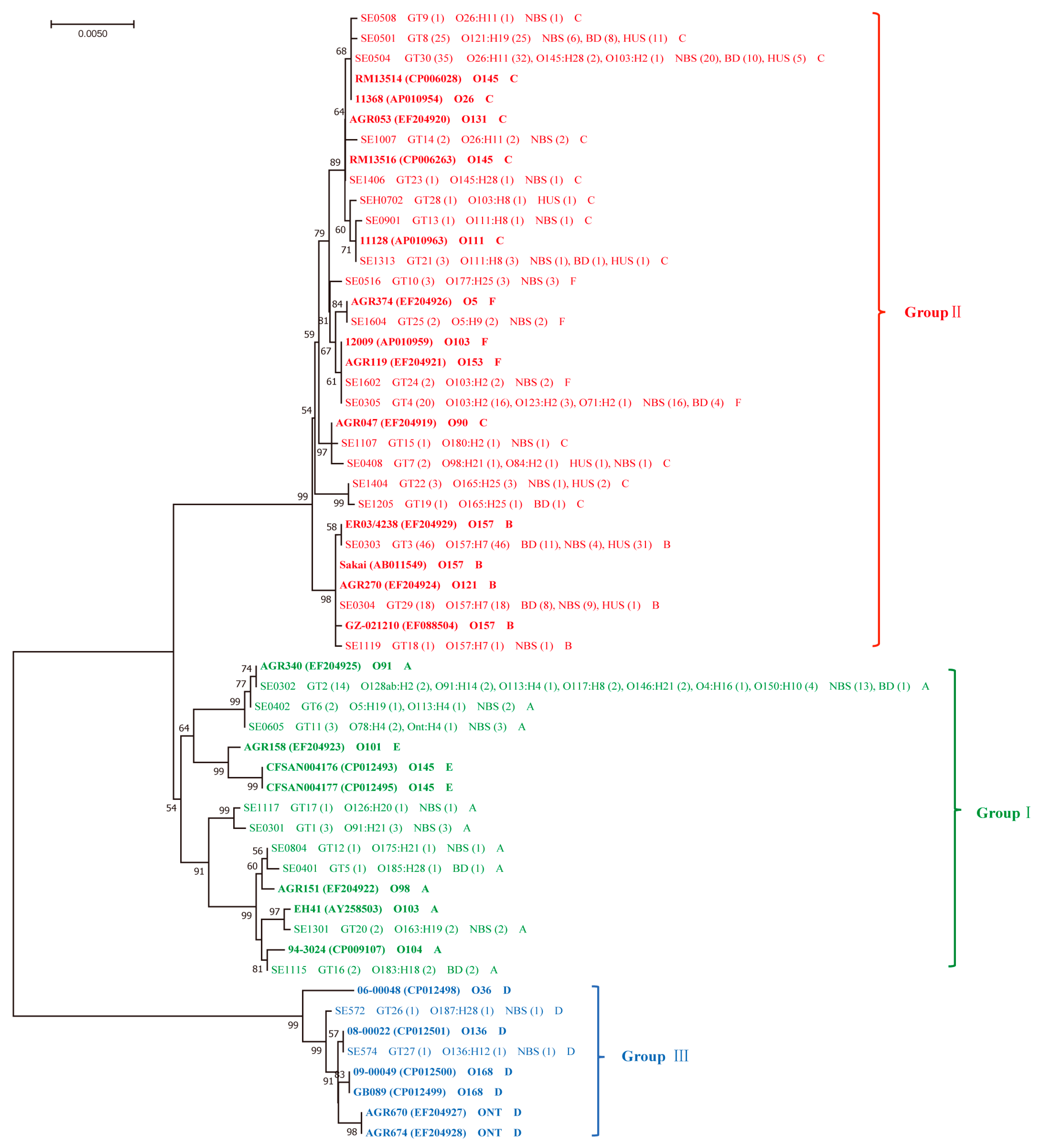
2.2. Diversity of ehxA and Its Correlation to Serotypes and the stx and eae Genes
2.3. ehxA Subtypes and Phylogenic Groups in Correlation with Clinical Variables and the Presence of eae
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Collection of STEC Isolates
4.3. ehxA Subtyping and Polymorphism Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaper, J.B.; Karmali, M.A. The continuing evolution of a bacterial pathogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4535–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majowicz, S.; Scallan, E.; Jones-Bitton, A.; Sargeant, J.M.; Stapleton, J.; Angulo, F.J.; Yeung, D.H.; Kirk, M.D. Global Incidence of Human Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli Infections and Deaths: A Systematic Review and Knowledge Synthesis. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, R.M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Taylor, C.M.; Adak, G.K.; Chart, H.; Cheasty, T.; Coia, J.E.; Gillespie, I.A.; Locking, M.E.; Reilly, W.J.; et al. Childhood Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome, United Kingdom and Ireland. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarr, P.I.; Gordon, C.A.; Chandler, W.L. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallan, E.; Griffin, P.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Hoekstra, R.M. Foodborne Illness Acquired in the United States—Unspecified Agents. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, C.C.; Stanford, K.; McAllister, T.A.; Thomas, J.; Reuter, T. Further development of sample preparation and detection methods for O157 and the top 6 non-O157 STEC serogroups in cattle feces. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 105, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etcheverria, A.I.; Padola, N.L. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli: Factors involved in virulence and cattle colonization. Virulence 2013, 4, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, S.; Karch, H.; Schmidt, H. Shiga toxin-encoding bacteriophages—Genomes in motion. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 294, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranzoni, G.M.; Fratamico, P.; Gangiredla, J.; Patel, I.; Bagi, L.K.; Delannoy, S.; Fach, P.; Boccia, F.; Anastasio, A.; Pepe, T. Characterization of Shiga Toxin Subtypes and Virulence Genes in Porcine Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, F.; Batisson, I.; Frankel, G.M.; Harel, J.; Fairbrother, J.M. Interaction of Enteropathogenic and Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli and Porcine Intestinal Mucosa: Role of Intimin and Tir in Adherence. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 6005–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, G.; Phillips, A.D.; Trabulsi, L.R.; Knutton, S.; Dougan, G.; Matthews, S. Intimin and the host cell—Is it bound to end in Tir(s)? Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, S.C.; Son, I.; Maounounen-Laasri, A.; Lin, A.; Fischer, M.; Kase, J.A. Prevalence of Hemolysin Genes and Comparison of ehxA Subtype Patterns in Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and Non-STEC Strains from Clinical, Food, and Animal Sources. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 20, 6301–6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutin, L.; Montenegro, M.A.; Orskov, I.; Orskov, F.; Prada, J.; Zimmermann, S.; Stephan, R. Close association of verotoxin (Shiga-like toxin) production with enterohemolysin production in strains of Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 11, 2559–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutin, L.; Aleksic’, S.; Zimmermann, S.; Gleier, K. Virulence factors and phenotypical traits of verotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli isolated from human patients in Germany. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1994, 183, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethelberg, S.; Olsen, K.E.P.; Scheutz, F.; Jensen, C.; Schiellerup, P.; Engberg, J.; Petersen, A.M.; Olesen, B.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Mølbak, K. Virulence Factors for Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome, Denmark1. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwidder, M.; Heinisch, L.; Schmidt, H. Genetics, Toxicity, and Distribution of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli Hemolysin. Toxins 2019, 11, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cookson, A.L.; Bennett, J.; Thomson-Carter, F.; Attwood, G.T. Molecular Subtyping and Genetic Analysis of the Enterohemolysin Gene (ehxA) from Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli and Atypical Enteropathogenic E. coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 6360–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, I.R.; Gangiredla, J.; Lacher, D.W.; Mammel, M.K.; Bagi, L.; Baranzoni, G.M.; Fratamico, P.M.; Roberts, E.L.; Debroy, C.; Lindsey, R.L.; et al. Interlaboratory Evaluation of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Escherichia coli Identification Microarray for Profiling Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Mernelius, S.; Jernberg, C.; Einemo, I.-M.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; Löfgren, S.; Matussek, A. Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Infection in Jönköping County, Sweden: Occurrence and Molecular Characteristics in Correlation With Clinical Symptoms and Duration of stx Shedding. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Bai, X.; Fan, R.; Sun, H.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, Y. Genetic diversity of the enterohaemolysin gene (ehxA) in non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains in China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, D. Virulence factors of Escherichia coli O157 and other Shiga toxin-producing E. coli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cookson, A.L.; Croucher, D.; Pope, C.; Bennett, J.; Thomson-Carter, F.; Attwood, G.T. Isolation, Characterization, and Epidemiological Assessment of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O84 Isolates from New Zealand. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1863–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Bielaszewska, M.; Liesegang, A.; Tschäpe, H.; Schmidt, H.; Bitzan, M.; Karch, H. Molecular characteristics and epidemiological significance of Shiga tox-in-producing Escherichia coli O26 strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 6, 2134–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, H.J. Shiga Toxin–producing Escherichia coli Strains Negative for Locus of Enterocyte Effacement. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, L.; Vanstone, G.L.; Perry, N.T.; Launders, N.; Adak, G.K.; Godbole, G.; Grant, K.A.; Smith, R.; Jenkins, C. Epidemiology and microbiology of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli other than serogroup O157 in England, 2009–2013. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugum, K.; Brandal, L.T.; Lindstedt, B.-A.; Wester, A.L.; Bergh, K.; Afset, J.E. PCR-Based Detection and Molecular Characterization of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Strains in a Routine Microbiology Laboratory over 16 years. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3156–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Boerlin, P.; McEwen, S.A.; Boerlin-Petzold, F.; Wilson, J.B.; Johnson, R.P.; Gyles, C.L. Associations between virulence factors of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and disease in humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 3, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werber, D.; Fruth, A.; Buchholz, U.; Prager, R.; Kramer, M.H.; Ammon, A.; Tschäpe, H. Strong Association Between Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O157 and Virulence Genes stx2 and eae as Possible Explanation for Predominance of Serogroup O157 in Patients with Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 22, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, M.; Bielaszewska, M.; Nakari, U.-M.; Karch, H.; Siitonen, A. Molecular and phenotypic profiling of sorbitol-fermenting Escherichia coli O157:H− human isolates from Finland. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schmidt, H.; Karch, H. Enterohemolytic phenotypes and genotypes of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O111 strains from patients with diarrhea and hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 10, 2364–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneike, I.; Zhang, H.-M.; Wakisaka-Saito, N.; Yamamoto, T. Enterohemolysin operon of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli: A virulence function of inflammatory cytokine production from human monocytes. FEBS Lett. 2002, 524, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhang, J.; Jernberg, C.; Chromek, M.; Hansson, S.; Frykman, A.; Yang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wan, C.; et al. Molecular characteristics of eae-positive clinical Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in Sweden. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matussek, A.; Jernberg, C.; Einemo, I.-M.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; Engelmann, I.; Löfgren, S.; Mernelius, S. Genetic makeup of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in relation to clinical symptoms and duration of shedding: A microarray analysis of isolates from Swedish children. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ehxA | No. (%) | p-Value | No. (%) | p-Value | No. (%) | p-Value | No. (%) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD (51) | NBS (128) | O157:H7 (65) | Non-O157 (174) | stx2a + stx2c (48) | Non-stx2a + stx2c (191) | eae + (173) | eae − (66) | |||||
| Positive | 47 (92.16) | 99 (77.34) | 0.021 * | 65 (100.00) | 134 (77.01) | <0.001 * | 48 (100.00) | 151 (79.06) | <0.001 * | 166 (95.95) | 33 (50.00) | <0.001 * |
| Negative | 4 (7.84) | 29 (22.66) | 0 (0.00) | 40 (22.99) | 0(0.00) | 40 (20.94) | 7(4.05) | 33 (50.00) | ||||
| ehxA Subtype | No. of Isolates | Genotype (No.) | Group (No.) | eae (No.) | Serotype (No.) | stx Subtype (No.) | Symptoms (No.) | Age Group (No.) | Duration of Bacterial Shedding (No.) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | |||||||||
