Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Long-Term Outcomes of Snakebite in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Clinical Manifestations of Snake Envenomation in Taiwan
2.2. Long-Term Effects of Snake Envenomations
2.2.1. Migraine-Like Syndrome
2.2.2. Brain Injuries
2.2.3. Chronic Kidney Disease
2.2.4. Hypopituitarism
3. Conclusions
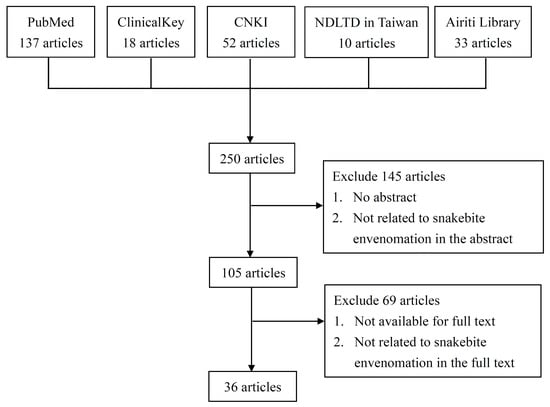
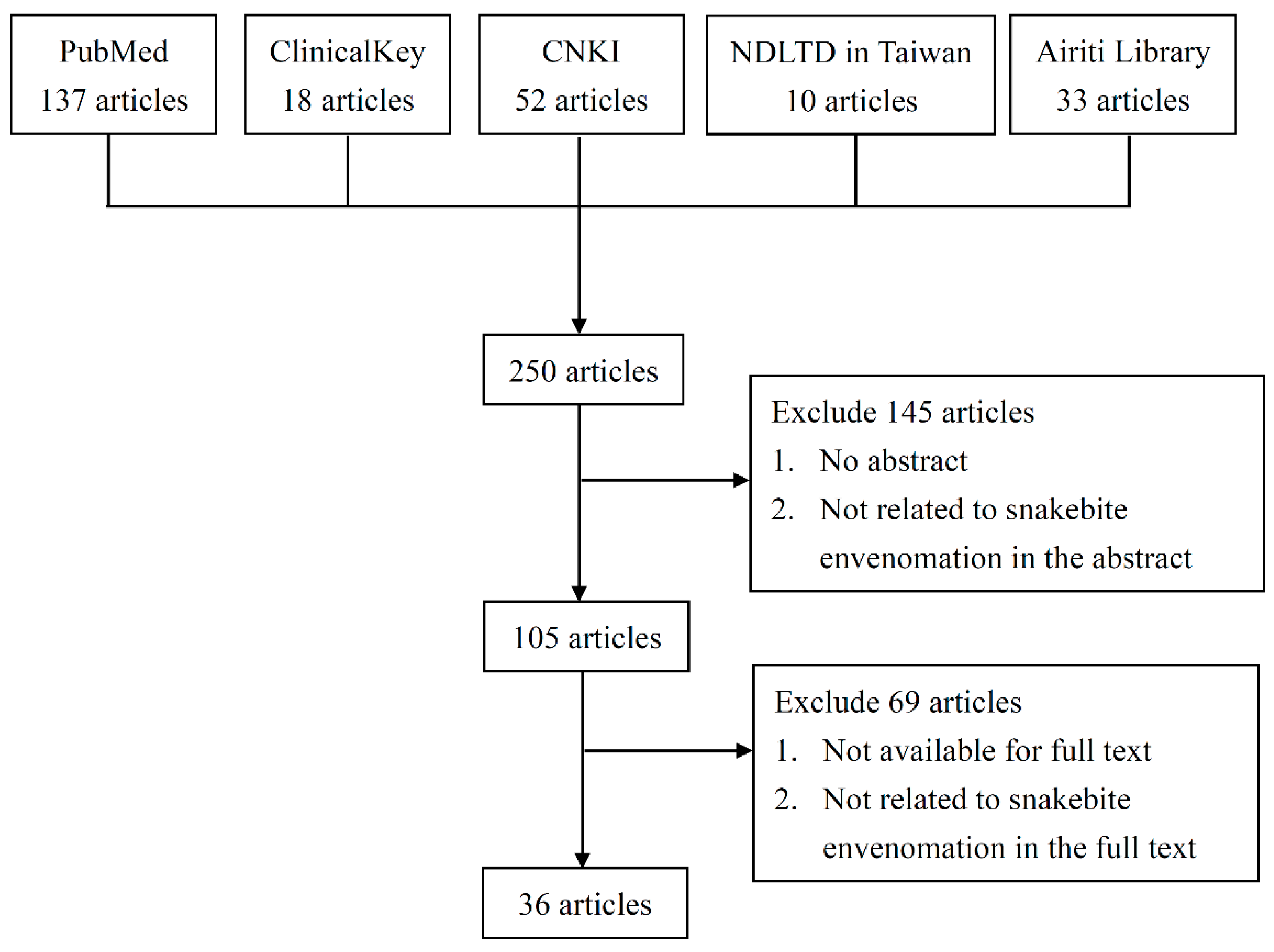
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutierrez, J.M.; Warrell, D.A.; Williams, D.J.; Jensen, S.; Brown, N.; Calvete, J.J.; Harrison, R.A.; Global Snakebite, I. The need for full integration of snakebite envenoming within a global strategy to combat the neglected tropical diseases: The way forward. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippaux, J.P. Snakebite envenomation turns again into a neglected tropical disease! J. Venom Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. The global burden of snakebite: A literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, D.Z. Taiwan’s venomous snakebite: Epidemiological, evolution and geographic differences. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 98, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.W. Venomous Snake Bites in Taiwan. J. Emerg. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 23, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creer, S.; Malhotra, A.; Thorpe, R.S.; Chou, W.H. Multiple causation of phylogeographical pattern as revealed by nested clade analysis of the bamboo viper (Trimeresurus stejnegeri) within Taiwan. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 10, 1967–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.C.; Huang, M.N.; Chang, J.F.; Liu, C.C.; Chen, C.K.; Hsieh, C.H. Snake venom proteome and immuno-profiling of the hundred-pace viper, Deinagkistrodon acutus, in Taiwan. Acta Trop. 2019, 189, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, D.-Z. ; S.-Y., L.-S. Studies on the Diagnosis, Treatment and Toxic Mechanism of Taiwan Venomous Snakebites; National Taiwan University: Taipei, Taiwan, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.M.; Huang, S.P.; Chen, Y.H.; Tu, M.C. Thermal Tolerance and Altitudinal Distribution of Three Trimeresurus Snakes (Viperidae: Crotalinae) in Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 2007, 46, 592–599. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.P.; Lai, C.S.; Lin, S.D. Management of poisonous snake bites in southern Taiwan. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2007, 23, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.H.; Hsu, W.H.; Huang, K.C.; Yu, P.A.; Chen, C.L.; Kuo, L.T. Necrotizing fasciitis following venomous snakebites in a tertiary hospital of southwest Taiwan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 63, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digital Taiwan-Culture & Nature. Available online: http://culture.teldap.tw/culture/index.php?option=com_content&id=1124 (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- Gutierrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.L.; Mao, Y.C.; Liu, P.Y.; Chiang, L.C.; Liao, S.C.; Yang, C.C. Deinagkistrodon acutus envenomation: A report of three cases. J. Venom Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkin, Y.N.; Gantsova, E.A.; Andreeva, T.V.; Starkov, V.G.; Ziganshin, R.H.; Anh, H.N.; Thao, N.T.; Khoa, N.C.; Tsetlin, V.I. Venoms of kraits Bungarus multicinctus and Bungarus fasciatus contain anticoagulant proteins. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 460, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.C.; Liu, P.Y.; Chiang, L.C.; Lai, C.S.; Lai, K.L.; Ho, C.H.; Wang, T.H.; Yang, C.C. Naja atra snakebite in Taiwan. Clin. Toxicol. 