Chronic Microcystin-LR Exposure Induces Abnormal Lipid Metabolism via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Male Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
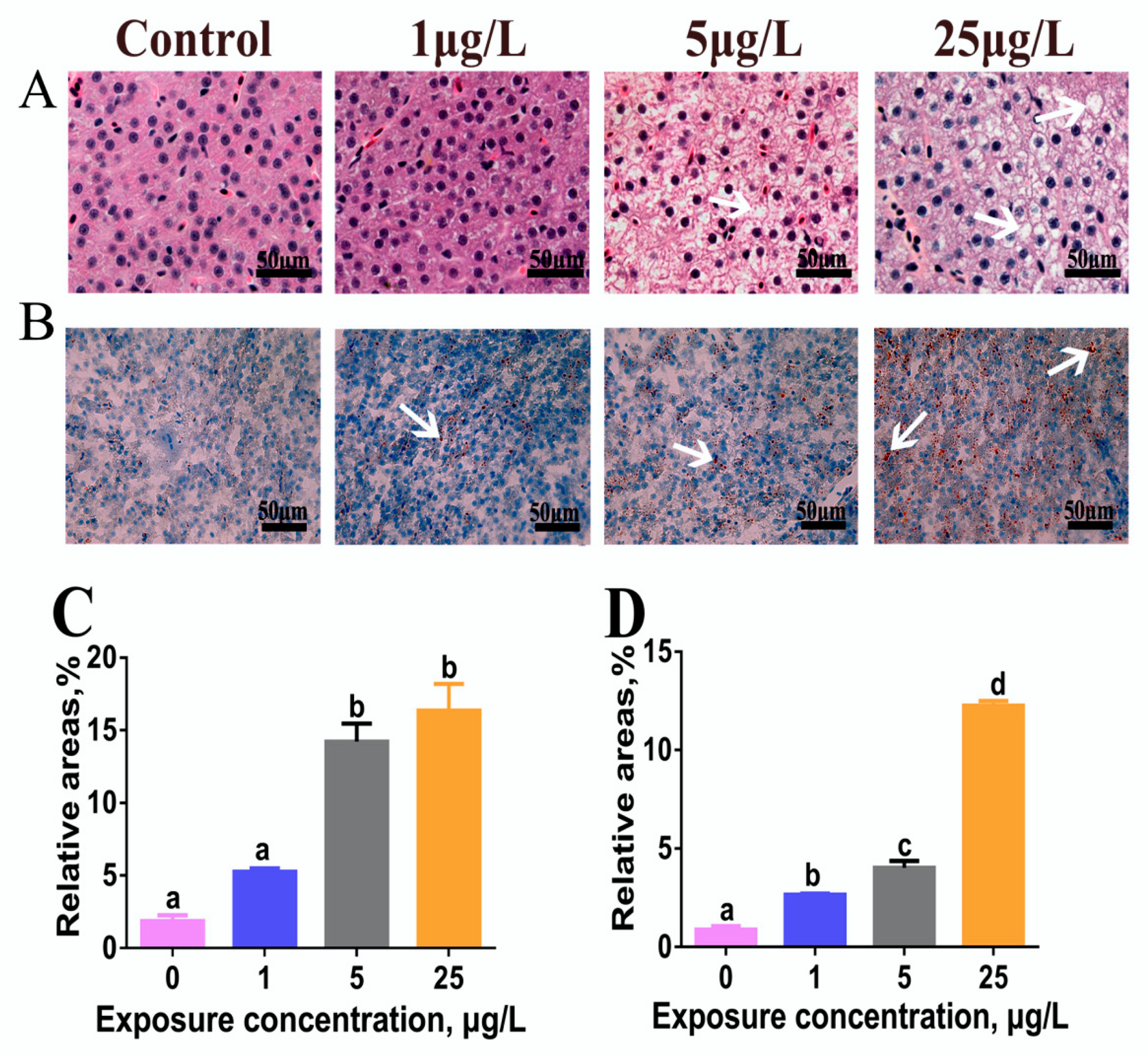
2.1. H&E and Oil Red-O Stain
2.2. Total Cholesterol and Triglyceride Levels in Liver Tissue
2.3. Marker Gene Transcription of ERS-UPR Pathways
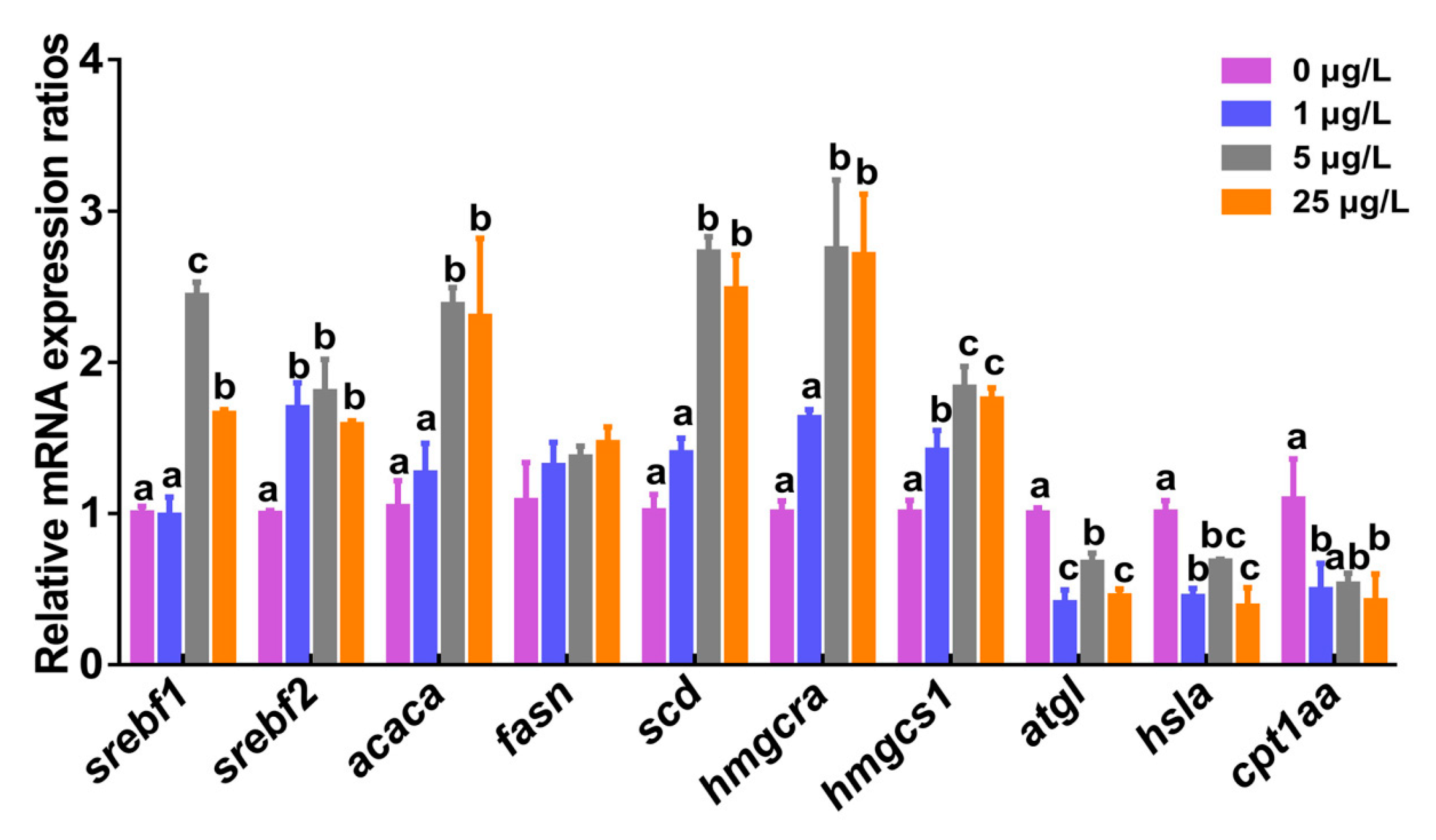
2.4. Transcription of Lipid Metabolism-related Genes
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents
5.2. Adult Fish Maintenance and MC-LR Treatment
5.3. Histological and Histochemical Examination
5.4. Biochemical Indicator Detection
5.5. qPCR Analysis
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Burke, J.M.; Dinsmore, W.P.; Prepas, E.E.; Fedorak, P.M. First assessment of cyanobacterial blooms and microcystin-LR in the Canadian portion of Lake of the Woods. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2007, 23, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinta-Kanto, J.M.; Konopko, E.A.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Bourbonniere, R.A.; Boyer, G.L.; Wilhelm, S.W. Lake Erie Microcystis: Relationship between microcystin production, dynamics of genotypes and environmental parameters in a large lake. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Via-Ordorika, L.; Fastner, J.; Kurmayer, R.; Hisbergues, M.; Dittmann, E.; Komarek, J.; Erhard, M.; Chorus, I. Distribution of microcystin-producing and non-microcystin-producing Microcystis sp. in European freshwater bodies: Detection of microcystins and microcystin genes in individual colonies. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 27, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, A.; John, J. Microcystins associated with Microcystis dominated blooms in the southwest wetlands, Western Australia. Environ. Toxicol. Int. J. 2006, 21, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Kong, F.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Shi, X.; Du, M. The dynamics of Microcystis genotypes and microcystin production and associations with environmental factors during blooms in Lake Chaohu, China. Toxins 2014, 6, 3238–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Gan, N.; Zheng, L.; Ma, H.; Shan, K.; Song, L. Seasonal dynamics of water bloom-forming Microcystis morphospecies and the associated extracellular microcystin concentrations in large, shallow, eutrophic Dianchi Lake. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Luo, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, J.; Liu, J. Occurrence and spatial distributions of microcystins in Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henao, E.; Rzymski, P.; Water, M.N. A Review on the Study of Cyanotoxins in Paleolimnological Research: Current Knowledge and Future Needs. Toxins 2020, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, S.M.; Carmichael, W.W.; Jochimsen, E.M.; Rinehart, K.L.; Lau, S.; Shaw, G.R.; Eaglesham, G.K. Human intoxication by microcystins during renal dialysis treatment in Caruaru—Brazil. Toxicology 2002, 181, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xue, Q.; Su, X.; Xie, L.; Yan, Y.; Steinman, A.D. Microcystin-LR induced thyroid dysfunction and metabolic disorders in mice. Toxicology 2015, 328, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaitabar, S.; Sari, A.E.; Bahramifar, N.; Ramezanpour, Z. Transfer, tissue distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystin LR in the phytoplanktivorous and carnivorous fish in Anzali wetland, with potential health risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meriluoto, J.; Spoof, L.; Codd, G.A. Appendix 3: Tables of Microcystins and Nodularins. Handb. Cyanobacterial Monit. Cyanotoxin Anal. 2016, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Pant, S.C.