| A | 29 | GT1 (3), GT2 (14), GT5 (1), GT6 (2), GT11 (3), GT12 (1), GT16 (2), GT17 (1), GT20 (2) | Ⅰ (29) | 0 | 29 | O91:H21 (3), O113:H4 (2), O146:H21 (2), O150:H10 (4), O128ab:H2 (2), O4:H16 (1), O117:H8 (2), O91:H14 (2), O117:H8 (2), O185:H28 (1), O5:H19 (1), Ont:H4 (1), O78:H4 (2), O175:H21 (1), O183:H18 (2), O126:H20 (1), O163:H19 (2) | stx2d (5), stx2b (6), stx1c (6), stx2a (1), stx1c + stx2b (5), stx1a + stx2b (2), stx1a + stx2a (4), stx1a + stx2d (2) | NBS (25), BD (4) | <10 years (11), ≥10 years (18) | Short (7),long (9),NA (13) |
| B | 65 | GT3 (46), GT18 (1), GT29 (18) | Ⅱ (65) | 65 | 0 | O157:H7 (65) | stx2a + stx2c (45), stx2c (9), stx2a (2), stx1a + stx2c (9) | HUS (32), BD (19), NBS (14) | <10 years (18), ≥10 years (16), NA (31) | Short (17), long (8), NA (40) |
| C | 76 | GT7 (2), GT8 (25), GT9 (1), GT13 (1), GT14 (2), GT15 (1), GT19 (1), GT21 (3), GT22 (3), GT23 (1), GT28 (1), GT30 (35) | Ⅱ (76) | 74 | 2 | O84:H2 (1), O98:H21 (1), O121:H19 (25), O26:H11 (35), O111:H8 (4), O180:H2 (1), O165:H25 (4), O145:H28 (3), O103:H8 (1), O103:H2 (1) | stx1a (36), stx2a (33), stx1a + stx2a (4), stx2a + stx2c (3) | HUS (21), BD (20), NBS (35) | <10 years (36), ≥10 years (21), NA (19) | Short (21), long (19), NA (36) |
| D | 2 | GT26 (1), GT27 (1) | Ⅲ (2) | 0 | 2 | O187:H28 (1), O136:H12 (1) | stx2g (1), stx2a (1) | NBS (2) | <10 years (1), ≥10 years (1) | Short (2) |
| F | 27 | GT4 (20), GT10 (3), GT24 (2), GT25 (2) | Ⅱ (27) | 27 | 0 | O103:H2 (18), O123:H2 (3), O71:H2 (1), O177:H25 (3), O5:H9 (2) | stx1a (24), stx2c (24) | NBS (23), BD (4) | <10 years (21), ≥10 years (6) | Short (12), long (13), NA (2) |
| ehxA + eae | No. (%) | p-Value | No. (%) | p-Value | No. (%) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-HUS (146) | HUS (53) | <10 Years of Age (87) | ≥10 Years of Age (62) | O157:H7 (65) | Non-O157 (134) | ||||
| + | 114 (78.08) | 52 (98.11) | <0.001 * | 75 (86.21) | 42 (67.74) | <0.001 * | 65 (100.00) | 101 (75.37) | <0.001 * |
| − | 32(21.92) | 1 (1.89) | 12 (13.79) | 20 (32.26) | 0 (0.00) | 33 (24.63) | |||
| stx Subtype | ehxA Subtype (No. Isolates) | p-Value | BH-Corrected p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| stx1 | F (27) | Non-F (172) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| + | 24 (88.89) | 42 (24.12) | ||
| − | 3 (11.11) | 130 (75.58) | ||
| stx1a | F (27) | Non-F (172) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| + | 24 (88.89) | 36 (20.93) | ||
| − | 3 (11.11) | 136 (79.07) | ||
| stx2 | B (65) | Non-B (134) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| + | 56 (86.15) | 51 (38.06) | ||
| − | 9 (13.85) | 83 (61.94) | ||
| stx2a + stx2c | B (65) | Non-B (134) | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| + | 45 (69.23) | 3 (2.24) | ||
| − | 20 (30.77) | 131 (97.76) | ||
| ehxA Subtype | No. Isolates | Symptoms | Age Group | Serotypes | eae | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBS (99) | BD (47) | p-Value | BH-Corrected p-Value | Non-HUS (146) | HUS (53) | p-Value | BH-Corrected p-Value | <10 Years (87) | ≥10 Years (62) | p-Value | BH-Corrected p-Value | O157:H7 (65) | non-O157 (134) | p-Value | BH-Corrected p-Value | Positive (166) | Negative (33) | p-Value | BH-Corrected p-Value | ||||||||||||
| Pos | Prevalence | Pos | Prevalence | Pos | Prevalence | Pos | Prevalence | Pos | Prevalence | Pos | Prevalence | Pos | Prevalence | Pos | Prevalence | Pos | Prevalence | Pos | Prevalence | ||||||||||||
