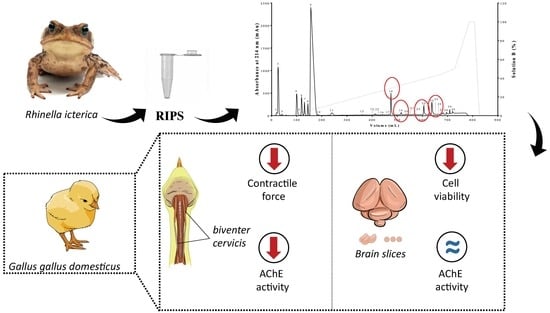
Chemical and Pharmacological Screening of Rhinella icterica (Spix 1824) Toad Parotoid Secretion in Avian Preparations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Biochemical Characterization of RIPS by FPLC
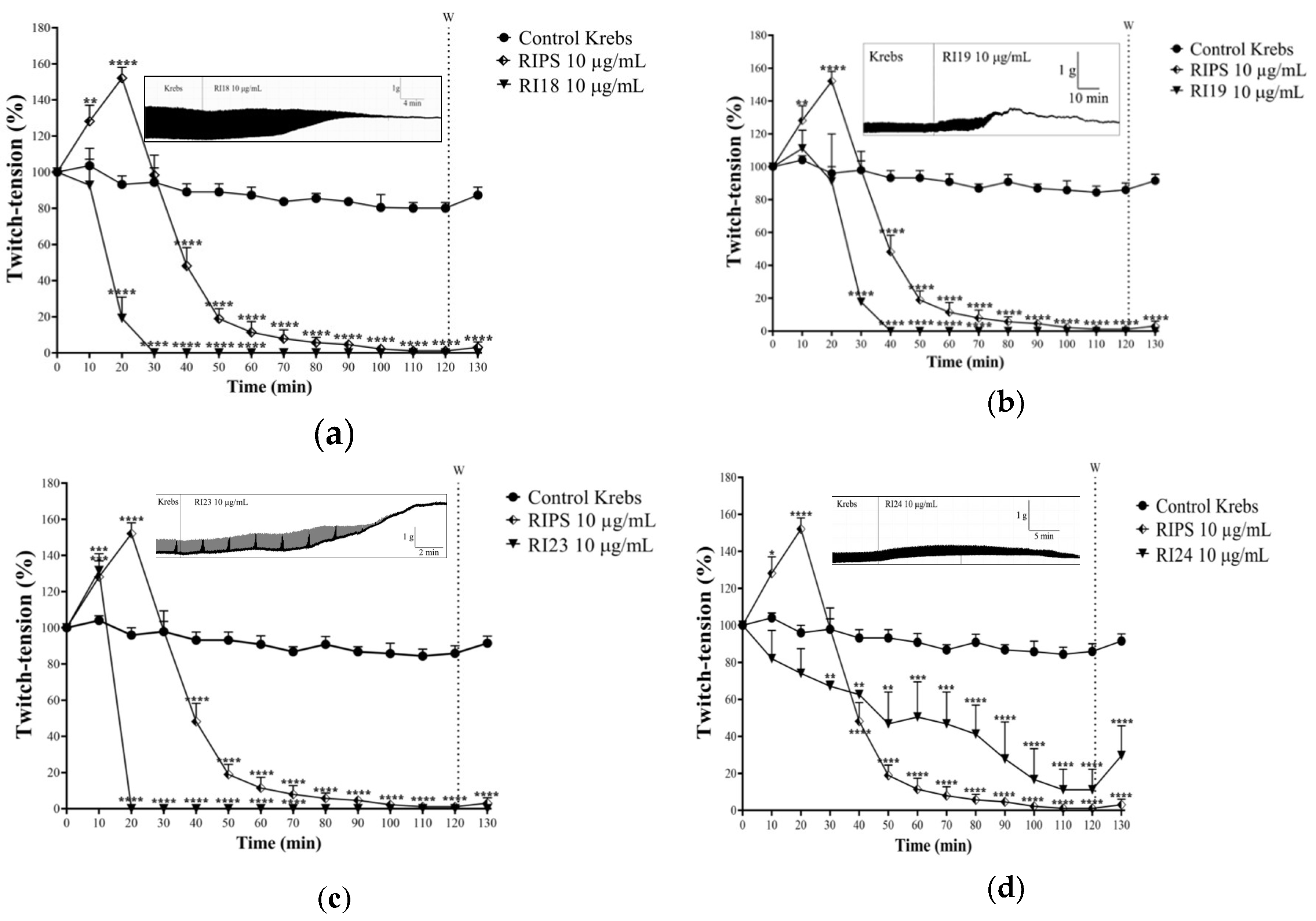
2.2. Neuromuscular Blockade Caused by RIPS and Its Fractions in Chick Biventer Cervicis Preparations
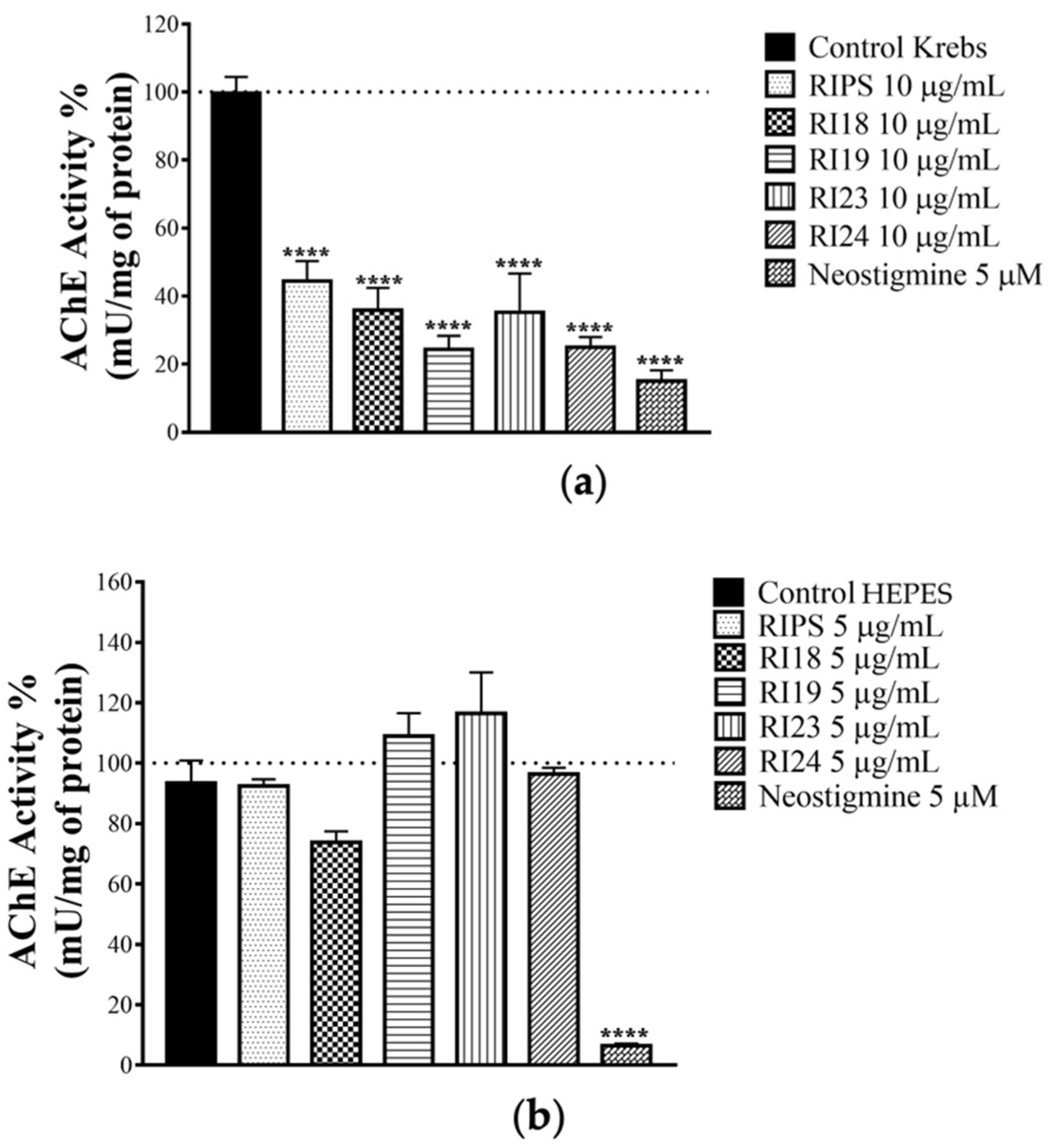
2.3. Effect of RIPS Fractions on Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity
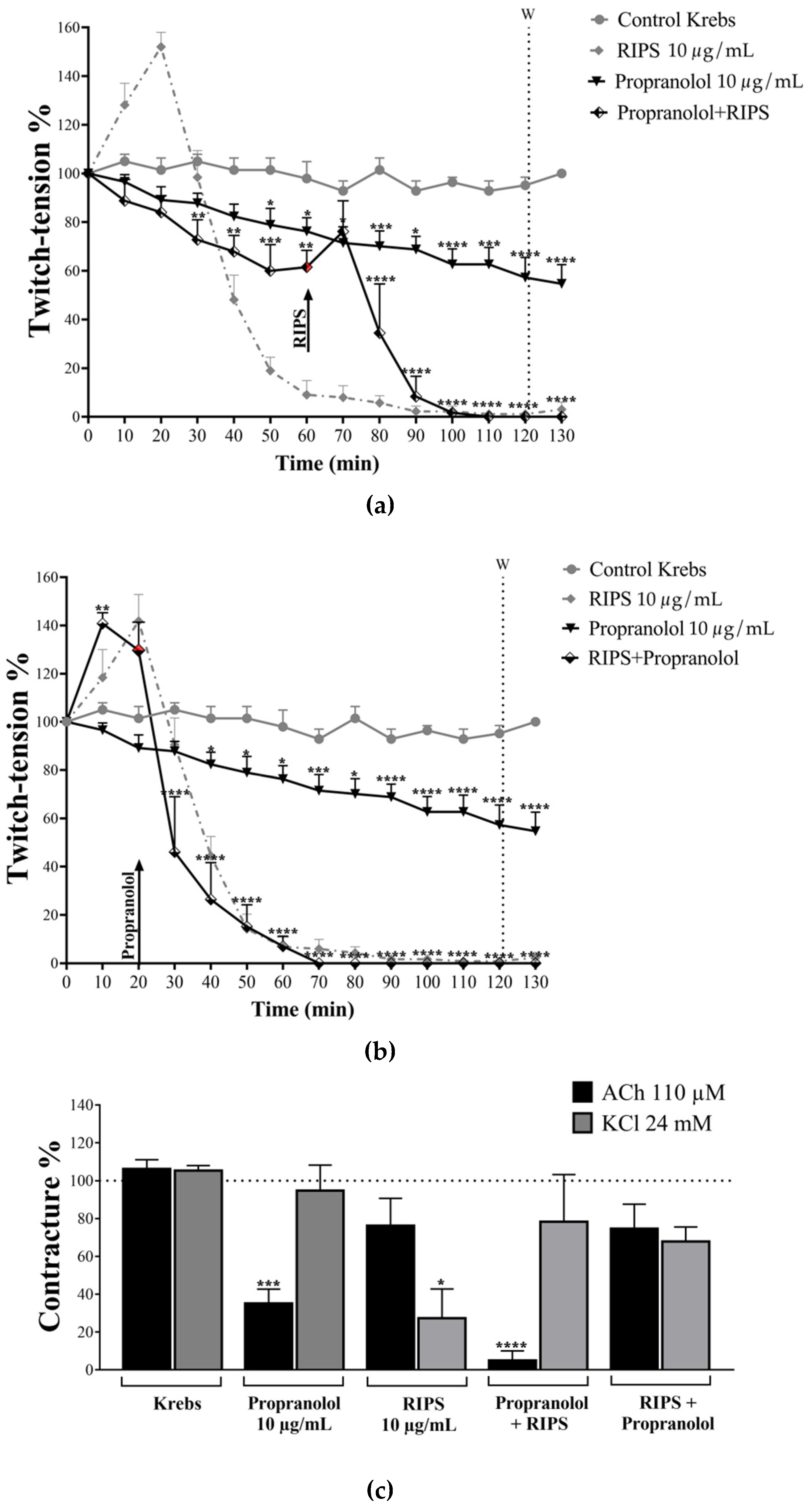
2.4. Effect of RIPS on Propranolol-Induced Neuromuscular Blockade
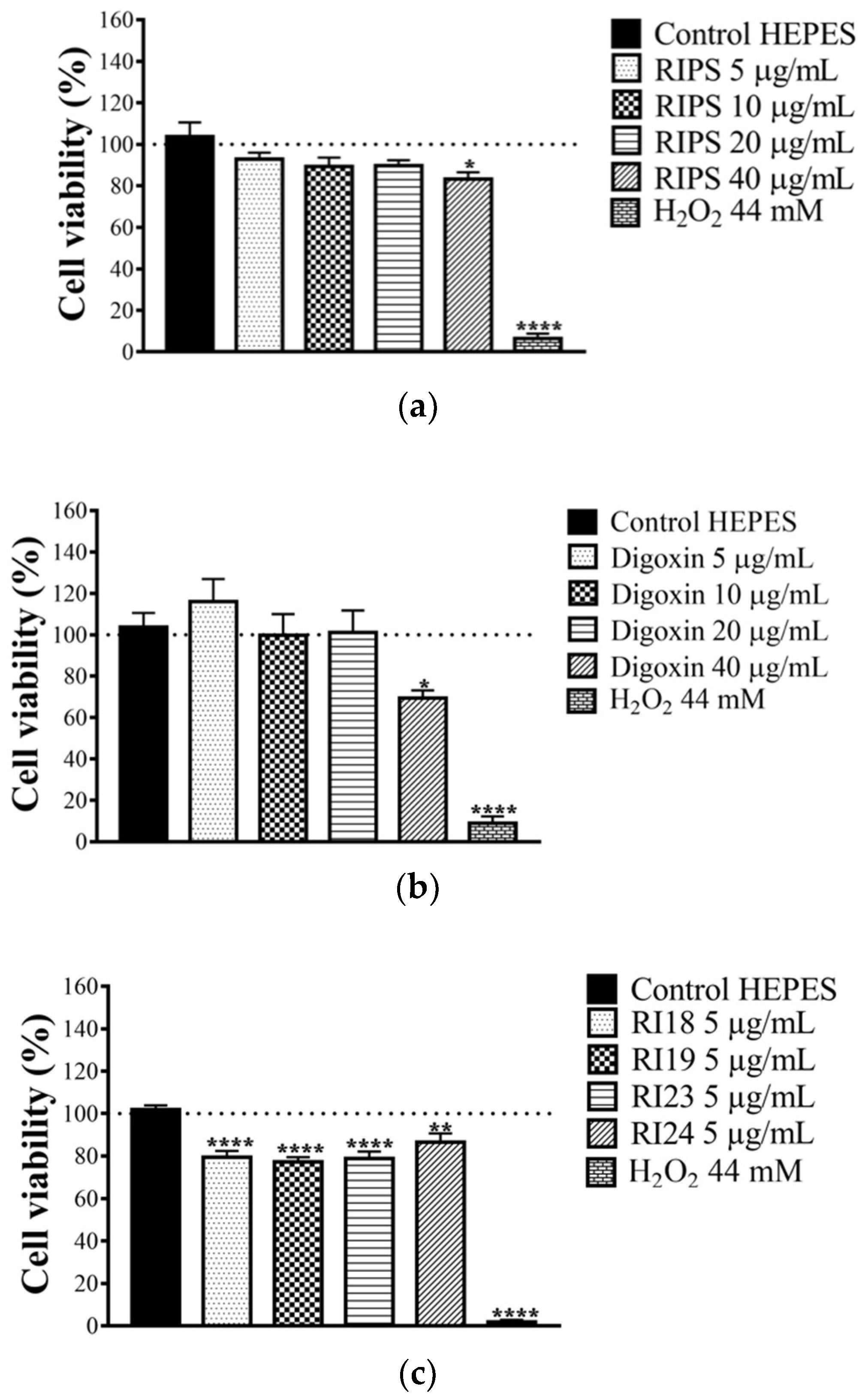