2018, 56, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.H.; Jeng, M.J.; Yang, C.C. Naja Atra Venom-Spit Ophthalmia in Taiwan: An Epidemiological Survey from 1990 to 2016; National Yang-Ming University: Taipei, Taiwan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.B.; Goonetilleke, A. Animal poisons and the nervous system: What the neurologist needs to know. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, iii40–iii46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Brutto, O.H.; Del Brutto, V.J. Neurological complications of venomous snake bites: A review. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2012, 125, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunitha, K.; Hemshekhar, M.; Thushara, R.M.; Santhosh, M.S.; Sundaram, M.S.; Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S. Inflammation and oxidative stress in viper bite: An insight within and beyond. Toxicon 2015, 98, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastin Santhosh, M.; Hemshekhar, M.; Thushara, R.M.; Devaraja, S.; Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S. Vipera russelli venom-induced oxidative stress and hematological alterations: Amelioration by crocin a dietary colorant. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2013, 31, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Maduwage, K.; Sedgwick, M.; Pilapitiya, S.; Weerawansa, P.; Dahanayaka, N.J.; Buckley, N.A.; Siribaddana, S.; Isbister, G.K. Neurotoxicity in Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) envenoming in Sri Lanka: A clinical and neurophysiological study. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, M.Y.; Huang, R.J. Toxoids and Antivenoms of Venomous Snakes in Taiwan. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 1997, 16, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Chaou, C.H.; Tseng, C.Y. An investigation of snakebite antivenom usage in Taiwan. J. Med. Assoc. 2016, 115, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourreau, F.; Pinsard, M.; Goyffon, M.; Plasse, F.; Desport, E.; Thierry, A.; Touchard, G.; Bridoux, F. Bilateral renal cortical necrosis with end-stage renal failure following envenoming by Proatheris superciliaris: A case report. Toxicon 2014, 84, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayawardana, S.; Gnanathasan, A.; Arambepola, C.; Chang, T. Chronic Musculoskeletal Disabilities following Snake Envenoming in Sri Lanka: A Population-Based Study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaprasad, C.; Aiswarya, Y.; Sridevi, A.; Anupam, B.; Amit, G.; Rakesh, B.; Annie, P.A.; Anish, K. Delayed hypopituitarism following Russell’s viper envenomation: A case series and literature review. Pituitary 2019, 22, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, D.J.; Wijegunasinghe, D.; Samarakoon, S.; Palipana, H.; Gunasekera, S.; de Silva, H.A.; Lalloo, D.G.; Ranawaka, U.K.; de Silva, H.J. Neurophysiological findings in patients 1 year after snake bite induced neurotoxicity in Sri Lanka. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 104, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Priyamvada, P.S.; Jaswanth, C.; Zachariah, B.; Haridasan, S.; Parameswaran, S.; Swaminathan, R.P. Prognosis and long-term outcomes of acute kidney injury due to snake envenomation. Clin. Kidney J. 2019, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.P.; Chuang, J.F.; Hsu, Y.P.; Wang, S.Y.; Fu, C.Y.; Yuan, K.C.; Chen, C.H.; Kang, S.C.; Liao, C.H. Predictors of the development of post-snakebite compartment syndrome. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2015, 23, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, M.J.; Tian, A.C.; Chu, C.C.; Hsu, Y.L.; Wang, P.H. The Respiratory Care for Acute Upper Airway Obstruction and Respiratory Failure in the Patient Bitten by Protobothrops Mucrosquamatus. J. Respir. Ther. 2017, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Lai, Y.H.; Tsai, J.H. Acute Renal Failure Following Russell’s Viper Envenomation: A Report of Two Cases. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 1988, 4, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, D.Z.; Wu, M.L.; Deng, J.F.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y. Russell’s viper snakebite in Taiwan: Differences from other Asian countries. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO/Regional Office for South-East Asia. Guidelines for the Management of Snakebites, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization/Regional Office for South-East Asia: Indraprastha Estate, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gretchen, E.; Tietjen, S.A.C. Hypercoagulability and Migraine. Headache 2018, 58, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardana, S.; Arambepola, C.; Chang, T.; Gnanathasan, A. Long-term health complications following snake envenoming. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2018, 11, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Clemetson, J.M.; Clemetson, K.J. Snake venoms and hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulfius, C.A.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Kryukova, E.V.; Spirova, E.N.; Shelukhina, I.V.; Starkov, V.G.; Andreeva, T.V.; Faure, G.; Zouridakis, M.; Tsetlin, V.I.; et al. Pancreatic and snake venom presynaptically active phospholipases A2 inhibit nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J. Snake venoms and coagulopathy. Toxicon 2005, 45, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Cheng, J.; Wang, T.; Li, F.; Luo, R.; Zhao, X. Traditional Chinese patent medicine for prophylactic treatment of migraine: A meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.L.; Zeng, R.; Gu, C.M.; Qu, Y.; Huang, L.F. Angelica sinensis in China-A review of botanical profile, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and chemical analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 190, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.S.; Xu, Q.Q.; Shi, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; He, Z.X.; Zheng, G.Q. Chuanxiong Formulae for Migraine: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of High-Quality Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Pharm. 2018, 9, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Guo, L.; Qiu, F.; Gong, M. Anti-Migraine Effect of the Herbal Combination of Chuanxiong Rhizoma and Cyperi Rhizoma and UPLC-MS/MS Method for the Simultaneous Quantification of the Active Constituents in Rat Serum and Cerebral Cortex. Molecules 2019, 24, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Chen, H.; Fu, K.; Wei, J.; Qin, L.; Pan, T.; Xu, S. Fructus Viticis methanolic extract attenuates trigeminal hyperalgesia in migraine by regulating injury signal transmission. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Hu, J.; Liang, X.; Wu, Y.; Yan, M.; Zhu, M.; Fu, Y. Acute cerebral infarction following a Trimeresurus stejnegeri snakebite: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e15684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartholdi, D.; Selic, C.; Meier, J.; Jung, H.H. Viper snakebite causing symptomatic intracerebral haemorrhage. J. Neurol. 2004, 251, 889–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Brutto, O.H. Neurological effects of venomous bites and stings: Snakes, spiders, and scorpions. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 114, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.W.; Wu, F.F.; Chang, W.H.; Lee, C.N.; Chou, C.C. A Case of Envenomation by Bungarus Multicinctus. J. Emerg. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 10, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waiddyanatha, S.; Silva, A.; Siribaddana, S.; Isbister, G.K. Long-term Effects of Snake Envenoming. Toxins 2019, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Tang, N.Y.; Kao, S.T.; Hsieh, C.L. Ferulic Acid Administered at Various Time Points Protects against Cerebral Infarction by Activating p38 MAPK/p90RSK/CREB/Bcl-2 Anti-Apoptotic Signaling in the Subacute Phase of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.H.; Huang, C.P.; Lin, Y.W.; Hsieh, C.L. Paeoniflorin has anti-inflammation and neurogenesis functions through nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 1174–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Peng, W.; Li, P.; Xia, Z.; Zhong, Y.; He, F.; Tulake, Y.; Feng, D.; Wang, Y.; Xing, Z. A Network Pharmacology Analysis to Explore the Effect of Astragali Radix-Radix Angelica Sinensis on Traumatic Brain Injury. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3951783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.K.; Ng, C.F.; Shiu, H.T.; Wong, H.L.; Chin, W.C.; Zhang, J.F.; Lam, P.K.; Poon, W.S.; Lau, C.B.; Leung, P.C.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of Da Chuanxiong Formula against cognitive and motor deficits in a rat controlled cortical impact model of traumatic brain injury. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 217, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, F.C.; Zhao, Y.M.; Chan, K.W.; Cheng, E.Y.; Tong, E.P.; Chandrashekar, O.; Fu, G.M.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Ip, N.Y. Neuroprotective effect of a novel Chinese herbal decoction on cultured neurons and cerebral ischemic rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waikhom, R.; Sircar, D.; Patil, K.; Bennikal, M.; Gupta, S.D.; Pandey, R. Long-term renal outcome of snake bite and acute kidney injury: A single-center experience. Ren. Fail. 2012, 34, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, H.M.; Wazil, A.W.; Abeysekara, D.T.; Jeewani, N.D.; Weerakoon, K.G.; Ratnatunga, N.V.; Bandara, E.H.; Kularatne, S.A. Chronic kidney disease in snake envenomed patients with acute kidney injury in Sri Lanka: A descriptive study. Postgrad. Med. J. 2012, 88, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.Y.; Chiu, Y.W.; Chang, J.S.; Lin, H.L.; Lee, C.T.; Chiu, G.F.; Kuo, M.C.; Wu, M.T.; Chen, H.C.; Hwang, S.J. Association of prescribed Chinese herbal medicine use with risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Menon, M.C.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, J.C. Recent Advances in Traditional Chinese Medicine for Kidney Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chuang, P.Y.; Cijiang He, J. Therapeutic use of traditional Chinese herbal medications for chronic kidney diseases. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonypillai, C.N.; Wass, J.A.; Warrell, D.A.; Rajaratnam, H.N. Hypopituitarism following envenoming by Russell’s vipers (Daboia siamensis and D. russelii) resembling Sheehan’s syndrome: First case report from Sri Lanka, a review of the literature and recommendations for endocrine management. QJM 2011, 104, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, P.; Phillips, R.E.; Warrell, D.A.; Moore, R.A.; Tin Nu, S.; Myint, L.; Burke, C.W. Acute and chronic pituitary failure resembling Sheehan’s syndrome following bites by Russell’s viper in Burma. Lancet 1987, 2, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, K.G.; Srividya, S.; Usha Nandhini, K.P.; Ramprabananth, S. Chronic Pituitary Failure Resembling Sheehan’s Syndrome Following a Bite of Russell’s Viper. A Case Report. Neuroradiol. J. 2010, 23, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, C.W. The Anterior Pituitary, Snakebite and Sheehan’s Syndrome. Q. J. Med. 1990, 75, 331–333. [Google Scholar]