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Lakshmana Rao, P.V. Comparative toxicity evaluation of cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin variants (LR, RR, YR) in mice. Toxicology 2003, 188, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, K.; Rapala, J.; Färdig, M.; Niemelä, M.; Sivonen, K. Persistence of cyanobacterial hepatotoxin, microcystin-LR in particulate material and dissolved in lake water. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, Y.; Xie, P.; Chen, J.; Ma, Z.; Tao, M.; Qi, M.; Wu, L.; Guo, L. Factors affecting temporal and spatial variations of microcystins in Gonghu Bay of Lake Taihu, with potential risk of microcystin contamination to human health. Sci. World J. 2010, 10, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xie, P. Hepatic histopathological characteristics and antioxidant response of phytoplanktivorous silver carp intraperitoneally injected with extracted microcystins. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2009, 22, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinchet, I.; Djediat, C.; Huet, H.; Dao, S.P.; Edery, M. Pathological modifications following sub-chronic exposure of medaka fish (Oryzias latipes) to microcystin-LR. Reprod. Toxicol. 2011, 32, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Li, L.; Xue, T.; Long, M.; Su, Y.; Wu, N. Hepatic positive and negative antioxidant responses in zebrafish after intraperitoneal administration of toxic microcystin-LR. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKintosh, C.; Beattie, K.A.; Klumpp, S.; Cohen, P.; Codd, G.A. Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett. 1990, 264, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svirčev, Z.; Baltić, V.; Gantar, M.; Juković, M.; Stojanović, D.; Baltić, M. Molecular aspects of microcystin-induced hepatotoxicity and hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2010, 28, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Xie, P.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Z. Simultaneous determination of microcystin contaminations in various vertebrates (fish, turtle, duck and water bird) from a large eutrophic Chinese lake, Lake Taihu, with toxic Microcystis blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3317–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Lee, J.; Liang, S.; Shum, C.K. Cyanobacteria blooms and non-alcoholic liver disease: Evidence from a county level ecological study in the United States. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, L.; Li, G.; Xie, P. Metabolic response to oral microcystin-LR exposure in the rat by NMR-based metabonomic study. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 5934–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Hu, Y.; He, J.; Chen, J.; Giesy, J.P.; Xie, P. Responses of the proteome and metabolome in livers of zebrafish exposed chronically to environmentally relevant concentrations of microcystin-LR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alverca, E.; Andrade, M.; Dias, E.; Bento, F.S.; Batoréu, M.C.C.; Jordan, P.; Pereira, P. Morphological and ultrastructural effects of microcystin-LR from Microcystis aeruginosa extract on a kidney cell line. Toxicon 2009, 54, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görlach, A.; Klappa, P.; Kietzmann, D.T. The endoplasmic reticulum: Folding, calcium homeostasis, signaling, and redox control. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 1391–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babour, A.; Bicknell, A.A.; Tourtellotte, J.; Niwa, M. A surveillance pathway monitors the fitness of the endoplasmic reticulum to control its inheritance. Cell 2010, 142, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 2010, 140, 900–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kaufman, R.J. The impact of the unfolded protein response on human disease. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 197, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Miao, A.; Yang, L. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in murine liver and kidney exposed to microcystin-LR. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Microcystin-LR altered mRNA and protein expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling molecules related to hepatic lipid metabolism abnormalities in mice. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christen, V.; Capelle, M.; Fent, K. Silver nanoparticles induce endoplasmatic reticulum stress response in zebrafish. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 272, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, F.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, J. Critical role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in cognitive impairment induced by microcystin-LR. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 28077–28086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.N.; Ye, J. Proteolytic activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein induced by cellular stress through depletion of Insig-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45257–45265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgan, S.M.; Tang, D.; Werstuck, G.H.; Austin, R.C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress causes the activation of sterol regulatory element binding protein-2. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.H.; Scapa, E.F.; Cohen, D.E.; Glimcher, L.H. Regulation of hepatic lipogenesis by the transcription factor XBP1. Science 2008, 320, 1492–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammoun, H.L.; Chabanon, H.; Hainault, I.; Luquet, S.; Magnan, C.; Koike, T.; Ferré, P.; Foufelle, F. GRP78 expression inhibits insulin and ER stress–induced SREBP-1c activation and reduces hepatic steatosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Xiang, R. Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and adipose tissue inflammation in high fat diet-induced mouse model of obesity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocher, D.R. Metabolism and functions of lipids and fatty acids in teleost fish. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2003, 11, 107–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xie, P.; Chen, J. In vivo studies on toxin accumulation in liver and ultrastructural changes of hepatocytes of the phytoplanktivorous bighead carp ip-injected with extracted microcystins. Toxicon 2005, 46, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xie, P.; Chen, J. Biochemical and ultrastructural changes of the liver and kidney of the phytoplanktivorous silver carp feeding naturally on toxic Microcystis blooms in Taihu Lake, China. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozio, M.S.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Crabb, D. The role of lipid metabolism in the pathogenesis of alcoholic and nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Chung, I.K.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, J.A. Subchronic oral toxicity of microcystin in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) exposed to Microcystis under laboratory conditions. Toxicon 2004, 44, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xie, P.; Li, S.; Qiu, T.; Guo, L. Sequential ultrastructural and biochemical changes induced in vivo by the hepatotoxic microcystins in liver of the phytoplanktivorous silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C: Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 146, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolotti, A.; Zhang, Y.; Hendershot, L.M.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chen, X.; Hendershot, L.; Prywes, R. ER stress regulation of ATF6 localization by dissociation of BiP/GRP78 binding and unmasking of Golgi localization signals. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, J.D.; Kaufman, R.J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress: A vicious cycle or a double-edged sword? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 2277–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postic, C.; Girard, J. The role of the lipogenic pathway in the development of hepatic steatosis. Diabetes Metab. 2008, 34, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgan, S.M.; Al-Hashimi, A.A.; Austin, R.C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipid dysregulation. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2011, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, D.L.; Lindtner, C.; Vacaru, A.M.; Sachidanandam, R.; Tsedensodnom, O.; Vasilkova, T.; Buettner, C.; Sadler, K.C. Activating transcription factor 6 is necessary and sufficient for alcoholic fatty liver disease in zebrafish. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Thematic review series: Adipocyte Biology. Adipocyte stress: The endoplasmic reticulum and metabolic disease. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passeri, M.J.; Cinaroglu, A.; Gao, C.; Sadler, K.C. Hepatic steatosis in response to acute alcohol exposure in zebrafish requires sterol regulatory element binding protein activation. Hepatology 2009, 49, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amemiya-Kudo, M.; Shimano, H.; Hasty, A.H.; Yahagi, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Matsuzaka, T.; Okazaki, H.; Tamura, Y.; Iizuka, Y.; Ohashi, K.; et al. Transcriptional activities of nuclear SREBP-1a,-1c, and-2 to different target promoters of lipogenic and cholesterogenic genes. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1220–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Q.L.; Luo, Z.; Shi, X.; Pan, Y.X.; Song, Y.F.; Zhuo, M.Q.; Wu, K. Time-dependent effects of waterborne copper exposure influencing hepatic lipid deposition and metabolism in javelin goby Synechogobius hasta and their mechanism. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 155, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, P.; Kong, T.; Yang, F.; Guan, W. Tributyltin promoted hepatic steatosis in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and the molecular pathogenesis involved. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.F.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, L.H.; Hogstrand, C.; Pan, Y.X. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and disturbed calcium homeostasis are involved in copper-induced alteration in hepatic lipid metabolism in yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2443–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.F.; Dai, Y.J.; Liu, M.Y.; Yuan, X.Y.; Wang, C.C.; Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, W.B.; Jiang, G.Z. High-fat diet induces aberrant hepatic lipid secretion in blunt snout bream by activating endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated IRE1/XBP1 pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhoták, Š.; Sood, S.; Brimble, E.; Carlisle, R.E.; Colgan, S.M.; Mazzetti, A.; Dickhout, J.G.; Ingram, A.J.; Austin, R.C. ER stress contributes to renal proximal tubule injury by increasing SREBP-2-mediated lipid accumulation and apoptotic cell death. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2012, 303, F266–F278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.; Cortes, V.A.; Rashid, S.; Anderson, N.N.; McDonald, J.G.; Liang, G.; Moona, Y.A.; Hammerb, R.E.; Horton, J.D. Expression of SREBP-1c requires SREBP-2-mediated generation of a sterol ligand for LXR in livers of mice. Elife 2017, 6, e25015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.T.; Lin, T.H.; Chen, W.L.; Lee, H.M. Alpha-lipoic acid induces adipose triglyceride lipase expression and decreases intracellular lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 692, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Hou, J.; Guo, H.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, D.; Tang, R. The synergistic effects of waterborne microcystin-LR and nitrite on hepatic pathological damage, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant responses of male zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Su, Y.; Lin, W.; Guo, H.; Li, L.; Anderson, D.M.; Li, D.; Tang, R.; Chi, W.; Zhang, X. Estrogenic potency of MC-LR is induced via stimulating steroidogenesis: In vitro and in vivo evidence. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Lin, W.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Li, L.; Li, D.; Tang, R. Chronic Microcystin-LR Exposure Induces Abnormal Lipid Metabolism via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Male Zebrafish. Toxins 2020, 12, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020107
Zhang D, Lin W, Liu Y, Guo H, Wang L, Yang L, Li L, Li D, Tang R. Chronic Microcystin-LR Exposure Induces Abnormal Lipid Metabolism via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Male Zebrafish. Toxins. 2020; 12(2):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020107
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Dandan, Wang Lin, Yinjie Liu, Honghui Guo, Lingkai Wang, Liping Yang, Li Li, Dapeng Li, and Rong Tang. 2020. "Chronic Microcystin-LR Exposure Induces Abnormal Lipid Metabolism via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Male Zebrafish" Toxins 12, no. 2: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020107
APA StyleZhang, D., Lin, W., Liu, Y., Guo, H., Wang, L., Yang, L., Li, L., Li, D., & Tang, R. (2020). Chronic Microcystin-LR Exposure Induces Abnormal Lipid Metabolism via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Male Zebrafish. Toxins, 12(2), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020107