2.5. Cell Viability in the Presence of RIPS and Its Fractions
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents and Secretion Collection
5.2. Animals
5.3. RP-FPLC of Parotoid Secretion
5.4. High Resolution Mass Spectrometry
5.5. Biological Assays
5.5.1. Tissue Slice Preparation and Treatment
5.5.2. Cell Viability
5.5.3. Chick Biventer Cervicis Preparation
5.5.4. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frost, D.R. Amphibian Species of the World: An Online Reference; American Museum of Natural History: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Available online: http://research.amnh.org/herpetology/amphibia/index.html (accessed on 16 July 2019).
- Marques, A.A.B. Lista das Espécies da Fauna Ameaçadas de Extinção no Rio Grande do Sul. Decreto n. 41.672, de 11 junho de 2002, FZB/MCT–PUCRS/PANGEA, Porto Alegre, 00155. 2002. Available online: http://www.tecniflora.com.br/fauna_ameacada_RS.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2019).
- Segalla, M.V.; Caramaschi, U.; Cruz, C.A.G.; Garcia, P.C.A.; Grant, T.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Santana, D.J.; Toledo, L.F.; Langone, J.A. Herpetologia Brasileira; Sociedade Brasileira de Herpetologia, 2019; Available online: http://sbherpetologia.org.br/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/hb-2019-01.pdf (accessed on 14 July 2019).