| A | 29 | 25 | 25.25% | 4 | 8.51% | 0.018 * | 0.535 | 29 | 19.86% | 0 | 0.00% | <0.001 * | 0.013 * | 11 | 12.64% | 18 | 29.03% | 0.013 * | 0.383 | 0 | 0.00% | 29 | 21.64% | <0.001 * | 0.002 * | 0 | 0.00% | 29 | 87.88% | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| B | 33 | 14 | 14.14% | 19 | 40.43% | <0.01 * | 0.012 * | 33 | 22.60% | 32 | 60.38% | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | 18 | 20.69% | 16 | 25.81% | 0.463 | 1.000 | 65 | 100.00% | 0 | 0.00% | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | 65 | 39.16% | 0 | 0.00% | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| C | 55 | 35 | 35.35% | 20 | 42.55% | 0.402 | 1.000 | 55 | 37.67% | 21 | 39.62% | 0.802 | 1.000 | 36 | 41.38% | 21 | 33.87% | 0.353 | 1.000 | 0 | 0.00% | 76 | 56.72% | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | 74 | 44.58% | 2 | 6.06% | <0.001 * | 0.001 * |
| D | 2 | 2 | 2.02% | 0 | 0.00% | 0.327 | 1.000 | 2 | 1.37% | 0 | 0.00% | 0.392 | 1.000 | 1 | 50.00% | 1 | 50.00% | 0.809 | 1.000 | 0 | 0.00% | 2 | 1.49% | 0.32 | 1.000 | 0 | 0.00% | 2 | 6.06% | 0.027 * | 0.810 |
| F | 27 | 23 | 23.23% | 4 | 8.51% | 0.032 | 0.969 | 27 | 18.49% | 0 | 0.00% | <0.001 * | 0.023 * | 21 | 24.14% | 6 | 9.68% | 0.024 * | 0.717 | 0 | 0.00% | 27 | 20.15% | <0.001 * | 0.003 * | 27 | 16.27% | 0 | 0.00% | 0.013 * | 0.381 |
| ehxA Group | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group Ⅰ | 29 | 25 | 25.25% | 4 | 8.51% | 0.018 * | 0.321 | 29 | 19.86% | 0 | 0.00% | <0.001 * | 0.008 * | 11 | 12.64% | 18 | 29.03% | 0.013 * | 0.230 | 0 | 0.00% | 29 | 21.64% | <0.001 * | 0.001 * | 0 | 0.00% | 29 | 87.88% | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Group Ⅱ | 115 | 72 | 72.73% | 43 | 91.49% | <0.01 * | 0.173 | 115 | 78.77% | 53 | 100.00% | <0.001 * | 0.005 * | 75 | 86.21% | 43 | 69.35% | 0.012 * | 0.225 | 65 | 100.00% | 103 | 76.87% | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | 166 | 100.00% | 2 | 6.06% | <0.001 * | <0.001 * |
| Group Ⅲ | 2 | 2 | 2.02% | 0 | 0.00% | 0.327 | 1.000 | 2 | 1.37% | 0 | 0.00% | 0.392 | 1.000 | 1 | 50.00% | 1 | 50.00% | 0.809 | 1.000 | 0 | 0.00% | 2 | 1.49% | 0.322 | 1.000 | 0 | 0.00% | 2 | 6.06% | 0.027 * | 0.486 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jernberg, C.; Chromek, M.; Hansson, S.; Frykman, A.; Xiong, Y.; Wan, C.; Matussek, A.; Bai, X. Molecular Characterization of the Enterohemolysin Gene (ehxA) in Clinical Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Isolates. Toxins 2021, 13, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010071
Hua Y, Zhang J, Jernberg C, Chromek M, Hansson S, Frykman A, Xiong Y, Wan C, Matussek A, Bai X. Molecular Characterization of the Enterohemolysin Gene (ehxA) in Clinical Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Isolates. Toxins. 2021; 13(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010071
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Ying, Ji Zhang, Cecilia Jernberg, Milan Chromek, Sverker Hansson, Anne Frykman, Yanwen Xiong, Chengsong Wan, Andreas Matussek, and Xiangning Bai. 2021. "Molecular Characterization of the Enterohemolysin Gene (ehxA) in Clinical Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Isolates" Toxins 13, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010071
APA StyleHua, Y., Zhang, J., Jernberg, C., Chromek, M., Hansson, S., Frykman, A., Xiong, Y., Wan, C., Matussek, A., & Bai, X. (2021). Molecular Characterization of the Enterohemolysin Gene (ehxA) in Clinical Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Isolates. Toxins, 13(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010071