- Golay, V.; Roychowdhary, A.; Dasgupta, S.; Pandey, R. Hypopituitarism in patients with vasculotoxic snake bite envenomation related acute kidney injury: A prospective study on the prevalence and outcomes of this complication. Pituitary 2014, 17, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, L.; Jin, X.; Fang, J.; Zhang, D. Er-Xian Decoction, a traditional Chinese herbal formula, intervening early in hypothalamic-pituitary axis of male rats with delayed puberty. Pharm. Mag. 2014, 10, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.J.; Ma, J.W.; Yang, G.J. Effects of traditional Chinese medicine TNY on PCNA expression pituitary cell of aging rats. J. Chengde Med. Coll. 2005, 22, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hemotoxic | ||||
| Snake Species | Main Toxins | Antivenom | Major Clinical Manifestations | References |
| T. stejnegeri T. mucrosquamatus | PLA2s, fibrinogenases, and platelet aggregation inhibitors | A | Local effects (local pain, petechiae, ecchymosis, swelling, blistering, necrosis). Systemic effects (hypotension, ischemic stroke, intracranial hemorrhage or disseminated intravascular coagulation). | [13,34,35,36,37] |
| De. acutus | SVMPs, C-type lectins, PLA2s and SVSPs | C | ||
| Neurotoxic | ||||
| Snake Species | Main toxins | Antivenom | Major Clinical Manifestations | References |
| B. multicinctus | α-bungarotoxin and β-bungarotoxin | B | Neurological symptoms (ptosis, dysarthria, dysphagia, blurred vision). Respiratory failure. | [5,15,38] |
| N. atra | PLA2s, postsynaptic neurotoxins and cardiotoxins | B | Severe local tissue swelling and necrosis. Ophthalmia. | [16,17] |
| Mixed (Hemotoxic and Neurotoxic) | ||||
| Snake Species | Main toxins | Antivenom | Major Clinical Manifestations | References |
| Da. siamensis | SVMPs, SVHYs, PLA2, factor V, and X activators | D | Hemotoxic effects (pain, swelling, intravascular hemolysis, hypotension). Neurological symptoms. Others (AKI, hypopituitarism). | [5,20,33] |
| Long-Term Sequelae | Potential TCM Treatment | Possible Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| “Migraine-like syndrome” | A. sinensis, L. chuanxiong | Regulate the release of CGRP | [41,42] |
| CRCR | Increases cerebral blood flow and decreased several substances involved in neurogenic inflammation | [43] | |
| F. Viticis | Regulates neuropeptides | [44] | |
| Brain injuries secondary to hypoxia, ischemic stroke or ICH | A. sinensis | Neuroprotective effects | [52] |
| G. elata | Reduce brain edema and neuronal loss and improve neural stem cell proliferation | [53] | |
| P. lactiflora | Suppress neuronal apoptosis and promote neurogenesis | [51] | |
| PSR | Neuroprotective effects | [54] | |
| CKD | As. Membranaceus O. sinensis R. palmatum Cortex Moutan | Unclear | [58] |
| Hypopituitarism | EXD | Trigger hypothalamic–pituitary–testicular axis | [65] |
| TNY | Elevate PCNA expression | [66] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, T.-I.; Hsieh, C.-L. Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Long-Term Outcomes of Snakebite in Taiwan. Toxins 2020, 12, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020132
Huang T-I, Hsieh C-L. Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Long-Term Outcomes of Snakebite in Taiwan. Toxins. 2020; 12(2):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020132
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Teng-I, and Ching-Liang Hsieh. 2020. "Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Long-Term Outcomes of Snakebite in Taiwan" Toxins 12, no. 2: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020132
APA StyleHuang, T.-I., & Hsieh, C.-L. (2020). Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Long-Term Outcomes of Snakebite in Taiwan. Toxins, 12(2), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020132