- Kowalski, K.; Marciniak, P.; Rosiński, G.; Rychlik, L. Toxic activity and protein identification from the parotoid gland secretion of the common toad Bufo bufo. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 205, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zulfiker, A.H.M.; Li, C.; Good, D.; Wei, M.Q. The development of toad toxins as potential therapeutic agents. Toxins 2018, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, C.; Rollins-Smith, L.; Ibáñez, R.; Durant-Archibold, A.A.; Gutiérrez, M. Toxins and pharmacologically active compounds from species of the family Bufonidae (Amphibia, Anura). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 198, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, C. Advancing drug discovery with reptile and amphibian venom peptides—Venom-based medicines. Biochemist 2009, 31, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.M. Structure-function strategies to improve the pharmacological value of animal toxins. In Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides; Kastin, A.J., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bücherl, W.; Buckley, E.E. (Eds.) Venomous Animals and their Venoms. Vol. 2. Venomous Vertebrates; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saporito, R.A.; Donnelly, M.A.; Spande, T.F.; Garraffo, H.M. A review of chemical ecology in poison frogs. Chemoecology 2012, 22, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lai, R. The chemistry and biological activities of peptides from amphibian skin secretions. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1760–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, J.W. The chemistry of poisons in amphibian skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciani, J.M.; Angeli, C.B.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Jared, C.; Pimenta, D.C. Differences and similarities among parotoid macrogland secretions in South American toads: A preliminary biochemical delineation. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 937407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, R.C.; Jared, C. Cutaneous granular glands and amphibian venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1995, 111, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Filho, G.A.; Resck, I.S.; Cavalcanti, B.C.; Pessoa, C.Ó.; Moraes, M.O.; Ferreira, J.R.O.; Rodrigues, F.A.R.; dos Santos, M.L. Cytotoxic profile of natural and some modified bufadienolides from toad Rhinella schneideri parotoid gland secretion. Toxicon 2010, 56, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jared, S.G.S.; Jared, C.; Egami, M.I.; Mailho-Fontana, P.L.; Rodrigues, M.T.; Antoniazzi, M.M. Functional assessment of toad parotoid macroglands: A study based on poison replacement after mechanical compression. Toxicon 2014, 87, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.J.; Tian, H.Y.; Zhang, D.M.; Lei, Y.H.; Wang, L.; Jiang, R.W.; Ye, W.C. Bufadienolides with cytotoxic activity from the skins of Bufo bufo gargarizans. Fitoterapia 2015, 105, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, L.Q.; Machado, K.C.; Oliveira, S.F.D.C.; Araújo, L.S.; Monção-Filho, E.S.; Melo-Cavalcante, A.A.C.; Vieira-Júnior, G.M.; Ferreira, P.M.P. Bufadienolides from amphibians: A promising source of anticancer prototypes for radical innovation, apoptosis triggering and Na+/K+-ATPase inhibition. Toxicon 2017, 127, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.L.; Lan, R.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.J.; Jia, J.M. A new cytotoxic bufadienolide from Chinese medicine Chansu. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2008, 19, 1445–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Guo, H.; Guo, H.; Han, J.; Guo, D. Simultaneous determination of cytotoxic bufadienolides in the Chinese medicine ChanSu by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with photodiode array and mass spectrometry detections. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 838, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadelha, I.C.N.; De Lima, J.M.; Batista, J.S.; Melo, M.M.; Soto-Blanco, B. Toxicity effects of toad (Rhinella jimi Stevaux, 2002) venom in chicken (Gallus gallus domesticus). Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Mata, É.C.G.; Mourão, C.B.F.; Rangel, M.; Schwartz, E.F. Antiviral activity of animal venom peptides and related compounds. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Kamano, Y. Bufadienolides. 21. Synthesis of cinobufagin from bufotalin. J. Org. Chem. 1972, 37, 4040–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.F.; Castoldi, L.; Vieira Junior, G.M.; Monção Filho, E.S.; Chaves, M.H.; Rodrigues, D.J.; Sugui, M.M. Evaluation of antimutagenic and cytotoxic activity of skin secretion extract of Rhinella marina and Rhaebo guttatus (Anura, Bufonidae). Acta Amaz. 2019, 49, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha Filho, G.A.; Schwartz, C.A.; Resck, I.S.; Murta, M.M.; Lemos, S.S.; Castro, M.S.; Kyaw, C.; Pires, O.R., Jr.; Leite, J.R.S.; Bloch, C., Jr.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of the bufadienolides marinobufagin and telocinobufagin isolated as major components from skin secretion of the toad Bufo rubescens. Toxicon 2005, 45, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempone, A.G.; Pimenta, D.C.; Lebrun, I.; Sartorelli, P.; Taniwaki, N.N.; de Andrade, H.F.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Jared, C. Antileishmanial and antitrypanosomal activity of bufadienolides isolated from the toad Rhinella jimi parotoid macrogland secretion. Toxicon 2008, 52, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, A.P.; Oliveira, R.S.; Perin, A.P.A.; Borges, B.T.; Vieira, P.B.; dos Santos, T.G.; Valsecchi, C.; Vinadé, L.; Belo, C.A.D. Entomotoxic activity of Rhinella icterica (Spix, 1824) toad skin secretion in Nauphoeta cinerea cockroaches: An octopamine-like modulation. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 148, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supratman, U.; Fujita, T.; Akiyama, K.; Hayashi, H. New insecticidal bufadienolide, bryophyllin C, from Kalanchoe pinnata. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 1310–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neerati, P. Detection of antidiabetic activity by crude paratoid gland secretions from common Indian toad (Bufomelano stictus). J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2015, 6, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Quispe, C.; Theoduloz, C.; De Sousa, P.T.; Parizotto, C. Antiproliferative activity and new argininyl bufadienolide esters from the “cururú” toad Rhinella (Bufo) schneideri. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Quispe, C.; Arana, G.V.; Theoduloz, C.; Urra, F.A.; Cárdenas, C. Antiproliferative activity and chemical composition of the venom from the Amazonian toad Rhinella marina (Anura: Bufonidae). Toxicon 2016, 121, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, J.R.; González, J.A. Los anfibios en la medicina popular española, la farmacopea de Plinio y el Dioscórides. História Ciências Saúde Manguinhos 2015, 22, 1283–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Gong, X. Bufalin induces the interplay between apoptosis and autophagy in glioma cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cui, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, N.; Yoshikawa, M. Quality evaluation of traditional Chinese drug toad venom from different origins through a simultaneous determination of bufogenins and indole alkaloids by HPLC. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.M.P.; Lima, D.J.B.; Debiasi, B.W.; Soares, B.M.; Machado, K.C.; Noronha, J.C.; Rodrigues, D.J.; Sinhorin, A.P.; Pessoa, C.; Vieira Júnior, G.M. Antiproliferative activity of Rhinella marina and Rhaebo guttatus venom extracts from southern Amazon. Toxicon 2013, 72, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailho-Fontana, P.L.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Sciani, J.M.; Pimenta, D.C.; Barbaro, K.C.; Jared, C. Morphological and biochemical characterization of the cutaneous poison glands in toads (Rhinella marina group) from different environments. Front. Zool. 2018, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, P.; Kindel, A.; Vinciprova, G.; Krause, L. Composição e ameaças à conservação dos anfíbios anuros do Parque Estadual de Itapeva, município de Torres, Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Biota Neotrop. 2008, 8, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, É.G.; Felipe, A.C.; Nadaletto, D.; Rall, V.L.M.; Martinez, R.M. Investigação da atividade antimicrobiana do veneno de Rhinella icterica (Amphibia, Anura). Rev. Inst. Adolfo Lutz 2009, 68, 471–475. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, R.S.; Leal, A.P.; Ogata, B.; de Almeida, C.G.M.; dos Santos, D.S.; Lorentz, L.H.; Moreira, C.M.; Bordon, K.C.F.; Arantes, E.C.; dos Santos, T.G.; et al. Mechanism of Rhinella icterica (Spix, 1824) toad poisoning using in vitro neurobiological preparations. Neurotoxicology 2018, 65, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryukova, E.V.; Lebedev, D.S.; Ivanov, I.A.; Ivanov, D.A.; Starkov, V.G.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. N-methyl serotonin analogues from the Bufo bufo toad venom interact efficiently with the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2017, 472, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Harari, R.R.; Dalton, B.A.; Osman, R.; Maayani, S. Kinetic characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor desensitization in isolated guinea-pig trachea and rabbit aorta. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1991, 257, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Takagi, N.; Yuan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Si, N.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Wei, X.; Zhao, H.; Bian, B. The protection of indolealkylamines from LPS-induced inflammation in zebrafish. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 243, 112122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, B.; Takagi, N.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Si, N.; Yang, J.; Wei, X.; Zhao, H.; Bian, B. Comparative analysis of hydrophilic ingredients in toad skin and toad venom using the UHPLC-HR-MS/MS and UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS methods together with the anti-inflammatory evaluation of indolealkylamines. Molecules 2019, 24, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Han, L.; Luo, M.; Bian, B.; Guan, M.; Yang, H.; Han, C.; Li, N.; Li, T.; Li, S.; et al. Multi-component identification and target cell-based screening of potential bioactive compounds in toad venom by UPLC coupled with high-resolution LTQ-Orbitrap MS and high-sensitivity Qtrap MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4419–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamboj, A.; Rathour, A.; Kaur, M. Bufadienolides and their medicinal utility: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.Y.; Zhang, P.W.; Liu, J.S.; Zhang, D.M.; Zhang, X.Q.; Jiang, R.W.; Ye, W.C. New cytotoxic C-3 dehydrated bufadienolides from the venom of Bufo bufo gargarizans. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 1104–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoner, W.; Scheiner-Bobis, G. Endogenous cardiac glycosides: Hormones using the sodium pump as signal transducer. Semin. Nephrol. 2005, 25, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagrov, A.Y.; Shapiro, J.I.; Fedorova, O.V. Endogenous cardiotonic steroids: Physiology, pharmacology, and novel therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Rev. 2009, 61, 9–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Ruan, Z.; Deng, L.; Wang, L.; Tian, H.; Yiu, A.; Fan, C.; et al. Discovery of bufadienolides as a novel class of ClC-3 chloride channel activators with antitumor activities. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5734–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Jiang, N.; Yu, C.; Li, S.; Chun, Z.; Zhu, X.; Song, C.; Xiao, Y.; Hui, J.; Qin, Y.; et al. Bufadienolides from the skins of Bufo melanosticus and their cytotoxic activity. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 31, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukawa, M.; Akizawa, T.; Ohigashi, M.; Morris, J.F.; Butler, V.P., Jr.; Yoshioka, M. A novel bufadienolide, marinosin, in the skin of the giant toad, Bufo marinus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akizawa, T.; Mukai, T.; Matsukawa, M.; Yoshioka, M.; Morris, J.F.; Butler, V.P., Jr. Structures of novel bufadienolides in the eggs of a toad, Bufo marinus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 754–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.; Banuls, Y.; Urban, E.; Gelbcke, M.; Dufrasne, F.; Kopp, B.; Kiss, R.; Zehl, M. Structure-activity relationship analysis of bufadienolide-induced in vitro growth inhibitory effects on mouse and human cancer cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera Córdova, W.H.; Leitão, S.G.; Cunha-Filho, G.; Bosch, R.A.; Alonso, I.P.; Pereda-Miranda, R.; Gervou, R.; Touza, N.A.; Quintas, L.E.M.; Noël, F. Bufadienolides from parotoid gland secretions of Cuban toad Peltophryne fustiger (Bufonidae): Inhibition of human kidney Na+/K+-ATPase activity. Toxicon 2016, 110, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, T.; Paiusco, A.D.; Kohl, L. Digitalis toxicity caused by toad venom. Chest 1992, 102, 949–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.L.; Lin, T.Y.; Lin, C.N.; Won, S.J. Involvement of caspases and apoptosis-inducing factor in bufotalin-induced apoptosis of hep 3B cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.M.; Liu, J.S.; Tang, M.K.; Yiu, A.; Cao, H.H.; Jiang, L.; Yuet-Wa Chan, J.; Tian, H.Y.; Fung, K.P.; Ye, W.C. Bufotalin from Venenum Bufonis inhibits growth of multidrug resistant HepG2 cells through G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 692, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Ro, J.S.; Ohishi, K.; Nambara, T. Isolation and characterization of cinobufagin 3-glutaroyl-L-arginine ester from Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1985, 33, 2767–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukawa, M.; Akizawa, T.; Morris, J.F.; Butler, V.P., Jr.; Yoshioka, M. Marinoic acid, a novel bufadienolide-related substance in the skin of the giant toad, Bufo marinus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 44, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazit, V. Biological activities of nanomaterials (bufadienolides, peptides and alkoloids) in the skin of amphibian on Gammarus pulex L. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2010, 5, 347–354. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, I.G. The effects of some hemicholinium-like substances on the chick biventer cervicis muscle preparation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1969, 8, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimann, C.; Torri-Tarelli, F.; Fesce, R.; Ceccarelli, B. Measurement of quantal secretion induced by ouabain and its correlation with depletion of synaptic vesicles. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 101, 1953–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wislicki, L.; Rosenblum, I. Effects of propranolol on the action of neuromuscular blocking drugs. Br. J. Anaesth. 1967, 39, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Whittaker, M.; Wicks, R.J.; Britten, J.J. Studies on the inhibition by propranolol of some human erythrocyte membrane enzymes and plasma cholinesterase. Clin. Chim. Acta 1982, 119, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Chu, X.; Zhang, X.; tao Song, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Zhang, J.; Chu, L. Bufalin, a bufadienolide steroid from the parotoid glands of the Chinese toad inhibits L-type Ca2+ channels and contractility in rat ventricular myocytes. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2017, 31, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, B.M.; Oliver, K.L.; Engel, W.K. Serotonin-induced muscle weakness. Arch. Neurol. 1974, 31, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, H.Y. Skeletal muscle necrosis following membrane-active drugs plus serotonin. J. Neurol. Sci. 1976, 28, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.S.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, Y.; Melcher, K.; Xu, H.E. Ion channels gated by acetylcholine and serotonin: Structures, biology, and drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, M.; Gurley, D.; Dabrowski, M.; Larsson, O.; Johnson, E.C.; Eriksson, L.I. Distinct pharmacologic properties of neuromuscular blocking agents on human neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: A possible explanation for the train-of-four fade. Anesthesiology 2006, 105, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haerter, F.; Eikermann, M. Reversing neuromuscular blockade: Inhibitors of the acetylcholinesterase versus the encapsulating agents sugammadex and calabadion. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2016, 17, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivoi, I.I.; Drabkina, T.M.; Kravtsova, V.V.; Vasiliev, A.N.; Eaton, M.J.; Skatchkov, S.N.; Mandel, F. On the functional interaction between nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and Na+,K+-ATPase. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2006, 452, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anadón, A.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Valerio, L.G. Onchidal and fasciculins. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents, 2nd ed.; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Belo, C.A.; Lucho, A.P.B.; Vinadé, L.; Rocha, L.; Seibert França, H.; Marangoni, S.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L. In vitro antiophidian mechanisms of Hypericum brasiliense Choisy standardized extract: Quercetin-dependent neuroprotection. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 943520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, A.; Takada-Takatori, Y.; Kume, T.; Izumi, Y. Mechanisms of neuroprotective effects of nicotine and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Role of α4 and α7 receptors in neuroprotection. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2010, 40, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahuguna, A.; Khan, I.; Bajpai, V.K.; Kang, S.C. MTT assay to evaluate the cytotoxic potential of a drug. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2017, 12, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvela, M.; Rosen, H.; Ben-Ami, H.C.; Lichtstein, D. Endogenous ouabain regulates cell viability. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012, 302, C442–C452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada-Takatori, Y.; Kume, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Katsuki, H.; Sugimoto, H.; Akaike, A. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease prevent glutamate neurotoxicity via nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase cascade. Neuropharmacology 2006, 51, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvir, H.; Silman, I.; Harel, M.; Rosenberry, T.L.; Sussman, J.L. Acetylcholinesterase: From 3D structure to function. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 187, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, H.M.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. Structural studies on vertebrate and invertebrate acetylcholinesterases and their complexes with functional ligands. Drug Dev. Res. 2000, 50, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhoff, J.; Noronha, J.C.; Bonfilio, R.; Sinhorin, A.P.; Rodrigues, D.J.; Chaves, M.H.; Vieira, G.M. Quantification of bufadienolides in the poisons of Rhinella marina and Rhaebo guttatus by HPLC-UV. Toxicon 2016, 119, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babula, P.; Masarik, M.; Adam, V.; Provaznik, I.; Kizek, R. Na+/K+-ATPase and cardiac glycosides to cytotoxicity and cancer treatment. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1069–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Oliveira, S.; Rostelato-Ferreira, S.; Rocha-e-Silva, T.A.A.; Randazzo-Moura, P.; Dal-Belo, C.A.; Sanchez, E.F.; Borja-Oliveira, C.R.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L. Beneficial effect of crotamine in the treatment of myasthenic rats. Muscle Nerve 2013, 47, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, L.S.; Lara, M.V.; Gonçalves, R.; Mandredini, V.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S.; Dal Belo, C.A.; Mello-Carpes, P.B. The intrahippocampal infusion of crotamine from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom enhances memory persistence in rats. Toxicon 2014, 85, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostelato-Ferreira, S.; Dal Belo, C.A.; Leite, G.B.; Hyslop, S.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L. Presynaptic neuromuscular action of a methanolic extract from the venom of Rhinella schneideri toad. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 20, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibao, P.Y.T.T.; Anjolette, F.A.P.P.; Lopes, N.P.; Arantes, E.C. First serine protease inhibitor isolated from Rhinella schneideri poison. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schagger, H.; Von Jagow, G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 166, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavran, J.M.; Leahy, D.J. Laboratory Methods in Enzymology: Protein Part C. In Methods in Enzymology; Lorsch, J., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinadé, L.; Rodnight, R. The dephosphorylation of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the immature rat hippocampus is catalyzed mainly by a type 1 protein phosphatase. Brain Res. 1996, 732, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsborg, B.L.; Warriner, J. The isolated chick biventer cervicis nerve-muscle preparation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1960, 15, 410–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostelato-Ferreira, S.; Dal Belo, C.A.; Silva Junior, P.I.; Hyslop, S.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Rocha-e-Silva, T.A.A. Presynaptic activity of an isolated fraction from Rhinella schneideri poison. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 8, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.J.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
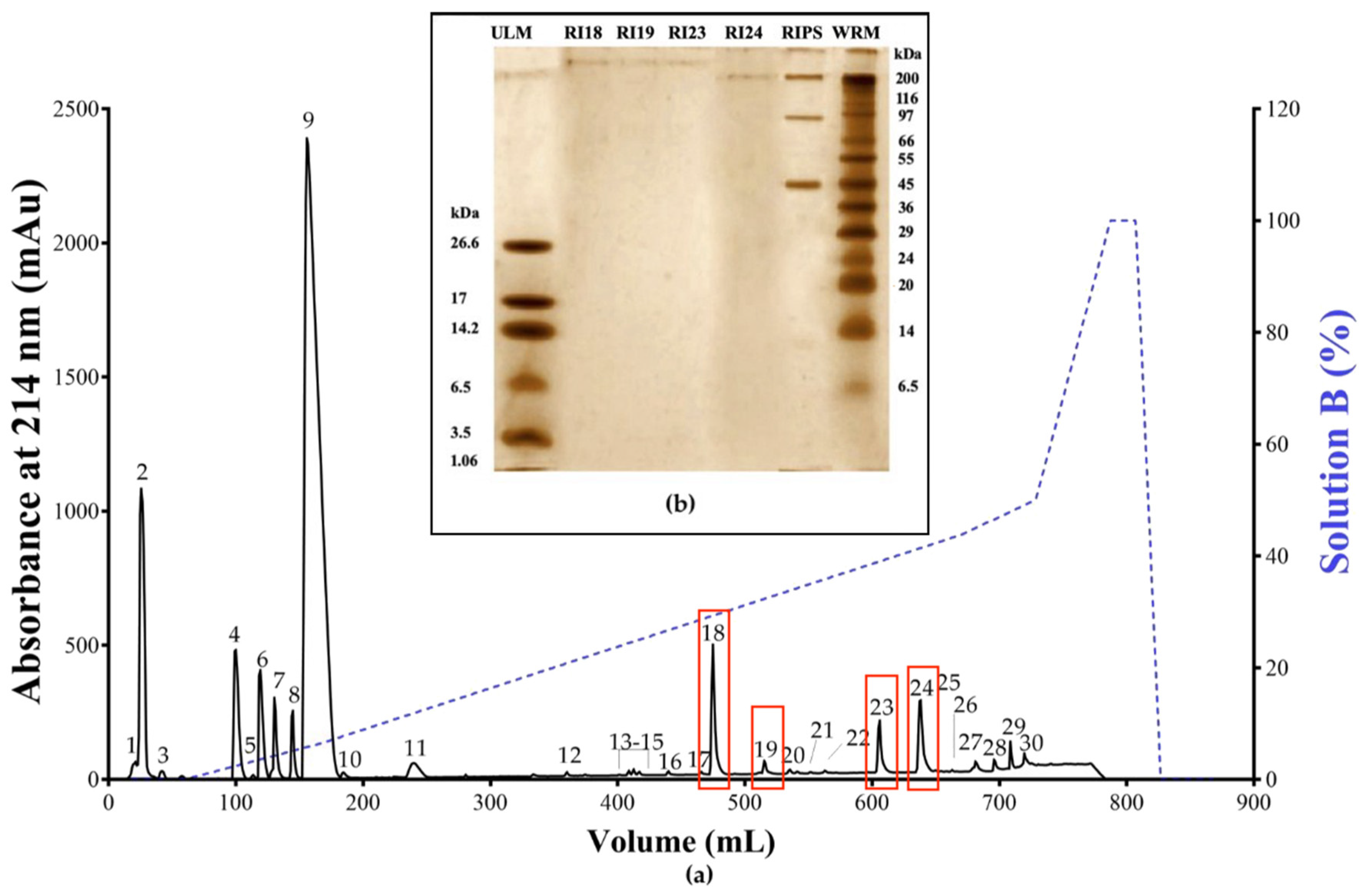
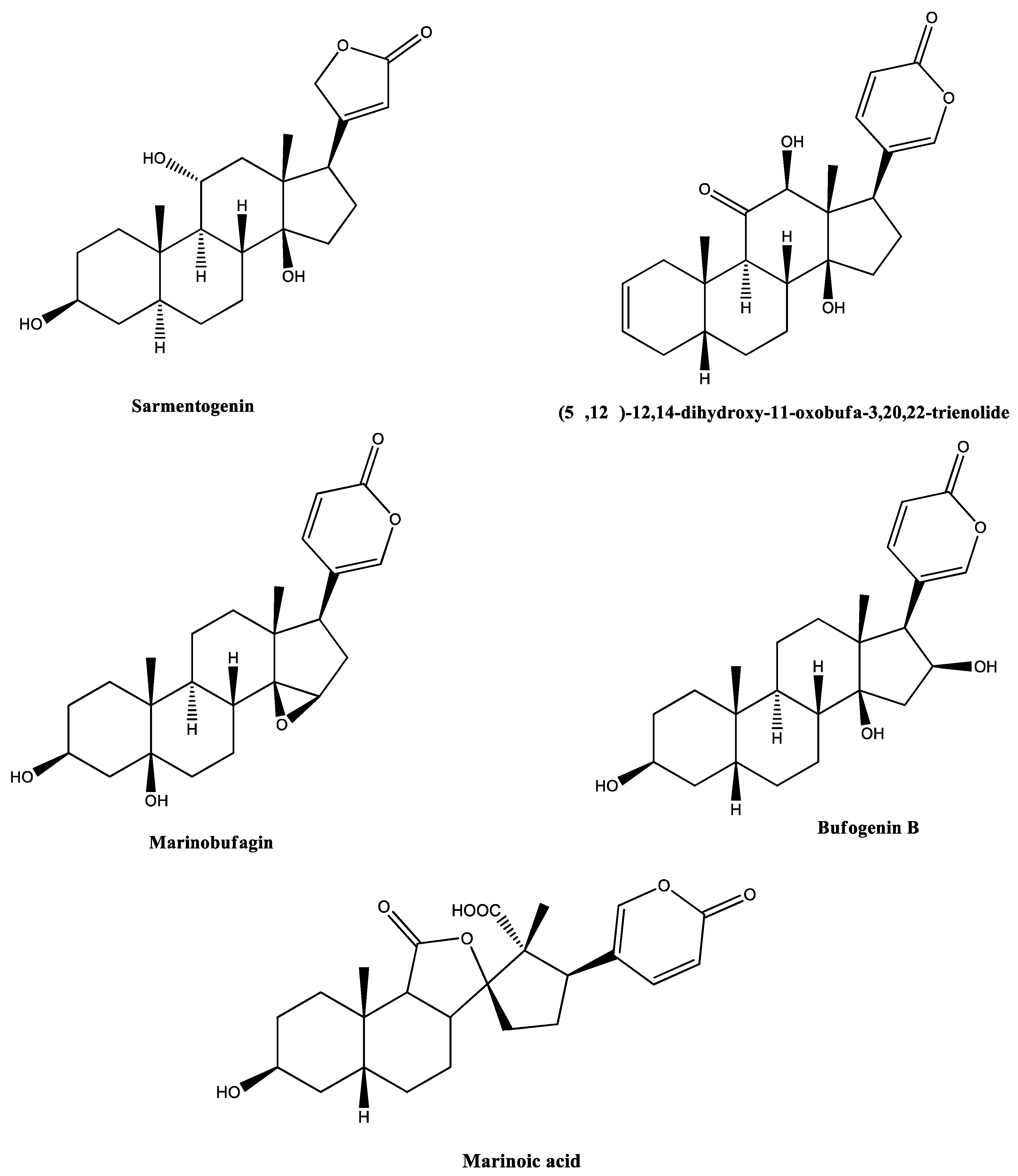
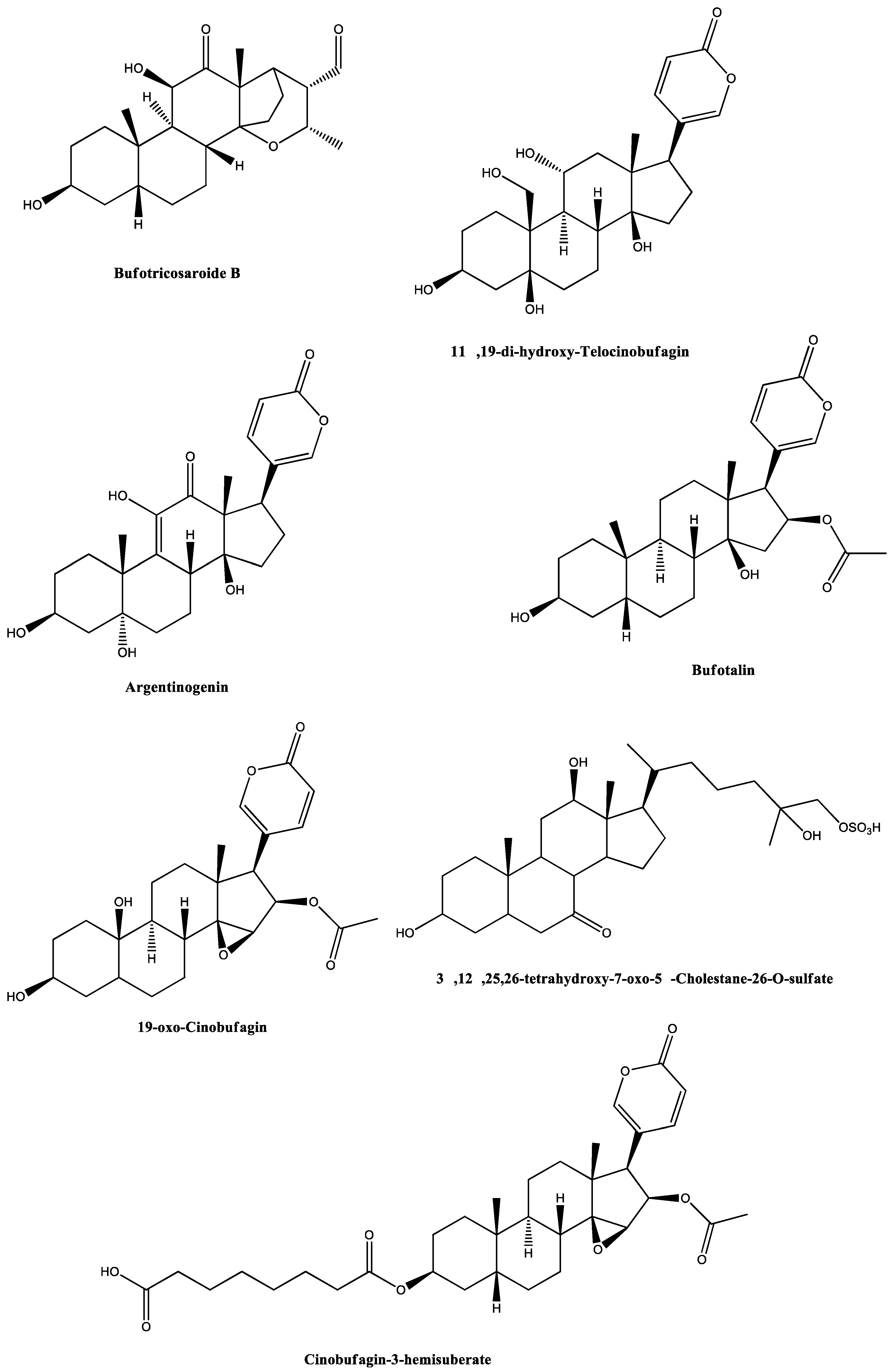

| Entry | Precursor Ion m/z | Extract | Identification | Elem. Comp. | Diff ppm | Comp. Type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extract analysis in positive mode ESI(+) | |||||||
| 1 | 191.1171 | RI24 | N-Methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine | C11H14N2O | 7.00 | Alkaloid | [40,41,42,43] |
| 2 | 391.2497 | RI23 | Sarmentogenin | C23H34O5 | 3.20 | Steroid | [44] |
| 3 | 399.2189 | RI18 | (5β,12β)-12,14-Dihydroxy-11-oxobufa-3,20,22-trienolide | C24H30O5 | 4.39 | Steroid | [45,46] |
| 399.2182 | RI23 | 2.63 | |||||
| 4 | 401.2306 | RI18 | 14,15-Epoxy-3,5-dihydroxybufa-20,22-dienolide (marinobufagin) | C24H32O5 | 5.48 | Steroid | [25,31,47,48] |
| 401.2318 | RI23 | 2.50 | |||||
| 5 | 403.2446 | RI23 | (3β,5β,16β)-3,5,16-Trihydroxy-bufa-14,20,22-dienolide (Bufogenin B) | C24H34O5 | 9.55 | Steroid | [49,50] |
| 6 | 435.2356 | RI19 | 11α,19-Di-hydroxy-telocinobufagin | C24H34O7 | 6.15 | Steroid | [46,51,52] |
| 433.2266 | RI24 | 9.17 | |||||
| 7 | 440.2167 | RI23 | Argentinogenin | C26H31O6 | 7.24 | Steroid | [44,53] |
| 8 | 445.2609 | RI18 | Bufotalin | C26H36O6 | 4.24 | Steroid | [35,44,54,55,56,57] |
| 9 | 458.2310 | RI23 | 19-Oxo-cinobufagin | C26H32O7 | 1.19 | Steroid | [36,44] |
| 10 | 461.2481 | RI24 | Monohydroxylbufotalin | C26H36O7 | 8.73 | Steroid | [6] |
| 11 | 531.2983 | RI23 | 3α,12β,25,26-Tetrahydroxy-7-oxo-5β-cholestane-26-O-sulfate | C27H46O8S | 1.63 | Steroid | [44] |
| 12 | 599.3231 | RI23 | Cinobufagin-3-hemisuberate | C34H46O9 | 1.82 | Steroid | [58] |
| Extract analysis in negative mode ESI(−) | |||||||
| 13 | 433.2266 | RI24 | 11α,19-Di-hydroxy-telocinobufagin (Marinosin) | C24H34O7 | 9.17 | Steroid | [46,52,53] |
| 14 | 431.2116 | RI19 | Marinoic acid (3β-hydroxy-11,12-seco-5β,14β-bufa-20,22-dienolide-11,14-olide-12-oic acid) | C24H30O7 | 3.43 | Steroid | [59,60] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, R.S.; Borges, B.T.; Leal, A.P.; Lailowski, M.M.; Bordon, K.d.C.F.; Souza, V.Q.d.; Vinadé, L.; Santos, T.G.d.; Hyslop, S.; Moura, S.; et al. Chemical and Pharmacological Screening of Rhinella icterica (Spix 1824) Toad Parotoid Secretion in Avian Preparations. Toxins 2020, 12, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060396
Oliveira RS, Borges BT, Leal AP, Lailowski MM, Bordon KdCF, Souza VQd, Vinadé L, Santos TGd, Hyslop S, Moura S, et al. Chemical and Pharmacological Screening of Rhinella icterica (Spix 1824) Toad Parotoid Secretion in Avian Preparations. Toxins. 2020; 12(6):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060396
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Raquel Soares, Bruna Trindade Borges, Allan Pinto Leal, Manuela Merlin Lailowski, Karla de Castro Figueiredo Bordon, Velci Queiróz de Souza, Lúcia Vinadé, Tiago Gomes dos Santos, Stephen Hyslop, Sidnei Moura, and et al. 2020. "Chemical and Pharmacological Screening of Rhinella icterica (Spix 1824) Toad Parotoid Secretion in Avian Preparations" Toxins 12, no. 6: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060396
APA StyleOliveira, R. S., Borges, B. T., Leal, A. P., Lailowski, M. M., Bordon, K. d. C. F., Souza, V. Q. d., Vinadé, L., Santos, T. G. d., Hyslop, S., Moura, S., Arantes, E. C., Corrado, A. P., & Dal Belo, C. A. (2020). Chemical and Pharmacological Screening of Rhinella icterica (Spix 1824) Toad Parotoid Secretion in Avian Preparations. Toxins, 12(6), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12060396